Mannose-Specific Lectins from Marine Algae: Diverse Structural Scaffolds Associated to Common Virucidal and Anti-Cancer Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Diversity of Mannose-Binding Lectins in Seaweeds
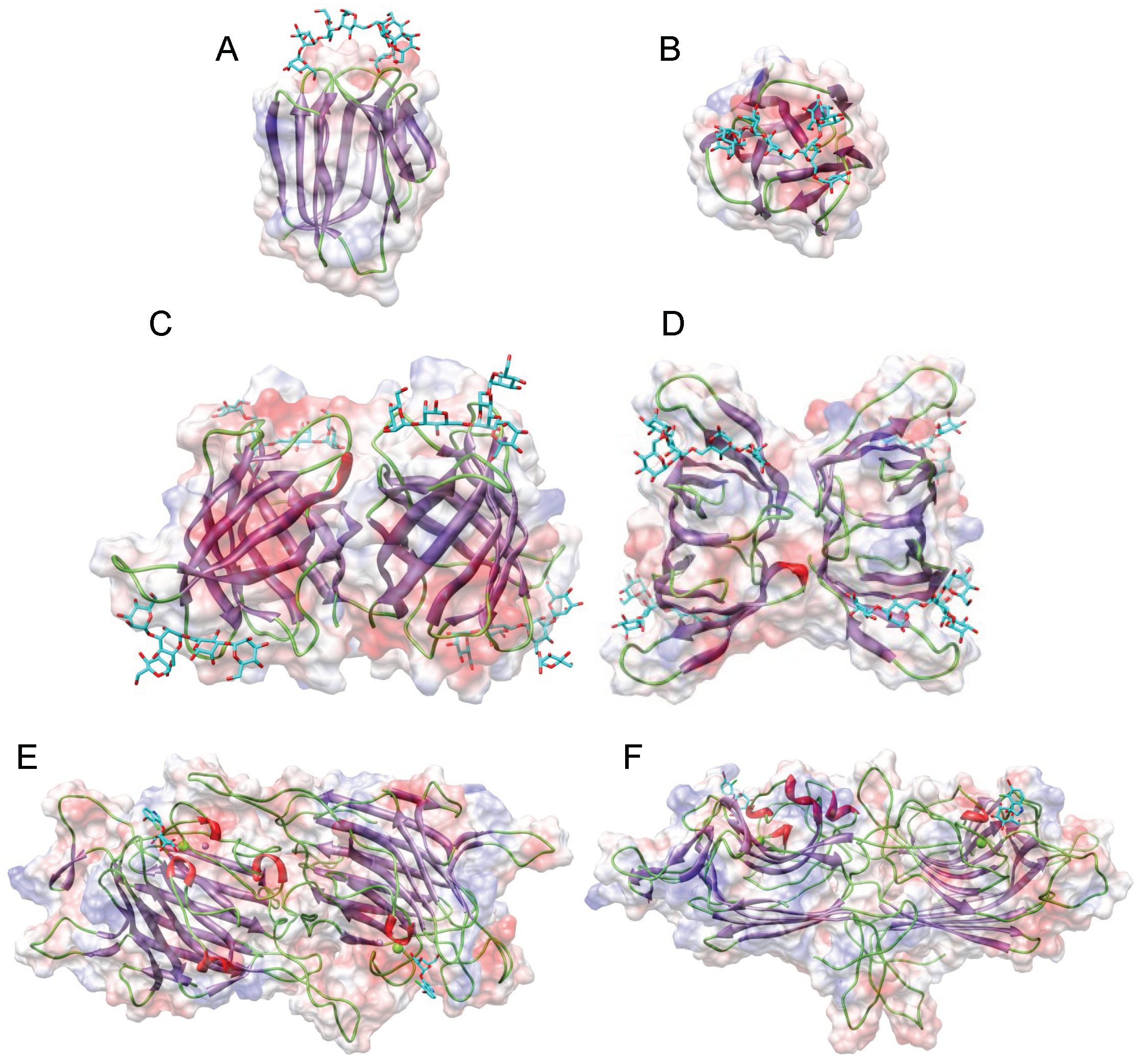
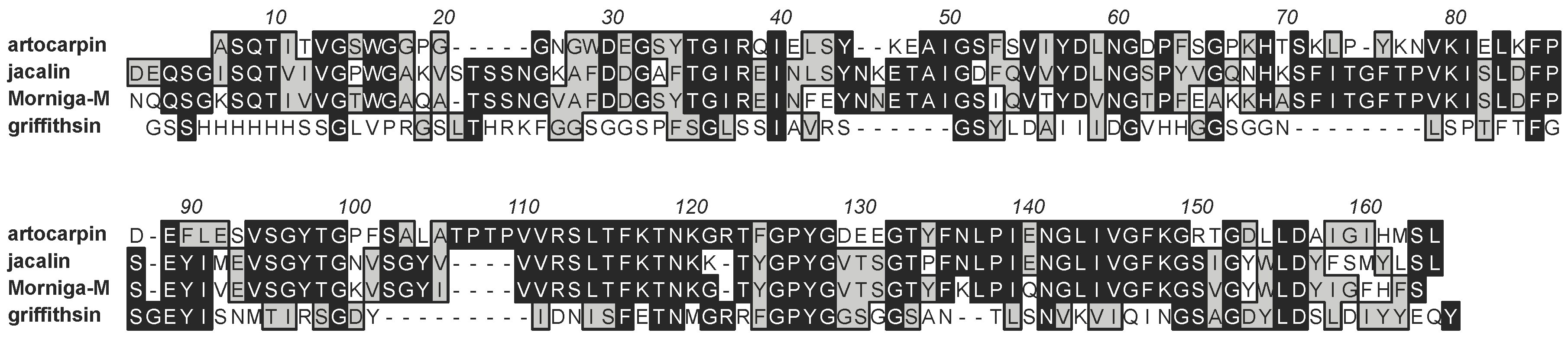
3. Structural Scaffolds of the Man-Specific Seaweed Lectins
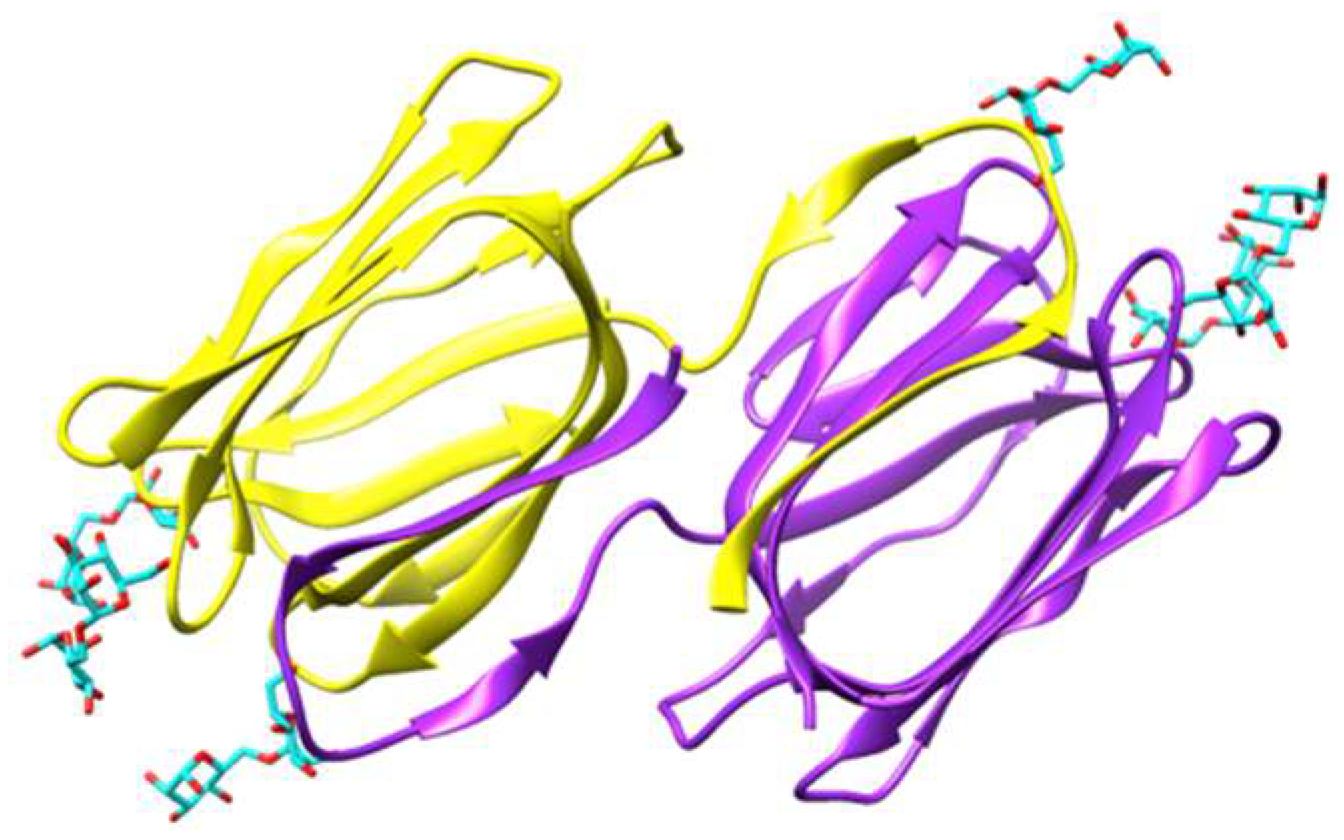
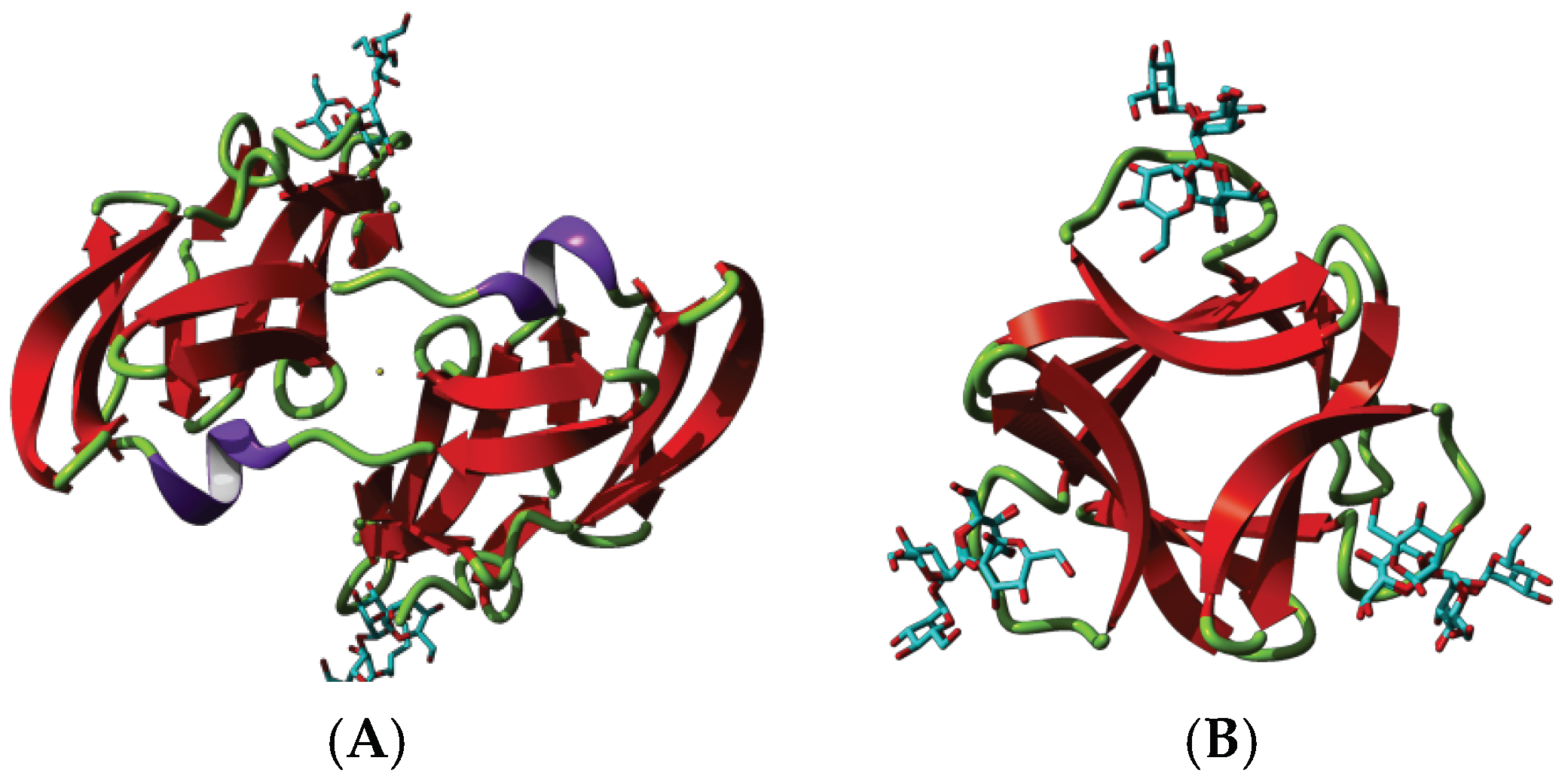
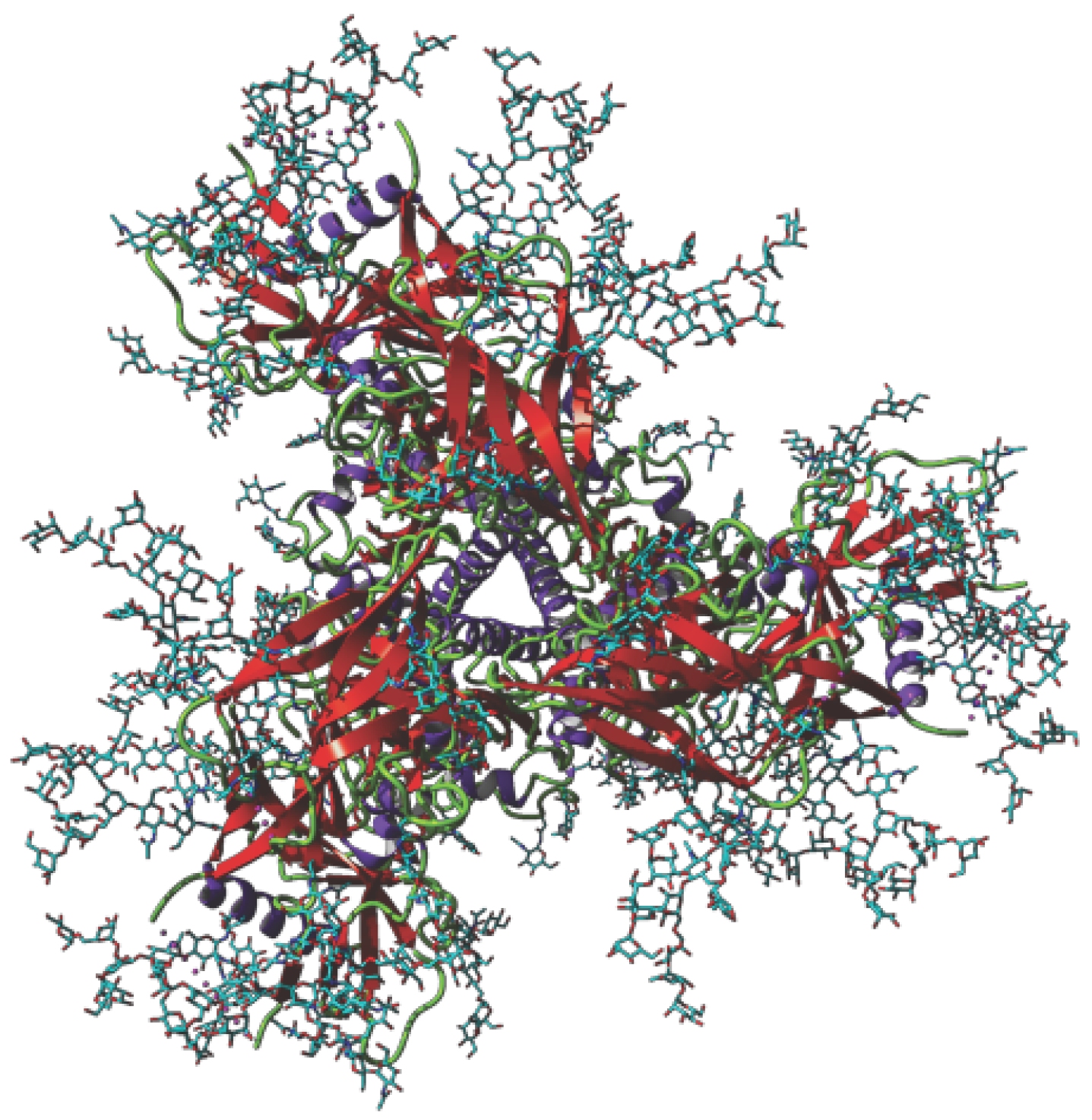
3.1. Griffithsin
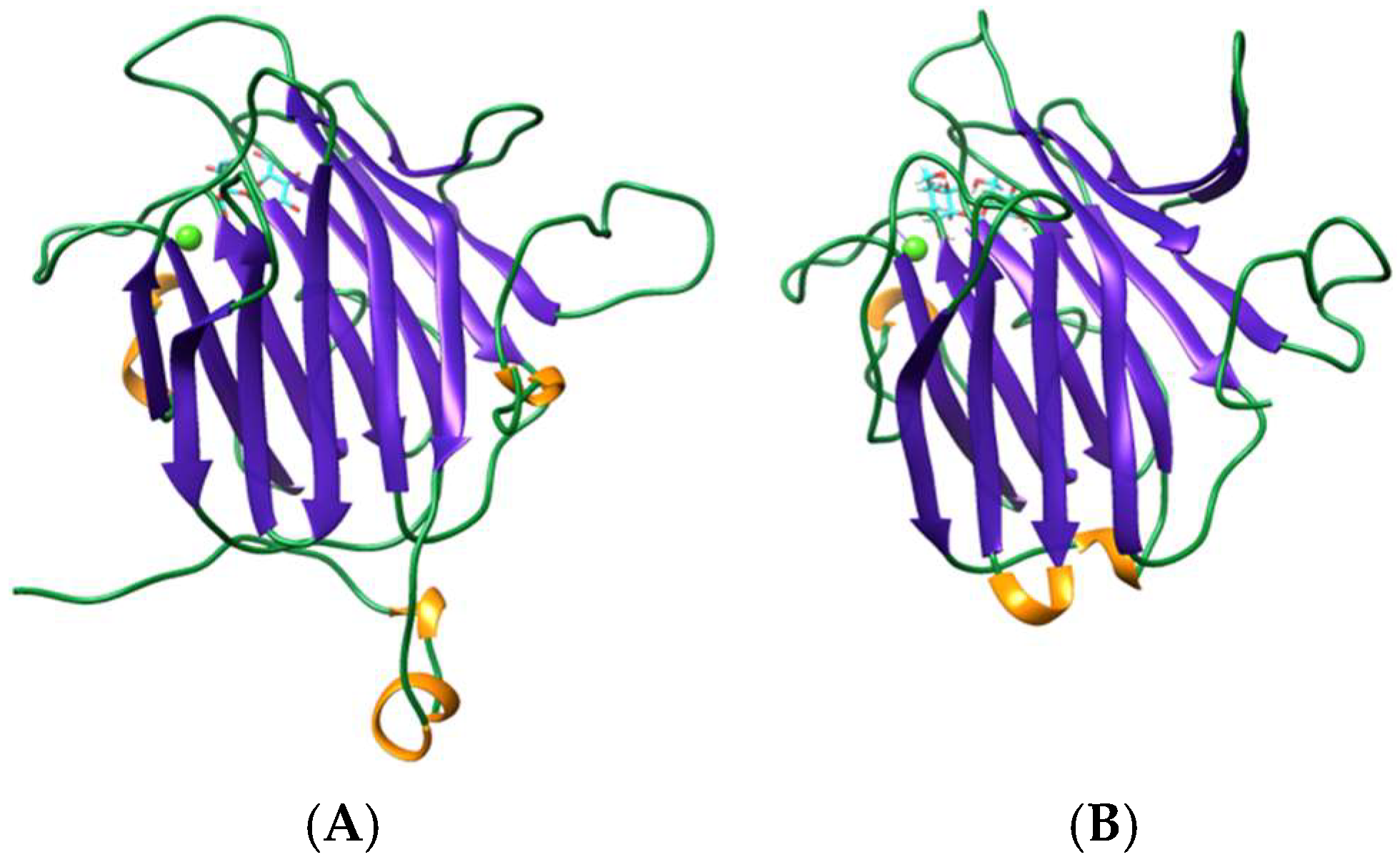
