Magma Seawater Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation through Suppression of Lipogenic Enzymes Regulated by SREBPs in Thioacetamide-Injected Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
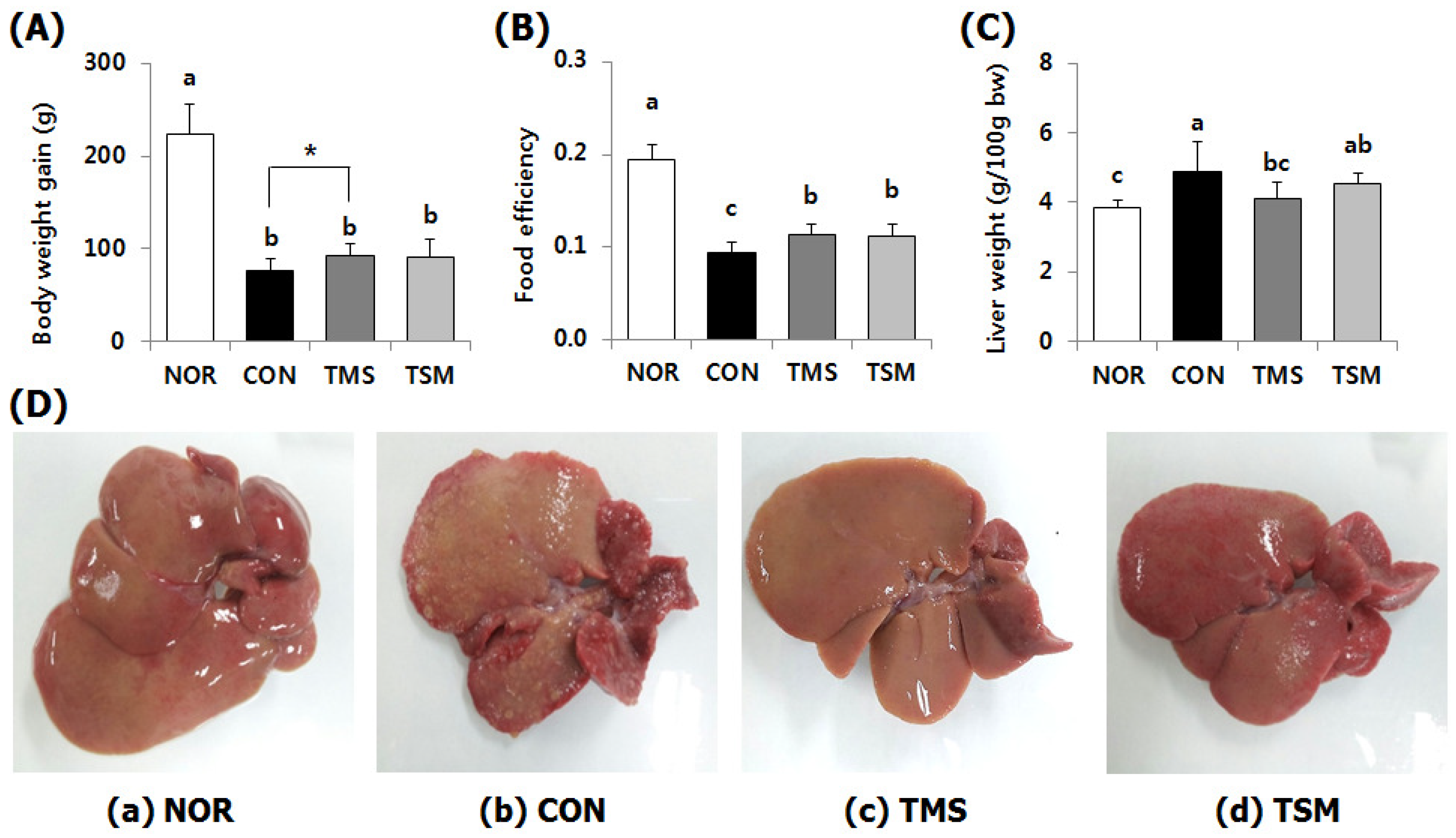
2.1. Changes in Body Weight, Food Efficiency, and Liver Weights
2.2. Macroscopic Examination of Liver
2.3. Lipid Concentrations in the Liver
2.4. TBARS and GSH/GSSG Levels
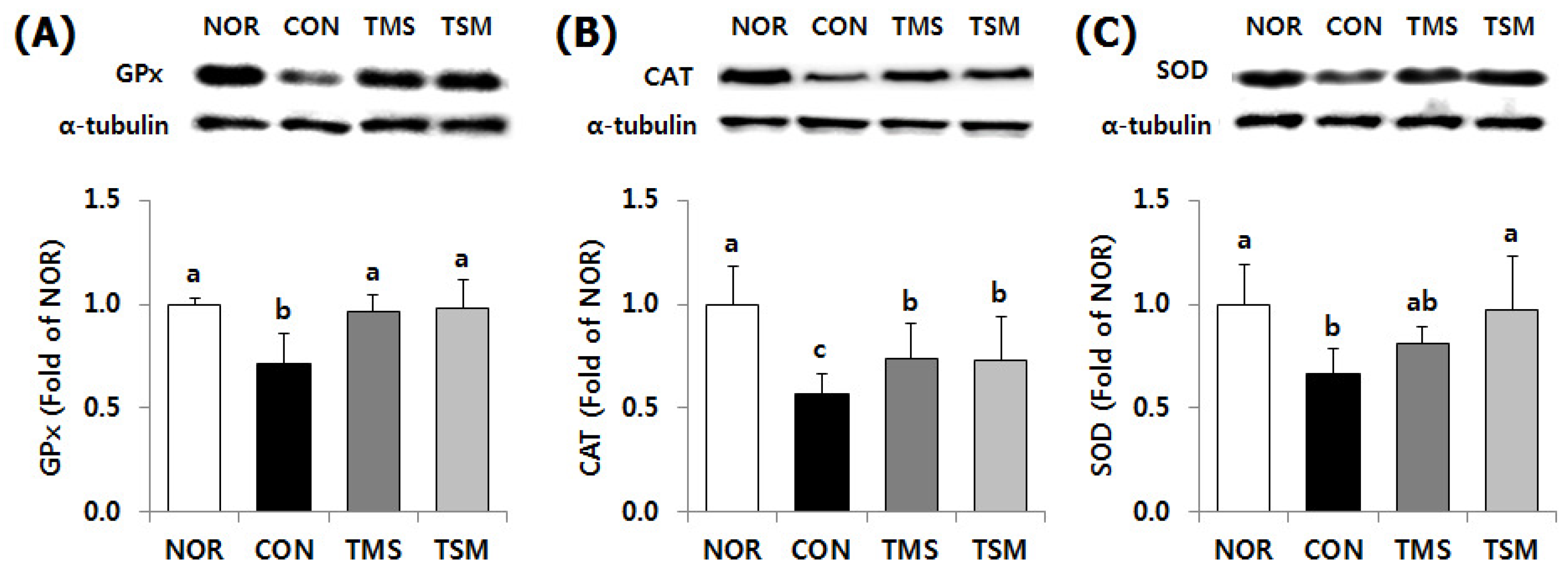
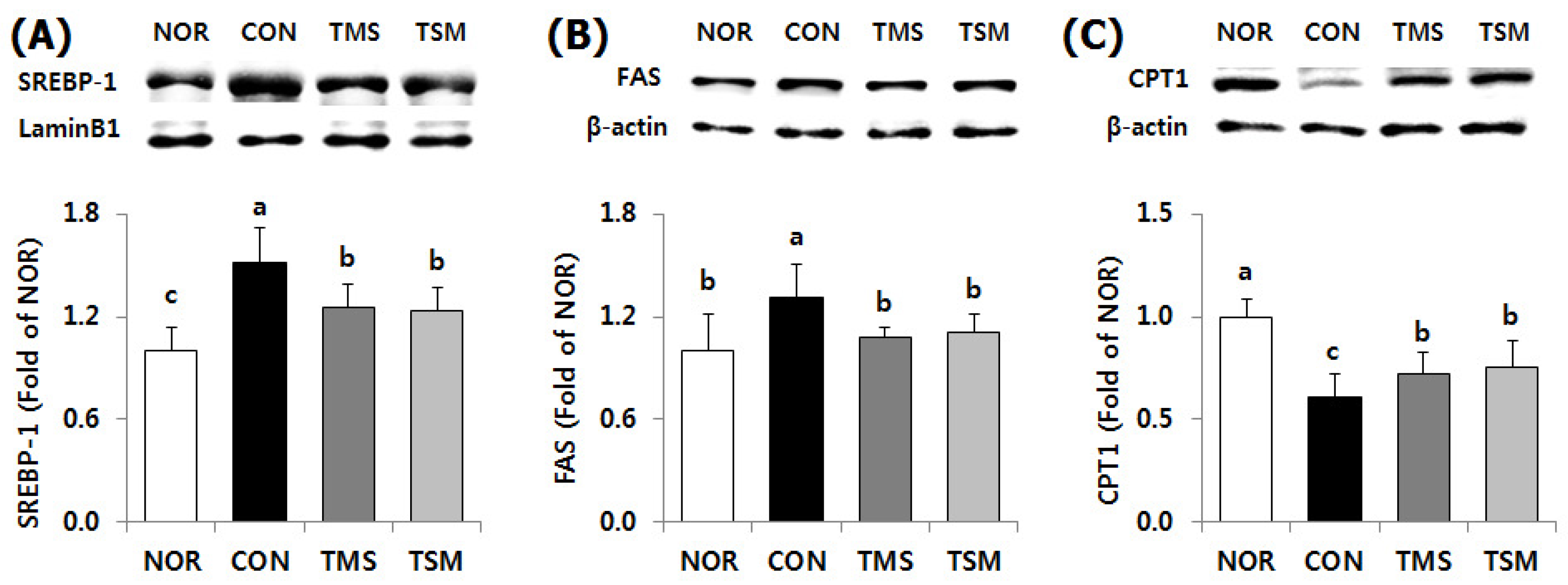
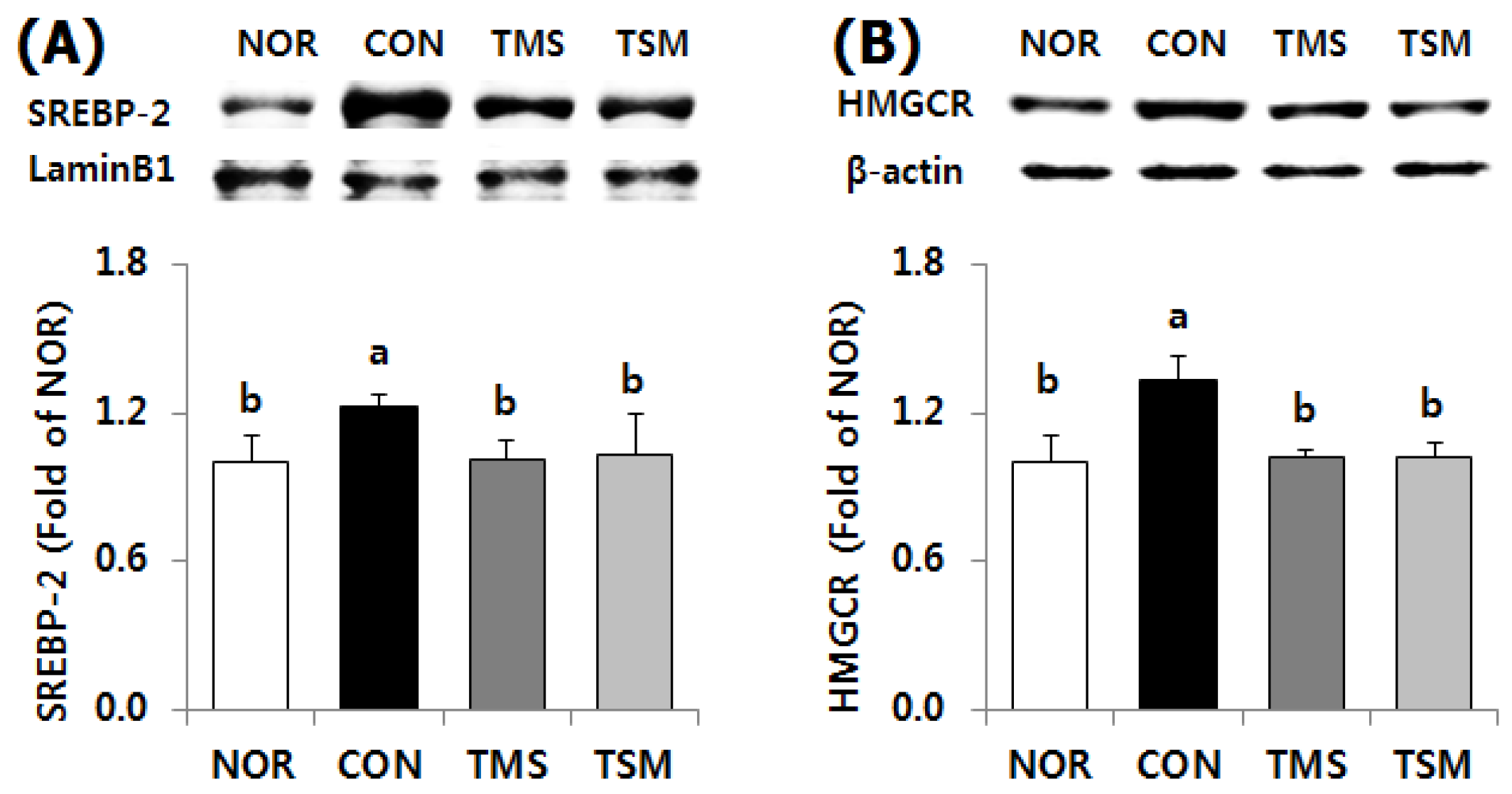
2.5. Western Blot Results
2.5.1. Expression of Antioxidative Enzymes
2.5.2. Expression of Lipid Metabolism-Related Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Experimental Diet
4.2. Experimental Groups and Treatment
4.3. Measurement of Thiobarbituric Acid-Related Substances and Glutathione
4.4. Hepatic Lipid Measurement
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, Y.-J.; Jung, I.-S.; Song, H.-J.; Choi, E.-Y.; Choi, I.-S.; Choi, Y.-J. Study of deep ground sea-like water on antioxidant activity and the immune response in raw 264. 7 macrophages. J. Life Sci. 2008, 18, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, T.; Lee, K.-S.; Chun, S.-Y.; Nam, K.-S. Mineral-balanced deep sea water enhances the inhibitory effects of chitosan oligosaccharide on atopic dermatitis-like inflammatory response. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.-S.; Chang, Y.-Y.; Hsu, C.-L.; Lin, H.-W.; Chang, M.-H.; Chen, J.-W.; Chen, S.-S.; Chen, Y.-C. Alleviative effects of deep-seawater drinking water on hepatic lipid accumulation and oxidation induced by a high-fat diet. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2013, 76, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, S.H.; Yun, J.W. Anti-obesity and antidiabetic effects of deep sea water on ob/ob mice. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Sim, E. A study on the industrialization of deep seawater in Japan and Korea, and its implications on the utilization of jeju magma seawater. Jpn. Cult. Stud. 2013, 45, 451–469. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Suh, I.S.; Woo, M.; Kim, M.J.; Jung, Y.-H.; Song, Y.O. Beneficial effects of desalinated magma seawater in ameliorating thioacetamide-induced chronic hepatotoxicity. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2019, 24, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.D.; Kang, K.A.; Zhang, R.; Piao, M.J.; Kim, S.; Jee, Y.; Lee, N.H.; Ho Jin You, K.S.K.; Hyun, J.W. Effects of Jeju water containing vanadium on antioxidant enzymes in vitro. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 15, 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, A.D.; Zhang, R.; Kang, K.A.; You, H.J.; Kang, K.G.; Hyun, J.W. Jeju ground water containing vanadium enhances antioxidant systems in human liver cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2012, 147, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.K.; Kim, Y.G. Protective role of germanium-132 against paraquat-induced oxidative stress in the livers of senescence-accelerated mice. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 1999, 58, 289–297. [Google Scholar]
- Baek, D.-H.; Jung, J.-W.; Sohn, T.-U.; Kang, J.-K. Germanium-fortified yeast activates macrophage, nk cells and b cells and inhibits tumor progression in mice. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 2007, 35, 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Messarah, M.; Klibet, F.; Boumendjel, A.; Abdennour, C.; Bouzerna, N.; Boulakoud, M.S.; Feki, E.A. Hepatoprotective role and antioxidant capacity of selenium on arsenic-induced liver injury in rats. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymchyshin, O. Hepatoprotective activity of a new germanium-organic biologically active substance (medgerm) in experimental hepatitis. Kazan Med. J. 2013, 94, 628–632. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.; Saari, J.T.; McClain, C.J.; Kang, Y.J. Zinc supplementation prevents alcoholic liver injury in mice through attenuation of oxidative stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabak, J.; Gazuwa, S.; Ubom, G. Hepatoprotective potential of calcium and magnesium against cadmium and lead induced hepatotoxicity in wistar rats. Asian J. Biotechnol. 2009, 1, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Domitrović, R.; Potočnjak, I. A comprehensive overview of hepatoprotective natural compounds: Mechanism of action and clinical perspectives. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 39–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amali, A.A.; Rekha, R.D.; Lin, C.J.-F.; Wang, W.-L.; Gong, H.-Y.; Her, G.-M.; Wu, J.