Wound Healing Potential of Spirulina Protein on CCD-986sk Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
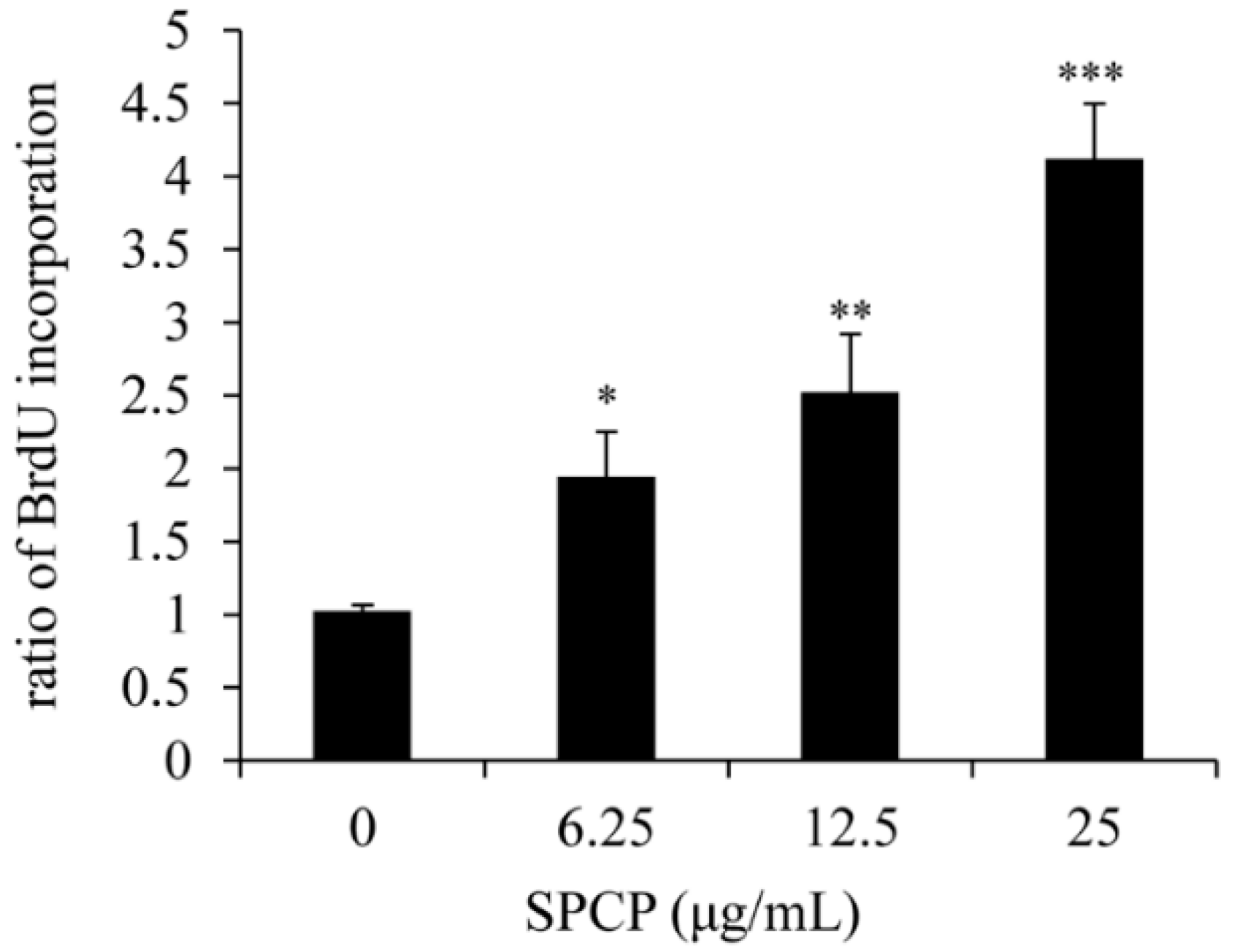
2.1. Effect of SPCP on Proliferation of CCD-986sk Cells
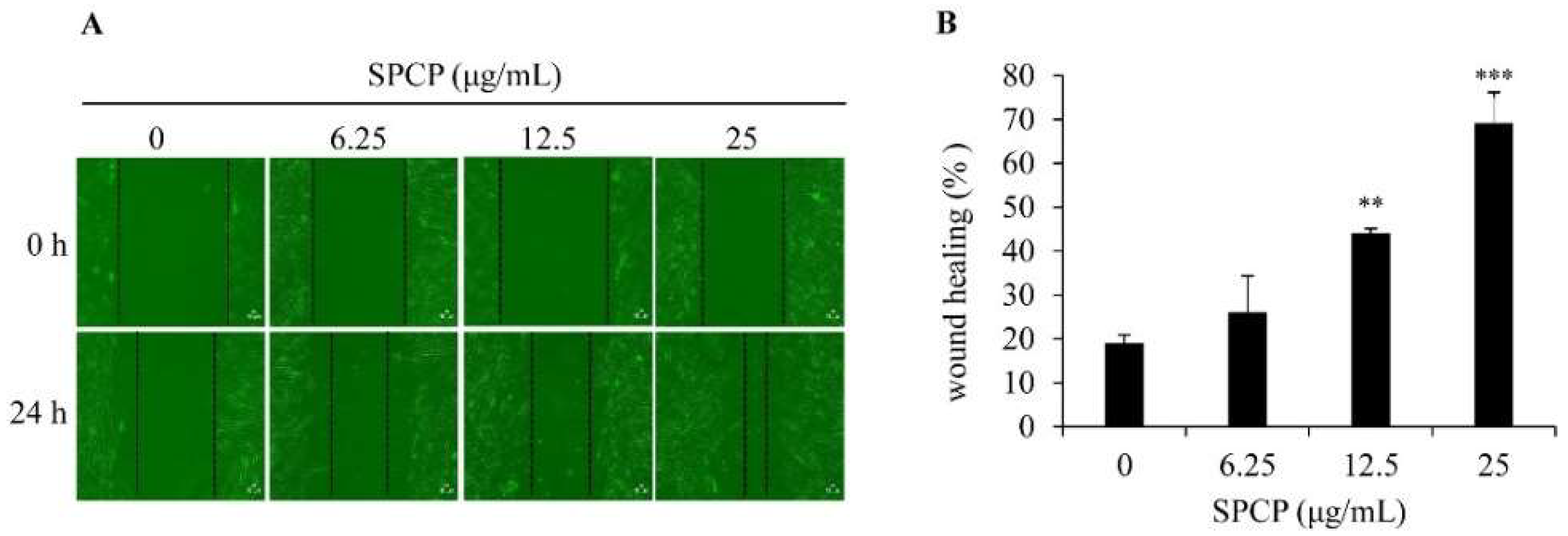
2.2. Effect of SPCP on Migration of CCD-986sk Cells
2.3. Effect of SPCP on the Cell Cycle of CCD-986sk Cells
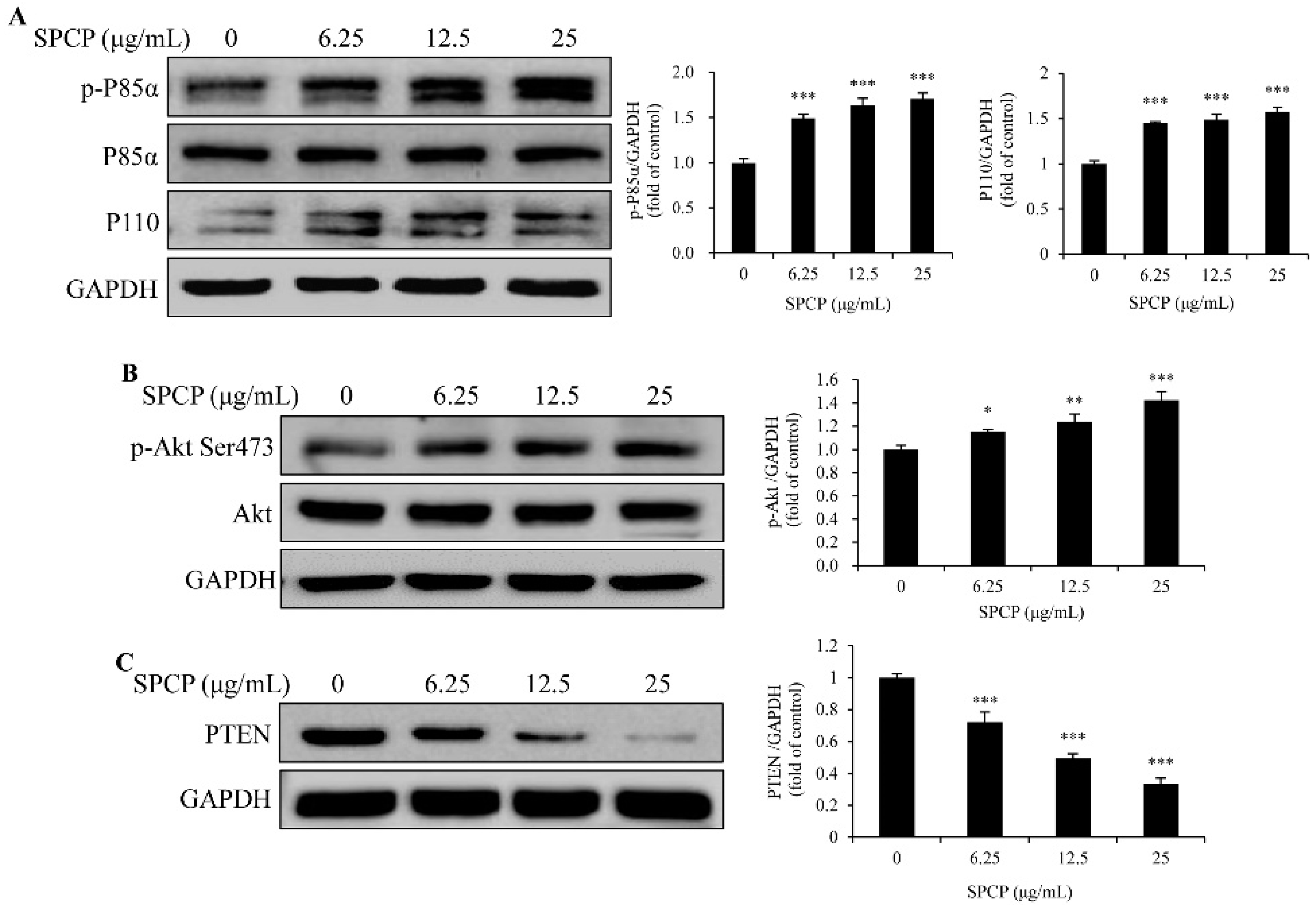
2.4. Treatment of SPCP Activated PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in the CCD-986sk Cells
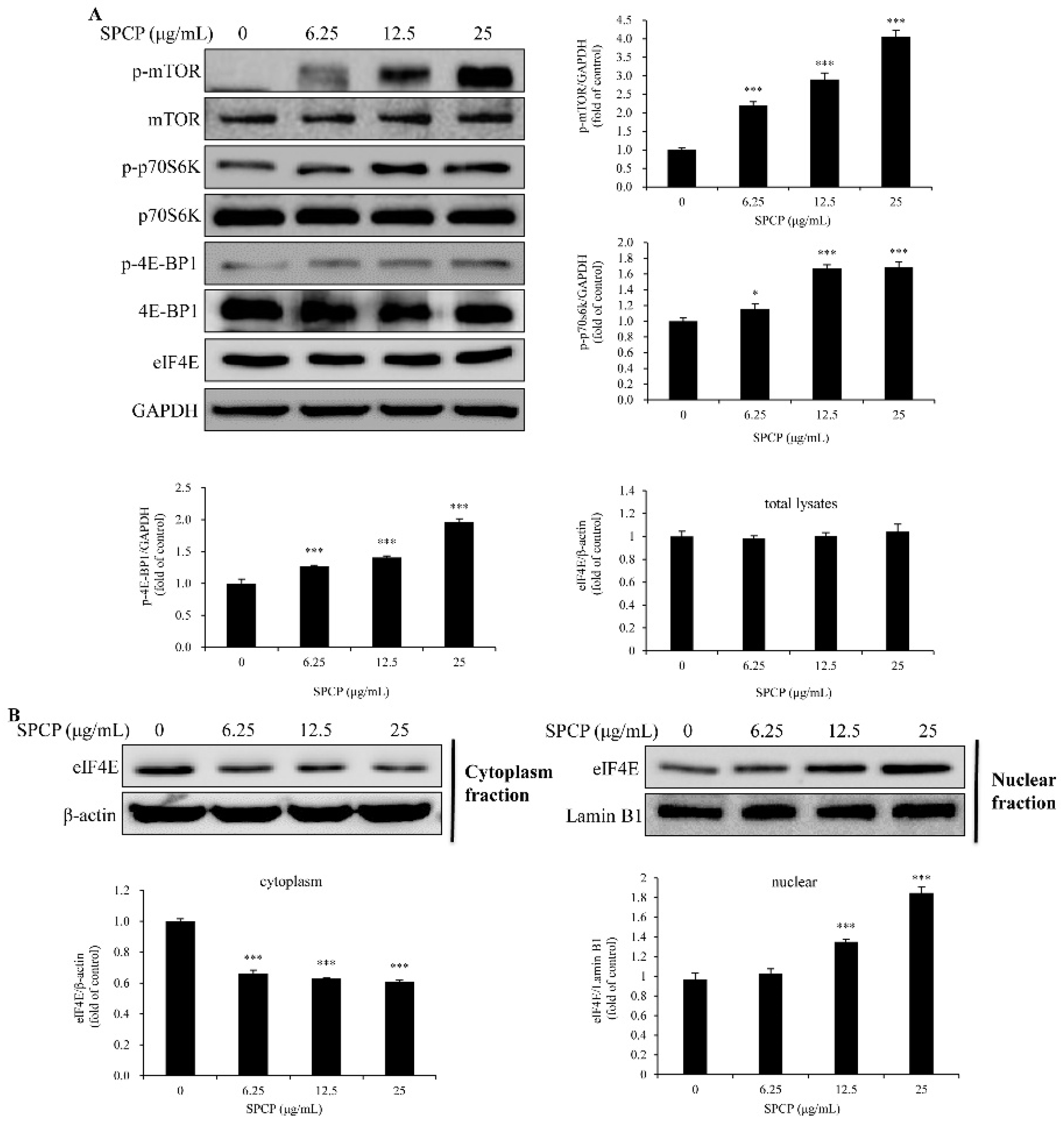
2.5. Treatment of SPCP-Activated Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Signaling Pathway in the CCD-986sk Cells
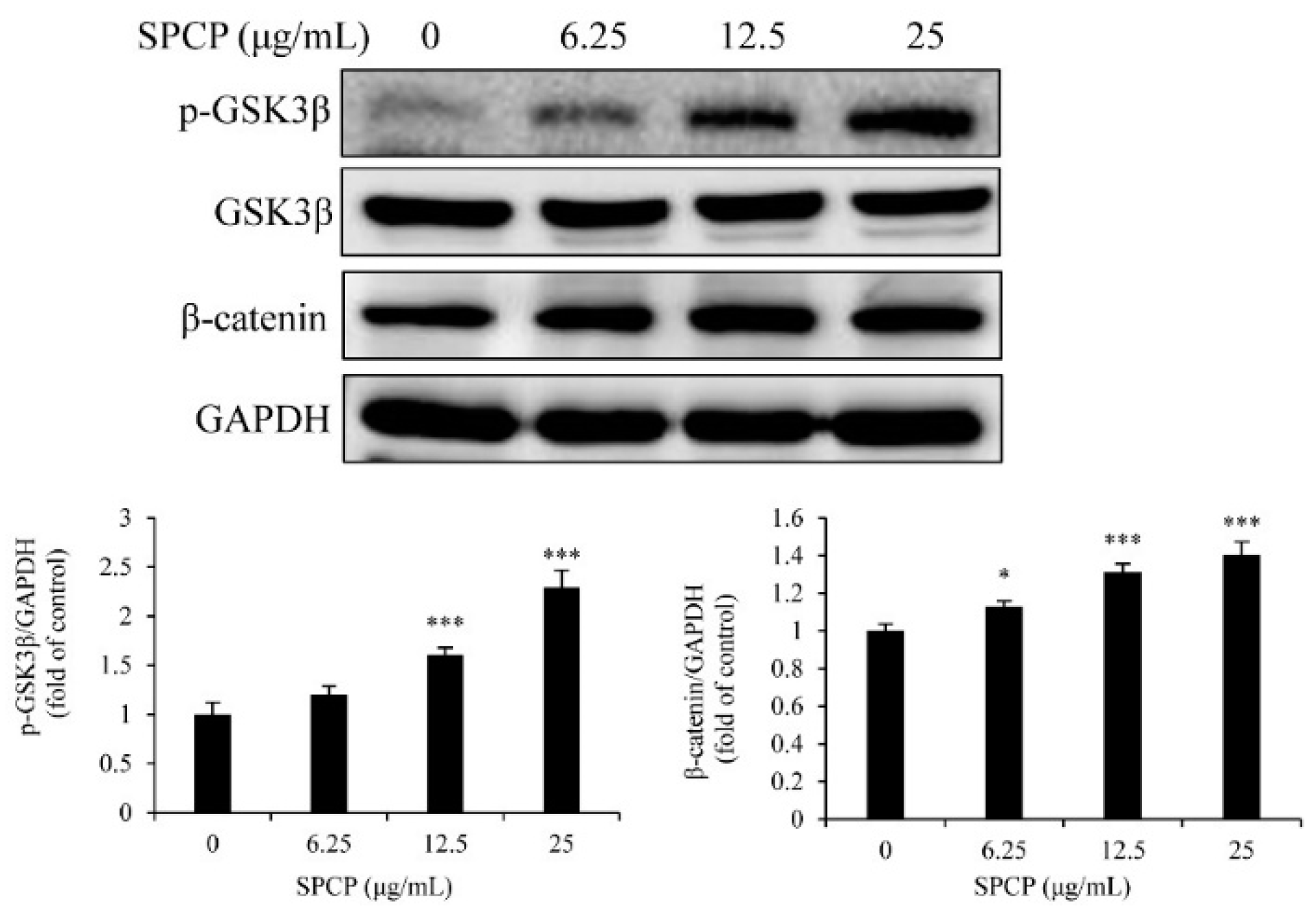
2.6. Treatment of SPCP Increased the Phosphorylation of Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta (GSK3β) in the CCD-986sk Cells
2.7. Inhibition of PI3K Reduced SPCP-Induced Proliferation and Migration of CCD-986sk Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of Spirulina Crude Protein
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. BrdU Assay
4.4. Wound Healing Assay
4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.6. Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Lysates
4.7. Whole Cell Lysates
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Makoto, T.; Wendy, L.; Mayumi, I. Wound healing and skin regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodley, D.T. Distinct fibroblasts in the papillary and reticular dermis: Implications for wound healing. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 35, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Yu, R.; Huang, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, L. Exosomes derived from human adipose mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, A.; Joshi, V.K.; Pandey, D.; Hemalatha, S. Systematic investigation of ethanolic extract from Leea macrophylla: Implications in wound healing. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiquet, M.; Katsaros, C.; Kletsas, D. Multiple functions of gingival and mucoperiosteal fibroblasts in oral wound healing and repair. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 68, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Ki, J.S. A Review of the Biological Activities of Microalgal Carotenoids and Their Potential Use in Healthcare and Cosmetic Industries. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jesus Raposo, M.F.; de Morais, R.M.; de Morais, A.M. Health applications of bioactive compounds from marine microalgae. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buono, S.; Langellotti, A.L.; Martello, A.; Rinna, F.; Fogliano, V. Functional ingredients from microalgae. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1669–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chang, G.K.; Kuo, S.M.; Huang, S.Y.; Hu, I.C.; Lo, Y.L.; Shih, S.R. Well-tolerated spirulina extract inhibits influenza virus replication and reduces virus-induced mortality. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Miron, A.; Klímová, B.; Wan, D.; Kuča, K. The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activities of spirulina: An overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1817–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Taminiau, B.; Walgrave, H.; Daube, G.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Spirulina protects against hepatic inflammation in aging: An effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota? Nutrients 2017, 9, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.C.; Ho, J.A.; Shieh, M.C.; Lu, I.W. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of spirulina and Chlorella water extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4207–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syarina, P.N.; Karthivashan, G.; Abas, F.; Arulselvan, P.; Fakurazi, S. Wound healing potential of Spirulina platensis extracts on human dermal fibroblast cells. EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachstetter, A.D.; Jernberg, J.; Schlunk, A.; Vila, J.L.; Hudson, C.; Cole, M.J.; Shytle, R.D.; Tan, J.; Sanberg, P.R.; Sanberg, C.D.; et al. Spirulina promotes stem cell genesis and protects against LPS induced declines in neural stem cell proliferation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, S.; Tamburaci, S.; Dalay, M.C.; Deliloglu Gurhan, I. In vitro evaluation of Spirulina platensis extract incorporated skin cream with its wound healing and antioxidant activities. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhyastha, H.; Madhyastha, R.; Nakajima, Y.; Omura, S.; Maruyama, M. Regulation of growth factors-associated cell migration by C-phycocyanin scaffold in dermal wound healing. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2012, 39, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Lee, M.K.; Choi, J.W.; Choi, Y.; Nam, T.J. Crude protein from spirulina increases the viability of CCD-986sk cells via the EGFR/MAPK signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 43, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jutten, B.; Rouschop, K.M. EGFR signaling and autophagy dependence for growth, survival, and therapy resistance. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.S.; Cui, W. Proliferation, survival and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development 2016, 143, 3050–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Zhou, P.; von Gise, A.; Gu, F.; Ma, Q.