3.2. Oscillatoria Agardhii Agglutinin Homolog (OAAH) Family
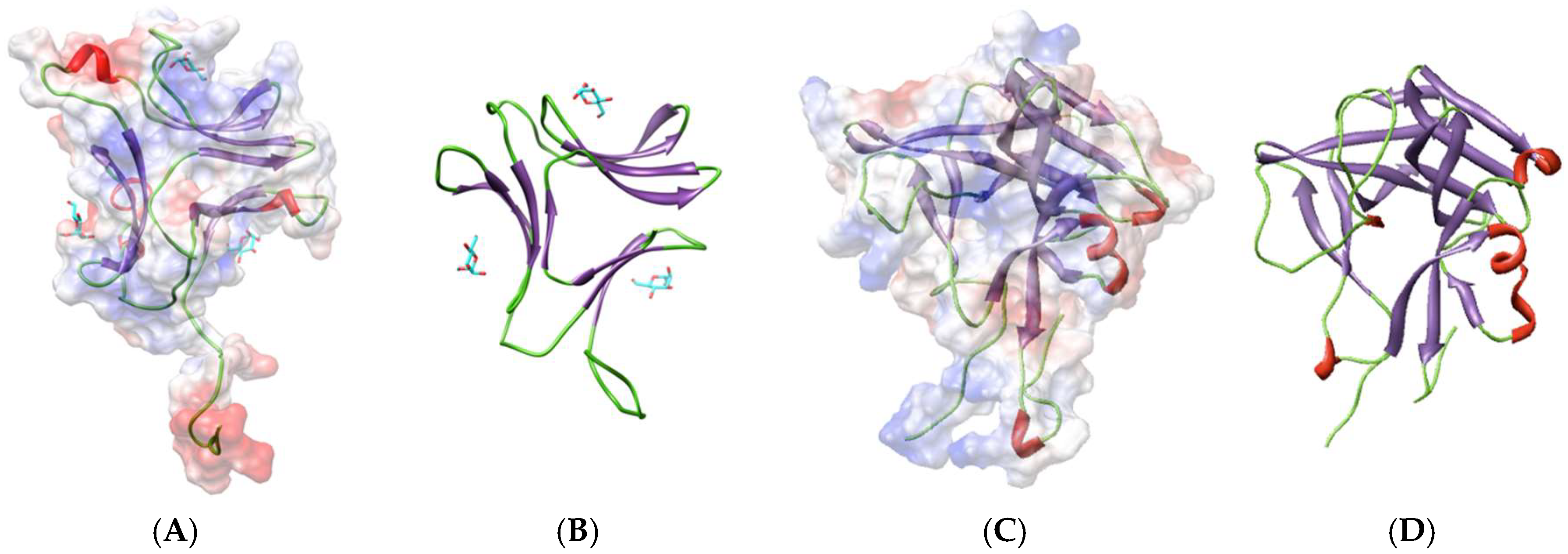
3.3. Legume Lectin-Like Family
3.4. GNA-Like Family
3.5. MFP2-Like Family
4. Mannose-Binding Specificities of Mannose-Binding Seaweed Lectins
- -
- A monosaccharide-binding specificity, allowing the lectins to specifically recognize a simple sugar, e.g., mannose, and its derivatives, e.g., α-methylmannoside. This monosaccharide recognition corresponds to the “broad sugar-binding specificity” that allows lectins to accommodate simple sugars in a monosaccharide-binding pocket located within the CBS.
