Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro
Abstract
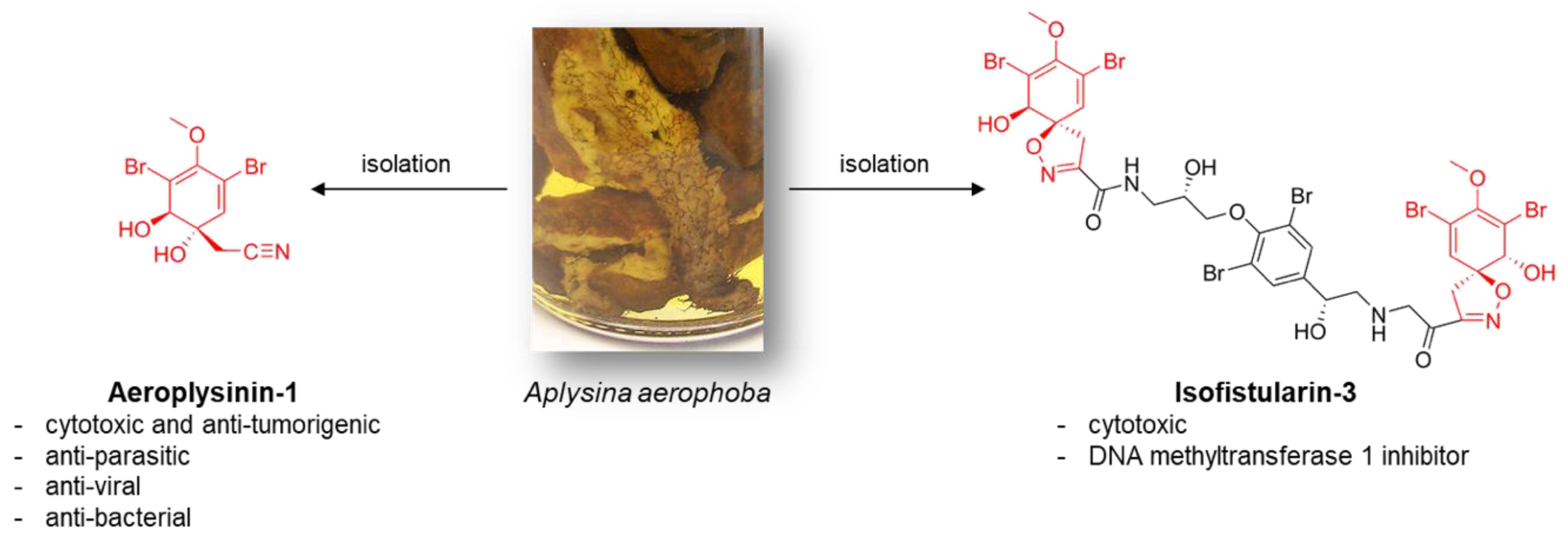
:1. Introduction
2. Results
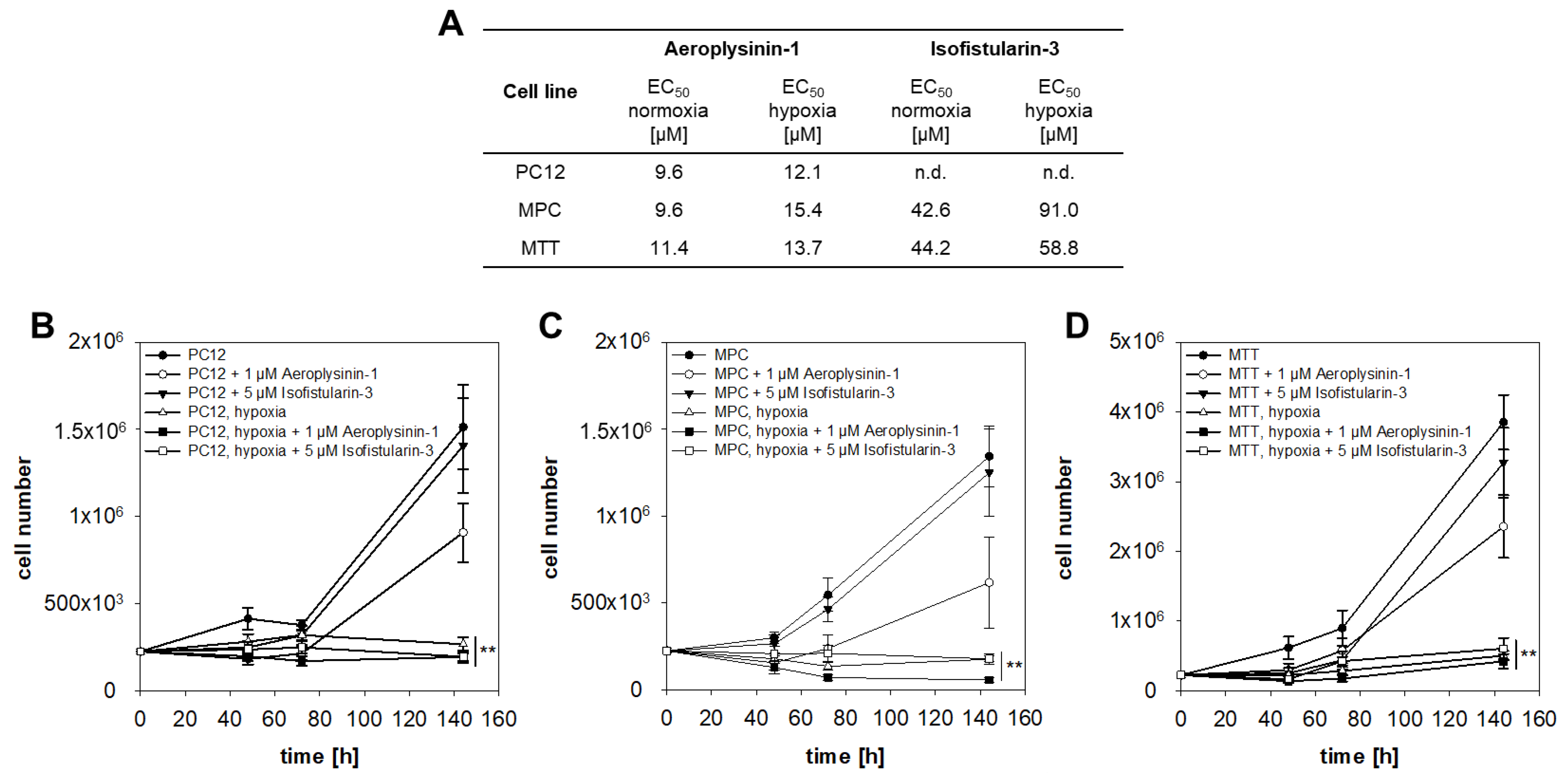
2.1. Anti-Proliferative Activity of Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 in Vitro
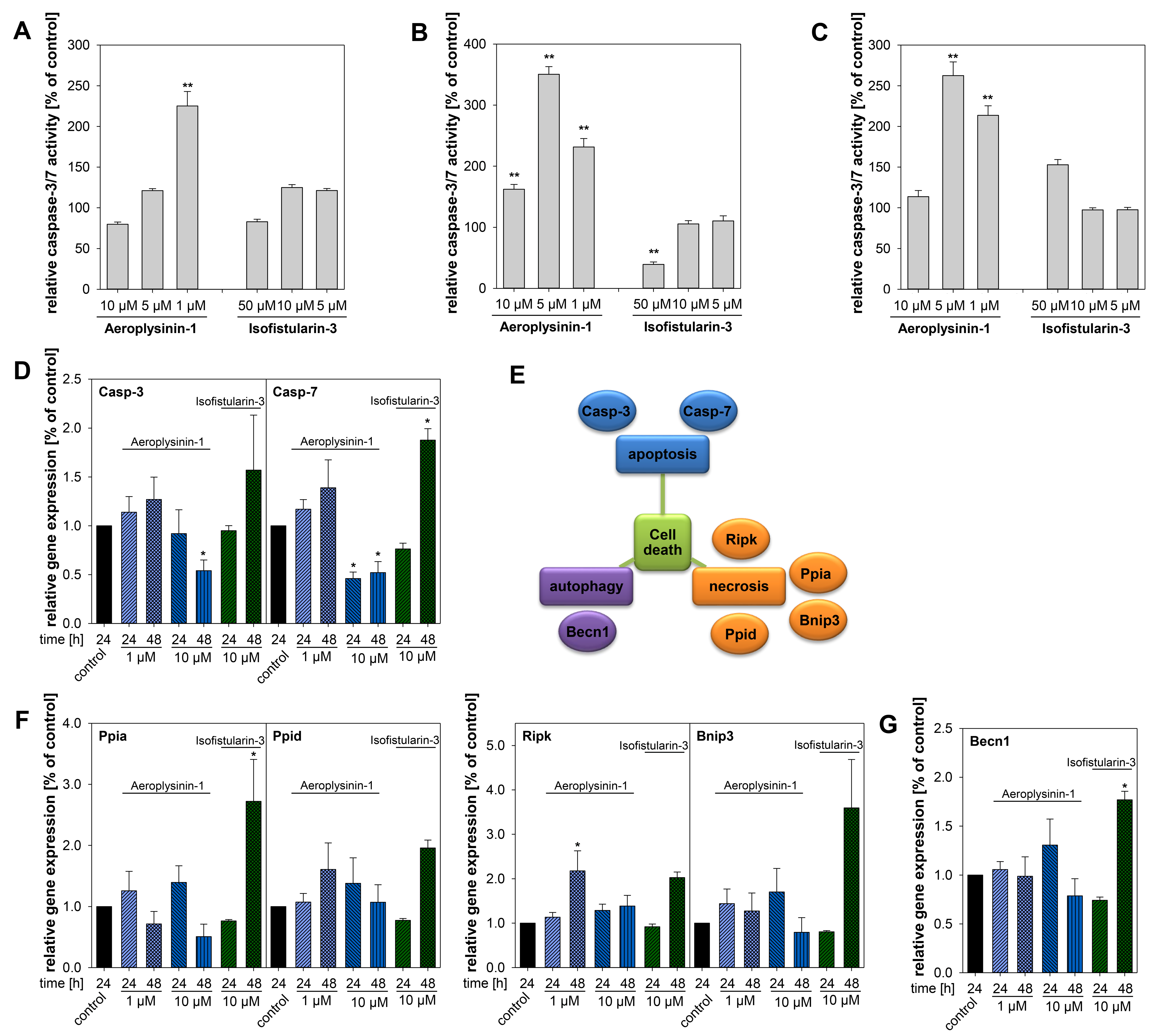
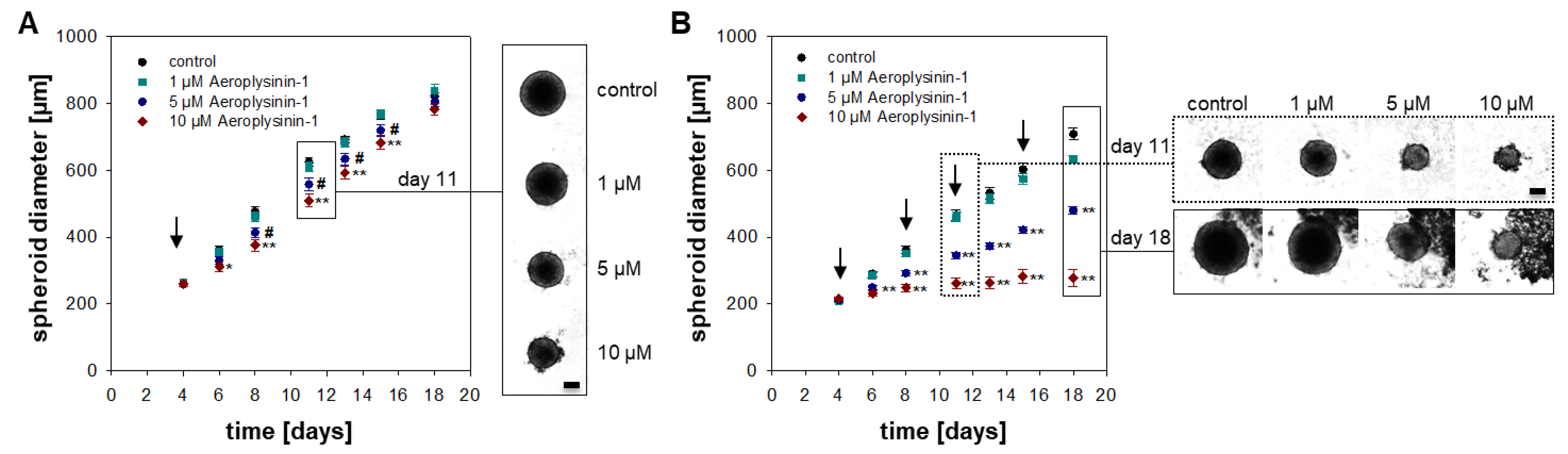
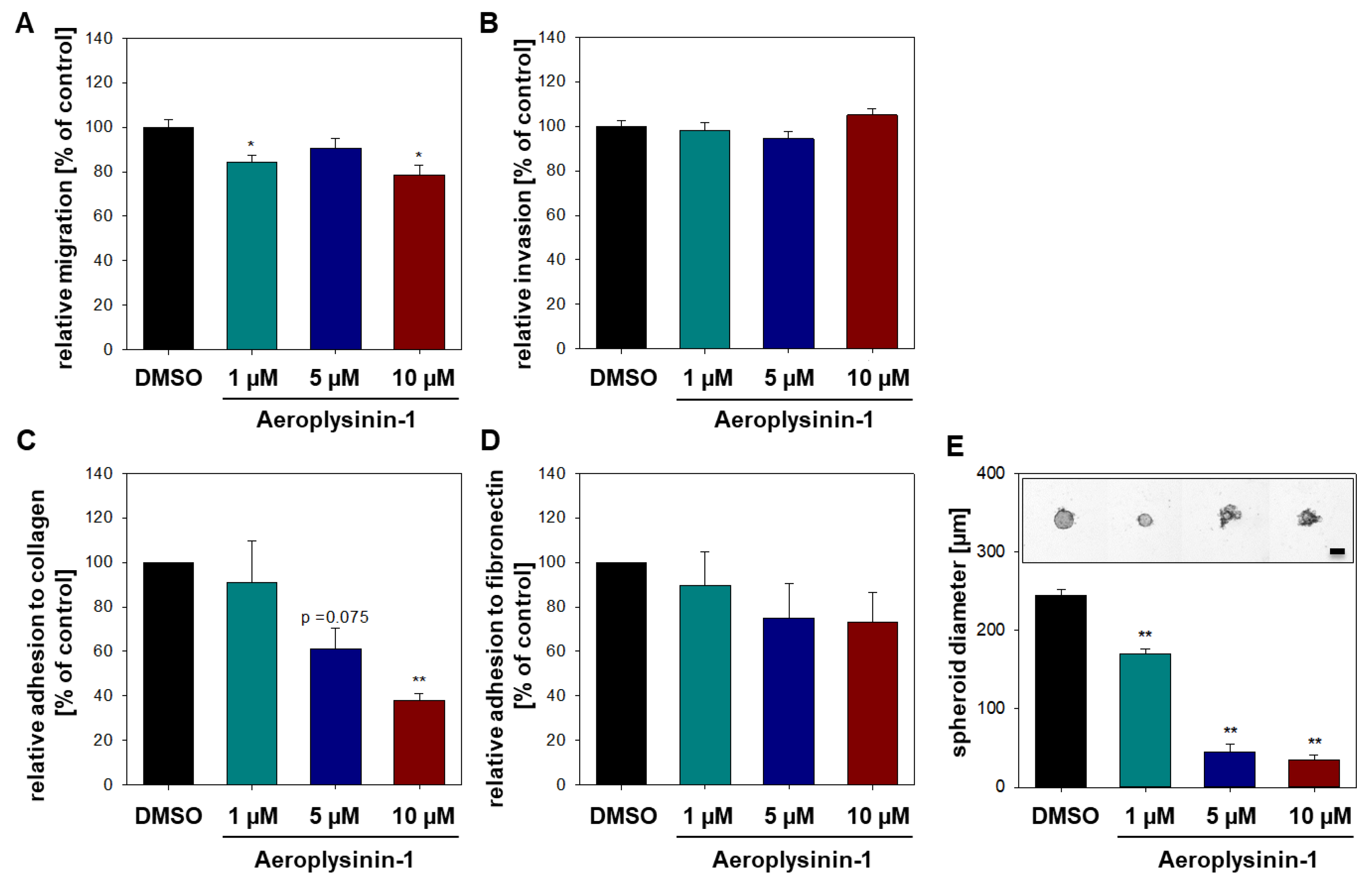
2.2. Influence of Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 on Cells’ Pro-Metastatic Behavior
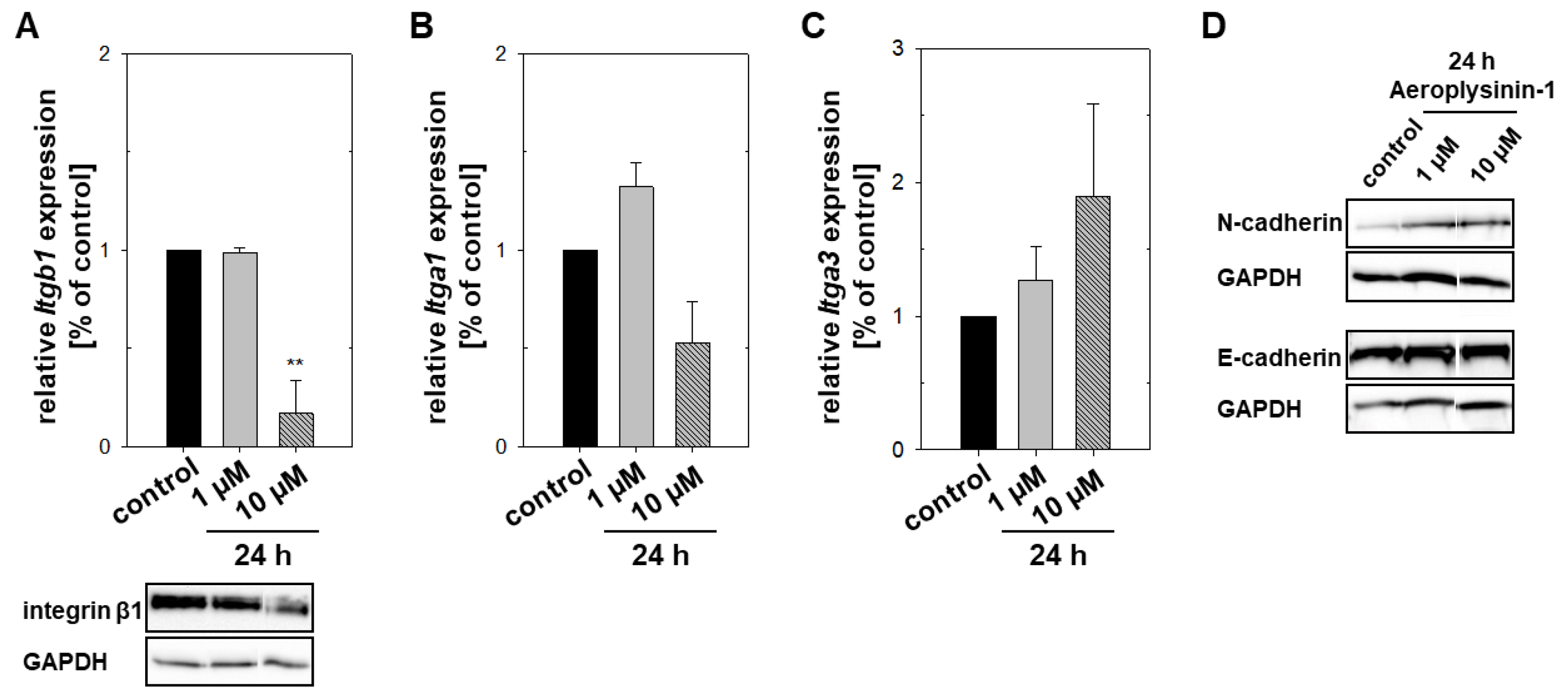
2.3. Impact of Aeroplysinin-1 on Cell Adhesion Molecules
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Viability Assay
4.3. Proliferation Assay
4.4. Apoptosis Assay
4.5. Migration Assay
4.6. Invasion Assay
4.7. Adhesion Assay
4.8. Generation and Cultivation of Tumor Cell Spheroids
4.9. Tumor Cell Spheroid Formation Assay
4.10. RNA Isolation
4.11. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.12. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.13. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisenhofer, G.; Bornstein, S.R.; Brouwers, F.M.; Cheung, N.-K.V.; Dahia, P.L.; De Krijger, R.R.; Giordano, T.J.; Greene, L.A.; Goldstein, D.S.; Lehnert, H. Malignant pheochromocytoma: Current status and initiatives for future progress. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2004, 11, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, H.; Ziegler, W.H.; Hauri, D.; Jaeger, P. Pheochromocytomas: Can malignant potential be predicted? Urology 1999, 53, 679–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, I.; Kim, S.-K. Marine antitumor drugs: Status, shortfalls and strategies. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 2702–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Honecker, F. Marine Compounds and Cancer: 2017 Updates; Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute: Basel, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Nieto, S.; González-Iriarte, M.; Carmona, R.; Muñoz-Chápuli, R.; Medina, M.A.; Quesada, A.R. Antiangiogenic activity of aeroplysinin-1, a brominated compound isolated from a marine sponge. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fattorusso, E.; Minale, L.; Sodano, G. Aeroplysinin-1, an antibacterial bromo-compound from the sponge verongia aerophoba. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1972, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Ilan, M.; Maldonado, M.; Muricy, G.; Bavestrello, G.; Kljajic, Z.; Carballo, J.; Schiaparelli, S.; Ereskovsky, A.; Schupp, P. Three-dimensional chitin-based scaffolds from verongida sponges (demospongiae: Porifera). Part i. Isolation and identification of chitin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2010, 47, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutsenko, V.V.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Rogulska, O.; Tarusin, D.N.; Schütz, K.; Brüggemeier, S.; Gossla, E.; Akkineni, A.R.; Meißner, H.; Lode, A. 3d chitinous scaffolds derived from cultivated marine demosponge aplysina aerophoba for tissue engineering approaches based on human mesenchymal stromal cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysokowski, M.; Motylenko, M.; Bazhenov, V.V.; Stawski, D.; Petrenko, I.; Ehrlich, A.; Behm, T.; Kljajic, Z.; Stelling, A.L.; Jesionowski, T. Poriferan chitin as a template for hydrothermal zirconia deposition. Front. Mater. Sci. 2013, 7, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; García-Vilas, J.A.; Cardenas, C.; Melgarejo, E.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.A. The brominated compound aeroplysinin-1 inhibits proliferation and the expression of key pro-inflammatory molecules in human endothelial and monocyte cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Vilas, J.A.; Martínez-Poveda, B.; Quesada, A.R.; Medina, M.Á. Aeroplysinin-1, a sponge-derived multi-targeted bioactive marine drug. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, A.A.; Ramasahayam, S.; Meyer, S.A.; Sayed, K.A.E. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of dibromotyrosine analogues inspired by marine natural products as inhibitors of human prostate cancer proliferation, invasion, and migration. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 7446–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.-H.; Leake, R.E.; Rinaldi, F.; Müller-Klieser, W.; Maidhof, A.; Müller, W.E.G.; Schröder, H.C. Inhibition of intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase activity of egf-receptor kinase complex from human breast cancer cells by the marine sponge metabolite (+)-aeroplysinin-1. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. 1990, 97, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teeyapant, R.; Woerdenbag, H.; Kreis, P.; Hacker, J.; Wray, V.; Witte, L.; Proksch, P. Antibiotic and cytotoxic activity of brominated compounds from the marine sponge verongia aerophoba. Z. Naturforsch. C 1993, 48, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Florean, C.; Schnekenburger, M.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, K.R.; Mazumder, A.; Song, S.; Kim, J.-M.; Grandjenette, C.; Kim, J.-G.; Yoon, A.-Y.; et al. Discovery and characterization of isofistularin-3, a marine brominated alkaloid, as a new DNA demethylating agent inducing cell cycle arrest and sensitization to trail in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24027–24049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, H.; Bazhenov, V.; Meschke, S.; Bürger, M.; Ehrlich, A.; Petovic, S.; Durovic, M. Marine invertebrates of boka kotorska bay unique sources for bioinspired materials science. Boka Kotorska Bay Environ. 2016, 54, 313–334. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, R.; Zeh, H.J.; Lotze, M.T.; Tang, D. The beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz-Schughart, L.A.; Freyer, J.P.; Hofstaedter, F.; Ebner, R. The use of 3-d cultures for high-throughput screening: The multicellular spheroid model. J. Biomol. Screen. 