-L. Thioacetamide induced liver damage in zebrafish embryo as a disease model for steatohepatitis. J. Biomed. Sci. 2006, 13, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unger, R.H.; Orci, L. Lipoapoptosis: Its mechanism and its diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2002, 1585, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.; Fernandez, M.; Gil, A.; Rios, A. Effect of dietary nucleotides on degree of fibrosis and steatosis induced by oral intake of thioacetamide. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1997, 42, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, S.M.; Abdulla, M.A.; AlRashdi, A.S.; Ismail, S.; Alkiyumi, S.S.; Golbabapour, S. Hepatoprotective effect of ethanolic extract of curcuma longa on thioacetamide induced liver cirrhosis in rats. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruck, R.; Aeed, H.; Schey, R.; Matas, Z.; Reifen, R.; Zaiger, G.; Hochman, A.; Avni, Y. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects against thioacetamide-induced fulminant hepatic failure in rats. J. Hepatol. 2002, 36, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.; Byrne, C.D. Modulation of sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPS) as potential treatments for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Drug Discov. Today 2007, 12, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekiya, M.; Hiraishi, A.; Touyama, M.; Sakamoto, K. Oxidative stress induced lipid accumulation via SREBP1C activation in HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.-W.; Feng, Y. The role of oxidative stress and antioxidants in liver diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, T.O.; Pedroso, G.L.; Hartmann, C.R.; Escobar, T.D.C.; Fracasso, L.B.; da Rosa, D.P.; Marroni, N.P.; Porawski, M.; da Silveira, T.R. The effect of taurine on hepatic steatosis induced by thioacetamide in zebrafish (danio rerio). Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noh, J.-R.; Gang, G.-T.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yang, K.-J.; Lee, C.-H.; Na, O.-S.; Kim, G.-J.; Oh, W.-K.; Lee, Y.-D. Desalinated underground seawater of Jeju Island (Korea) improves lipid metabolism in mice fed diets containing high fat and increases antioxidant potential in t-BHP treated HepG2 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nido, S.A.; Shituleni, S.A.; Mengistu, B.M.; Liu, Y.; Khan, A.Z.; Gan, F.; Kumbhar, S.; Huang, K. Effects of selenium-enriched probiotics on lipid metabolism, antioxidative status, histopathological lesions, and related gene expression in mice fed a high-fat diet. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 171, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassir, F.; Moundras, C.; Bayle, D.; Serougne, C.; Gueux, E.; Rock, E.; Rayssiguier, Y.; Mazur, A. Effect of selenium deficiency on hepatic lipid and lipoprotein metabolism in the rat. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 78, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba, G.; Russo, P. Dairy foods, dietary calcium and obesity: A short review of the evidence. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Tani, M.; Uto-Kondo, H.; Saita, E.; Iizuka, M.; Sone, H.; Yokota, K.; Kondo, K. Effects of magnesium on postprandial serum lipid responses in healthy human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, L.; Halstenson, C.E.; Halstenson, C.J.; Macres, M.; Keane, W.F. Cholesterol-lowering effects ohypercholesterolemiain patients with mild to moderate hypercholesterolemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 2441–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, A.V.; Lanca, M.; Vasconcelos, S.; Andrade, V.; Rodrigues, H.; Santos, M. Effect of selenium supplementation on some blood biochemical parameters in male rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1995, 47, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Wathurapatha, W.; Ishara, M.; Jayawardana, R.; Galappatthy, P.; Katulanda, P.; Constantine, G. Effects of zinc supplementation on serum lipids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 12, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, P.; Hettiarachchi, M.; Liyanage, C.; Lekamwasam, S. Effects of zinc and multimineral vitamin supplementation on glycemic and lipid control in adult diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2011, 4, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz, A.; Padillo, F.J.; Torres, E.; Navarrete, C.M.; Muñoz-Castañeda, J.R.; Caballero, F.J.; Briceño, J.; Marchal, T.; Túnez, I.; Montilla, P. Melatonin prevents experimental liver cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 39, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamura, M.; Yoshioka, S.; Hamada, A.; Takuma, D.; Yokota, J.; Kusunose, M.; Kyotani, S.; Kawakita, H.; Odani, K.; Tsutsui, Y. Difference