Mixtures of Lipophilic Phycotoxins: Exposure Data and Toxicological Assessment
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Problematic of Phycotoxins Contamination
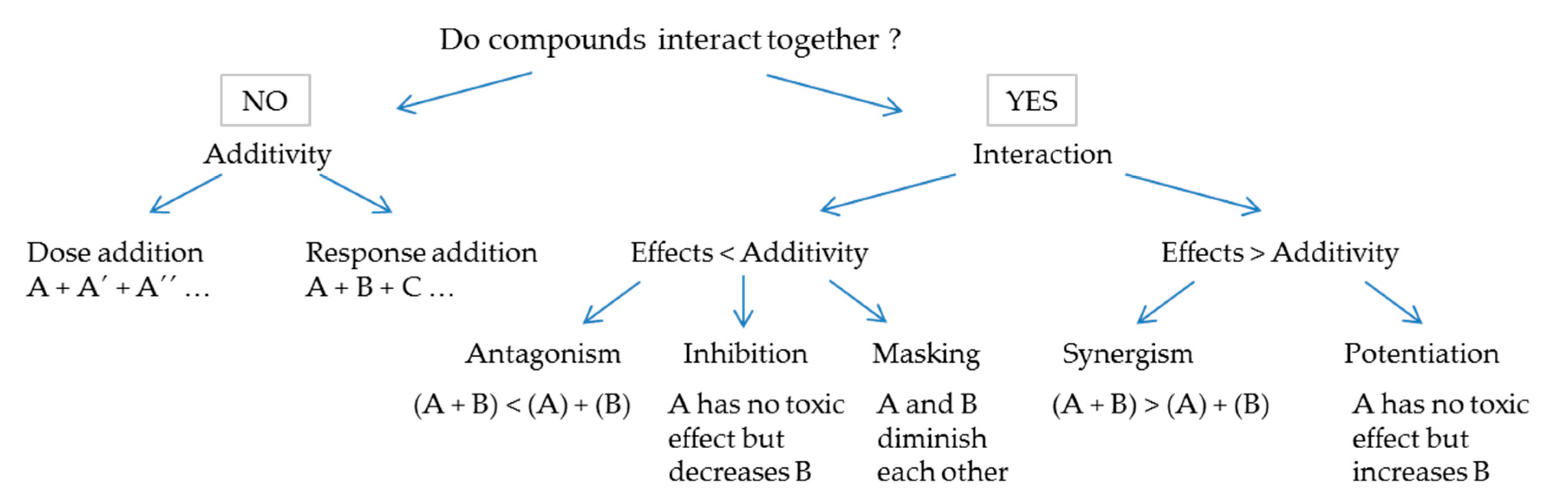
1.2. Methodology for Mixture Hazard Assessment
1.3. Toxicological Features of Phycotoxins
2. Exposure Data
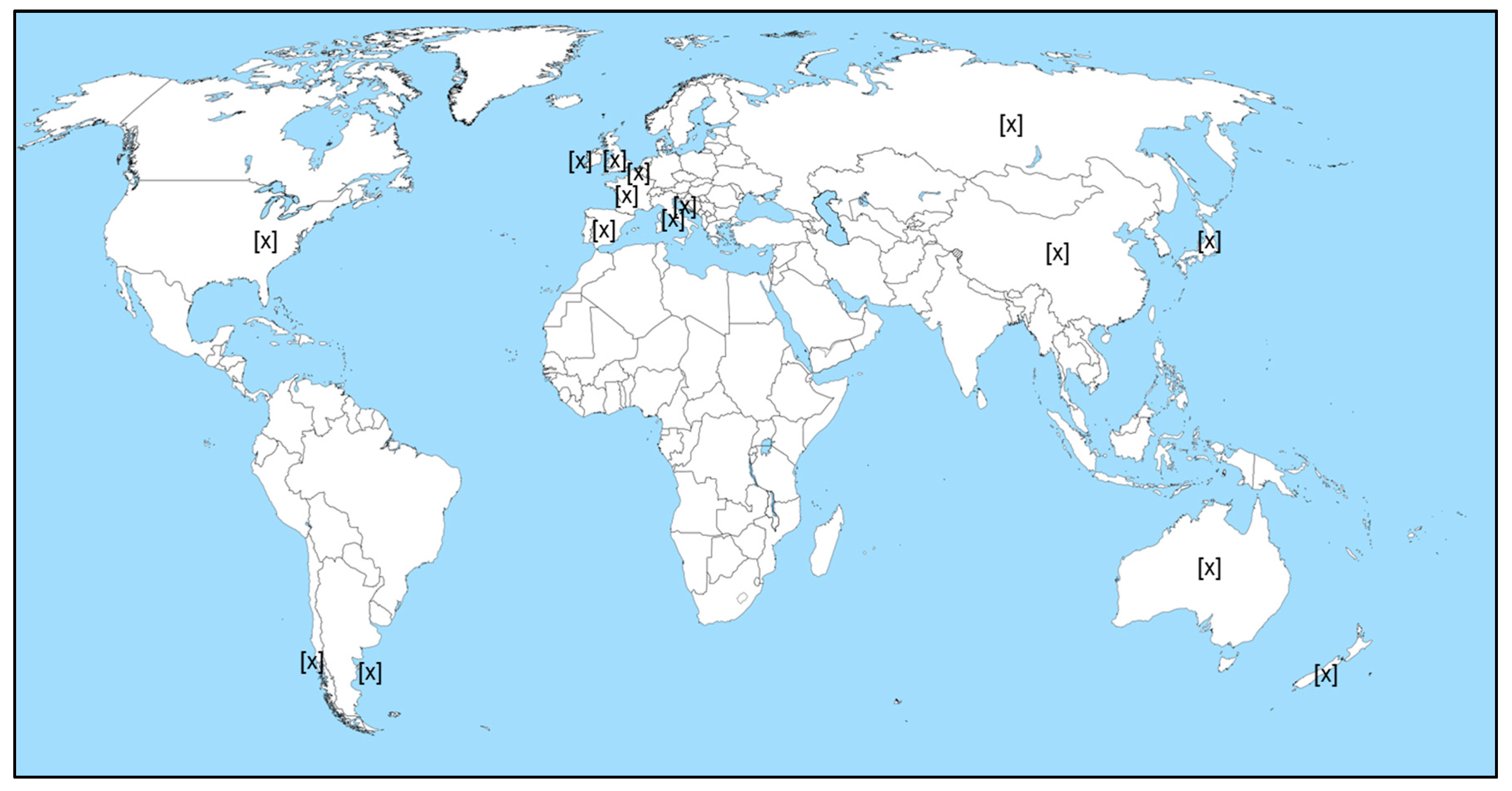
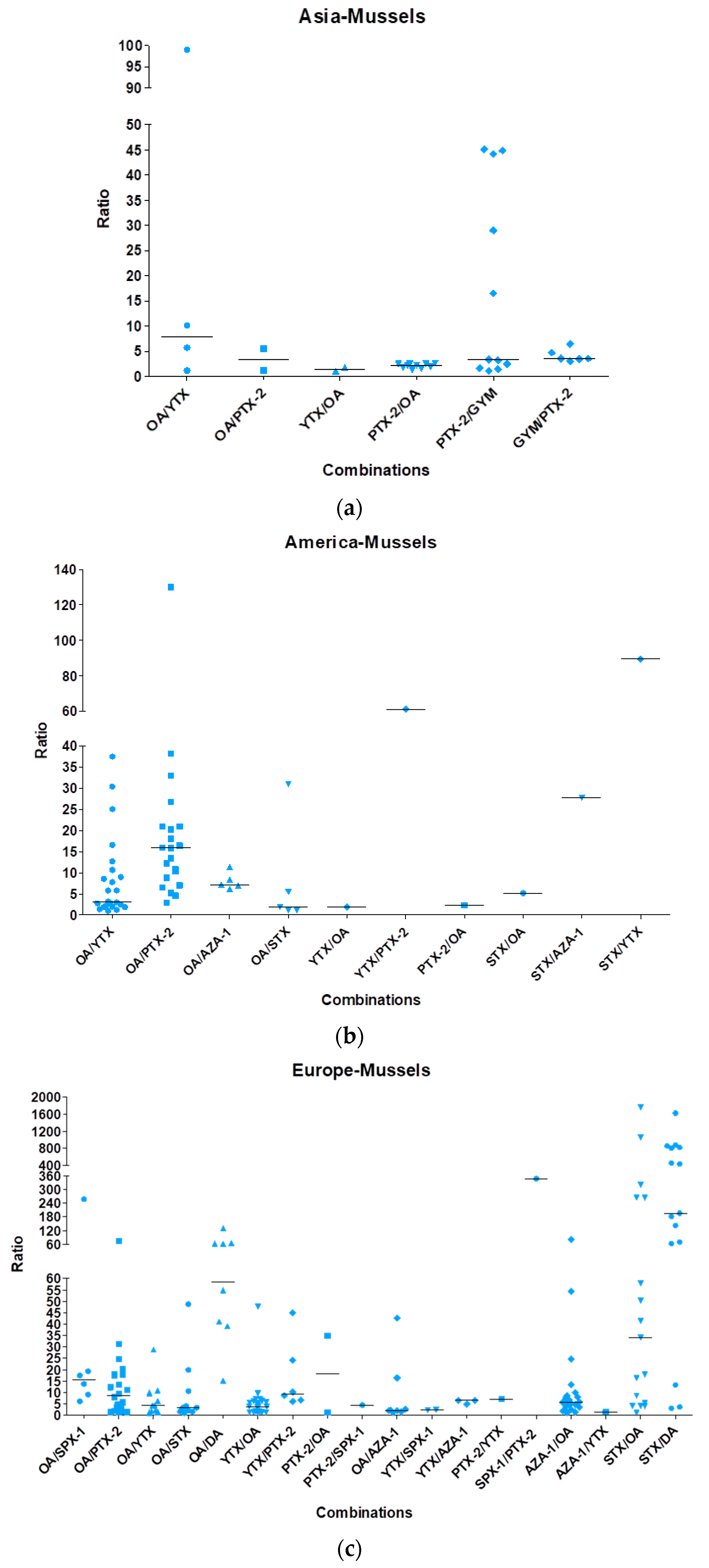
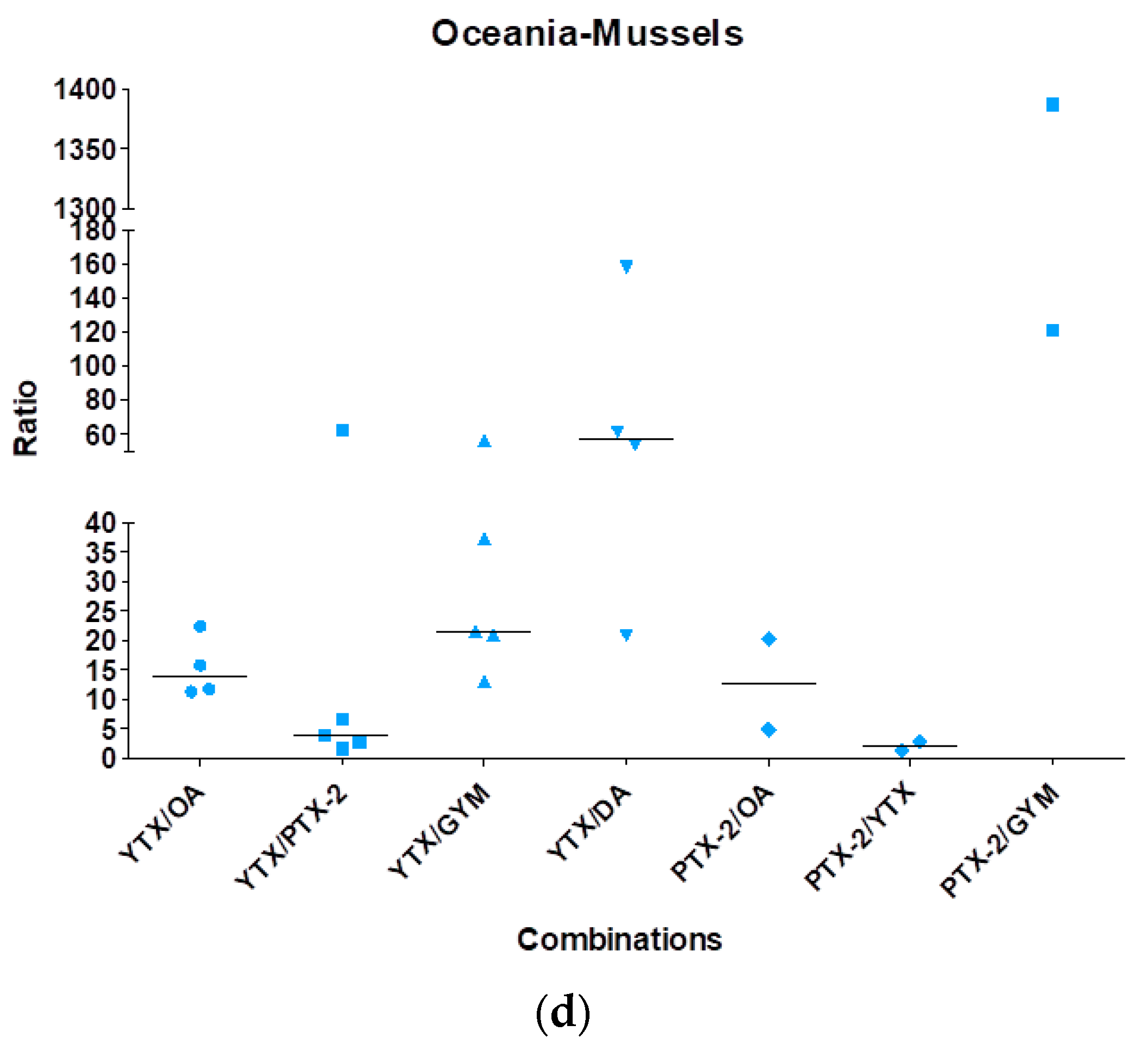
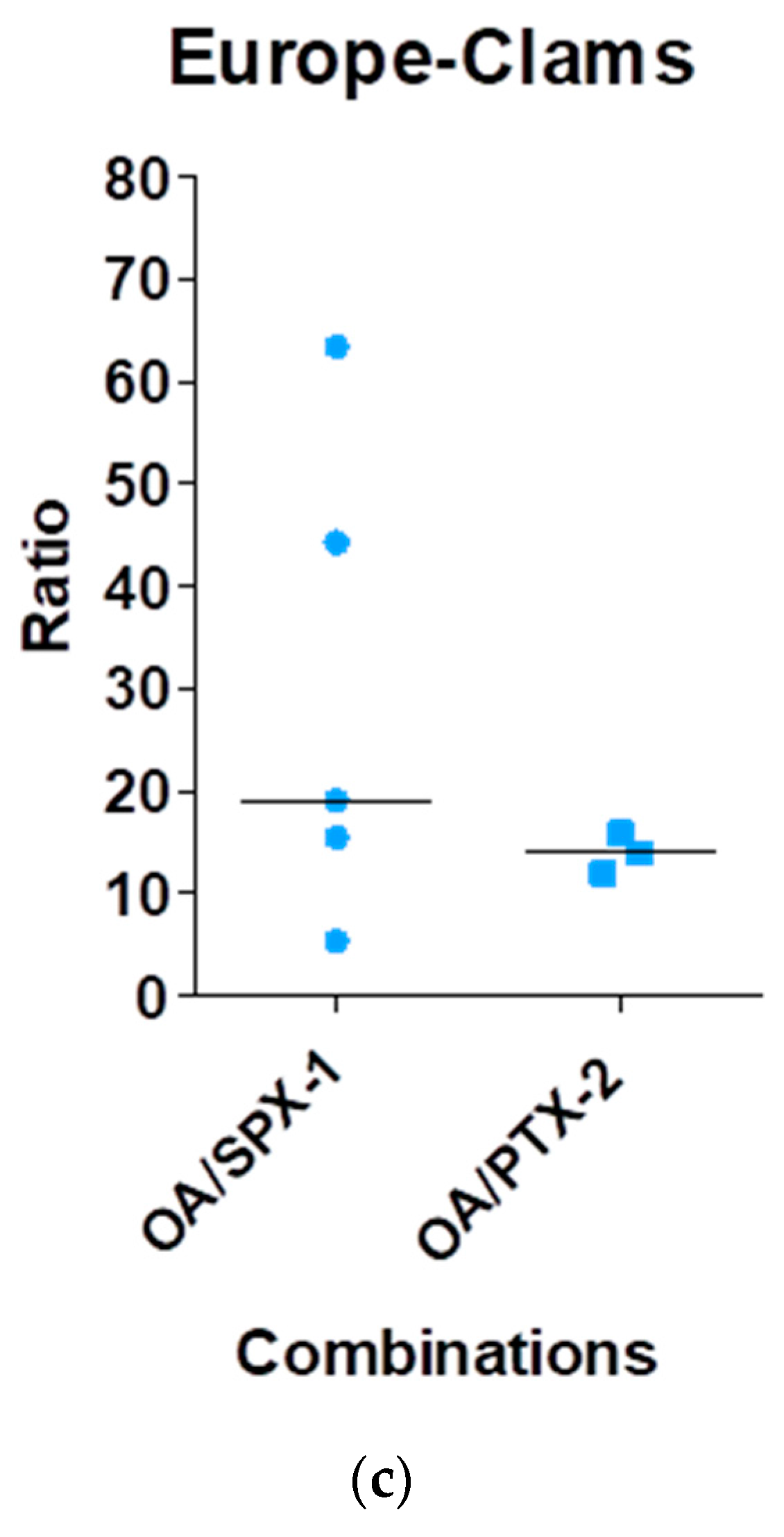
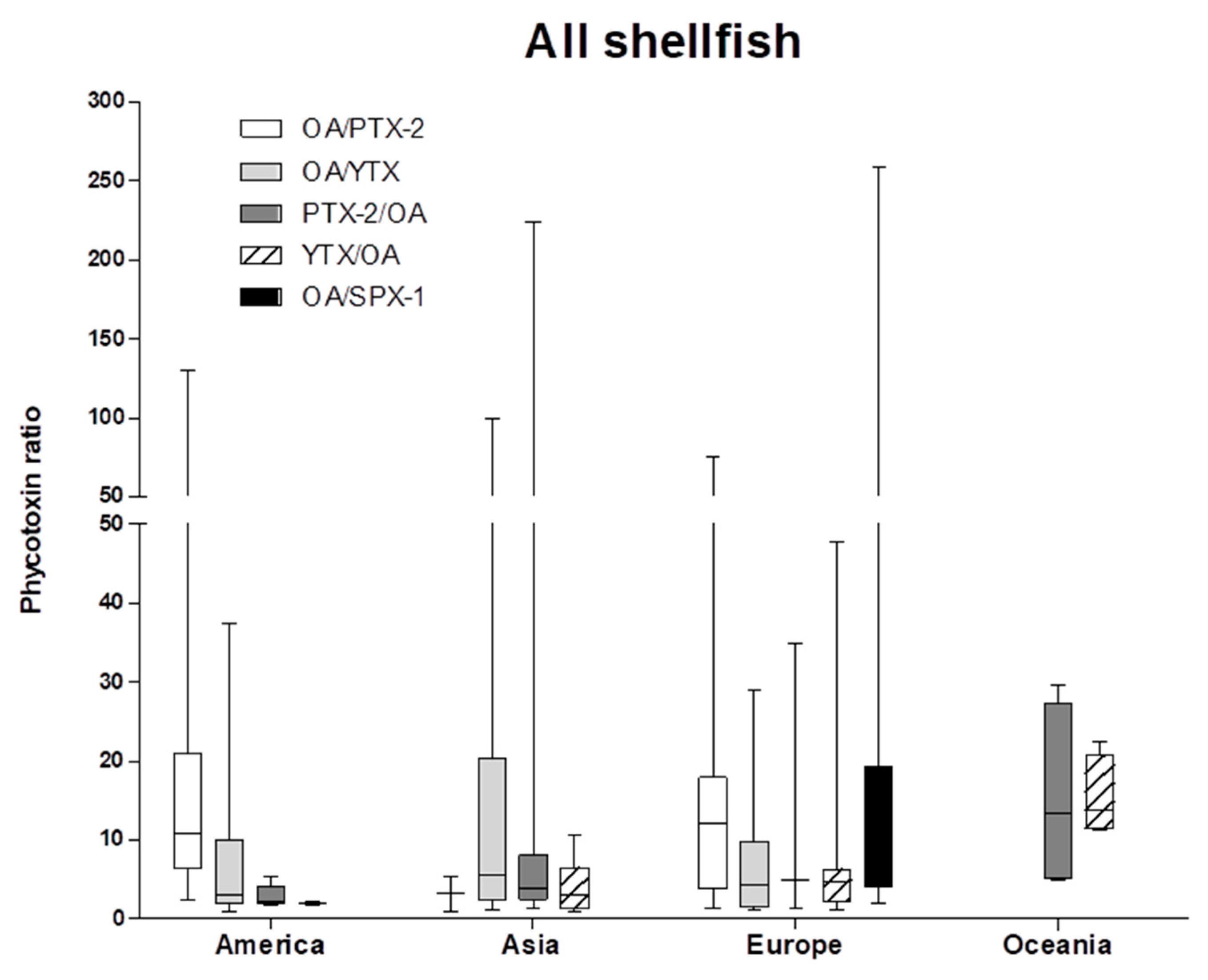
2.1. Case Study of Multi-Phycotoxins Contamination in Shellfish
2.2. Multi-Phycotoxins Contamination in Other Matrices
2.3. Conclusions and Perspectives Regarding Multi-Phycotoxins Contamination in Shellfish
3. Toxicological Assessment
3.1. In Vivo Studies
3.2. In Vitro Studies
3.3. Conclusions and Perspectives Regarding Multi-Phycotoxins’ Toxicological Assessment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Visciano, P.; Schirone, M.; Berti, M.; Milandri, A.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G. Marine biotoxins: Occurrence, toxicity, regulatory limits and reference methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Benford, D.; Boobis, A.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Di Domenico, A.; Doerge, D.; Dogliotti, E.; Edler, L.; Farmer, P.; et al. Scientific Opinion of the Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain on a request from the European