Integrating Molecular Network and Culture Media Variation to Explore the Production of Bioactive Metabolites by Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
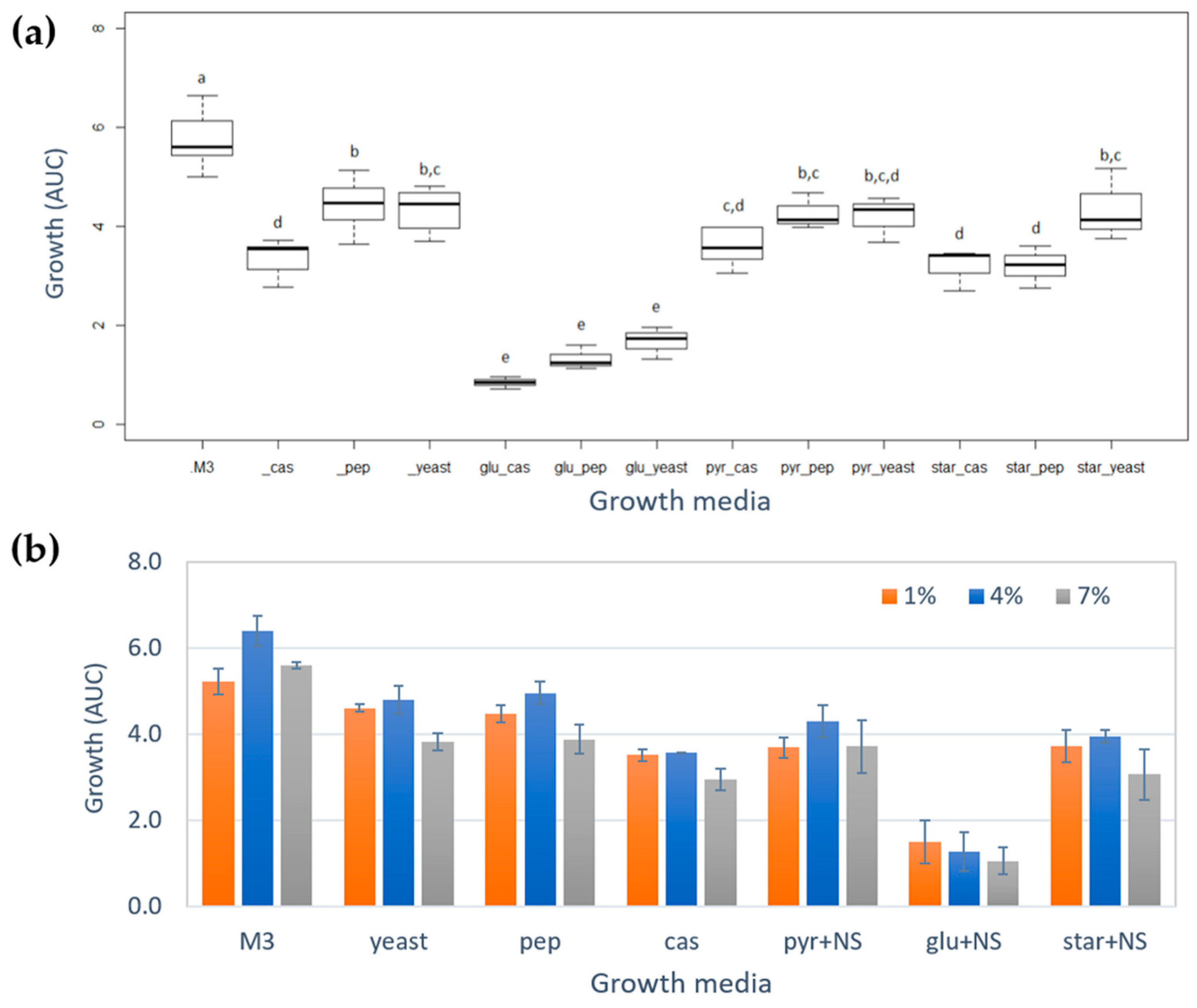
2.1. Growth of Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3 in Modified Culture Media
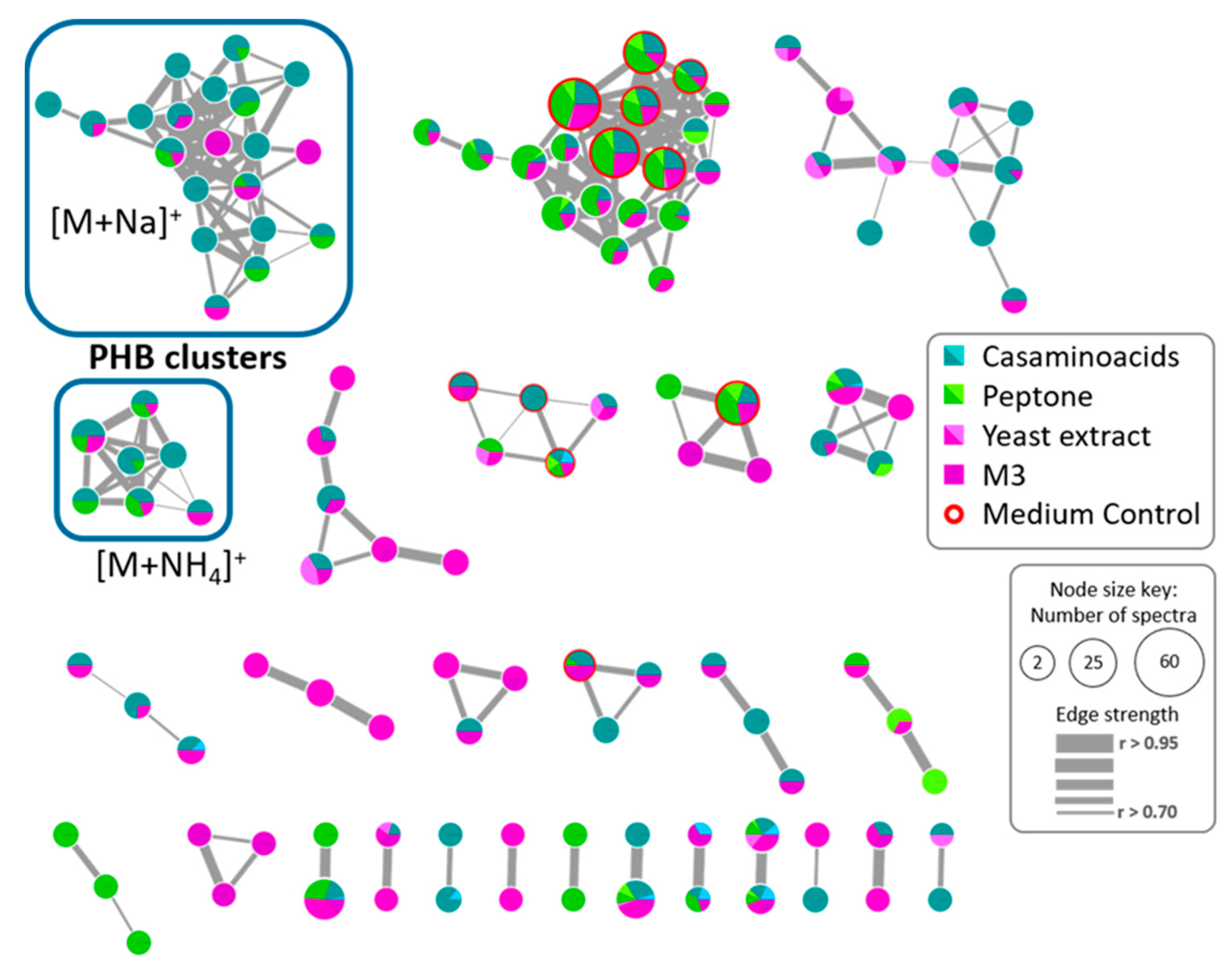
2.2. Study of the Metabolic Profile of Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3 in the Modified Culture Media
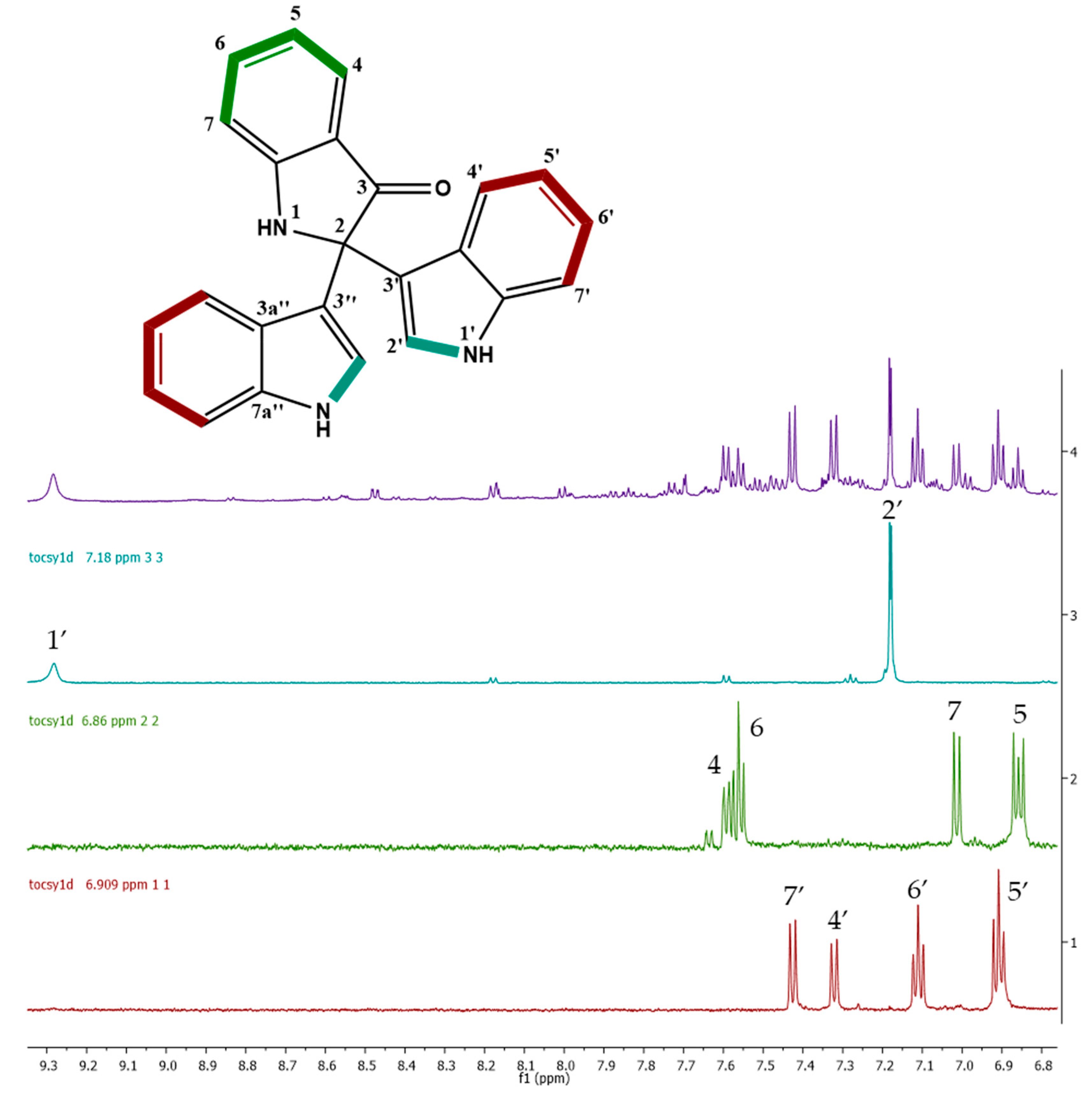
2.3. Cytotoxic Activity and Dereplication of the Fractions from Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3 Grown in M3 Medium
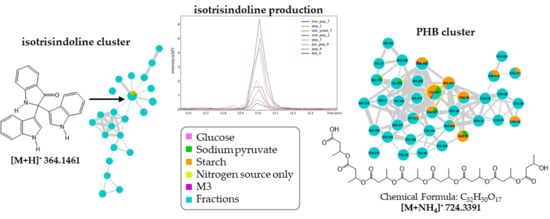
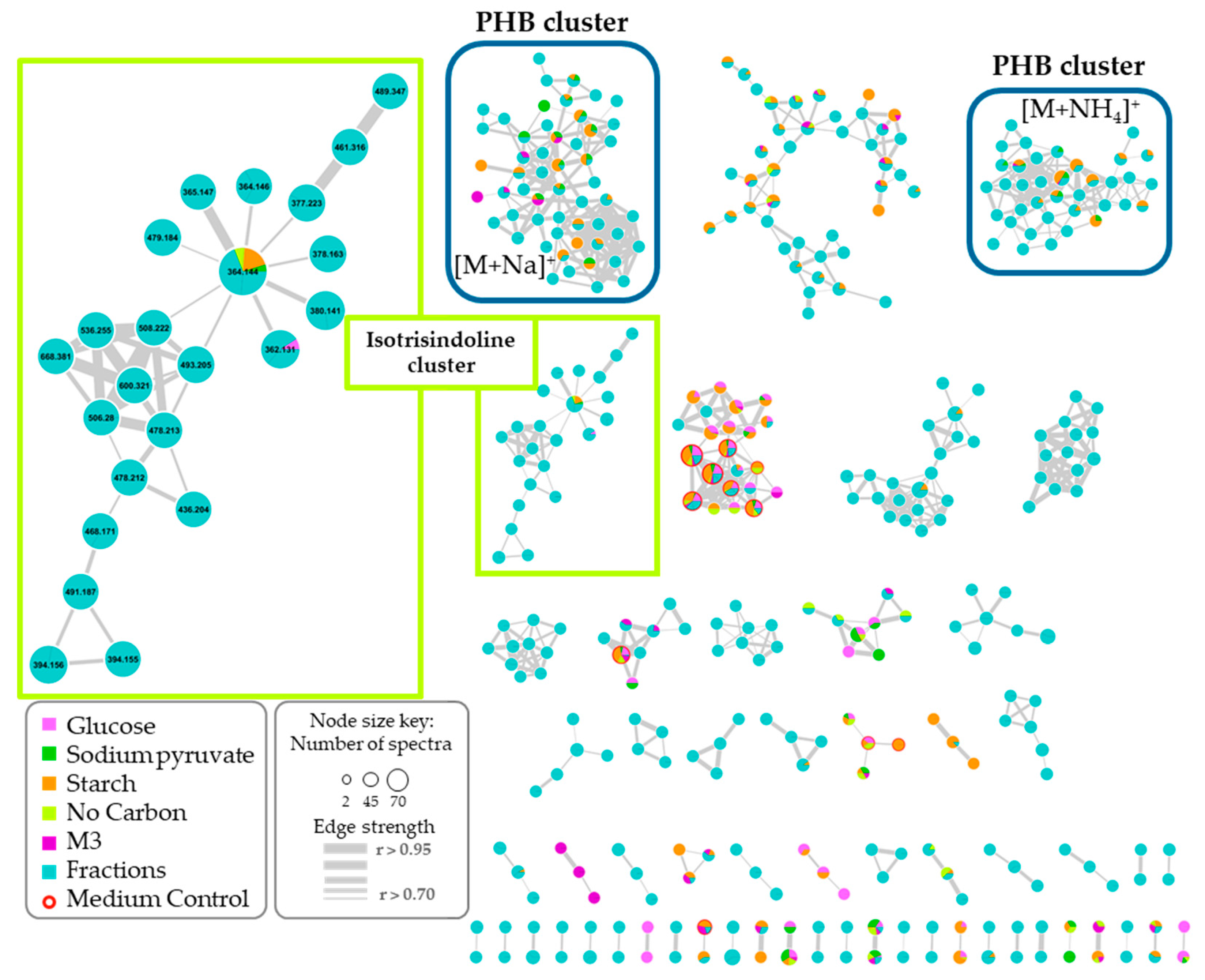
2.4. Molecular Networking and Isotrisindoline Production
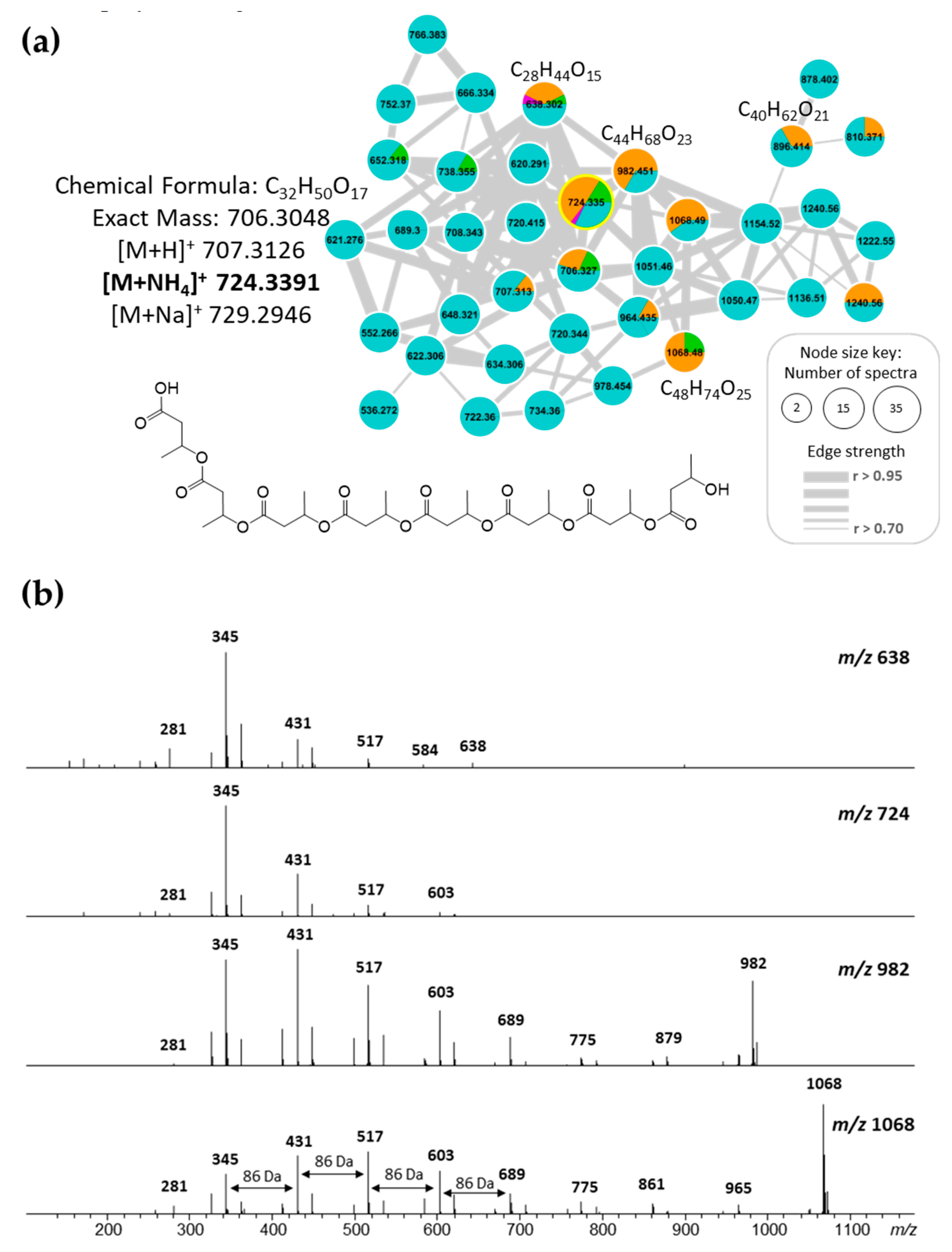
2.5. Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHB) Molecular Family
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3 Strain: Crude Extract Production and Fractionation
4.2. Cytotoxic Activity
4.3. Modified Culture Media and Metabolite Extraction of Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3 Cultures
4.4. HPLC-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. HPLC-MS Data Processing
4.6. MS/MS Data Processing for Molecular Networking
4.7. NMR Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thompson, F.; Iida, T.; Swings, J. Biodiversity of Vibrios. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 403–431. [Google Scholar]
- Mansson, M.; Gram, L.; Larsen, T.O. Production of bioactive secondary metabolites by marine Vibrionaceae. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1440–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Wietz, M.; Mansson, M.; Gotfredsen, C.H.; Larsen, T.O.; Gram, L. Antibacterial compounds from marine Vibrionaceae isolated on a global expedition. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2946–2960. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, C.-C.; Chen, P.-C.; Shih, C.-J.; Tseng, S.-P.; Lai, Y.-M.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Yang, Y.-L. Vitroprocines, new antibiotics against Acinetobacter baumannii, discovered from marine Vibrio sp. QWI-06 using mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics approach. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluri, R.; Oka, I.; Wagner-dobler, I.; Laatsch, H. New indole alkaloids from the North Sea bacterium vibrio parahaemolyticus. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, R.; Carmeli, S.; Sar, N. Vibrindole A, a metabolite of the marine bacterium, vibrio parahaemolyticus, isolated from the toxic mucus of the boxfish ostracion cubicus. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1587–1590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.M.; Aoki, S.; Gato, K.; Matsunami, K.; Kurosu, M.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXXIV. 1) Trisindole, a new antibiotic indole trimer, produced by a Bacterium of Vibrio sp. separated from the marine sponge Hyrtios altum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1994, 42, 2449–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.J.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hai, L.; Wu, Y. The synthesis and biological evaluation of unsymmetrical 2,2-di(1H-indol-3-yl)-N-phenylacetamide derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2829–2832. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, K.; Ramasamy, R.; Dhinakarasamy, I. Polyhydroxybutyrate production from marine source and its application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 111, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Aksenov, A.A.; Da Silva, R.; Knight, R.; Lopes, N.P.; Dorrestein, P.C. Global chemical analysis of biology by mass spectrometry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017, 1, 0054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeckh, V.; Scherlach, K.; Nutzmann, H.