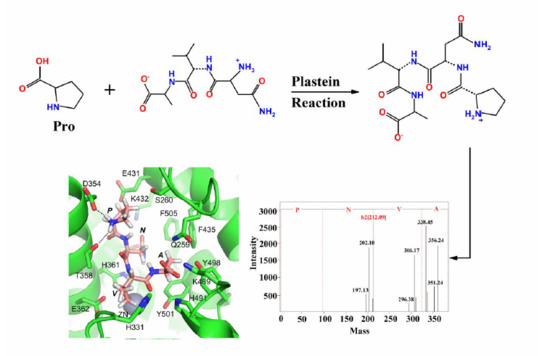
Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure–Activity Relationship
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
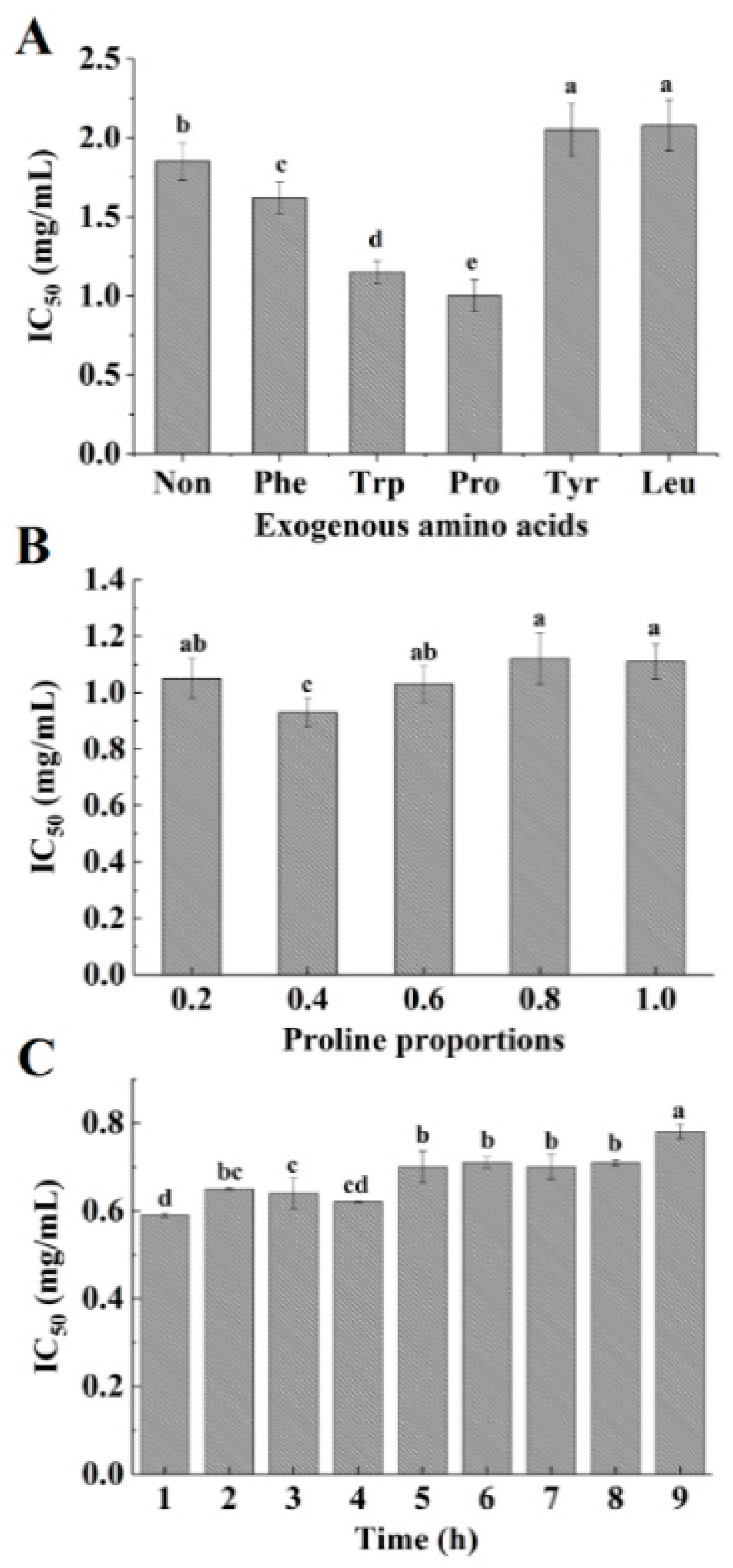
2.1. Modification of Acaudina molpadioidea Protein Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Amino Acids
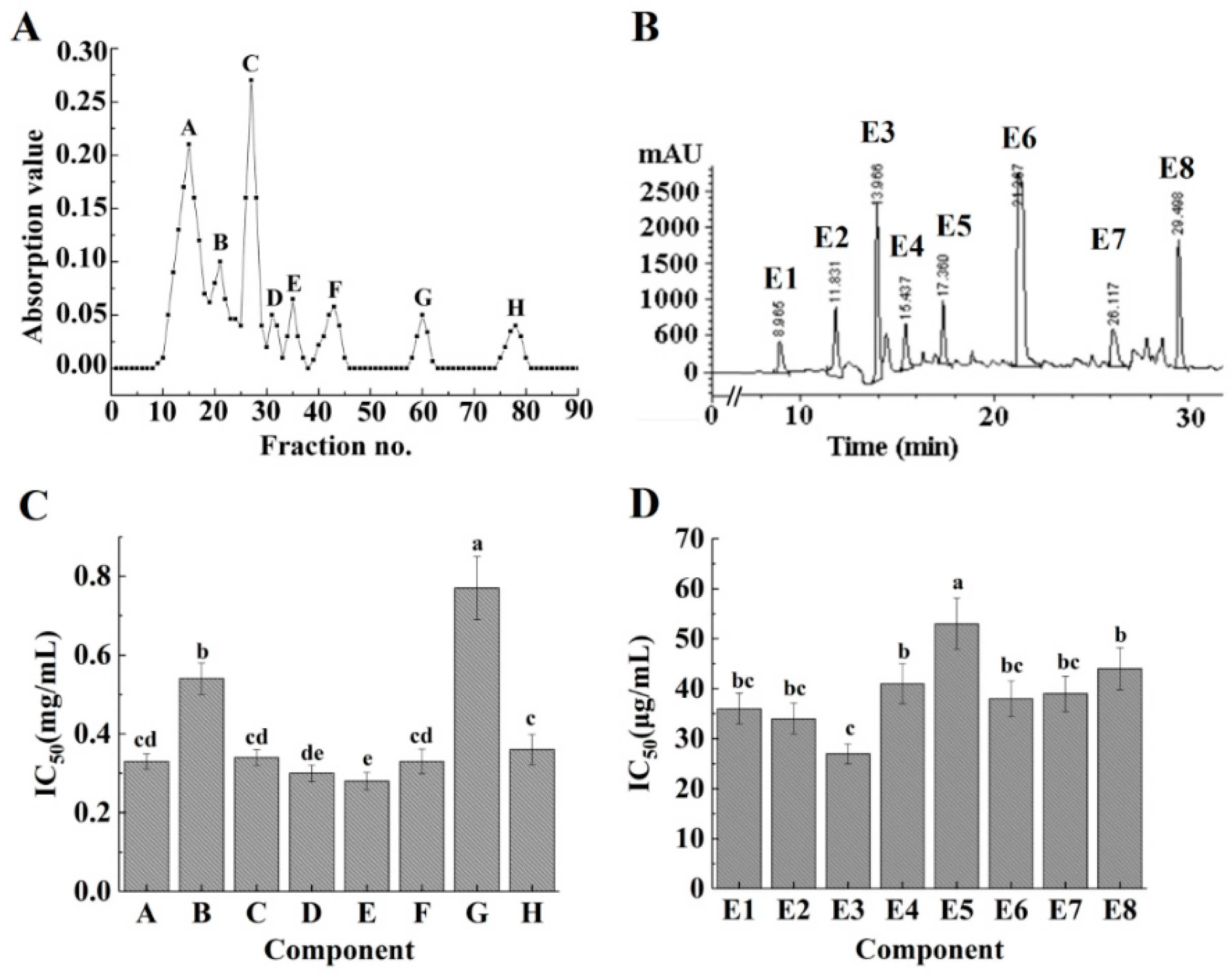
2.2. Isolation and Purification of Modified ACE-Inhibitory Peptides and the ACE-Inhibitory Activity of Each Fraction
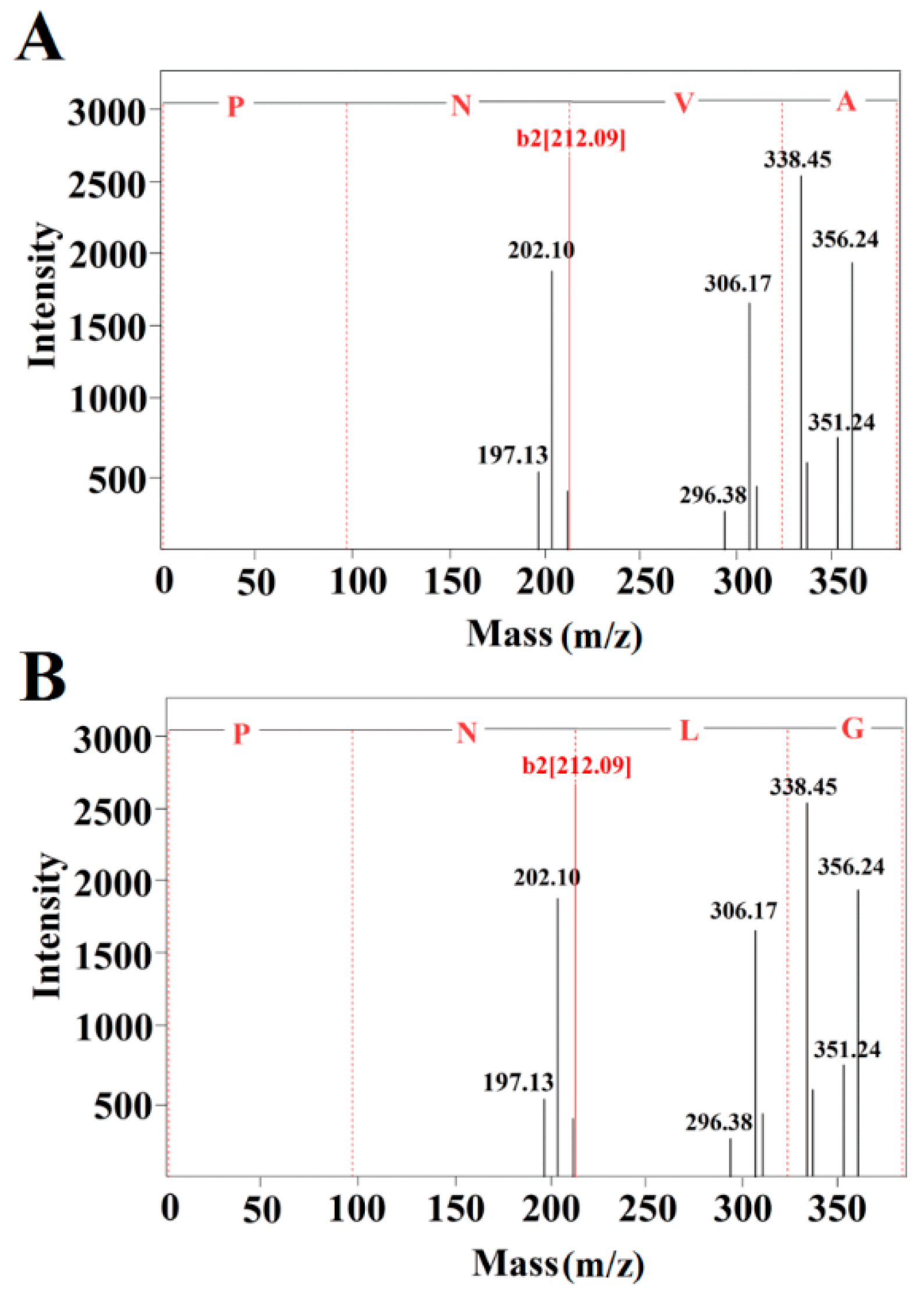
2.3. Identification of the Purified Peptides and Evaluation of Their ACE-Inhibitory Activity
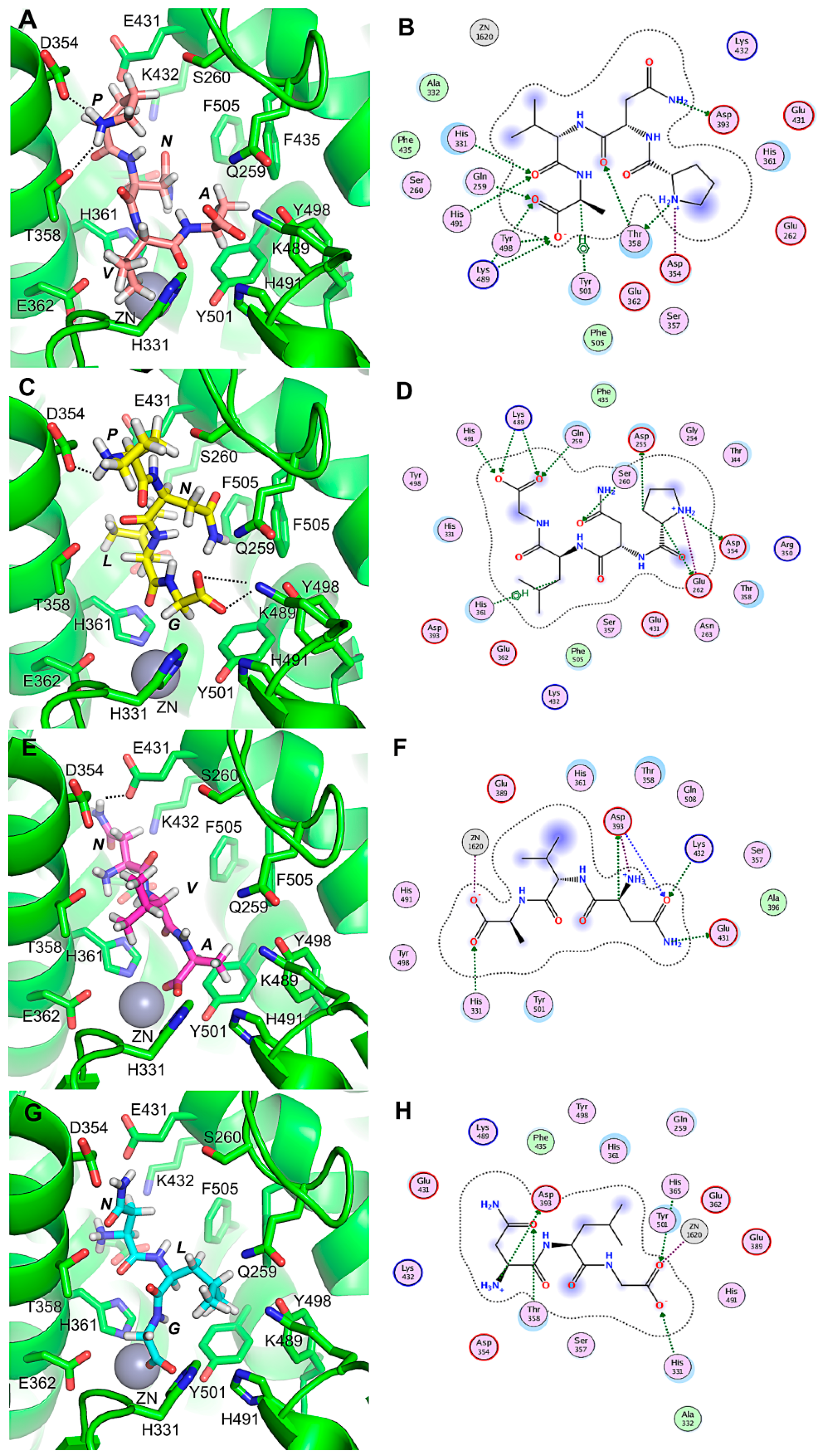
2.4. Molecular Docking of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials and Chemicals
3.2. Acaudina molpadioidea Body Wall Protein Extraction
3.3. Acaudina molpadioidea Protein Hydrolysates Preparation
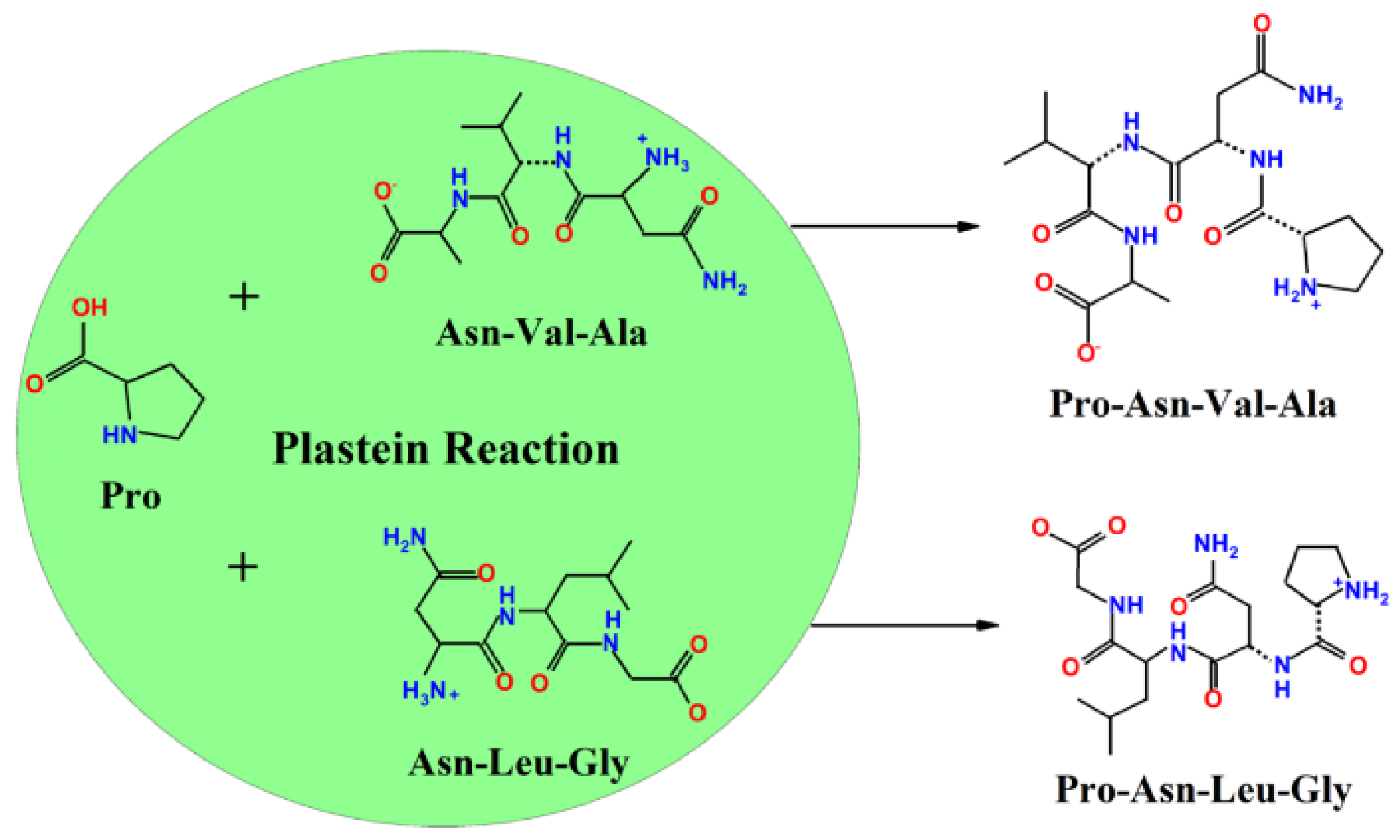
3.4. Modification of Acaudina molpadioidea Protein Hydrolysates by Plastein Reaction
3.5. Changes in the Content of Free Amino Groups during the Plastein Reaction
3.6. Determination of the ACE-Inhibitory Activity of Hydrolysates
3.7. Solvent Fractionation of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides by Chromatography
3.8. Analysis and Purification of ACE-Inhibitory Peptides in Hydrolysates by RP-HPLC
3.9. Mass Spectrometric Analysis and Synthesis of Purified Peptides
3.10. Molecular Docking
3.11. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kivimäki, M.; Steptoe, A. Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forouzanfar, M.H.; Liu, P.; Roth, G.A.; Ng, M.; Biryukov, S.; Marczak, L.; Alexander, L.; Estep, K.; Hassen Abate, K.; Akinyemiju, T.F.; et al. Global burden of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of at least 110 to 115 mm Hg, 1990–2015. JAMA 2017, 317, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z.; Giani, J.F.; Cao, D.Y.; Bernstein, E.A.; Shen, X.Z. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangsawad, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Choowongkomon, K.; Kitts, D.D.; Chen, X.M.; Meng, G.; Lichan, E.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Transepithelial transport across Caco-2 cell monolayers of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of cooked chicken muscles. Food Chem. 2018, 251, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R. Bronchospasm and cough as adverse reactions to the ACE inhibitors captopril, enalapril and lisinopril. A controlled retrospective cohort study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 39, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Hu, J.; Miyaguchi, Y.; Bai, X.; Du, Y.; Lin, B. Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from porcine hemoglobin. Peptides 2006, 27, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, G.P.; Chadwick, I.G.; Higgins, K.S.; Yeo, W.W.; Jackson, P.R.; Ramsay, L.E. Relation between changes in blood pressure and serum ACE activity after a single dose of enalapril and ACE genotype in healthy subjects. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 39, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bougatef, A.; Nedjar-Arroume, N.; Ravallec-Plé, R.; Leroy, Y.; Guillochon, D.; Barkia, A.; Nasri, M. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) by-products protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chem. 2008, 111, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, K.; Cheung, B.W.; Schröder, H. The possible roles of food-derived bioactive peptides in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2008, 19, 643–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raia, J.J., Jr.; Barone, J.A.; Byerly, W.G.; Lacy, C.R. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: A comparative review. Ann. Pharmacother. 1990, 24, 506–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, T.J.; Zhao, X.H. ACE inhibition and enzymatic resistance in vitro of a casein hydrolysate subjected to plastein reaction in the presence of extrinsic proline and ethanol- or methanol-eater fractionation. Int. J. Food Prop. 2014, 17, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrons, M.A.; Liggieri, C.S.; Trejo, S.A.; Bruno, M.A. ACE-inhibitory peptides from bovine caseins released with peptidases from Maclura pomifera latex. Food Res. Int. 2017, 93, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Preparation and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated polysaccharide sulfate from a sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioidea. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 87, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, M. A novel ACE-inhibitory peptide isolated from Acaudina molpadioidea hydrolysate. Peptides 2009, 30, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.H.; Li, B.F.; Ma, J.J.; Dong, S.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zeng, M.Y. Purification and synthesis of ACE-inhibitory peptide from Acaudina molpadioidea protein hydrolysate. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2012, 33, 308–312. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.J.; Zeng, M.Y.; Ma, G.L.; Zhao, Y.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Dong, S.Y. Research on plastein reaction-basic modification of Acaudina molpadioidea protein hydrolysates and its effects on ACE activity. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2011, 30, 6–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Zeng, M.; Zhao, Y. Modification of Acaudina molpadioides hydrolysates by plastein reaction and preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2014, 35, 965–970. [Google Scholar]