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; van Gorp, P.R.; Wang, D.Z.; Pu, W.T. Pi3kcb Links Hippo-YAP and PI3K-AKT signaling pathways to promote cardiomyocyte proliferation and survival. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.L.; Turlova, E.; Sun, C.L.; Kim, J.S.; Huang, S.; Zhong, X.; Guan, Y.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Rutka, J.T.; Feng, Z.P.; et al. Xyloketal B suppresses glioblastoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro through inhibiting TRPM7-regulated PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2505–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Lee, J.T.; Navolanic, P.M.; Steelman, L.S.; Shelton, J.G.; Blalock, W.L.; Franklin, R.A.; McCubrey, J.A. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 2003, 17, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, X.; Sun, D.; Han, Q.; Yi, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X. Hypoxia induces pulmonary arterial fibroblast proliferation, migration, differentiation and vascular remodeling via the PI3K/Akt/p70S6K signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2461–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Cheng, Y.; Ye, J.; Cai, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; et al. bFGF promotes the migration of human dermal fibroblasts under diabetic conditions through reactive oxygen species production via the PI3K/Akt-Rac1-JNK pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 845–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinda, M.; Dasgupta, U.; Singh, N.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Karmakar, P. PI3K-mediated proliferation of fibroblasts by calendula officinalis tincture: Implication in wound healing. Phytother. Res. 2015, 29, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, T.F. PI3K/Akt: Getting it right matters. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6473–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qin, Y.; Li, K.; Yu, H.; Li, P. Immunostimulatory effects of Chitooligosaccharides on RAW 264.7 mouse macrophages via regulation of the MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, J.A.; Luo, J.; Cantley, L.C. The evolution of phosphatidyl 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2006, 7, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingar, D.C.; Richardson, C.J.; Tee, A.R.; Cheatham, L.; Tsou, C.; Blenis, J. mTOR controls cell cycle progression through its cell growth effectors S6K1 and 4E-BP1/eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 200–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.H.; Park, N.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Jeong, K.T.; Lee, E.J.; Lee, E. Potential wound healing activities of galla rhois in human fibroblasts and keratinocytes. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannas, I.V.; Tzeranis, D.S.; So, P.T.C. Regeneration of injured skin and peripheral nerves requires control of wound contraction, not scar formation. Wound Repair Regen. 2017, 25, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadelmann, W.K.; Digenis, A.G.; Tobin, G.R. Physiology and healing dynamics of chronic cutaneous wounds. Am. J. Surg. 1998, 176, 26S–38S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Kim, D.S.; Ju, J.H.; Shin, H.S. Assessment of spirulina-PCL nanofiber for the regeneration of dermal fibroblast layers. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2013, 49, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, E.; Arciola, C.R.; Vigani, B.; Crivelli, B.; Moro, P.; Marrubini, G.; Sorrenti, M.; Catenacci, L.; Bruni, G.; Chlapanidas, T.; et al. In vitro effectiveness of microspheres based on silk sericin and Chlorella vulgaris or Arthrospira platensis for wound healing applications. Materials 2017, 10, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duronio, R.J.; Xiong, Y. Signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, M.; Li, P.F.; Wang, K. Understanding cardiomyocyte proliferation: An insight into cell cycle activity. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1019–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Wei, T.; He, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhang, W.; Xiong, Z. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound activates ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt signalling pathways and promotes the proliferation of human amnion-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif. 2017, 50, e12383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoli, C.; Skotheim, J.M.; de Bruin, R.A. Control of cell cycle transcription during G1 and S phases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coqueret, O. New roles for p21 and p27 cell-cycle inhibitors: A function for each cell compartment? Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 13, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheaff, R.J.; Groudine, M.; Gordon, M.; Roberts, J.M.; Clurman, B. Cyclin E-CDK2 is a regulator of p27Kip1. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 1464–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, F.; Wen, L.; Ouyang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Luo, L.; Jian, Z. Osteocalcin induces proliferation via positive activation of the PI3K/Akt, P38 MAPK pathways and promotes differentiation through activation of the GPRC6A-ERK1/2 pathway in C2C12 myoblast cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1100–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, S.; Xue, P.; Li, Y. Liraglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, facilitates osteogenic proliferation and differentiation in MC3T3-E1 cells through phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT), extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK)1/2, and cAMP/protein kinase A (PKA) signaling pathways involving β-catenin. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, P.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, S. IKVAV regulates ERK1/2 and Akt signalling pathways in BMMSC population growth and proliferation. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.P.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Jiang, W. High mobility group box-1 promotes the proliferation and migration of hepatic stellate cells via TLR4-dependent signal pathways of PI3K/Akt and JNK. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.S.; Li, Q.; Hamdan, N.; Bian, Y.F.; Zhuang, S.; Fan, K.; Liu, Z.J. Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside regulates proliferation, differentiation, and OPG/RANKL/M-CSF expression in MC3T3-E1 cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Molecules 2018, 23, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, C.A.; Jope, R.S. The multifaceted roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3β in cellular signaling. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 65, 391–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR signaling at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3589–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini David, M. mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.C.; Abraham, R.T. PHAS/4E-BPs as regulators of mRNA translation and cell proliferation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997, 22, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tee, A.R.; Blenis, J. mTOR, translational control and human disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 16, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Semenov, M.; Han, C.; Baeg, G.H.; Tan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, X.; He, X. Control of β-Catenin Phosphorylation/Degradation by a Dual-Kinase Mechanism. Cell 2002, 108, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
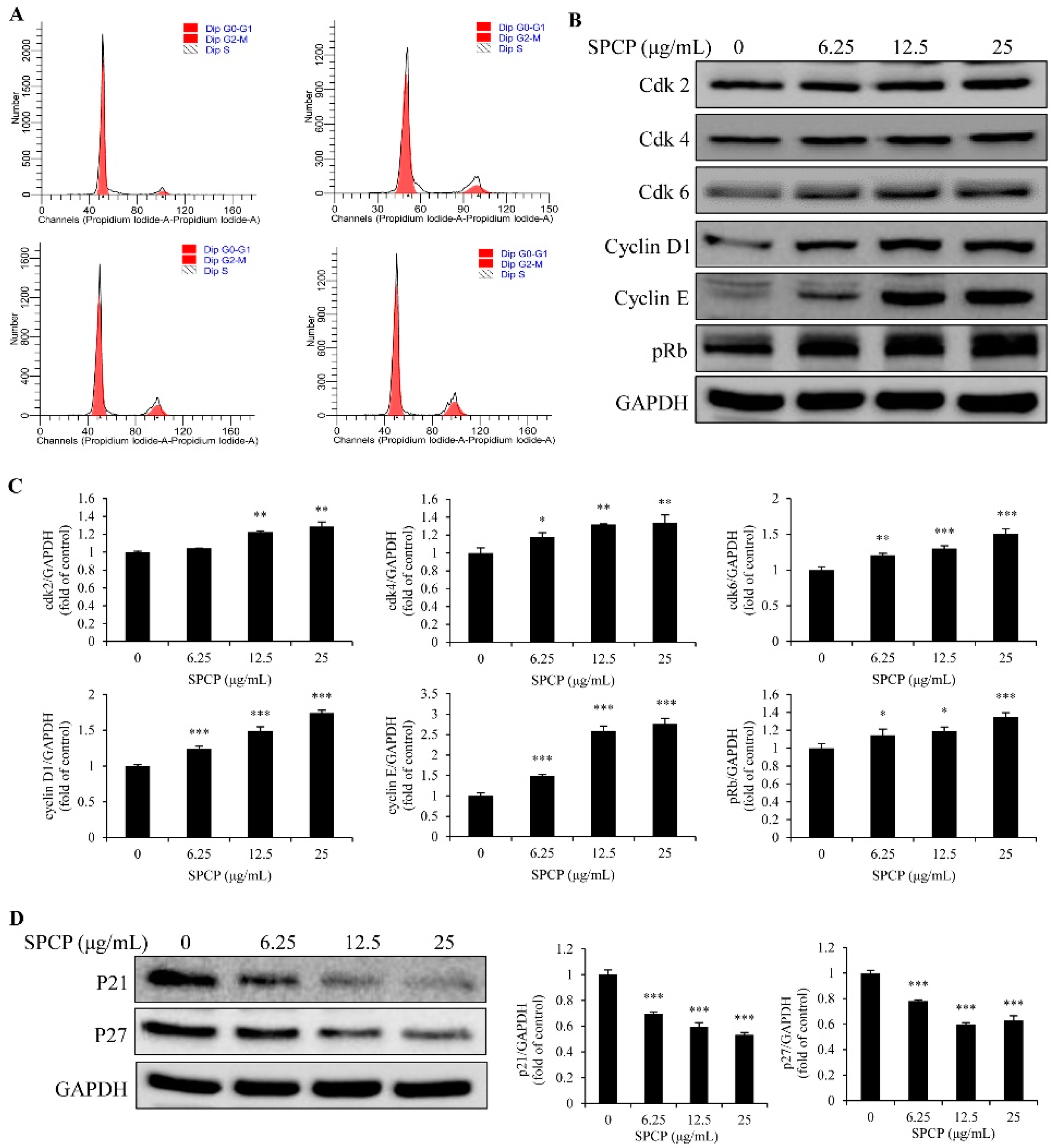

| SPCP (μg/mL) | G0/G1 (%) | S (%) | G2/M (%) | S + G2/M (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 94.01 ± 2.494 | 1.84 ± 0.875 | 4.15 ± 1.759 | 5.99 ± 2.493 |
| 6.25 | 87.47 ± 3.604 | 3.513 ± 0.587 * | 9.087 ± 3.500 | 12.6 ± 3.586 * |
| 12.5 | 83.0233 ± 3.647 ** | 3.647 ± 0.387 ** | 13.33 ± 1.970 ** | 16.977 ± 2.350 ** |
| 25 | 81.113 ± 2.045 ** | 3.73 ± 0.732 ** | 15.157 ± 1.339 ** | 18.887 ± 2.045 *** |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, M.-K.; Choi, Y.-H.; Nam, T.-J. Wound Healing Potential of Spirulina Protein on CCD-986sk Cells. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020130
Liu P, Choi J-W, Lee M-K, Choi Y-H, Nam T-J. Wound Healing Potential of Spirulina Protein on CCD-986sk Cells. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(2):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ping, Jeong-Wook Choi, Min-Kyeong Lee, Youn-Hee Choi, and Taek-Jeong Nam. 2019. "Wound Healing Potential of Spirulina Protein on CCD-986sk Cells" Marine Drugs 17, no. 2: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020130
APA StyleLiu, P., Choi, J.-W., Lee, M.-K., Choi, Y.-H., & Nam, T.-J. (2019). Wound Healing Potential of Spirulina Protein on CCD-986sk Cells. Marine Drugs, 17(2), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020130





