Novel Natural Products from Extremophilic Fungi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Piezophilic Fungi
3. Psychrophilic Fungi
4. Thermophilic Fungi
5. Halophilic Fungi
6. Xerophilic Fungi
7. Acidophilic or Alkaliphilic Fungi
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macelroy, R.D. Some comments on the evolution of extremophiles. BioSystem 1974, 6, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woese, C.R.; Kandler, O.; Wheelis, M.L. Towards a natural system of organisms: Proposal for the domains archaea, bacteria, and eucarya. PNAS 1990, 87, 4576–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D. Deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 1131–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yayanos, A.A. Microbiology to 10,500 meters in the deep sea. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1995, 49, 777–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horikoshi, K. Barophiles: Deep-sea microorganisms adapted to an extreme environment. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 1998, 1, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, Z.E.; Brimble, M.A. Molecules derived from the extremes of life. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 44–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deming, J.W. Psychrophiles and polar regions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2002, 5, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, R.D.; Johansen, J.R. Microbiotic crusts and ecosystem processes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1999, 18, 183–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetter, K.O. Extremophiles and their adaptation to hot environments. FEBS Lett. 1999, 452, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, R.; Thomas, T.; Curmi, P.M.G. Cold stress response in archaea. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madern, D.; Ebel, C.; Zaccai, G. Halophilic adaptation of enzymes. Extremophiles 2000, 4, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, L.J.; Mancinelli, R.L. Life in extreme environments. Nature 2001, 409, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakchung, A.A.H.; Simpson, P.J.L.; Codd, R. Life on earth. Extremophiles continue to move the goal posts. Environ. Chem. 2006, 3, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebar, M.D.; Heimbegner, J.L.; Baker, B.J. Cold-water marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldatou, S.; Baker, B.J. Cold-water marine natural products, 2006 to 2016. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2017, 34, 585–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
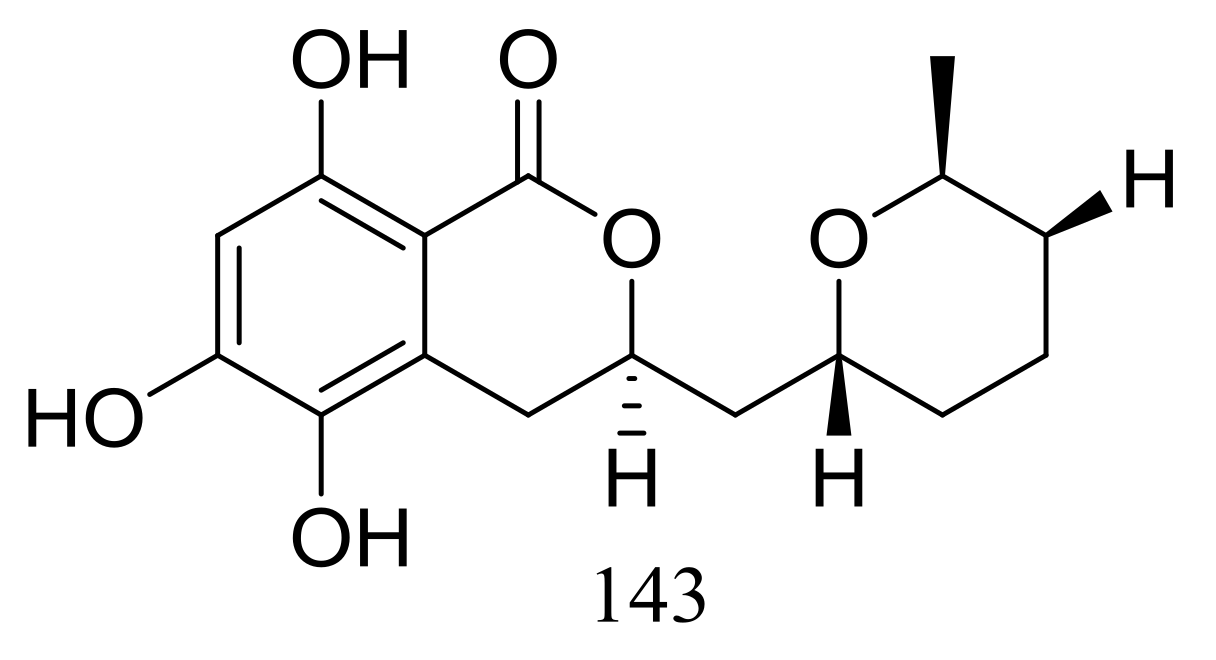
- Jing-Tang, L.; Xiao-Ling, L.; Xiao-Yu, L.; Yun, G.; Bo, H.; Bing-Hua, J.; Heng, Z. Bioactive natural products from the antarctic and arctic organisms. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Li, Y.-L.; Zhao, F.-C. Secondary metabolites from polar organisms. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skropeta, D.; Wei, L. Recent advances in deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 999–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Xue, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H. A brief review of bioactive metabolites derived from deep-sea fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Cai, S.; Zeng, X.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Two new bisorbicillinoids isolated from a deep-sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Trisorbicillinone a, a novel sorbicillin trimer, from a deep sea fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 5235–5238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. Three new sorbicillin trimers, trisorbicillinones b, c, and d, from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus, Phialocephala sp. FL30r. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 5101–5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-H.; Cai, S.-X.; Zhu, T.-J.; Wang, F.-P.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q.-Q. New cytotoxic metabolites from a deep-sea-derived fungus, Phialocephala sp., strain FL30r. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Yang, X.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Park, H.; Gu, Q. Diketopiperazine alkaloids from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus Penicillium sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 873–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Li, D.; Zhu, T.; Cai, S.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. New alkaloids and diterpenes from a deep ocean sediment derived fungus Penicillium sp. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Feng, T.; Zhao, B.; Li, D.; Cai, S.; Zhu, T.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Gu, Q. Alkaloids from a deep ocean sediment-derived fungus Penicillium sp. and their antitumor activities. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Peng, J.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Keyzers, R.A.; Li, D. Sorbicillamines a–e, nitrogen-containing sorbicillinoids from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. F23-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penicyclones a–e, antibacterial polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium sp. F23-2. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2699–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y. Breviane spiroditerpenoids from an extreme-tolerant Penicillium sp. isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ye, D.; Shao, Z.; Cui, C.; Che, Y. A sterol and spiroditerpenoids from a Penicillium sp. isolated from a deep sea sediment sample. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.-Q.; Lin, X.-P.; Liu, J.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Ai, W.; Ju, Z.-R.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.-W.; Liu, Y. Ascomycotin a, a new citromycetin analogue produced by Ascomycota sp. Ind19F07 isolated from deep sea sediment. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Wei, X.; Qi, S. Oxindole alkaloids from the fungus Penicillium commune DFFSCS026 isolated from deep-sea-derived sediments. Tetrahedron 2015, 71, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredimoses, M.; Zhou, X.; Ai, W.; Tian, X.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Xian, J.-Y.; Liu, Y. Westerdijkin a, a new hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivative from deep sea fungus Aspergillus westerdijkiae SCSIO 05233. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredimoses, M.; Zhou, X.; Lin, X.; Tian, X.; Ai, W.; Wang, J.; Liao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, X.; et al. New prenylxanthones from the deep-sea derived fungus Emericella sp. SCSIO 05240. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Xu, X.; Qi, S. Cytotoxic polyketides from the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album DFFSCS021. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Qin, X.; Lin, X.; Kaliyaperumal, K.; Zhou, X.; Liu, J.; Ju, Z.; Tu, Z.; Liu, Y. Sydoxanthone c and acremolin b produced by deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO Ind09F01. J. Antibiot. 2015, 68, 703–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Sun, Z.