Fluostatins M–Q Featuring a 6-5-6-6 Ring Skeleton and High Oxidized A-Rings from Marine Streptomyces sp. PKU-MA00045
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
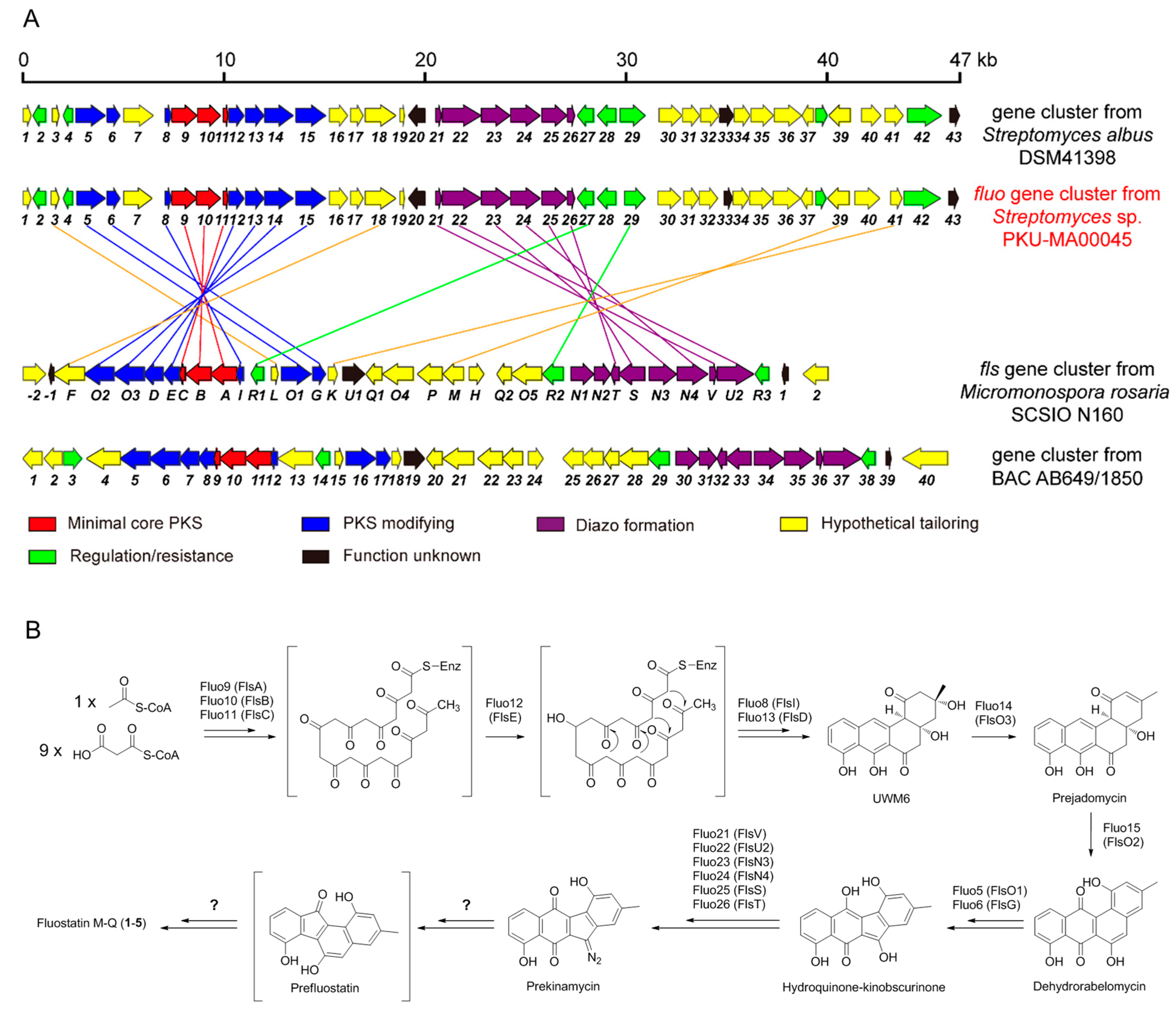
2.1. Genome Mining, Fermentation, Isolation and Phylogenetic Analysis
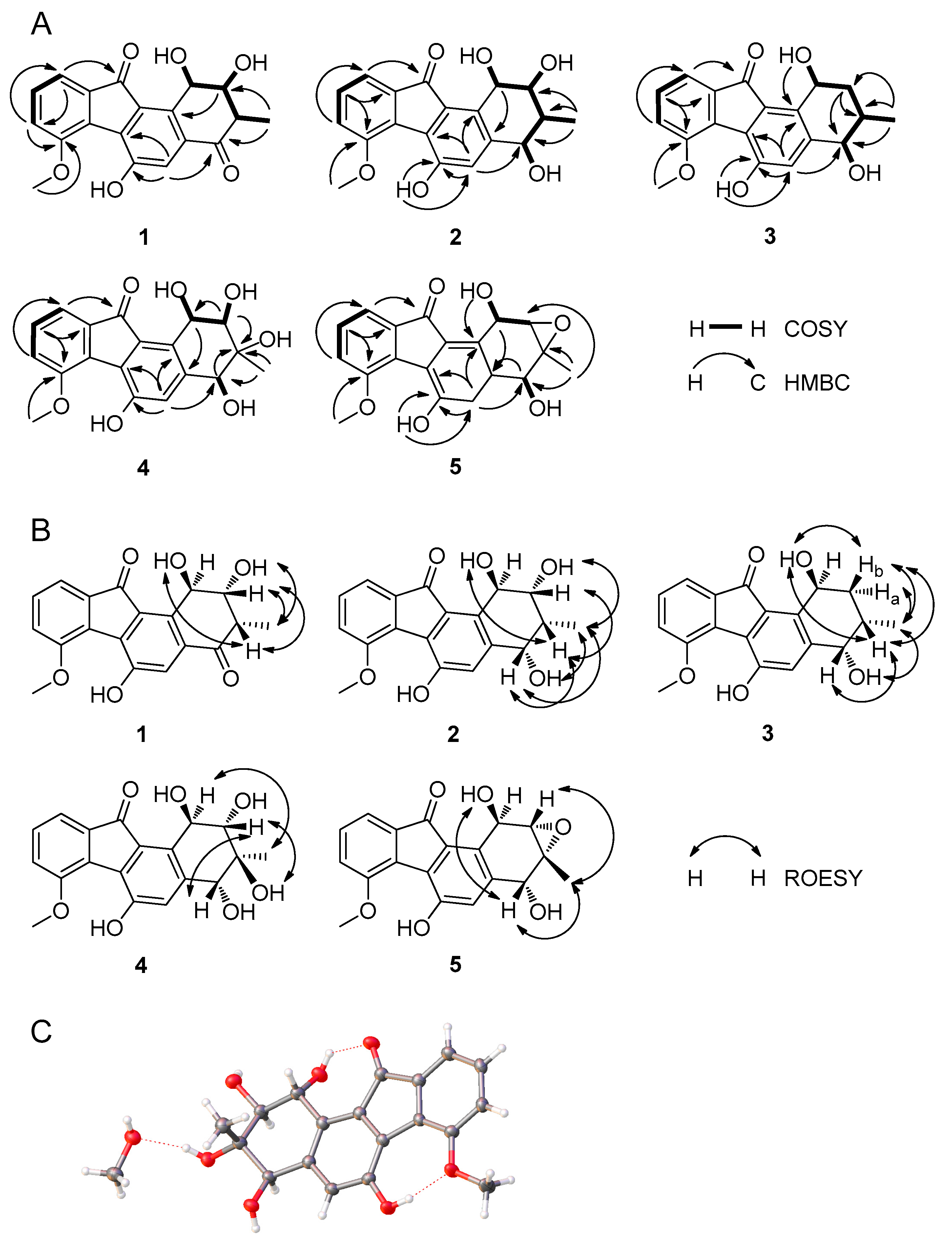
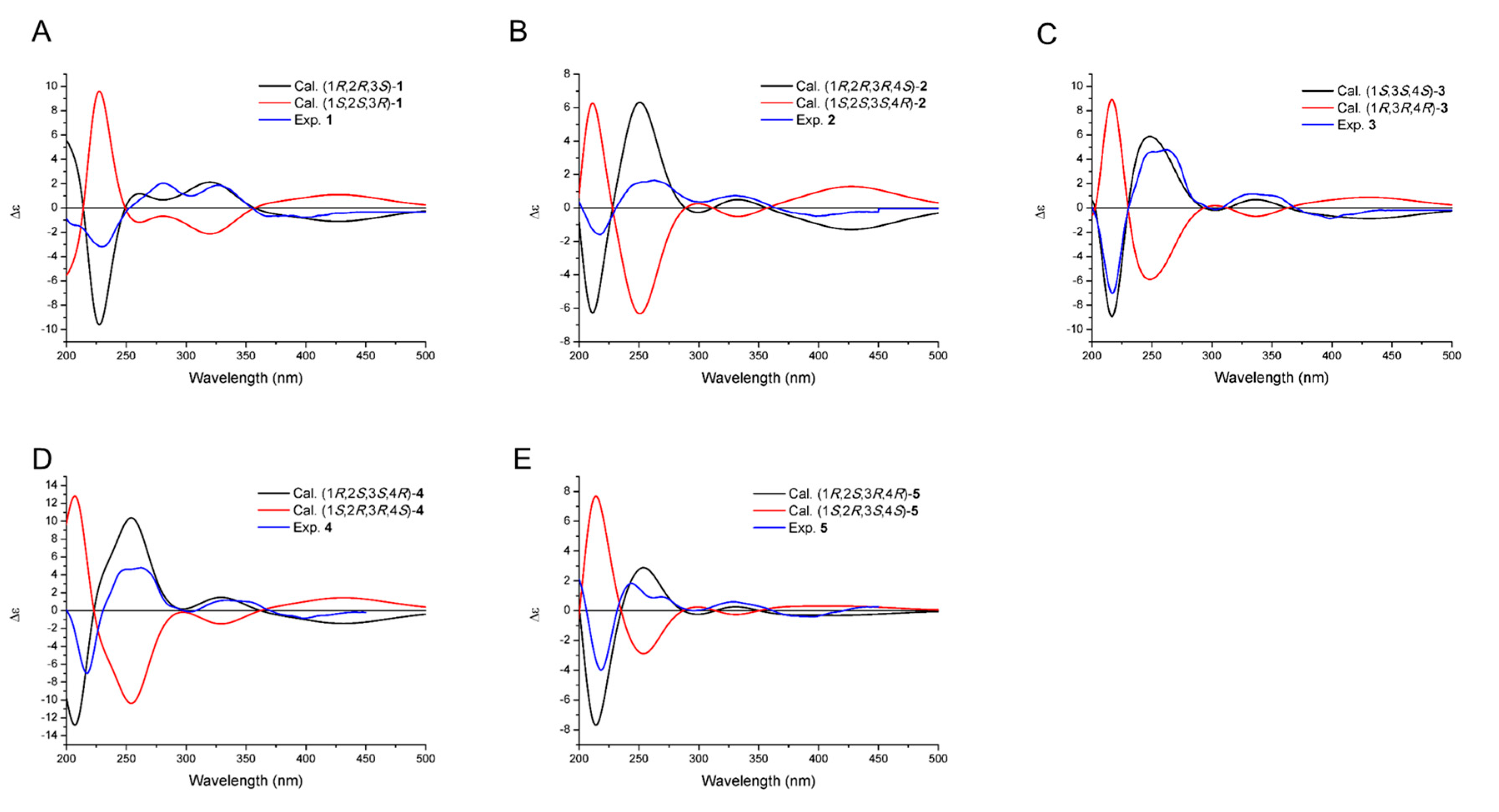
2.2. Structural Elucidation of Compounds 1–5 and Biological Activity Assays
2.3. Proposed Biosynthetic Pathways of Compounds 1–5
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. PCR Screening for Potential Producers of Angucyclinones from a Marine Bacteria Collection
3.3. Small-Scale Fermentation and HPLC Analysis
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.5. Large-Scale Fermentation and Isolation
3.6. ECD Calculation of 1–5
3.7. X-ray Crystallographic Analysis of Compound 4
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R. Developing a new resource for drug discovery: Marine Actinomycete bacteria. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valliappan, K.; Sun, W.; Li, Z.Y. Marine actinobacteria associated with marine organisms and their potentials in producing pharmaceutical natural products. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 7365–7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Kang, K.H.; Sivakumar, K.; Li-Chan, E.C.; Oh, H.M.; Kim, S.K. Marine actinobacteria: An important source of bioactive natural products. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2014, 38, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.R.; Moore, B.S.; Fenical, W. The marine actinomycete genus Salinispora: A model organism for secondary metabolite discovery. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmke, E.; Weyland, H. Rhodococcus marinonascens sp. nov., an actinomycete from the sea. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1984, 34, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjam, M.; Sivalingam, P.; Deng, Z.X.; Hong, K. Deep sea actinomycetes and their secondary metabolites. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, D.; Pokhrel, A.R.; Shrestha, B.; Sohng, J.K. Marine rare actinobacteria: Isolation, characterization, and strategies for harnessing bioactive compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassana, S.S.U.; Shaikh, A.L. Marine actinobacteria as a drug treasure house. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.Y.; Ding, W.D.; Bernan, V.S.; Richardso, A.D.; Ireland, C.M.; Greenstein, M.; Ellestad, G.A.; Carter, G.T. Lomaiviticins A and B, potent antitumor antibiotics from Micromonospora lomaivitiensis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 5362–5363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskey, R.P.; Helmke, E.; Kayser, O.; Fiebig, H.H.; Maier, A.; Busche, A.; Laatsch, H. Anti-cancer and antibacterial trioxacarcins with high anti-malaria activity from a marine Streptomycete and their absolute stereochemistry. J. Antibiot. 2004, 57, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, T.; Kinoshita, M.; Aoki, S.; Kobayashi, M. Komodoquinone, A, a novel neuritogenic anthracycline, from marine Streptomyces sp. KS3. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1373–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Khosla, C. Biosynthesis of aromatic polyketides in bacteria. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharel, M.K.; Pahari, P.; Shepherd, M.D.; Tibrewal, N.; Nybo, S.E.; Shaaban, K.A.; Rohr, J. Angucyclines: Biosynthesis, mode-of-action, new natural products, and synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 264–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertweck, C. The biosynthetic logic of polyketide diversity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2009, 48, 4688–4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, T.; Blin, K.; Duddela, S.; Krug, D.; Kim, H.U.; Bruccoleri, R.; Lee, S.Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; Müller, R.; Wohlleben, W.; et al. AntiSMASH 3.0—A comprehensive resource for the genome mining of biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W237–W243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikesit, A.A.; Stadler, P.F.; Prohaska, S.J. Evolution and quantitative comparison of genome-wide protein domain distributions. Genes 2011, 2, 912–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prohaska, S.J.; Stadler, P.F.; Krakauer, D.C. Innovation in gene regulation: The case of chromatin computation. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 265, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddy, S.R. Hidden Markov models. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 1996, 6, 361–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.J.; Liu, F.W.; Yang, X.Y.; Jin, J.; Dong, X.; Zeng, K.W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.T.; Ma, M.; Yang, D.H. Bacillibactin and bacillomycin analogues with cytotoxicities against human cancer cell lines from marine Bacillus sp. PKU-MA00093 and PKU-MA00092. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Ma, M.; Rateb, M.E.; Shaaban, K.A.; Yu, Z.; Huang, S.X.; Zhao, L.X.; Zhu, X.; Yan, Y.; Peterson, R.M.; et al. Biosynthetic potential-based strain prioritization for natural product discovery: A showcase for diterpenoid-producing actinomycetes. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohr, J.; Thiericke, R. Angucycline group antibiotics. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1992, 2, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Nakamura, K.T.; Takahashi, Y.; Naganawa, H.; Muraoka, Y.; Aoyagi, T.; Takeuchi, T. Fluostatins A and B, new inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase III, produced by Streptomyces sp. TA-3391. II. Structure determination. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 586–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Liu, Z.; Li, S.M.; Lu, Y.Z.; Chen, Y.C.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, G.T.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, G.Y.; Zhang, W.M.; et al. Fluostatins I–K from the South China Sea-derived Micromonospora rosaria SCSIO N160. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 1937–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.; Nicholson, G.; Ströbele, M.; Baur, S.; Niehaus, J.; Fiedler, H.P.; Süssmuth, R.D. The structures of fluostatins C, D and E, novel members of the fluostatin family. J. Antibiot. 2006, 59, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.F.; Huang, C.S.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, C.S. Heterologous expression of fluostatin gene cluster leads to a bioactive heterodimer. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5324–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yang, C.F.; Huang, C.S.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, H.B.; Zhang, Q.B.; Yuan, C.S.; Zhu, Y.G.; Zhang, C.S. Pyrazolofluostatins A-C, pyrazole-fused benzo[a]fluorenes from South China Sea-Derived Micromonospora rosaria SCSIO N160. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Brady, S.F. Fluostatins produced by the heterologous expression of a TAR reassembled environmental DNA derived type II PKS gene cluster. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 11902–11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Guo, F.; Ren, J.W.; Ai, G.M.; Aigle, B.; Fan, K.Q.; Yang, K.Q. Identification of Alp1U and Lom6 as epoxy hydrolases and implications for kinamycin and lomaiviticin biosynthesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7674–7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janso, J.E.; Haltli, B.A.; Eustáquio, A.S.; Kulowski, K.; Waldman, A.J.; Zha, L.; Nakamura, H.; Bernan, V.S.; He, H.Y.; Carter, G.T.; et al. Discovery of the lomaiviticin biosynthetic gene cluster in Salinispora pacifica. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 4156–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Ren, J.W.; Li, L.Y.; Guo, F.; Pan, G.H.; Ai, G.M.; Aigle, B.; Fan, K.Q.; Yang, K.Q. Kinamycin biosynthesis employs a conserved pair of oxidases for B-ring contraction. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 8845–8848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, H.; Krsek, M.; Baker, P.; Smalla, K.; Wellington, E.M. Analysis of actinomycete communities by specific amplification of genes encoding 16S rRNA and gel-electrophoretic separation in denaturing gradients. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3233–3241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- O’Boyle, N.M.; Tenderholt, A.L.; Langner, K.M. Cclib: A library for package-independent computational chemistry algorithms. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5.46, d (3.5) a | 5.12, t (4.3) | 5.30, m | 4.74, dd (6.7, 4.8) | 5.82, dd (6.0, 3.1) |
| 2 | 4.01, dd (3.5, 2.3) a | 3.75, td (4.5, 2.3) | 1.86, td (13.6, 4.0) | 3.59, dd (6.7, 3.8) | 3.28, d (3.1) |
| 1.52, dt (13.6, 2.5) | |||||
| 3 | 3.17, qd (6.8, 2.3) a | 2.24, m | 2.19, m | ||
| 4 | 4.41, dd (7.8, 4.0) | 4.30, t (4.0) | 4.31, br d (5.2) | 4.80, d (8.0) | |
| 5 | 7.40, s | 7.00, s | 6.93, s | 7.09, d (1.0) | 7.17, d (1.0) |
| 8 | 7.45, dd (8.3, 1.4) | 7.41, dd (8.2, 1.3) | 7.40, dd (8.3, 1.3) | 7.40, dd (8.3, 1.0) | 7.40, dd (8.3, 1.2) |
| 9 | 7.47, dd (8.3, 6.6) | 7.38, dd (8.2, 6.8) | 7.37, dd (8.3, 6.7) | 7.37, dd (8.3, 7.0) | 7.37, dd (8.3, 6.8) |
| 10 | 7.36, dd (6.6, 1.4) | 7.29, dd (6.8, 1.3) | 7.28, dd (6.7, 1.3) | 7.29, dd (7.0, 1.0) | 7.27, dd (6.8, 1.2) |
| 12 | 1.17, d (6.9) a | 1.04, d (7.1) | 0.98, d (7.0) | 0.85, s | 1.47, s |
| 13 | 4.11, s | 4.10, s | 4.10, s | 4.08, s | 4.09, s |
| 1-OH | 5.46, overlap | 4.96, d (4.4) | 4.53, d (3.7) | 5.08, d (4.8) | 5.31, d (6.1) |
| 2-OH | 5.31, d (3.5) | 5.19, d (4.8) | 4.77, br s | ||
| 3-OH | 5.10, br s | ||||
| 4-OH | 4.81, d (8.0) | 4.94, d (5.8) | 5.44, d (5.8) | 5.93, d (8.2) | |
| 6-OH | 9.54, s | 9.32, s | 9.30, s | 9.33, s | 9.33, s |
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δc, Type | δc, Type | δc, Type | δc, Type | δc, Type | |
| 1 | 63.6, CH | 66.2, CH | 60.4, CH | 70.2, CH | 59.9, CH |
| 2 | 74.8, CH | 74.0, CH | 33.0, CH2 | 77.4, CH | 59.2, CH |
| 3 | 41.6, CH | 33.3, CH | 28.1, CH | 74.2, C | 58.2, C |
| 4 | 197.7, C | 69.5, CH | 68.7, CH | 73.5, CH | 67.7, CH |
| 4a | 134.0, C | 143.9, C | 144.2, C | 143.6, C | 142.6, C |
| 5 | 119.8, CH | 124.4, CH | 125.1, CH | 122.5, CH | 121.6, CH |