between deep seawater and surface seawater in the preventive effect of atherosclerosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranzo, O. Manganese complexes displaying superoxide dismutase activity: A balance between different factors. Bioorg. Chem. 2011, 39, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maseko, T.; Howell, K.; Dunshea, F.R.; Ng, K. Selenium-enriched agaricus bisporus increases expression and activity of glutathione peroxidase-1 and expression of glutathione peroxidase-2 in rat colon. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, J.; Cockell, K.; Hidiroglou, N.; Madere, R.; Trick, K.; Kubow, S. The effects of vitamine and selenium intake on oxidative stress and plasma lipids in hamsters fed fish oil. Lipids 2002, 37, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carocho, M.; Ferreira, I.C. A review on antioxidants, prooxidants and related controversy: Natural and synthetic compounds, screening and analysis methodologies and future perspectives. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 51, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.-H.; Liu, C.-W.; Yang, D.-J.; Wu, Y.-H.S.; Chen, Y.-C. Amino acid, mineral, and polyphenolic profiles of black vinegar, and its lipid lowering and antioxidant effects in vivo. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Mahmood, A.; Pathak, R.; Dhawan, D. Effect of zinc on hepatic lipid peroxidation and antioxidative enzymes in ethanol-fed rats. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2002, 22, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Homma, T.; Fujii, J. Mice in the early stage of liver steatosis caused by a high fat diet are resistant to thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity and oxidative stress. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 277, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Homma, T.; Kurahashi, T.; Kang, E.S.; Fujii, J. Oxidative stress triggers lipid droplet accumulation in primary cultured hepatocytes by activating fatty acid synthesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 464, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahidol University National Laboratory Animal Center. Available online: http://www.nlac.mahidol.ac.th/nlacen/index.php/component/content/article/24-productservice/animals/117-mlac-wr?Itemid=101 (accessed on 17 January 2014).