- -
- An oligosaccharide-binding specificity, allowing the lectins to simultaneously accommodate several sugar units of a complex N-glycan, e.g., high-mannose glycans, also known as the “fine sugar-binding specificity” of the lectins. This oligosaccharide recognition involves the whole surface of the CBS, including the monosaccharide-binding pocket, which also participates in the binding of the complex glycans.
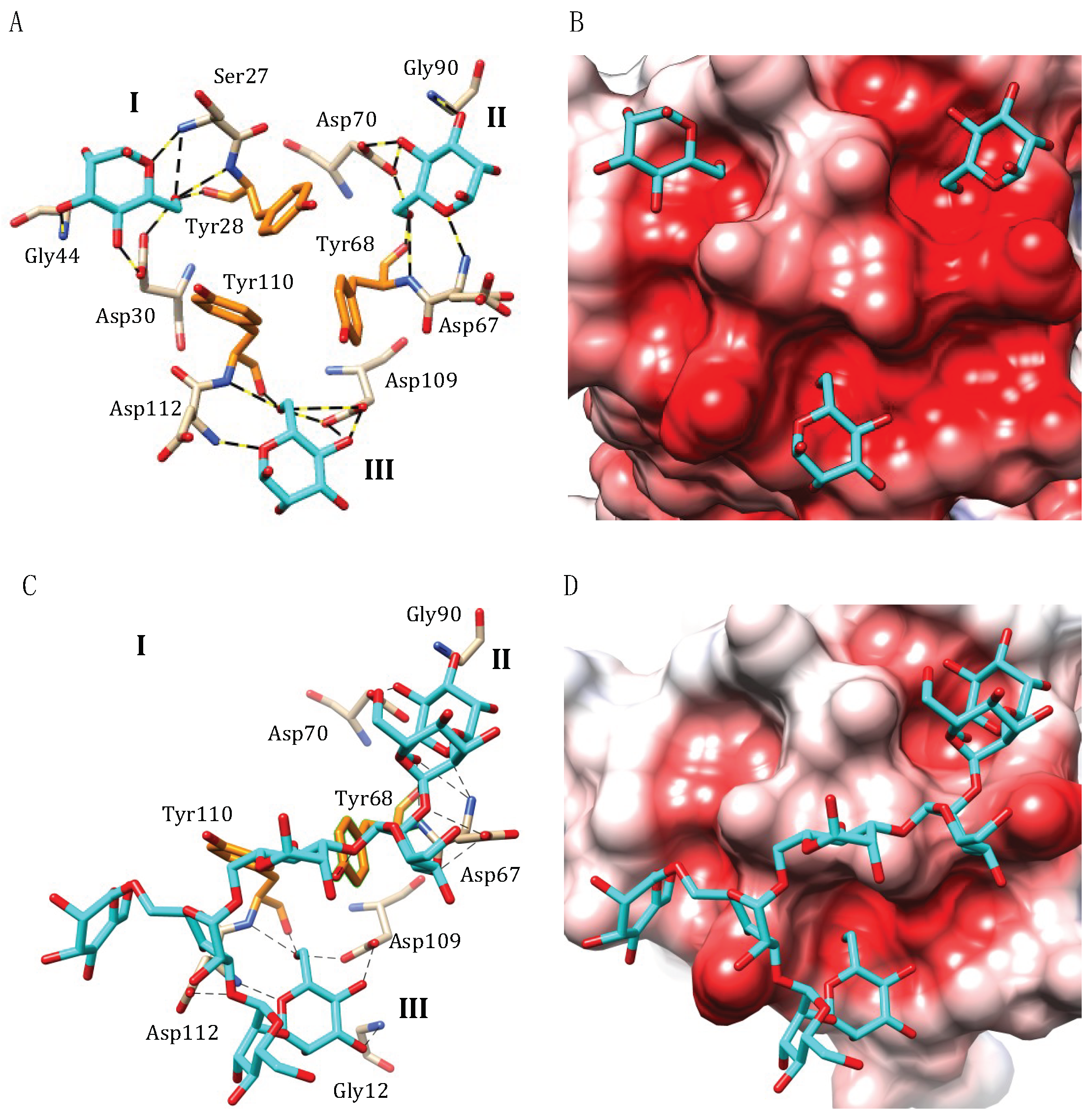
4.1. Griffithsin
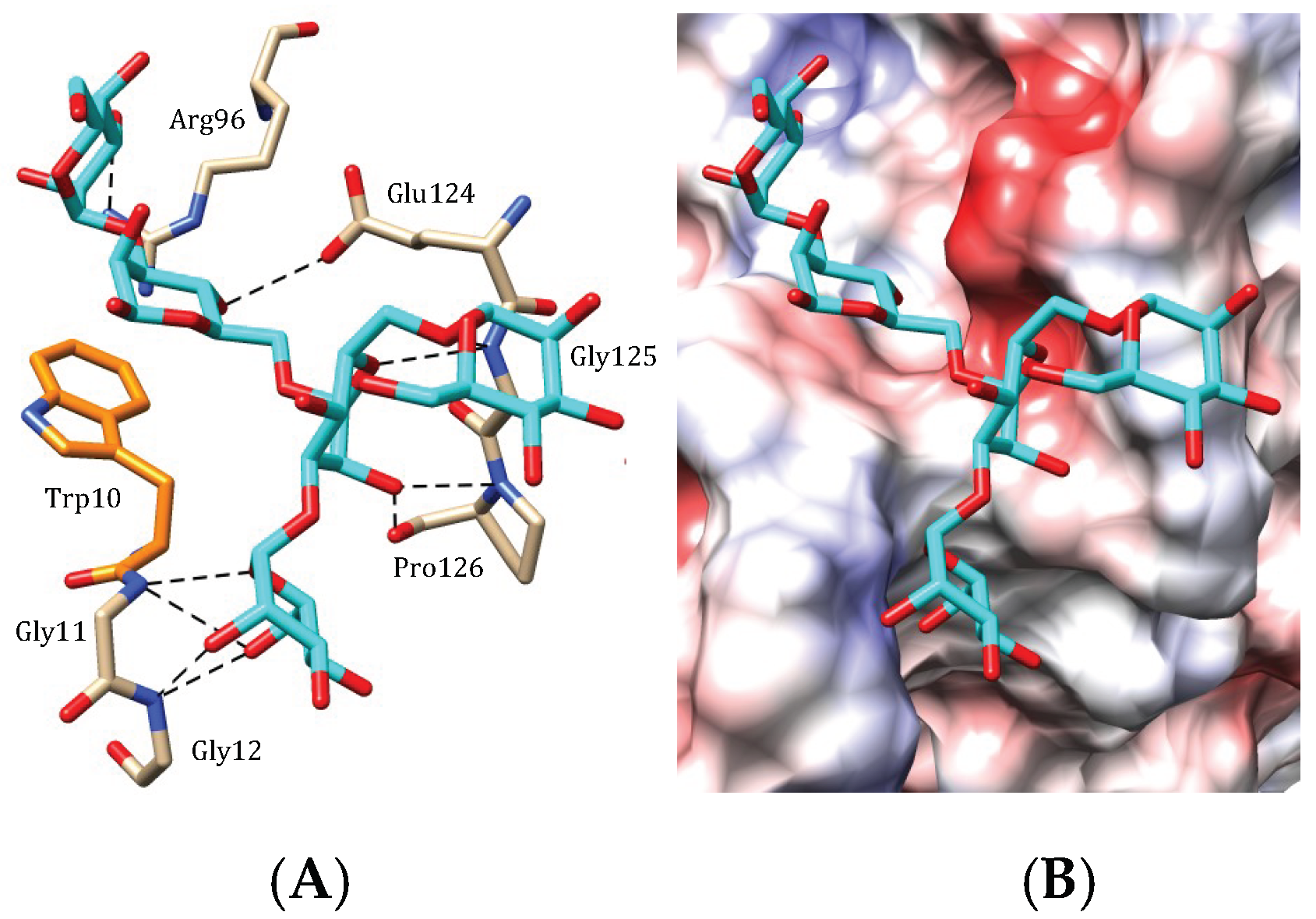
4.2. OAAH Lectins
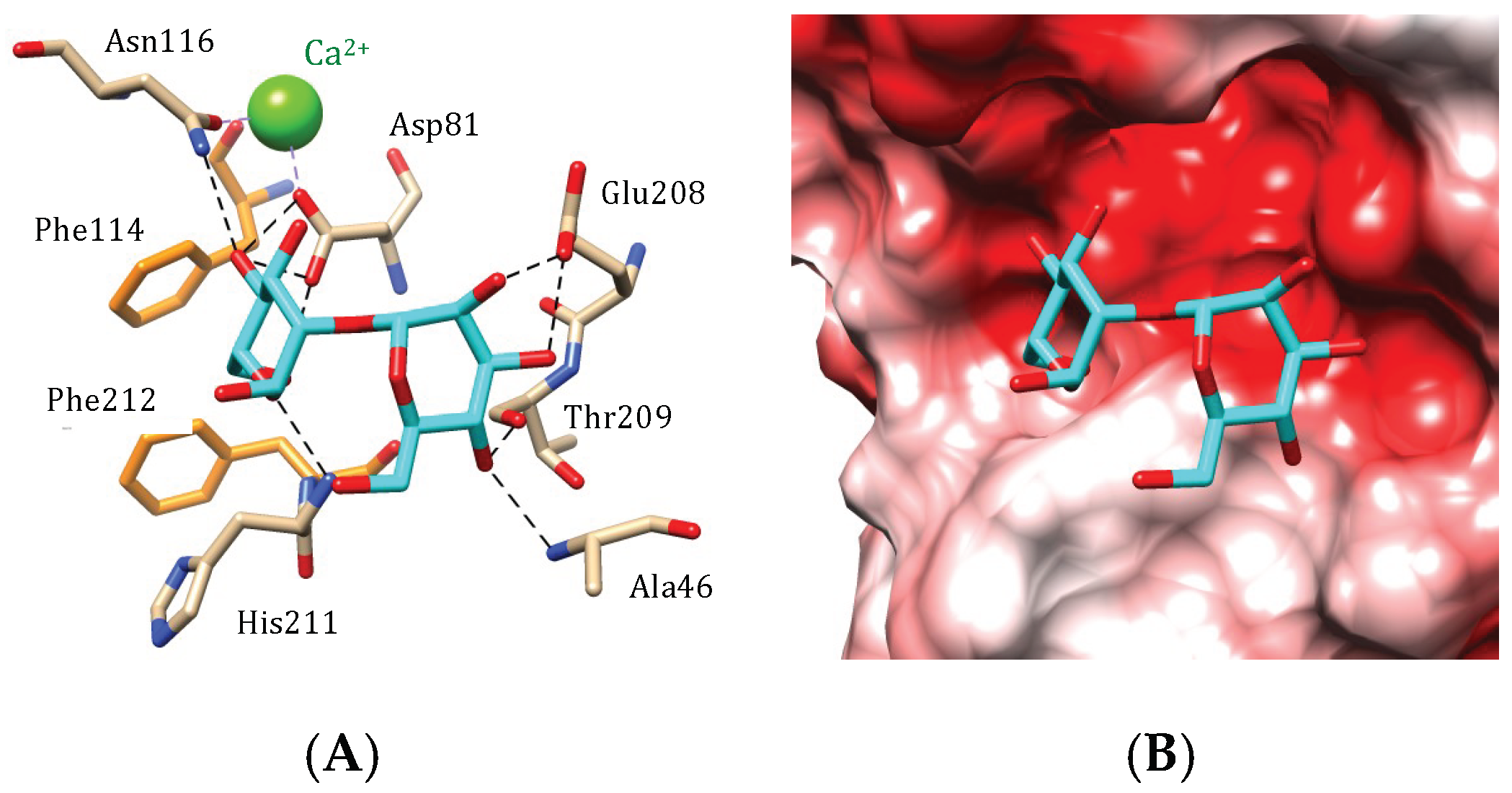
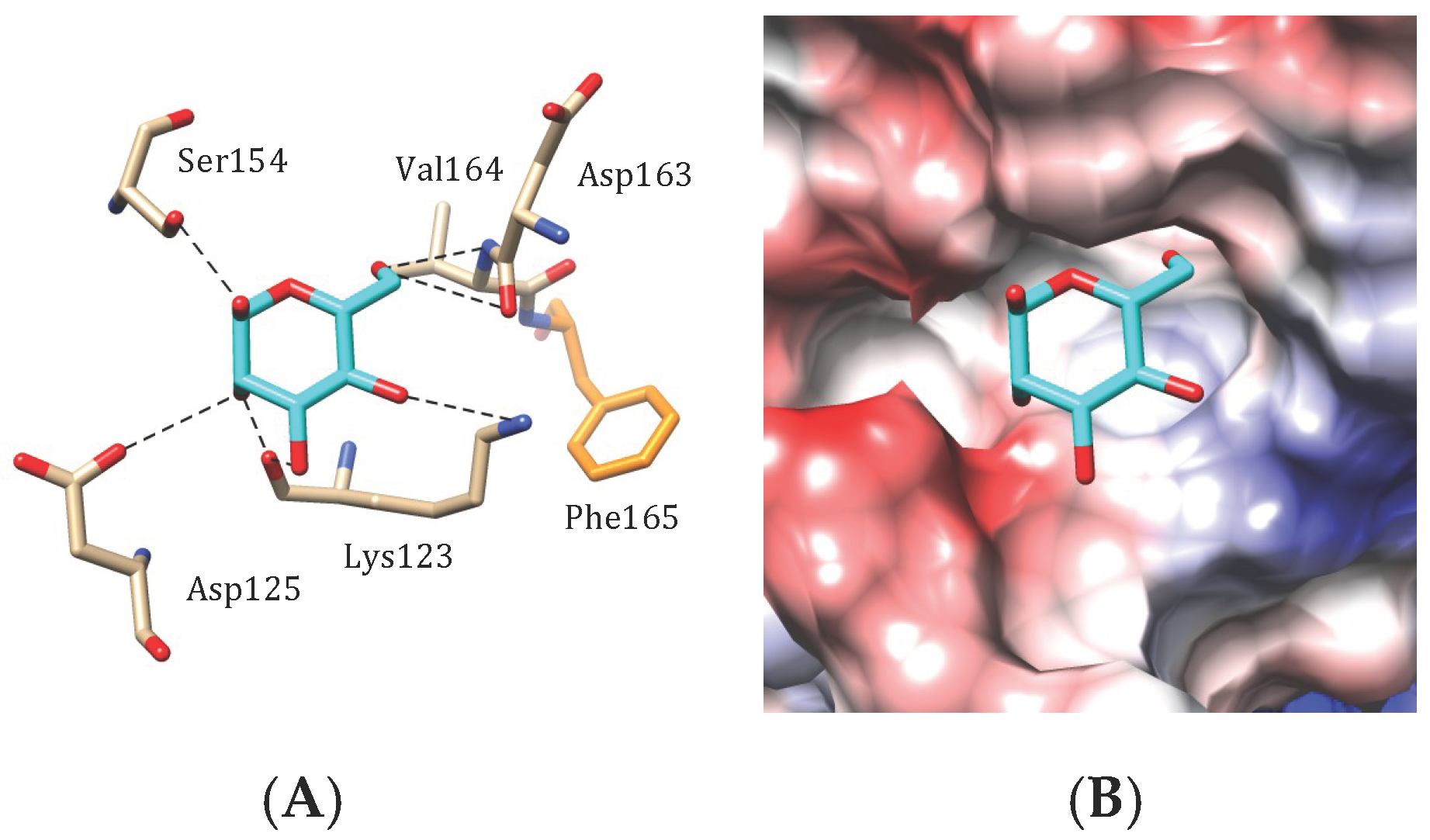
4.3. Legume Lectin-Like Seaweed Lectins
4.4. GNA-Like Seaweed Lectins
4.5. MFP2B-Like Seaweed Lectins
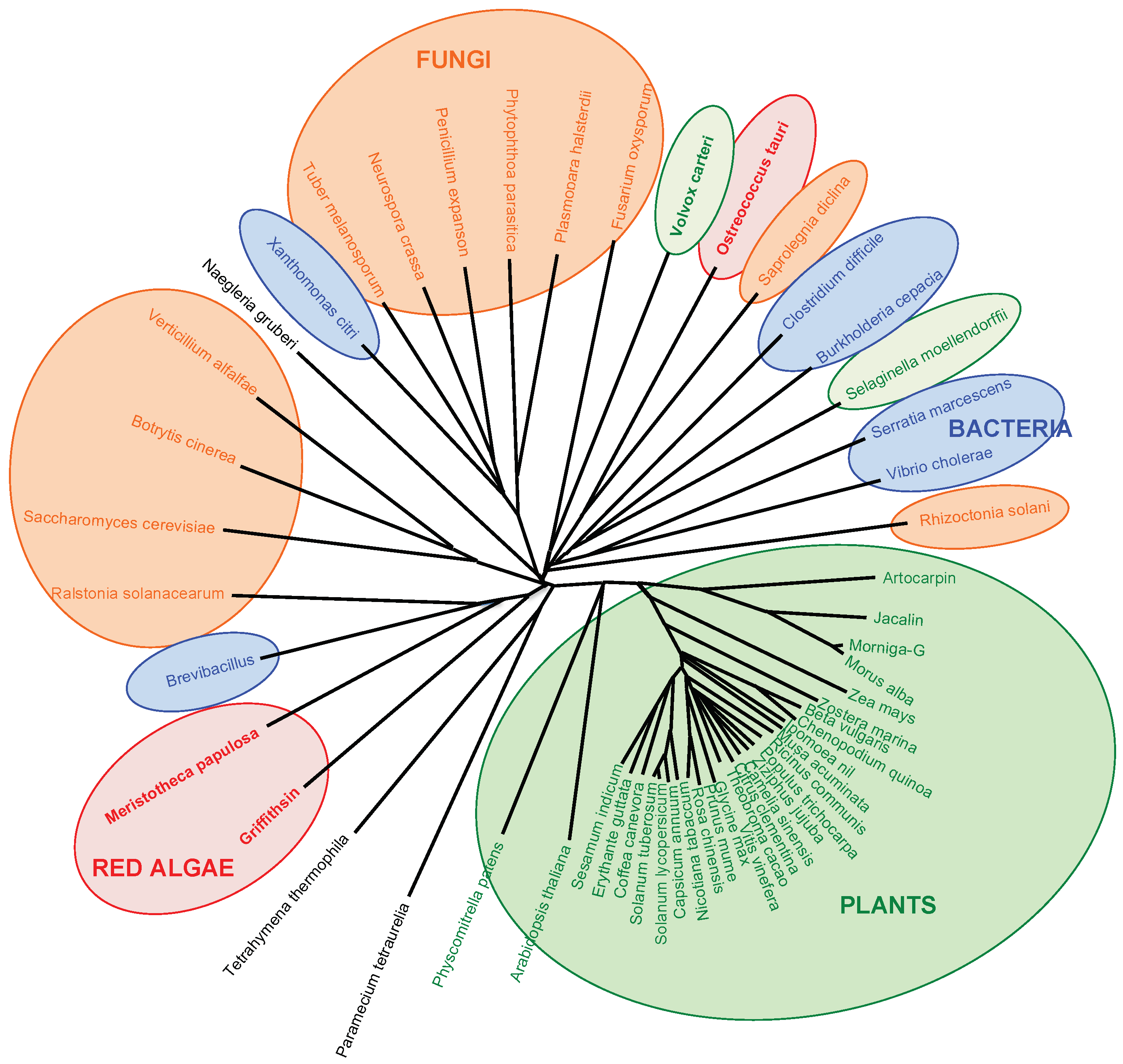
5. Phylogenetic Relationships between Mannose-Binding Seaweed Lectins and Higher Plants
6. Biomedical Applications for the Man-Specific Seaweed Lectins
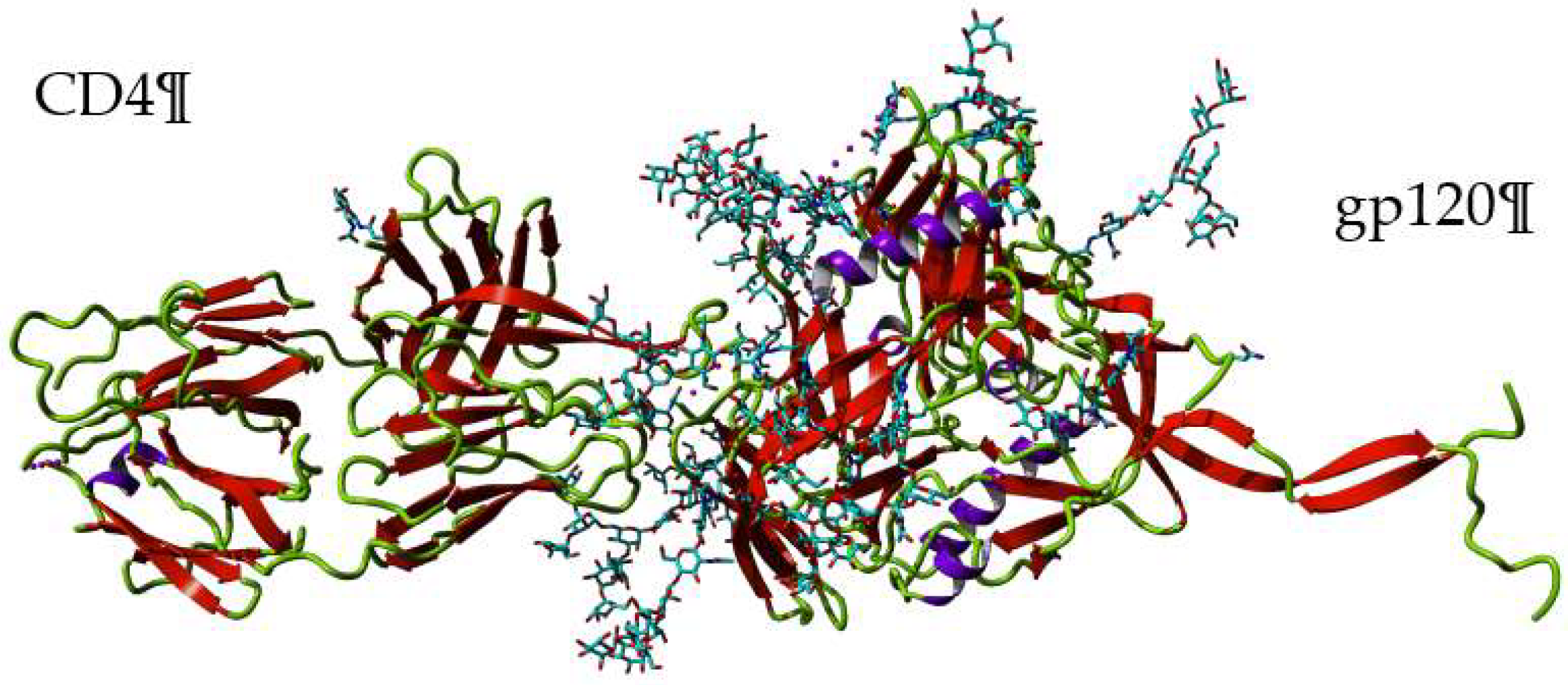
6.1. Mannose-Specific Seaweed Lectins as Virucidal Agents against HIV-I Infection
6.2. Mannose-Specific Lectins as Cancer Biomarkers and Anti-Cancer Drugs
6.3. Other Biomedical Applications of Mannose-Specific Seaweed Lectins
7. Methods
8. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CBA | Carbohydrate-binding agent |
| CBM | Carbohydrate-binding module |
| CBS | Carbohydrate-binding site |
| Con A | Concanavalin A |
| CVN | Cyanovirin N |
| GNA | Galanthus nivalis agglutinin |
| Heltuba | Helianthus tuberosus agglutinin |
| HIV | Human Immunodeficiency virus |
| LCA | Lens culinaris agglutinin |
| OAA | Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin |
| PDB | Protein data bank |
| PsA | Pisum sativum agglutinin |
| VfA | Vicia faba agglutinin |
References
- Wu, A.M.; Song, S.C.; Tsai, M.S.; Herp, A. A guide to the carbohydrate specificities of applied lectins-2. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2001, 491, 551–585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Rougé, P.; Peumans, W.J. Plant lectins. In Carbohydrate-Protein Interactions: Plant Lectins; Kamerling, J.P., Boons, G.J., Lee, Y.C., Suzuki, A., Taniguchi, N., Voragen, A.G.I., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 564–599. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, T.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Sowder, R.C., 2nd; Bringans, S.; Gardella, R.; Berg, S.; Cochran, P.; Turpin, J.A.; Buckheit, R.W., Jr.; McMahon, J.B.; et al. Isolation and characterization of griffithsin, a novel HIV-inactivating protein, from the red alga Griffithsia sp. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 9345–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akkouh, O.; Ng, T.B.; Singh, S.S.; Yin, C.; Dan, X.; Chan, Y.S.; Pan, W.; Cheung, R.C.F. Lectins with anti-HIV activity: A review. Molecules 2015, 20, 648–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.S.; Walia, A.K. Lectins from red algae and their biomedical potential. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 1833–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, E.J.M.; Peumans, W.J.; Barre, A.; Rougé, P. Plant lectins: A composite of several distinct families of structurally and evolutionary related proteins with diverse biological roles. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1998, 17, 575–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barre, A.; Bourne, Y.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Rougé, P. Overview of the structure-function relationships of mannose-specific lectins from plants, algae and fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, R.P.; da Silva, S.R.; da Silva, J.P.F.A.; Carneiro, R.F.; de Sousa, B.L.; Abreu, J.O.; de Carvalho, F.C.T.; Rocha, C.R.C.; Farias, W.R.L.; de Sousa, O.V.; et al. Meristiella echinocarpa lectin (MEL): A new member of the OAAH-lectin family. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 2629–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, A.; Makino, H.; Ohnishi, J.; Hirohara, H.; Kanji, H. Occurrence of highly yielded lectins homologous within genus Eucheuma. J. Appl. Phycol. 1999, 11, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.D.; Hirayama, M.; Ly, B.M.; Hori, K. Purification, primary structure, and biological activity of the high-mannose N-glycan-specific lectin from cultivated Eucheuma denticulatum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2015, 27, 1657–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakubo, A.; Makino, H.; Ohnishi, J.; Hirohara, H.; Kanji, H. The marine alga Eucheuma serra J. Agardh, a high yielding source of two isolectins. J. Appl. Phycol. 1997, 9, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Sato, Y.; Ito, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Makino, H.; Kawakubo, A. Strict specificity for high-mannose type N-glycans and primary structure of a red alga Eucheuma serra lectin. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Hirayama, M.; Hori, K. High mannose-specific lectin (KAA-2) from the red alga Kappaphycus alvarezii potently inhibits influenza virus infection in a strain-independent manner. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 405, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung le, D.; Sato, Y.; Hori, K. High-mannose N-glycan-specific lectin from the red alga Kappaphycus striatum (Carrageenophyte). Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, R.P.; da Silva, S.R.; Nascimento Neto, L.G.; Carneiro, R.F.; Coelho da Silva, A.L.; Sampaio, A.H.; Lopes de Sousa, B.; Cabral, M.G.; Videira, P.A.; Teixeira, E.H.; et al. Structural characterization of two isolectins from the marine red alga Solieria filiformis (Kützing) P.W. Gabrielson and their anticancer effect on MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corteggiani Carpinelli, E.; Telatin, A.; Vitulo, N.; Forcato, C.; D’Angelo, M.; Schiavon, R.; Vezzi, A.; Giacometti, G.M.; Morosinotto, T.; Valle, G. Chromosome scale genome assembly and transcriptome profiling of Nannochloropsis gaditana in nitrogen depletion. Mol. Plant. 2014, 7, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derelle, E.; Ferraz, C.; Rombauts, S.; Rouze, P.; Worden, A.Z.; Robbens, S.; Partensky, F.; Degroeve, S.; Echeynie, S.; Cooke, R.; et al. Genome analysis of the smallest free-living eukaryote Ostreococcus tauri unveils many unique features. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11647–11652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Morimoto, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Okuyama, S.; Hori, K. High-mannose-binding lectin with preference for the cluster of α1-2-mannose from the green alga Boodlea coacta is a potent entry inhibitor of HIV-1 and influenza viruses. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19446–19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Hirayama, M.; Sato, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Hori, K. A novel high-mannose specific lectin from the green alga Halimeda renschii exhibits a potent anti-influenza virus activity through high-affinity binding to the viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Holle, S.; Van Damme, E.J.M. Messages from the past: New insights in plant lectin evolution. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, J.V.; Jeyaprakash, A.A.; Rani, P.G.; Sekar, K.; Surolia, A.; Vijayan, M. Crystal structure of artocarpin, a Moraceae lectin with mannose specificity, and its complex with methyl-α-D-mannose: Implications to the generation of carbohydrate specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 317, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Sekar, K.; Banerjee, R.; Sharma, V.; Surolia, A.; Vijayan, M. A novel mode of carbohydrate recognition in jacalin, a Moraceae plant lectin with a β-prism fold. