Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
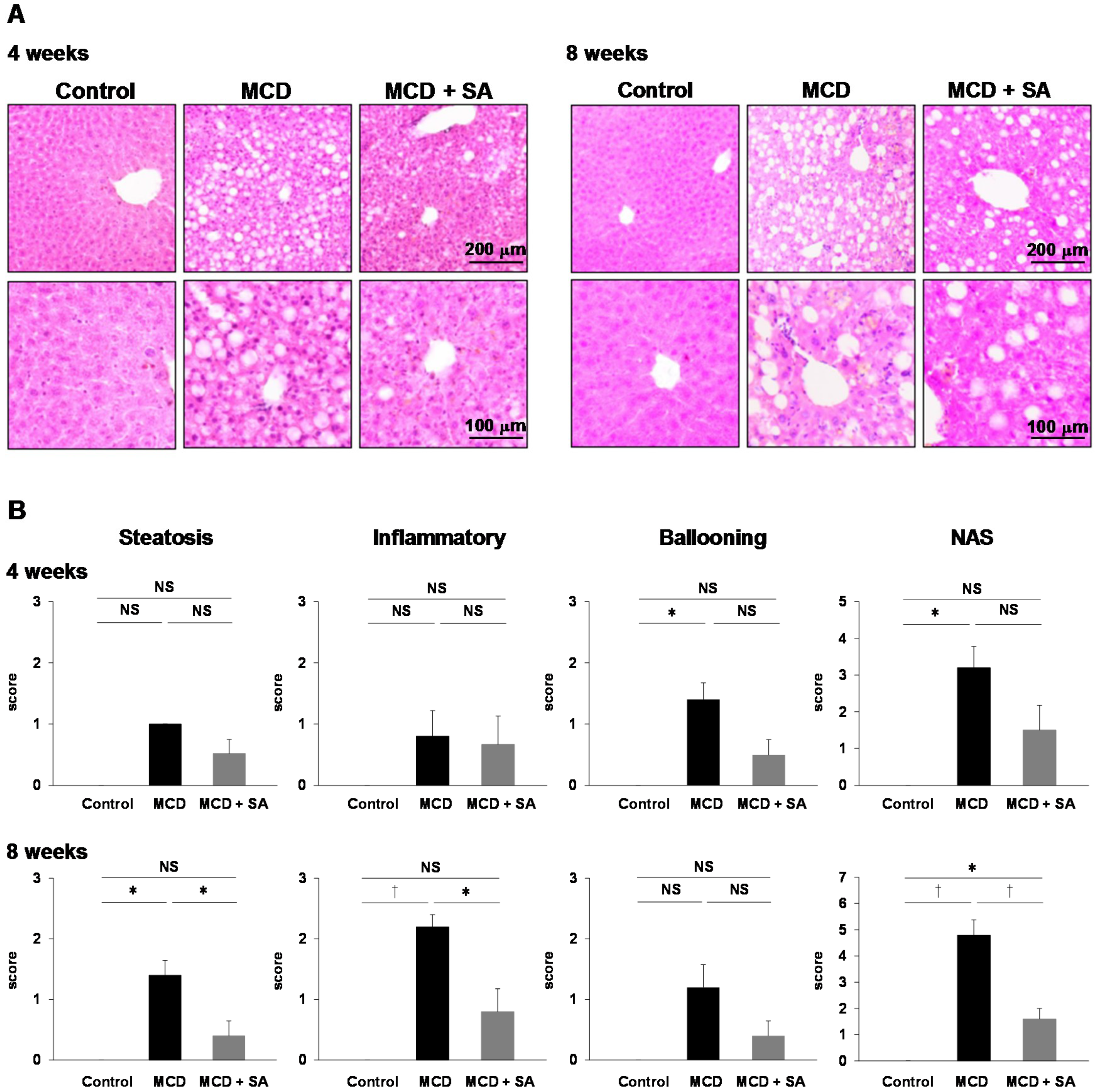
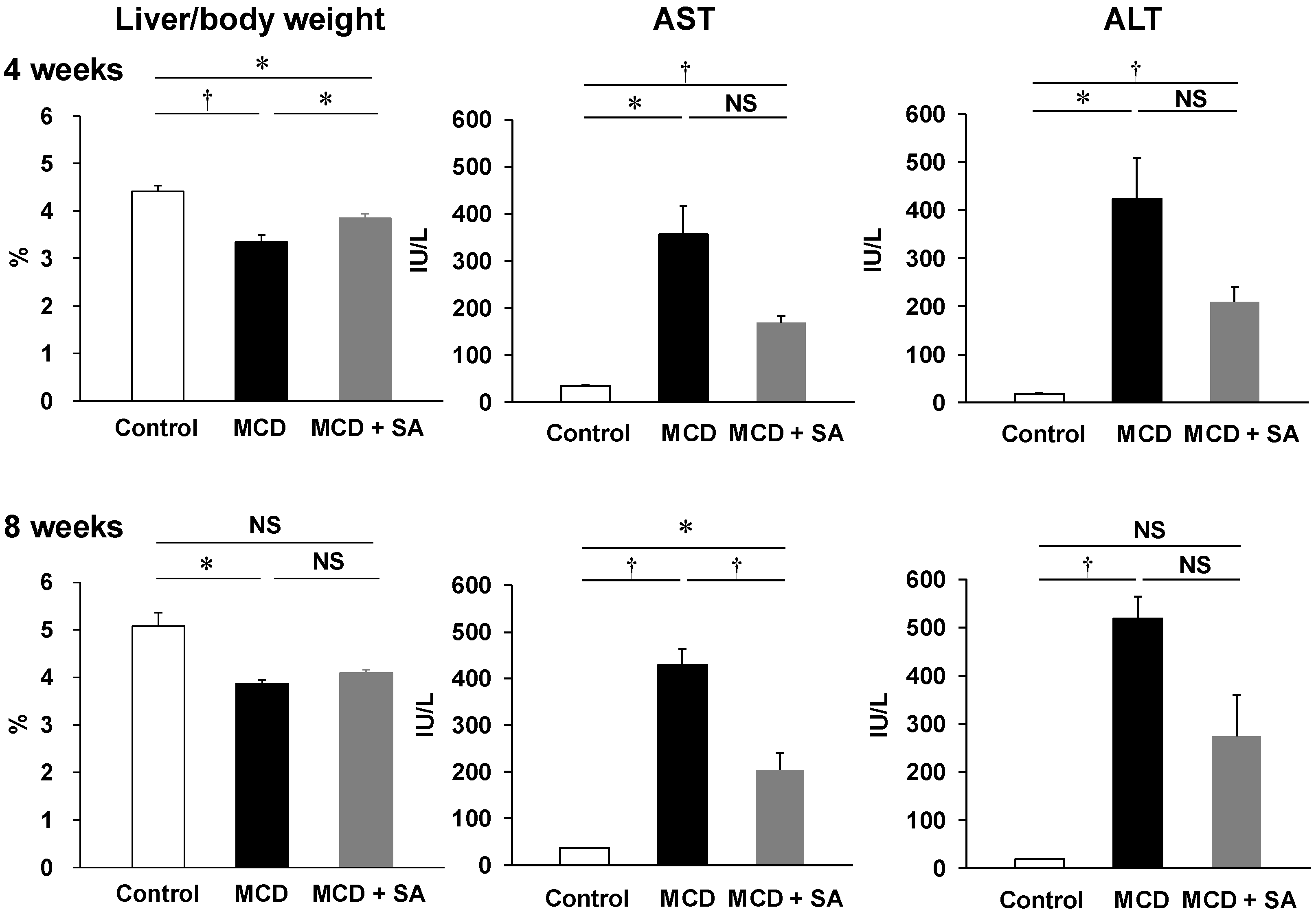
2.1. Inhibitory Effects of SA on MCD Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis and Liver Injury
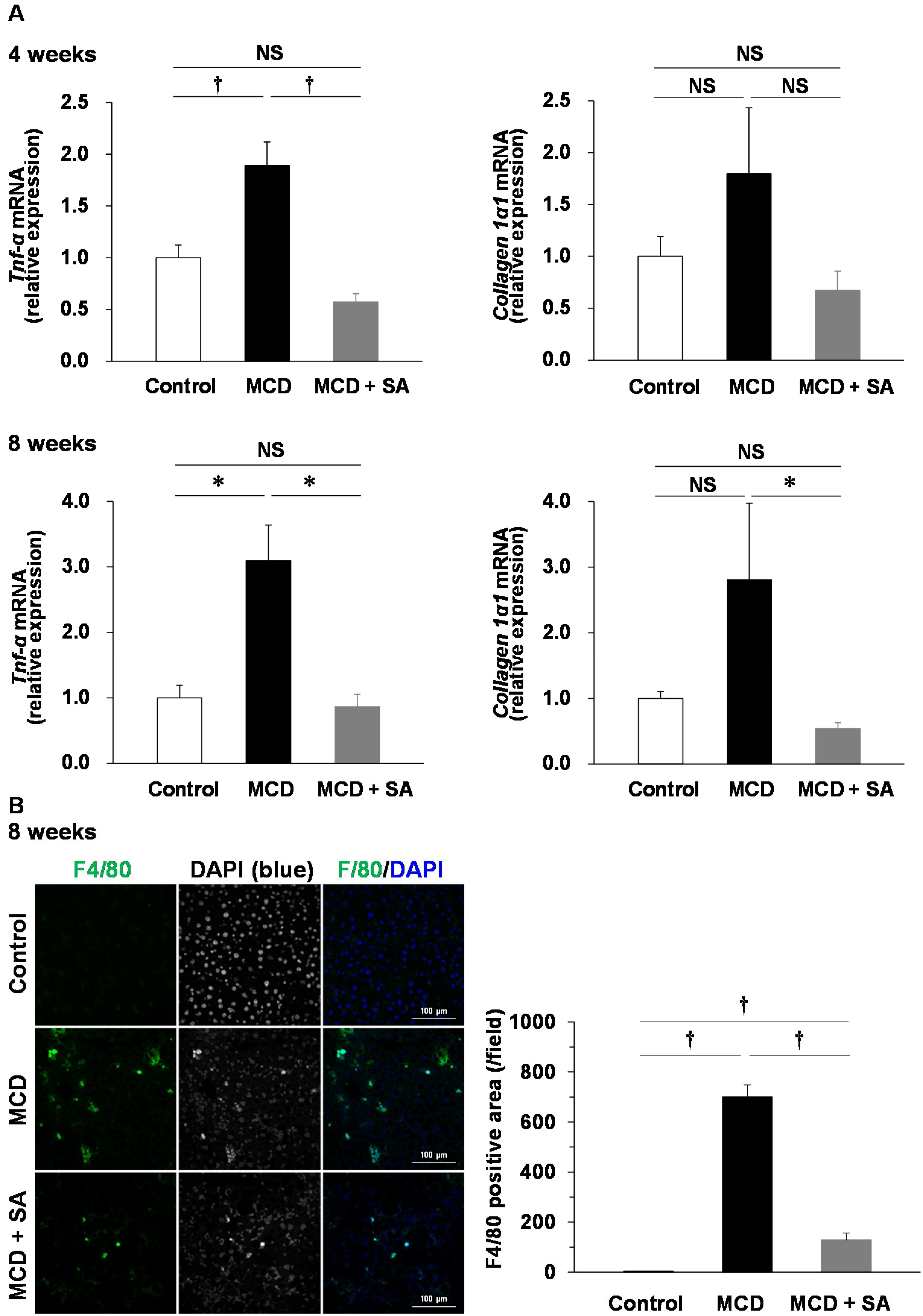
2.2. Effects of SA on Expression of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (Tnf-α) and Collagen 1α1 mRNA and Macrophage Infiltration in the Liver of Mice with MCD Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis
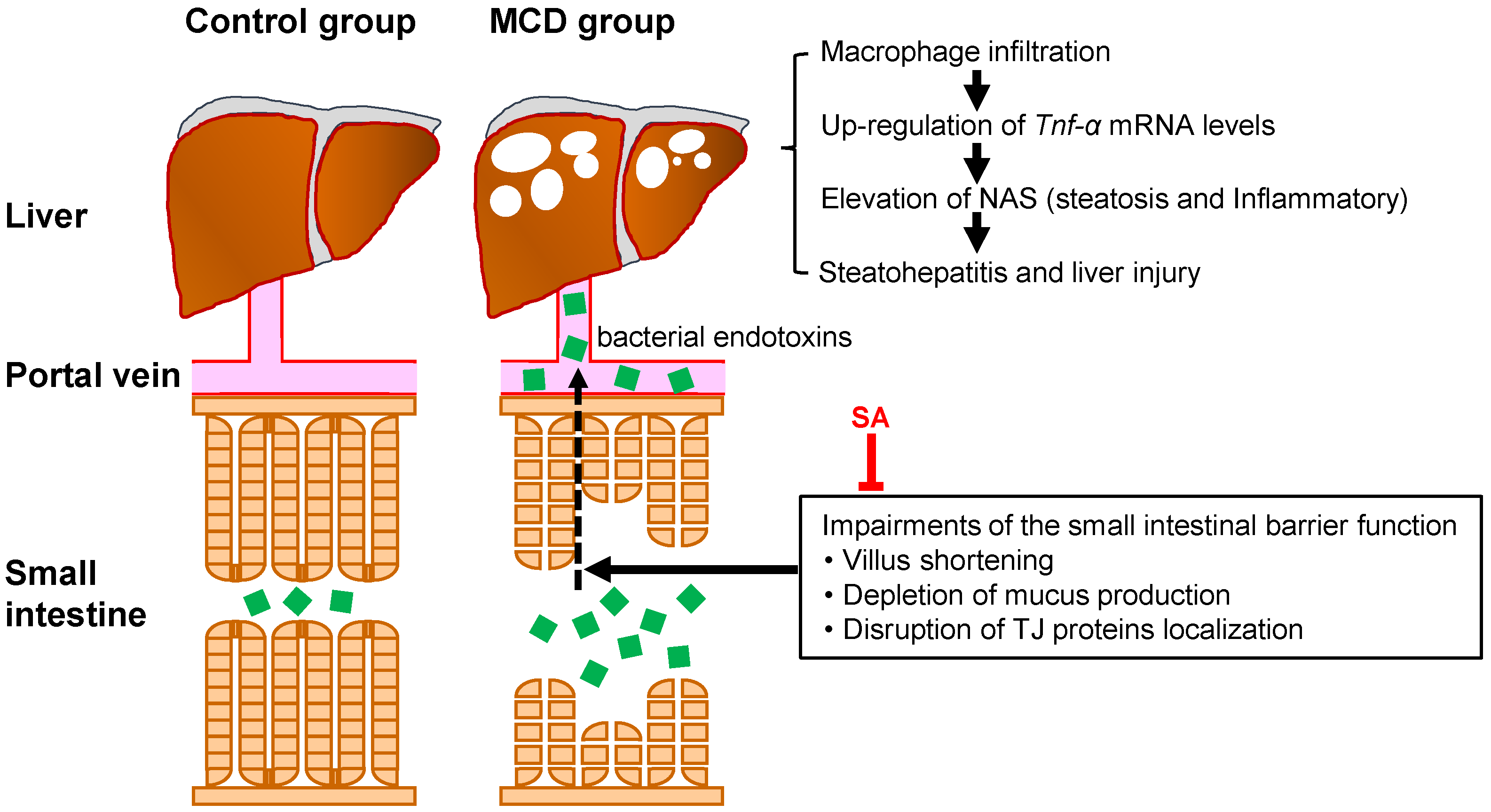
2.3. Effects of SA on Small-Intestinal Injury in Mice with MCD Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Induction of Steatohepatitis Using a MCD Diet
4.2. Histology
4.3. Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.4. Analyses of Biochemical Data
4.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.6. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascha, M.S.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Lopez, R.; Tamimi, T.A.; Feldstein, A.F.; Zein, N.N. The incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1972–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: The multiple parallel hits hypothesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauner, M.; Arrese, M.; Wagner, M. Fatty liver and lipotoxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1801, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Loomba, R.; Sanyal, A.J.; Lavine, J.E.; Van Natta, M.L.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Chalasani, N.; Dasarathy, S.; Diehl, A.M.; Hameed, B.; et al. Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2015, 385, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigg, A.J.; Roberts-Thomson, I.C.; Dymock, R.B.; McCarthy, P.J.; Grose, R.H.; Cummins, A.G. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, intestinal permeability, endotoxaemia, and tumour necrosis factor alpha in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut 2001, 48, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, J.; Garber, J.J.; Khalili, H.; Dave, M.; Bale, S.S.; Jindal, R.; Motola, D.L.; Luther, S.; Bohr, S.; Jeoung, S.W.; et al. Hepatic injury in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis contributes to altered intestinal permeability. Cell Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Itoh, T.; Nasu, R.; Nishida, R. Effect of sodium alginate on dextran sulfate sodium- and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced experimental colitis in mice. Pharmacology 2013, 92, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poynard, T.; Vernisse, B.; Agostini, H. Randomized, multicentre comparison of sodium alginate and cisapride in the symptomatic treatment of uncomplicated gastro-oesophageal reflux. Aliment Pharmacol. Ther. 1998, 12, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horibe, S.; Tanahashi, T.; Kawauchi, S.; Mizuno, S.; Rikitake, Y. Preventative effects of sodium alginate on indomethacin-induced small-intestinal injury in mice. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, S.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Watkins, P.A.; Moser, A.B.; Desimone, C.; Song, X.Y.; Diehl, A.M. Probiotics and antibodies to TNF inhibit inflammatory activity and improve nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2003, 37, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariscal, L.; Betanzos, A.; Avila-Flores, A. MAGUK proteins: Structure and role in the tight junction. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 11, 315–324. [Google Scholar]