| 6 | 150.9, C | 150.2, C | 150.0, C | 150.4, C | 150.5, C |
| 6a | 132.5, C | 126.7, C | 126.2, C | 126.2,C | 125.1, C |
| 6b | 127.9, C | 128.9, C | 128.9, C | 129.1, C | 128.9, C |
| 7 | 151.8, C | 151.0, C | 151.0, C | 151.1, C | 151.0, C |
| 8 | 120.5, CH | 119.6, CH | 119.4, CH | 120.0, CH | 119.5, CH |
| 9 | 131.8, CH | 130.6, CH | 130.5, CH | 130.7, CH | 130.5, CH |
| 10 | 117.7, CH | 117.7, CH | 117.6, CH | 118.0, CH | 117.6, CH |
| 10a | 135.3, C | 134.7, C | 134.8, C, | 134.5, C | 134.7, C |
| 11 | 192.1, C | 193.4, C | 193.2, C | 194.4, C | 193.0, C |
| 11a | 131.6, C | 132.0, C | 131.1, C | 130.8, C | 130.6, C |
| 11b | 134.7, C | 129.8, C | 131.5, C | 131.7, C | 128.3, C |
| 12 | 11.3, CH3 | 12.2, CH3 | 17.2, CH3 | 15.4, CH3 | 18.8, CH3 |
| 13 | 57.5, CH3 | 57.4, CH3 | 57.4, CH3 | 57.4, CH3 | 57.4, CH3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Xiao, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, M.; Liu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, M.; et al. Fluostatins M–Q Featuring a 6-5-6-6 Ring Skeleton and High Oxidized A-Rings from Marine Streptomyces sp. PKU-MA00045. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16030087
Jin J, Yang X, Liu T, Xiao H, Wang G, Zhou M, Liu F, Zhang Y, Liu D, Chen M, et al. Fluostatins M–Q Featuring a 6-5-6-6 Ring Skeleton and High Oxidized A-Rings from Marine Streptomyces sp. PKU-MA00045. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Jing, Xiaoyan Yang, Tan Liu, Hua Xiao, Guiyang Wang, Mengjie Zhou, Fawang Liu, Yingtao Zhang, Dong Liu, Minghua Chen, and et al. 2018. "Fluostatins M–Q Featuring a 6-5-6-6 Ring Skeleton and High Oxidized A-Rings from Marine Streptomyces sp. PKU-MA00045" Marine Drugs 16, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16030087
APA StyleJin, J., Yang, X., Liu, T., Xiao, H., Wang, G., Zhou, M., Liu, F., Zhang, Y., Liu, D., Chen, M., Cheng, W., Yang, D., & Ma, M. (2018). Fluostatins M–Q Featuring a 6-5-6-6 Ring Skeleton and High Oxidized A-Rings from Marine Streptomyces sp. PKU-MA00045. Marine Drugs, 16(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16030087