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.D.; Saikrishnan, K.; Kumar, P.; Surolia, A.; Sekar, K.; Vijayan, M. Unusual sugar specificity of banana lectin from Musa paradisiaca and its probable evolutionary origin. Crystallographic and modelling studies. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, Y.; Zamboni, V.; Barre, A.; Peumans, W.J.; Van Damme, E.J.; Rougé, P. Helianthus tuberosus lectin reveals a widespread scaffold for mannose-binding lectins. Structure 1999, 7, 1473–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Okuyama, S.; Hori, K. Primary structure and carbohydrate binding specificity of a potent anti-HIV lectin isolated from the filamentous cyanobacterium Oscillatoria agardhii. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11021–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koharudin, L.M.; Gronenborn, A.M. Structural basis of the anti-HIV activity of the cyanobacterial Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin. Structure 2011, 19, 1170–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koharudin, L.M.I.; Furey, W.; Gronenborn, A.M. Novel fold and carbohydrate specificity of the potent anti-HIV cyanobacterial lectin from Oscillatoria agardhii. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarwood, A.; Richardson, M.; Morphet, B.; Westby, M.; Père, D.; Rougé, P. The amino acid sequences of two atypical single-chain Vicieae isolectins from seeds of Lathyrus nissolia L. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 1719–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, M.; Yarwood, A.; Rougé, P. The amino acid sequence of an atypical single-chain lectin from seeds of Lathyrus sphaericus (Retz.). FEBS Lett. 1987, 216, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einspahr, H.; Pareks, E.H.; Suguna, K.; Subramanian, E.; Suddath, F.L. The crystal structure of pea lectin at 3.0-Å resolution. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 16518–16527. [Google Scholar]
- Foriers, A.; Van Driessche, E.; De Neve, R.; Kanarek, L.; Strosberg, A.D. The subunit structure and N-terminal sequences of the α- and β-subunits of the lentil lectin (Lens culinaris). FEBS Lett. 1977, 75, 237–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, Y.; Abergel, C.; Cambillau, C.; Frey, M.; Rougé, P.; Fontecilla-Camps, J.C. X-ray crystal structure determination and refinement at 1.9 Å resolution of isolectin I from the seeds of Lathyrus ochrus. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 214, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeke, G.N., Jr.; Becker, J.W. Three-dimensional structure of favin: Saccharide binding-cyclic permutation in leguminous lectins. Science 1986, 234, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buts, L.; Garcia-Pino, A.; Wyns, L.; Loris, R. Structural basis of carbohydrate recognition by a Man(α1-2)Man-specific lectin from Bowringia Milbraedii. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, A.C.; Osterne, V.J.; Santiago, M.Q.; Pinto-Junior, V.R.; Silva-Filho, J.C.; Lossio, C.F.; Nascimento, F.L.; Almeida, R.P.; Teixeira, C.S.; Leal, R.B.; et al. Structural analysis of Centrolobium tomentosum seed lectin with inflammatory activity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 596, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loris, R.; Imberty, A.; Beeckmans, S.; Van Driessche, E.; Read, J.S.; Bouckaert, J.; De Greve, H.; Buts, L.; Wyns, L. Crystal structure of Pterocarpus angolensis lectin in complex with glucose, sucrose, and turanose. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16297–16303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, K.D.; Ainsworth, C.F. Structure of concanavalin A at 2.4-Å resolution. Biochemistry 1972, 11, 4910–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, B.A.; Delatorre, P.; Oliveira, T.M.; Benevides, R.G.; Pires, A.F.; Sousa, A.A.; Souza, L.A.; Assreuy, A.M.; Debray, H.; de Azevedo, W.F., Jr.; et al. Structural basis for both pro-and anti-inflammatory response induced by mannose-specific legume lectin from Cymbosema roseum. Biochimie 2011, 93, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozwarski, D.A.; Swami, B.M.; Brewer, C.F.; Sacchetini, J.C. Crystal structure of the lectin from Dioclea grandiflora complexed with core trimannoside of asparagine-linked carbohydrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32818–32825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Cowleson, N.P.; Hakamata, W.; Ideo, H.; Fukushima, K.; Kurihara, M.; Kato, R.; Yamashita, K.; Wakatsuki, S. Structural basis for recognition of high mannose type glycoproteins by mammalian transport lectin VIP36. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28246–28255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velloso, L.M.; Svensson, K.; Schneider, G.; Pettersson, R.F.; Lindqvist, Y. Crystal structure of the carbohydrate recognition domain of p58/ERGIC-53, a protein involved in glycoprotein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 15979–15984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, R.P.; Buttery, S.M.; Ekman, G.C.; Roberts, T.M.; Stewart, M. Structure of MFP2 and its function in enhancing MSP polymerization in Ascaris sperm amoeboid motility. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 347, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosio, A.L.; Sanz, L.; Sánchez, E.I.; Wolfenstein-Todel, C.; Calvete, J.J. Isolation of two novel mannan- and L-fucose-binding lectins from the green alga Enteromorpha prolifera: Biochemical characterization of EPL-2. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 415, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, M.R.; Gustafson, K.R.; McMahon, J.B.; Shoemaker, R.H.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mori, T.; Gulakowski, R.J.; Wu, L.; Rivera, M.I.; Laurencot, C.M.; et al. Discovery of cyanovirin-N, a novel human immunodeficiency virus-inactivating protein that binds viral surface envelope glycoprotein gp120: Potential applications to microbicide development. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, H.; Inokoshi, J.; Okamoto, M.; Matsuzaki, K.; Iwama, M.; Mizumoto, K.; Tanaka, H.; Oheda, M.; Fujita, K.; Nakashima, H.; et al. Actinohivin, a novel anti-HIV protein from an actinomycete that inhibits syncytium formation: Isolation, characterization, and biological activities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huskens, D.; Schols, D. Algal lectins as potential HIV microbicide candidates. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1476–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewley, C.A.; Gustafson, K.R.; Boyd, M.R.; Covell, D.G.; Bax, A.; Clore, G.M.; Gronenborn, A.M. Solution structure of cyanovirin-N, a potent HIV-inactivating protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1998, 5, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Chiba, H.; Inokoshi, J.; Kuno, A.; Sugai, T.; Takahashi, A.; Ito, Y.; Tsunoda, M.; Suzuki, K.; Takénaka, A.; et al. Mechanism by which the lectin actinohivin blocks HIV infection of target cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 15633–15638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botos, I.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Shenoy, S.R.; Cartner, L.K.; Ratner, D.M.; Seeberger, P.H.; Boyd, M.R.; Wlodawer, A. Structures of the complexes of a potent anti-HIV protein cyanovirin-N and high mannose oligosaccharides. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 34336–34342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hoque, M.M.; Jiang, J.; Suzuki, K.; Tsunoda, M.; Takeda, Y.; Ito, Y.; Kawai, G.; Tanaka, H.; Takenaka, A. The characteristic structure of anti-HIV actinohivin in complex with three HMTG D1 chains of HIV-gp120. Chembiochem 2014, 15, 2766–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlólkowska, N.E.