Commission on Marine Biotoxins in Shellfish—Summary on regulated marine biotoxins. EFSA J. 2009, 1306, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, J.; Benford, D.; Boobis, A.; Ceccatelli, S.; Cravedi, J.-P.; Di Domenico, A.; Doerge, D.; Dogliotti, E.; Edler, L.; Farmer, P.; et al. Scientific Opinion on marine biotoxins in shellfish—Cyclic imines (spirolides, gymnodimines, pinnatoxins and pteriatoxins). EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-S.; Igarashi, T.; Fraga, S.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J. Appl. Phycol. 1989, 1, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.; Winshell, J.; Scorzetti, G.; Fell, J.W.; Rein, K.S. Identification of okadaic acid production in the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum rhathymum from Florida Bay. Toxicon 2010, 55, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draisci, R.; Lucentini, L.; Giannetti, L.; Boria, P.; Poletti, R. First report of pectenotoxin-2 (PTX-2) in algae (Dinophysis fortii) related to seafood poisoning in Europe. Toxicon 1996, 34, 923–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Beuzenberg, V.; Mackenzie, L.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatographymass spectrometry of spiroketal stereoisomers of pectenotoxins and the analysis of novel pectenotoxin isomers in the toxic dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta from New Zealand. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 992, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; Beuzenberg, V.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Suzuki, T.; Selwood, A. Pectenotoxin and okadaic acid-based toxin profiles in Dinophysis acuta and Dinophysis acuminata from New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2005, 4, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisa Fernández, M.; Reguera, B.; González-Gil, S.; Míguez, A. Pectenotoxin-2 in single-cell isolates of Dinophysis caudata and Dinophysis acuta from the Galician Rías (NW Spain). Toxicon 2006, 48, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, M.; Ichimura, T.; Sekiguchi, K.; Yoshimatsu, S.; Oshima, Y. Confirmation of yessotoxin and 45,46,47-trinoryessotoxin production by Protoceratium reticulatum collected in Japan. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistocchi, R.; Guerrini, F.; Pezzolesi, L.; Riccardi, M.; Vanucci, S.; Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Forino, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Tartaglione, L.; et al. Toxin levels and profiles in microalgae from the north-Western Adriatic Sea—15 years of studies on cultured species. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 140–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillmann, U.; Elbrächter, M.; Krock, B.; John, U.; Cembella, A. Azadinium spinosum gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) identified as a primary producer of azaspiracid toxins. Eur. J. Phycol. 