- Ono, S.; Kasai, D.; Sugano, T.; Ohba, K.; Takahashi, K. Production of water soluble antioxidative plastein from squid hepatopancreas. J. Oil Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2004, 53, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, T.J.; Zhao, X.H. Coupled neutraseâ catalyzed plastein reaction mediated the ACE-inhibitory activity in vitro of casein hydrolysates prepared by alcalase. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 429–443. [Google Scholar]
- Sangsawad, P.; Roytrakul, S.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from the simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion of cooked chicken breast. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 29, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otte, J.; Shalaby, S.M.; Zakora, M.; Pripp, A.H.; El-Shabrawy, S.A. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity of milk protein hydrolysates: Effect of substrate, enzyme and time of hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2007, 17, 488–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terashima, M.; Oe, M.; Ogura, K.; Matsumura, S. Inhibition strength of short peptides derived from an ACE-inhibitory peptide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11234–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xue, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Xia, L. Progress in research on structure–activity relationship of ACE-inhibitory peptides. Food Sci. 2017, 38, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Kleekayai, T.; Harnedy, P.A.; O’Keeffe, M.B.; Poyarkov, A.A.; Cunhaneves, A.; Suntornsuk, W.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Extraction of antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory peptides from Thai traditional fermented shrimp pastes. Food Chem. 2015, 176, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.M.; Bo, T.; Brodkorb, A.; Huo, G.C. Production, analysis and in vivo evaluation of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from bovine casein. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.H.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Active peptides from skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin diminish angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity and intracellular free radical-mediated oxidation. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluko, R.E.; Girgih, A.T.; He, R.; Malomo, S.; Li, H.; Offengenden, M.; Wu, J. Structural and functional characterization of yellow field pea seed (Pisum sativum L.) protein-derived antihypertensive peptides. Food Res. Int. 2015, 77, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, A.; Jo, C.; Kang, K.S.; Lee, M. Antimicrobial and human cancer cell cytotoxic effect of synthetic angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownsell, V.L.; Williams, R.J.H.; Andrews, A.T. Application of the plastein reaction to mycoprotein. II. plastein properties. Food Chem. 2001, 72, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, X. Separation of aromatic monomers from oxidatively depolymerized products of lignin by combining sephadex and silica gel column chromatography. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E. Antihypertensive peptides from food proteins. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charton, M.; Charton, B.I. The structural dependence of amino acid hydrophobicity parameters. J. Theor. Biol. 1982, 99, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuohashish, H.M.; Ahmed, M.M.; Sabry, D.; Khattab, M.M.; Al-Rejaie, S.S. ACE-2/Ang1-7/Mas cascade mediates ACE inhibitor, captopril, protective effects in