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Mori, T.; Zhu, C.; Giomarelli, B.; Vojdani, F.; Palmer, K.E.; McMahon, J.B.; Wlodawer, A. Domain-swapped structure of the potent antiviral protein griffithsin and its mode of carbohydrate binding. Structure 2006, 14, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlólkowska, N.E.; Shenoy, S.R.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Wlodawer, A. Crystallographic studies of the complexes of antiviral protein griffithsin with glucose and N-acetylglucosamine. Protein Sci. 2007, 16, 1485–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zlólkowska, N.E.; Shenoy, S.R.; O’Keefe, B.R.; McMahon, J.B.; Palmer, K.E.; Dwek, R.A.; Wormald, M.R.; Wlodawer, A. Crystallographic, thermodynamic, and molecular modeling studies of the mode of binding of oligosaccharides to the potent antiviral protein griffithsin. Proteins 2007, 67, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulaei, T.; Shenoy, S.R.; Giomarelli, B.; Thomas, C.; McMahon, J.B.; Dauter, Z.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Wlodawer, A. Monomerization of viral entry inhibitor griffithsin elucidates the relationship between multivalent binding to carbohydrates and anti-HIV activity. Structure 2010, 18, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.I.; Moore, C.E.; Archibald, J.M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Yi, G.; Yoon, H.S.; Shon, W. Evolutionary dynamics of cryptophyte plastid genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1859–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brawley, S.H.; Blouin, N.A.; Ficko-Blean, E.; Wheeler, G.L.; Lohr, M.; Goodson, H.V.; Jenkins, J.W.; Blaby-Haas, C.E.; Helliwell, K.E.; Chan, C.X.; et al. Insights into the red algae and eukaryotic evolution from the genome of Porphyra umbilicalis (Bangiophyceae, Rhodophyta). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6361–E6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, F.; Hassan, M.; Rosli, R.; Almousally, I.; Hanano, A.; Murphy, D.J. Evolutionary and genomic analysis of the caleosin/peroxygenase (CLO/PXG) gene/protein families in the Viridiplantae. PLoS ONE 2018, 19, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Kingdom Chromista and its eightphyla: A new synthesis emphasising periplastid protein targeting, cytoskeletal and periplastid evolution, and ancient divergences. Protoplasma 2018, 255, 297–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart-Jones, G.B.; Soto, C.; Lemmin, T.; Chuang, G.Y.; Druz, A.; Kong, R.; Thomas, P.V.; Wagh, K.; Zhou, T.; Behrens, A.J.; et al. Trimeric HIV-structures define glycan shields from clades A, B, and G. Cell 2016, 165, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jin, W.; Griffin, G.E.; Shattock, R.J.; Hu, Q. Removal of two high-mannose N-linked glycans on gp120 renders human immunodeficiency virus 1 largely resistant to the carbohydrate-binding agent griffithsin. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 2367–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micevicz, E.D.; Cole, A.L.; Jung, C.L.; Luong, H.; Phillips, M.L.; Pratikhya, P.; Sharma, S.; Waring, A.J.; Cole, A.M.; Ruchala, P. Grifonin-I: A small HIV-1 entry inhibitor derived from the algal lectin, griffithsin. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emau, P.; Tina, B.; O’Keefe, B.K.; Mori, T.; McMahon, J.B.; Palmer, K.E.; Jiang, Y.; Bekele, G.; Tsai, C.C. Griffithsin, a potent HIV entry inhibitor, is an excellent candidate for anti-HIV microbicide. J. Med. Primatol. 2007, 36, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, B.R.; Vojdani, F.; Buffa, V.; Shattock, R.J.; Montefiori, D.C.; Bakke, J.; Mirsalis, J.; d’Andrea, A.L.; Hume, S.D.; Bratcher, B.; et al. Scaleable manufacture of HIV-1 entry inhibitor griffithsin and validation of its safety and efficacy as a topical microbicide component. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6099–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, K.B.; Gray, E.S.; Lambson, B.E.; Moore, P.L.; Choge, I.A.; Mlisana, K.; Karim, S.S.; McMahon, J.; O’Keefe, B.; Chikwamba, R.; et al. Mannose-rich glycosylation patterns on HIV-1 subtype C gp120 and sensitivity to the lectins, griffithsin, cyanovirin-N and scytovirin. Virology 2010, 402, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, K.B.; Gray, E.S.; Pantophlet, R.; Moore, P.L.; McMahon, J.B.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Chikwamba, R.; Morris, L. Binding of the mannose-specific lectin, griffithsin, to HIV-1 gp120 exposes the CD4-binding site. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 9039–9050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandre, K.B.; Gray, E.S.; Mufhandu, H.; McMahon, J.B.; Chakauya, E.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Chikwamba, R.; Morris, L. The lectins griffithsin, cyanovirin-N and scytovirin inhibit HIV-1 binding to the DC-SIGN receptor and transfer to CD4(+) cells. Virology 2012, 423, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férir, G.; Palmer, K.E.; Schols, D. Synergistic activity profile of griffithsin in combination with tenofovir, maraviroc and enfuvirtide against HIV-1 clade C. Virology 2011, 417, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouokam, J.C.; Huskens, D.; Schols, D.; Johannemann, A.; Riedell, S.K.; Walter, W.; Walker, J.M.; Matoba, N.; O’Keefe, B.R.; Palmer, K.E. Investigation of griffithsin’s interactions with human cells confirms its outstanding safety and efficacy profile as a microbicide candidate. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Gao, Y.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Kagiampakis, I.; Zhao, B.; Demeler, B.; Balzarini, J.; Liwang, P.J. The role of individual carbohydrate-binding sites in the function of the potent anti-HIV lectin griffithsin. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 2613–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoorelbeke, B.; Xue, J.; Liwang, P.J.; Balzarini, J. Role of the carbohydrate-binding sites of griffithsin in the prevention of DC-SIGN-mediated capture and transmission of HIV-1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nixon, B.; Stefanidou, M.; Mesquita, P.M.; Fakioglu, E.; Segarra, T.; Rohan, L.; Halford, W.; Palmer, K.E.; Herold, B.C. Griffithsin protects mice from genital herpes by preventing cell-to-cell spread. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 6257–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Hoorelbeke, B.; Kagiampakis, I.; Demeler, B.; Balzarini, J.; Liwang, P.J. The griffithsin dimer is required for high-potency inhibition of HIV-1: Evidence for manipulation of the structure of gp120 as part of the griffithsin dimer mechanism. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3976–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, C.; Kouokam, J.C.; Lasnik, A.B.; Foreman, O.; Cambon, A.; Brock, G.; Montefiori, D.C.; Vojdani, F.; McCormick, A.A.; O’Keefe, B.R.; et al. Activity of and effect of subcutaneous treatment with the broad-spectrum antiviral lectin griffithsin in two laboratory rodent models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulaei, T.; Alexandre, K.B.; Shenoy, S.R.; Meyerson, J.R.; Krumpe, L.R.; Constantine, B.; Wilson, J.; Buckheit, R.W., Jr.; McMahon, J.B.; Subramaniam, S.; et al. Griffithsin tandemers: Flexible and potent lectin inhibitors of the human immunodeficiency virus. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, C.; Kouokam, J.C.; Hurst, I.; Palmer, K.E. Pharmacokinetics of the antiviral lectin griffithsin administered by different routes indicates multiple potential uses. Viruses 2016, 8, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouokam, J.C.; Lasnik, A.B.; Palmer, K.E. Studies in a murine model confirm the safety of griffithsin and advocate its further development as a microbicide targeting HIV-1 and other enveloped viruses. Viruses 2016, 8, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuong, H.R.; Tyo, K.M.; Steinbach-Rankins, J.M. Fabrication and characterization of griffithsin-modified fiber scaffolds for prevention of sexually transmitted infections. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 128, e56492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, M.; Lai, M.; Ugaonkar, S.; Wesenberg, A.; Kízima, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Levendosky, K.; Mizenina, O.; Fernández-Romero, J.; Zydowsky, T. Development of a vaginal fast-dissolving insert combining griffithsin and carrageenan for potential use against sexually transmitted infections. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Li, J.; Patel, S.K.; Palmer, K.E.; Devlin, B.; Rohan, L.C. Design of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles for vaginal co-delivery of griffithsin and dapivirin and their synergistic effect for HIV prophylaxis. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahyama, M.; Shibata, H.; Imamura, K.; Sakaguchi, T.; Hori, K. High-mannose specific lectin and its recombinants from a carrageenophyta Kappaphycus alvarezii represent a potent anti-HIV activity through high-affinity binding to the viral envelope glycoprotein gp120. Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuleman, P.; Albecka, A.; Belouzard, S.; Vercauteren, K.; Verhoye, L.; Wychowski, C.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Palmer, K.E.; Dubuisson, J. Griffithsin has antiviral activity against hepatitis C virus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5159–5167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takebe, Y.; Saucedo, C.J.; Lund, G.; Uenishi, R.; Hase, S.; Tsuchiura, T.; Kneteman, N.; Ramessar, K.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Shirakura, M.; et al. Antiviral lectins from red and blue-green algae show potent in vitro and in vivo activity against hepatitis C virus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levendosky, K.; Mizenina, O.; Martinelli, E.; Jean-Pierre, N.; Kizima, L.; Rodríguez, A.; Kleinbeck, K.; Bonnaire, T.; Robbiani, M.; Zydowsky, T.M.; et al. Griffithsin and carrageenan combination to target Herpes simplex virus 2 and human papillomavirus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 7290–7298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Keefe, B.R.; Giomarelli, B.; Barnard, D.L.; Shenoy, S.R.; Chan, P.K.; McMahon, J.B.; Palmer, K.E.; Barnett, B.W.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Vohlford-lenane, C.L.; et al. Broad-spectrum in vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of the antiviral protein griffithsin against emerging viruses of the family coronaviridae. J. Virol. 2010, 84, 2511–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Morimoto, K.; Kubo, T.; Sakaguchi, T.; Nishizono, A.; Hirayama, M.; Hori, K. Entry inhibition of influenza viruses with high mannose binding lectin ESA-2 from the red alga Eucheuma serra through the recognition of viral hemagglutinin. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3454–3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahzad-ul-Huassan, S.; Gustchina, E.; Ghirlando, R.; Clore, G.M.; Bewley, C.A. Solution structure of the monovalent lectin microvirin in complex with Manα(1-2)Man provides a basis for anti-HIV activity with low toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20788–20796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, K.; Kamiya, H.; Shimizu, Y. Purification and characterization of an agglutinin in the red alga Agardhiella tenera. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 576, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, V.P.; Debray, H.; Dus, D.; Teixeira, E.H.; de Oliveira, T.M.; Carneiro, V.A.; Teixeira, A.H.; Filho, G.C.; Nagano, C.S.; Nascimento, K.S.; et al. Lectins from the red marine algal species Bryothamnion seaforthii and Bryothamnion triquetrum as tools to differentiate human colon carcinoma cells. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 2009, 862162. [Google Scholar]
- Conrado, F.M.; Furtado, L.E.T.A.; Teixeira, A.H.; Coutinho, N.L.P.; Sampaio, A.H.; Cavada, B.S.; Bezerra, M.M.; Silva, A.A.R.; Barbosa, F.C.B.; Chaves, H.V.; et al. Erythrina velutina and Bryothamnion seaforthii lectins binding to proteins of primary central nervous system tumors. J. Cancer Res. Exp. Oncol. 2012, 4, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugahara, T.; Ohama, Y.; Fukuda, A.; Hayashi, M.; Kawakubo, A.; Kato, K. The cytotoxic effect of Eucheuma serrata agglutinin (ESA) on cancer cells and its application to molecular probe for drug delivery system using lipid vesicles. Cytotechnology 2001, 36, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, Y.; Sugahara, T.; Ueno, M.; Fukuta, Y.; Ochi, Y.; Akiyama, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Masuda, S.; Kawakubo, A.; Kato, K. The anti-tumor effect of Eucheuma serra agglutinin on colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Anticancer Drugs 2006, 17, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokawa, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Walde, P.; Akiyama, K.; Sugahara, T.; Masuda, S.; Inada, A.; Ohnishi, Y.; Saeki, T.; Kato, K. In vitro and in vivo anti-tumor effects of novel Span 80 vesicles containing immobilized Eucheuma serra agglutinin. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 389, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Walde, P.; Miyazaki, T.; Sakayama, K.; Nakamura, A.; Kameda, K.; Masuda, S.; Umakoshi, H.; Kato, K. Active targeting to osteosarcoma cells and apoptotic cell death induction by the novel lectin Eucheuma serra agglutinin isolated from a marine red alga. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 842785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.R.; Lin, J.Y.; Shieh, W.Y.; Jeng, W.L.; Huang, R. Antibiotic activity of lectins from marine algae against marine vibrios. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holanda, M.L.; Melo, V.M.; Silva, L.M.; Amorim, R.C.; Pereira, M.G.; Benevides, N.M. Differential activity of a lectin from Solieria filiformis against human pathogenic bacteria. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, T.M.; Ribeiro, N.A.; Chaves, H.V.; Jorge, R.J.; Bezerra, M.M.; Monteiro, H.S.; Vasconcelos, I.M.; Mota, E.F.; Benevides, N.M. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of the lectin from marine alga Solieria filiformis. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 596–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abreu, T.M.; Monteiro, V.S.; Martins, A.B.S.; Teles, F.B.; da Conceição Rivanor, R.L.; Mota, E.F.; Macedo, D.S.; de Vasconcelos, S.M.M.; Júnior, J.E.R.H.; Benevides, N.M.B. Involvement of the dopaminergic system in the antidepressant-like effect of the lectin isolated from the red marine alga Solieria filiformis in mice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Nascimento-Neto, L.G.; Carneiro, R.F.; da Silva, S.R.; da Silva, B.R.; Vassiliepe Sousa Arruda, F.; Carneiro, V.A.; do Nascimento, K.S.; Saker-Sampaio, S.; da Silva, V.A., Jr.; Porto, A.L.; et al. Characterization of isoforms of the lectin isolated from the red algae Bryothamnion seaforthii and its pro-healing effect. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1936–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.D.; Gibson, T.J.; Plewniak, F.; Jeanmougin, F.; Higgins, D.G. The CLUSTAL-X windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 15, 4876–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaboriaud, C.; Bissery, V.; Benchetrit, T.; Mornon, J.P. Hydrophobic cluster analysis: An efficient new way to compare and analyse amino acid sequences. FEBS Lett. 1987, 224, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, R.D. TreeView: An application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 1996, 12, 357–358. [Google Scholar]
