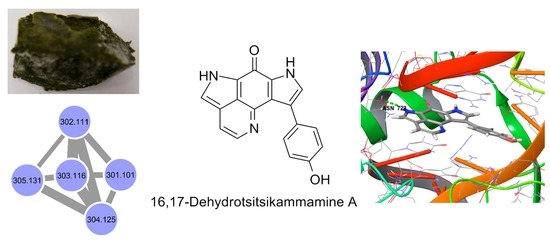
Targeted Isolation of Tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis by Molecular Networking and Anticancer Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
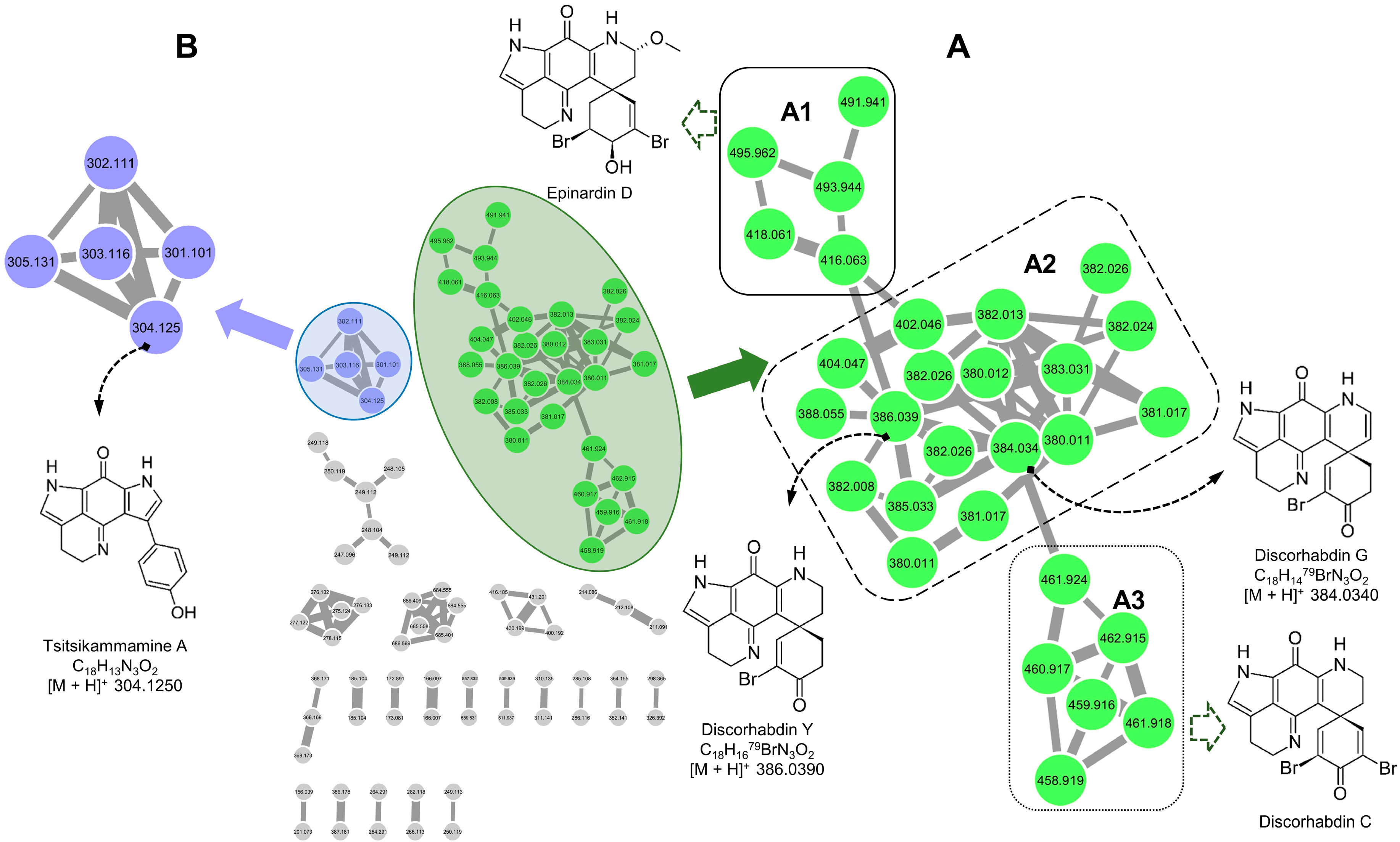
2.1. Molecular Networking-Based Dereplication
2.2. Purification and Structure Elucidation
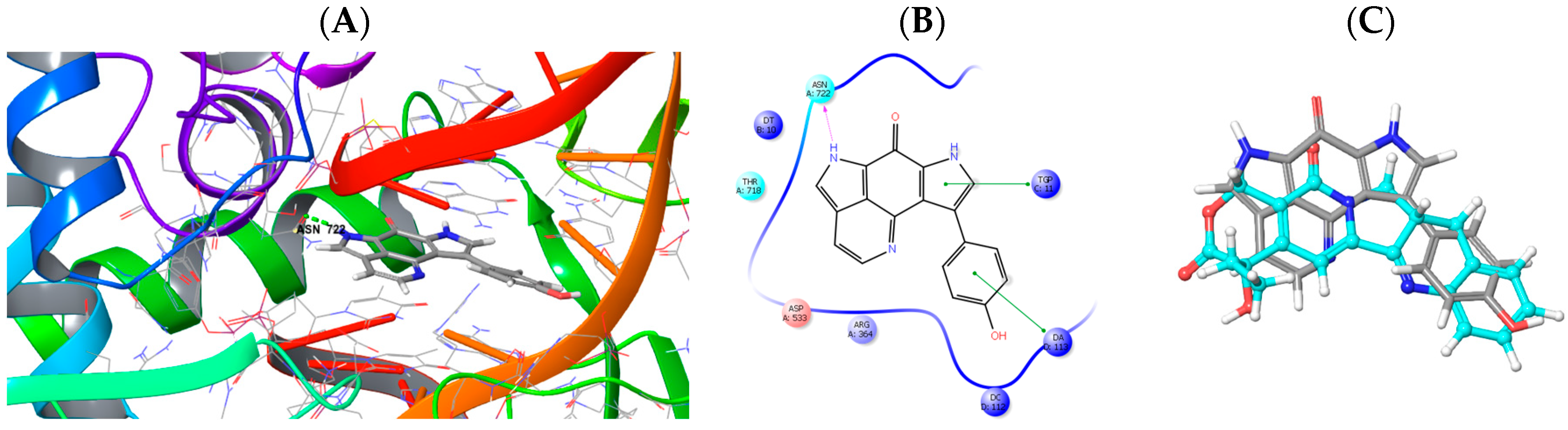
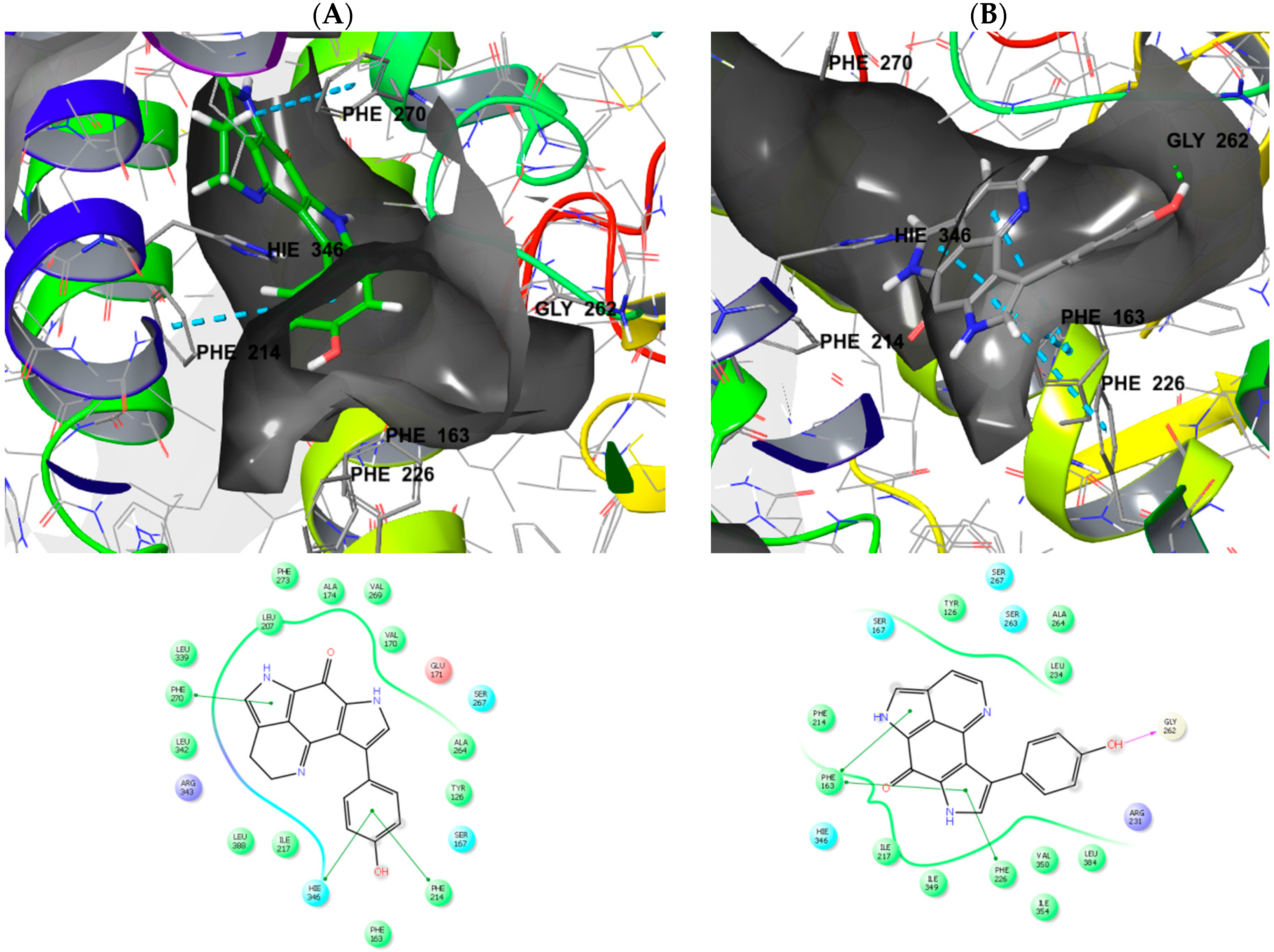
2.3. Molecular Modeling and Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Procedures
4.2. Sponge Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. UPLC-QToF-MS/MS Analysis
4.5. Molecular Networking
4.6. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.7. Molecular Modeling and Docking
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, C.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Hua, T.E. Precambrian sponges with cellular structures. Science 1998, 279, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehbub, M.F.; Lei, J.; Franco, C.; Zhang, W. Marine sponge derived natural products between 2001 and 2010: Trends and opportunities for discovery of bioactives. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4539–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, T.; Avguštin, J.A.; Batista, U.; Strugar, G.; Kosmina, R.; Čivović, S.; Janussen, D.; Kauferstein, S.; Mebs, D.; Sepčić, K. Biological activities of ethanolic extracts from deep-sea Antarctic marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1126–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.; Broady, P. Biological soil crusts of Antarctica. In Biological Soil Crusts: Structure, Function, and Management; Belnap, J., Lange, O.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 150, pp. 133–139. [Google Scholar]
- McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. A review of the chemical ecology of Antarctic marine invertebrates. Am. Zool. 1997, 37, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClintock, J.B.; Amsler, C.D.; Baker, B.J.; Van Soest, R.W. Ecology of Antarctic marine sponges: An overview. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2005, 45, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, A. Antarctic marine benthic diversity: patterns and processes. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2008, 366, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.; Gooday, A.J.; Brandao, S.N.; Brix, S.; Brökeland, W.; Cedhagen, T.; Choudhury, M.; Cornelius, N.; Danis, B.; De Mesel, I. First insights into the biodiversity and biogeography of the Southern Ocean deep sea. Nature 2007, 447, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, S.; Kelly, M.; Schnabel, K.; Mills, S.; Bowden, D.; Wörheide, G. Diversity in a cold hot-spot: DNA-barcoding reveals patterns of evolution among Antarctic Demosponges (class Demospongiae, phylum Porifera). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, C.; Taboada, S.; Núñez-Pons, L. Antarctic marine chemical ecology: What is next? Mar. Ecol. 2008, 29, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, S.; Blum, A.; Burkepile, D.; Rutland, T.; Wierzbicki, A.; Kelly, M.; Hamann, M. Isolation of an antifreeze peptide from the Antarctic sponge Homaxinella balfourensis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002, 59, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Baker, B.J.; Grimwade, J.; Leonard, A.; McClintock, J.B. Discorhabdin alkaloids from the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1596–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; Kopitzke, R.W.; Yoshida, W.Y.; McClintock, J.B. Chemical and ecological studies of the Antarctic sponge Dendrilla membranosa. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebar, M.D.; Heimbegner, J.L.; Baker, B.J. Cold-water marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.; Kelly, M.; Bowling, J.; Sims, J.; Waters, A.; Hamann, M. Advancement into the Arctic region for bioactive sponge secondary metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2423–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaai, T.; Govender, V.; Kelly, M. Cyclacanthia n.g. (Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida: Latrunculiidae incertae sedis), a new genus of marine sponges from South African waters, and description of two new species. Zootaxa 2004, 725, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M.; Davies-Coleman, M. South African Latrunculiidae (Porifera: Demospongiae: Poecilosclerida): Descriptions of new species of Latrunculia du Bocage, Strongylodesma Levi, and Tsitsikamma Samaai & Kelly. Zootaxa 2003, 371, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Samaai, T.; Kelly, M. Family Latrunculidae Topsent, 1922. In Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Hooper, J.N., Van Soest, R.W., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 1, pp. 708–719. ISBN 978-1-4615-0747-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, M.; Sim-Smith, C.; Stone, R.; Samaai, T.; Reiswig, H.; Austin, W. New taxa and arrangements within the family Latrunculiidae (Demospongiae, Poecilosclerida). Zootaxa 2016, 4121, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urban, S.; Hickford, S.J.H.