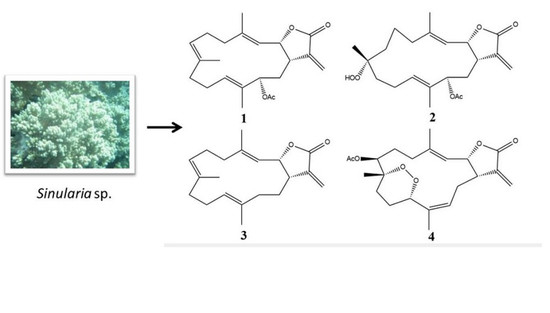
Bioactive Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
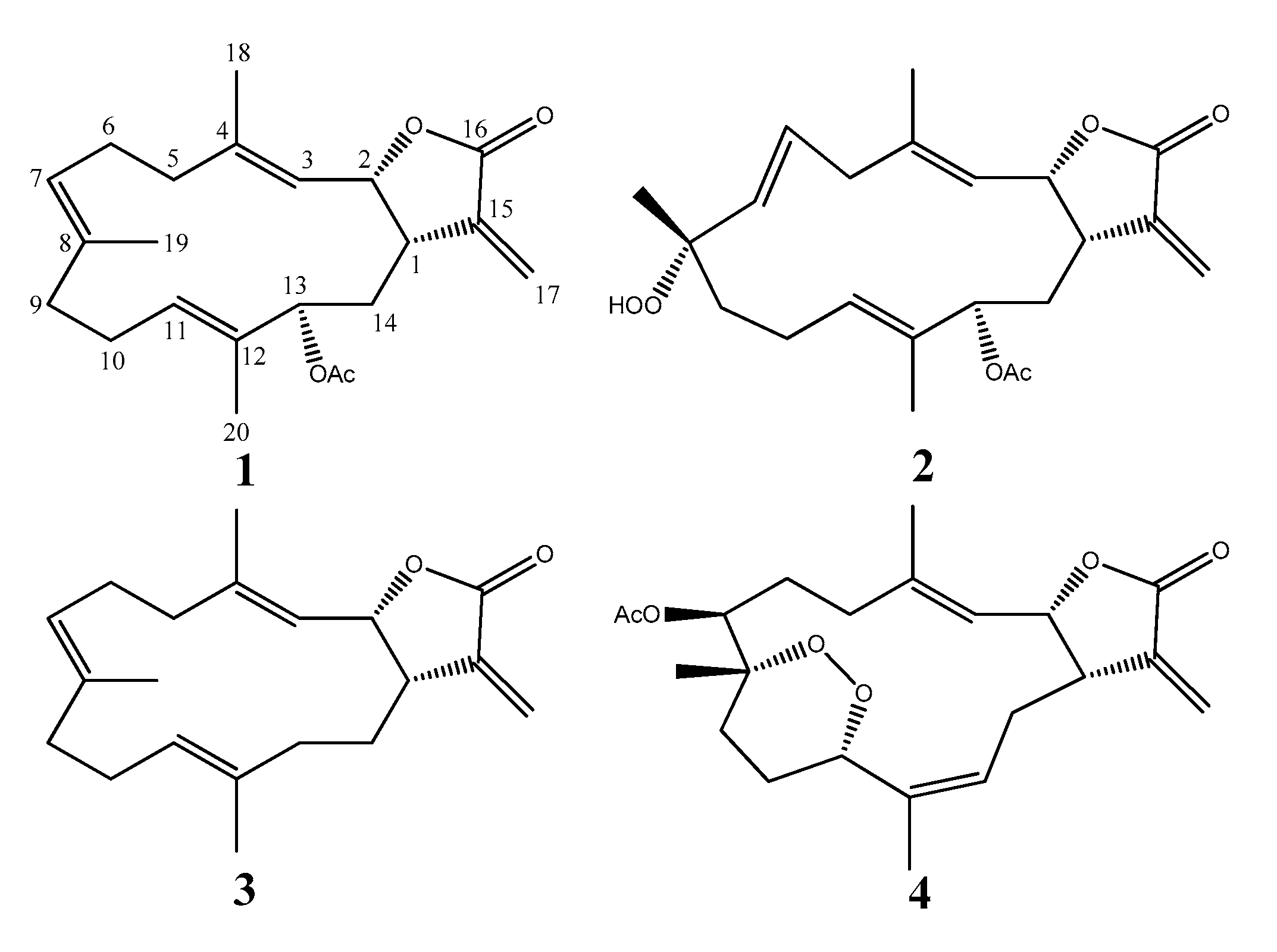
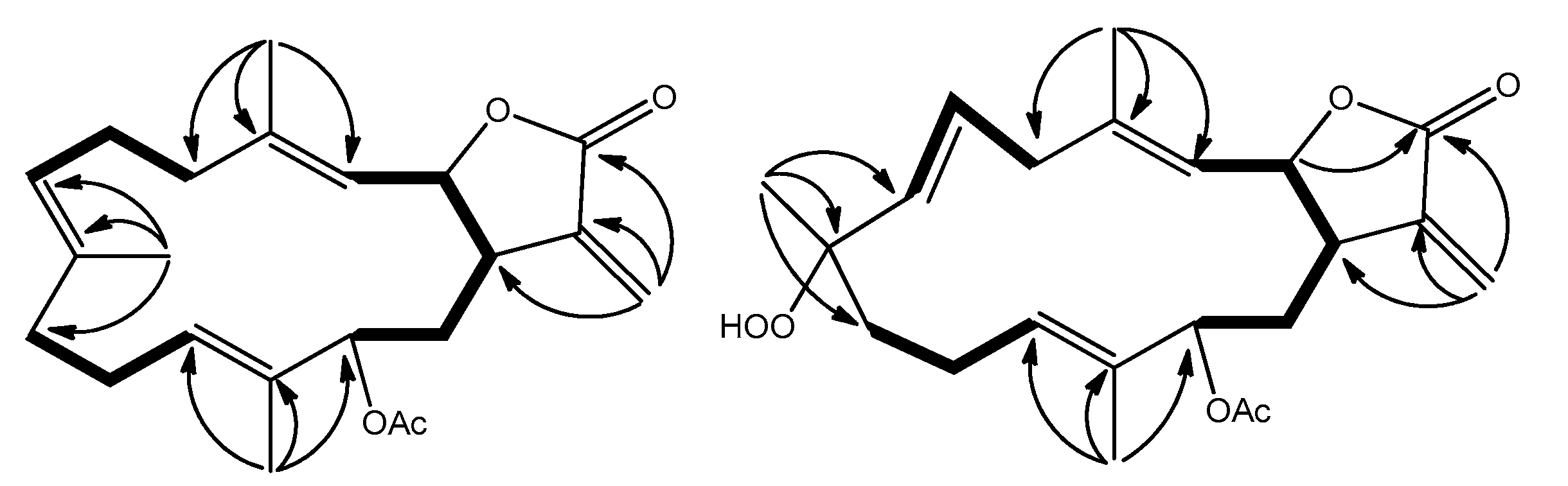
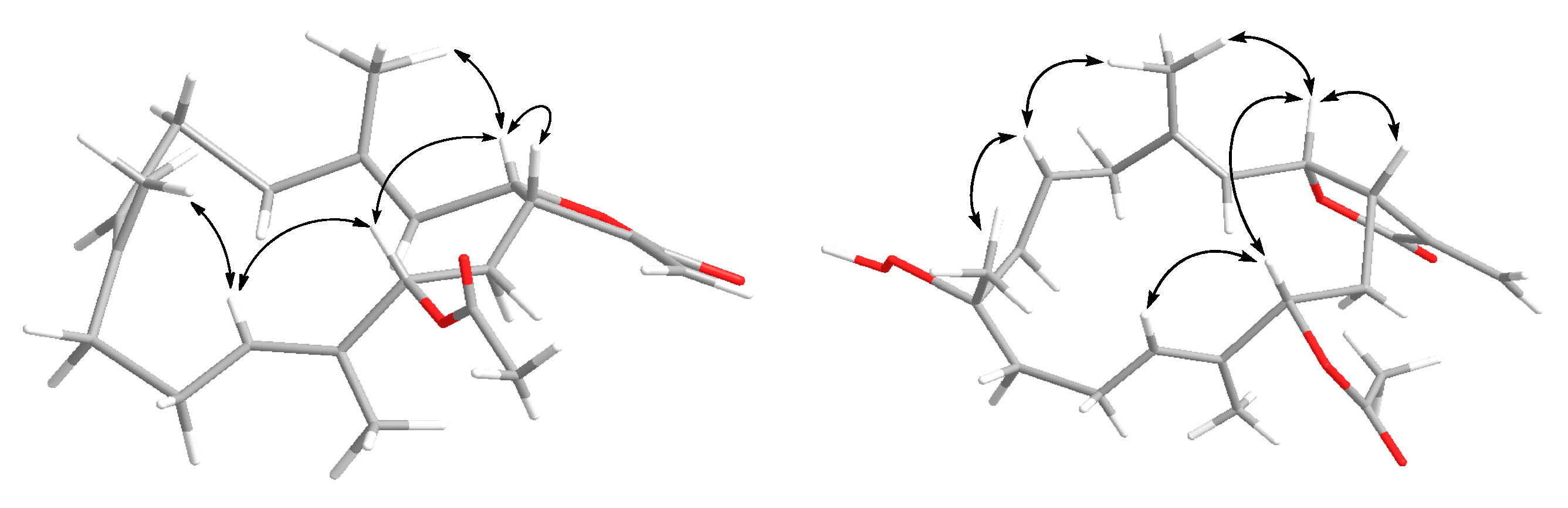
2.1. Cembranolide (1)
2.2. Sinularolide F (2)
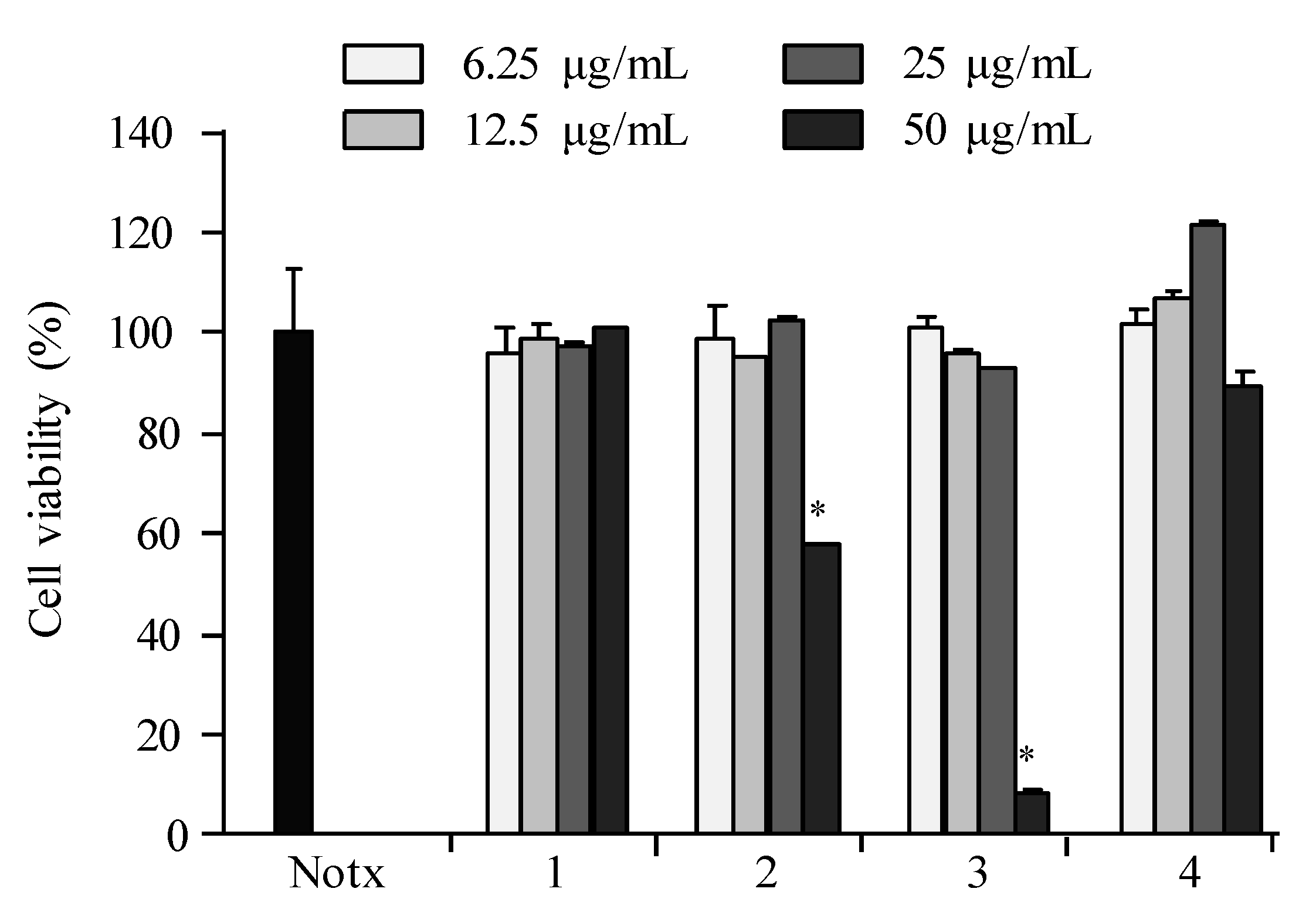
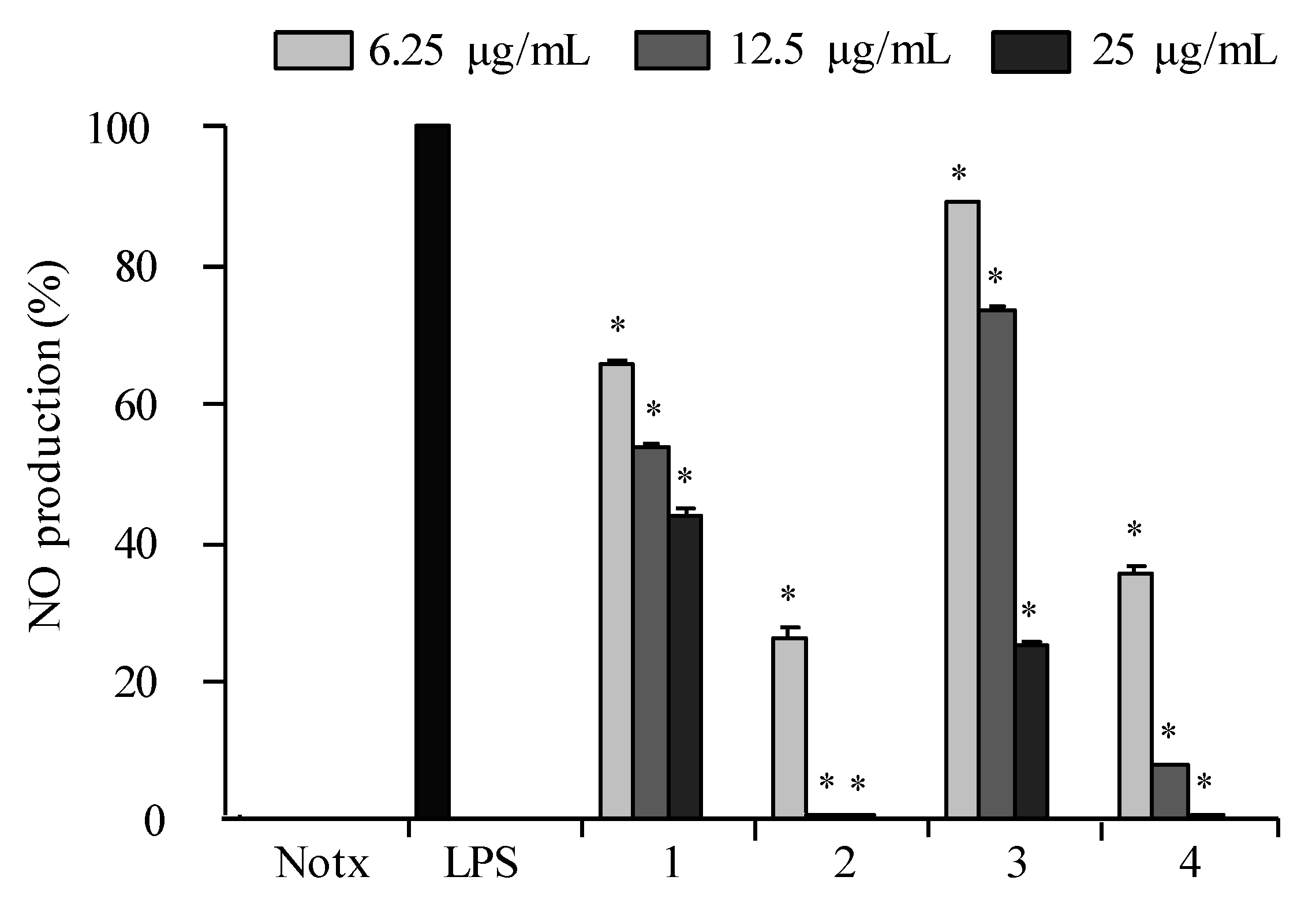
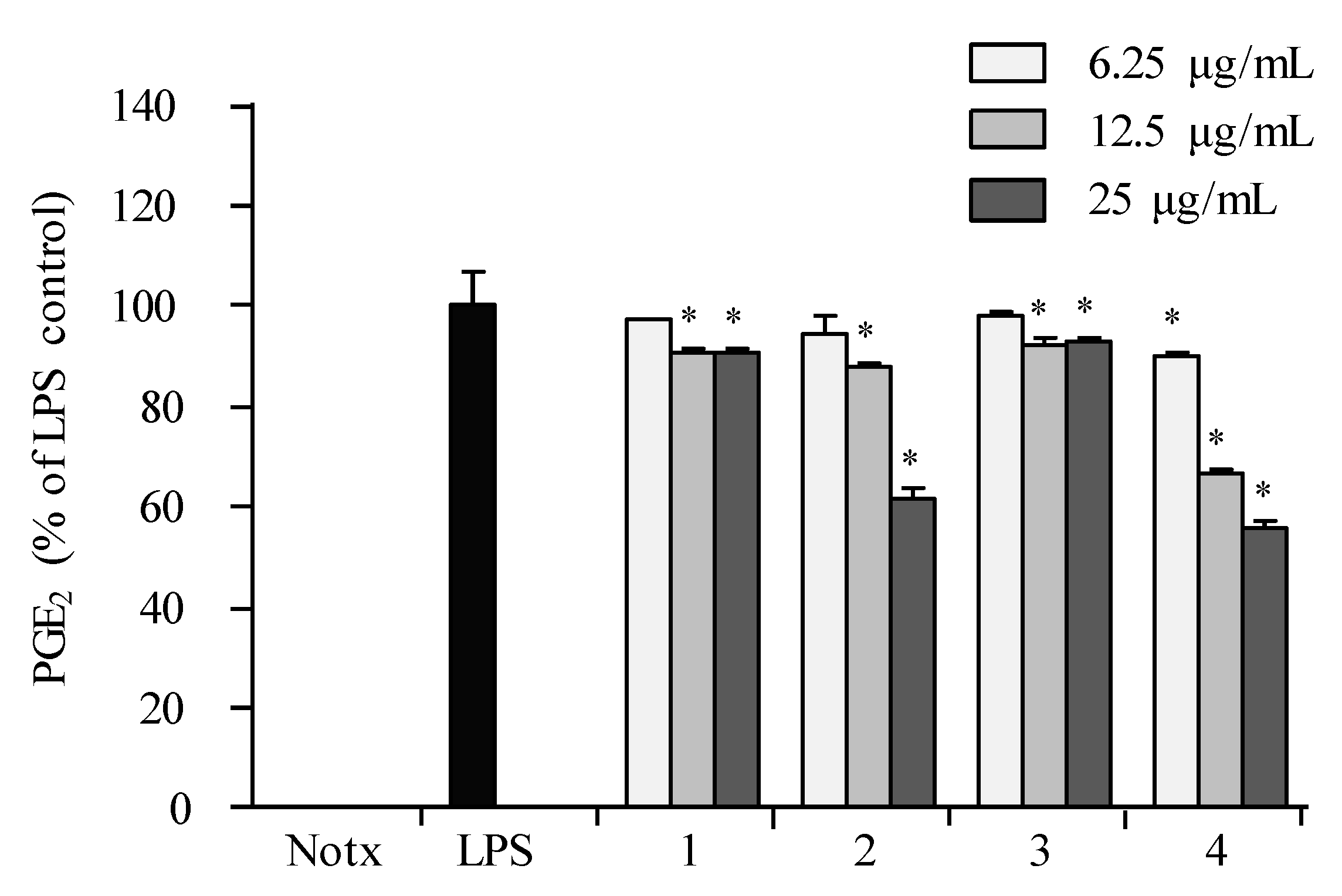
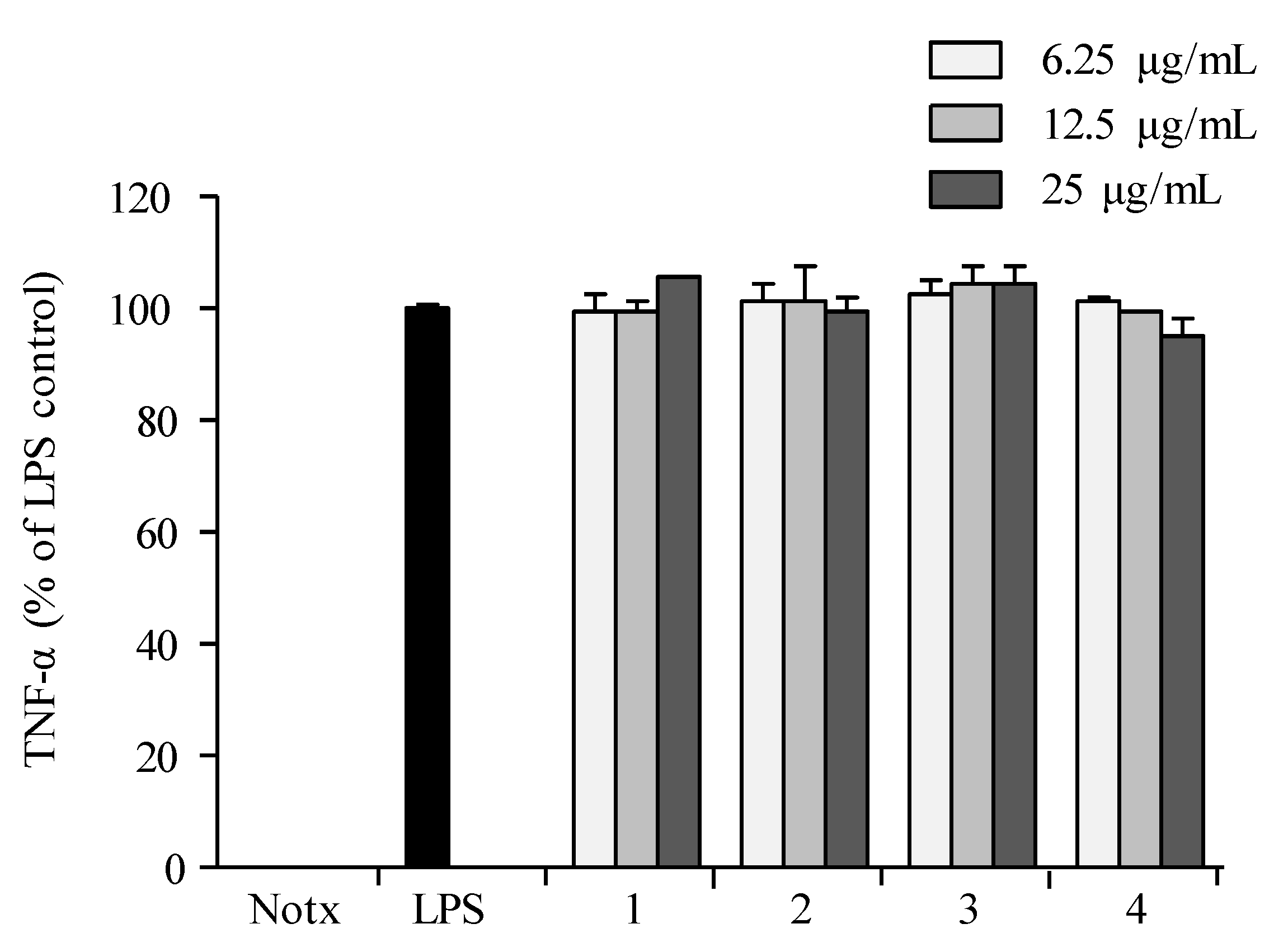
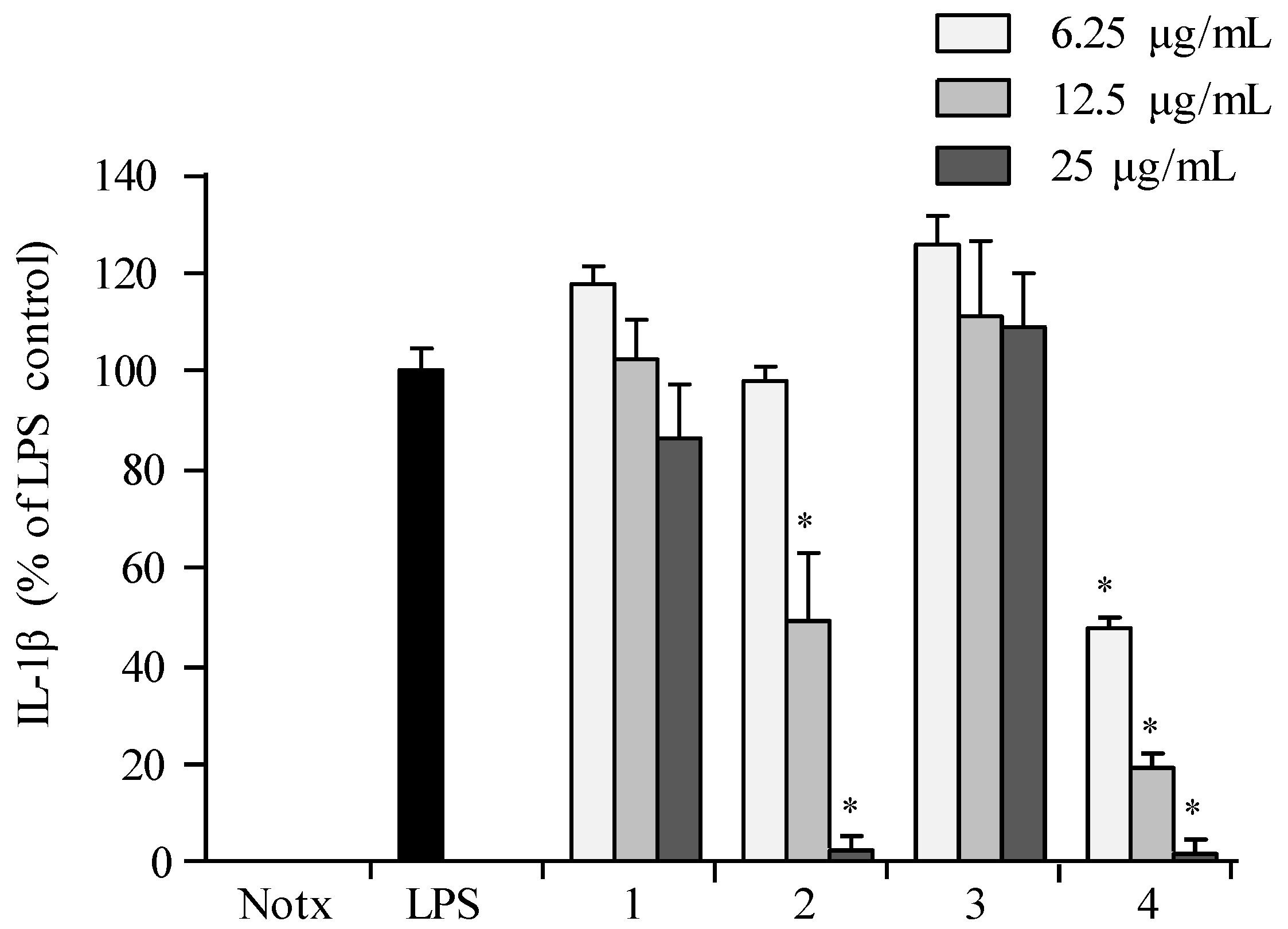
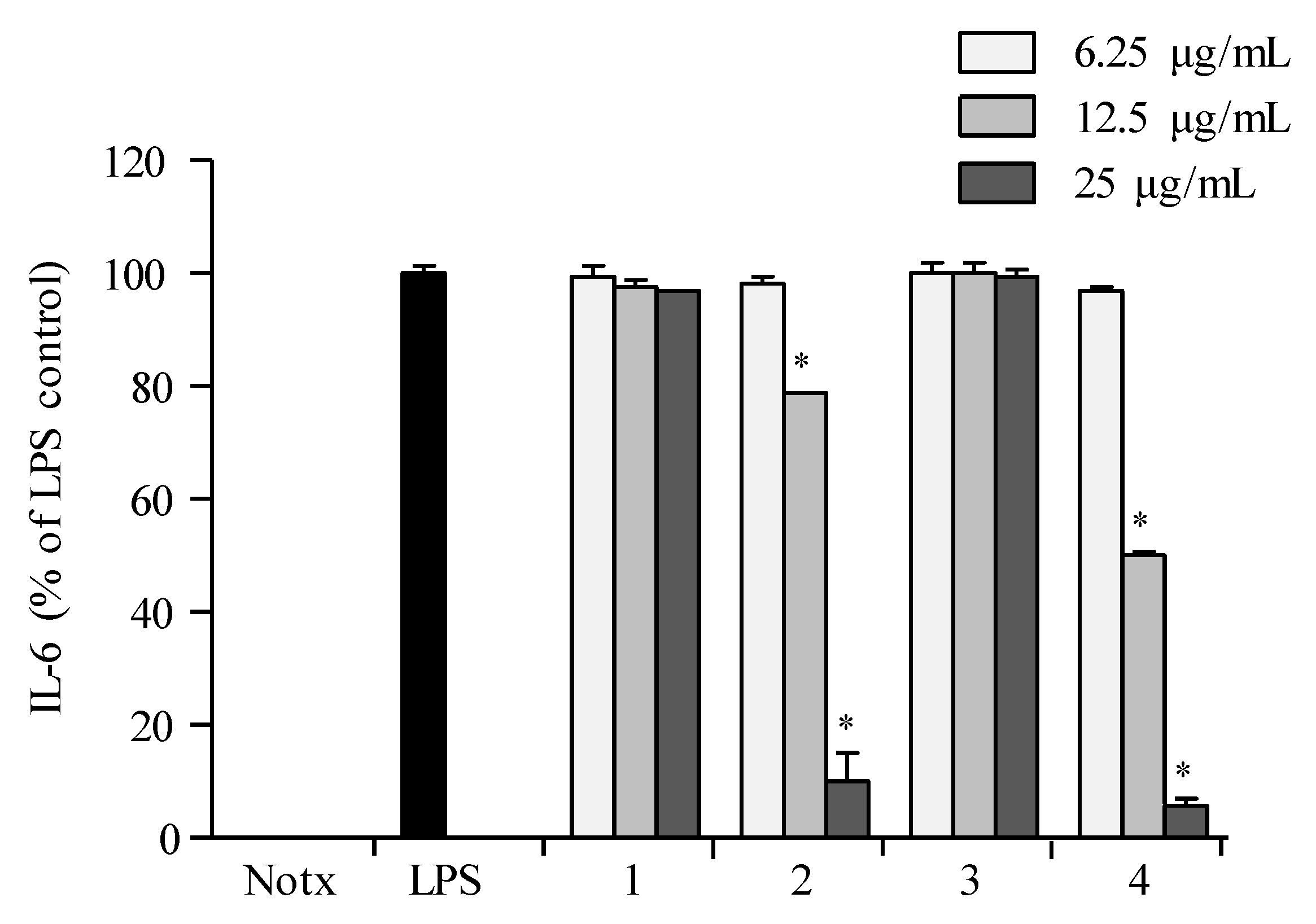
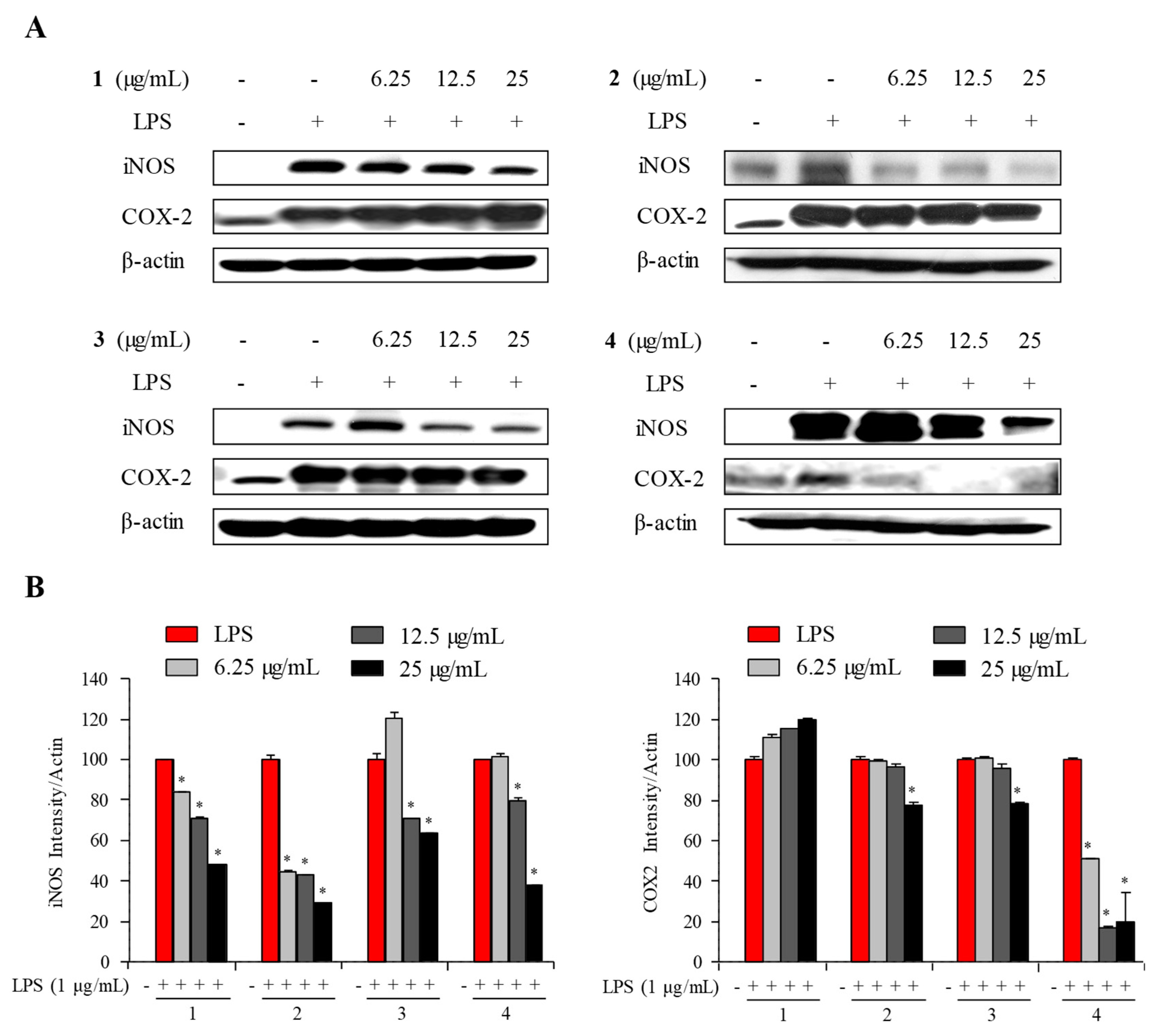
2.3. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
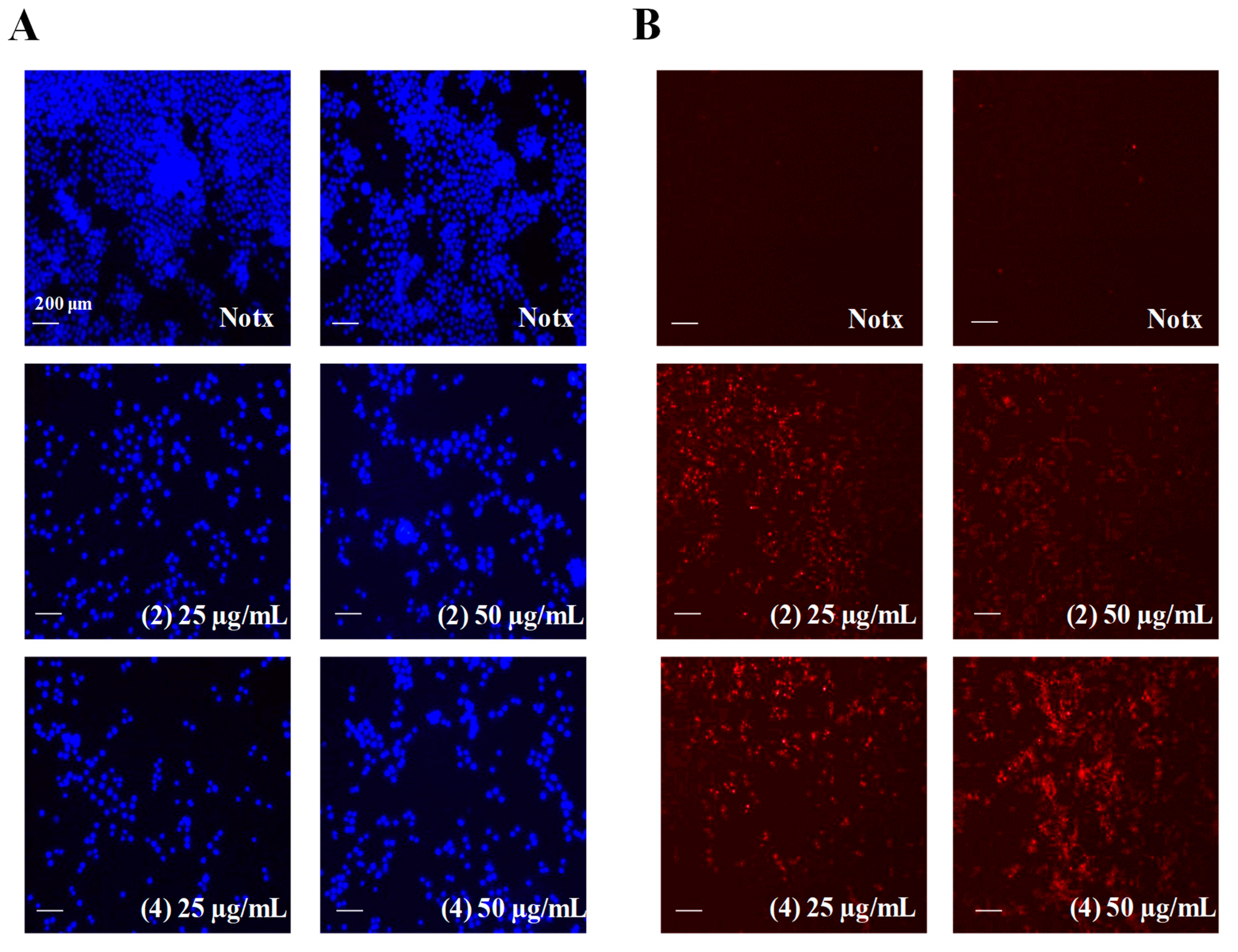
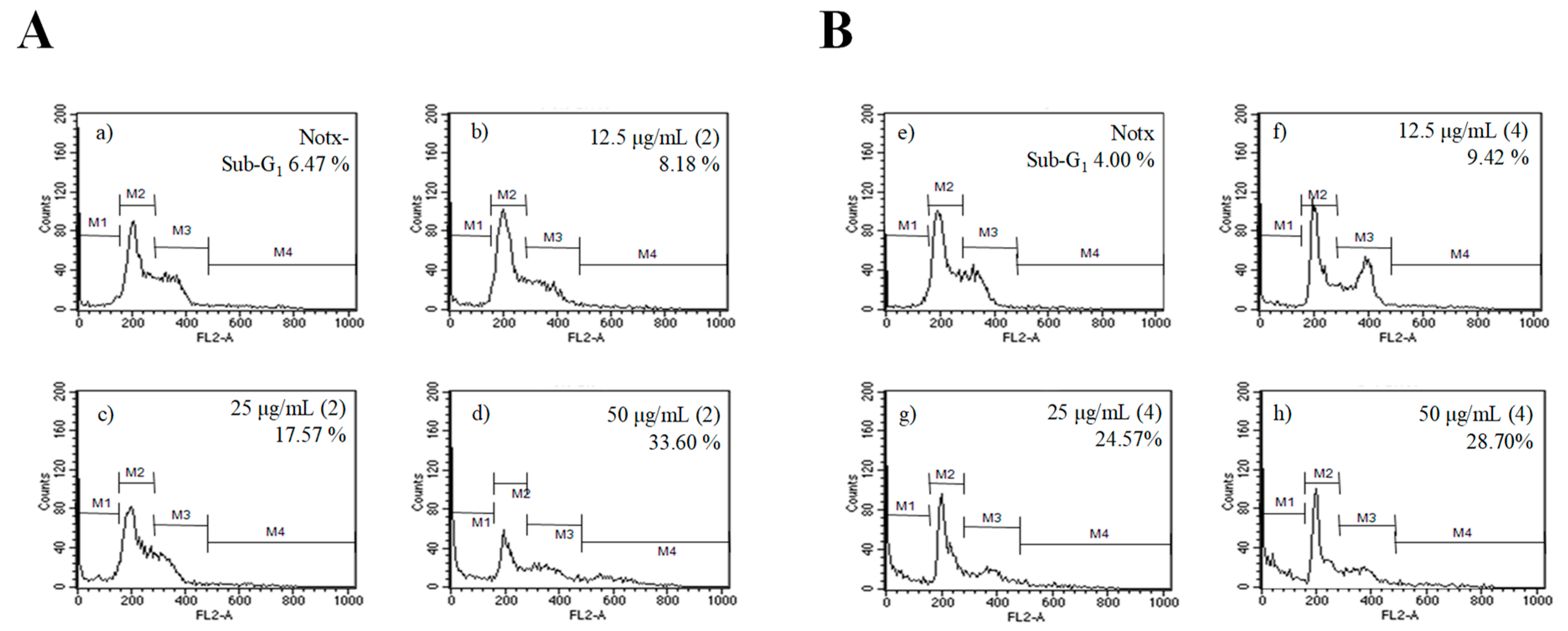
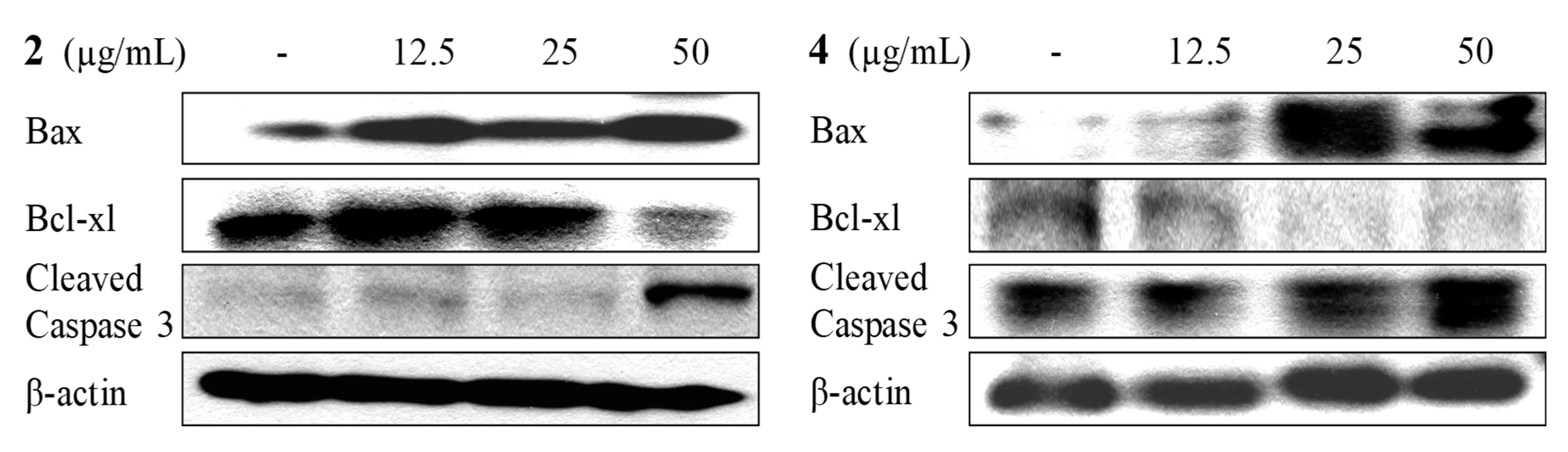
2.4. Apoptosis Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Extraction and Isolation
4.4. Anti-Inflammatory Assay
4.5. Apoptotic Assay
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Phan, C.S.; Ng, S.Y.; Kim, E.A.; Jeon, Y.J.; Palaniveloo, K.; Vairappan, C.S. Capgermacrenes A and B, bioactive secondary metabolites from a Bornean soft coral, Capnella sp. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3103–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Phan, C.S.; Kamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. Capgermacrene C, a new sesquiterpenoid from a Bornean soft coral, Capnella sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, C.S.; Vairappan, C.S. Capgermacrenes D-G, new sesquiterpenoids from a Bornean soft coral, Capnella imbricata. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 31, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Ueoka, R.; Matsunaga, S.; Vairappan, C.S. Bioactive secondary metabolites from the Bornean soft corals of the genus Nephthea. Malays. J. Sci. 2010, 29, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, T.; Matsuura, H.; Zhaoqi, Z.; Vairappan, C.S. A new norsesquiterpenoid from a Bornean soft coral genus Nephthea. Molecules 2009, 14, 4591–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, C.S.; Ng, S.Y.; Kamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. Two new lobane diterpenes from a Bornean soft coral Sinularia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 899–900. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, C.S.; Vairappan, C.S. Isopropyl(ene)-type cembrane diterpene an important chemotaxonomical marker in Bornean soft coral genus Sarcophyton. J. Trop. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 12, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, T.; Zhaoqi, Z.; Vairappan, C.S. A new cembrane diterpene from the Bornean soft coral Nephthea sp. Molecules 2010, 15, 3857–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, T.; Phan, C.S.; Tin, H.S.; Vairappan, C.S.; Muhammad, T.S.T. 16-Hydroxycembra-1,3,7,11-tetraene, a new cembrane diterpene from Malaysian soft coral genus Sarcophyton. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1077–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Ishii, T.; Kamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. Three new cembranoids from the Bornean soft coral Nephthea sp. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, T.; Phan, C.S.; Hamada, T.; Hatai, K.; Vairappan, C.S. Cytotoxic and antifungal terpenoids from Bornean soft coral, Sinularia flexibilis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2018, 13, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, C.S.; Kamada, T.; Ishii, T.; Hamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. 12-Epi-9-deacetoxyxenicin, new cytotoxic diterpenoid from a Bornean soft coral, Xenia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, C.S.; Kamada, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Hamada, T.; Vairappan, C.S. 15-Deoxy-isoxeniolide-A, new diterpenoid from a Bornean soft coral, Xenia sp. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Matsuura, H.; Zhaoqi, Z.; Vairappan, C.S. A new 4α-methylated sterol from a Nephthea sp. (Nephtheidae) Bornean soft coral. Molecules 2009, 14, 3360–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.C.; Mitchell, S.J.; Stokie, G.J. Studies of Australian soft corals. II. A novel cembranoid diterpene from Lobophytum michaelae. Aust. J. Chem. 1977, 30, 1859–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ishizaka, T.; Miura, N.; Mitsuhashi, H. Marine terpenes and terpenoids. III. Isolation and structures of two cembrane diols from the soft coral Sinularia mayi. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 2314–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Yeh, H.C.; Sheu, J.H. Cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1819–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchio, Y.; Eguchi, S.; Kuramoto, J.; Nakayama, M.; Hase, T. Denticulatolide, an ichthyotoxic peroxide-containing cembranolide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 4487–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchio, Y.; Eguchi, S.; Nakayama, M.; Hase, T. Abstracts of papers. In Proceedings of the 27th Symposium on the Chemistry of Terpenes, Essential oils and Aromatics, Kanazawa, Japan, 1984; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, A.J.; Bowden, B.F.; Coll, J.C.; Frick, B.; Mahendran, M.; Mitchell, S.J. Studies of Australian soft corals. XXIX. Several new cembranoid diterpenes from Nephthea brassica and related diterpenes from a Sarcophyton species. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chung, S.G.; Chou, G.C.; Dai, C.F. Cytotoxic cembrenolides and steroids from the Formosan soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchio, Y.; Toyota, J.; Nozaki, H.; Nakayama, M.; Nishizono, Y.; Hase, T. Lobohedleolide and (7Z)-lobohedleolide, new cembranolides from the soft coral Lobophytum hedleyi Whitelegge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1981, 22, 4089–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Huang, B.T.; Dai, C.F. Cytotoxic cembrenolide diterpenes from the Formosan soft coral Lobophytum crassum. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 884–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sinulaflexiolides A-K, cembrane-type diterpenoids from the Chinese soft coral Sinularia flexibilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampman, G.M.; Pavia, D.L.; Kriz, G.S.; Vyvyan, J.R. Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Brooks/Cole: Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, S.J.; Kim, K.N.; Yoon, W.J.; Oh, C.; Choi, Y.U.; Affan, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, D.H. Chromene induces apoptosis via caspase-3 activation in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Gamal Eldeen, A.M.; Shahat, A.A.; Abdel-Latif, F.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; Whittlesey, B.R.; Paré, P.W. Bioactive hydroperoxyl cembranoids from the Red Sea soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.Y.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Bioactive cembranoids from the Dongsha Atoll soft coral Sarcophyton crassocaule. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H. Bioactive cembrane-based diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia triangular. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Kang, M.C.; Li, Y.; Kim, E.A.; Kang, S.M.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of questinol isolated from marine-derived fungus Eurotium amstelodami in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vairappan, C.S.; Kamada, T.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of halogenated secondary metabolites of Laurencia snackeyi (Weber-van Bosse) Masuda in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Appl. Phycol. 2013, 25, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ramasamy, P.; Wahid, M.E.; Vairappan, C.S. Anticancer activity and mediation of apoptosis in human HL-60 leukemia cells by edible sea cucumber (Holothuria edulis) extract. Food Chem. 2013, 139, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| No. | 1 | 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 1 | 40.2 (CH) | 3.10 ddd (3.4, 8.3, 11.7) | 39.1 (CH) | 3.12 ddd (2.8, 8.3, 11.7) |
| 2 | 77.6 (CH) | 5.53 dd (8.3, 11.0) | 77.1 (CH) | 5.48 dd (8.3, 11.0) |
| 3 | 119.8 (CH) | 4.90 d (11.0) | 120.0 (CH) | 5.00 d (11.0) |
| 4 | 143.8 (C) | 142.4 (C) | ||
| 5 | 39.6 (CH2) | 2.16 m | 43.1 (CH2) | 2.78 m |
| 1.80 dt (4.8, 12.4) | 2.76 m | |||
| 6 | 24.2 (CH2) | 2.39 m | 128.6 (CH) | 5.80 td (8.3, 15.8) |
| 2.03 m | ||||
| 7 | 125.6 (CH) | 4.70 br d (8.9) | 136.4 (CH) | 5.46 d (15.8) |
| 8 | 133.2 (C) | 84.4 (C) | ||
| 9 | 39.5 (CH2) | 2.31 br d (13.8) | 37.7 (CH2) | 1.77 m |
| 2.14 m | 1.72 m | |||
| 10 | 22.9 (CH2) | 2.14 m | 22.5 (CH2) | 2.36 m |
| 2.00 m | 1.96 m | |||
| 11 | 129.8 (CH) | 5.23 dd (5.5, 9.6) | 130.5 (C) | 5.31 dd (4.1, 10.3) |
| 12 | 132.0 (C) | 131.9 (C) | ||
| 13 | 77.3 (CH) | 5.04 d (11.0) | 76.8 (CH) | 5.00 d (11.7) |
| 14 | 32.4 (CH2) | 2.41 m | 32.6 (CH2) | 2.20 ddd (2.8, 11.7, 14.4) |
| 1.54 m | 1.52 dd (11.7, 14.4) | |||
| 15 | 138.3 (C) | 138.1 (C) | ||