- Krieger, E.; Koraimann, G.; Vriend, G. Increasing the precision of comparative models with YASARA NOVA—A self-parametrizing force field. Proteins 2002, 47, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemistry of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 126, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, F.; Feytmans, E. Assessing protein structures with a non-local atomic interaction energy. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkert, P.; Biasini, M.; Schwede, T. Toward the estimation of the absolute quality of individual protein structure models. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, K.; Bordoli, L.; Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: A web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, K.N.; Yongye, A.B.; Tschampel, S.M.; Daniels, C.R.; Foley, B.L.; Woods, R.J.J. GLYCAM06: A generalizable biomolecular force field. Carbohydrates. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 622–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Schloissnig, S. Bioinformaticsand and molecular modeling in glycobiology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 2749–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohne, A.; Lang, E.; von der Lieth, C.W. SWEET—WWW-based rapid 3D construction of oligo-and polysaccharides. Bioinformatics 1999, 15, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock VINA: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. SwissDock, a protein-small molecule docking web service based on EADock DSS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W270–W277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosdidier, A.; Zoete, V.; Michielin, O. Fast docking using the CHARMM force field with EADock DSS. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagano, C.S.; Debray, H.; Nascimento, K.S.; Pinto, V.P.; Cavada, B.S.; Saker-Sampaio, S.; Farias, W.R.; Sampaio, A.H.; Calvete, J.J. HCA and HML isolated from the red marine algae Hypnea cervicormis and Hypnea musciformis define a novel lectin family. Protein Sci. 2005, 14, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Férir, G.; Huskens, D.; Noppen, S.; Koharudin, L.M.; Gronenborn, A.M.; Schols, D. Broad anti-HIV activity of the Oscillatoria agardhii agglutinin homologue lectin family. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuck, R.; Paul, C.; Wieland, B.; Heldrich, C.; Geilen, C.C.; Reutter, W. Comparative study of high mannose-type oligosaccharides in membrane glycoproteins of rat hepatocytes and different rat hepatoma cell lines. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 216, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylo, M.; Hoja-Lukowicz, D.; Litynska, A.; Laidler, P. Different glycosylation of cadherins from human bladder non-malignant and cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 2002, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xing, Y.; Geng, M. Role of cell surface oligosaccharides of mouse mammary tumor cell lines in cancer metastasis. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 44, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- De Leoz, M.L.; An, H.J.; Krnonewitter, S.; Kim, J.; Beecroft, S.; Vinall, R.; Miyamoto, S.; de Were White, R.; Lam, K.S.; Lebrilla, C. Glycomic approach for potential biomarkers on prostate cancer: Profiling of N-linked glycans in human sera and pRNS cell lines. Dis. Markers 2008, 25, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leoz, M.M.; Young, L.J.; An, H.J.; Kronewitter, S.R.; Kim, J.; Miyamoto, S.; Borowsky, A.D.; Chew, H.K.; Lebrilla, C.B. High-mannose glycans are elevated during breast cancer progression. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2011, 10, M110.002717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Nie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Maitikabili, A.; Qu, Y.; Shi, S.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Cell surface-specific N-glycan profiling in breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, M.K.; Thaysen-Andersen, M.; Smith, J.T.; Baker, M.S.; Packer, N.H.; Hancock, W.S.; Fanayan, S. Comparative N-glycan profiling of colorectal cancer cell lines reveals unique bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,3-linked sialic acid determinants are associated with membrane proteins of the more metastatic/aggressive cell lines. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaprio, T.; Satomaa, T.; Heiskanen, A.; Hokke, C.H.; Deelder, A.M.; Mustonen, H.; Hagström, J.; Carpen, O.; Saarinen, J.; Haglund, C. N-glycomic profiling as a tool to separate rectal adenomas from carcinomas. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2015, 14, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, S.; Wuhrer, M.; Rombouts, Y. Glycosylation characteristics of colorectal cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2015, 126, 203–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.M.; Hwang, M.P.; Kim, Y.W.; Kim, K.J.; Jin, J.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.G. Mass spectrometry-based N-linked glycomic profiling as a means for tracking pancreatic cancer metastasis. Carbohydr. Res. 2015, 413, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Deng, Z.; Huang, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y. Mass spectrometric profiling reveals association of N-glycan patterns with epithelial ovarian cancer progression. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317716249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talabnin, K.; Talabnin, C.; Ishihara, M.; Azadi, P. Increased expression of the high-mannose M6N2 and NeuAc3H3N3M3N2F tri-antennary N-glycans in cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 15, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Miao, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, T.; Cao, X.; Li, Y. Mass spectrometry analysis reveals aberrant N-glycans in colorectal cancer tissues. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derby, N.; Lal, M.; Aravantinou, M.; Kizima, L.; Barnable, P.; Rodriguez, A.; Lai, M.; Kleinbeck, K.; Lifison, J.D.; Peet, M.M.; et al. Griffithsin carrageenan fast dissolving inserts prevent SHIV HSV2 and HPV infections in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Férir, G.; Huskens, D.; Palmer, K.E.; Boudreaux, D.M.; Swanson, M.D.; Markovitz, D.M.; Balzarini, J.; Schols, D. Combinations of griffithsin with other carbohydrate-binding agents demonstrate superior activity against HIV type 1, HIV type 2, and selected carbohydrate-ding agent-resistant HIV type 1 strains. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2012, 28, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grooms, T.N.; Vuung, H.R.; Tyo, K.M.; Malik, D.A.; Sims, L.B.; Whittington, C.P.; Palmer, K.E.; Matoba, N.; Steinbach-Rankins, J.M. Griffithsin-modified electrospun fibers as a delivery scaffold to prevent HIV infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 6518–6531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamvaka, E.; Farré, G.; Molinos-Albert, L.M.; Evans, A.; Canela-Xandri, A.; Twyman, R.M.; Carrillo, J.; Ordóñez, A.; Shattock, R.J.; O’Keefe, B.R.; et al. Unexpected synergistic HIV neutralization by a triple microbicide produced in rice endosperm. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7854–E7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
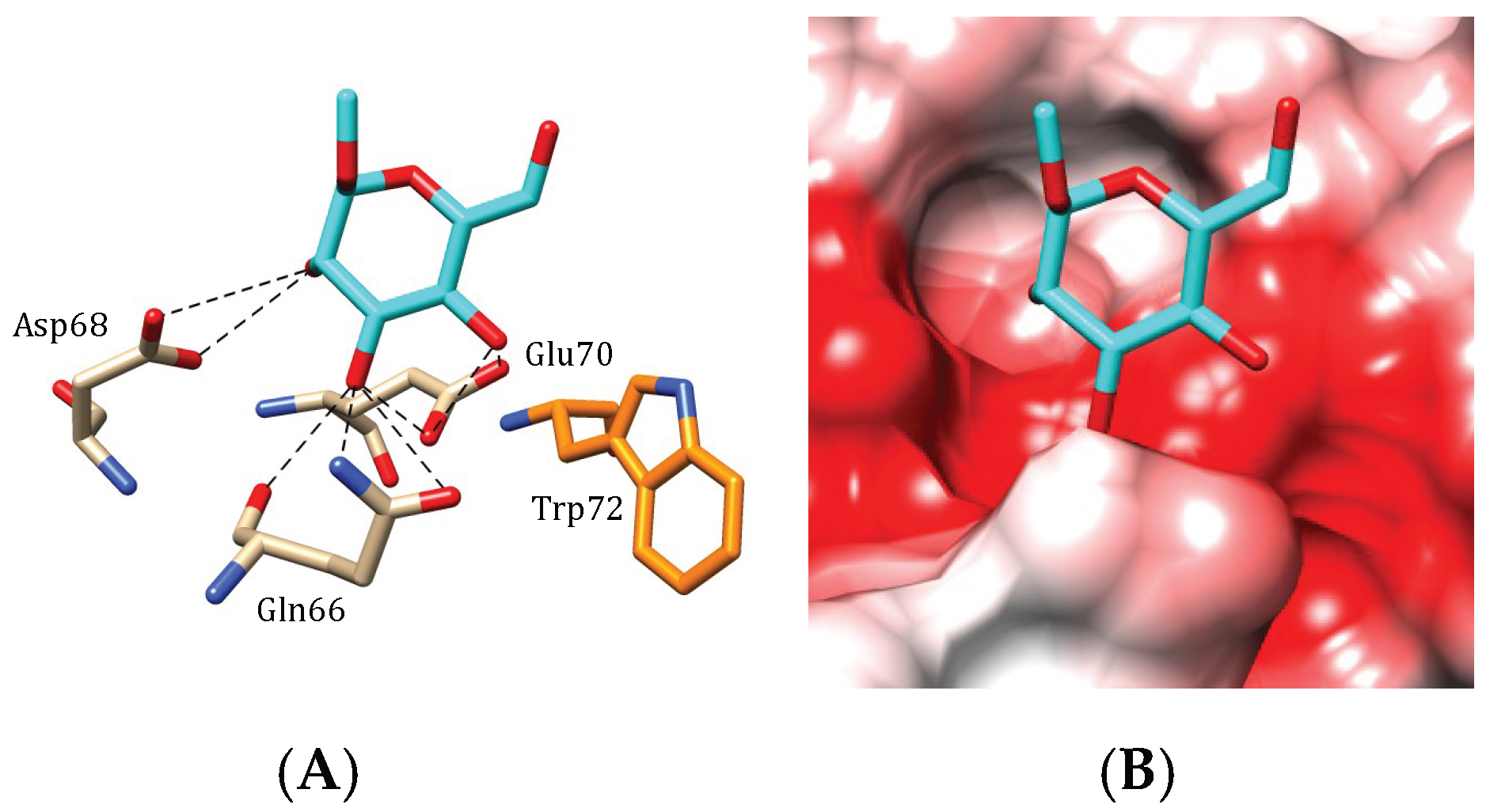
 ) and GlcNAc (
) and GlcNAc ( ) were used to draw the molecular cartoons of high-mannose glycan chains.
