Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
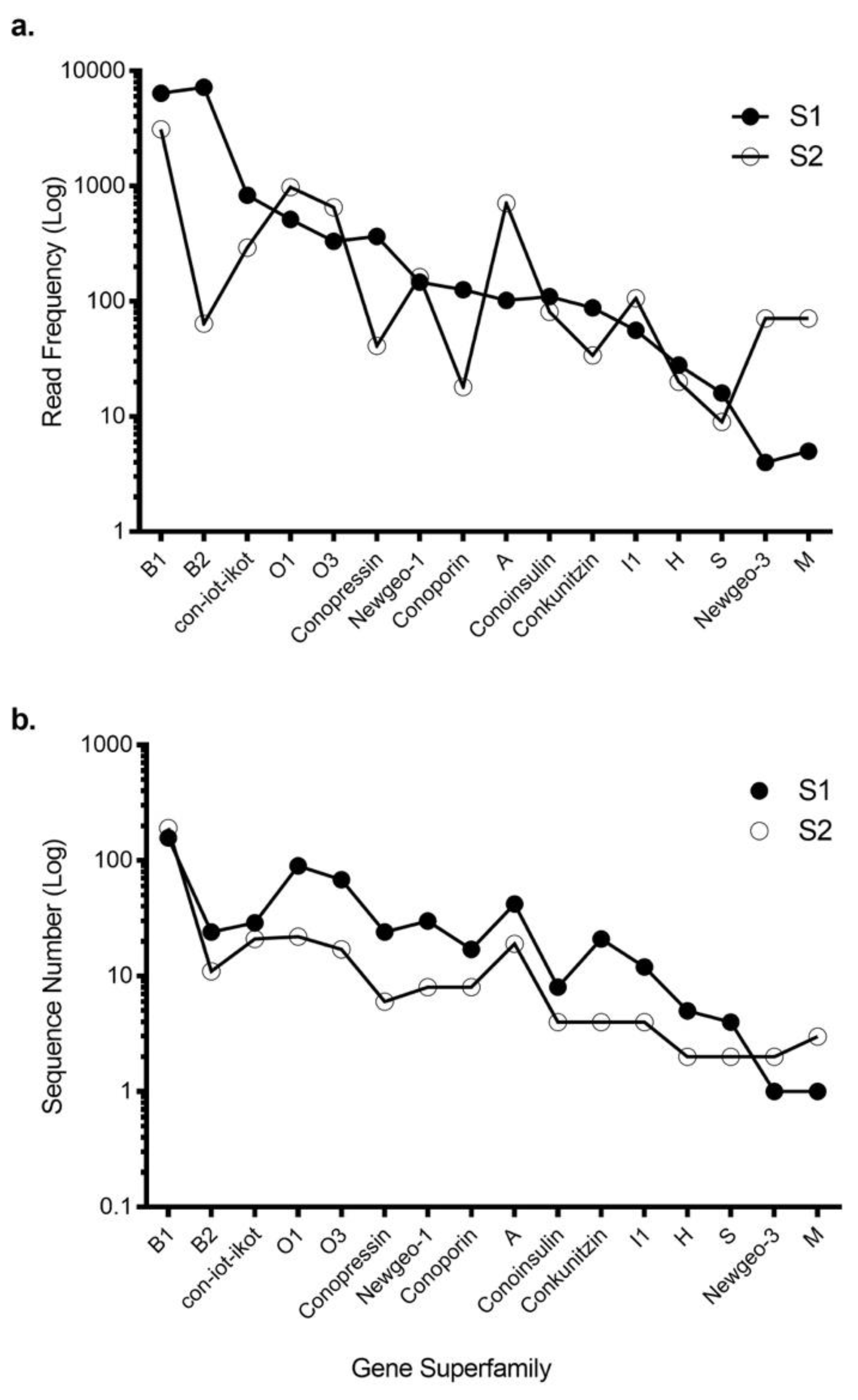
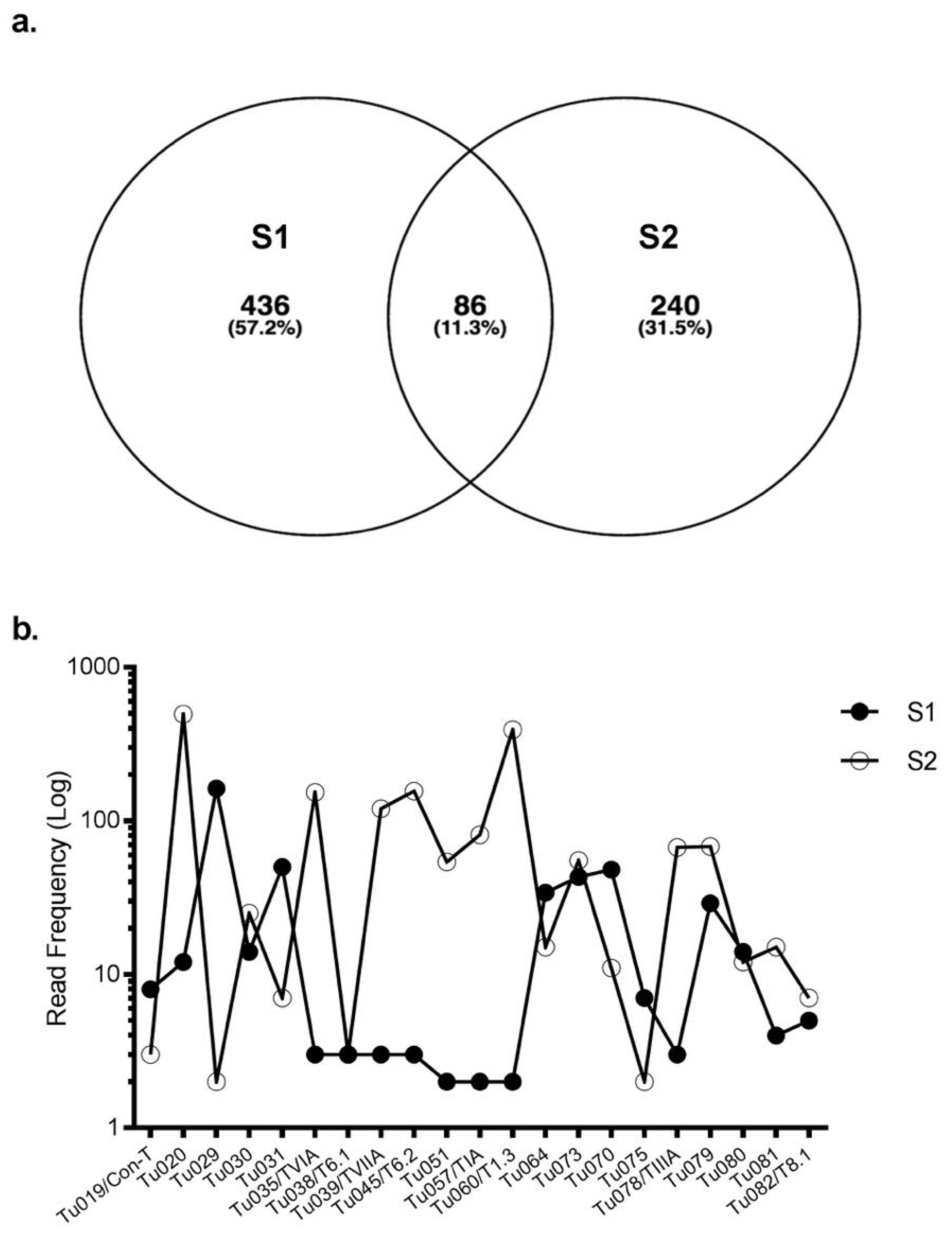
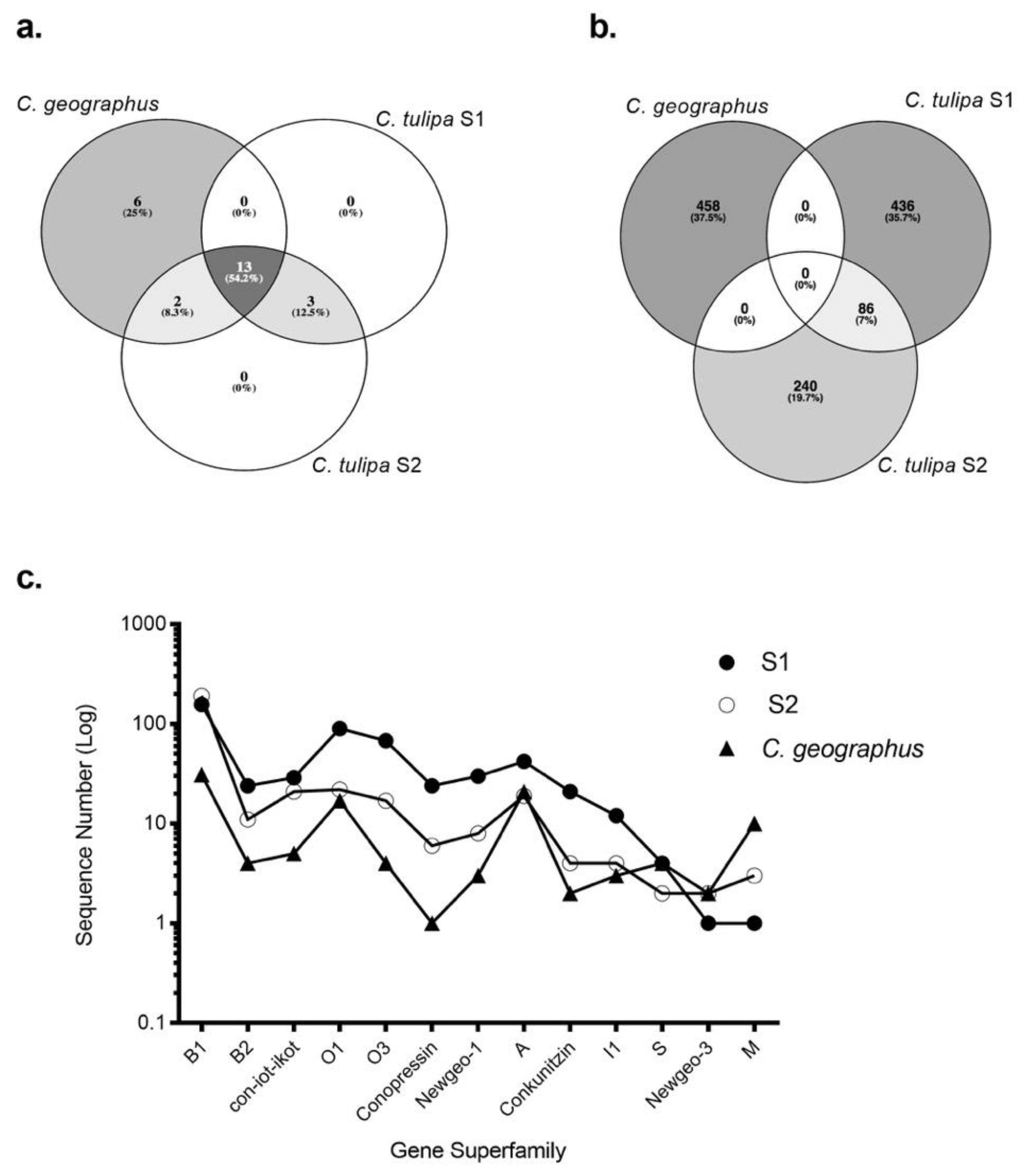
2.1. Transcriptomic Intraspecific Variation
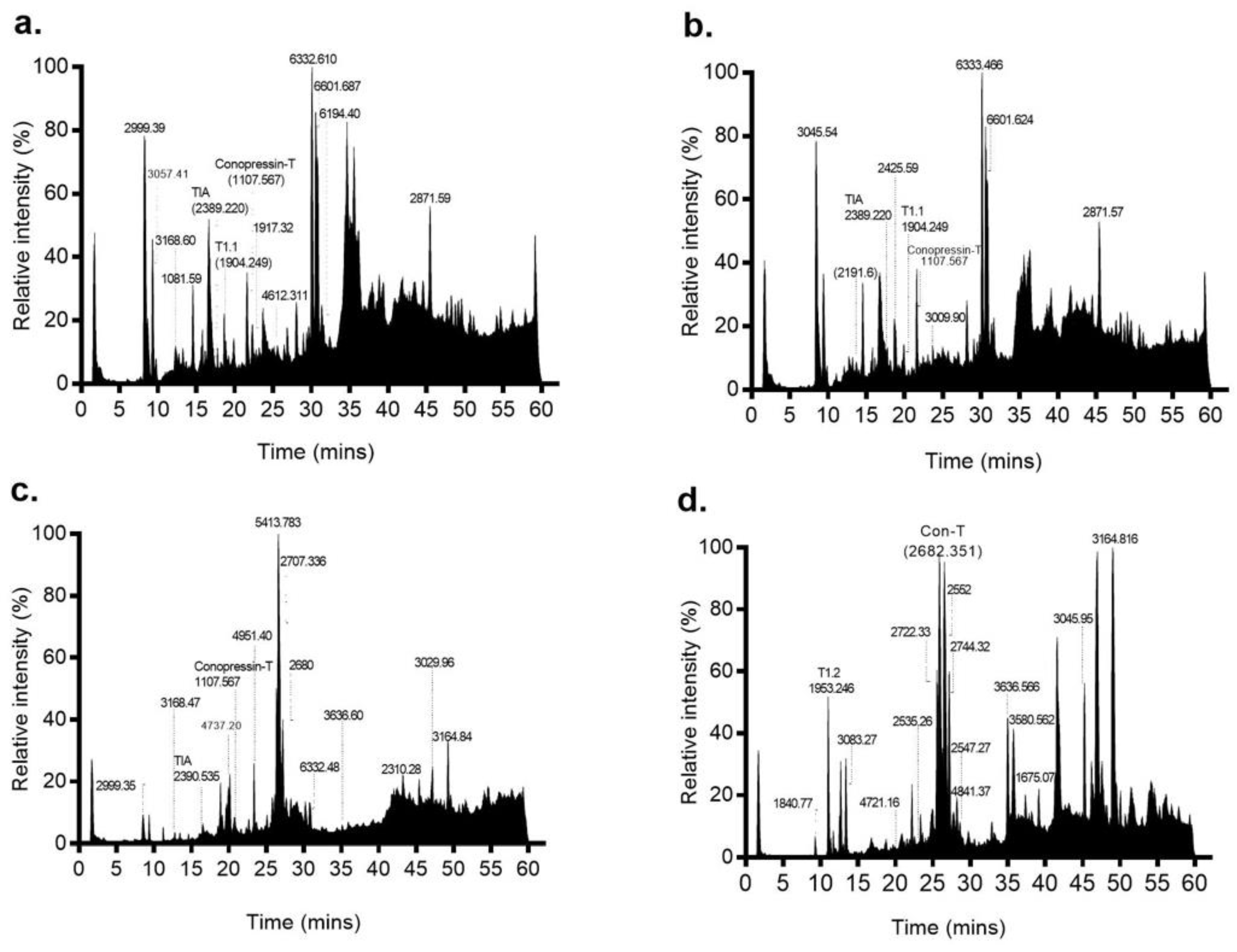
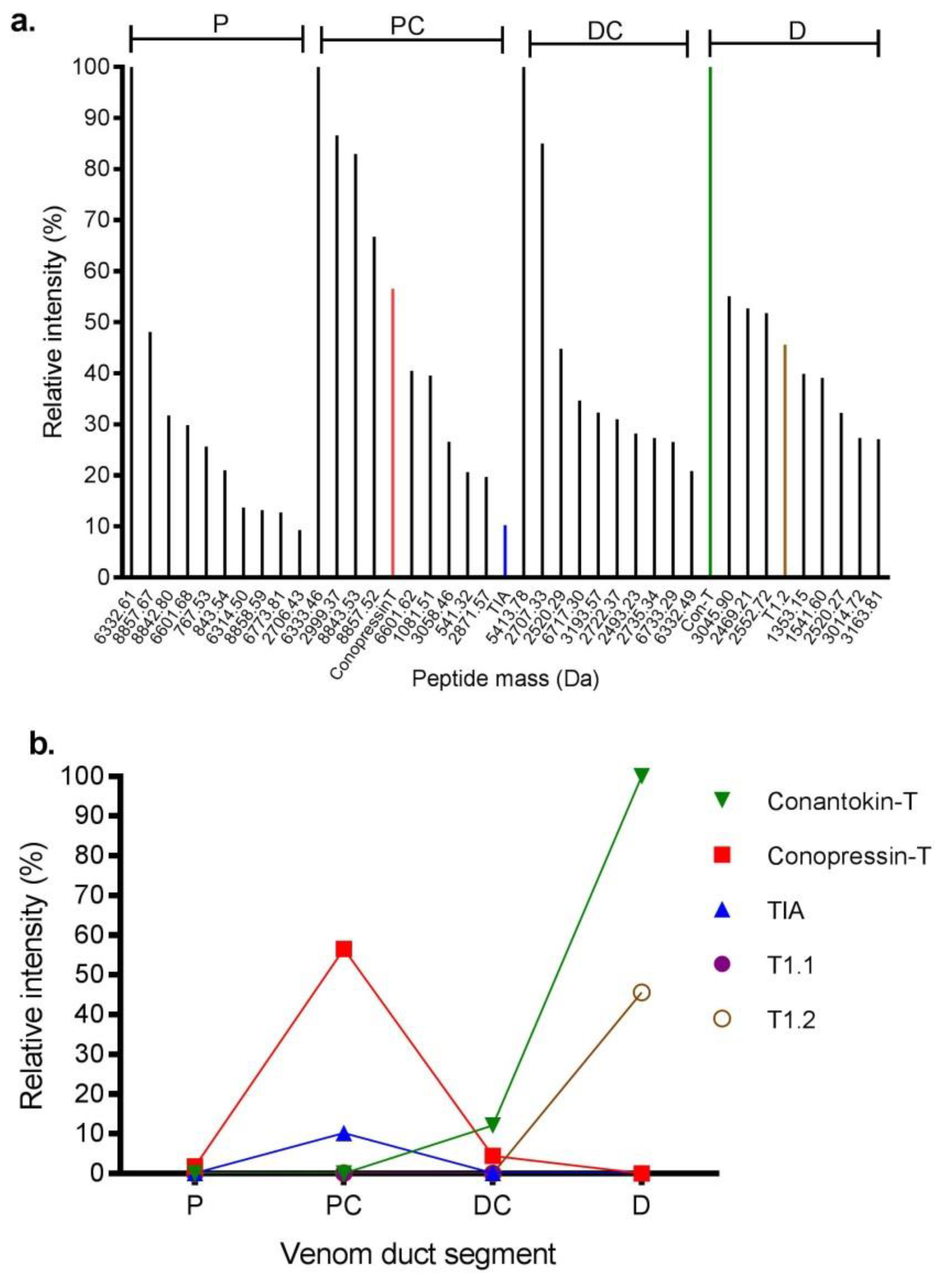
2.2. Proteome Analysis
2.3. Transcriptomic Variance Within Gene Superfamilies
2.3.1. Superfamily B1 [33]
2.3.2. Superfamily B2 [14]
2.3.3. Superfamily O1 [34]
2.3.4. Superfamily O3 [35]
2.3.5. Superfamily A [36]
2.3.6. Conopressins-Conophysin [22]
2.3.7. Con-ikot-ikots [37]
2.3.8. Conoporins [40]
2.3.9. Superfamily M [41]
2.3.10. Conoinsulin [42]
2.3.11. Conkunitzins [43]
2.3.12. Superfamily S [44]
2.3.13. NewGeo-1 [12]
2.4. Intra-Clade Transcriptomic Comparison
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Transcriptome Analysis
4.1.1. Venom Collection, mRNA Extraction, cDNA Library, 454 Pyrosequencing and Assembly
4.1.2. Conopeptide Sequence Analysis
4.1.3. Conotoxin Nomenclature
4.2. Proteome Analysis
4.2.1. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
4.2.2. Enzyme Digestion
4.2.3. Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry/Mass Spectrometry (LC-ESI-MS/MS)
4.3. Data Visualisation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex cocktails: The evolutionary novelty of venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, D.W.; Ondetti, M.A. History of the design of captopril and related inhibitors of angiotensin converting enzyme. Hypoertension 1991, 17, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bittl, J.A.; Strony, J.; Brinker, J.A.; Ahmed, W.H.; Meckel, C.R.; Chaitman, B.R.; Maraganore, J.; Deutsch, E.; Adelman, B. Treatment with bivalirudin (Hirulog) as compared with heparin during coronary angioplasty for unstable or postinfarction angina. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.G.; Bandyopadhyay, P.; Olivera, B.M. Post-translationally modified neuropeptides from Conus venoms. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puillandre, N.; Duda, T.; Meyer, C.; Olivera, B.M.; Bouchet, P. One, four or 100 genera? A new classification of the cone snails. J. Mollusc Stud. 2014, 81, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Remarkable inter-and intra-species complexity of conotoxins revealed by LC/MS. Peptides 2009, 30, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favreau, P.; Stocklin, R. Marine snail venoms: Use and trends in receptor and channel neuropharmacology. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 594–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic potential of venom peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, I.; Davis, J.L.; Rash, L.D.; Anangi, R.; Mobli, M.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J.; King, G.F. Venomics: A new paradigm for natural products-based drug discovery. Amino Acids 2011, 40, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Vetter, I.; Hamilton, B.; Sunagar, K.; Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, V.; Fry, B.G.; Antunes, A.; Venter, D.J.; et al. Evolution of separate predation- and defence-evoked venoms in carnivorous cone snails. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, A.-H.; Dutertre, S.; Kaas, Q.; Lavergne, V.; Kubala, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Transcriptomic messiness in the venom duct of Conus miles contributes to conotoxin diversity. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 3824–3833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.-H.; Kaas, Q.; Jones, A.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Deep venomics reveals the mechanism for expanded peptide diversity in cone snail venom. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 312–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barghi, N.; Concepcion, G.P.; Olivera, B.M.; Lluisma, A.O. High conopeptide diversity in Conus tribblei revealed through analysis of venom duct transcriptome using two high-throughput sequencing platforms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavergne, V.; Harliwong, I.; Jones, A.; Miller, D.; Taft, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Optimized deep-targeted proteotranscriptomic profiling reveals unexplored Conus toxin diversity and novel cysteine frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3782–E3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Olenzek, A.M.; Duda, T.F. Effects of geographical heterogeneity in species interactions on the evolution of venom genes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 2015, 282, 20141984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.H.