-W.; Shelest, E.; Schmidt-Heck, W.; Schuemann, J.; Martin, K.; Hertweck, C.; Brakhage, A.A. Intimate bacterial-fungal interaction triggers biosynthesis of archetypal polyketides in Aspergillus nidulans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 14558–14563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bode, H.; Bethe, B.; Höfs, R.; Zeeck, A. Big effects from small changes: Possible ways to explore nature’s chemical diversity. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aghcheh, R.K.; Kubicek, C.P. Epigenetics as an emerging tool for improvement of fungal strains used in biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 6167–6181. [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann, S.; Schümann, J.; Scherlach, K.; Lange, C.; Brakhage, A.A.; Hertweck, C. Genomics-driven discovery of PKS-NRPS hybrid metabolites from Aspergillus nidulans. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 213–217. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, A.E.; Carnevale Neto, F.; Vera, M.C.; Taboada, C.; Pavarini, D.P.; Bauermeister, A.; Lopes, N.P. An integrative omics perspective for the analysis of chemical signals in ecological interactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1574–1591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T.; et al. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with global natural products social molecular networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar]
- Conde-Martínez, N.; Acosta-González, A.; Díaz, L.E.; Tello, E. Use of a mixed culture strategy to isolate halophilic bacteria with antibacterial and cytotoxic activity from the Manaure solar saltern in Colombia. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giddings, L.