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.G. Bioactive marine alkaloids. Curr. Org. Chem. 2000, 4, 765–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, N.B.; Blunt, J.W.; McCombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H. Discorhabdin C, a highly cytotoxic pigment from a sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 5476–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, J.; Capon, R.J. Discorhabdin R: A new antibacterial pyrroloiminoquinone from two latrunculiid marine sponges, Latrunculia sp. and Negombata sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1527–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, G.; Pinkert, A.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H. Discorhabdin W, the first dimeric discorhabdin. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1796–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grkovic, T.; Pearce, A.N.; Munro, M.H.; Blunt, J.W.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Copp, B.R. Isolation and characterization of diastereomers of discorhabdins H and K and assignment of absolute configuration to discorhabdins D, N, Q, S, T, and U. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botić, T.; Defant, A.; Zanini, P.; Žužek, M.C.; Frangež, R.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Ž.; Mancini, I.; Sepčić, K. Discorhabdin alkaloids from Antarctic Latrunculia spp. sponges as a new class of cholinesterase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 136, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.; Alvarez, B.; Battershill, C.; Northcote, P.; Parthasarathy, H. Genetic, morphological, and chemical divergence in the sponge genus Latrunculia (Porifera: Demospongiae) from New Zealand. Mar. Biol. 2001, 139, 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- Furrow, F.B.; Amsler, C.D.; McClintock, J.B.; Baker, B.J. Surface sequestration of chemical feeding deterrents in the Antarctic sponge Latrunculia apicalis as an optimal defense against sea star spongivory. Mar. Biol. 2003, 143, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, E.M.; Beukes, D.R.; Kelly, M.; Samaai, T.; Barrows, L.R.; Marshall, K.M.; Sincich, C.; Davies-Coleman, M.T. Cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from four new species of South African latrunculid sponges. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, M.; Ding, Y.; Wang, B.; Tekwani, B.L.; Schinazi, R.F.; Franzblau, S.; Kelly, M.; Stone, R.; Li, X.C.; Ferreira, D. Anti-infective discorhabdins from a deep-water Alaskan sponge of the genus Latrunculia. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 73, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, G.J.