| 16 | 170.3 (C) | 170.2 (C) | ||
| 17 | 120.2 (CH2) | 6.25 d (3.4) | 120.9 (CH2) | 6.28 d (3.4) |
| 5.49 d (3.4) | 5.52 d (3.4) | |||
| 18 | 15.1 (CH3) | 1.75 s | 16.1 (CH3) | 1.91 s |
| 19 | 15.2 (CH3) | 1.58 s | 20.7 (CH3) | 1.42 s |
| 20 | 10.2 (CH3) | 1.60 s | 10.2 (CH3) | 1.61 s |
| 13-OAc | 170.9 (C) | 170.9 (C) | ||
| 21.2 (CH3) | 2.05 s | 21.2 (CH3) | 2.05 s | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kamada, T.; Kang, M.-C.; Phan, C.-S.; Zanil, I.I.; Jeon, Y.-J.; Vairappan, C.S. Bioactive Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040099
Kamada T, Kang M-C, Phan C-S, Zanil II, Jeon Y-J, Vairappan CS. Bioactive Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(4):99. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040099
Chicago/Turabian StyleKamada, Takashi, Min-Cheol Kang, Chin-Soon Phan, Intan Irna Zanil, You-Jin Jeon, and Charles S. Vairappan. 2018. "Bioactive Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo" Marine Drugs 16, no. 4: 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040099
APA StyleKamada, T., Kang, M.-C., Phan, C.-S., Zanil, I. I., Jeon, Y.-J., & Vairappan, C. S. (2018). Bioactive Cembranoids from the Soft Coral Genus Sinularia sp. in Borneo. Marine Drugs, 16(4), 99. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16040099