2009, 44, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cembella, A.D.; Lewis, N.I.; Quilliam, M.A. The marine dinoflagellate Alexandriumostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) as the causative organism of spirolide shellfish toxins. Phycologia 2000, 39, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzet, N.; Franco, J.M.; Raine, R. Morphogenetic diversity and biotoxin composition of Alexandrium (dinophyceae) in Irish coastal waters. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 782–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.; Benford, D.; Leblanc, J.-C.; Hougaard-Bennekou, S.; Dorne, J.-L.; Binaglia, M.; Castoldi, A.; Chiusolo, A.; Cortinas-Abrahantes, J.; Heraud, F.; et al. European Food Safety Authority, 2013. International Frameworks Dealing with Human Risk Assessment of Combined Exposure to Multiple Chemicals. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakura, N.; Sanders, P.; Fessard, V.; Le Hégarat, L. In vitro combined cytotoxic effects of pesticide cocktails simultaneously found in the French diet. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 52, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, N.J.; Crockett, P.W.; Nyska, A.; Brix, A.E.; Jokinen, M.P.; Sells, D.M.; Hailey, J.R.; Easterling, M.; Haseman, J.K.; Yin, M.; et al. Dose-additive carcinogenicity of a defined mixture of “dioxin-like compounds”. Environ. Health Perspect. 