Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum
Abstract
1. Introduction
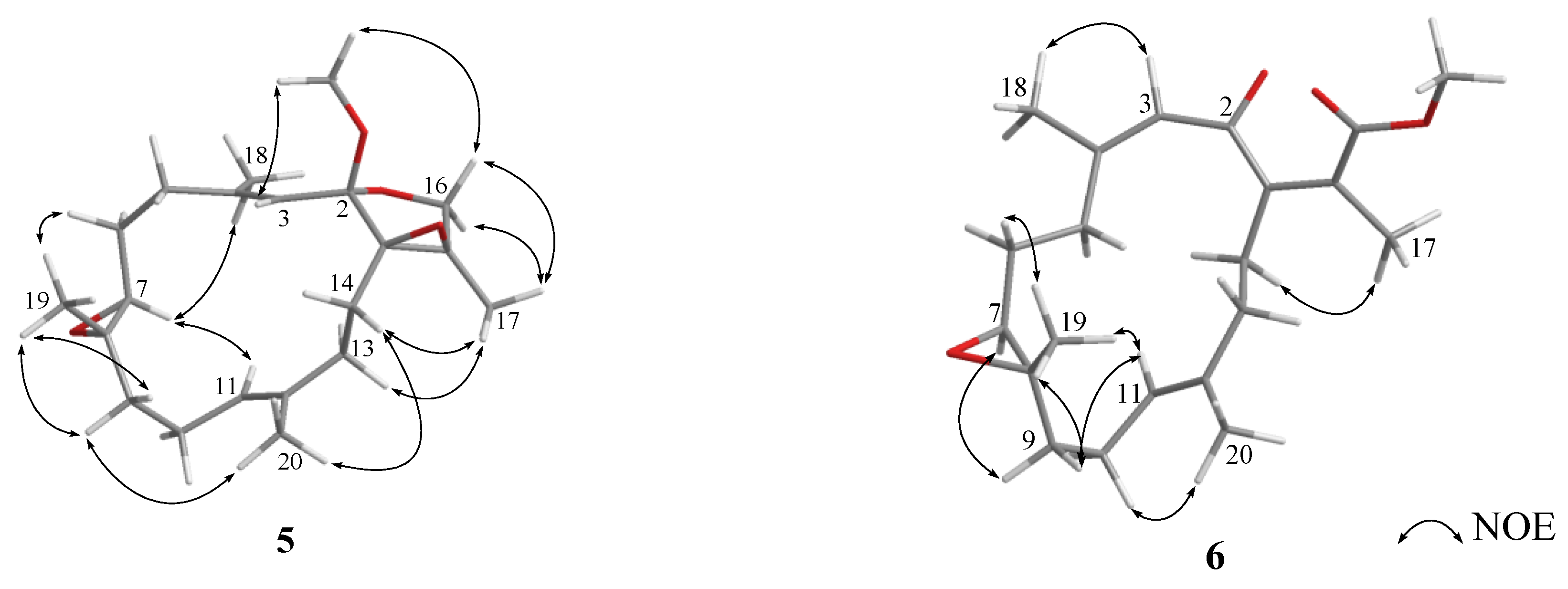
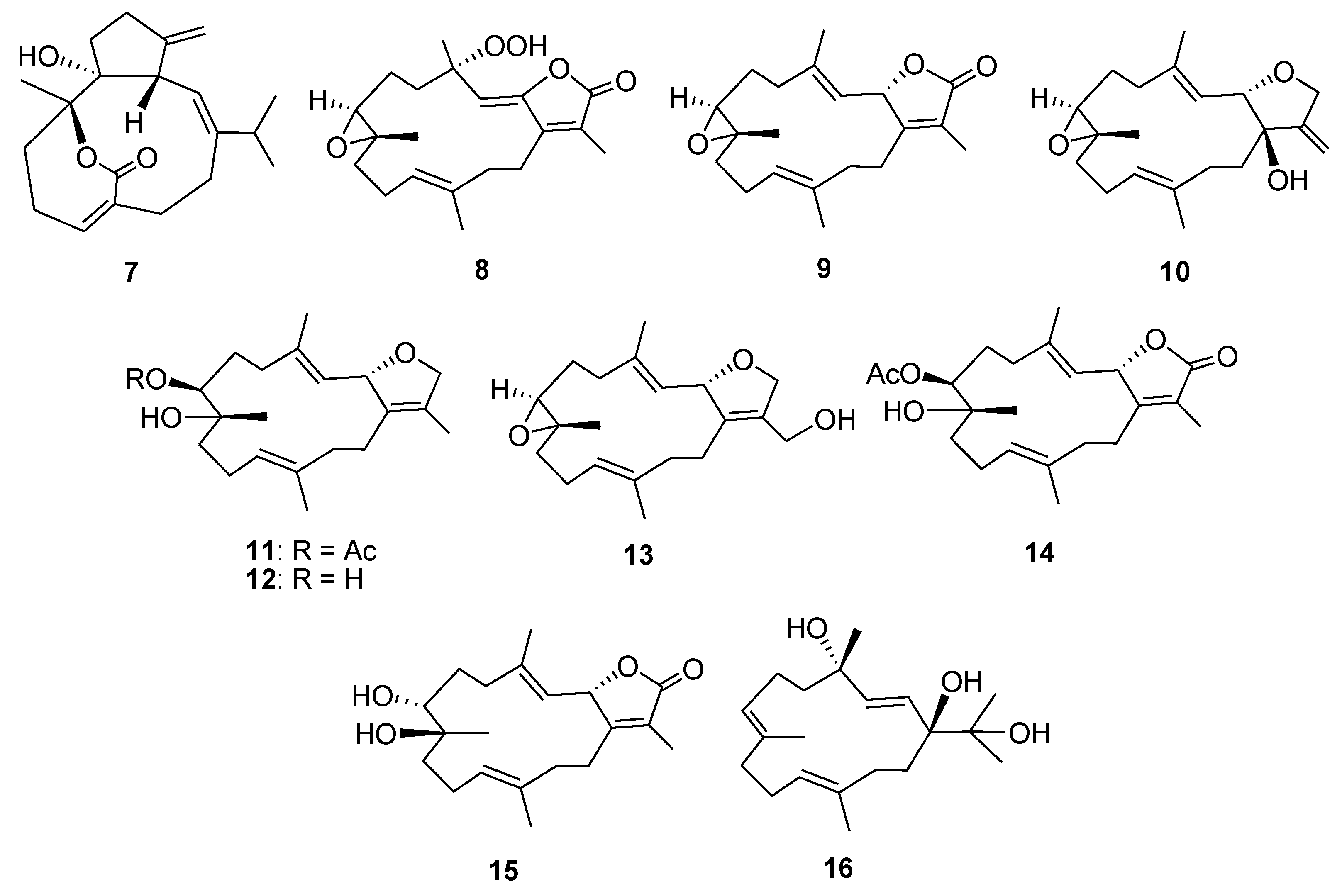
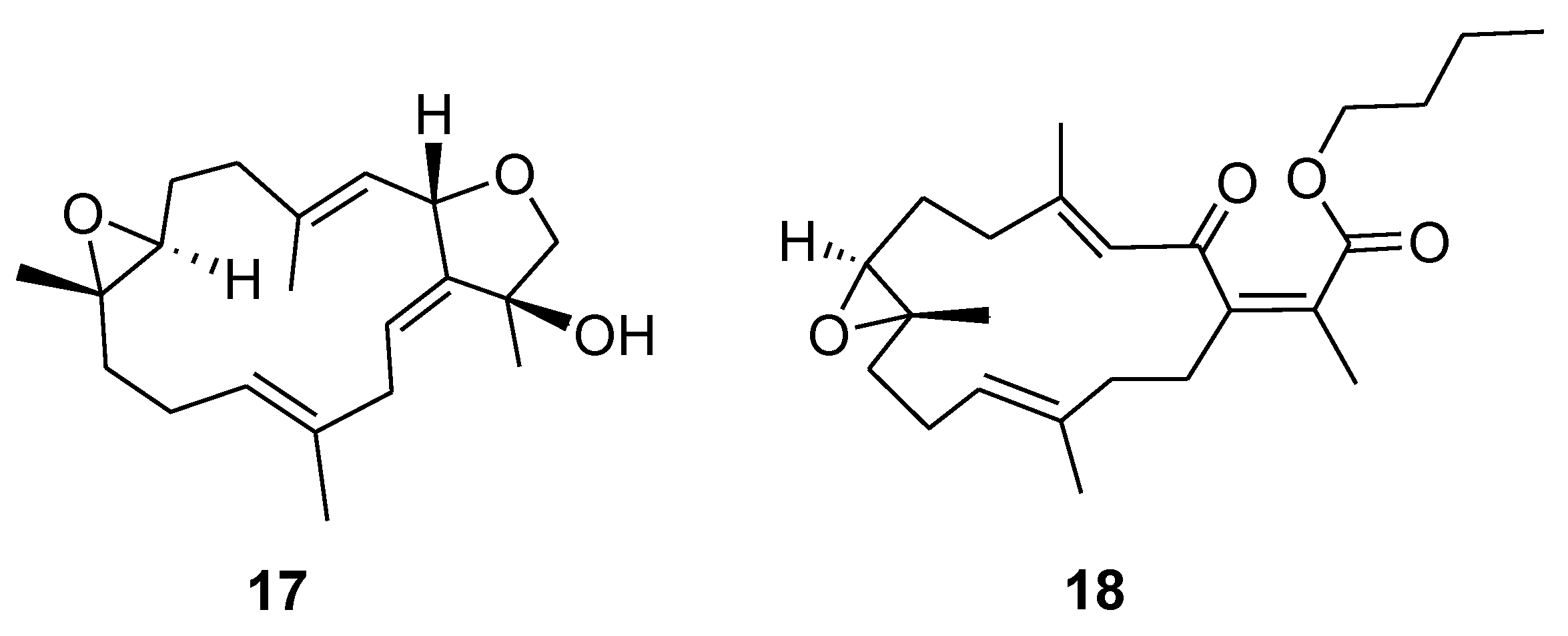
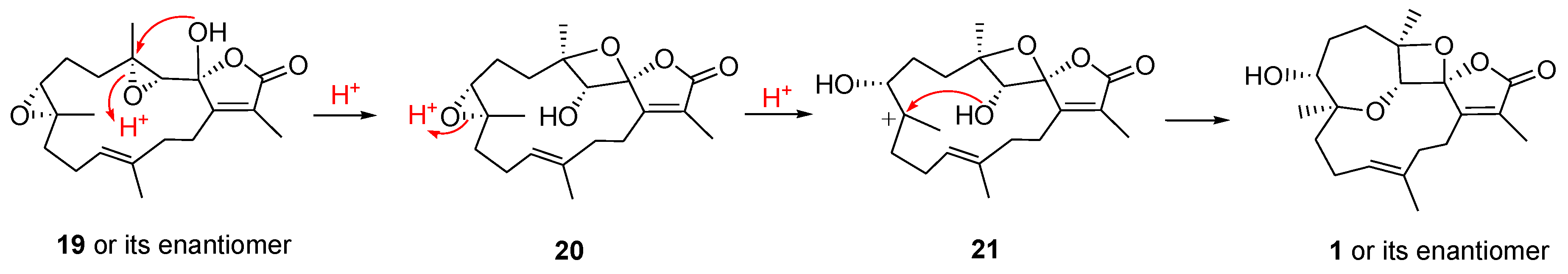
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Animal Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cytotoxicity Assay
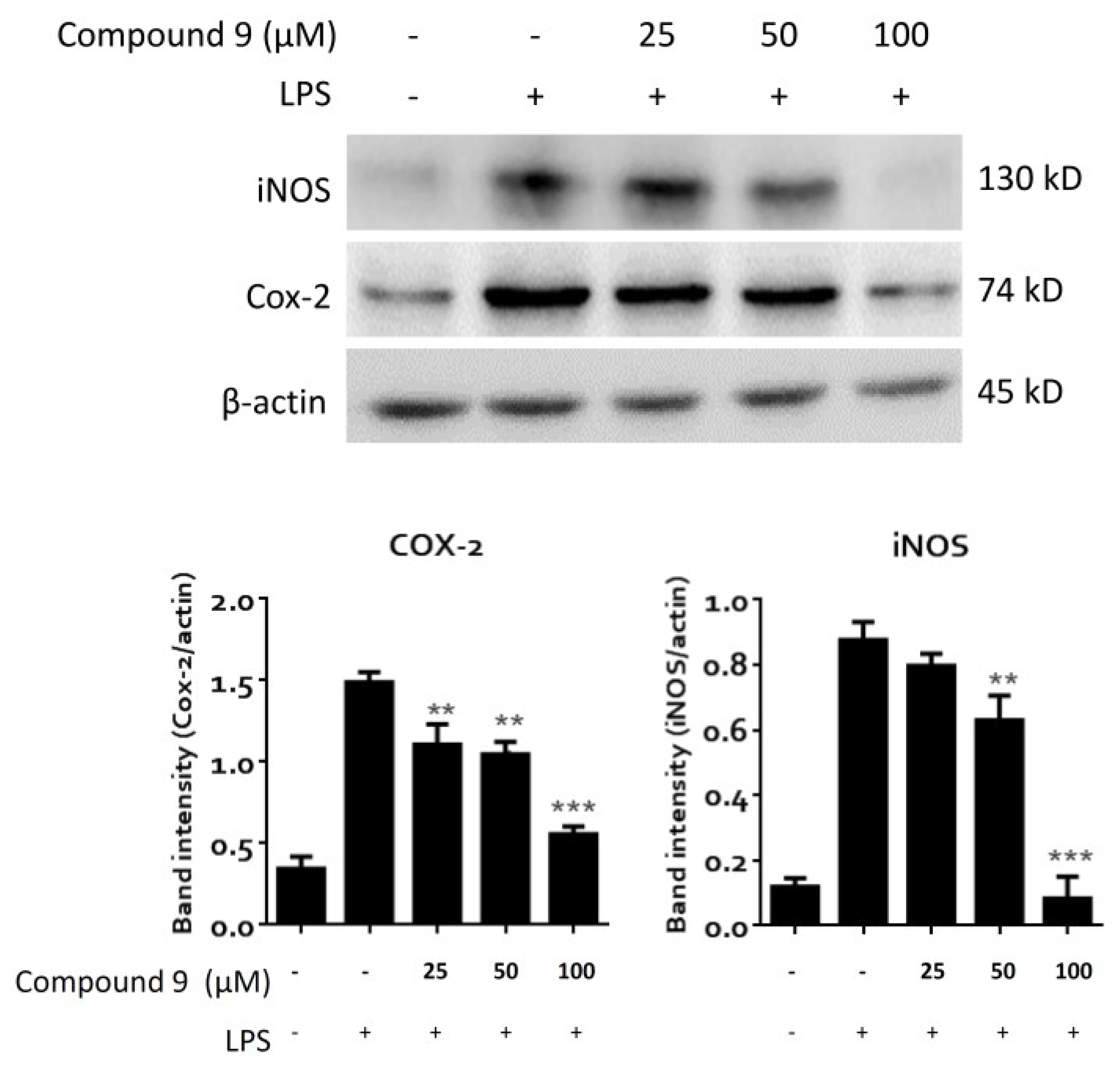
3.5. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Assay
3.6. Western Blotting Analysis
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blunt, J.W.; Carroll, A.R.; Copp, B.R.; Davis, R.A.; Keyzers, R.A.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2018, 35, 8–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, J.; Shmeuli, U.; Zadock, E.; Kashman, Y.; Néeman, I. Sarcophine, a new epoxy cembranolide from marine origin original research article. Tetrahedron 1974, 30, 2817–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.C.; Ahmed, A.F.; Su, J.H.; Chao, C.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Crassocolides A–F, cembranoids with a trans-fused lactone from the soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chung, S.G.; Chou, G.C.; Dai, C.F. Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.H.; Huang, H.C.; Su, J.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Hsu, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Crassocolides N–P, three cembranoids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 7201–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhateeb, A.; El-Beih, A.A.; Gamal-Eldeen, A.M.; Alhammady, M.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W.; Hegazy, M.E.F. New terpenes from the Egyptian soft coral Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1977–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Z.; Bie, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, D.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sarcophyolides B–E, new cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3186–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Eldeen, A.M.G.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Paré, P.W. Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the red sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zou, Y.H.; Ge, M.X.; Lou, L.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Ahmed, A.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.S.; Tang, G.H.; Yin, S. Biscembranoids and cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton elegans. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Riccio, R.; Lauro, G.; Bifulco, G.; Kurtan, T.; Mandi, A.; Tang, H.; Li, T.J.; et al. Bissubvilides A and B, cembrane-capnosane heterodimers from the soft coral Sarcophyton subviride. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2552–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Uvarani, C.; Su, J.H.; Lu, M.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Dai, C.F.; Wu, S.L.; Sheu, J.H. Glaucumolides A and B, biscembranoids with new structural type from a cultured soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; Issa, M.Y.; Ghani, M.A.; Hamed, A.; Abdelwahab, A.B. New pyranosyl cembranoid diterpenes from Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.F.; Chen, W.T.; Li, X.W.; Wang, H.Y.; Guo, Y.W. New bicyclic cembranoids from the South China Sea soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Tsai, C.R.; Huang, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Klyflaccicembranols A–I, new cembranoids from the soft coral Klyxum flaccidum. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Elshamy, A.I.; Mohamed, T.A.; Hamed, A.R.; Ibrahim, M.A.A.; Ohta, S.; Paré, P.W. Cembrene diterpenoids with ether linkages from Sarcophyton ehrenbergi: An anti-proliferation and molecular-docking assessment. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, K.H.; You, W.J.; Lin, C.C.; El-Shazly, M.; Liao, Z.J.; Su, J.H. Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chokkalingam, U.; Hwang, T.L.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Sung, P.J.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive isoprenoid-derived natural products from a Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sinularia erecta. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Cheng, S.M.; Yuan, W.P.; Xi, Y.Y.; Li, X.B.; Dong, J.Y.; Huang, K.X.; Gustafson, K.R.; Yan, P.C. Cembranoids from a Chinese collection of the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Lateff, A.; Alarif, W.M.; Ayyad, S.E.N.; Al-Lihaibi, S.S.; Basaif, S.A. New cytotoxic isoprenoid derivatives from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.H.; Tseng, Y.J.; Chen, B.W.; Hwang, T.L.; Chen, H.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Tortuosenes A and B, new diterpenoid metabolites from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton tortuosum. Org. Lett. 2014, 16, 1314–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.T.; Wu, C.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Liaw, C.C.; Wu, S.H.; Sheu, J.H.; Chang, H.W. Sinularin induces oxidative stress-mediated G2/M arrest and apoptosis in oral cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.T.; Huang, C.Y.; Tang, J.Y.; Liaw, C.C.; Li, R.N.; Liu, J.R.; Sheu, J.H.; Chang, H.W. Reactive oxygen species mediate soft corals-derived sinuleptolide-induced antiproliferation and DNA damage in oral cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 3289–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, S.P.; Hung, W.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.S.; Chan, M.Y.; Lu, P.L.; Lin, L.; Sheu, J.H. 5-Episinuleptolide decreases the expression of the extracellular matrix in early biofilm Formation of multi-drug resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.C.; Chen, H.Y.; Sheu, J.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Su, J.H. Structural elucidation and structure—Anti-inflammatory activity relationships of cembranoids from cultured soft corals Sinularia sandensis and Sinularia flexibilis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.J.; Neoh, C.A.; Tsao, C.Y.; Su, J.H.; Li, H.H. Sinulariolide suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 through MAPKs and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 16469–16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Jean, Y.H.; Lee, H.P.; Chen, W.F.; Sun, Y.M.; Su, J.H.; Lu, Y.; Huang, S.Y.; Hung, H.C.; Sung, P.J.; et