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Kelly-Borges, M.; Coetzee, P.S. New alkaloids from a South African latrunculid sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 7135–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Buchanan, M.S.; Duffy, S.; Avery, V.M.; Charman, S.A.; Charman, W.N.; White, K.L.; Shackleford, D.M.; Edstein, M.D.; Andrews, K.T. Antimalarial activity of pyrroloiminoquinones from the Australian marine sponge Zyzzya sp. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5851–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walmsley, T.A.; Matcher, G.F.; Zhang, F.; Hill, R.T.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Dorrington, R.A. Diversity of bacterial communities associated with the Indian Ocean sponge Tsitsikamma favus that contains the bioactive pyrroloiminoquinones, tsitsikammamine A and B. Mar. Biotechnol. 2012, 14, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matcher, G.F.; Waterworth, S.C.; Walmsley, T.A.; Matsatsa, T.; Parker-Nance, S.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Dorrington, R.A. Keeping it in the family: Coevolution of latrunculid sponges and their dominant bacterial symbionts. MicrobiologyOpen 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goey, A.K.; Chau, C.H.; Sissung, T.M.; Cook, K.M.; Venzon, D.J.; Castro, A.; Ransom, T.R.; Henrich, C.J.; McKee, T.C.; McMahon, J.B. Screening and biological effects of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Potential inhibitors of the HIF-1α/p300 interaction. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delfourne, E. Analogues of marine pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids: Synthesis and antitumor properties. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2008, 8, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolušić, E.; Larrieu, P.; Meinguet, C.; Colette, D.; Rives, A.; Blanc, S.; Ferain, T.; Pilotte, L.; Stroobant, V.; Wouters, J. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase inhibitory activity of derivatives of marine alkaloid tsitsikammamine A. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Carver, J.J.; Phelan, V.V.; Sanchez, L.M.; Garg, N.; Peng, Y.; Nguyen, D.D.; Watrous, J.; Kapono, C.A.; Luzzatto-Knaan, T. Sharing and community curation of mass spectrometry data with Global Natural Products Social Molecular Networking. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 828–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, R.A.; Nothias, L.F.; Vining, O.; Meehan, M.; Esquenazi, E.; Dorrestein, P.C. Molecular networking as a drug discovery, drug metabolism, and precision medicine strategy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosio, M.; Guerriero, A.; Chiasera, G.; Pietra, F.; Tatò, M. Epinardins A-D, new pyrroloiminoquinone alkaloids of undetermined deep-water green demosponges from pre-Antarctic Indian ocean. Tetrahedron 1996, 52, 8899–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grkovic, T.; Ding, Y.; Li, X.C.; Webb, V.L.; Ferreira, D.; Copp, B.R. Enantiomeric discorhabdin alkaloids and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 9133–9136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Repasky, M.P.