2004, 113, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Du, Q. Combined toxic effects of heavy metals and antibiotics on a pseudomonas fluorescens strain zy2 isolated from swine wastewater. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2839–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Prego-Faraldo, M.V.; Pásaro, E.; Méndez, J.; Laffon, B. Okadaic acid: More than a diarrheic toxin. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4328–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takai, A.; Murata, M.; Torigoe, K.; Isobe, M.; Mieskes, G.; Yasumoto, T. Inhibitory effect of okadaic acid derivatives on protein phosphatases. A study on structure-affinity relationship. Biochem. J. 1992, 284 Pt 2, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, E.; Suzuki, T.; Oshima, Y.; Yasumoto, T. Studies of diarrhetic activity on pectenotoxin-6 in the mouse and rat. Toxicon 2008, 51, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allingham, J.S.; Miles, C.O.; Rayment, I. A Structural Basis for Regulation of Actin Polymerization by Pectenotoxins. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 371, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, T.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Miles, C.O.; Larsen, S. Effect of mouse strain and gender on LD50 of yessotoxin. Toxicon 2008, 52, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Giangaspero, A.; Ardizzone, M.; Soranzo, M.R.; Vita, F.; Yasumoto, T.; Maucher, J.M.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Sosa, S. Ultrastructural damage to heart tissue from repeated oral exposure to yessotoxin resolves in 3 months. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1225–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korsnes, M.S. Yessotoxin as a Tool to Study Induction of Multiple Cell Death Pathways. Toxins 2012, 4, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubaro, A.; Dell’Ovo, V.; Sosa, S.; Florio, C. Yessotoxins: A toxicological overview. Toxicon 2010, 56, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Araujo, A.; Alfonso, A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Key role of phosphodiesterase 4A (PDE4A) in autophagy triggered by yessotoxin. Toxicology 2015, 329, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, T.; Silke, J. West coast of Ireland; winter toxicity of unknown aetiology in mussels. In Harmfull Algae News; The Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kilcoyne, J.; Jauffrais, T.; Twiner, M.J.; Doucette, G.J.; Aasen-Bunes, J.A.; Sosa, S.; Krock, B.; Séhet, V.; Nulty, C.; Salas, R.; et al. Azaspiracids—Toxicological Evaluation, Test Methods and Identification of the Source Organism (ASTOX II). Available online: http://oar.marine.ie/handle/10793/970 (accessed on 19 February 2017).