2004, 9, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-M.; Li, J.; Yan, M.-X.; Liu, L.; Jia, D.-S.; Geng, Q.; Lin, H.-C.; He, X.-H.; Li, J.-J.; Yao, M. Integrative analyses identify osteopontin, lamb3 and itgb1 as critical pro-metastatic genes for lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowy, C. Tenascin C Interacts with Integrin Receptors to Promote Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Lungs. Ph.D. Dissertation, Ruperto-Carola University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdem, M.; Erdem, S.; Sanli, O.; Sak, H.; Kilicaslan, I.; Sahin, F.; Telci, D. In Up-regulation of tgm2 with itgb1 and sdc4 is important in the development and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 25, e13–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beavon, I.R.G. The e-cadherin-catenin complex in tumour metastasis: Structure, function and regulation. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 1607–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, K.; Shimura, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Wada, W.; Yajima, T.; Kobayahi, T.; Kubo, N.; Kuwano, H. E/N-cadherin switch mediates cancer progression via tgf-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.E.; Song, G.-Y.; Zhou, W.; Goh, S.-H.; Na, M.; Oh, S. Cytotoxic activity of aeroplysinin-1 against colon cancer cells by promoting β-catenin degradation. Food Chem.Toxicol. 2016, 93, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulman, A.; Proksch, P.; Ebel, R.; Beekman, A.C.; van Uden, W.; Konings, A.W.T.; Pedersen, J.A.; Pras, N.; Woerdenbag, H.J. Cytoxicity and mode of action of aeroplysinin-1 and a related dienone from the sponge aplysina aerophoba. J. Nat. Prod. 1996, 59, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuhldreier, F.; Kassel, S.; Schumacher, L.; Wesselborg, S.; Proksch, P.; Fritz, G. Pleiotropic effects of spongean alkaloids on mechanisms of cell death, cell cycle progression and DNA damage response (ddr) of acute myeloid leukemia (aml) cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 361, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldmann, H.; Hinterding, K.; Herrlich, P.; Rahmsdorf, H.J.; Knebel, A. Selective inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases by synthetic analogues of aeroplysinin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1541–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Poveda, B.; Rodríguez-Nieto, S.; García-Caballero, M.; Medina, M.-Á.; Quesada, A.R. The antiangiogenic compound aeroplysinin-1 induces apoptosis in endothelial cells by activating the mitochondrial pathway. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Córdoba, R.; Tormo, N.S.; Medarde, A.F.; Plumet, J. Antiangiogenic versus cytotoxic activity in analogues of aeroplysinin-1. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007, 15, 5300–5315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuter, M.; Bernd, A.; Holzmann, H.; Müller-Klieser, W.; Maidhof, A.; Weissmann, N.; Kljajić, Z.; Batel, R.; Schröder, H.; Müller, W. Cytostatic activity of aeroplysinin-1 against lymphoma and epithelioma cells. Z. Naturforsch. C 1989, 44, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Fink, K.L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Cloughesy, T.F.; O’Neill, A.; Plotkin, S.; Glantz, M.; Ravin, P.; Raizer, J.J.; Rich, K.M. Randomized phase ii study of cilengitide, an integrin-targeting arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide, in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 5610–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Gorlia, T.; Erridge, S.C.; Perry, J.; Hong, Y.-K.; Aldape, K.D.; Lhermitte, B.; Pietsch, T.; Grujicic, D. Cilengitide combined with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma with methylated mgmt promoter (centric eortc 26071–22072 study): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manegold, C.