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Intraspecific variations in Conus geographus defence-evoked venom and estimation of the human lethal dose. Toxicon 2014, 91, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, S.; Biass, D.; Stocklin, R.; Favreau, P. Dramatic intraspecimen variations within the injected venom of Conus consors: An unsuspected contribution to venom diversity. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Ortiz, J.A.; Cano, H.; Marí, F. Intraspecies variability and conopeptide profiling of the injected venom of Conus ermineus. Peptides 2011, 32, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abalde, S.; Tenorio, M.J.; Afonso, C.M.; Zardoya, R. Conotoxin Diversity in Chelyconus ermineus (Born, 1778) and the Convergent Origin of Piscivory in the Atlantic and Indo-Pacific Cones. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 2643–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivera, B.M.; Cruz, L.J. Conotoxins, in retrospect. Toxicon 2001, 39, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlau, H.; Olivera, B.M. Conus venoms: A rich source of novel ion channel-targeted peptides. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 41–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockel, D.; Korn, W.; Kohn, A.J. Manual of the Living Conidae Volume 1: Indo-Pacific Region; Mal de Mer Enterprises: Hemmen, Wiesbaden, Germany, 1995; Volume 1, p. 517. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, J.K.; Tenorio, M.J. Systematic Classification of Recent and Fossil Conoidean Gastropods: With Keys to the Genera of Cone Shells; Conchbooks: Hackenheim, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe, I.A.; Gehrmann, J.; Loughnan, M.L.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.A.; Atkins, A.; Palant, E.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; et al. Two new classes of conopeptides inhibit the α1-adrenoceptor and noradrenaline transporter. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, I.A.; Thomas, L.; Loughnan, M.; Motin, L.; Palant, E.; Croker, D.E.; Alewood, D.; Chen, S.; Graham, R.M.; Alewood, P.F.; et al. Allosteric α1-adrenoreceptor antagonism by the conopeptide ρ-TIA. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 34451–34457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragnarsson, L.; Wang, C.-I.A.; Andersson, Å.; Fajarningsih, D.; Monks, T.; Brust, A.; Rosengren, K.J.; Lewis, R.J. Conopeptide ρ-TIA defines a new allosteric site on the extracellular surface of the α1B-adrenoceptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1814–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Schroeder, C.I.; Ekberg, J.; Nielsen, K.J.; Loughnan, M.; Thomas, L.; Adams, D.A.; Drinkwater, R.; Adams, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Isolation and structure-activity of μ-conotoxin TIIIA, a potent inhibitor of tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-gated sodium channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haack, J.A.; Rivier, J.; Parks, T.N.; Mena, E.E.; Cruz, L.J.; Olivera, B.M. Conantokin-T. A gamma-carboxyglutamate containing peptide with N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 6025–6029. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.M.; Atkins, A.R.; Loughnan, M.L.; Jones, A.; Adams, D.A.; Martin, R.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F. Conotoxin TVIIA, a novel peptide from the venom of Conus tulipa 1. Isolation, characterization and chemical synthesis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 4642–4648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, S.; Croker, D.; Daly, N.L.; Andersson, A.; Muttenthaler, M.; Lumsden, N.G.; Craik, D.J.; Alewood, P.F.; Guillon, G.; Lewis, R.J. Conopressin-T from Conus tulipa reveals an antagonist switch in vasopressin-like peptides. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 7100–7108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puillandre, N.; Koua, D.; Favreau, P.; Olivera, B.M.; Stocklin, R. Molecular phylogeny, classification and evolution of conopeptides. J. Mol. Evol. 2012, 74, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, J.M.; Hasson, A.; Spira, M.E.; Gray, W.R.; Li, W.; Marsh, M.; Hillyard, D.R.; Olivera, B.M. A new family of conotoxins that blocks voltage-gated sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16796–16802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhangsun, D.