-H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-X.; Li, H.-H.; Zhang, W.-M. Dichotocejpins a–c: New diketopiperazines from a deep-sea-derived fungus Dichotomomyces cejpii FS110. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-W.; Liu, H.-X.; Sun, Z.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Tan, Y.-Z.; Zhang, W.-M. Secondary metabolites from the deep-sea derived fungus Acaromyces ingoldii FS121. Molecules 2016, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, W.; He, X.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Peniphenylanes a–g from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium fellutanum HDN14-323. Planta Med. 2016, 82, 872–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Huang, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Wang, F.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Antifungal new oxepine-containing alkaloids and xanthones from the deep-sea-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor SCSIO 05879. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 2910–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, W. Antioxidative phenolic compounds from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Liu, C.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Clindanones a and b and cladosporols f and g, polyketides from the deep-sea derived fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides HDN14-342. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76498–76504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Nong, X.; Wang, J.; Qi, S. Brevianamides and mycophenolic acid derivatives from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium brevicompactum DFFSCS025. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, B.; Ma, Z. Inhibitors of BRD4 protein from a marine-derived fungus Alternaria sp. NH-F6. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J. Secondary metabolites produced by the deep-sea-derived fungus Engyodontium album. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 224–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Salendra, L.; Pang, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Isobenzofuranones and isochromenones from the deep-sea derived fungus Leptosphaeria sp. SCSIO 41005. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, G.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Inducing secondary metabolite production by combined culture of Talaromyces aculeatus and Penicillium variabile. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 3167–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Eutypellazines a-m, thiodiketopiperazine-type alkaloids from deep sea derived fungus Eutypella sp. MCCC 3A00281. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 33580–33590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Shao, Z.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Eutypellazines n−s, new thiodiketopiperazines from a deep sea sediment derived fungus Eutypella sp. with anti-VRE activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 3695–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Sakai, K.; Nagano, Y.; Orui Sakaguchi, S.; Lima, A.O.; Pellizari, V.H.; Iwatsuki, M.; Takishita, K.; Nonaka, K.; Fujikura, K.; et al. Cladomarine, a new anti-saprolegniasis compound isolated from the deep-sea fungus, Penicillium coralligerum YK-247. J. Antibiot. 2017, 70, 911–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalsgaard, P.W.; Larsen, T.O.; Christophersen, C. Bioactive cyclic peptides from the psychrotolerant fungus Penicillium algidum. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.-C.