al. A soft coral-derived compound, 11-epi-sinulariolide acetate suppresses inflammatory response and bone destruction in adjuvant-induced Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 62926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahelivao, M.P.; Lübken, T.; Gruner, M.; Kataeva, O.; Ralambondrahety, R.; Andriamanantoanina, H.; Checinski, M.P.; Bauer, I.; Knölker, H.J. Isolation and structure elucidation of natural products of three soft corals and a sponge from the coast of Madagascar. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 2593–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centko, R.M.; Ramon-Garcia, S.; Taylor, T.; Patrick, B.O.; Thompson, C.J.; Miao, V.P.; Andersen, R.J. Ramariolides A−D, antimycobacterial butenolides isolated from the mushroom Ramaria cystidiophora. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 2178–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CONFLEX 7, Conflex Corp., Japan. 2017. Available online: http://www.conflex.net/index.html (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- Góreck, M. A configurational and conformational study of (−)-Oseltamivir using a multi-chiroptical approach. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 2999–3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.B.; Liao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Fan, C.Q.; Huang, Z.Y.; Xu, X.J.; Yin, S. Four new cembranoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton sp. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2014, 52, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.G.; Liu, H.L.; Guo, Y.W.; Mollo, E. New cembranoids from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Helv. Chim. Acta 2009, 92, 1085–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Kurtan, T.; Mandi, A.; Yan, X.H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.W. Biscembranoids formed from an α,β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring as a dienophile: Structure revision and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Long, K.; Huang, S.; Shi, K.; Mak, T.C.W. A novel diterpenolide from the soft coral Sarcophyton solidun. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1672–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.F.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Gao, L.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.W. Sarsolenane and capnosane diterpenes from the Hainan soft coral Sarcophyton trocheliophorum Marenzeller as PTP1B Inhibitors. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 9, 1841–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. Part 12. Autoxidation of dihydrofuranocembranoids. J. Chem. Res. 1991, 11, 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Quang, T.H.; Ha, T.T.; Minh, C.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Huong, H.T.; Ngan, N.T.; Nhiem, N.X.; Tung, N.H.; Tai, B.H.; Thuy, D.T.; et al. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the Vietnamese soft coral Lobophytum laevigatum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.T.; Wang, S.K.; Duh, C.Y. Cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Lobophytum crassum. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2705–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Hirase, T. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. XI.: Structures of new dihydrofuranocembranoids isolated from a Sarcophyton sp. soft coral of Okinawa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1990, 38, 2442–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, D.; Shaker, K.H.; Soliman, H.S.M.; Hegazi, M.M.; Seifert, K. Cembranoid diterpenes from the soft corals Sarcophyton sp. and Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2008, 3, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Shaker, K.H.; Muller, M.; Ghani, M.A.; Dahse, H.M.; Seifert, K. Terpenes from the soft corals Litophyton arboreum and Sarcophyton ehrenbergi. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 2007–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czarkie, D.; Carmely, S.; Groweiss, A.; Kashman, Y. Attempted acid-catalyzed transannular reactions in the cembranoids. Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, D.; Soliman, H.S.; Shaker, K.H.; Hamza, M.; Seifert, K. Cembranoid diterpenes and a briarane diterpene from corals. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.J.; Choi, M.J.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, M.; Choi, H.E.; Kang, S.M.; Jin, J.H.; Lee, K.T.; Lee, J.Y. Synthesis, biological evaluation, and docking analysis of a novel family of 1-methyl-1H-pyrrole-2,5-diones as highly potent and selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1958–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, Y.; Chen, P.; Zheng, C.L.; Yang, Y.; Duan, W.G.; Wang, L.; He, B.; Ma, J.Q.; Wang, D.H.; Shen, Z.Q. Copper-aspirin complex inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 more selectively than aspirin. Yakugaku Zasshi 2007, 127, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.R.; Vyas, P.; Attur, M.; Leszczynska-Piziak, J.; Patel, I.R.; Weissmann, G.; Abramson, S.B. The mode of action of aspirin-like drugs: Effect on inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7926–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alley, M.C.; Scudiero, D.A.; Monks, A.; Hursey, M.L.; Czerwinski, M.J.; Fine, D.L.; Abbott, B.J.; Mayo, J.G.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Boyd, M.R. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scudiero, D.A.; Shoemaker, R.H.; Paull, K.D.; Monks, A.; Tierney, S.; Nofziger, T.H.; Currens, M.J.; Seniff, D.; Boyd, M.R. Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 4827–4833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
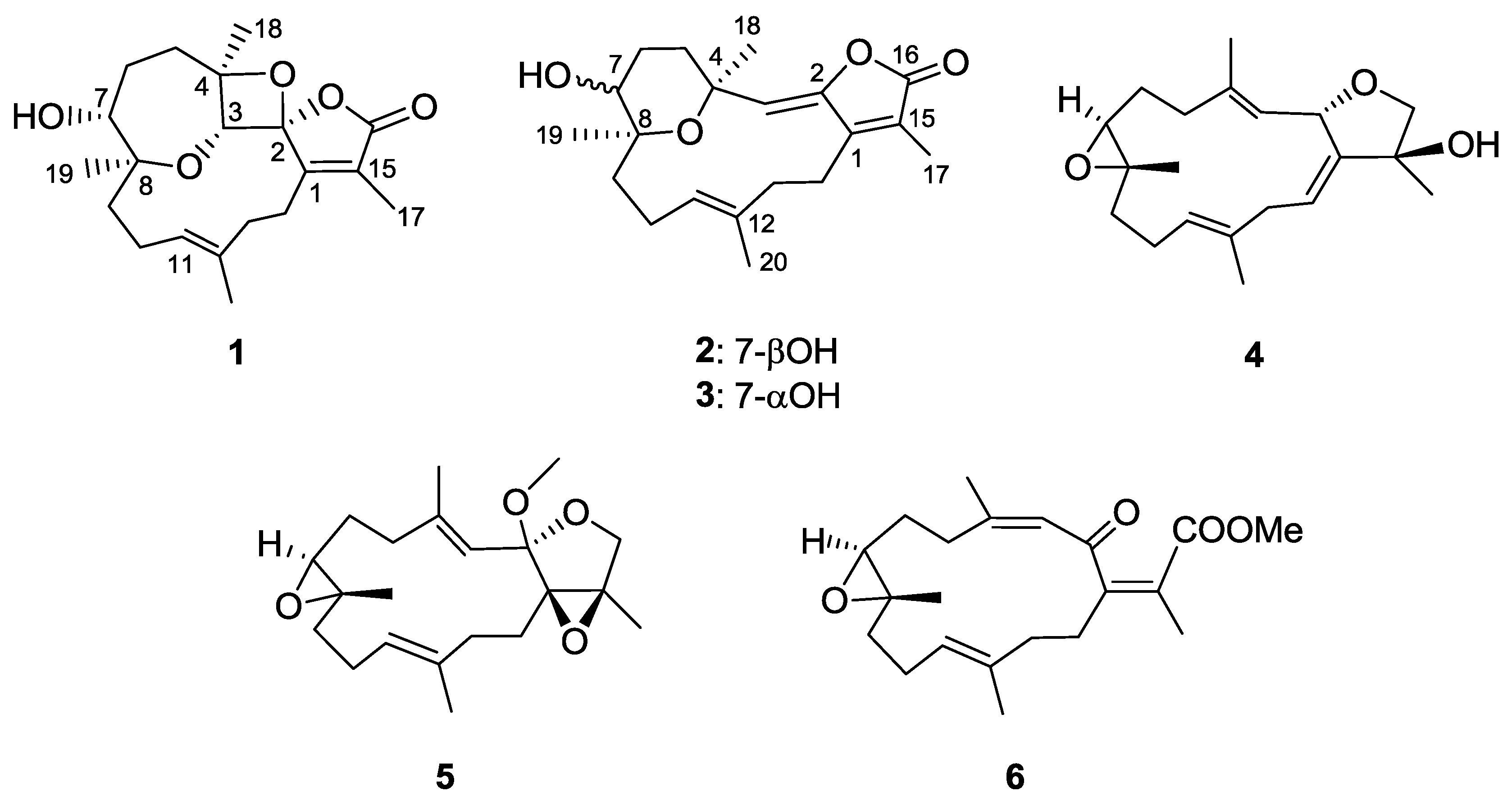
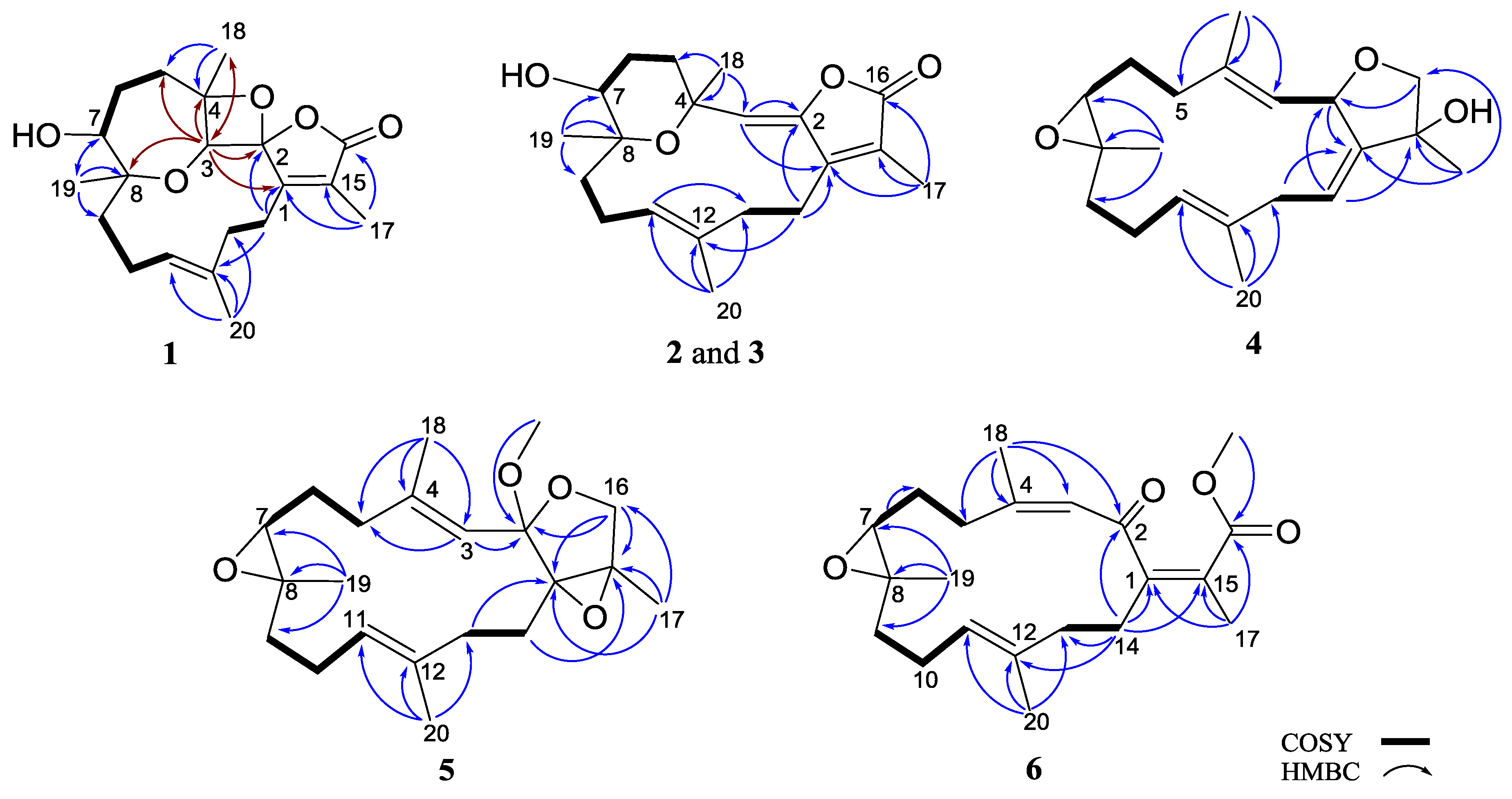
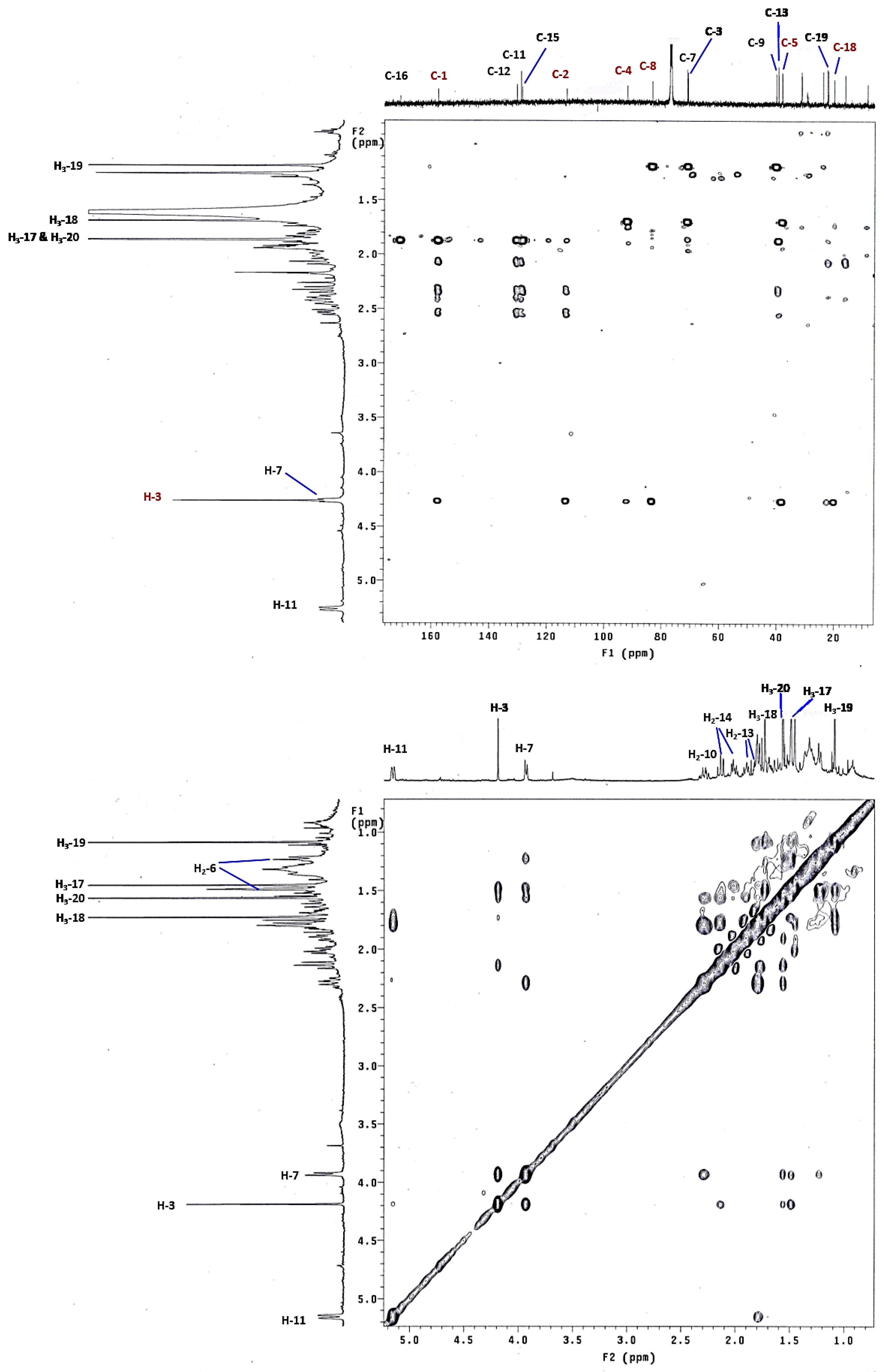
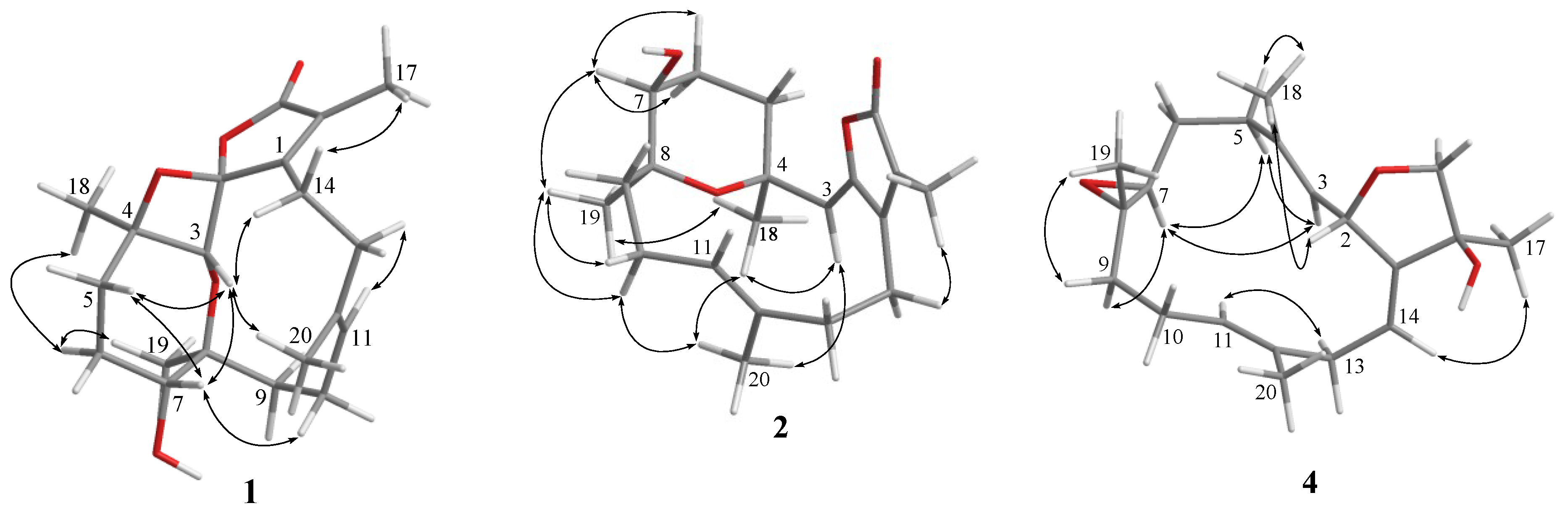

| Position | 1 a | 2 a | 3 a | 4 a | 5 a | 6 a | 18 c,d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 157.9 (C) b | 152.2 (C) | 152.2 (C) | 147.8 (C) | 63.3 (C) | 155.3 (C) | 151.0 (C) |
| 2 | 113.4 (C) | 147.8 (C) | 148.2 (C) | 76.2 (CH) | 107.4 (C) | 197.8 (C) | 196.7 (C) |
| 3 | 71.1 (CH) | 117.4 (CH) | 116.5 (CH) | 125.3 (CH) | 120.6 (CH) | 125.3 (CH) | 123.8 (CH) |