-A.; Newman, D.J. Bioactive Compounds from Marine Extremophiles; Tiquia-Arashiro, S.M., Mormile, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.L.; Yang, X.L. Indole derivatives produced by the metagenome genes of the Escherichia coli-harboring marine sponge Discodermia calyx. Molecules 2017, 22, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshige, Y.; Egami, Y.; Wakimoto, T.; Abe, I. Production of indole antibiotics induced by exogenous gene derived from sponge metagenomes. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Sasidharan, R.S.; Bhat, S.G.; Chandrasekaran, M. Biocompatible polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) production by marine Vibrio azureus BTKB33 under submerged fermentation. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 65, 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Quillaguamán, J.; Guzmán, H.; Van-Thuoc, D.; Hatti-Kaul, R. Synthesis and production of polyhydroxyalkanoates by halophiles: Current potential and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Cao, J.G.; Teng, K.; Meighen, E.A. Biosynthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate in the luminescent bacterium, Vibrio harveyi, and regulation by the lux autoinducer, N-(3- hydroxybutanoyl)homoserine lactone. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 20785–20790. [Google Scholar]
- Numata, K.; Doi, Y. Biosynthesis of Polyhydroxyalkanaotes by a novel facultatively anaerobic Vibrio sp. under marine conditions. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Choi, M.-H.; Kung, S.-S.; Wei, Y.-H. Production of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) by Vibrio spp. isolated from marine environment. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, S.X.; Li, D.H.; Zhu, T.J.; Wang, F.P.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.Q. Two new indole alkaloids from the marine-derived bacterium Aeromonas sp. CB101. Helv. Chim. Acta 2010, 93, 791–795. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed, M.T.; Suzen, S.; Altanlar, N.; Ohlsen, K.; Hilgeroth, A. Discovery of bisindolyl-substituted cycloalkane-anellated indoles as novel class of antibacterial agents against S. aureus and MRSA. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 218–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Wood, T.K.; Lee, J. Roles of indole as an interspecies and interkingdom signaling molecule. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 707–718. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, R.S.; Beyhan, S.; Saini, S.G.; Yildiz, F.H.; Bartlett, D.H. Indole acts as an extracellular cue regulating gene expression in Vibrio cholerae. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 3504–3516. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J. Indole as an intercellular signal in microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 426–444. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, R.T.; Ducker, C.E.; Diller, J.D.; Ruan, C. Purification of native, defined chromatin segments. Methods Enzymol. 2004, 375, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-M.; Weiss, B. Production of 3-Nitrosoindole derivatives by Escherichia coli during anaerobic growth. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 5369–5376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, M.; Choi, S.-U.; Choi, K.Y.; Yon, G.H.; Chae, J.-C.; Kim, D.; Zylstra, G.J.; Kim, E. Trisindoline synthesis and anticancer activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 96–99. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, N.R.; Chae, J.C.; Choi, K.Y.; Yoo, M.; Zylstra, G.J.; Kim, Y.M.; Kang, B.S.; Kim, E. Identification of functionally important amino acids in a novel indigo-producing oxygenase from Rhodococcus sp. strain T104. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 79, 417–422. [Google Scholar]