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.A.; Fenical, W. Libertellenones a–d: Induction of cytotoxic diterpenoid biosynthesis by marine microbial competition. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5267–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.-L.; Liu, J.-T.; Liu, X.-Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiao, B.-H.; Zheng, H. Pimarane diterpenes from the arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Xu, N.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X.; Yin, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y. Stimulatory effect of ethanol on libertellenone h biosynthesis by arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-T.; Hu, B.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.-P.; Jiao, B.-H.; Lu, X.-L.; Liu, X.-Y. Bioactive tyrosine-derived cytochalasins from fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-Q.; Chen, X.-C.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Wang, G.-M.; Zhu, S.-G.; Yang, Y.-F.; Chen, K.-X.; Liu, X.-Y.; Li, Y.-M. Eutypenoids a–c: Novel pimarane diterpenoids from the arctic fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhang, J.-P.; Yu, H.-B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, X.-L.; Jiao, B.-H. A new sesquiterpene lactone from fungus Eutypella sp. D-1. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 1676–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Sun, B.; Liu, S.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Che, Y. Bioactive asterric acid derivatives from the antarctic ascomycete fungus Geomyces sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, L.; Jiménez, C.; Rodríguez, J.; Areche, C.; Chávez, R.; Henríquez, M.; de la Cruz, M.; Díaz, C.; Segade, Y.; Vaca, I. 3-nitroasterric acid derivatives from an antarctic sponge-derived Pseudogymnoascus sp. Fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, D.; Luan, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Cytotoxic metabolites from the antarctic psychrophilic fungus Oidiodendron truncatum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Ma, H.; Zhu, T.; Li, J.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Penilactones a and b, two novel polyketides from antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2. Tetrahedron 2012, 68, 9745–9749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Lin, A.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Four new chloro-eremophilane sesquiterpenes from an antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, A.; Wu, G.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. New eremophilane-type sesquiterpenes from an antarctic deep-sea derived fungus, Penicillium sp. PR19N-1. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Kramer, A.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Lindgomycin, an unusual antibiotic polyketide from a marine fungus of the Lindgomycetaceae. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, W.; Qin, X.; Wei, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Tu, Z.; Chen, B.; et al. Three new indolyl diketopiperazine metabolites from the antarctic soil-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 05705. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68736–68742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wang, W.; Che, Q.; Li, D.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T. Chrodrimanins i and j from the antarctic moss-derived fungus Penicillium funiculosum GWT2-24. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Li, L.; Wu, C.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Guo, P.; Li, D. Penipyridones a–f, pyridone alkaloids from Penicillium funiculosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, M.