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Cardenal, F.; Schuette, W.; Woll, P.J.; Ulsperger, E.; Kerber, A.; Eckmayr, J.; von Pawel, J. Randomized phase ii study of three doses of the integrin inhibitor cilengitide versus docetaxel as second-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2013, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Barlesi, F.; Waller, C.; Bennouna, J.; Gridelli, C.; Goekkurt, E.; Verhoeven, D.; Szczesna, A.; Feurer, M.; Milanowski, J. Cilengitide combined with cetuximab and platinum-based chemotherapy as first-line treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (nsclc) patients: Results of an open-label, randomized, controlled phase ii study (certo). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, K.W.; Colevas, A.D.; Cooney, K.; DiPaola, R.; Dunn, R.L.; Gross, M.; Keller, E.T.; Pienta, K.J.; Ryan, C.J.; Smith, D. Phase ii evaluations of cilengitide in asymptomatic patients with androgen-independent prostate cancer: Scientific rationale and study design. Clin. Genitourin. Cancer 2006, 4, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaskar, V.; Zhang, D.; Fox, M.; Seto, P.; Wong, M.H.; Wales, P.E.; Powers, D.; Chao, D.T.; DuBridge, R.B.; Ramakrishnan, V. A function blocking anti-mouse integrin α5β1 antibody inhibits angiogenesis and impedes tumor growth in vivo. J. Transl. Med. 2007, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricart, A.D.; Tolcher, A.W.; Liu, G.; Holen, K.; Schwartz, G.; Albertini, M.; Weiss, G.; Yazji, S.; Ng, C.; Wilding, G. Volociximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody that specifically binds α5β1 integrin: A phase i, pharmacokinetic, and biological correlative study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7924–7929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell-McGuinn, K.M.; Matthews, C.M.; Ho, S.N.; Barve, M.; Gilbert, L.; Penson, R.T.; Lengyel, E.; Palaparthy, R.; Gilder, K.; Vassos, A. A phase ii, single-arm study of the anti-α5β1 integrin antibody volociximab as monotherapy