- Yup Lee, S. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) production from xylose by recombinant Escherichia coli. Bioprocess Eng. 1998, 18, 397–399. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.Y.; Chang, H.N. Effect of complex nitrogen source on the synthesis and accumulation of poly(3-hydroxybutyric acid) by recombinant Escherichia coli in flask and fed-batch cultures. J. Environ. Polym. Degrad. 1994, 2, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- Bormann, E.J.; Roth, M. The production of polyhydroxybutyrate by Methylobacterium rhodesianum and Ralstonia eutropha in media containing glycerol and casein hydrolysates. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 1059–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, I.Y.; Kim, M.K.; Park, Y.H.; Lee, S.Y. Regulatory effects of cellular nicotinamide nucleotides and enzyme activities on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) synthesis in recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1996, 52, 707–712. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaiyezhini, D.; Ramachandran, K.B. Biosynthesis of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) from glycerol by Paracoccus denitrificans in a batch bioreactor: Effect of process variables. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 45, 69–83. [Google Scholar]
- Antón, J.; Oren, A.; Benlloch, S.; Rodrıguez-Valera, F.; Amann, R.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Salinibacter ruber gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel, extremely halophilic member of the Bacteria from saltern crystallizer ponds. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2002, 52, 485–491. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Ghamdi, S.S. Time and dose dependent study of doxorubicin induced DU-145 cytotoxicity. Drug Metab. Lett. 2008, 2, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sebaugh, J.L. Guidelines for accurate EC50/IC50 estimation. Pharm. Stat. 2011, 10, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Z.; Han, Y. Optimization of natural fermentative medium for selenium-enriched yeast by d-optimal mixture design. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 42, 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 27 March 2019).
