Effect of Cyclophilin from Pyropia Yezoensis on the Proliferation of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Ras Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
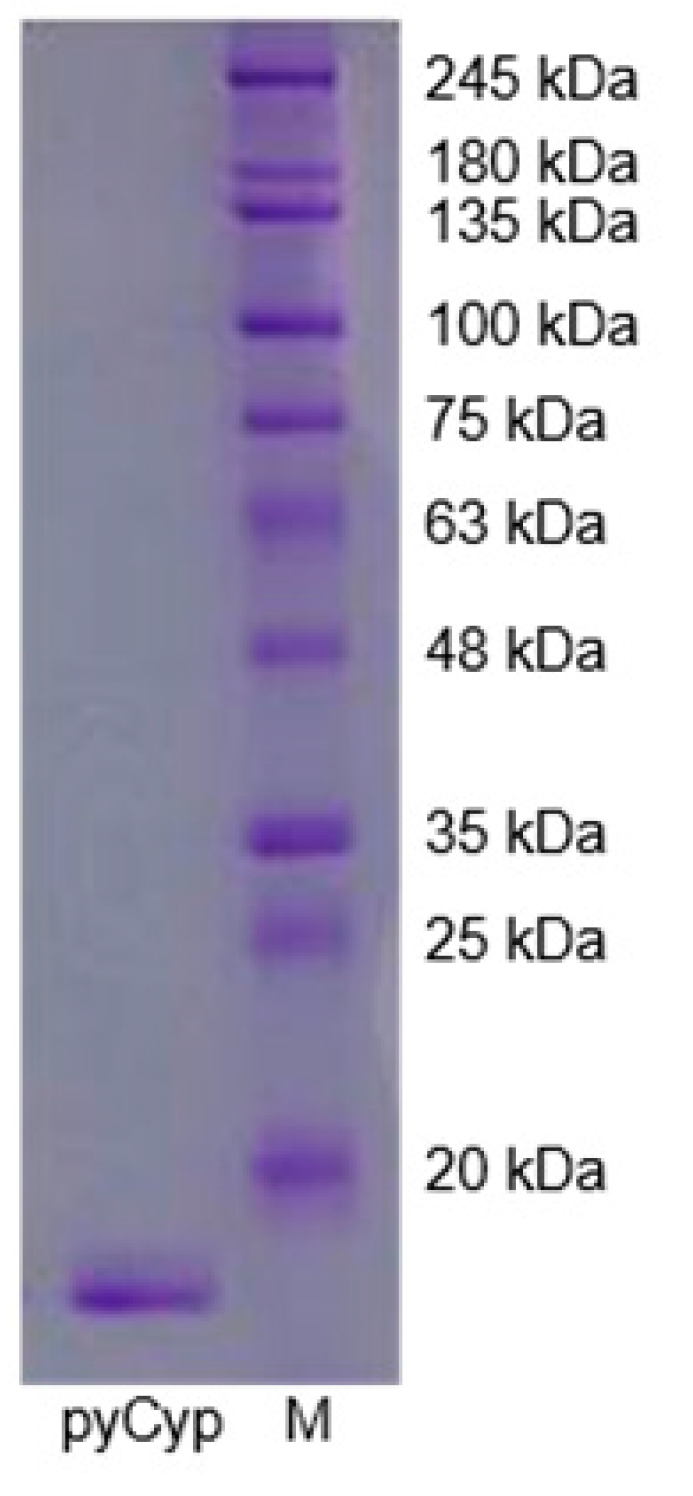
2.1. Expression and Purification of pyCyp
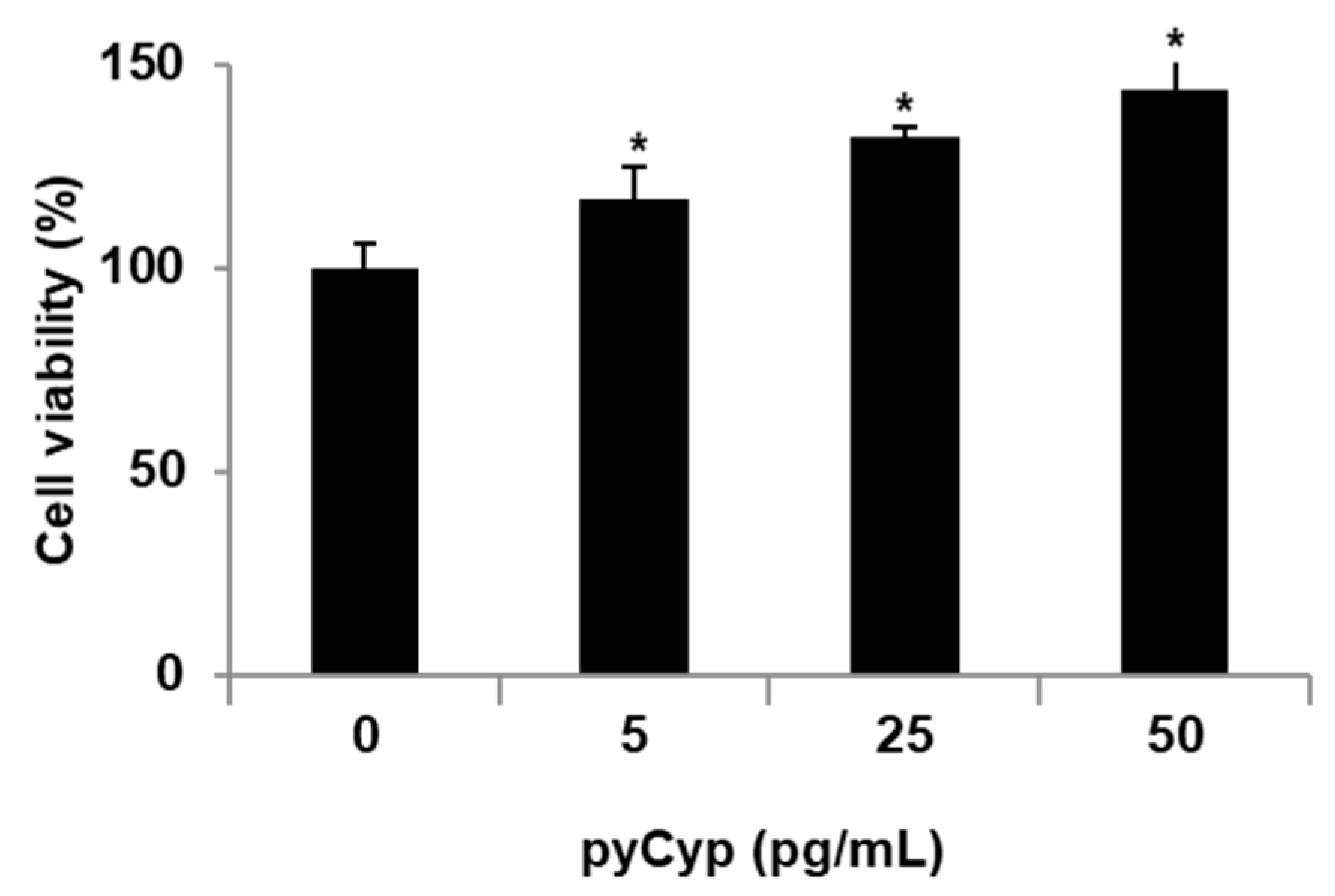
2.2. Proliferative Effect of pyCyp in IEC-6 Cells
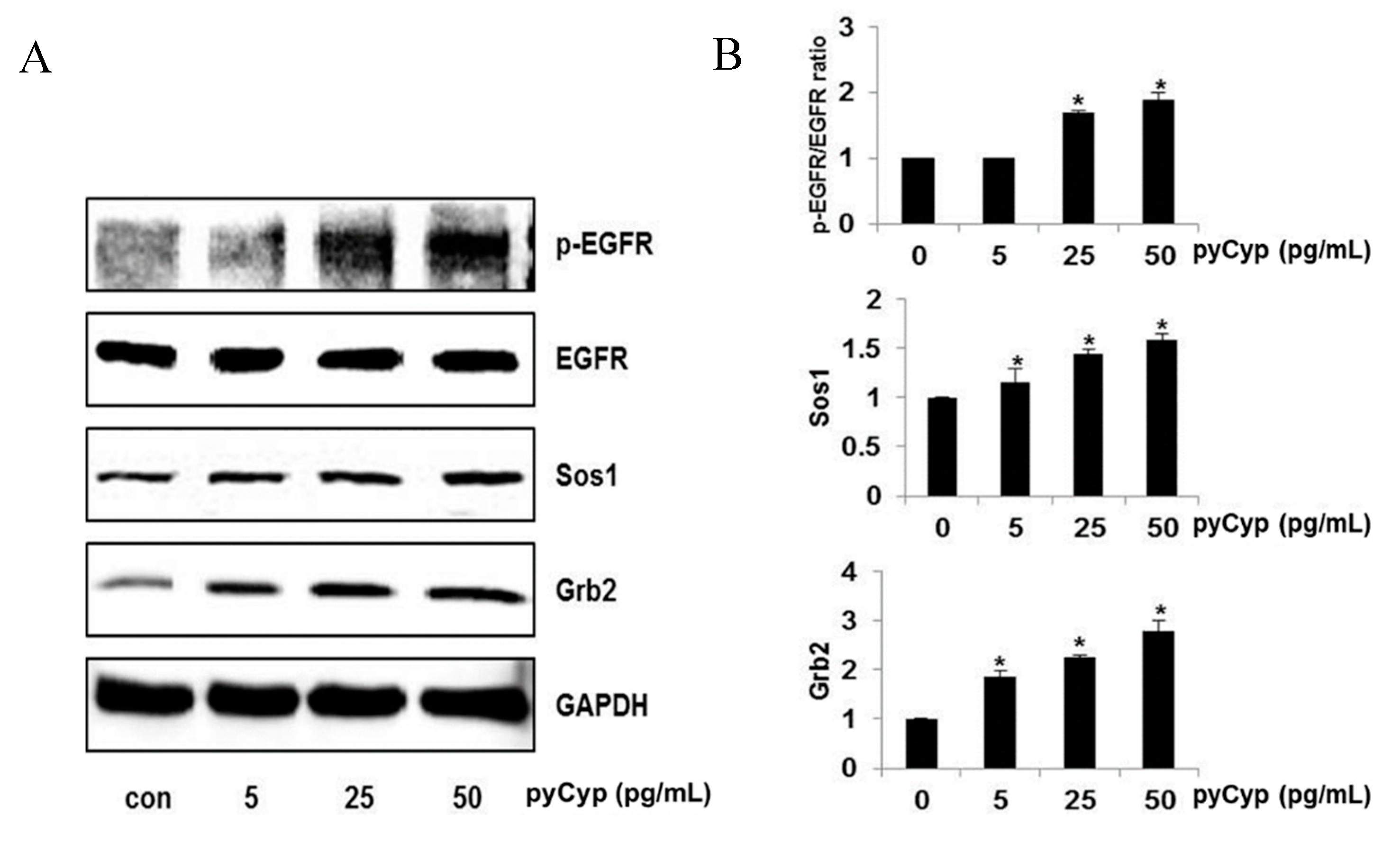
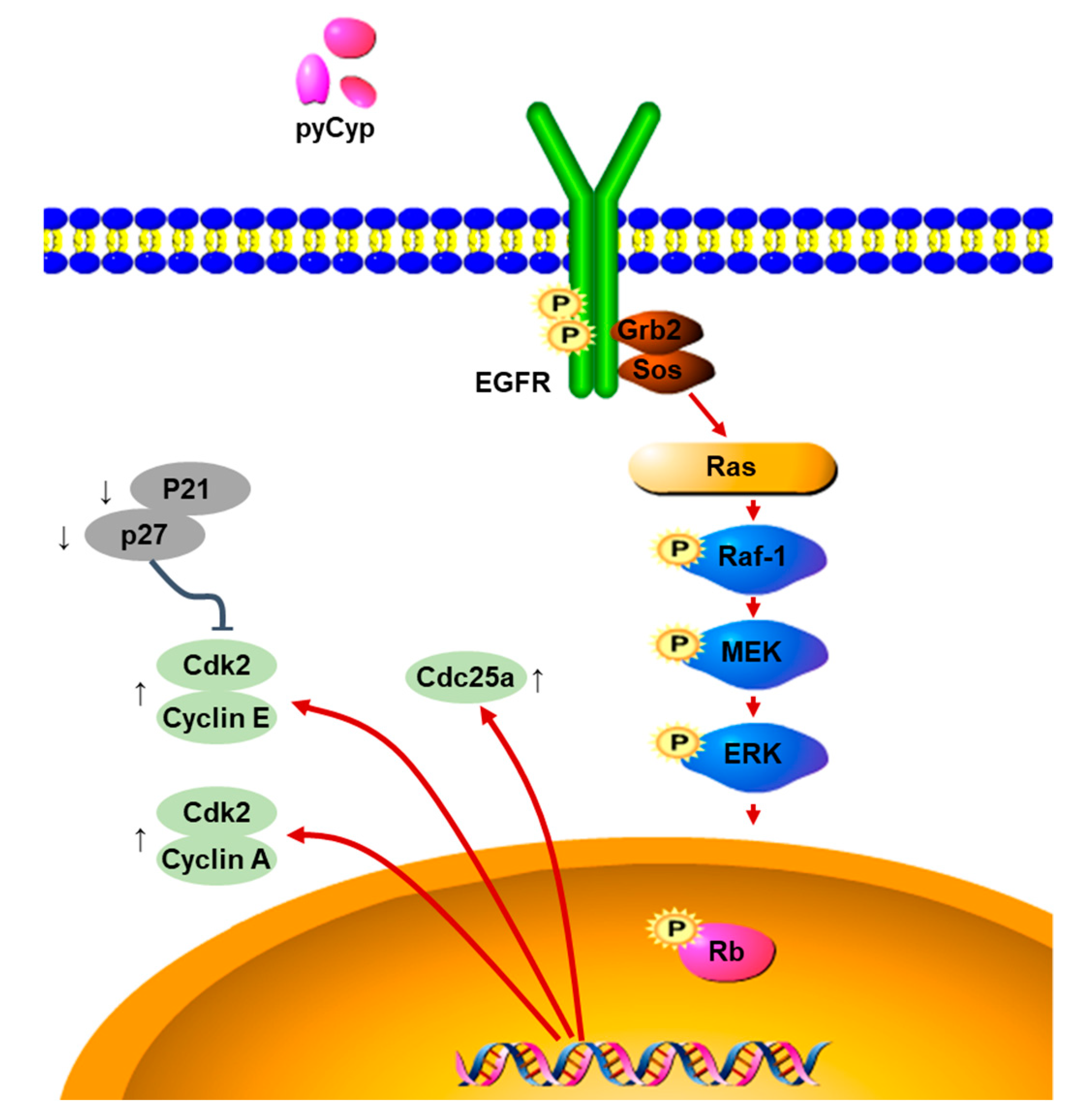
2.3. Effect of pyCyp Treatment on EGFR Signaling Pathway
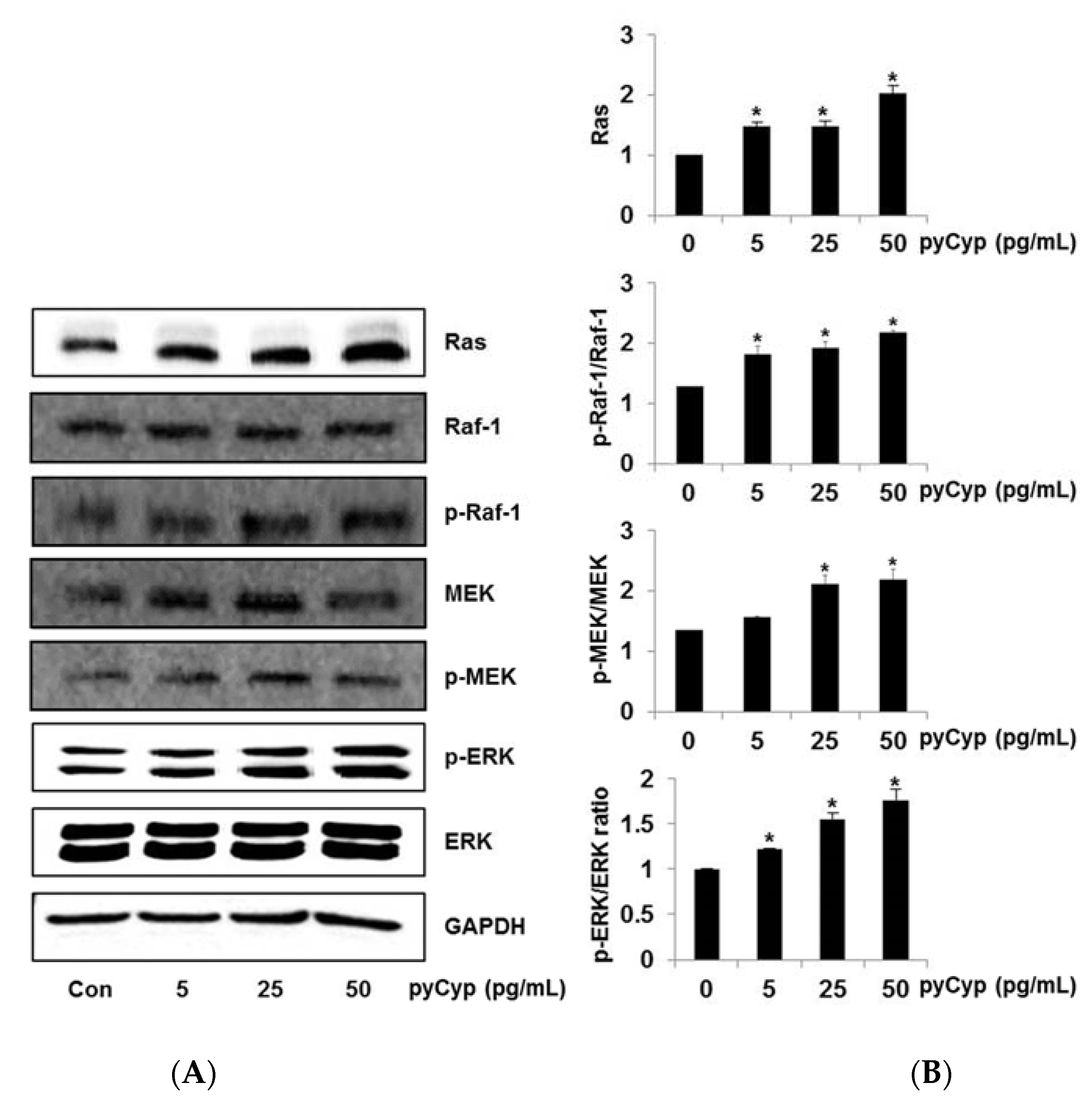
2.4. Effect of Treatment of pyCyp on the Ras-ERK Signaling Pathway
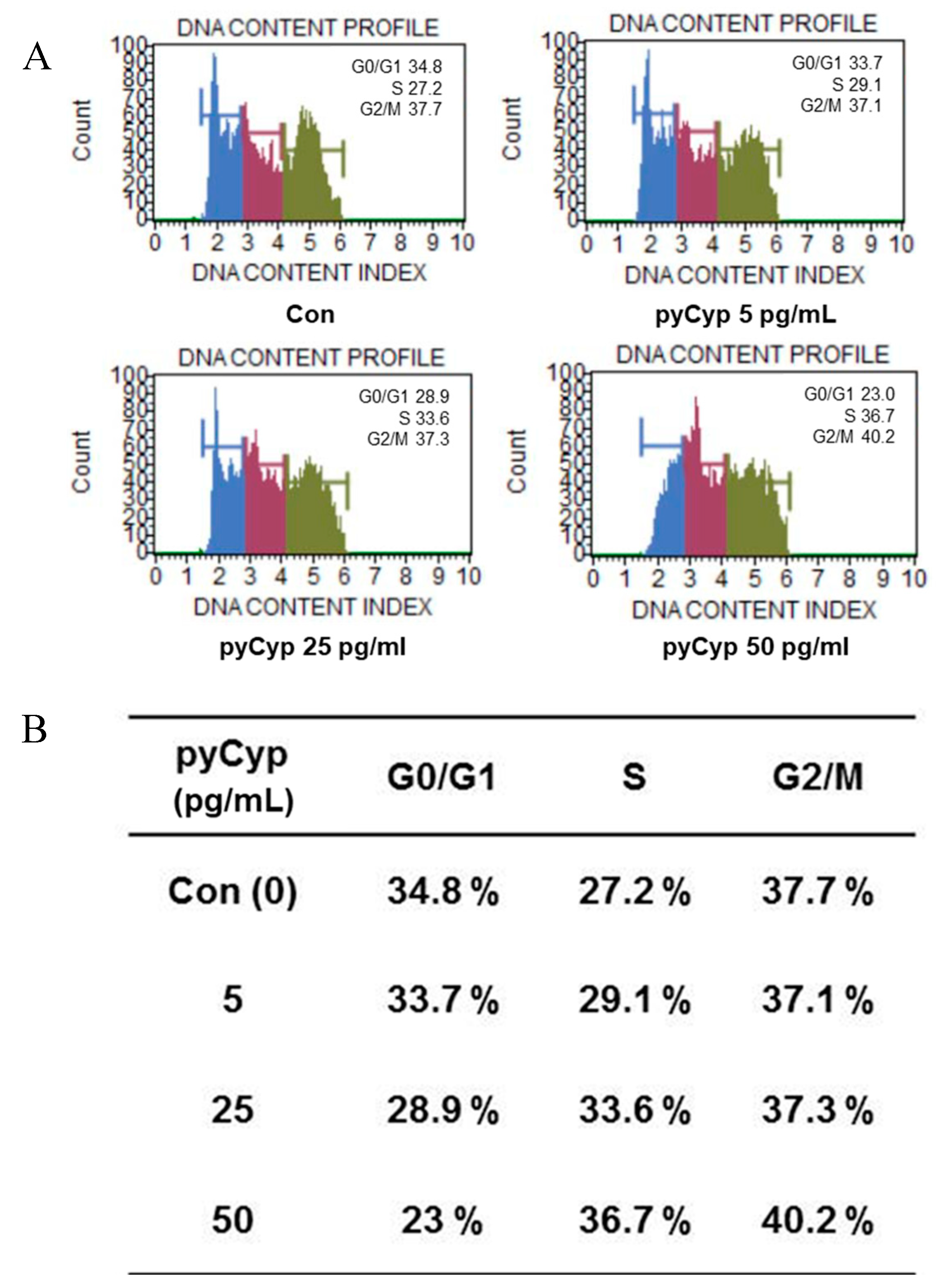
2.5. Effect of pyCyp on Cell Cycle Progression
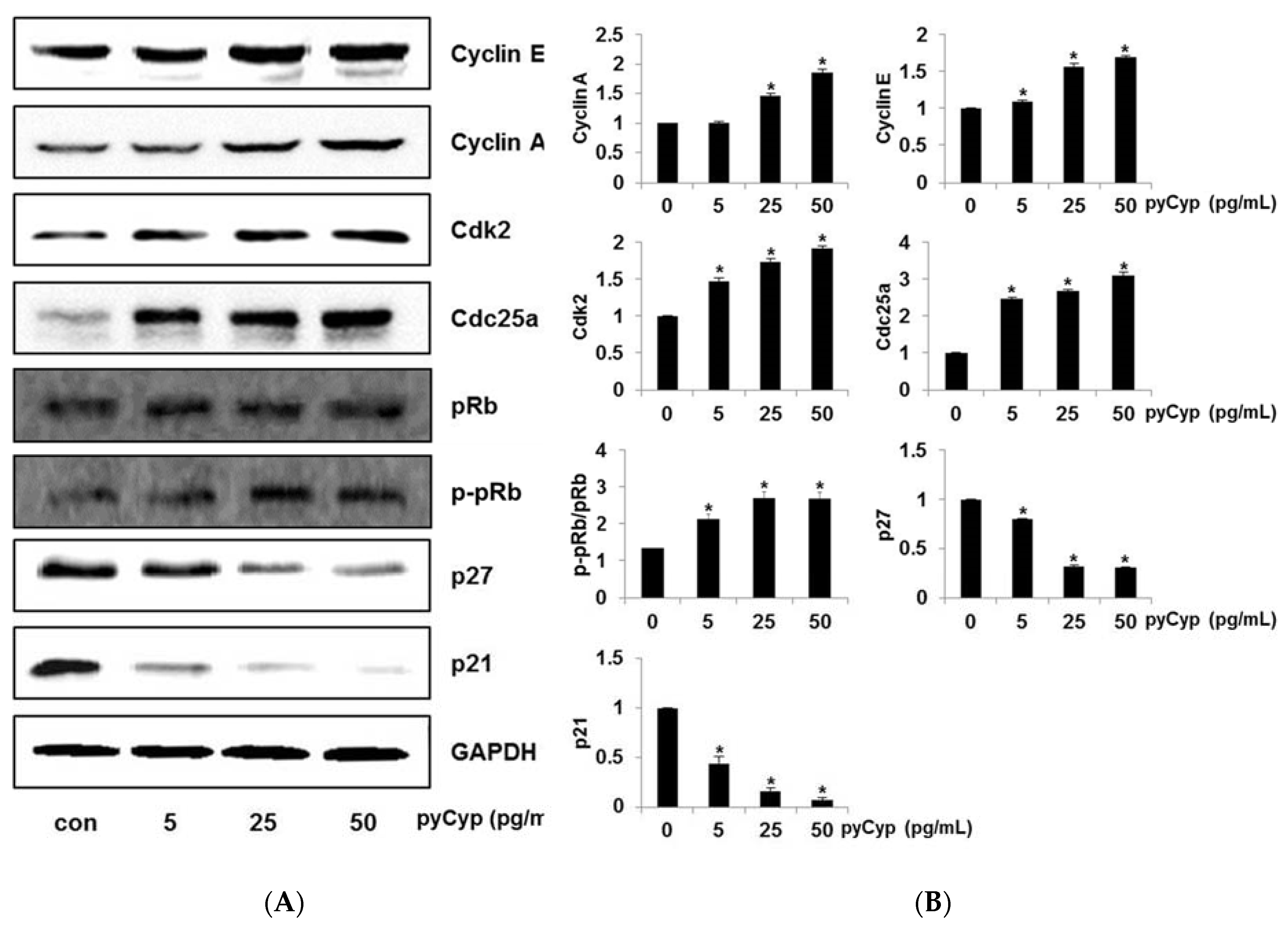
2.6. Effect of pyCyp Treatment on Cell Cycle-Related Protein
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recombinant Protein Construction
4.2. Recombinant Protein Expression and Cell Lysis
4.3. Recombinant Protein Purification
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Whole-Cell Protein Lysate Extraction