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hu, Y.; Xie, L. Novel O-superfamily Conotoxins Identified by cDNA Cloning From Three Vermivorous Conus Species. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 68, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.D.; McIntosh, J.M.; Hillyard, D.R.; Cruz, L.J.; Olivera, B.M. The A-superfamily of conotoxins structural and functional divergence. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17596–17606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Olivera, B.M.; Yandell, M. Elucidation of the molecular envenomation strategy of the cone snail Conus geographus through transcriptome sequencing of its venom duct. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, L.; De Santos, V.; Zafaralla, G.; Ramilo, C.; Zeikus, R.; Gray, W.; Olivera, B.M. Invertebrate vasopressin/oxytocin homologs. Characterization of peptides from Conus geographus and Conus straitus venoms. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 15821–15824. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, C.S.; Jensen, S.; Ellison, M.; Matta, J.A.; Lee, W.Y.; Imperial, J.S.; Duclos, N.; Brockie, P.J.; Madsen, D.M.; Isaac, J.T.; et al. A novel Conus snail polypeptide causes excitotoxicity by blocking desensitization of AMPA receptors. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Violette, A.; Biass, D.; Dutertre, S.; Koua, D.; Piquemal, D.; Pierrat, F.; Stocklin, R.; Favreau, P. Large-scale discovery of conopeptides and conoproteins in the injectable venom of a fish-hunting cone snail using a combined proteomic and transcriptomic approach. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 5215–5225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpuz, G.P.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Jimenez, E.C.; Watkins, M.; Walker, C.; Colledge, C.; Garrett, J.E.; McDougal, O.; Li, W.; Gray, W.R.; et al. Definition of the M-conotoxin superfamily: Characterization of novel peptides from molluscivorous Conus venoms. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 8176–8186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Gajewiak, J.; Karanth, S.; Robinson, S.D.; Ueberheide, B.; Douglass, A.D.; Schlegel, A.; Imperial, J.S.; Watkins, M.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; et al. Specialized insulin is used for chemical warfare by fish-hunting cone snails. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 1743–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrhuber, M.; Vijayan, V.; Ferber, M.; Graf, R.; Korukottu, J.; Imperial, J.; Garrett, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Terlau, H.; Zweckstetter, M.; et al. Conkunitzin-S1 is the first member of a new Kunitz-type neurotoxin family. Structural and functional characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23766–23770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Yuan, D.; Chi, C.; Wang, C. Identification of a novel S-superfamily conotoxin from vermivorous Conus caracteristicus. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safavi-Hemami, H.; Hu, H.; Gorasia, D.G.; Bandyopadhyay, P.K.; Veith, P.D.; Young, N.D.; Reynolds, E.C.; Yandell, M.; Olivera, B.M.; Purcell, A.W. Combined proteomic and transcriptomic interrogation of the venom gland of Conus geographus uncovers novel components and functional compartmentalization. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, mcp-M113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J.; Marí, F. Intraspecific variations in Conus purpurascens injected venom using LC/MALDI-TOF-MS and LC-ESI-TripleTOF-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6105–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romeo, C.; Di Francesco, L.; Oliverio, M.; Palazzo, P.; Massilia, G.R.; Ascenzi, P.; Polticelli, F.; Schininà, M.E. Conus ventricosus venom peptides profiling by HPLC-MS: A new insight in the intraspecific variation. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himaya, S.; Marí, F.; Lewis, R.J. Accelerated proteomic visualization of individual predatory venoms of Conus purpurascens reveals separately evolved predation-evoked venom cabals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endean, R.; Duchemin, C. The venom apparatus of Conus magus. Toxicon 1967, 4, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.; Kelley, W.P.; Rubakhin, S.S.; Bingham, J.