estrogen-deficient osteoporotic rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.Q.; Ju, T.; Sun, J.; Su, Y.J.; Xu, R.R.; Yang, Y.J. Purification and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysate of hen egg white lysozyme. Food Res. Int. 2012, 46, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Shi, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Characterization of ACE-inhibitory peptides from Mactra veneriformis hydrolysate by nano-liquid chromatography electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (Nano-LC-ESI-MS) and molecular docking. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3917–3928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Du, K.; Ji, P.; Feng, W. Molecular mechanism of the interactions between inhibitory tripeptides and angiotensin-converting enzyme. Biophys. Chem. 2012, 168, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, G.E.; Chang, O.K.; Jo, S.M.; Han, G.S.; Park, B.Y.; Ham, J.S.; Jeong, S.G. Identification of antihypertensive peptides derived from low molecular weight casein hydrolysates generated during fermentation by Bifidobacterium longum KACC 91563. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2015, 35, 738–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Sun, S.; Liu, R.; Hong, B.; Gao, R.; Bai, K. Processing optimization and characterization of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from Lizardfish (Synodus macrops) scale gelatin. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salampessy, J.; Reddy, N.; Kailasapathy, K.; Phillips, M. Functional and potential therapeutic ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from bromelain hydrolysis of trevally proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamilah, B.; Harvinder, K.G. Properties of gelatins from skins of fish--black tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) and