| 4 | 92.2 (C) | 73.7 (C) | 74.2 (C) | 136.1 (C) | 142.8 (C) | 153.2 (C) | 155.8 (C) |
| 5 | 38.3 (CH2) | 40.4 (CH2) | 38.8 (CH2) | 36.2 (CH2) | 37.6 (CH2) | 29.2 (CH2) | 37.6 (CH2) |
| 6 | 31.5 (CH2) | 26.7 (CH2) | 26.9 (CH2) | 25.9 (CH2) | 25.7 (CH2) | 25.9 (CH2) | 24.9 (CH2) |
| 7 | 71.3(CH) | 77.3 (CH) | 74.6 (CH) | 61.9 (CH) | 62.0 (CH) | 62.3 (CH) | 62.0 (CH) |
| 8 | 83.5 (C) | 74.6 (C) | 74.9 (C) | 59.7 (C) | 60.7 (C) | 60.6 (C) | 60.5 (C) |
| 9 | 40.4 (CH2) | 37.8 (CH2) | 38.0 (CH2) | 39.2 (CH2) | 37.1 (CH2) | 37.6 (CH2) | 37.2 (CH2) |
| 10 | 24.0 (CH2) | 21.6 (CH2) | 22.1 (CH2) | 24.1 (CH2) | 22.5 (CH2) | 22.9 (CH2) | 22.7 (CH2) |
| 11 | 129.2 (CH) | 129.1 (CH) | 128.5 (CH) | 123.6 (CH) | 124.6 (CH) | 125.1 (CH) | 125.9 (CH) |
| 12 | 130.6 (C) | 130.9 (C) | 131.4 (C) | 132.7 (C) | 134.6 (C) | 134.4 (C) | 134.3 (C) |
| 13 | 39.6 (CH2) | 38.7 (CH2) | 38.3 (CH2) | 38.2 (CH2) | 33.7 (CH2) | 36.3 (CH2) | 36.6 (CH2) |
| 14 | 22.2 (CH2) | 21.8 (CH2) | 22.2 (CH2) | 120.1 (CH) | 21.6 (CH2) | 28.8 (CH2) | 29.3 (CH2) |
| 15 | 128.8 (C) | 123.3 (C) | 123.7 (C) | 77.4 (C) | 71.3 (C) | 125.0 (C) | 127.8 (C) |
| 16 | 171.1 (C) | 170.3 (C) | 170.3 (C) | 78.8 (CH2) | 68.8 (CH2) | 168.5 (C) | 168.8 (C) |
| 17 | 8.6 (CH3) | 8.7 (CH3) | 8.8 (CH3) | 22.1 (CH3) | 11.7 (CH3) | 14.1 (CH3) | 15.1 (CH3) |
| 18 | 20.1 (CH3) | 29.7 (CH3) | 29.5 (CH3) | 17.1 (CH3) | 16.8 (CH3) | 24.2 (CH3) | 19.6 (CH3) |
| 19 | 22.5 (CH3) | 26.1 (CH3) | 25.6 (CH3) | 16.3 (CH3) | 17.8 (CH3) | 17.1 (CH3) | 17.4 (CH3) |
| 20 | 16.3 (CH3) | 15.6 (CH3) | 15.9 (CH3) | 16.6 (CH3) | 16.3 (CH3) | 16.1 (CH3) | 15.5 (CH3) |
| OMe | 49.3 (CH3) | 52.0 (CH3) |
| Position | 1 a | 2 a | 3 a | 4 a | 5 a | 6 a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5.27 d (9.5) | |||||
| 3 | 4.27 s | 5.16 s | 5.21 s | 5.37 d (9.5) | 5.21 s | 6.10 s |
| 5 | 1.72 m; 1.88 m | 1.90 m; 1.97 m | 1.79, m; 2.09, m | 2.32 dd (14.0, 8.0); 2.09 m | 2.28 2H, m | 2.70 m; 2.97 m |
| 6 | 1.94 2H, m | 1.48 2H, m | 1.49 m; 1.54 m | 1.52 m; 1.83 m | 1.70 m; 1.88 m | 1.61 m; 2.00 m |
| 7 | 4.27 br d (10.0) b | 3.44 dd (7.0, 5.0) | 3.52 dd (9.5, 3.0) | 2.85 dd (5.0, 5.0) | 2.84 dd (7.5, 4.0) | 2.65 dd (8.0, 3.0) |