-P.; Sweedler, J.V.; Gilly, W.F. Anatomical correlates of venom production in Conus californicus. Biol. Bull. 2002, 203, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivera, B.M.; Seger, J.; Horvath, M.P.; Fedosov, A.E. Prey-Capture Strategies of Fish-Hunting Cone Snails: Behavior, Neurobiology and Evolution. Brain Behav. Evol. 2015, 86, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlau, H.; Finol-Urdaneta, R.; Becker, S.; Raasch, W. Use of Conkunitzin-s1 for the Modulation of Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion. U.S. Patent 13/057,809, 15 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Puillandre, N.; Bouchet, P.; Duda, T.F., Jr.; Kauferstein, S.; Kohn, A.J.; Olivera, B.M.; Watkins, M.; Meyer, C. Molecular phylogeny and evolution of the cone snails (Gastropoda, Conoidea). Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2014, 78, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavergne, V.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Taft, R.J.; Alewood, P.F. Systematic interrogation of the Conus marmoreus venom duct transcriptome with ConoSorter reveals 158 novel conotoxins and 13 new gene superfamilies. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Westermann, J.C.; Craik, D.J. Conopeptide characterization and classifications: An analysis using ConoServer. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1491–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F.; Gentz, M.C.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. A rational nomenclature for naming peptide toxins from spiders and other venomous animals. Toxicon 2008, 52, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, J.E.; Butler, J.P.; Gelfanova, V.; You, J.-S.; Knierman, M.D. A simplified procedure for the reduction and alkylation of cysteine residues in proteins prior to proteolytic digestion and mass spectral analysis. Anal. Biochem. 2004, 333, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveros, J.C. Venny. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn Diagrams. Available online: http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 30 November 2018).