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.A.; Kim, I.H.; Nam, T.J. Bioactive peptide from Pyropia yezoensis and its anti-inflammatory activities. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 36, 1701–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cian, R.E.; Drago, S.R.; de Medina, F.S.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Proteins and Carbohydrates from Red Seaweeds: Evidence for Beneficial Effects on Gut Function and Microbiota. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5358–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosano, G.L.; Ceccarelli, E.A. Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli: Advances and challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, H.; Schiene-Fischer, C. Functional aspects of extracellular cyclophilins. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Roy, S.; Singh, P.; Singla-Pareek, S.L.; Pareek, A. Cyclophilins: Proteins in search of function. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e22734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, P.; Pompilio, G.; Capogrossi, M.C. Cyclophilin A: A key player for human disease. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, I.T.; Gasser, C.S. Characterization of the cyclophilin gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana and phylogenetic analysis of known cyclophilin proteins. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 35, 873–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallon O: Chlamydomonas immunophilins and parvulins: Survey and critical assessment of gene models. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 230–241. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Oh, I.K.; Yoon, K.S.; Ha, J.; Kang, I.; Choe, W. Antioxidant activity is required for the protective effects of cyclophilin A against oxidative stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurchenko, V.; Constant, S.; Eisenmesser, E.; Bukrinsky, M. Cyclophilin-CD147 interactions: A new target for anti-inflammatory therapeutics. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2010, 160, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.G.; Melaragno, M.G.; Liao, D.F.; Yan, C.; Haendeler, J.; Suh, Y.A.; Lambeth, J.D.; Berk, B.C. Cyclophilin A is a secreted growth factor induced by oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, C.G.; Nam, T.J. Effects of the cyclophilin-type peptidylprolyl cis-trans isomerase from Pyropia yezoensis