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Halgren, T.A.; Sanschagrin, P.C.; Mainz, D.T. Extra precision glide: Docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein–ligand complexes. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6177–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staker, B.L.; Feese, M.D.; Cushman, M.; Pommier, Y.; Zembower, D.; Stewart, L.; Burgin, A.B. Structures of three classes of anticancer agents bound to the human topoisomerase I–DNA covalent complex. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 2336–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Li, T.K.; Farh, L.; Lin, L.Y.; Lin, T.S.; Yu, Y.J.; Yen, T.J.; Chiang, C.W.; Chan, N.L. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science 2011, 333, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelp, M.T.; Kates, P.A.; Hunt, J.T.; Newitt, J.A.; Balog, A.; Maley, D.; Zhu, X.; Abell, L.; Allentoff, A.; Borzilleri, R. Immune-modulating enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is effectively inhibited by targeting its apo-form. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3249–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Zuleta, I.A.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Discorhabdins S, T, and U, new cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from a deep-water Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijoux, M.G.; Gamble, W.R.; Hallock, Y.F.; Cardellina, J.H.; van Soest, R.; Boyd, M.R. A new discorhabdin from two sponge genera. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 636–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, R.E.; Major, D.A.; Blunt, J.W.; Munro, M.H.; Battershill, C.N.; McLean, M.G.; Baxter, R.L. Studies on the biosynthesis of discorhabdin B in the New Zealand sponge Latrunculia sp. B. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taboada, S.; García-Fernández, L.F.; Bueno, S.; Vázquez, J.; Cuevas, C.; Avila, C. Antitumoural activity in Antarctic and sub-Antarctic benthic organisms. Antarct. Sci. 2010, 22, 494–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watrous, J.; Roach, P.; Alexandrov, T.; Heath, B.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Kersten, R.D.; van der Voort, M.; Pogliano, K.; Gross, H.; Raaijmakers, J.M. Mass spectral molecular networking of living microbial colonies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciá-Vicente, J.G.; Shi, Y.N.; Cheikh-Ali, Z.; Grün, P.; Glynou, K.; Kia, S.H.; Piepenbring, M.; Bode, H.B. Metabolomics-based chemotaxonomy of root endophytic fungi for natural products discovery. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1253–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, E.M.; Copp, B.R.; Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Samaai, T. Pyrroloiminoquinone and related metabolites from marine sponges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2005, 22, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaai, T.; Gibbons, M.J.; Kelly, M. Revision of the genus Latrunculia du Bocage, 1869 (Porifera: Demospongiae: Latrunculiidae) with descriptions of new species from New Caledonia and the Northeastern Pacific. Zootaxa 2006, 112, 3–71. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, M.; Mothes, B.; Veitenheimer Mendes, I.L. Antarctic sponges (Porifera, Demospongiae) of the South Shetland Islands and vicinity: Part II. Poecilosclerida. Rev. Bras. Zool. 2007, 24, 742–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botić, T.; Cör, D.; Anesi, A.; Guella, G.; Sepčić, K.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Knez, Ž. Fatty acid composition and antioxidant activity of Antarctic marine sponges of the genus Latrunculia. Polar Biol. 2015, 38, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkpatrick, R. The World Porifera Database. 1907. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/porifera/porifera.php?p=taxdetails&id=169300 (accessed on 31 July 2018).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sample | A-375 | HCT-116 | A-549 | MB-231 | Hep G2 | HT-29 | HaCaT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crude extract | 2.5 | 0.8 | 6.3 | 3.3 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.0 |
| Fraction 3 | 4.3 | 1.2 | 5.0 | 5.6 | 5.1 | 5.2 | 6.5 |
| Positive control | 0.13 | 10.6 | 31.4 | 15.2 | 14.6 | 3.0 | - |
| Position | 1 a | 1 b | 2 b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δHc, Mult. (J in Hz) | δHd, Mult. (J in Hz) | δHe, Mult. (J in Hz) | δHc, Mult. (J in Hz) | δHc, Mult. (J in Hz) | |
| 1 | 7.71 d (8.5) | 6.87 d (8.4) | 7.36 d (8.5) | 7.50 d (8.5) | 7.84 d (8.4) |
| 2 | 6.70 d (8.5) | 7.37 d (8.4) | 6.86 d (8.5) | 6.85 d (8.5) | 6.85 d (8.4) |
| 3 | |||||
| 4 | 6.70 d (8.5) | 7.37 d (8.4) | 6.86 d (8.5) | 6.85 d (8.5) | 6.85 d (8.4) |
| 5 | 7.71 d (8.5) | 6.87 d (8.4) | 7.36 d (8.5) | 7.50 d (8.5) | 7.84 d (8.4) |
| 6 | |||||
| 7 | |||||
| 8 | 7.14 d (1.8) | 7.16 d (2.5) | 7.17 d (2.9) | 7.02 s | 7.22 s |
| NH-9 | 12.28 s | 13.28 br s | 13.32 s | ||
| 10 | |||||
| 11 | |||||
| 12 | |||||
| NH-13 | 12.00 s | 13.01 br s | 13.04 s | ||