| Transcriptome Features | Specimen 1 (S1) | Specimen 2 (S2) |
|---|---|---|
| 454 raw reads generated | 100,564 | 33,516 |
| Number of final conotoxin precursors | 522 | 328 |
| Number of gene superfamilies | 16 | 18 |
| Total read frequency (level of transcription) | 16,333 | 6426 |
| 1 Section | Matched Precursor (S2) | MS/MS Fragment | PTM | Precursor (Da) | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | Tu0051/T1.2 | SNPACAGNNPH | Ala->Gly@5 | 1169.430 | 2 |
| D | Tu316 | AIASSVVTPGSSMK | 1333.691 | 2 | |
| D | Tu068 | MINAETQTR | 1062.510 | 2 | |
| D | Tu065 | NCMLINVQQLGLR | Asn -> Thr @1, carbamidometh@2 | 1544.830 | 2 |
| D | Tu020 | MLENLREAEVK | Carboxy(E)@3 | 1374.681 | 3 |
| DC | Tu076 | ADRDTDPDDENPR | Oxidation(P)@7 | 1530.618 | 3 |
| DC | Tu056/T1.3 | VKDFK | 635.364 | 2 | |
| DC | Tu316 | AIASSVVTPGSSMK | 1333.691 | 2 | |
| DC | Tu065 | NCMLINVQQLGLR | 1524.820 | 2 | |
| DC | Tu068 | MINAETQTR | 1062.500 | 2 | |
| DC | Tu314 | DLADTRYR | Arg -> Ser @ 6 | 939.4289 | 2 |
| DC | Tu320 | AAFHMFYFDQFSK | 1637.730 | 3 | |
| PC | Tu298/T6.4 | DGTGQCAPK | Gln->Asp@5, Carbamydomethyl @ 8, oxid(P)@10, | 1190.560 | 3 |
| PC | Tu297/T6.4 | VRDNR | 658.351 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu032/T6.1 | DALKNLK | 800.457 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu035/TVIA | SCNPYSR | Carbamydometh@2, Deamidated(N)@3, Oxidation(P)@4, | 899.342 | 2 |
| PC | Tu274/TVIA | ALKNLKDSRGGSAR | Deamidated(R)@8. | 1474.787 | 2 |
| PC | Tu314 | VVTSGSSLQGTSLK | 1362.730 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu075 | VFIYGGCDGNANR | 1428.640 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu316 | AIASSVVTPGSSMK | 1333.690 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu059/conopressin-T | NLDNIEGH | 910.413 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu296/T6.4 | VRDNR | 658.340 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu314 | GIASKVVTSGSSLQ | 1332.830 | 2 | |
| PC | Tu030 | VPEDASNLQGFDQG | 1475.780 | 2 | |
| P | Tu030 | LPFNNVEGATNDLGQFEPSAENEDGKFRFF | 1475.650 | 2 | |
| P | Tu076 | LTLSAPK | Deam @ 3 | 728.443 | 2 |
| P | Tu075 | AAFHMFYFDQFSK | 1637.735 | 3 | |
| P | Tu059/conopressin-T | NLDNIEGH | 910.414 | 2 | |
| P | Tu314 | FALKNPVLQINSGVTTSTPTGIEPGK | Deamidated(N)@5; Deamidated(N)@11; Ser->Gly@12 | 2640.405 | 3 |
| P | Tu314 | AVRAIASSVVTPGSSMKGGPLK | 2112.360 | 3 | |
| P | Tu314 | VVTSGSSLQGTSLKDLADTRYRVTCAIQVENWTK | 2321.149 | 3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dutt, M.; Dutertre, S.; Jin, A.-H.; Lavergne, V.; Alewood, P.F.; Lewis, R.J. Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010071
Dutt M, Dutertre S, Jin A-H, Lavergne V, Alewood PF, Lewis RJ. Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa. Marine Drugs. 2019; 17(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleDutt, Mriga, Sébastien Dutertre, Ai-Hua Jin, Vincent Lavergne, Paul Francis Alewood, and Richard James Lewis. 2019. "Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa" Marine Drugs 17, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010071
APA StyleDutt, M., Dutertre, S., Jin, A.-H., Lavergne, V., Alewood, P. F., & Lewis, R. J. (2019). Venomics Reveals Venom Complexity of the Piscivorous Cone Snail, Conus tulipa. Marine Drugs, 17(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17010071