-L.; Sun, G.-Y.; Li, N.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Li, D.-H.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.-J. Exopisiod b and farylhydrazone c, two new alkaloids from the antarctic-derived fungus Penicillium sp. HDN14-431. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wei, X.; Qin, X.; Tian, X.; Liao, L.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, T.; et al. Antiviral merosesquiterpenoids produced by the antarctic fungus Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis SCSIO 05702. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.-H.; Yu, H.-B.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, X.-L.; Jiao, B.-H. Furanone derivative and sesquiterpene from antarctic marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. S-1-18. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Fan, Z.-W.; Xie, C.-L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, Z.-H.; Liu, G.; Yang, X.-W. Spirograterpene a, a tetracyclic spiro-diterpene with a fused 5/5/5/5 ring system from the deep-sea-derived fungus Penicillium granulatum MCCC 3A00475. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2174–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.L.; Lu, C.P.; Chen, M.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Wu, Y.C.; Wu, S.H. Cytotoxic polyketides containing tetramic acid moieties isolated from the fungus Myceliophthora Thermophila: Elucidation of the relationship between cytotoxicity and stereoconfiguration. Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 13, 6985–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Liao, W.-Y.; Liu, W.-Y.; Liaw, C.-C.; Shen, C.-N.; Huang, Z.-Y.; Wu, S.-H. Discovery of new natural products by intact-cell mass spectrometry and LC-SPE-NMR: Malbranpyrroles, novel polyketides from thermophilic fungus Malbranchea sulfurea. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11573–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.-S.; Niu, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-L.; Guo, J.-P.; Pan, W.-Z.; Huang, X.-W.; Zhang, K.-Q. Isolation of putative biosynthetic intermediates of prenylated indole alkaloids from a thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4356–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-P.; Tan, J.-L.; Wang, Y.-L.; Wu, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.-P.; Niu, X.-M.; Pan, W.-Z.; Huang, X.-W.; Zhang, K.-Q. Isolation of talathermophilins from the thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus YM3-4. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.-P.; Zhu, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.-P.; Chu, Y.-S.; Wang, Y.-L.; Zhang, J.-X.; Wu, D.-K.; Zhang, K.-Q.; Niu, X.-M. Thermolides, potent nematocidal pks-nrps hybrid metabolites from thermophilic fungus Talaromyces thermophilus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 20306–20309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Ye, P.; Chen, A.C.-T.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; He, S.; Wu, X.; Gan, L.; Ye, Y.; Wu, B. Two novel hepatocellular carcinoma cycle inhibitory cyclodepsipeptides from a hydrothermal vent crab-associated fungus Aspergillus clavatus C2WU. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-W.; Li, C.-W.; Cui, C.-B.; Hua, W.; Zhu, T.-J.; Gu, Q.-Q. Nine new and five known polyketides derived from a deep sea-sourced Aspergillus sp. 16-02-1. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Shi, Y.; Auckloo, N.B.; Chen, X.; Chen, A.C.-T.; Tao, X.; Wu, B. An unusual conformational isomer of verrucosidin backbone from a hydrothermal vent fungus, Penicillium sp. Y-50-10. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; El-Metwally, M.M.; Abdel-Razek, A.A.; Laatsch, H. Terretonin m: A new meroterpenoid from the thermophilic Aspergillus terreus TM8 and revision of the absolute configuration of penisimplicins. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhu, T.; Tao, H.; Lu, Z.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Two new cytotoxic quinone type compounds from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus variecolor. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-L.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Tao, H.-W.; Zhu, T.-J.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Isoechinulin-type alkaloids, variecolorins a–l, from halotolerant Aspergillus variecolor. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-L.; Zhu, T.-J.; Tao, H.-W.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Three novel, structurally unique spirocyclic alkaloids from the halotolerant B-17 fungal strain of Aspergillus variecolor. Chem. Biodivers. 2007, 4, 2913–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.-Y.; Lin, Z.-J.; Wang, W.-L.; Du, L.; Zhu, T.-J.; Fang, Y.-C.; Gu, Q.-Q.; Zhu, W.-M. Citrinin dimers from the halotolerant fungus Penicillium citrinum B-57. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Tao, H.; Peng, X.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cerebrosides of the halotolerant fungus Alternaria raphani isolated from a sea salt field. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1695–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhu, H.; Hong, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Peng, X.; Zhu, W. Novel cyclic hexapeptides from marine-derived fungus, Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 5262–5265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Hong, K.; Liu, P.; Zhu, W. Cyclic tripeptides from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zheng, J.-K.; Qu, H.-J.; Liu, P.-P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W.-M. A new cytotoxic indole-3-ethenamide from the halotolerant fungus Aspergillus sclerotiorum PT06-1. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashyal, B.P.; Wijeratne, E.M.K.; Faeth, S.H.; Gunatilaka, A.A.L. Globosumones a−c, cytotoxic orsellinic acid esters from the sonoran desert endophytic fungus Chaetomium globosum. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itabashi, T.; Matsuishi, N.; Hosoe, T.; Toyazaki, N.; Udagawa, S.; Imai, T.; Adachi, M.; Kawai, K. Two new dioxopiperazine derivatives, arestrictins a and b, isolated from Aspergillus restrictus and Aspergillus penicilloides. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 54, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhu, T.; Fang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, W. Unusual C25 steroid isomers with bicyclo[4.4.1]a/b rings from a volcano ash-derived fungus Penicillium citrinum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Hobbs, J.D.; Stokken, J.; Clardy, J. Berkeleydione and berkeleytrione, new bioactive metabolites from an acid mine organism. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Kelly, K. Berkelic acid, a novel spiroketal with selective anticancer activity from an acid mine waste fungal extremophile. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 5357–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Patacini, B. The berkeleyacetals, three meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste Penicillium. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1820–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bender, C.F.; Paradise, C.L.; Lynch, V.M.; Yoshimoto, F.K.; De Brabander, J.K. A biosynthetically inspired synthesis of (−)-berkelic acid and analogs. Tetrahedron 2018, 74, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stierle, A.A.; Stierle, D.B.; Patacini, B. The berkeleyamides, amides from the acid lake fungus Penicillum rubrum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Patacini, B.; McIntyre, K.; Girtsman, T.; Bolstad, E. Berkeleyones and related meroterpenes from a deep water acid mine waste fungus that inhibit the production of interleukin 1-β from induced inflammasomes. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stierle, D.B.; Stierle, A.A.; Girtsman, T.; McIntyre, K.; Nichols, J. Caspase-1 and -3 inhibiting drimane sesquiterpenoids from the extremophilic fungus Penicillium solitum. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





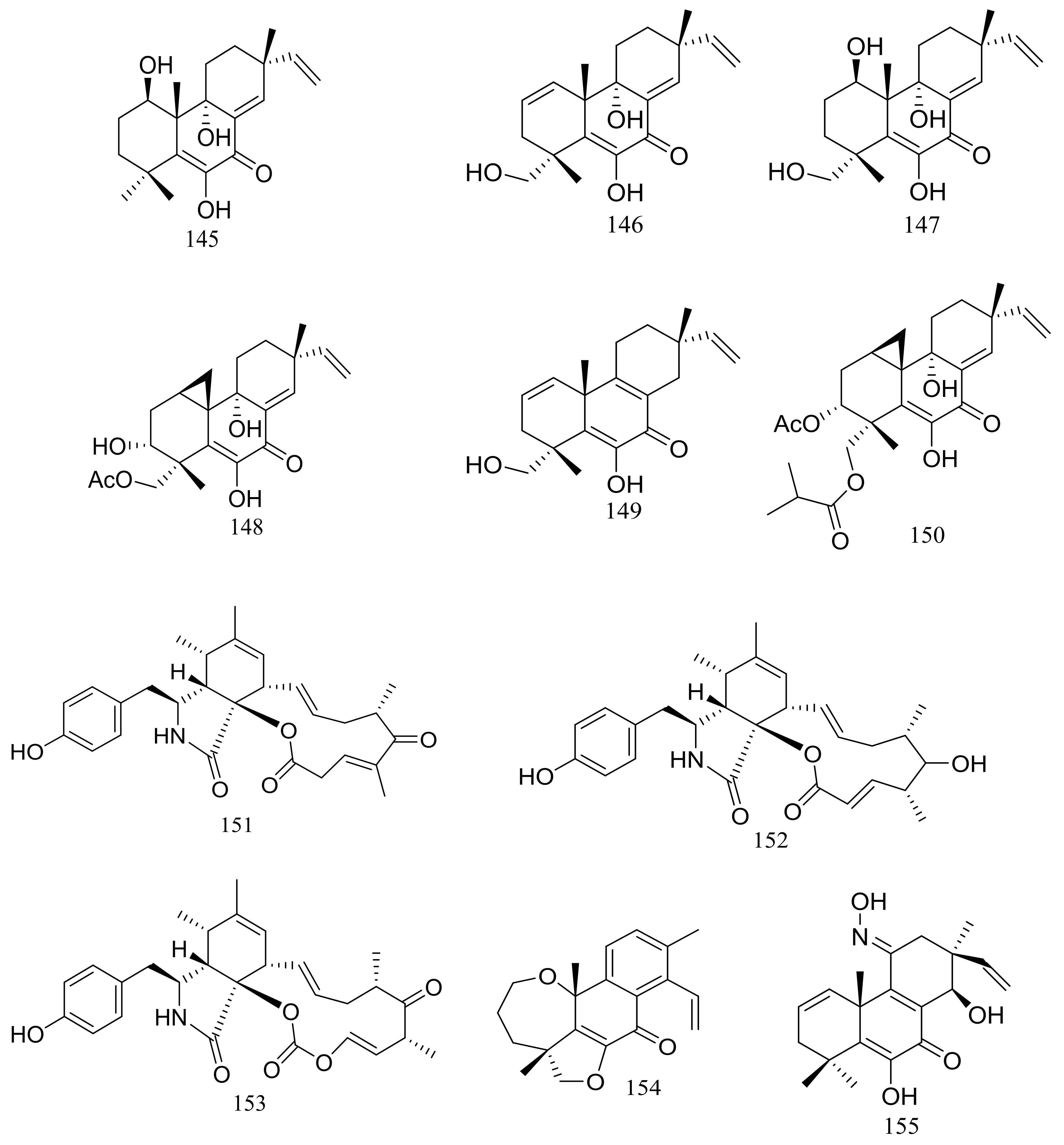
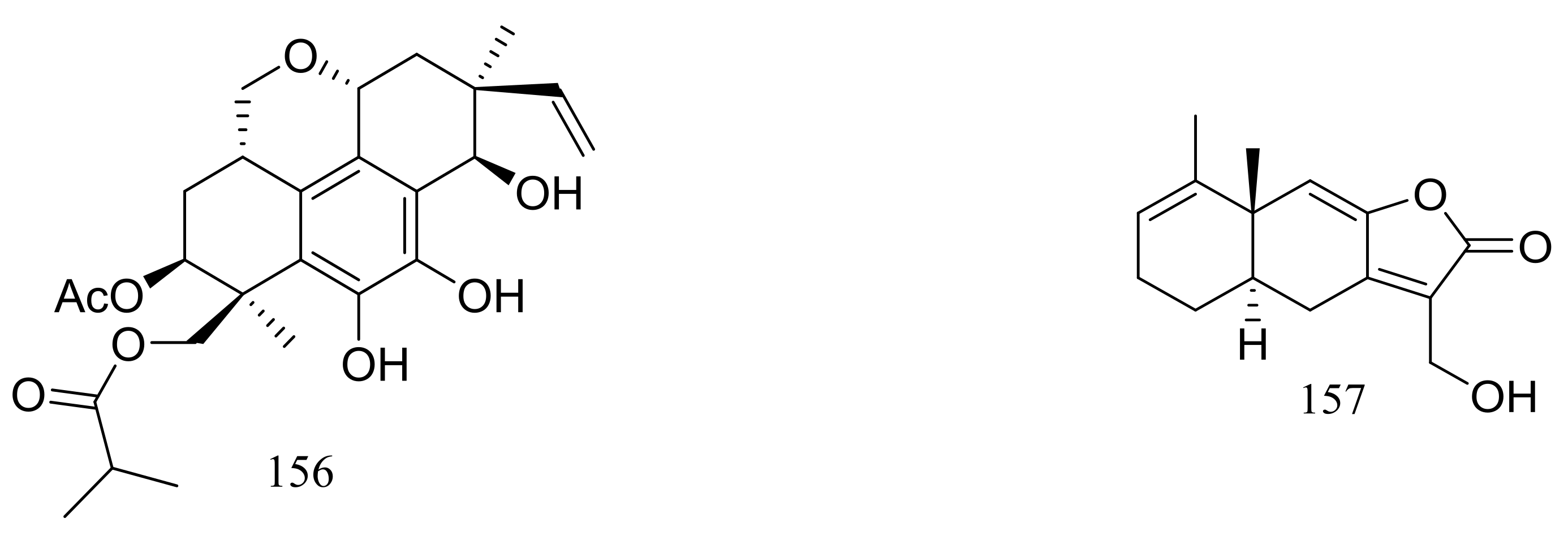
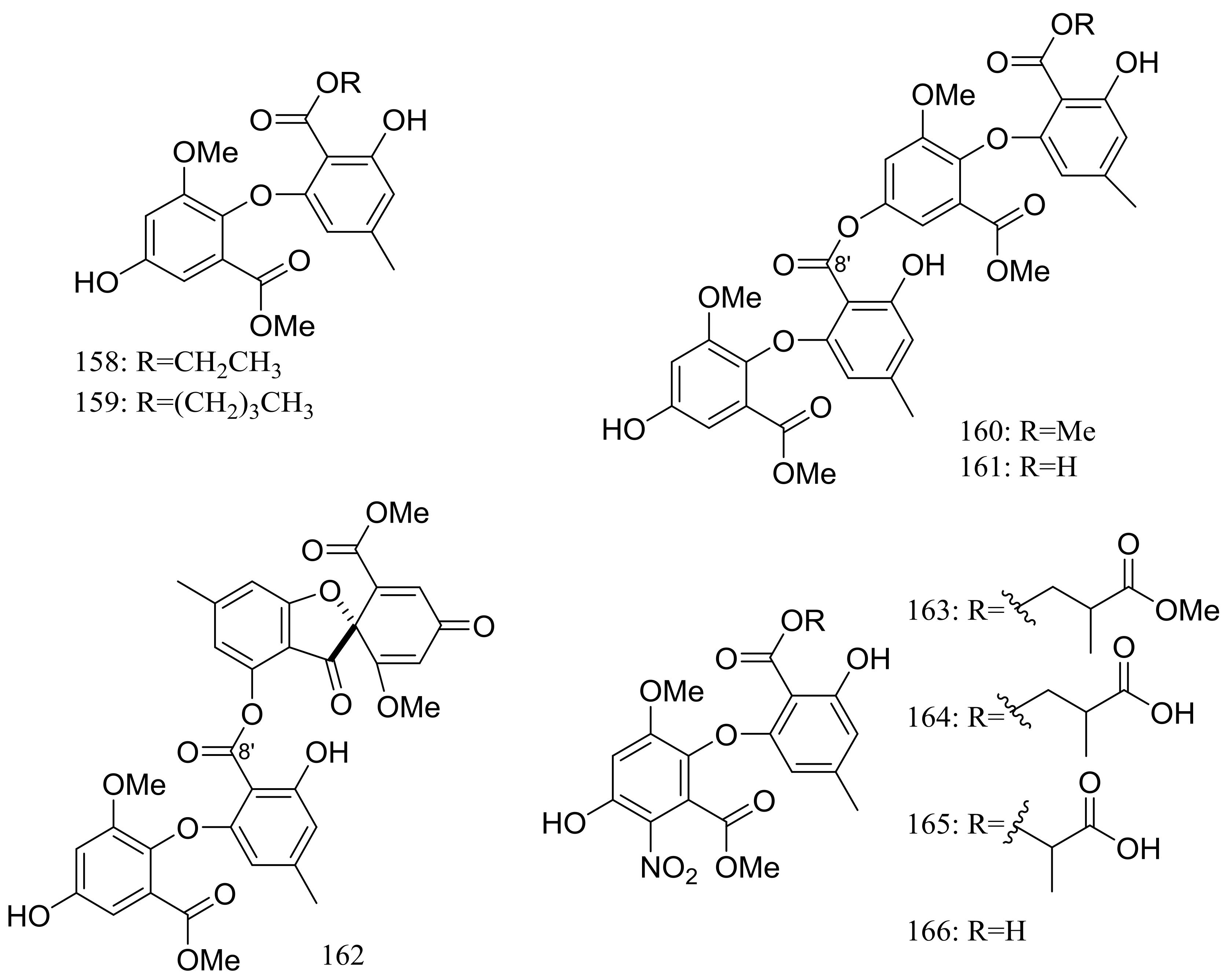
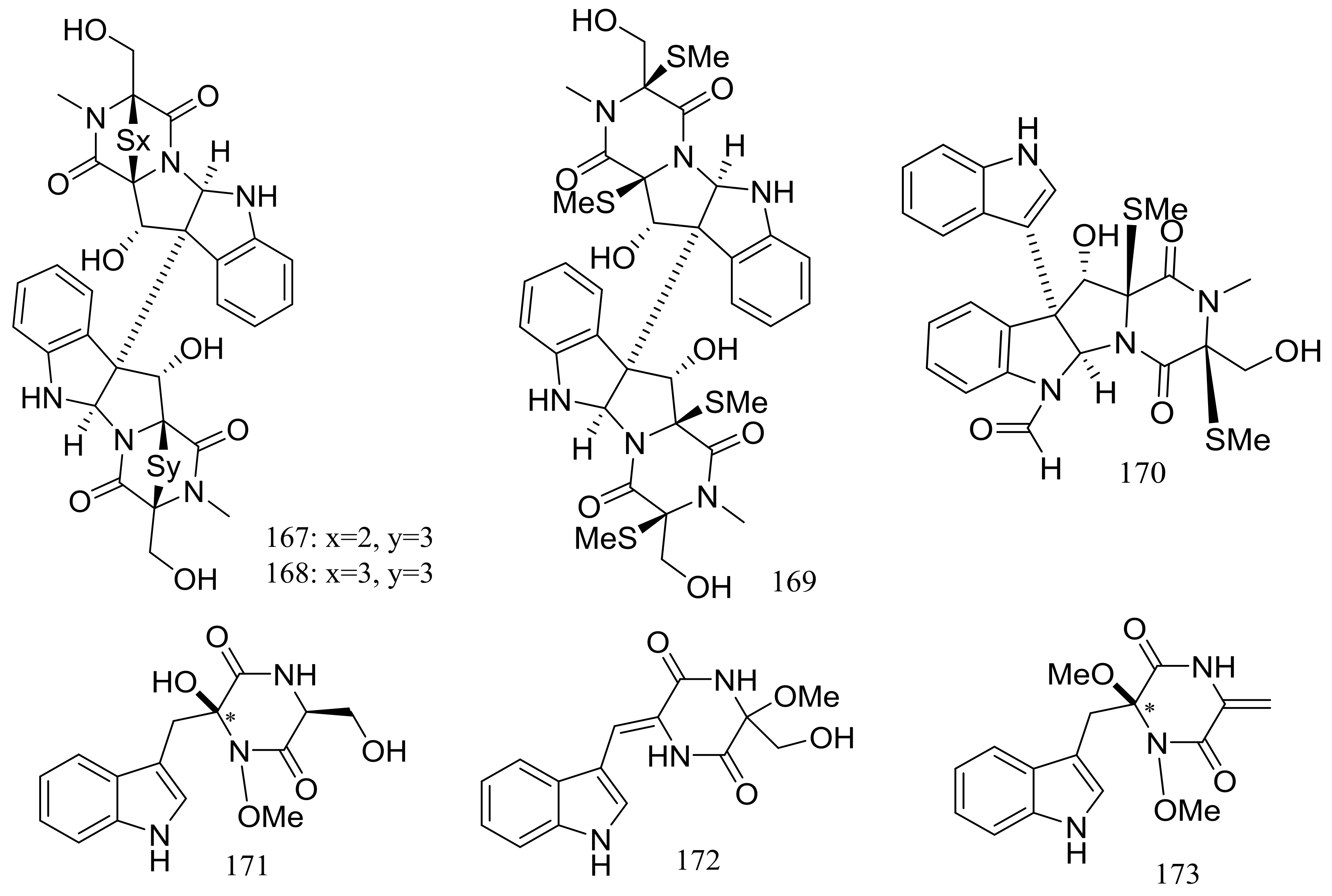




| The Type of Compound | Compounds | Biological Activity | References |
|---|---|---|---|
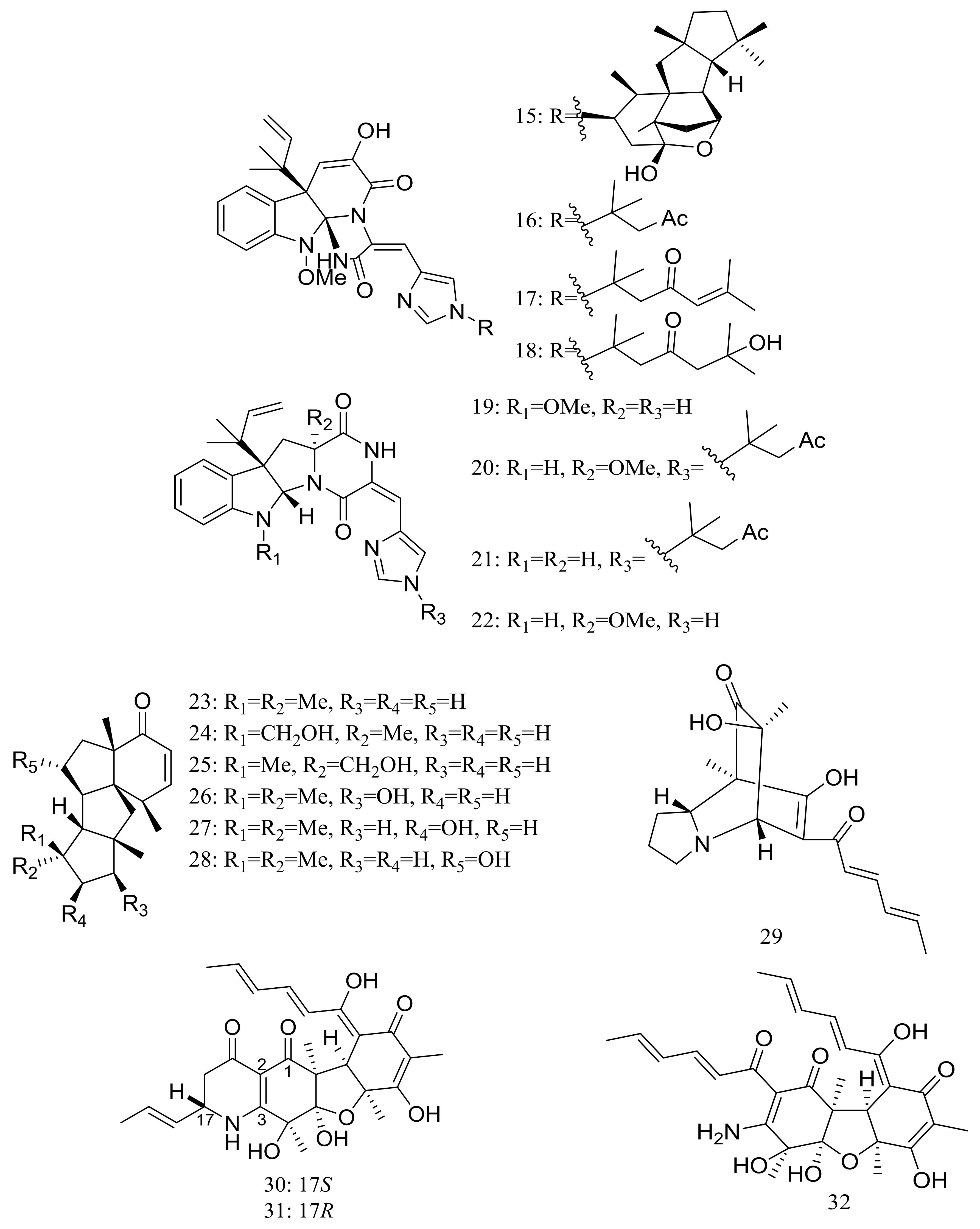
| Terpenoids and steroids | 23, 24 *, 25–28 | Cytotoxic | [25] |
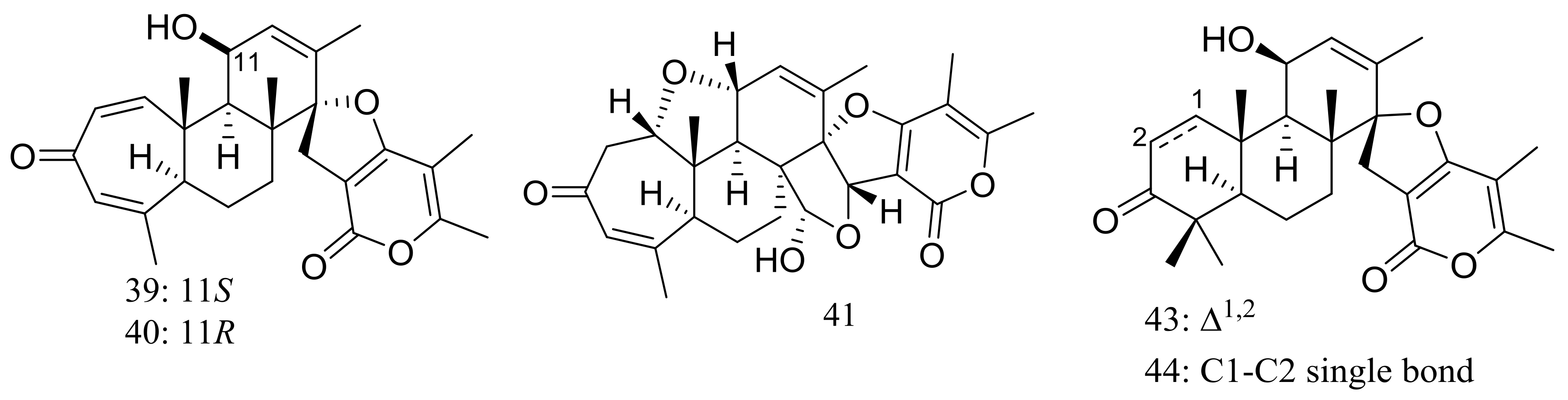
| (39–41) *, 42, 43 *, 44, 45 | Cytotoxic and/or antiviral | [29,30] | |
| (145–150) *, 154, 155 *, 156, 157 * | Cytotoxic and/or antimicrobial | [52,53,56,57] | |
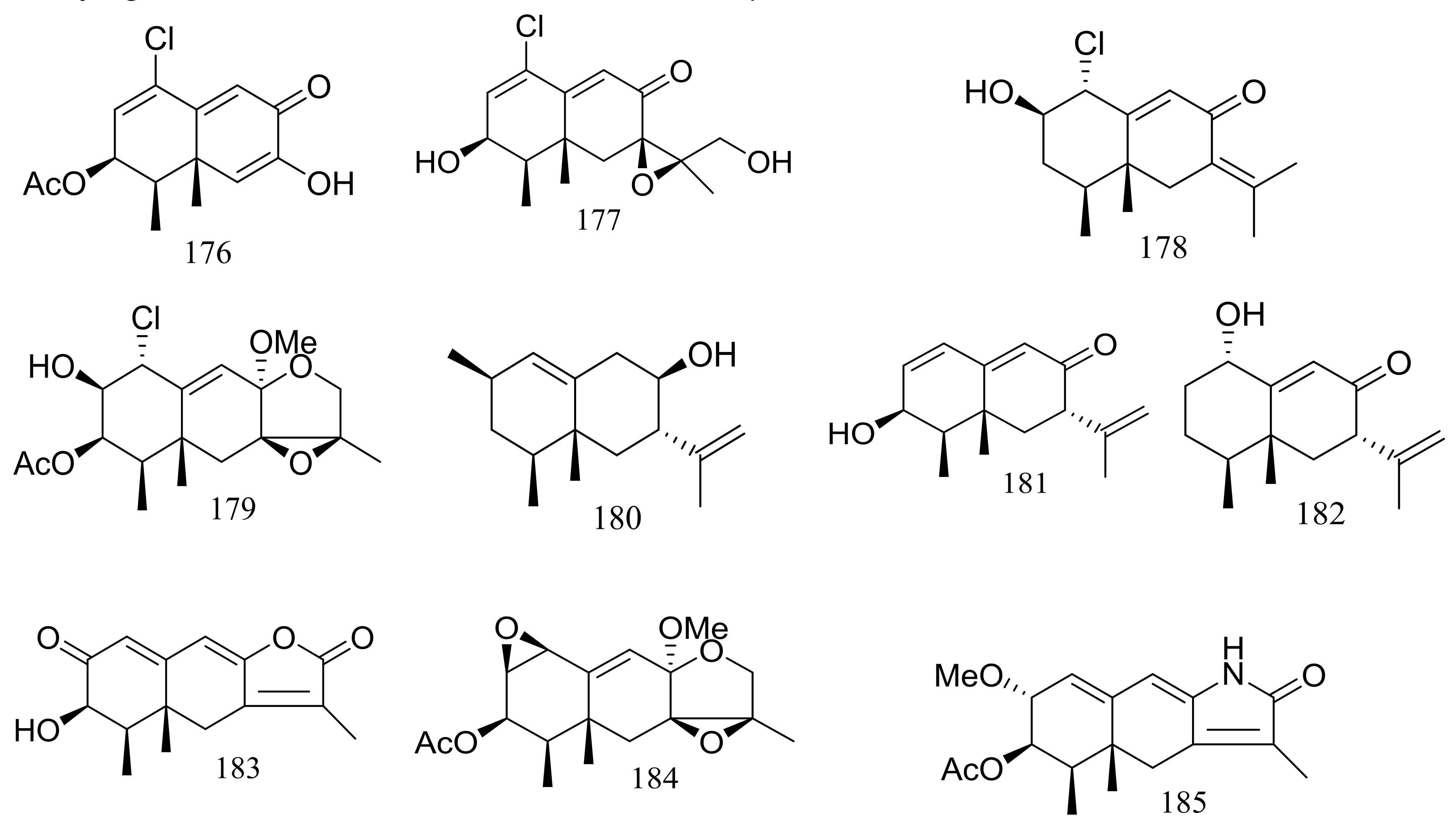
| 176 *, 177–179, 180 *, 181–183, 184 * | Cytotoxic | [62,63] | |
| 190, 191 | [66] | ||
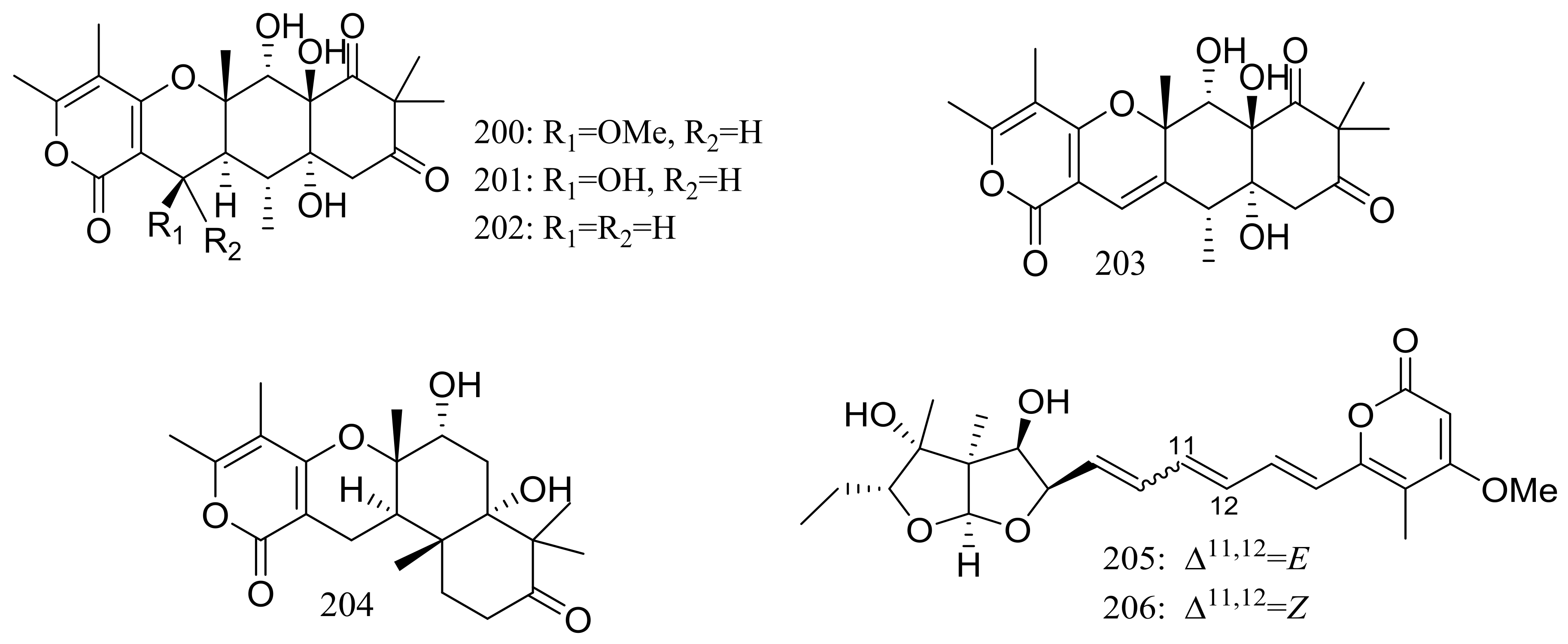
| 200 *, 201–204 | Antiviral | [69] | |
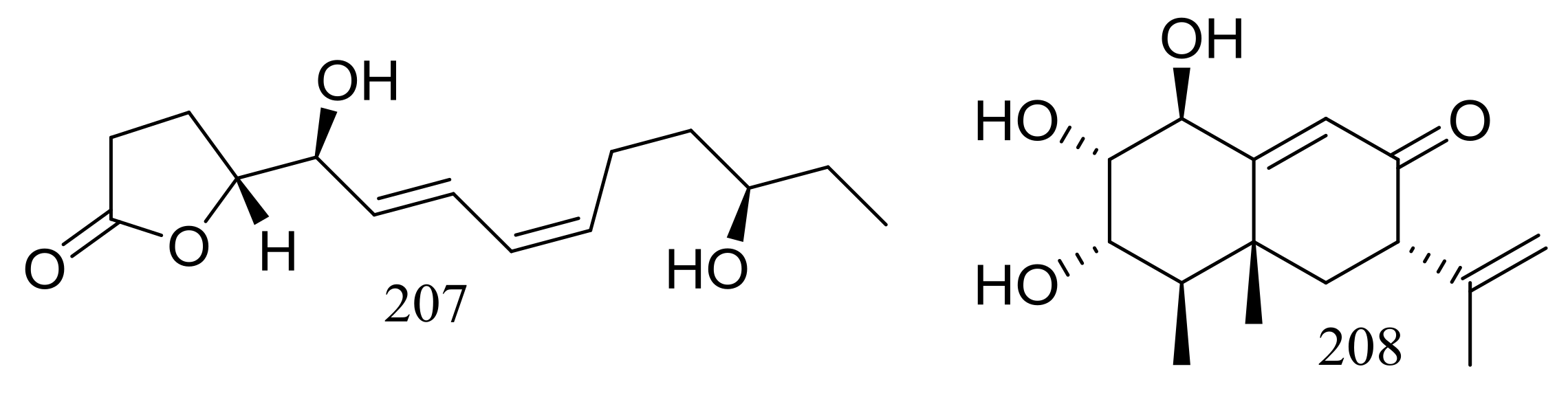
| 208 | [70] | ||
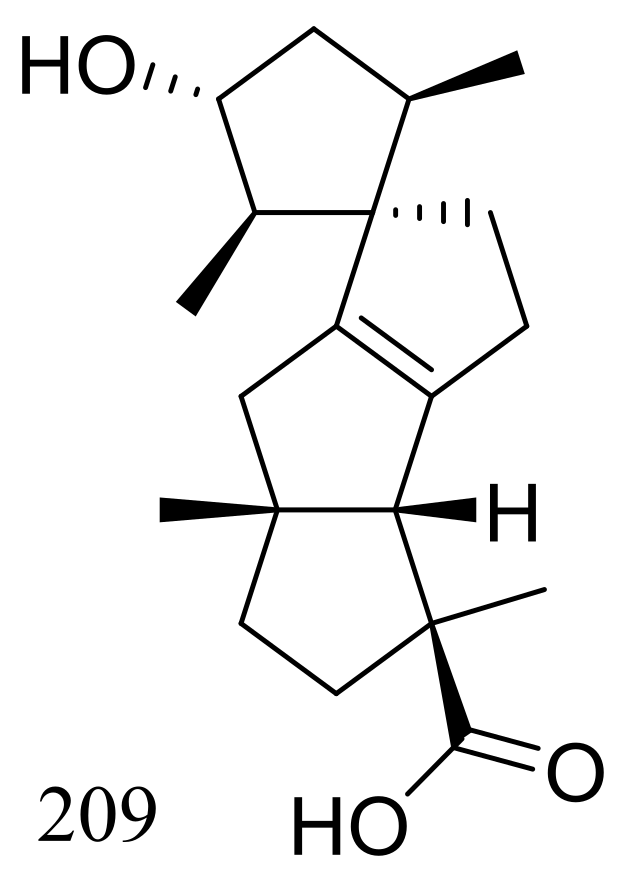
| 209 | Antiallergic | [71] | |
| 245 | [80] | ||
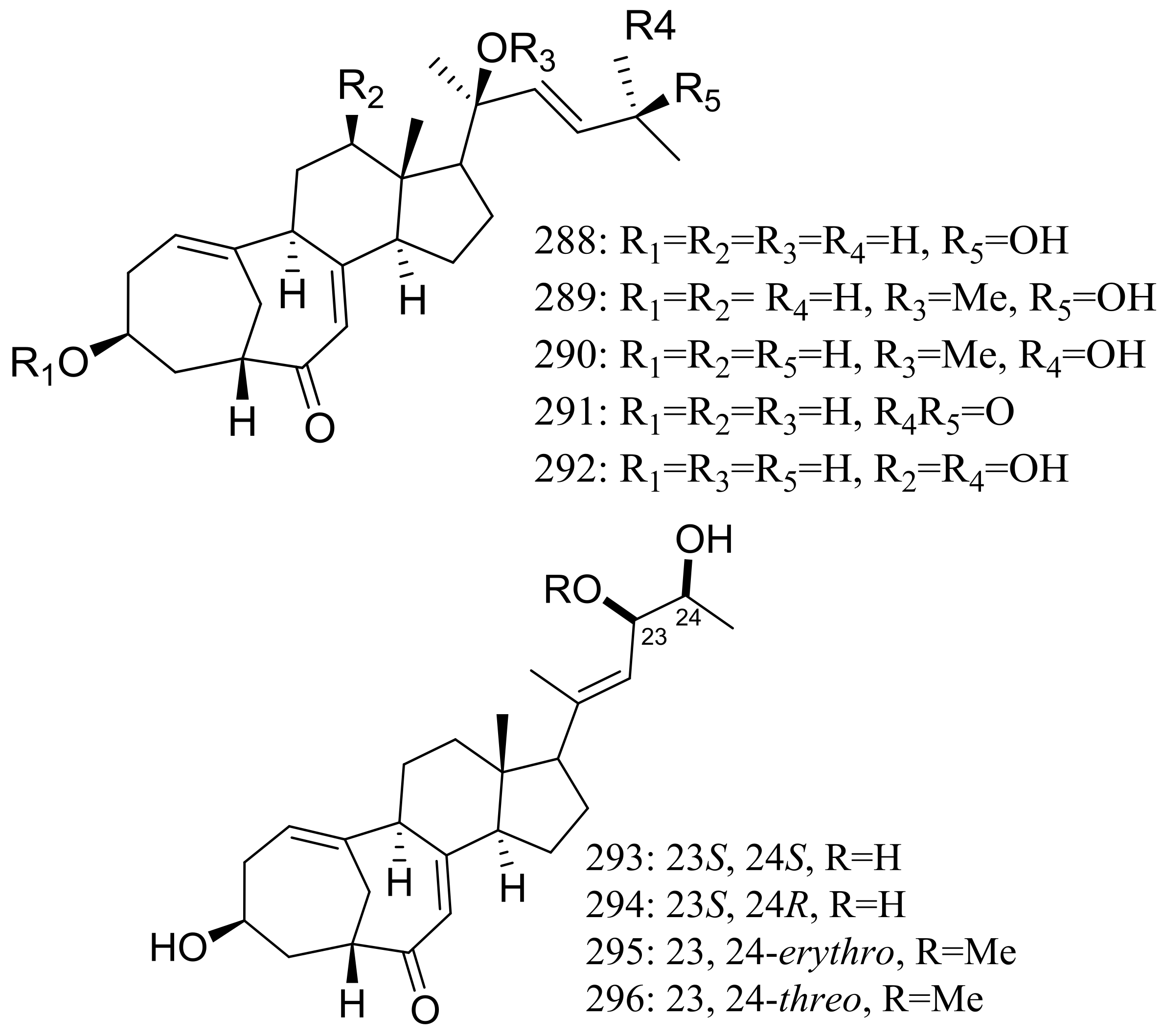
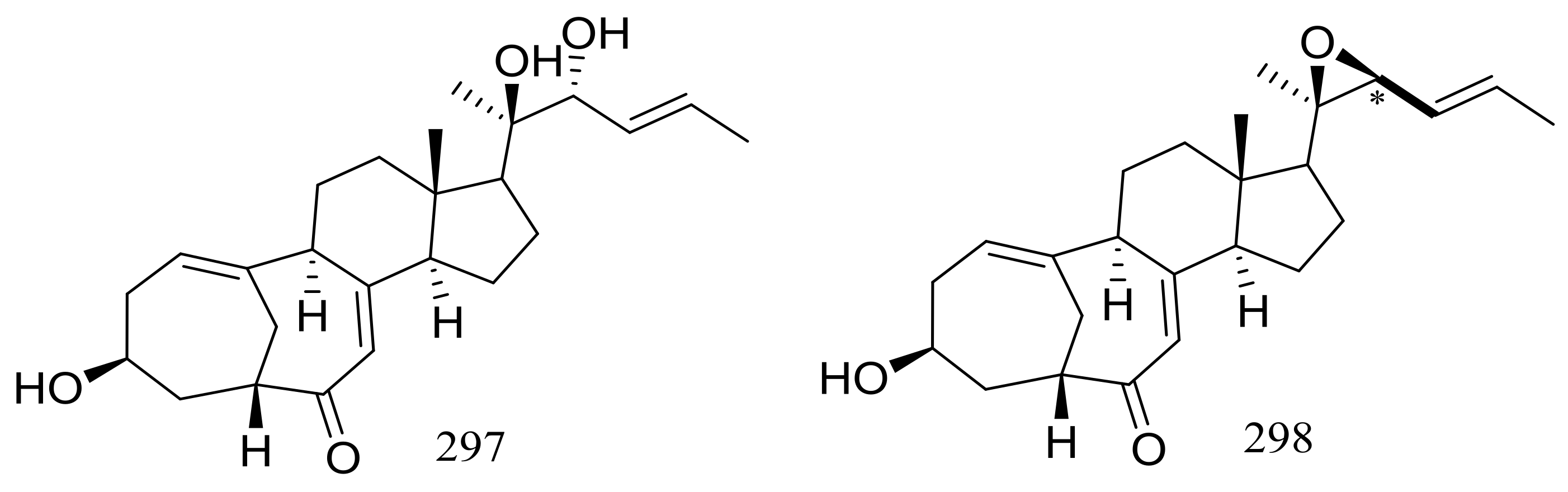
| 288 *, 289–292, 293 *, 294, 295, 296 *, 297, 298 | Induce cAMP production | [91] | |
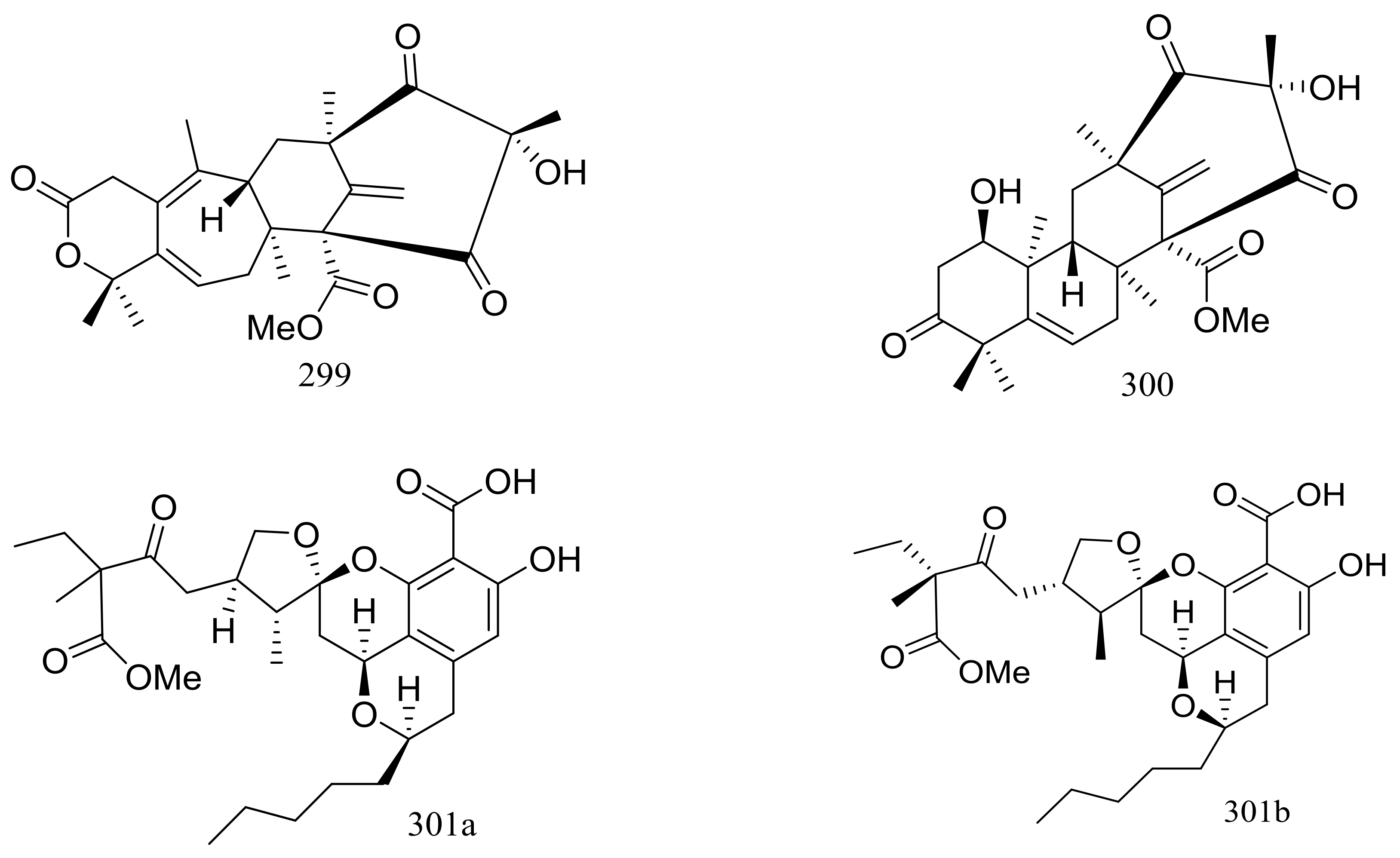
| 299 *, 300 * | Inhibit MMP-3 and Casp-1 and/or cytotoxic | [92] | |
| 309 *, 310 *, 311 | Mitigate IL-1β production | [97] | |
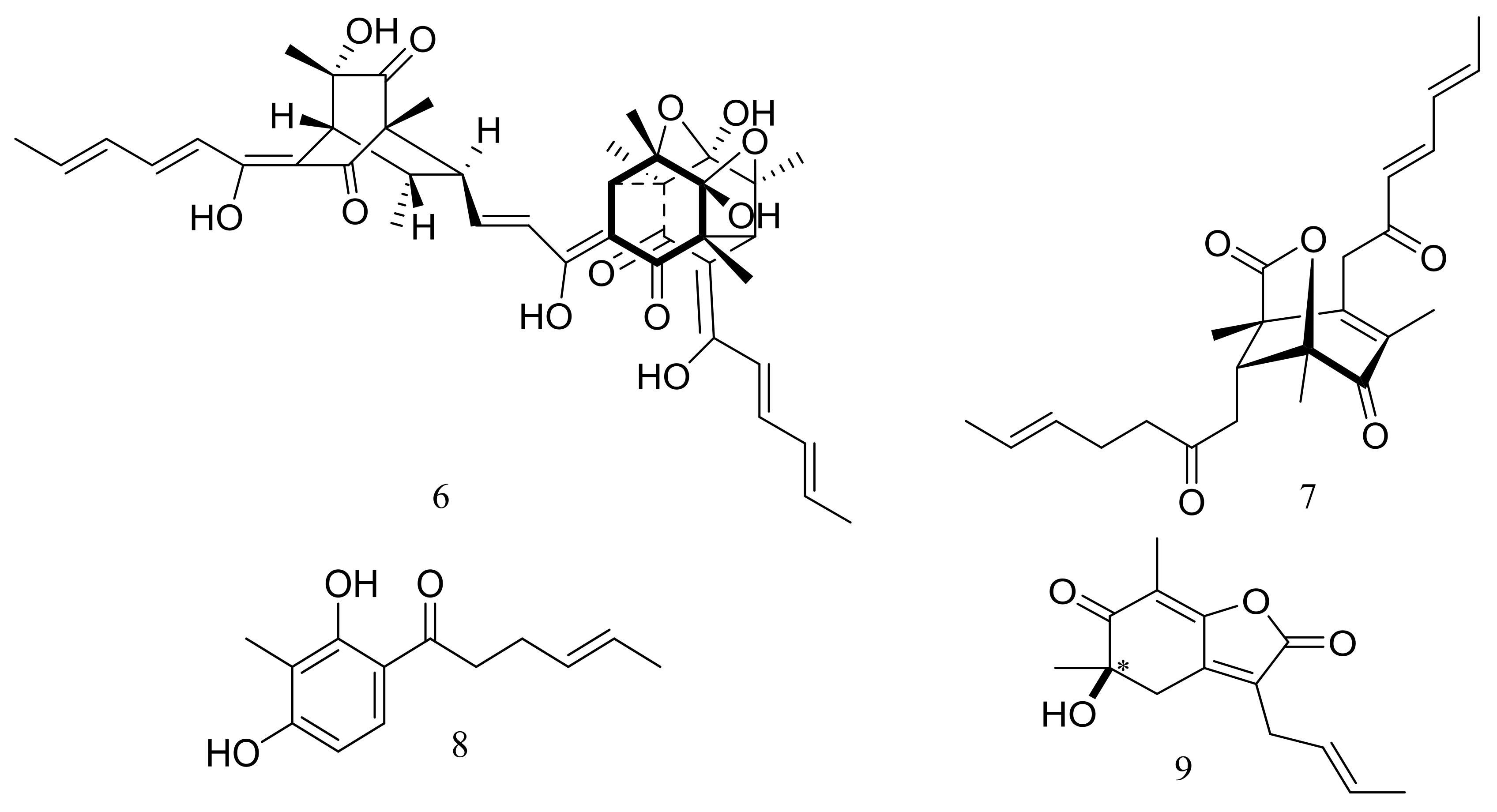
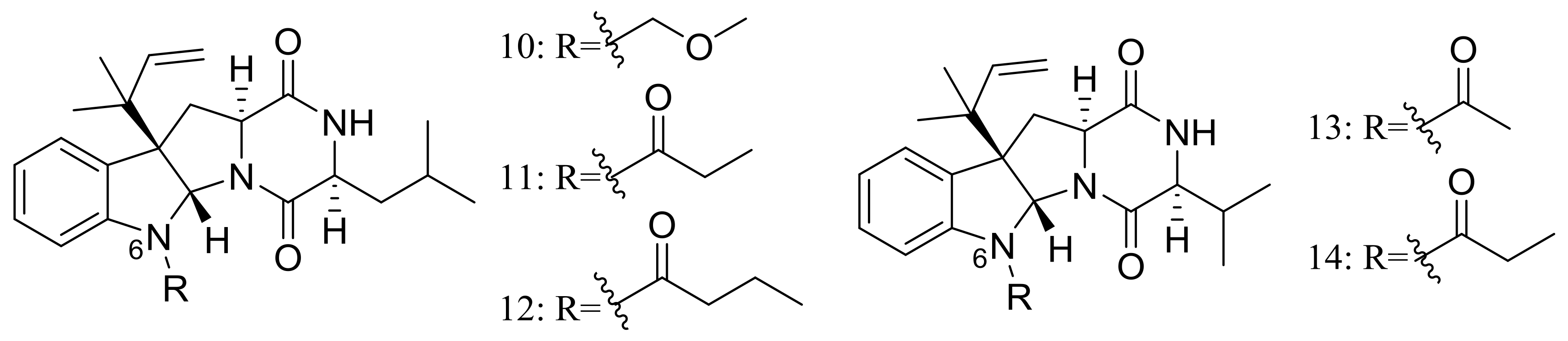
| Alkaloids, peptides, and amides | 10, 11 *, 12, 13, 14 * | Anti-inflammatory | [24] |
| 15 *, 16, 17 *, 18 *, 19–22 | Cytotoxic | [25,26] | |
| 29–33 | [27] | ||
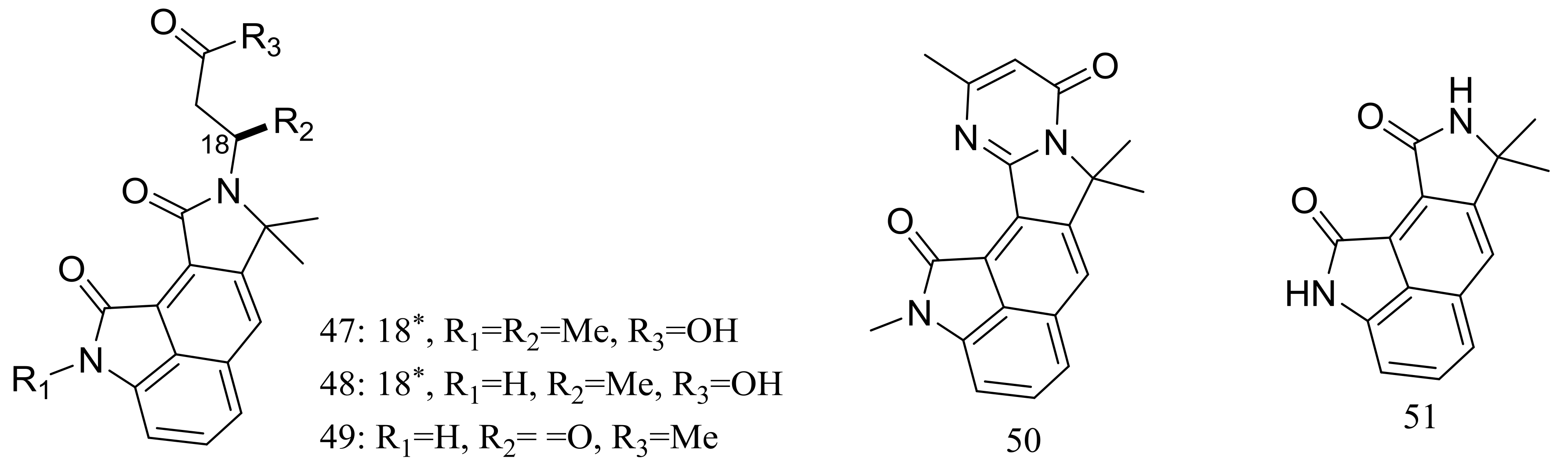
| (47–55) * | Insecticidal | [32] | |
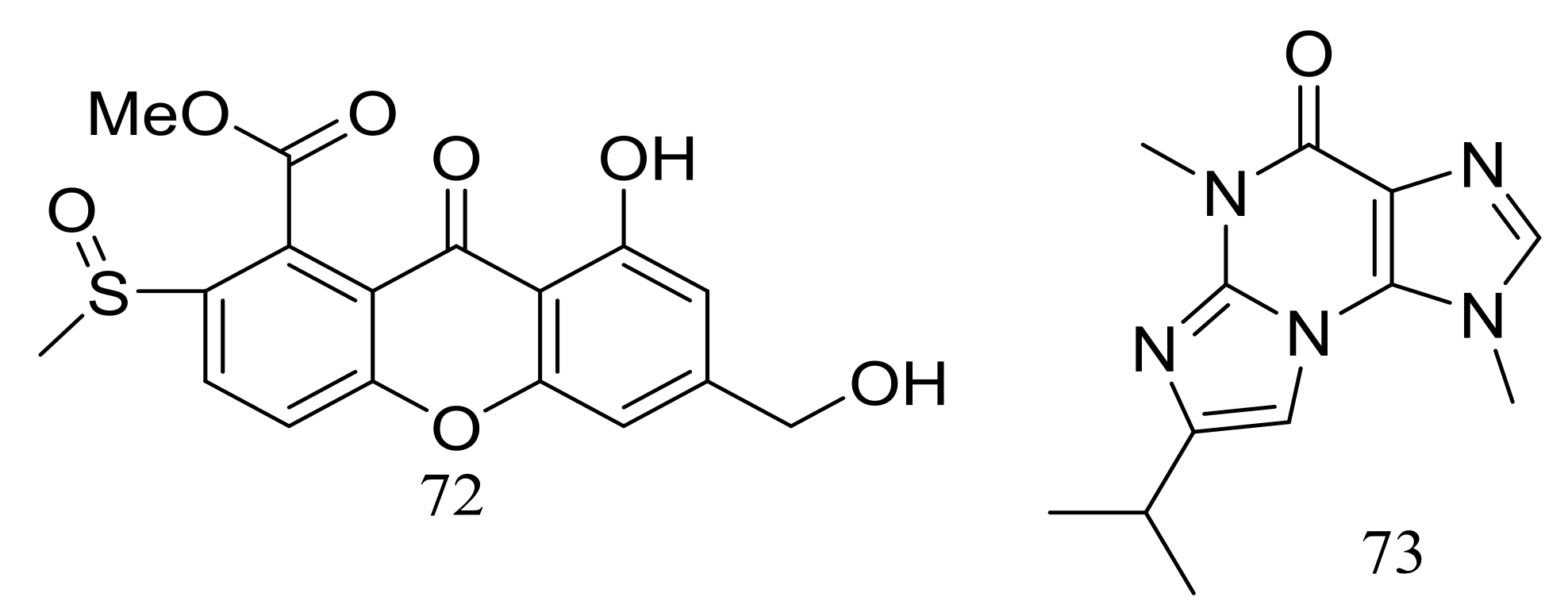
| 73 | [36] | ||
| 74 *, 75, 76 | Inhibit α-glucosidase | [37] | |
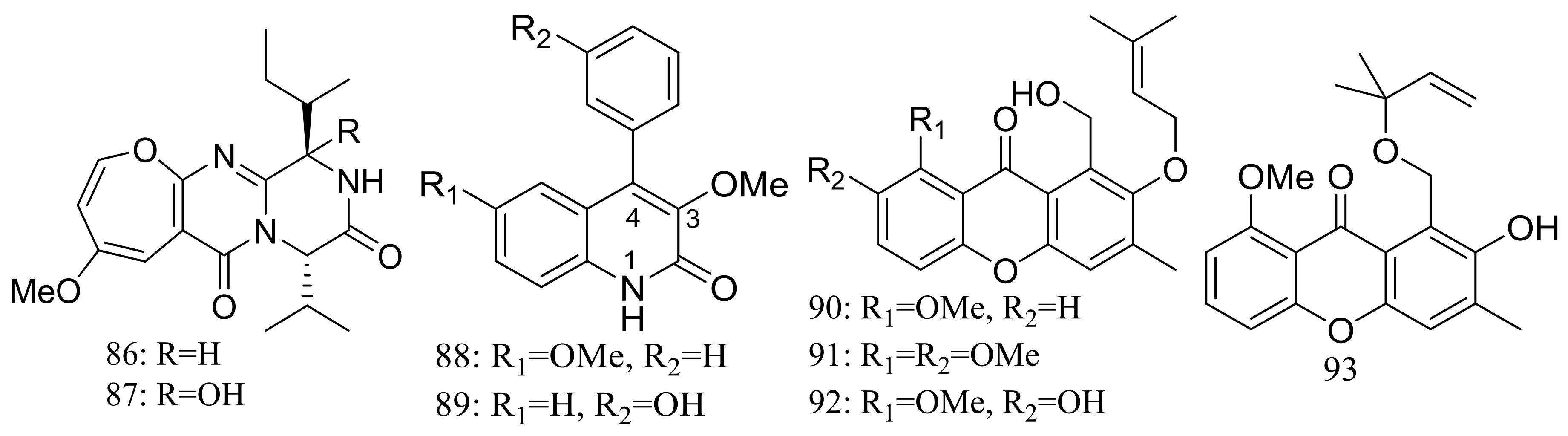
| 86 *, 87 *, 88, 89 | Antimicrobial | [40] | |
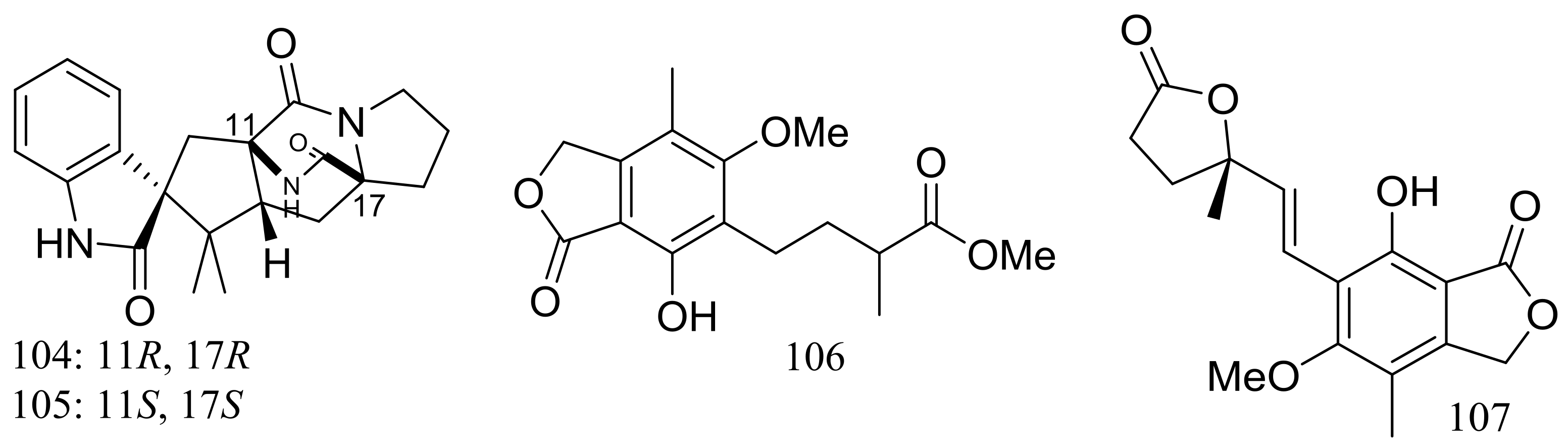
| 104, 105 | [43] | ||
| 108, 112 | [44] | ||
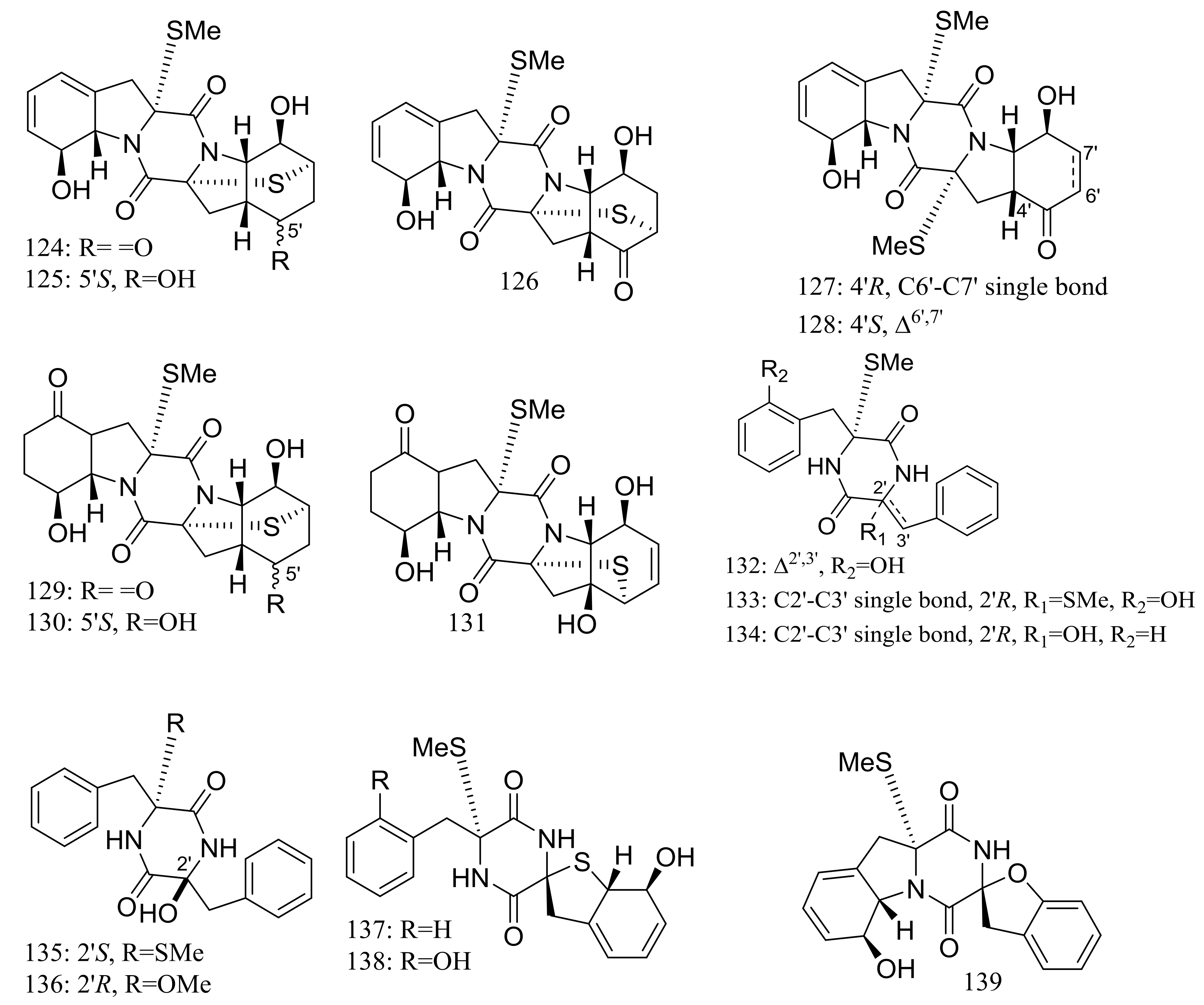
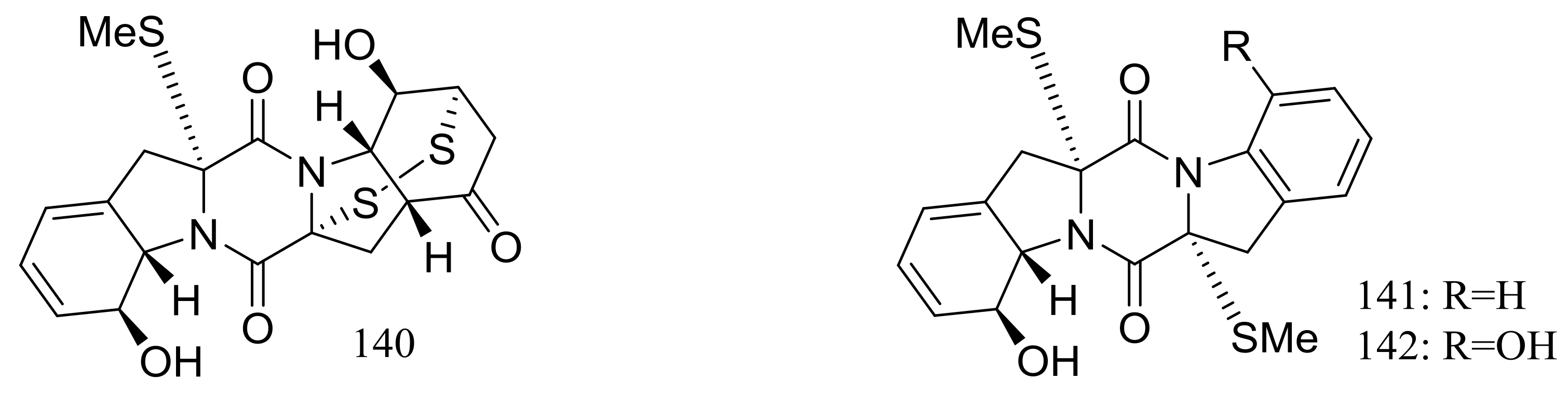
| (124–135) *, 136–138, (139–142) * | Antiviral or antimicrobial | [48,49] | |
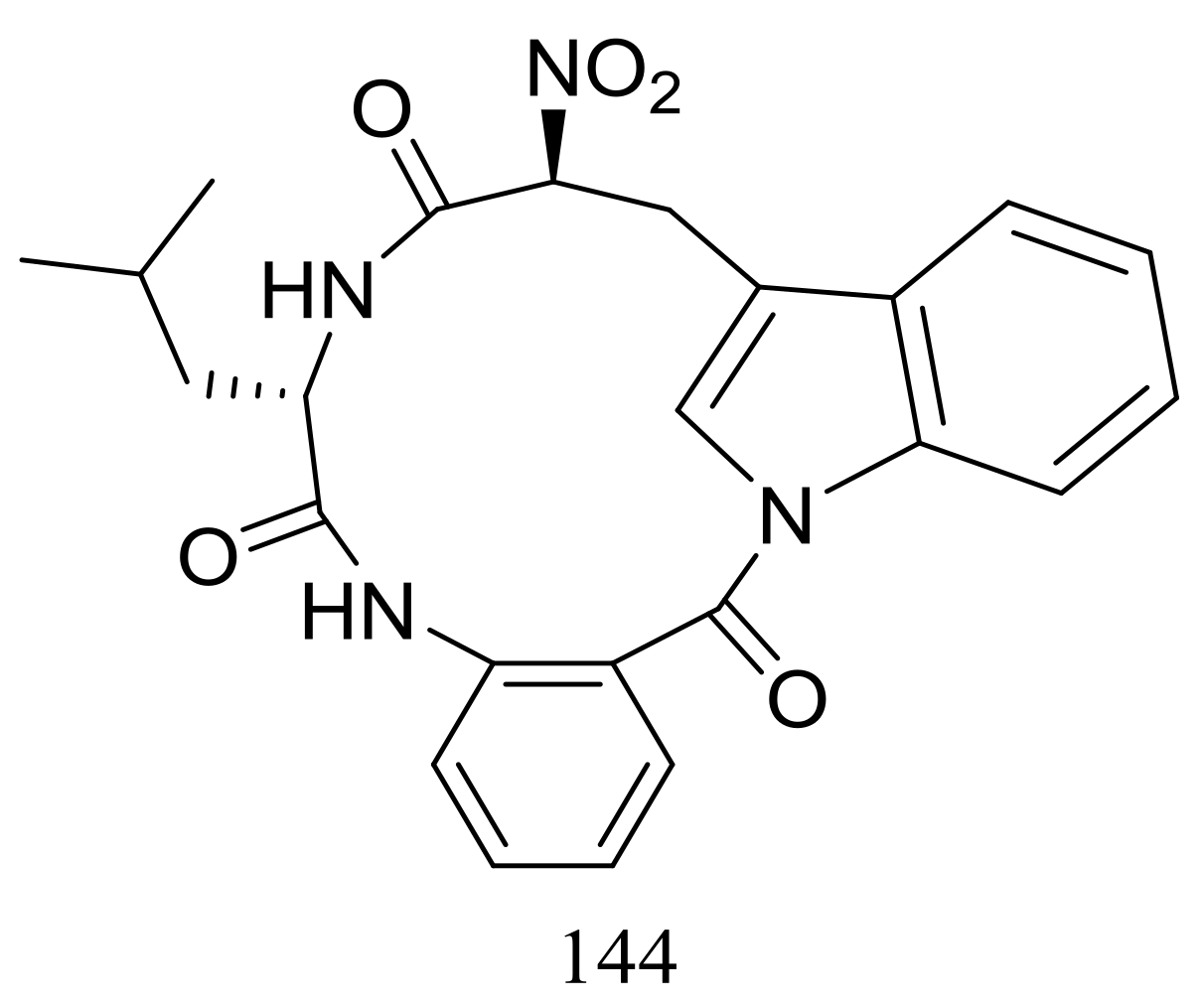
| 144 * | Cytotoxic | [51] | |
| 151 *, 152, 153 | Cytotoxic | [55] | |
| (167–169) *, 170–173 | Cytotoxic | [60] | |
| 185 | [63] | ||
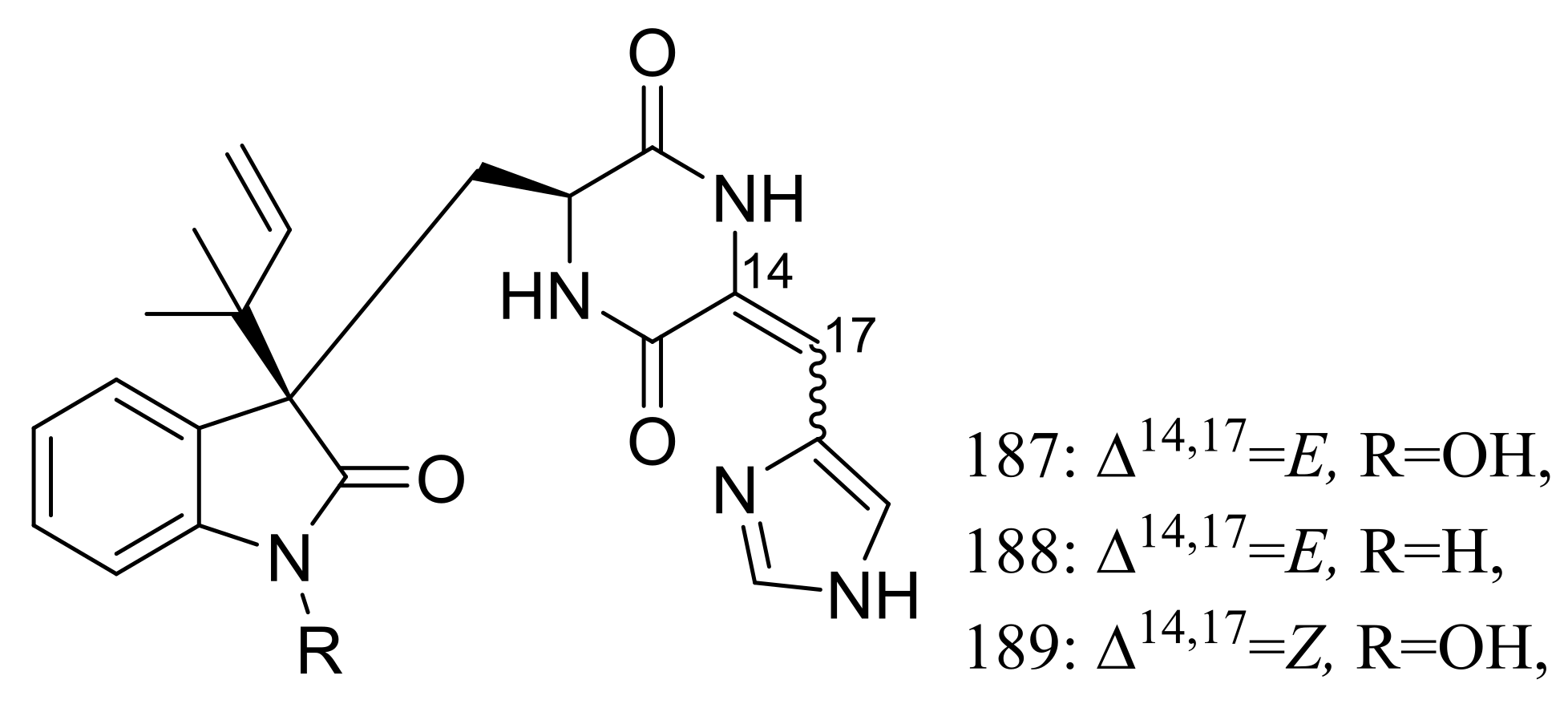
| 187–189 | [65] | ||
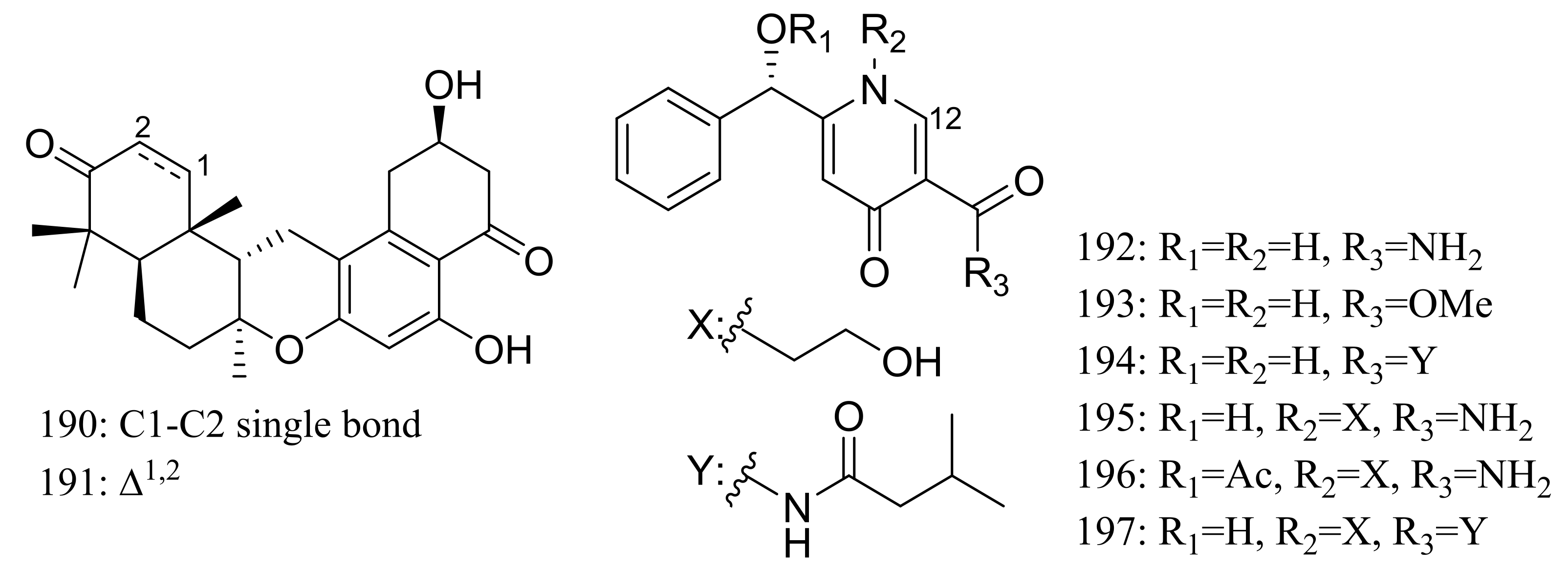
| 192 *, 193 *, 194, 195, 196 *, 197 | Reduce intracellular lipid accumulation | [67] | |
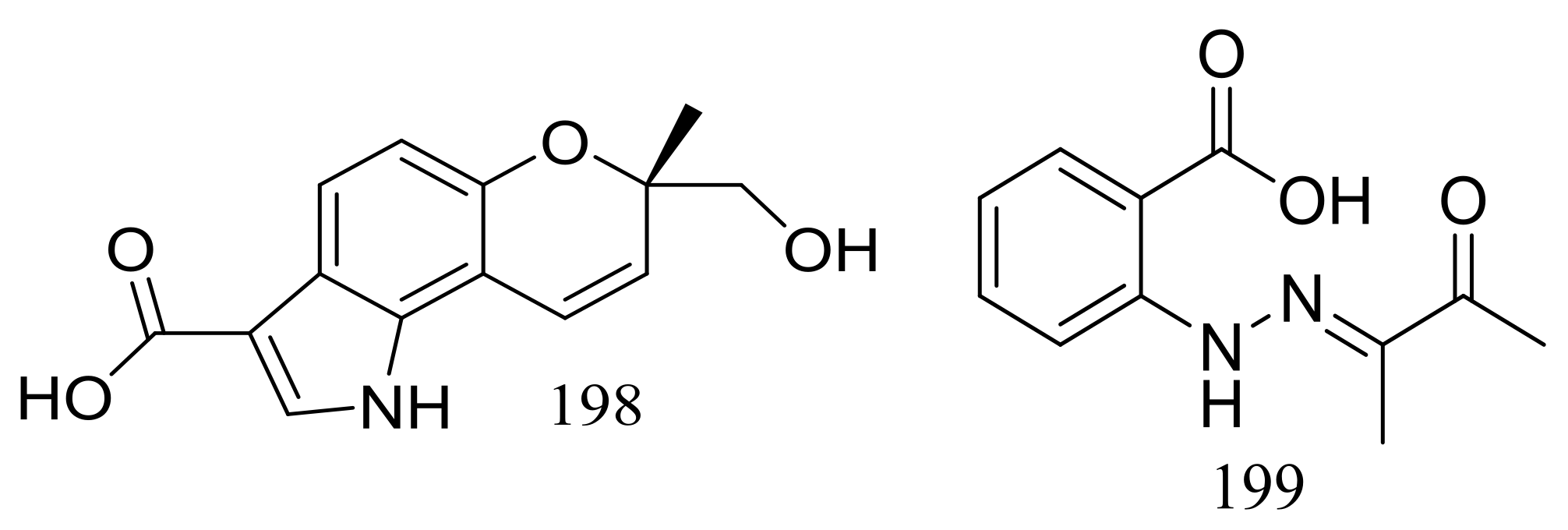
| 198, 199 * | Antimicrobial | [68] | |
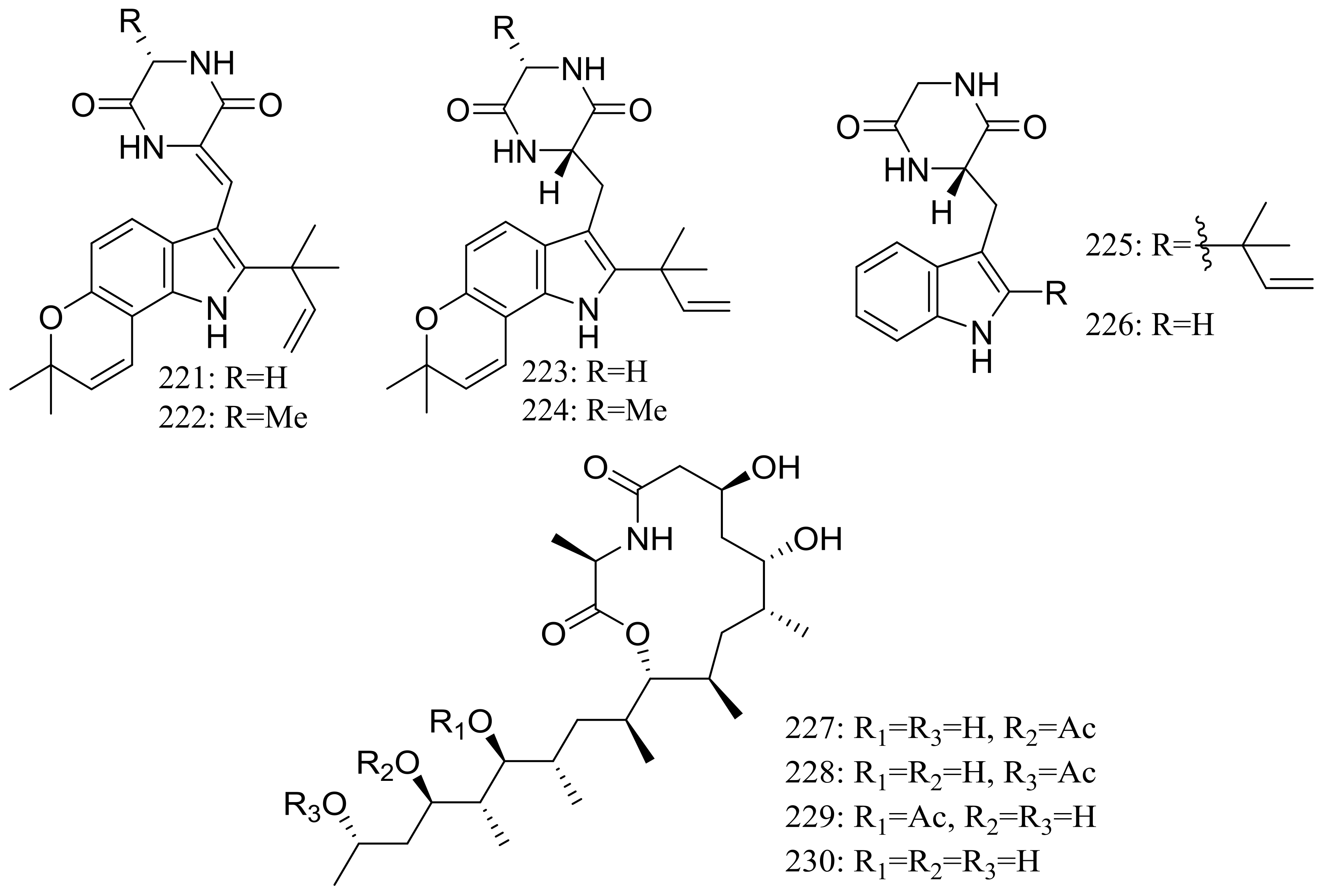
| 221 *, 222 *, 223–226 | Nematicidal | [74,75] | |
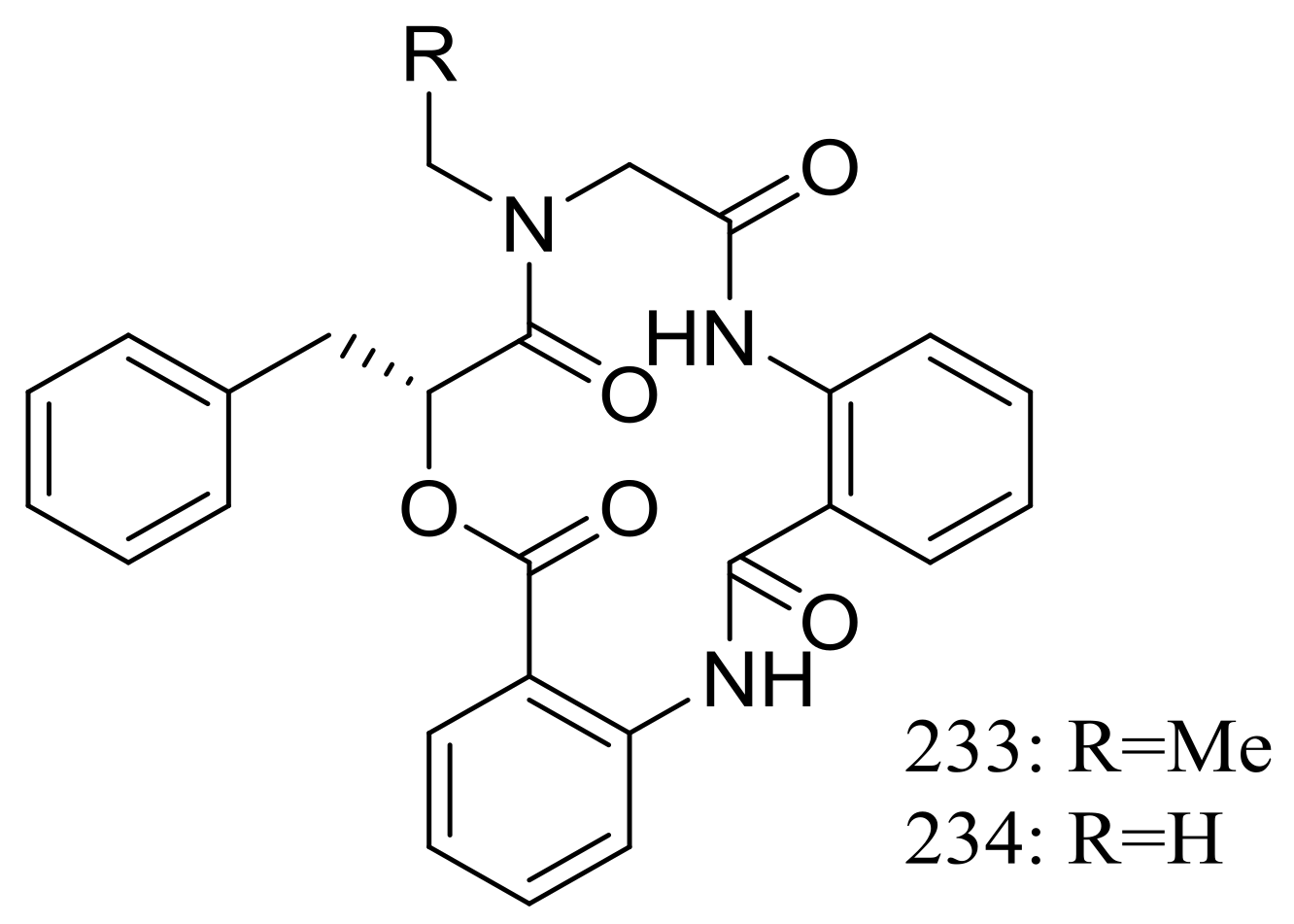
| 233 *, 234 * | Cytotoxic | [77] | |
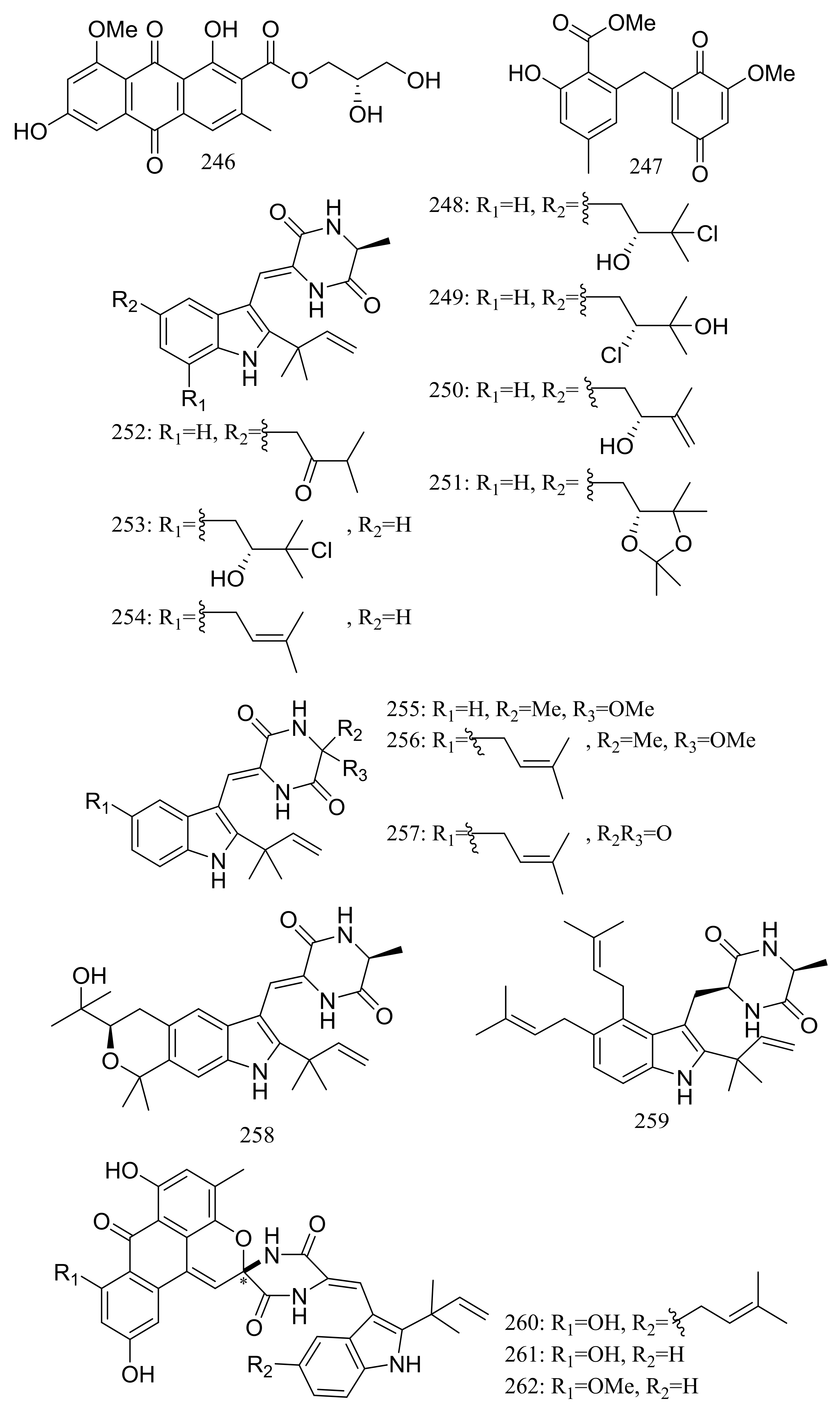
| (248–258) *, 259, (260–262) * | Radical-scavenging and/or cytotoxic | [82,83] | |