- Twiner, M.J.; Doucette, G.J.; Rasky, A.; Huang, X.-P.; Roth, B.L.; Sanguinetti, M.C. Marine Algal Toxin Azaspiracid Is an Open-State Blocker of hERG Potassium Channels. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1975–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R.; Quilliam, M.A.; LeBlanc, P.; Lewis, N.; Gallant, P.; Sperker, S.A.; Ewart, H.S.; MacKinnon, S.L. Investigations into the Toxicology of Spirolides, a Group of Marine Phycotoxins. Toxins 2011, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molgó, J.; Marchot, P.; Aráoz, R.; Benoit, E.; Iorga, B.I.; Zakarian, A.; Taylor, P.; Bourne, Y.; Servent, D. Cyclic imine toxins from dinoflagellates: A growing family of potent antagonists of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Neurochem. 2017, 142 (Suppl. S2), 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, H.; Vale, P.; Amanhir, R.; Benhadouch, A.; Sagou, R.; Chafik, A. First detection of azaspiracids in mussels in North West Africa. J. Shellfish Res. 2006, 25, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Elgarch, A.; Vale, P.; Rifai, S.; Fassouane, A. Detection of Diarrheic Shellfish Poisoning and Azaspiracids Toxins in Moroccan Mussels: Comparison of LC-MS Method with the Commercial Immunoassay Kit. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Haddouch, A.; Amanhi, R.; Amzil, Z.; Taleb, H.; Rovillon, G.-A.; Adly, F.; Loutfi, M. Lipophilic Toxin Profile in Mytilus galloprovincialis from the North Atlantic Coast of Morocco: LC-MS/MS and Mouse Bioassay Analyses. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2017, 6, 186. [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A.D. Accumulation of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins in the oyster Crassostrea gigas and the mussel Choromytilus meridionalis in the southern Benguela ecosystem. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2011, 33, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Goya, A.B. Occurrence and profiles of lipophilic toxins in shellfish harvested from Argentina. Toxicon 2015, 102, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarron, P.; Wright, E.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry of Domoic Acid and Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins with Selected Reaction Monitoring and Optional Confirmation by Library Searching of Product Ion Spectra. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, G.; Uribe, E.; Ávalos, P.; Mariño, C.; Blanco, J. First identification of azaspiracid and spirolides in Mesodesma donacium and Mulinia edulis from Northern Chile. Toxicon 2010, 55, 638–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, C.; Rodriguez-Unda, N.; Contreras, C.; Barriga, A.; Lagos, N. Lipophilic toxin profiles detected in farmed and benthic mussels populations from the most relevant production zones in Southern Chile. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamorano, R.; Marín, M.; Cabrera, F.; Figueroa, D.; Contreras, C.; Barriga, A.; Lagos, N.; García, C. Determination of the variability of both hydrophilic and lipophilic toxins in endemic wild bivalves and carnivorous gastropods from the Southern part of Chile. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2013, 30, 1660–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-de-Souza, C.; Varela, D.; Contreras, C.; de La Iglesia, P.; Fernández, P.; Hipp, B.; Hernández, C.; Riobó, P.; Reguera, B.; Franco, J.M.; et al. Seasonal variability of Dinophysis spp. and Protoceratium reticulatum associated to lipophilic shellfish toxins in a strongly stratified Chilean fjord. Deep-Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 101, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, C.; Pérez, F.; Contreras, C.; Figueroa, D.; Barriga, A.; López-Rivera, A.; Araneda, O.F.; Contreras, H.R. Saxitoxins and okadaic acid group: Accumulation and distribution in invertebrate marine vectors from Southern Chile. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2015, 32, 984–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, C.; Oyaneder-Terrazas, J.; Contreras, C.; del Campo, M.; Torres, R.; Contreras, H.R. Determination of the toxic variability of lipophilic biotoxins in marine bivalve and gastropod tissues treated with an industrial canning process. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2016, 33, 1711–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Mendoza, E.; Sánchez-Bravo, Y.A.; Turner, A.; Blanco, J.; O’Neil, A.; Mancera-Flores, J.; Pérez-Brunius, P.; Rivas, D.; Almazán-Becerril, A.; Peña-Manjarrez, J.L. Lipophilic toxins in cultivated mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) from Baja California, Mexico. Toxicon 2014, 90, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainer, V.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.; Adams, N.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; da Silva, D.A.; Eberhart, B.T. Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins and Other Lipophilic Toxins of Human Health Concern in Washington State. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Marcoval, M.A.; Berry, D.L.; Fire, S.; Wang, Z.; Morton, S.L.; Gobler, C.J. The emergence of Dinophysis acuminata blooms and DSP toxins in shellfish in New York waters. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhart, B.-T.; Moore, L.; Harrington, N.; Adams, N.; Borchert, J.; Trainer, V. Screening Tests for the Rapid Detection of Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxins in Washington State. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3718–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, J.-H. Contamination of shellfish from Shanghai seafood markets with paralytic shellfish poisoning and diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins determined by mouse bioassay and HPLC. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Liang, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L. First report on the detection of pectenotoxin groups in Chinese shellfish by LC–MS/MS. Toxicon 2011, 57, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Ma, J.; Cao, J.; McCarron, P. Toxins in mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning episodes in China. Toxicon 2012, 60, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhai, Y. Simultaneous determination of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin, pectenotoxin and yessotoxin in shellfish by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Chin. J. Chromatogr. 