| 9 | 1.82 m; 1.92 m | 1.52, m ; 1.63 m | 1.49 m; 1.64 m | 1.05 dd (14.0, 14.0, 5.0); 2.07 m | 1.47, dd (13.0, 13.0); 1.98 m | 1.30 m; 2.02 m |
| 10 | 2.00, m (11.0); 2.44, m | 1.82, m; 2.26 m | 1.87, m; 2.17 ddd (14.0, 7.0, 7.0) | 2.09 m; 2.11 m | 1.94 m; 2.12 m | 2.00 m; 2.18 m |
| 11 | 5.26 d (11.0) | 4.97 dd (6.5, 6.5) | 5.00 dd (7.0, 7.0) | 4.88 dd (7.0, 7.0) | 5.24, m | 5.05 dd (6.5, 6.5) |
| 13 | 2.07 dd (13.0, 13.0); 2.40 m | 2.22 m; 2.30 m | 2.25 m; 2.30 m | 2.58 2H, m | 2.13 2H, m | 2.16 2H, m |
| 14 | 2.33 dd (13.0, 13.0); 2.53 dd (13.0, 7.5) | 2.56 2H, m | 2.57 2H, dd (7.5, 7.5) | 5.68 ddd (8.5, 6.5, 2.0) | 1.82 m; 2.14 m | 2.40 dd (14.0, 7.0); 2.45 dd (14, 7.0) |
| 16 | 3.57 d (9.0); 3.94 d (9.0) | 3.64 d (10.0); 3.88 d (10.0) | ||||
| 17 | 1.87 s | 1.94 s | 1.95 s | 1.41 s | 1.40 s | 1.92 s |
| 18 | 1.69 s | 1.48 s | 1.54 s | 1.82 s | 1.86 s | 1.92 s |
| 19 | 1.19 s | 1.18 s | 1.23 s | 1.25 s | 1.28 s | 1.23 s |
| 20 | 1.87 s | 1.63 s | 1.63 s | 1.63 s | 1.59 s | 1.58 s |
| OMe | 3.20 s | 3.68 s |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.F.; Chen, Y.-W.; Huang, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Dai, C.-F.; Wu, Y.-C.; Sheu, J.-H. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060210
Ahmed AF, Chen Y-W, Huang C-Y, Tseng Y-J, Lin C-C, Dai C-F, Wu Y-C, Sheu J-H. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(6):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060210
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Atallah F., Yi-Wei Chen, Chiung-Yao Huang, Yen-Ju Tseng, Chi-Chen Lin, Chang-Feng Dai, Yang-Chang Wu, and Jyh-Horng Sheu. 2018. "Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum" Marine Drugs 16, no. 6: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060210
APA StyleAhmed, A. F., Chen, Y.-W., Huang, C.-Y., Tseng, Y.-J., Lin, C.-C., Dai, C.-F., Wu, Y.-C., & Sheu, J.-H. (2018). Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Cembranoids from a Dongsha Atoll Soft Coral Sarcophyton stellatum. Marine Drugs, 16(6), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060210