- Chen, I.S.; Chen, Y.C.; Chou, C.H.; Chuang, R.F.; Sheen, L.Y.; Chiu, C.H. Hepatoprotection of silymarin against thioacetamide-induced chronic liver fibrosis. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 92, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, C.H.; Xu, F.H.; Roh, S.-S.; Song, Y.O.; Uebaba, K.; Noh, J.S.; Yokozawa, T. Astaxanthin and corni fructus protect against diabetes-induced oxidative stress, inflammation, and advanced glycation end product in livers of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Group | TBARS (nmol/g Tissue) | GSH (μmol/g Tissue) | GSSG (μmol/g Tissue) | GSH/GSSG Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOR | 24.89 ± 6.17 c | 2.98 ± 0.96 b | 0.13 ± 0.04 a | 23.65 ± 6.36 c |
| CON | 50.00 ± 8.51 a | 6.52 ± 0.76 a | 0.13 ± 0.06 a | 53.08 ± 14.43 b |
| TMS | 37.85 ± 6.64 b | 7.05 ± 1.68 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 b | 73.55 ± 21.18 a |
| TSM | 40.36 ± 6.94 b | 7.16 ± 1.14 a | 0.09 ± 0.02 b | 81.95 ± 16.49 a |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Woo, M.; Noh, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Song, Y.O.; Lee, H. Magma Seawater Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation through Suppression of Lipogenic Enzymes Regulated by SREBPs in Thioacetamide-Injected Rats. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060317
Woo M, Noh JS, Kim MJ, Song YO, Lee H. Magma Seawater Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation through Suppression of Lipogenic Enzymes Regulated by SREBPs in Thioacetamide-Injected Rats. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(6):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060317
Chicago/Turabian StyleWoo, Minji, Jeong Sook Noh, Mi Jeong Kim, Yeong Ok Song, and Hyunjoo Lee. 2019. "Magma Seawater Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation through Suppression of Lipogenic Enzymes Regulated by SREBPs in Thioacetamide-Injected Rats" Marine Drugs 17, no. 6: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060317
APA StyleWoo, M., Noh, J. S., Kim, M. J., Song, Y. O., & Lee, H. (2019). Magma Seawater Inhibits Hepatic Lipid Accumulation through Suppression of Lipogenic Enzymes Regulated by SREBPs in Thioacetamide-Injected Rats. Marine Drugs, 17(6), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17060317