- Marcolin, E.; Forgiarini, L.F.; Tieppo, J.; Dias, A.S.; Freitas, L.A.; Marroni, N.P. Methionine- and choline-deficient diet induces hepatic changes characteristic of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2011, 48, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.Y.; Choi, H.; Yoon, J.Y.; Lee, I.Y.; Seo, Y.; Moon, H.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Jun, H.S. Polyphenol-rich fraction of ecklonia cava improves nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in high fat diet-fed mice. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6866–6883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbia, D.; Dall’Acqua, S.; Di Gangi, I.M.; Bogialli, S.; Caputi, V.; Albertoni, L.; Marsilio, I.; Paccagnella, N.; Carrara, M.; Giron, M.C.; et al. The phytocomplex from fucus vesiculosus and ascophyllum nodosum controls postprandial plasma glucose levels: An in vitro and in vivo study in a mouse model of NASH. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, M.V.; Michelotti, G.A.; Xie, G.; Almeida Pereira, T.; Boursier, J.; Bohnic, B.; Guy, C.D.; Diehl, A.M. Mouse models of diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis reproduce the heterogeneity of the human disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, K.; Tamiya, G.; Ando, S.; Ohsumi, K.; Chiyo, T.; Mizutani, A.; Kitamura, N.; Toda, K.; Kaneko, T.; Horie, Y.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor alpha signalling through activation of Kupffer cells plays an essential role in liver fibrosis of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Gut 2006, 55, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, K.; Risby, T.; Diehl, A.M. Increased gastrointestinal ethanol production in obese mice: Implications for fatty liver disease pathogenesis. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritze, Y.; Bárdos, G.; Claus, A.; Ehrmann, V.; Bergheim, I.; Schwiertz, A.; Bischoff, S.C. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG protects against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e80169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, H.; Niioka, M.; Kobayashi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Watanabe, T. Butyrate-producing probiotics reduce nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression in rats: New insight into the probiotics for the gut-liver axis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Q.; Lin, H.Z.; Lane, M.D.; Clemens, M.; Diehl, A.M. Obesity increases sensitivity to endotoxin liver injury: Implications for the pathogenesis of steatohepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2557–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.H.; Cui, T.; Huang, F.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Xu, L.L.; Feng, Q.; Hu, Y.Y. Puerarin ameliorates experimental alcoholic liver injury by inhibition of endotoxin gut leakage, Kupffer cell activation, and endotoxin receptors expression. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 344, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphreys, E.R.; Triffitt, J.T. Absorption by the rat of alginate labelled with carbon-14. Nature 1968, 219, 1172–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daigo, K.; Wada, Y.; Yamada, C.; Yamaji, M.; Okuda, S.; Okada, M.; Miyazato, T. Pharmacological studies of sodium alginate. I. Protective effect of sodium alginate on mucous membranes of upper-gastrointestinal tract. Yakugaku Zasshi 1981, 101, 452–457. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, A.; Itoh, T.; Nasu, R.; Nishida, R. Sodium alginate ameliorates indomethacin-induced gastrointestinal mucosal injury via inhibiting translocation in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Hamouda, N.; Kano, Y.; Oikawa, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Matsumoto, K.; Amagase, K.; Shimakawa, M. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 attenuates 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice. via suppression of dysbiosis-related secondary inflammatory responses. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2017, 44, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluk, P.; Yao, L.C.; Feng, J.; Romano, T.; Jung, S.S.; Schreiter, J.L.; Yan, L.; Shealy, D.J.; McDonald, D.M. TNF-alpha drives remodeling of blood vessels and lymphatics in sustained airway inflammation in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 2954–2964. [Google Scholar]
- Overbergh, L.; Valckx, D.; Waer, M.; Mathieu, C. Quantification of murine cytokine mRNAs using real time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR. Cytokine 1999, 11, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, B.; Luyendyk, J.P.; Tawfik, O.; Guo, G.L. Farnesoid X receptor deficiency induces nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in low-density lipoprotein receptor-knockout mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 328, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kawauchi, S.; Horibe, S.; Sasaki, N.; Tanahashi, T.; Mizuno, S.; Hamaguchi, T.; Rikitake, Y. Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020104
Kawauchi S, Horibe S, Sasaki N, Tanahashi T, Mizuno S, Hamaguchi T, Rikitake Y. Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKawauchi, Shoji, Sayo Horibe, Naoto Sasaki, Toshihito Tanahashi, Shigeto Mizuno, Tsuneo Hamaguchi, and Yoshiyuki Rikitake. 2019. "Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet" Marine Drugs 17, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020104
APA StyleKawauchi, S., Horibe, S., Sasaki, N., Tanahashi, T., Mizuno, S., Hamaguchi, T., & Rikitake, Y. (2019). Inhibitory Effects of Sodium Alginate on Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Induced by a Methionine- and Choline-Deficient Diet. Marine Drugs, 17(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17020104