| 14 | 6.91 s | 7.10 d (1.8) | 7.12 d (2.6) | 6.91 s | 7.93 s |
| 15 | |||||
| 16 | 2.65 t (7.8) | 2.93 t (7.8) | 2.93 t (7.8) | 2.89 t (7.8) | 7.66 d (5.9) |
| 17 | 3.97 t (7.8) | 3.85 t (7.8) | 3.84 t (7.8) | 3.94 t (7.8) | 8.34 d (5.9) |
| 19 | |||||
| 20 | |||||
| 21 | |||||
| OH | 9.31 br s | 10.60 br s | 10.43 s | ||
| Position | 1 a | 2 b,c | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δCd, Type | δCe, Type | δCf, Type | δCd, Type | |
| 1 | 129.8, CH | 116.2, CH | 129.1, CH | 129.8, CH |
| 2 | 114.4, CH | 128.9, CH | 116.4, CH | 114.4, CH |
| 3 | 156.1, C | 157.6, C | 157.7, C | 156.1, C |
| 4 | 114.4, CH | 128.9, CH | 116.4, CH | 114.4, CH |
| 5 | 129.8, CH | 116.2, CH | 129.1, CH | 129.8, CH |
| 6 | 125.1, C | 127.2, C | 127.5, C | 126.1, C |
| 7 | 124.3, C | 122.4, C | 122.5, C | 124.9, C |
| 8 | 122.8, CH | 125.0, CH | 125.2, CH | 123.1, CH |
| 10 | 133.2, C | 134.6, C | 134.8, C | 134.5, C |
| 11 | 167.7, C | 166.3, C | 166.5, C | n.o. |
| 12 | 124.7, C | 127.8, C | 128.0, C | 125.2, C |
| 14 | 121.2, CH | 123.1, CH | 123.3, CH | 123.9, CH |
| 15 | 117.4, C | 119.2, C | 119.4, C | 124.8, C |
| 16 | 17.9, CH2 | 17.6, CH2 | 17.8, CH2 | 114.0, CH |
| 17 | 49.7, CH2 | 45.0, CH2 | 45.0, CH2 | 140.6, CH |
| 19 | 154.1, C | 157.6, C | 157.0, C | 146.7, C |
| 20 | 121.6, C | 113.5, C | 113.5, C | 122.7, C |
| 21 | 121.8, C | 120.7, C | 120.9, C | 120.7, C |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Janussen, D.; Peifer, C.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; Tasdemir, D. Targeted Isolation of Tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis by Molecular Networking and Anticancer Activity. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080268
Li F, Janussen D, Peifer C, Pérez-Victoria I, Tasdemir D. Targeted Isolation of Tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis by Molecular Networking and Anticancer Activity. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(8):268. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080268
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Fengjie, Dorte Janussen, Christian Peifer, Ignacio Pérez-Victoria, and Deniz Tasdemir. 2018. "Targeted Isolation of Tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis by Molecular Networking and Anticancer Activity" Marine Drugs 16, no. 8: 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080268
APA StyleLi, F., Janussen, D., Peifer, C., Pérez-Victoria, I., & Tasdemir, D. (2018). Targeted Isolation of Tsitsikammamines from the Antarctic Deep-Sea Sponge Latrunculia biformis by Molecular Networking and Anticancer Activity. Marine Drugs, 16(8), 268. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080268