against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 4132–4138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Matoba, T.; Suzuki, J.; O’Dell, M.R.; Nigro, P.; Cui, Z.; Mohan, A.; Pan, S.; Li, L.; Jin, Z.G.; et al. Cyclophilin A mediates vascular remodeling by promoting inflammation and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 2008, 117, 3088–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Lessner, S.M.; Sakurai, Y.; Galis, Z.S. Cyclophilin A as a novel biphasic mediator of endothelial activation and dysfunction. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obchoei, S.; Wongkhan, S.; Wongkham, C.; Li, M.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Cyclophilin A: potential functions and therapeutic target for human cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. 2009, 15, RA221–RA232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obchoei, S.; Sawanyawisuth, K.; Wongkham, C.; Kasinrerk, W.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C.; Wongkham, S. Secreted Cyclophilin A Mediates G1/S Phase Transition of Cholangiocarcinoma Cells via CD147/ ERK1/2 Pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.M.; Yao, Y.L.; Seto, E. The FK506-binding protein 25 functionally associates with histone deacetylases and with transcription factor YY1. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4814–4825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, J.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Nam, T.J. The proliferative effects of Porphyra yezoensis peptide on IEC-6 cells are mediated through the epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelblum, K.L.; Yan, F.; Yamaoka, T.; Polk, D.B. Regulation of apoptosis during homeostasis and disease in the intestinal epithelium. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2006, 12, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlnhofer, B.M.; Thompson, C.A.; Walker, E.M.; Battle, M.A. GATA4 regulates epithelial cell proliferation to control intestinal growth and development in mice. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 2, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Qin, H.; Shen, T. Culture of human intestinal epithelial cell using the dissociating enzyme thermolysin and endothelin-3. Braz J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zwick, E.; Bange, J.; Ullrich, A. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signalling as a Target for Cancer Intervention Strategies. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2001, 8, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, E52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, M.; Granata, R.; Ghigo, E. The IGF system. Acta Diabetol. 2011, 48, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grajek, W.; Olejnik, A. Epithelial cell culture in vitro as a model to study functional properties of food. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2004, 54, 5–24. [Google Scholar]
- Rajalingam, K.; Schreck, R.; Rapp, U.R.; Albert, S. Ras oncogenes and their downstream targets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK Pathway in Cell Growth, Malignant Transformation and Drug Resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, I.I.; Saha, S.B.; Thomas, G. The RAS Subfamily Evolution—Tracing Evolution for its Utmost Exploitation. Bioinformation 2014, 10, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Luo, C.; Li, R.; Qiao, A.; Zhang, L.; Mines, M.; Nyanda, A.M.; Zhang, J.; Fan, G.H. Cyclophilin A is required for CXCR4-mediated nuclear export of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, activation and nuclear translocation of ERK1/2, and chemotactic cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, K.J.; O’Connell, M.J. Cell cycle regulation by checkpoints. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1170, 29–40. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagosklonny, M.V.; Pardee, A.B. The restriction point of the cell cycle. Cell Cycle 2002, 1, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gérard, C.; Goldbeter, A. The balance between cell cycle arrest and cell proliferation: Control by the extracellular matrix and by contact inhibition. Interface Focus 2014, 4, 20130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, A.K.; Reikvam, H.; Lavecchia, A.; Bruserud, Ø. Therapeutic targeting the cell division cycle 25 (CDC25) phosphatases in human acute myeloid leukemia—The possibility to target several kinases through inhibition of the various CDC25 isoforms. Molecules 2014, 19, 18414–18447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, J.-H.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, M.-K.; Choi, Y.-H.; Nam, T.-J. Effect of Cyclophilin from Pyropia Yezoensis on the Proliferation of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Ras Signaling Pathway. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050297
Jung J-H, Choi J-W, Lee M-K, Choi Y-H, Nam T-J. Effect of Cyclophilin from Pyropia Yezoensis on the Proliferation of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Ras Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(5):297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050297
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Jae-Hun, Jeong-Wook Choi, Min-Kyeong Lee, Youn-Hee Choi, and Taek-Jeong Nam. 2019. "Effect of Cyclophilin from Pyropia Yezoensis on the Proliferation of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Ras Signaling Pathway" Marine Drugs 17, no. 5: 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050297
APA StyleJung, J.-H., Choi, J.-W., Lee, M.-K., Choi, Y.-H., & Nam, T.-J. (2019). Effect of Cyclophilin from Pyropia Yezoensis on the Proliferation of Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor/Ras Signaling Pathway. Marine Drugs, 17(5), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050297