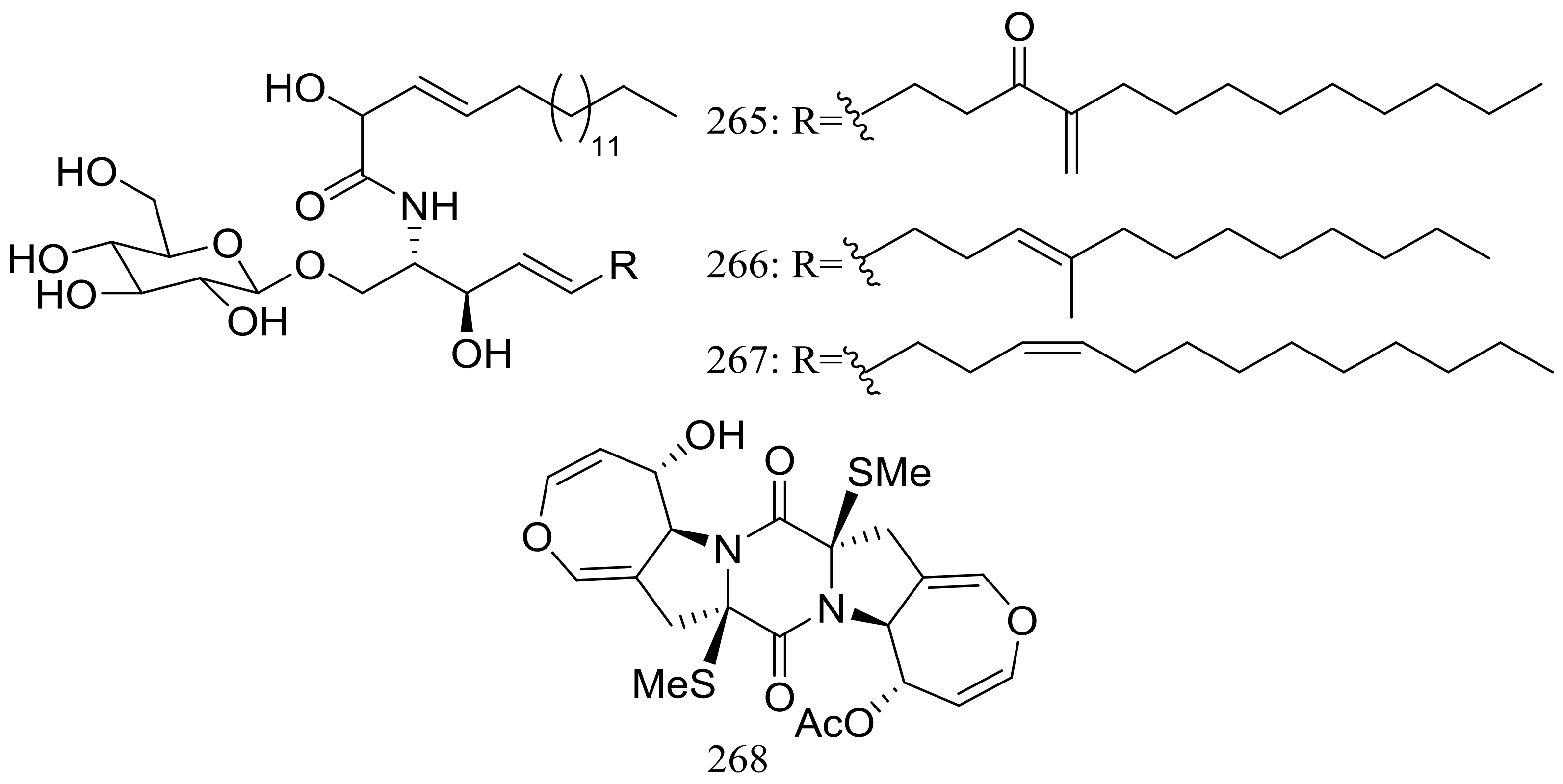
| (265–268) * | Antimicrobial | [85] | |
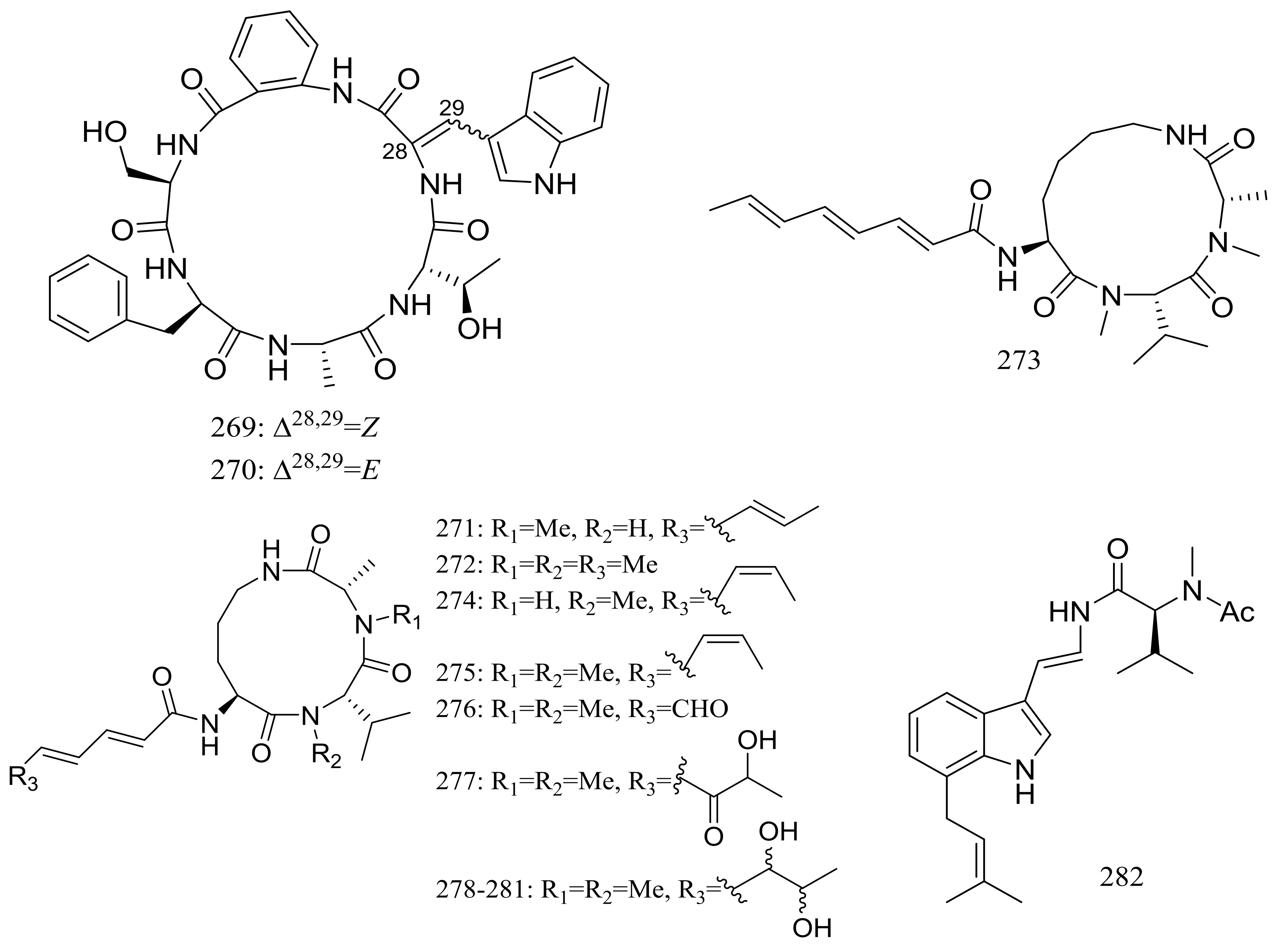
| (269–272) *, 273–275, 276 *, 277, 278, 279 *, 280, 281, 282 * | Antimicrobial and/or cytotoxic | [86,87,88] | |
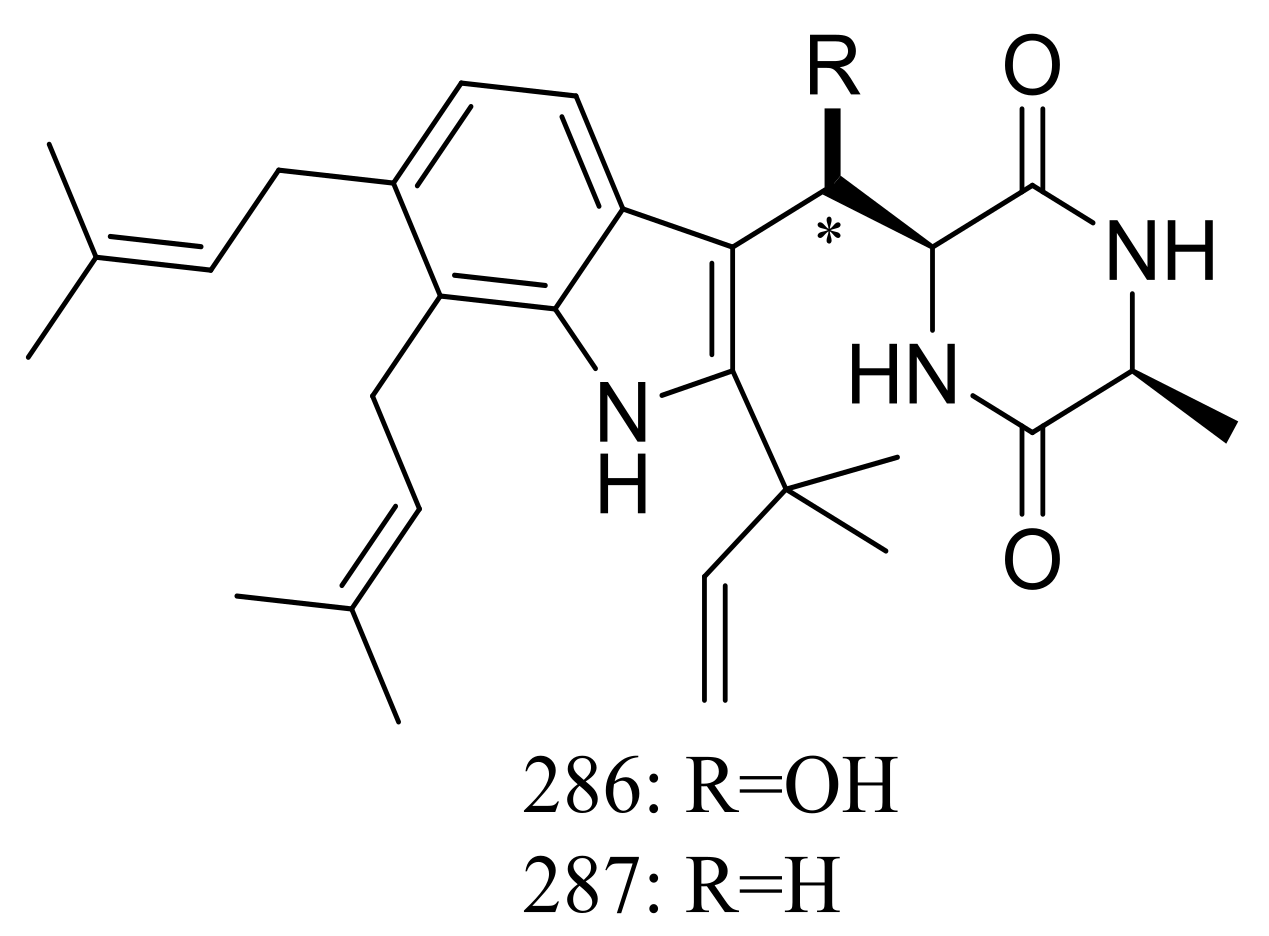
| 286, 287 | [90] | ||
| (305–308) * | Inhibit MMP-3 and Casp-1 | [96] | |
| 312 *, 313 * | Inhibit MMP-3 and Casp-1, and mitigate IL-1β production | [98] | |
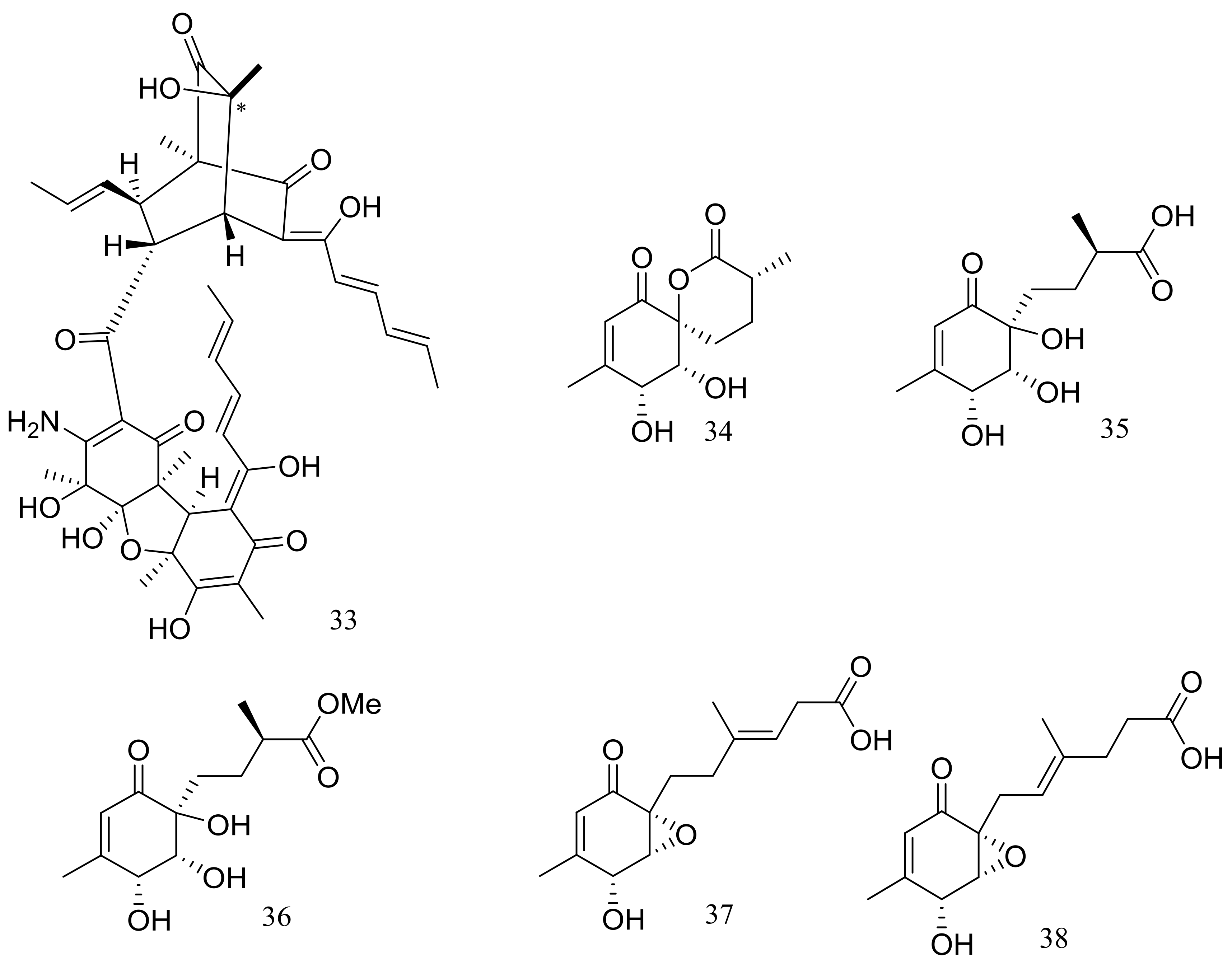
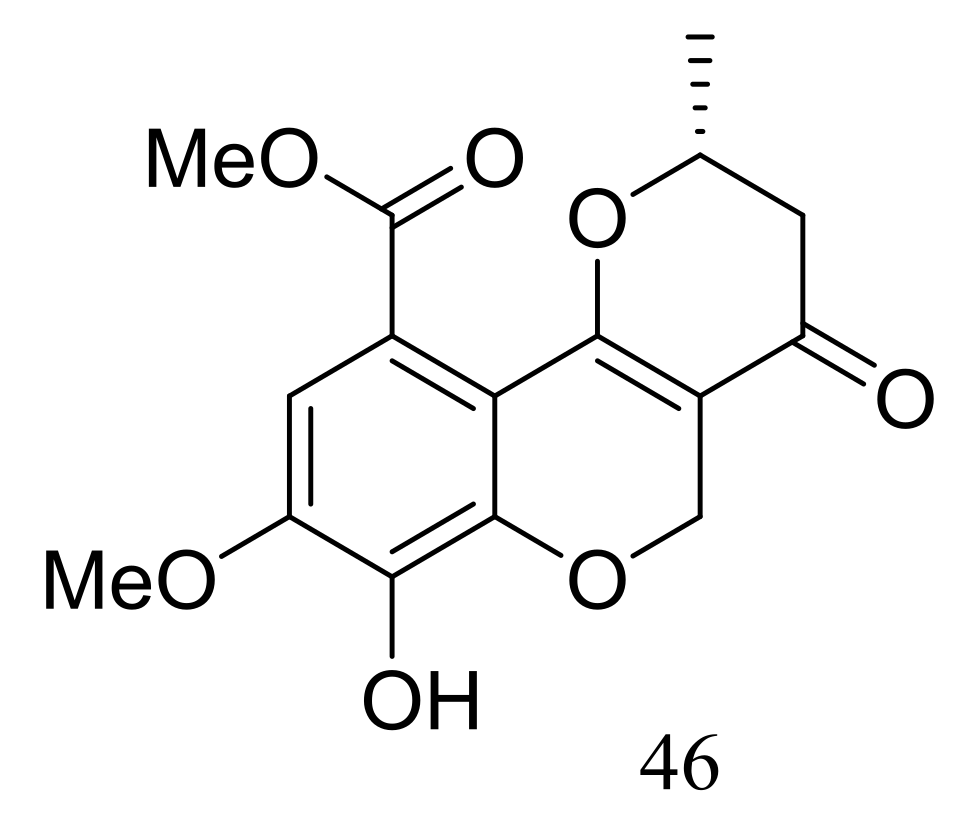
| Quinones and phenols | 46 | [31] | |
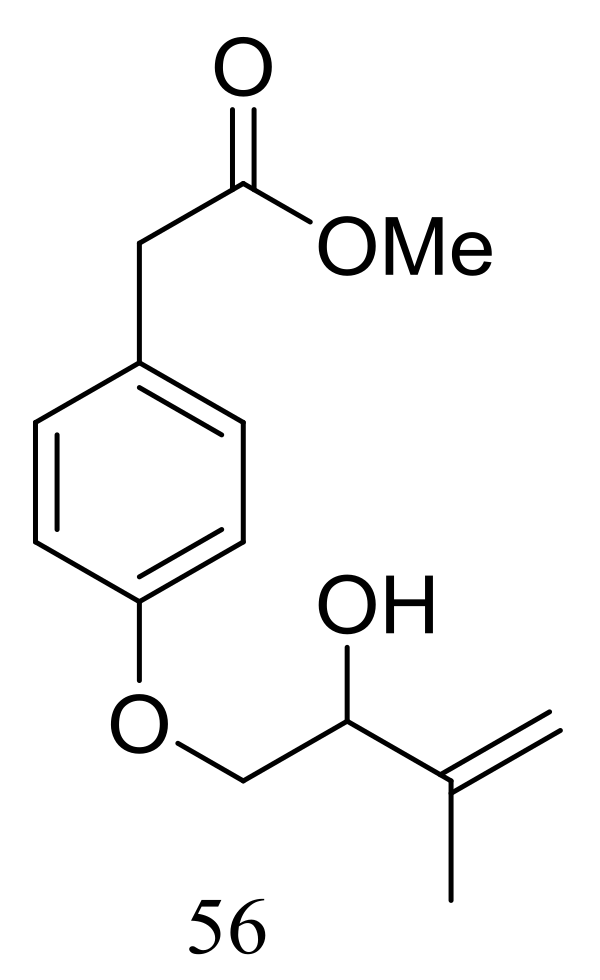
| 56 | [33] | ||
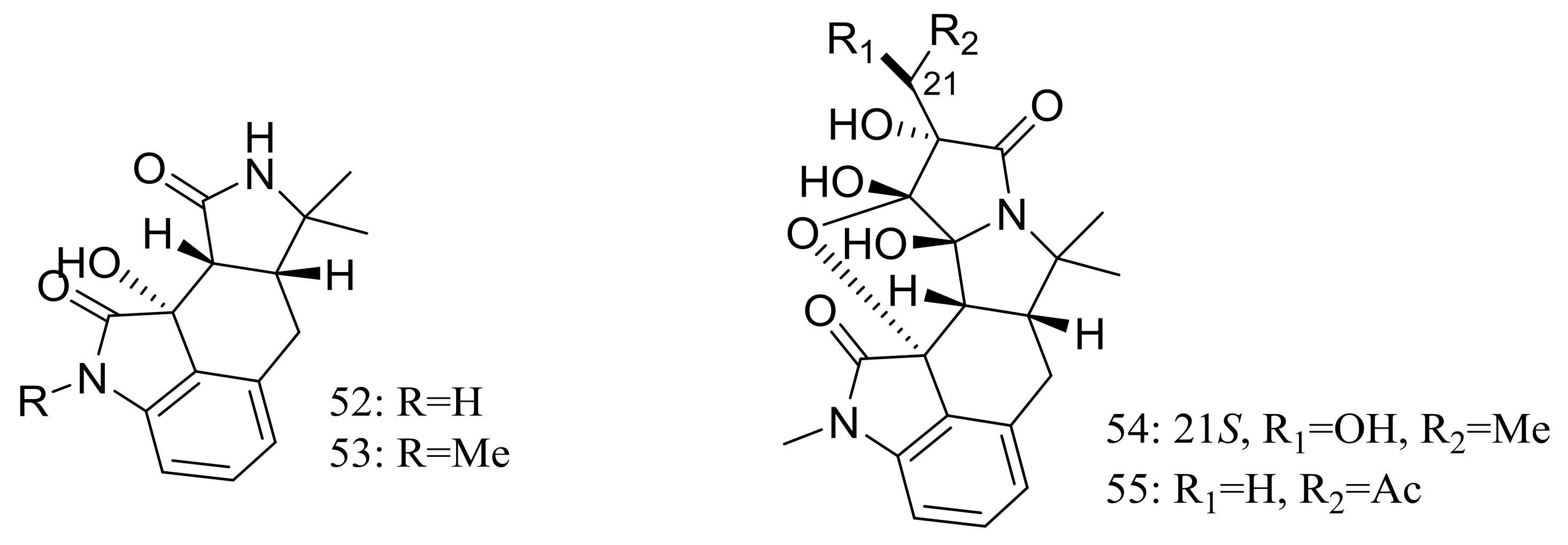
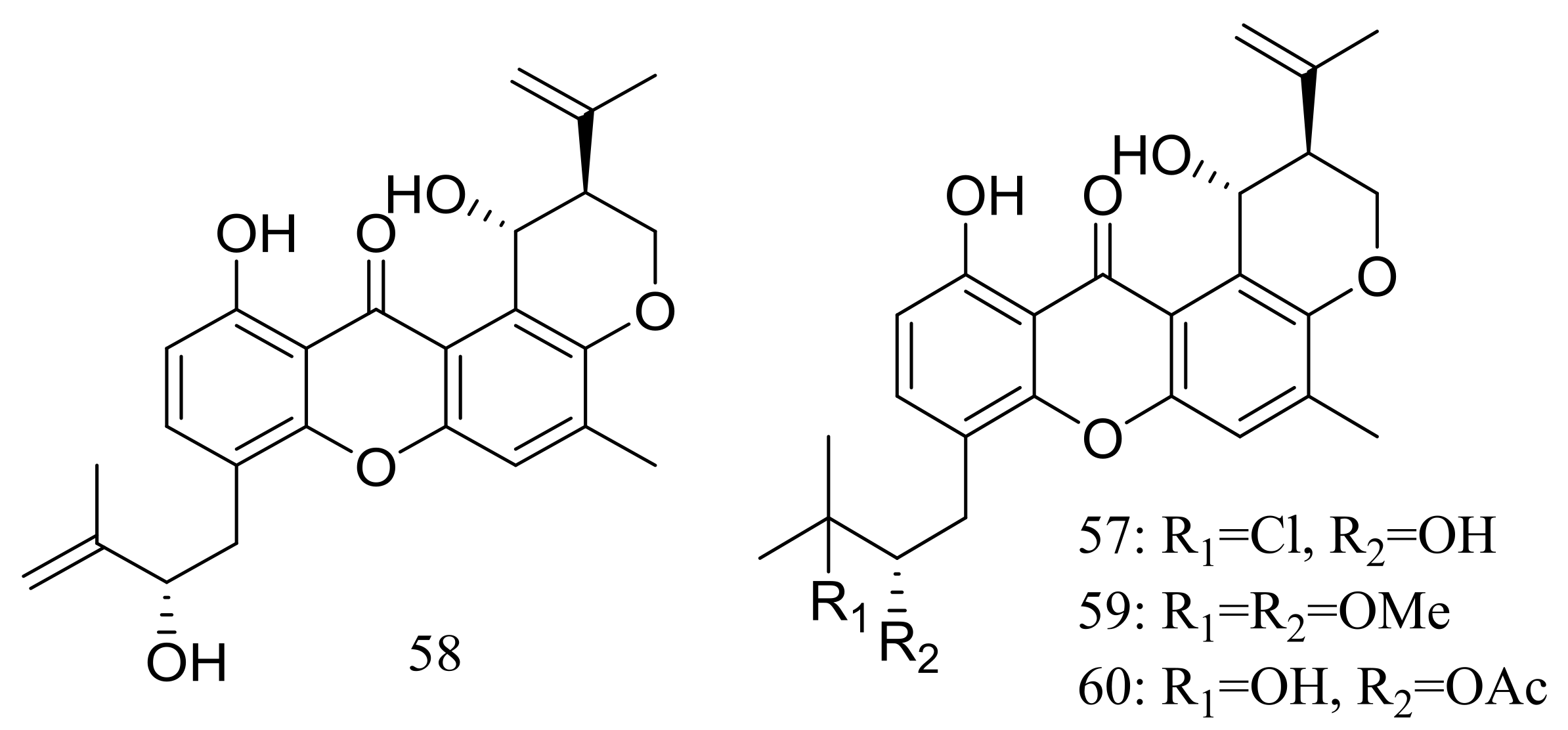
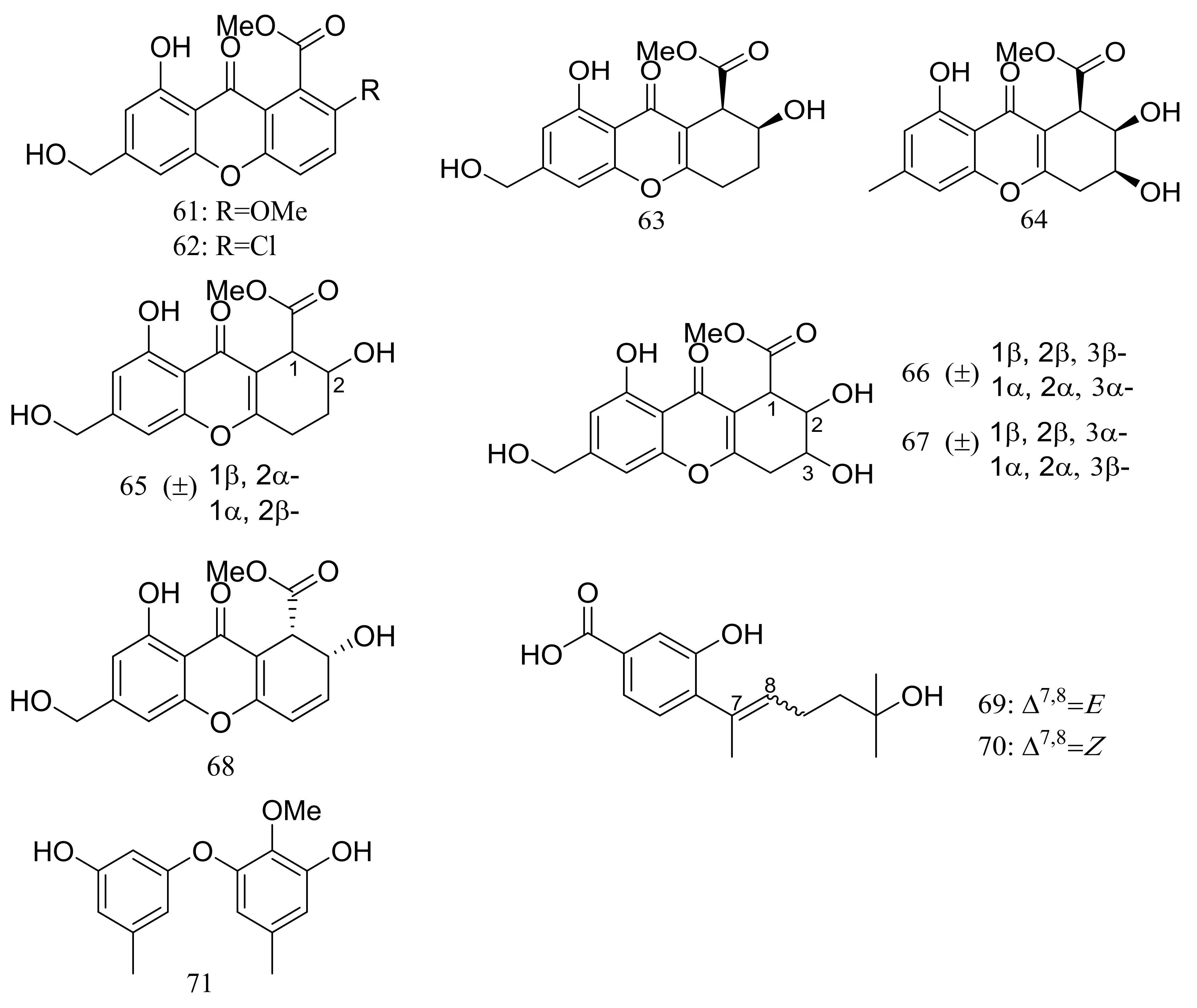
| 63–67, 68 *, 69–71 | Antimicrobial and cytotoxic | [35] | |
| 77 | Cytotoxic | [38] | |
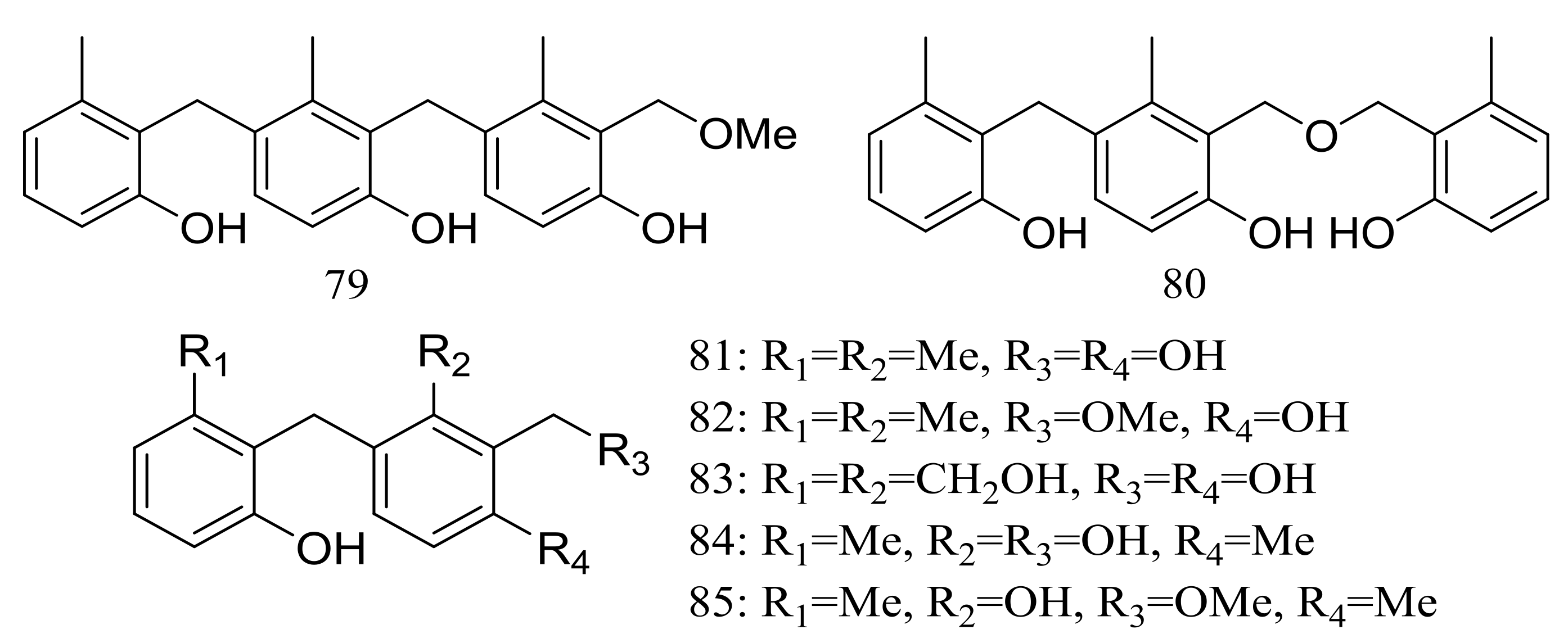
| 79 *, 80 *, 81, 82 *, 83, 84 *, 85 * | Cytotoxic | [39] | |
| 94–97, 98 *, 99 | Activate Nrf2 | [41] | |
| 106 *, 107 | Antilarval | [43] | |
| 109, 110 *, 111 * | Inhibit BRD4 | [44] | |
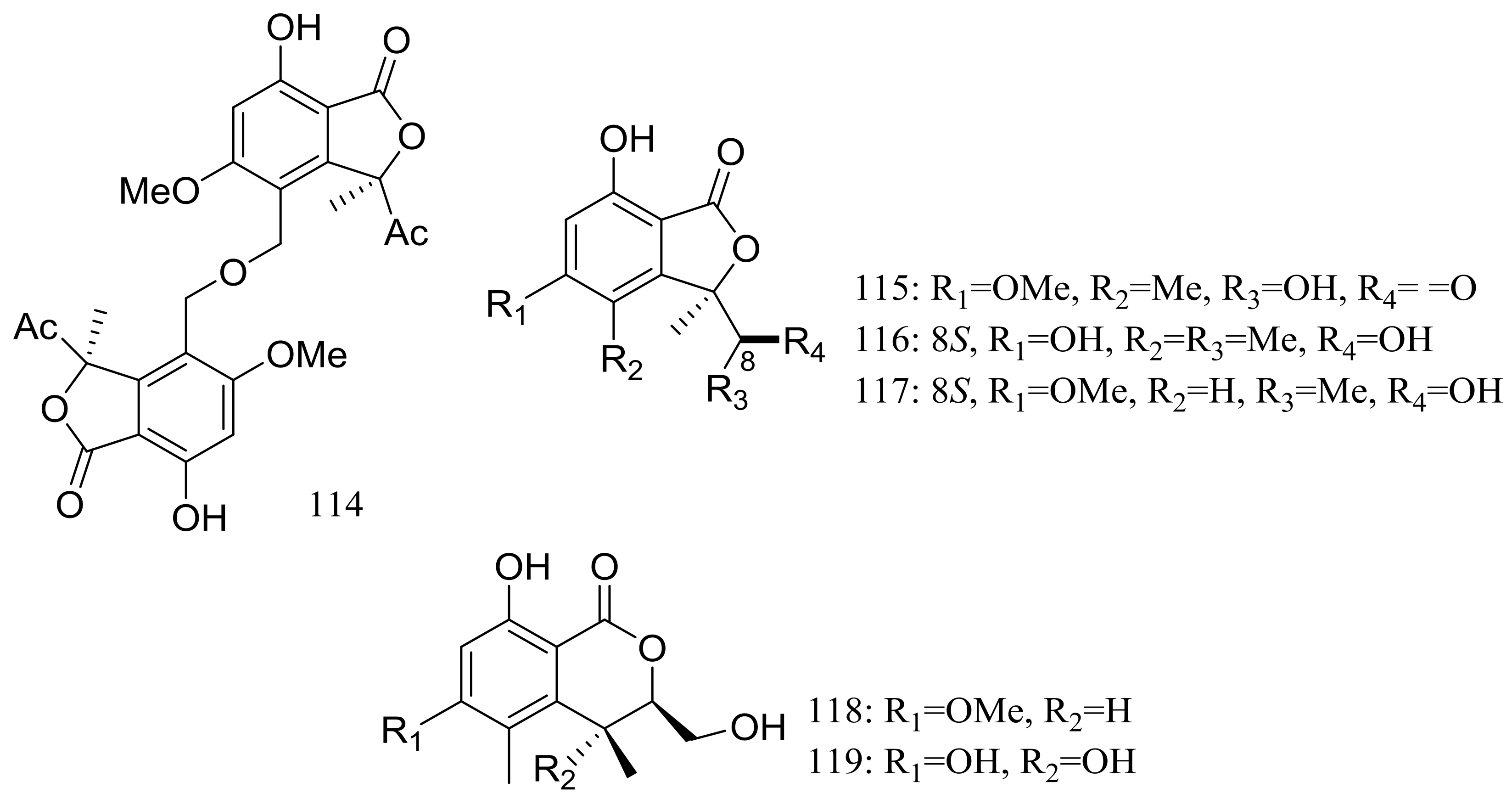
| 114–119 | [46] | ||
| 143 * | Antimicrobial | [50] | |
| 158–160, 161 *, 162 *, 163–166 | Antimicrobial | [58,59] | |
| 246 *, 247 * | Cytotoxic | [81] | |
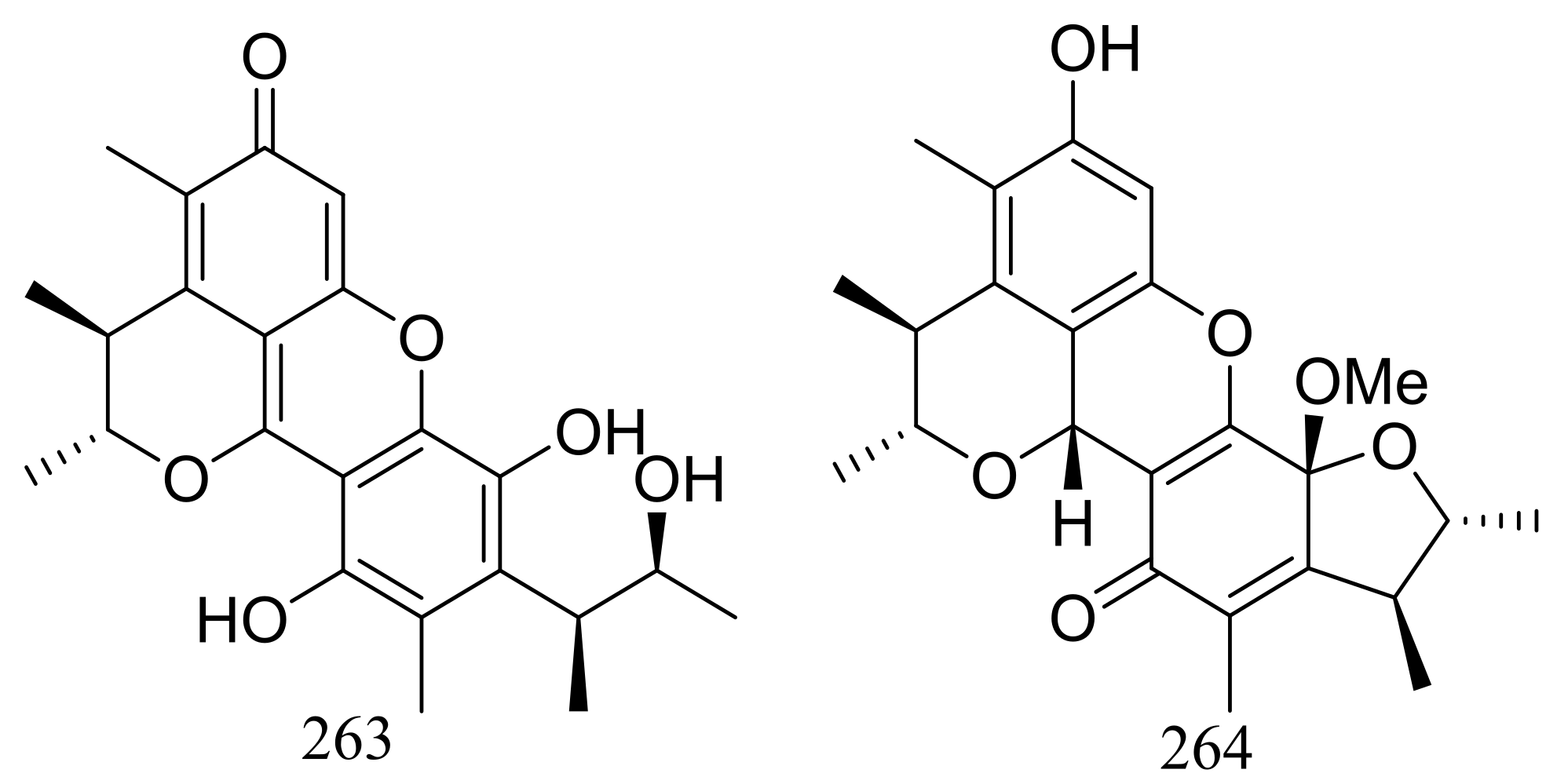
| 263 *, 264 | Radical-scavenging | [84] | |
| Esters and lactones | 78 | [38] | |
| 207 * | Inhibit PTP1B | [70] | |
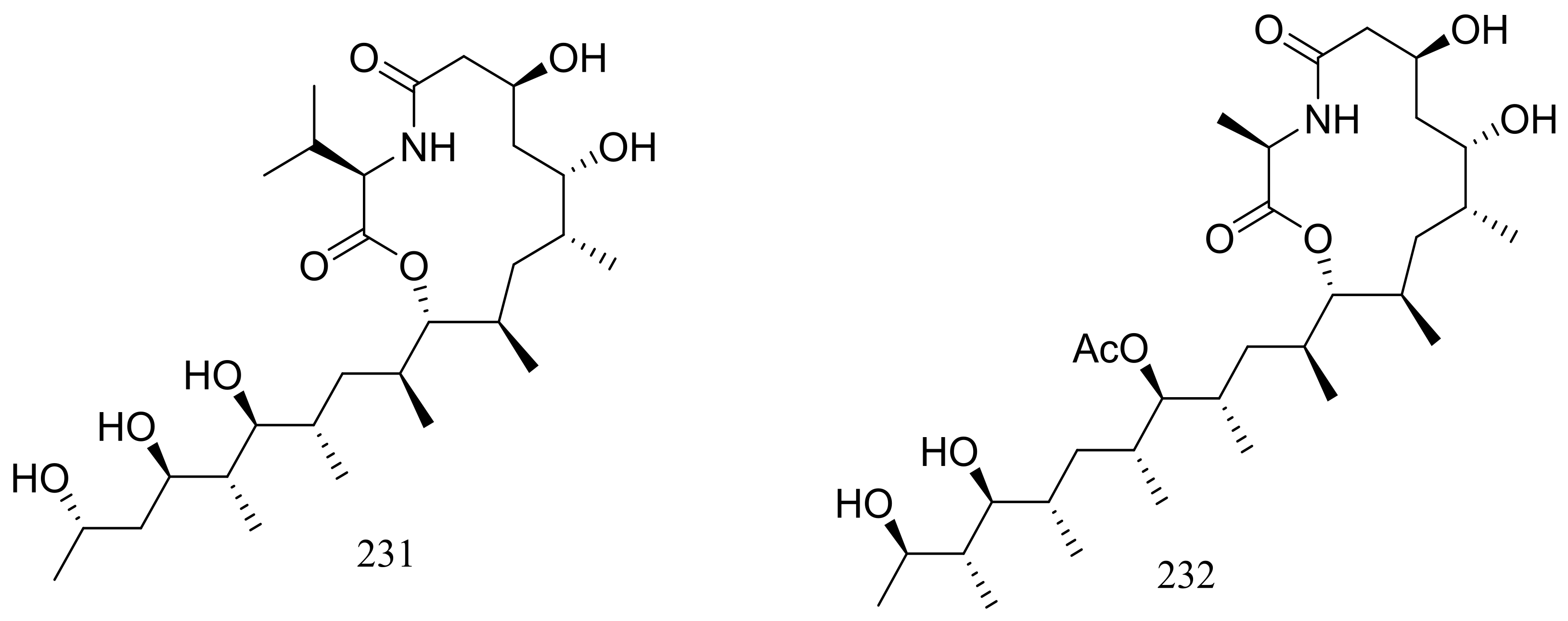
| 227 *, 228 *, 229–232 | Nematicidal | [76] | |
| 283 *, 284 *, 285 | Cytotoxic | [89] | |
| (302–304) * | Cytotoxic and/or inhibit MMP-3 | [94] | |
| Xanthones | 57 *, 58, 59 *, 60 * | Antimicrobial | [34] |
| 61, 62 | [35] | ||
| 72 | [36] | ||
| 90–93 | [40] | ||
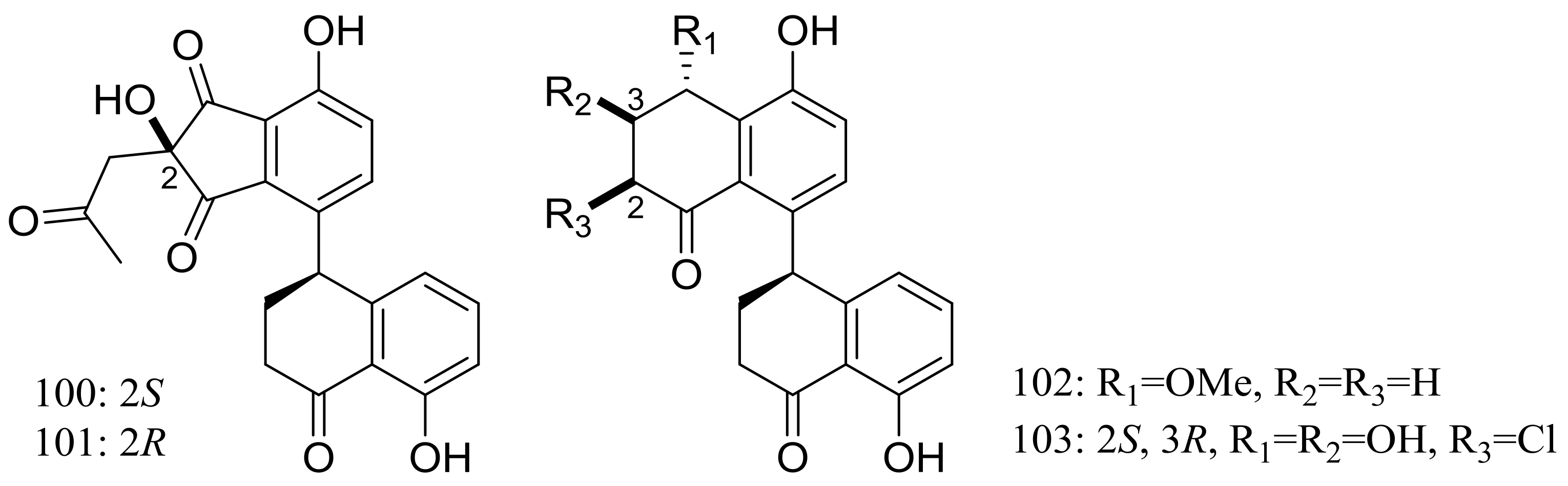
| Polyketides | 100, 101, 102 *, 103 * | Cytotoxic | [42] |
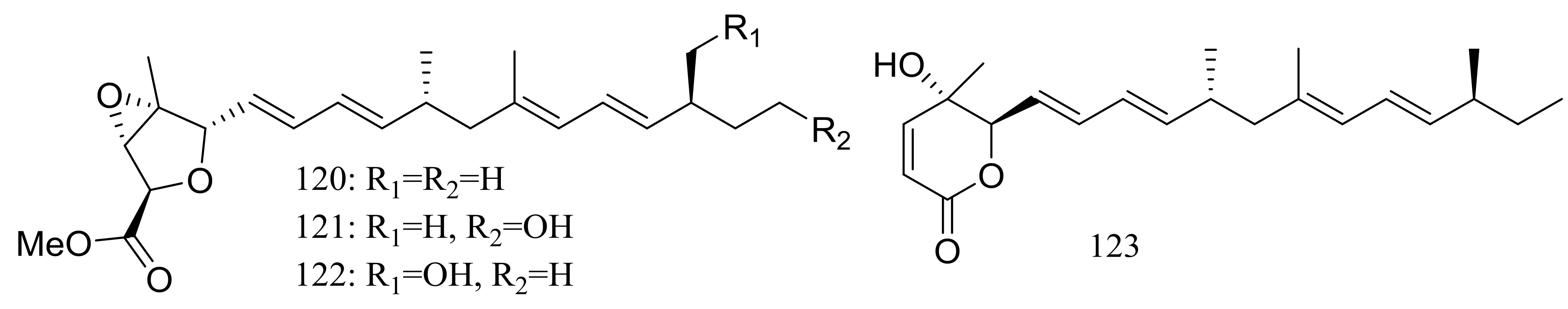
| 120–122, 123 * | Cytotoxic | [47] | |
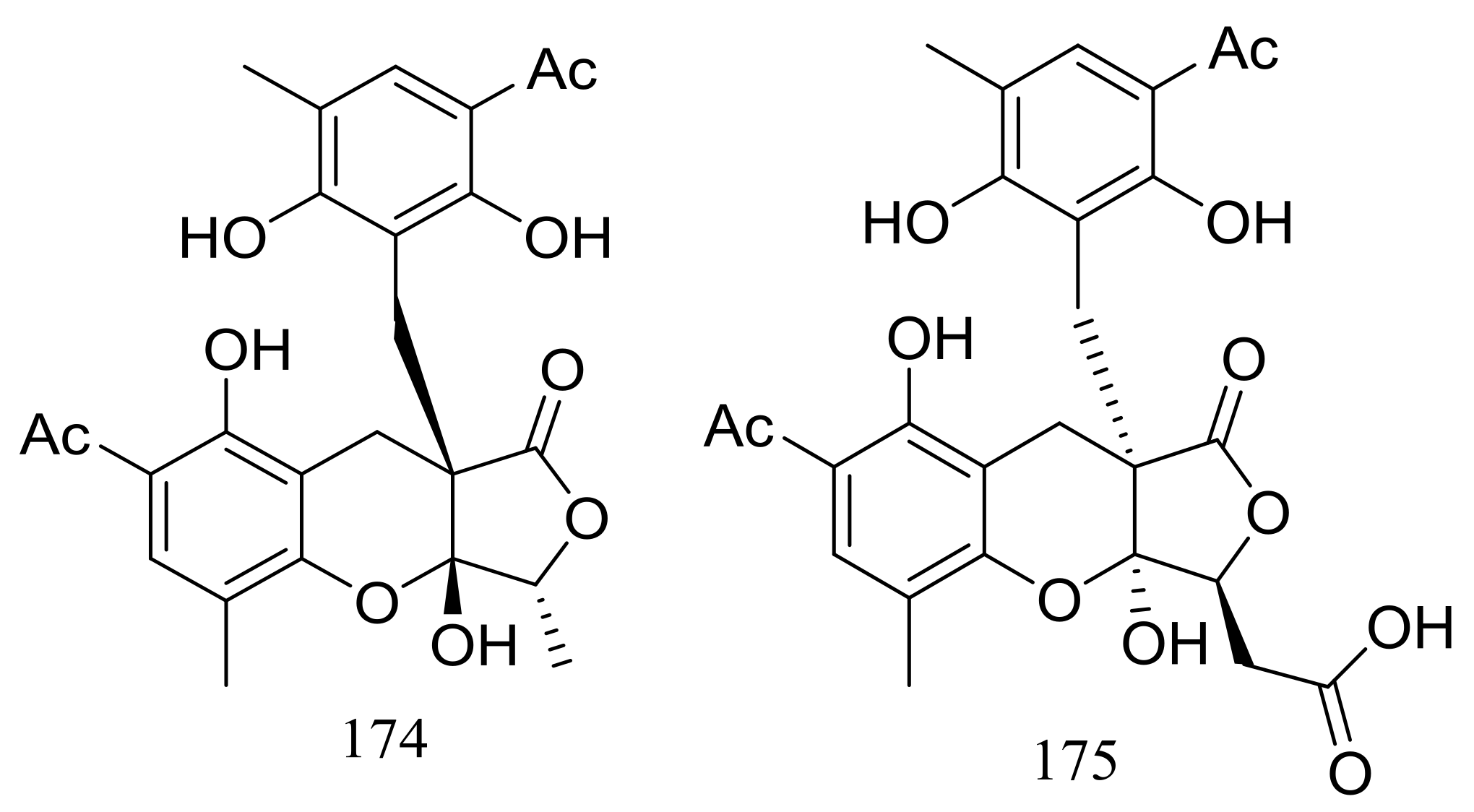
| 174 *, 175 | Inhibit NF-κB | [61] | |
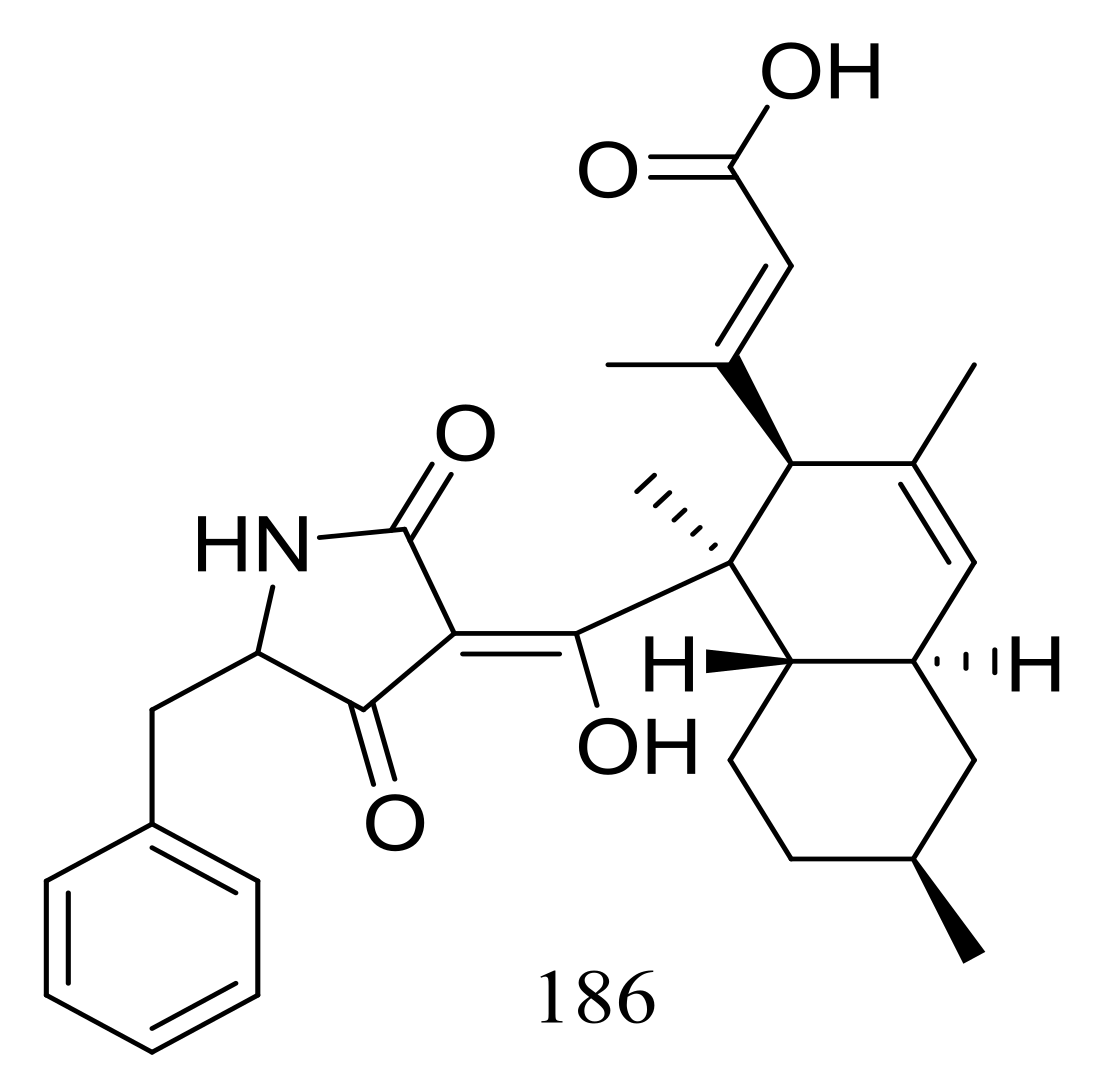
| 186 * | Antimicrobial | [64] | |
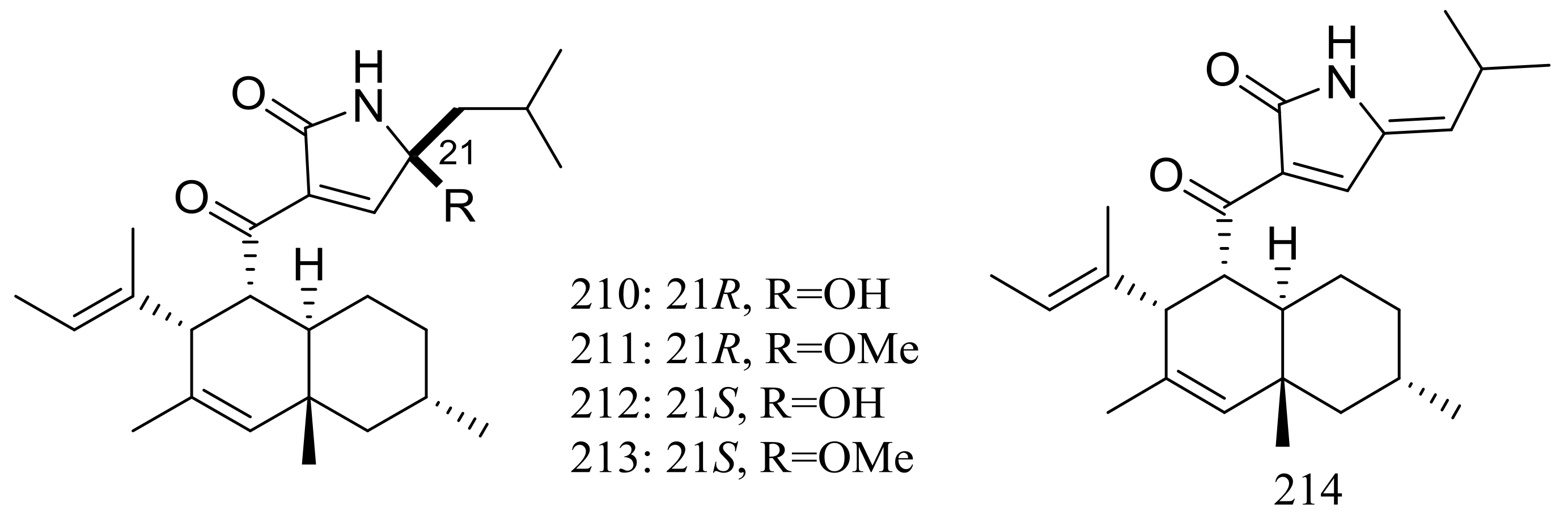
| (210–212) *, 213, 214 | Cytotoxic | [72] | |
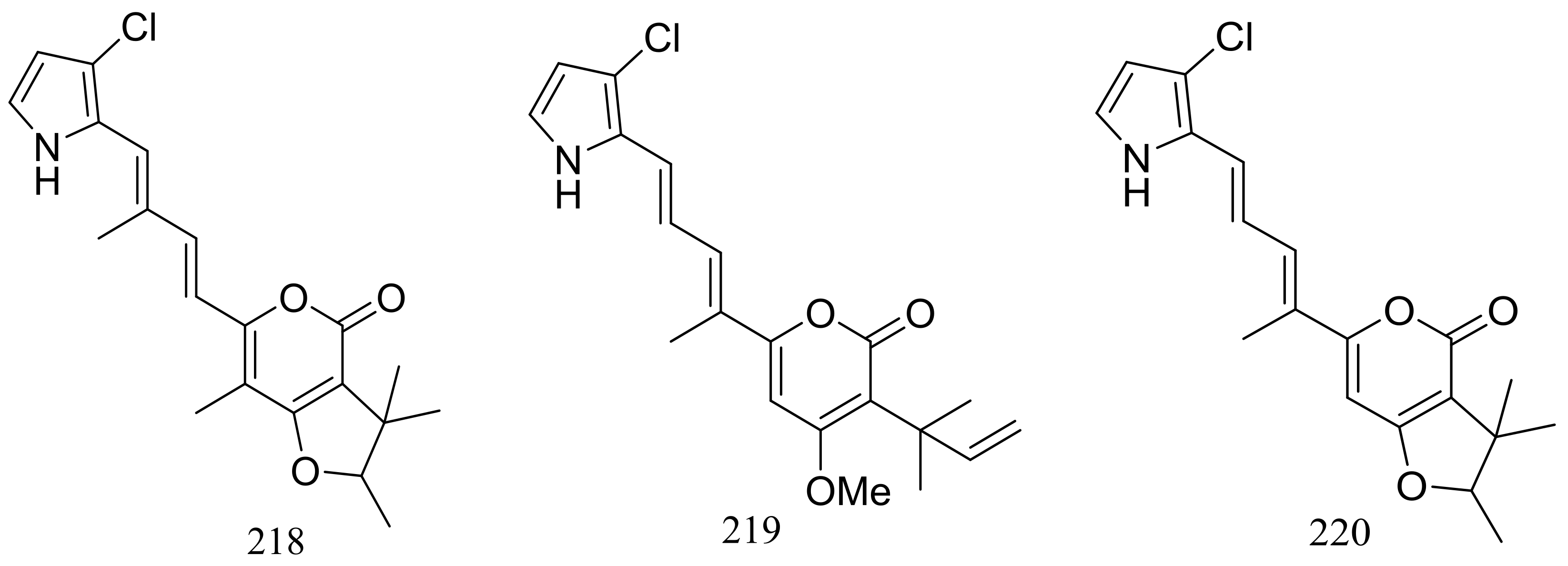
| 215, 216, (217–220) * | Cytotoxic | [73] | |
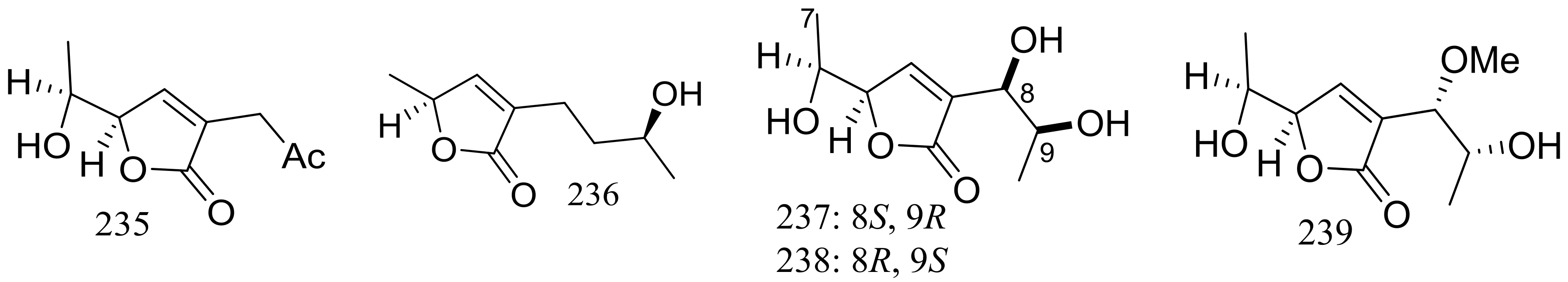
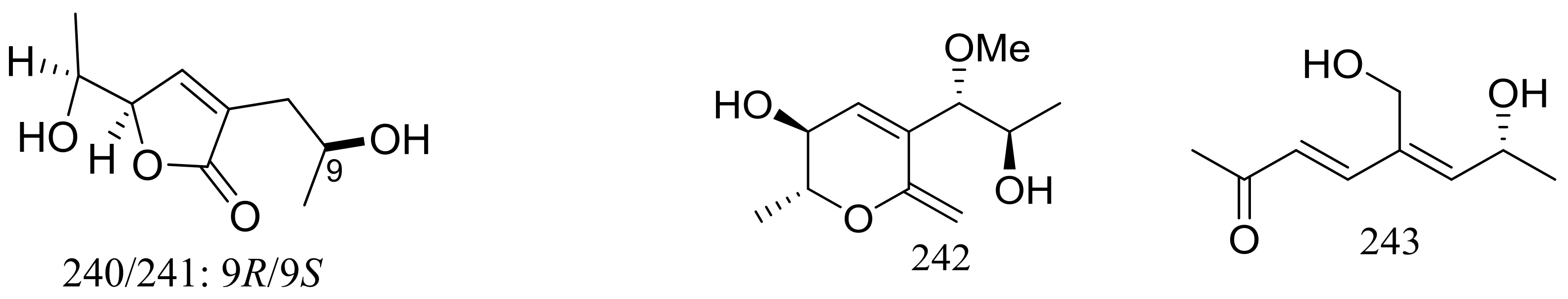
| 235–241, 242 *, 243 * | Cytotoxic | [78] | |
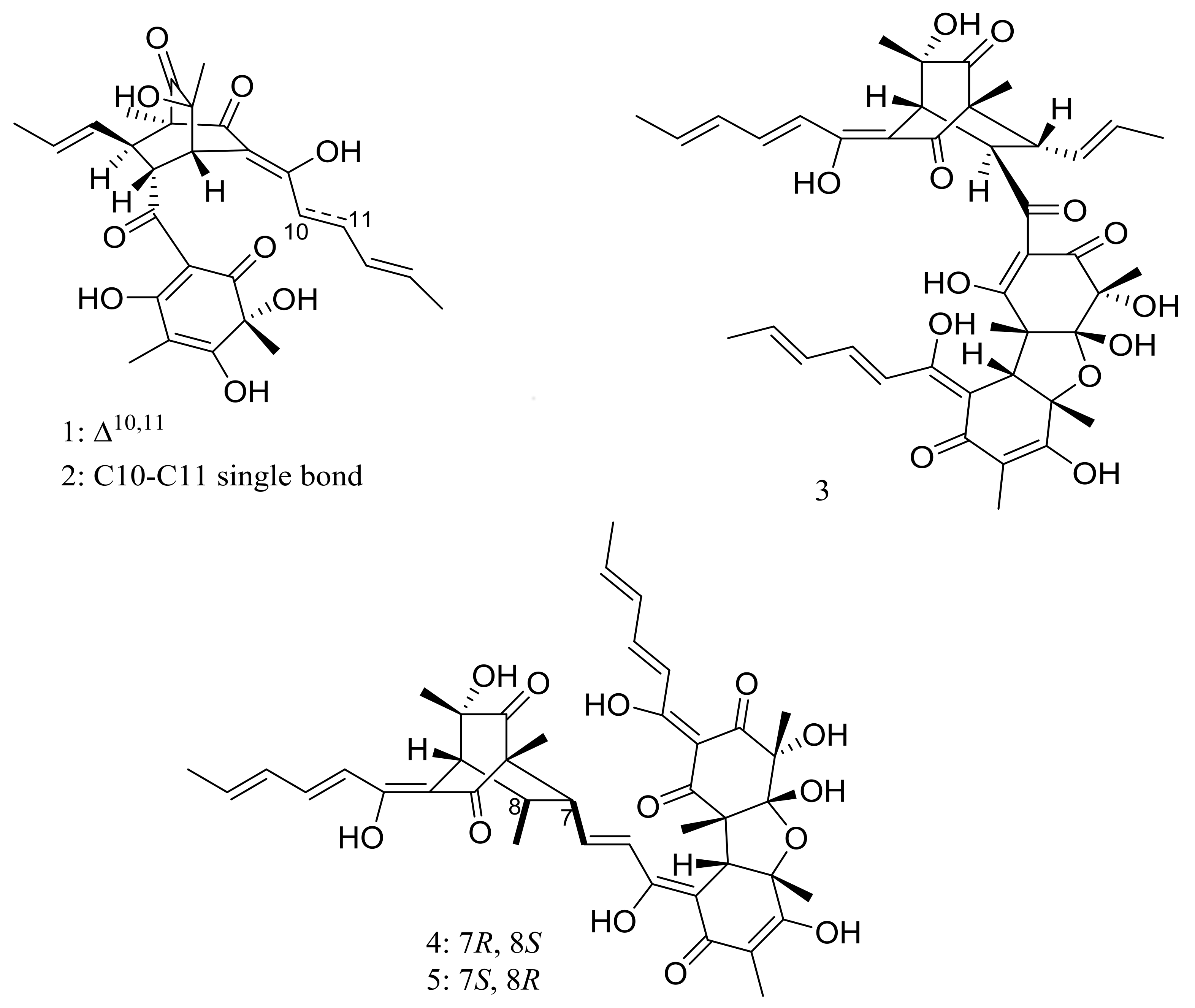
| Others | (1–9) * | Cytotoxic | [20,21,22,23] |
| (34–38) * | Antimicrobial | [28] | |
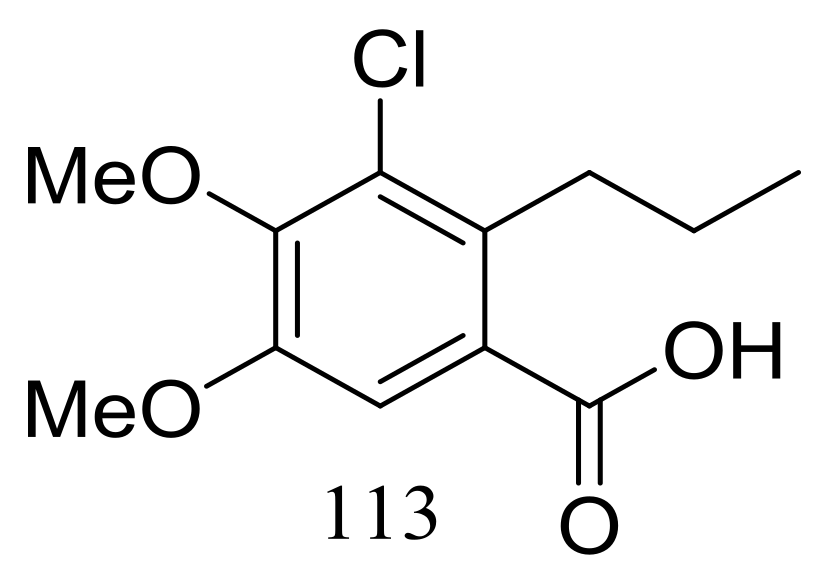
| 113 * | Antimicrobial | [45] | |
| 205 *, 206 * | Antiviral | [69] | |
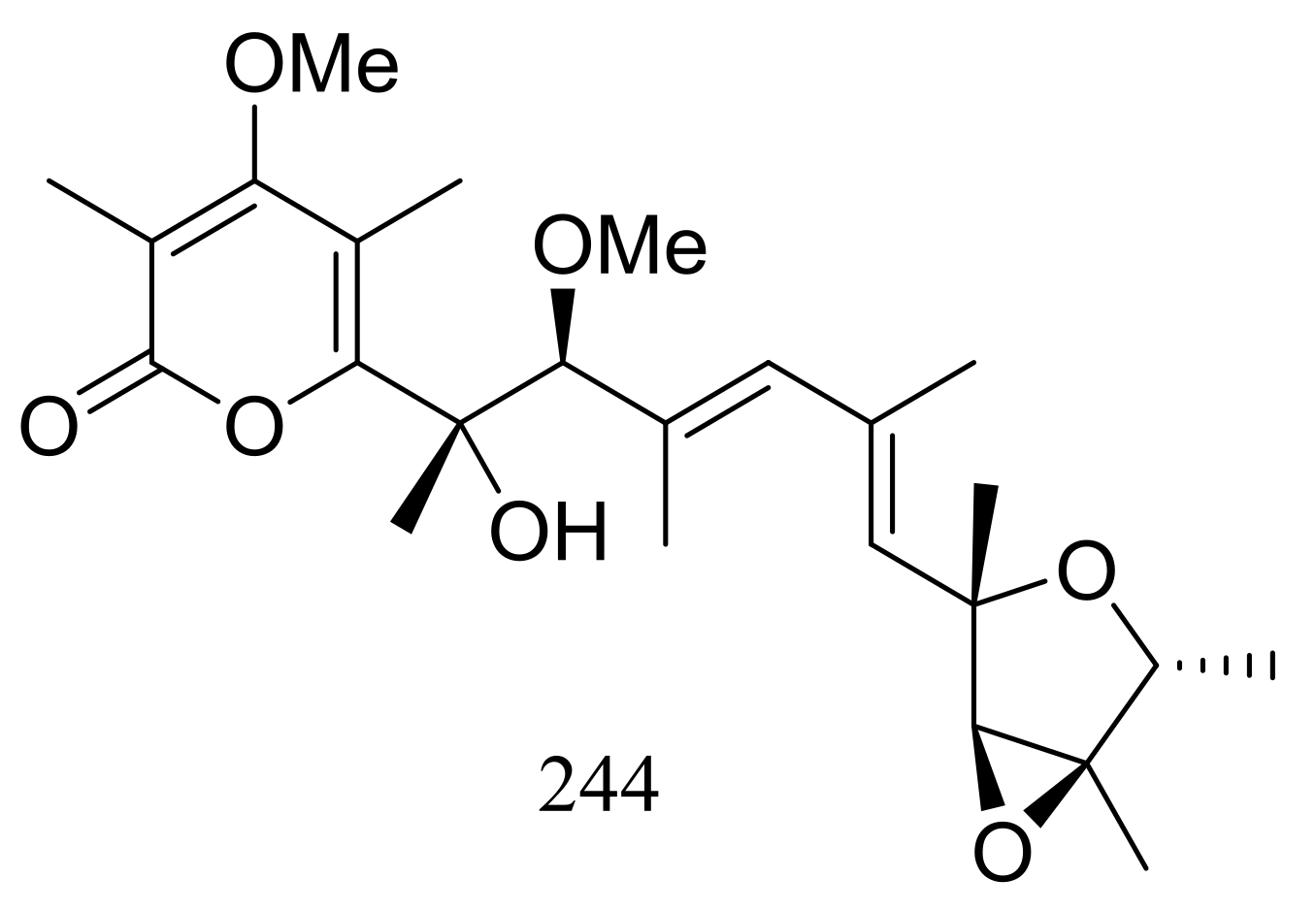
| 244 * | Antimicrobial | [79] | |
| 301 * | Inhibit MMP-3 and Casp-1 | [93] | |
| 314 | [98] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Li, S.-J.; Li, J.-J.; Liang, Z.-Z.; Zhao, C.-Q. Novel Natural Products from Extremophilic Fungi. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060194
Zhang X, Li S-J, Li J-J, Liang Z-Z, Zhao C-Q. Novel Natural Products from Extremophilic Fungi. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(6):194. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060194
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xuan, Shou-Jie Li, Jin-Jie Li, Zi-Zhen Liang, and Chang-Qi Zhao. 2018. "Novel Natural Products from Extremophilic Fungi" Marine Drugs 16, no. 6: 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060194
APA StyleZhang, X., Li, S.-J., Li, J.-J., Liang, Z.-Z., & Zhao, C.-Q. (2018). Novel Natural Products from Extremophilic Fungi. Marine Drugs, 16(6), 194. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16060194