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry- based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, L.; Zhang, T.; Viegelmann, C.; Martinez, I.J.; Cheng, C.; Dowdells, C.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Gernert, C.; Hentschel, U.; Edrada-Ebel, R.A. Metabolomic tools for secondary metabolite discovery from marine microbial symbionts. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3416–3448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorrochategui, E.; Jaumot, J.; Lacorte, S.; Tauler, R. Data analysis strategies for targeted and untargeted LC-MS metabolomic studies: Overview and workflow. Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 82, 425–442. [Google Scholar]
- Katajamaa, M.; Orešič, M. Data processing for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1158, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kessner, D.; Chambers, M.; Burke, R.; Agus, D.; Mallick, P. ProteoWizard: Open source software for rapid proteomics tools development. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 2534–2536. [Google Scholar]
- Kassambara, A.; Mundt, F. Factoextra: Extract and Visualize the Results of Multivariate Data Analyses. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=factoextra (accessed on 26 March 2019).
- Galili, T. dendextend: An R package for visualizing, adjusting and comparing trees of hierarchical clustering. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3718–3720. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Modified Culture Media | Composition of Nutrient Sources* (g/L) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | Starch | Sodium Pyruvate | Yeast Extract | Peptone | Casamino Acids | |
| pyr_cas | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| pyr_pep | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 |
| pyr_yeast | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| star_cas | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| star_pep | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 |
| star_yeast | 0.0 | 1.3 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| glu_cas | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 |
| glu_pep | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 |
| glu_yeast | 1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| cas | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 |
| pep | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 0.0 |
| yeast | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Conde-Martínez, N.; Bauermeister, A.; Pilon, A.C.; Lopes, N.P.; Tello, E. Integrating Molecular Network and Culture Media Variation to Explore the Production of Bioactive Metabolites by Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040196
Conde-Martínez N, Bauermeister A, Pilon AC, Lopes NP, Tello E. Integrating Molecular Network and Culture Media Variation to Explore the Production of Bioactive Metabolites by Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleConde-Martínez, Natalia, Anelize Bauermeister, Alan Cesar Pilon, Norberto Peporine Lopes, and Edisson Tello. 2019. "Integrating Molecular Network and Culture Media Variation to Explore the Production of Bioactive Metabolites by Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3" Marine Drugs 17, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040196
APA StyleConde-Martínez, N., Bauermeister, A., Pilon, A. C., Lopes, N. P., & Tello, E. (2019). Integrating Molecular Network and Culture Media Variation to Explore the Production of Bioactive Metabolites by Vibrio diabolicus A1SM3. Marine Drugs, 17(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17040196