red tilapia (Oreochromis nilotica). Food Chem. 2002, 77, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, D.; McEvoy, E.; O’Cuinn, G.; Fitzgerald, R.J. Proteinase and exopeptidase hydrolysis of whey protein: Comparison of the TNBS, OPA and pH stat methods for quantification of degree of hydrolysis. Int. Dairy J. 2003, 13, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar, S.; Cozza, G.; Moro, S. Medicinal chemistry and the molecular operating environment (MOE): Application of QSAR and molecular docking to drug discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 1555–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Amino Acids | Original | 1 h g/(100 mL) | 4 h g/(100 mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thr | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Ser | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Glu | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Gly | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| Ala | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 |
| Cys | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.05 ± 0.01 |
| Val | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Met | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Ile | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Leu | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 0.04 ± 0.01 | 0.04 ± 0.02 |
| Tyr | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Phe | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| Lys | 0.02 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| His | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.01 ± 0.01 |
| Arg | 0.14 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.11 ± 0.02 |
| Pro | 0.29 ± 0.04 a | 0.23 ± 0.02 b | 0.2 ± 0.02 b |
| Total | 0.90 ± 0.09 a | 0.69 ± 0.08 b | 0.66 ± 0.08 b |
| Component | Purification | IC50 (mg/mL) | Purification Fold |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrolysates | Ultrafiltration | 0.590 ± 0.030 a | 1.00 |
| E | Sephadex G-15 | 0.288 ± 0.013 b | 2.05 |
| E3 | RP-HPLC | 0.027 ± 0.002 c | 21.85 |
| Sequence | Molecular Mass (Da) | ACE IC50 (µM) 2 |
|---|---|---|
| PNVA 1 | 399.45 | 8.18 ± 0.24 a |
| PNLG 1 | 399.45 | 13.16 ± 0.39 b |
| NVA | 302.33 | 12.69 ± 1.50 b |
| NLG | 302.33 | 17.45 ± 0.89 c |
| Peptide | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | Experimental Binding Affinity (kcal/mol) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| PNVA | −7.13 | −2.34 |
| PNLG | −6.77 | −2.47 |
| NVA | −5.14 | −2.46 |
| NLG | −5.12 | −2.54 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yu, R.; Dong, S.; Wu, H. Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure–Activity Relationship. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080271
Li J, Liu Z, Zhao Y, Zhu X, Yu R, Dong S, Wu H. Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure–Activity Relationship. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(8):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080271
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianpeng, Zunying Liu, Yuanhui Zhao, Xiaojie Zhu, Rilei Yu, Shiyuan Dong, and Haohao Wu. 2018. "Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure–Activity Relationship" Marine Drugs 16, no. 8: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080271
APA StyleLi, J., Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhu, X., Yu, R., Dong, S., & Wu, H. (2018). Novel Natural Angiotensin Converting Enzyme (ACE)-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Sea Cucumber-Modified Hydrolysates by Adding Exogenous Proline and a Study of Their Structure–Activity Relationship. Marine Drugs, 16(8), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080271