in patients with platinum-resistant advanced epithelial ovarian or primary peritoneal cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2011, 121, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cianfrocca, M.; Kimmel, K.; Gallo, J.; Cardoso, T.; Brown, M.; Hudes, G.; Lewis, N.; Weiner, L.; Lam, G.; Brown, S. Phase 1 trial of the antiangiogenic peptide atn-161 (ac-phscn-nh 2), a beta integrin antagonist, in patients with solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 94, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskelley, C.D.; Williams, D.E.; McHardy, L.M.; Leong, K.G.; Troussard, A.; Karsan, A.; Andersen, R.J.; Dedhar, S.; Roberge, M. Inhibition of tumor cell invasion and angiogenesis by motuporamines. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 6788–6794. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordes, N.; Park, C.C. Beta 1 integrin as a molecular therapeutic target. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2007, 83, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ozaki, I.; Mizuta, T.; Matsuhashi, S.; Yoshimura, T.; Hisatomi, A.; Tadano, J.; Sakai, T.; Yamamoto, K. Β1-integrin protects hepatoma cells from chemotherapy induced apoptosis via a mitogen-activated protein kinase dependent pathway. Cancer 2002, 95, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; De Cubas, A.A.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Richter, S.; Peitzsch, M.; Menschikowski, M.; Lenders, J.W.; Timmers, H.J.; Mannelli, M.; Opocher, G. Opposing effects of HIF1α and HIF2α on chromaffin cell phenotypic features and tumor cell proliferation: Insights from MYC-associated factor X. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keely, S.; Glover, L.E.; MacManus, C.F.; Campbell, E.L.; Scully, M.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Colgan, S.P. Selective induction of integrin β1 by hypoxia-inducible factor: Implications for wound healing. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.F.; Evinger, M.J.; Tsokas, P.; Bedri, S.; Alroy, J.; Shahsavari, M.; Tischler, A.S. Pheochromocytoma cell lines from heterozygous neurofibromatosis knockout mice. Cell Tissue Res. 2000, 302, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiniova, L.; Lai, E.W.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Abu-Asab, M.; Wickremasinghe, A.; Solis, D.C.; Perera, S.M.; Huynh, T.-T.; Lubensky, I.A.; Tischler, A.S.; et al. Characterization of an animal model of aggressive metastatic pheochromocytoma linked to a specific gene signature. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2009, 26, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tischler, A.S.; Greene, L.A.; Kwan, P.W.; Slayton, V.W. Ultrastructural effects of nerve growth factor on pc 12 pheochromocytoma cells in spinner culture. Cell Tissue Res. 1983, 228, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(–delta delta ct) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bechmann, N.; Ehrlich, H.; Eisenhofer, G.; Ehrlich, A.; Meschke, S.; Ziegler, C.G.; Bornstein, S.R. Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050172
Bechmann N, Ehrlich H, Eisenhofer G, Ehrlich A, Meschke S, Ziegler CG, Bornstein SR. Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(5):172. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050172
Chicago/Turabian StyleBechmann, Nicole, Hermann Ehrlich, Graeme Eisenhofer, Andre Ehrlich, Stephan Meschke, Christian G. Ziegler, and Stefan R. Bornstein. 2018. "Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro" Marine Drugs 16, no. 5: 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050172
APA StyleBechmann, N., Ehrlich, H., Eisenhofer, G., Ehrlich, A., Meschke, S., Ziegler, C. G., & Bornstein, S. R. (2018). Anti-Tumorigenic and Anti-Metastatic Activity of the Sponge-Derived Marine Drugs Aeroplysinin-1 and Isofistularin-3 against Pheochromocytoma In Vitro. Marine Drugs, 16(5), 172. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16050172