) were used to draw the molecular cartoons of high-mannose glycan chains.
 ) and GlcNAc (
) and GlcNAc ( ) were used to draw the molecular cartoons of high-mannose glycan chains.
) were used to draw the molecular cartoons of high-mannose glycan chains.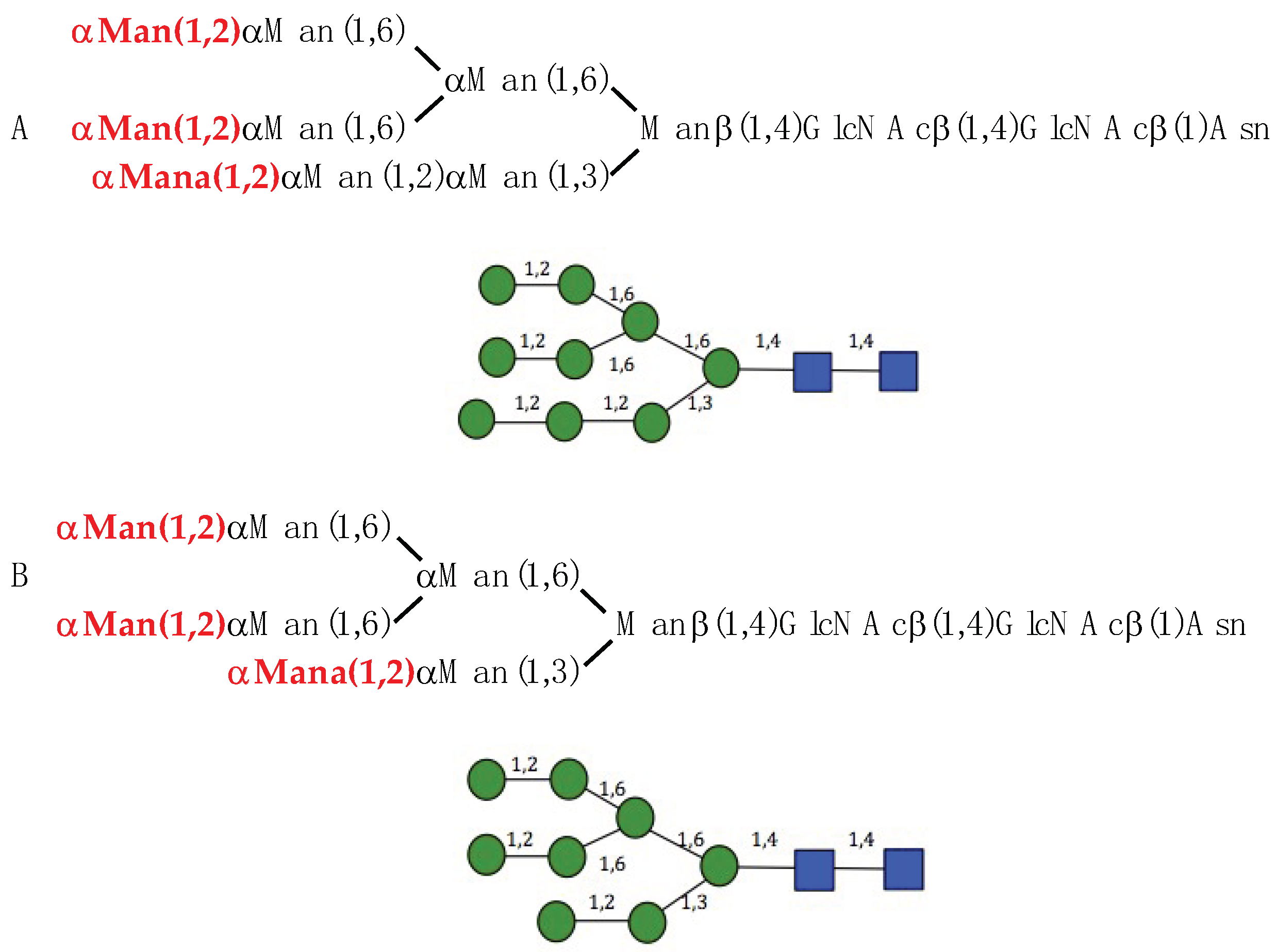
| Algae Phylum | Algae Family | Algae Species | Lectin | Structural Scaffold | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red algae | Griffithsin | Griffithsia sp. | griffithsin | β-prism I | [3] |
| Brown algae | OAAH-like | Agardhiella subulata | ASL-1, | β-barrel | [8] |
| ASL-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Eucheuma amakusaensis | EAA-1 | β-barrel | [9] | ||
| EAA-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| EAA-3 | β-barrel | ||||
| Eucheuma cottonii | ECA-1 | β-barrel | [9] | ||
| ECA-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Eucheuma denticulatum | EDA-1 | β-barrel | [10] | ||
| EDA-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Eucheuma serra | ESA-1 | β-barrel | [11,12] | ||
| ESA-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Kappaphycus alvarezii | KAA-2 | β-barrel | [13] | ||
| Kappaphycus striatum | KSA-2 | β-barrel | [14] | ||
| Meristiella echinocarpa | MEL | β-barrel | [8] | ||
| Meristotheca papulosa | MPA-1 | β-barrel | [8] | ||
| MPA-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Solieria filiformis | SfL-1 | β-barrel | [15] | ||
| SfL-2 | β-barrel | ||||
| Yellow- | Legume-like | Hydropuntia fisheri | HFA | β-sandwich | [Ac. GQ906709] |
| Nannochloropsis gaditana | NgL | β-sandwich | [16] | ||
| Porphyra umbilicalis | BU14 | β-sandwich | [Ac. OSX69288] | ||
| Ostreococcus tauri | OtL | β-sandwich | [17] | ||
| green algae | GNA-like | Boodlea coacta | BCA | β-prism II | [18] |
| Green algae | MFP2-like | Bryopsis plumosa | BPL-2 | MFP2-like | [Ac. BAI43482] |
| scaffold? | |||||
| unknown | Halimeda renschii | HRL40-1/2 | β-prism I | [19] |
| Algae Species | Lectin | PDB Code (Complexed Sugar) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Griffithsia sp. | griffithsin | 2GUC, 2GUD (Man) | [51] |
| 2NUO (Glc) | [52] | ||
| 2GUE (GlcNAc), 2NU5 (GlcNAc) | [51,52] | ||
| 2HYQ (α 1,6-mannobiose), 2HYR (maltose) | [53] | ||
| 3LL2 (9ManGlcNAc2) | [54] |
| Algae Phylum | Algae Family | Lectin | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red algae | Griffithsin | Griffithsin (Griffithsia sp.) | [4,54,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79] |
| (Rhodophyta) | GRFN-1 or Grifonin-1 (Griffithsia sp.) | [61] | |
| OAAH-like family | KAA-2 (Kappaphycus alvarezii) | [80] | |
| Green algae | GNA-like family | BCA (Boodlea coacta) | [4,18] |
| (Chlorophyta) | Legume-like family | OtL (Ostreococcus tauri) | [17] |
| Phylum | Species | Lectin | Cancer cell | Apopt. | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red algae | Agardhiella tenera | ATA | mouse leukemia cell L5178Y | [87] | |
| Bryoyhamnion seaforthii | BSL | human colon carcinoma cells L5178Y | [88] | ||
| oligodendroglioma, ependymona, | [89] | ||||
| meningioma, medullo-blastoma | |||||
| Bryothamnion triquetrum | BTL | human colon carcinoma | + | [89] | |
| Eucheuma serra | ESA | Colo201, HeLa | + | [90] | |
| Solieria filiformis | SfL-1 | mouse Colon26 adenocarcinoma | + | [91] | |
| SfL-2 | Colo201 | + | [92] | ||
| human osteocarcinoma, murine | + | [93] | |||
| osteocarcinoma LM8 | |||||
| MCF-7 | [15] |
| Alga Phylum | Alga Species | Lectin | Biomedical Property | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red algae | Eucheuma serra | ESA | Anti-bacterial | [94] |
| Solieria filiformis | SfL | Anti-bacterial | [95] | |
| Solieria filiformis | SfL | Anti-nociceptive | [96] | |
| Solieria filiformis | SfL | Anti-depressant | [97] | |
| Bryothamnion seaforthii | BSL | Pro-healing | [98] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barre, A.; Simplicien, M.; Benoist, H.; Van Damme, E.J.M.; Rougé, P. Mannose-Specific Lectins from Marine Algae: Diverse Structural Scaffolds Associated to Common Virucidal and Anti-Cancer Properties. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080440
Barre A, Simplicien M, Benoist H, Van Damme EJM, Rougé P. Mannose-Specific Lectins from Marine Algae: Diverse Structural Scaffolds Associated to Common Virucidal and Anti-Cancer Properties. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(8):440. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080440
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarre, Annick, Mathias Simplicien, Hervé Benoist, Els J.M. Van Damme, and Pierre Rougé. 2019. "Mannose-Specific Lectins from Marine Algae: Diverse Structural Scaffolds Associated to Common Virucidal and Anti-Cancer Properties" Marine Drugs 17, no. 8: 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080440
APA StyleBarre, A., Simplicien, M., Benoist, H., Van Damme, E. J. M., & Rougé, P. (2019). Mannose-Specific Lectins from Marine Algae: Diverse Structural Scaffolds Associated to Common Virucidal and Anti-Cancer Properties. Marine Drugs, 17(8), 440. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080440