2012, 30, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, X. Isolation and identification of shellfish toxins from contaminated blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) from the East China Sea. J. Hyg. Res. 2012, 41, 819–823. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.; Fan, L. Lipophilic shellfish toxins in Dinophysis caudata picked cells and in shellfish from the East China Sea. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3116–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Yao, X.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Solid-Phase Extraction-Based Ultra-Sensitive Detection of Four Lipophilic Marine Biotoxins in Bivalves by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Cheng, H.; Li, Z.; Zhai, Y. Liquid chromatography quadrupole linear ion trap mass spectrometry for multiclass screening and identification of lipophilic marine biotoxins in bivalve mollusks. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1358, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-Z.; Cheng, Y.; Li, N.; Wen, H.-M.; Liu, R.; Shan, C.-X.; Chai, C.; Wu, H. Occurrence and Seasonal Variations of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Commercial Clam Species along the Coast of Jiangsu, China. Toxins 2016, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Yao, J.; Guo, M.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, D.; Zhai, Y. Distribution of Marine Lipophilic Toxins in Shellfish Products Collected from the Chinese Market. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4281–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Chen, H.; Qiu, J.; Lin, H.; Gu, H. Determination of multiple toxins in whelk and clam samples collected from the Chukchi and Bering seas. Toxicon 2016, 109, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Jiang, T.; Lu, S. Occurrence of marine algal toxins in oyster and phytoplankton samples in Daya Bay, South China Sea. Chemosphere 2017, 183, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Yasumoto, T. Liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of the diarrhetic shellfish-poisoning toxins okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1 and pectenotoxin-6 in bivalves. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 874, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Tsukada, K. Matrix effect and correction by standard addition in quantitative liquid chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2002, 943, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Jin, T.; Shirota, Y.; Mitsuya, T.; Okumura, Y.; Kamiyama, T. Quantification of lipophilic toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in Japanese bivalves by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry and comparison with mouse bioassay. Fish Sci. 2005, 71, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Suzuki, T.; Shirota, Y.; Honma, M.; Itabashi, Y.; Chyounan, T.; Kamiyama, T. Lipophilic toxin profiles associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in scallops, Patinopecten yessoensis, collected in Hokkaido and comparison of the quantitative results between LC/MS and mouse bioassay. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 47, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Quilliam, M.A. LC-MS/MS analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins, okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin analogues, and other lipophilic toxins. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushima, R.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, S.; Watanabe, R.; Kamio, M.; Nagai, H.; Kaneniwa, M.; Suzuki, T. Assimilation, Accumulation, and Metabolism of Dinophysistoxins (DTXs) and Pectenotoxins (PTXs) in the Several Tissues of Japanese Scallop Patinopecten yessoensis. Toxins 2015, 7, 5141–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.J.; Suzuki, T.; Kang, Y.S.; Ho Kim, P.; Song, K.C.; Lee, T.S. Seasonal Variability of Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalves and Waters, and Abundance of Dinophysis spp. in Jinhae Bay, Korea. J. Shellfish Res. 2010, 29, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Mok, J.S.; Song, K.C.; Yu, H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.H. Geographical and Annual Variation in Lipophilic Shellfish Toxins from Oysters and Mussels along the South Coast of Korea. J Food Prot. 2011, 74, 2127–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vershinin, A.; Moruchkov, A.; Morton, S.L.; Leighfield, T.A.; Quilliam, M.A.; Ramsdell, J.S. Phytoplankton composition of the Kandalaksha Gulf, Russian White Sea: Dinophysis and lipophilic toxins in the blue mussel (Mytilus edulis). Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.L.; Vershinin, A.; Smith, L.L.; Leighfield, T.A.; Pankov, S.; Quilliam, M.A. Seasonality of Dinophysis spp. and Prorocentrum lima in Black Sea phytoplankton and associated shellfish toxicity. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; Van Meulebroek, L.; De Rijcke, M.; Janssen, C.R.; Vanhaecke, L. High resolution mass spectrometry-based screening reveals lipophilic toxins in multiple trophic levels from the North Sea. Harmful Algae 2017, 64, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavela-Vrančič, M.; Meštrović, V.; Marasović, I.; Gillman, M.; Furey, A.; James, K.K. The occurrence of 7-epi-pectenotoxin-2 seco acid in the coastal waters of the central Adriatic (Kaštela Bay). Toxicon 2001, 39, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela-Vrančič, M.; Meštrović, V.; Marasović, I.; Gillman, M.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. DSP toxin profile in the coastal waters of the central Adriatic Sea. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1601–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavela-Vrančić, M.; Ujević, I.; Ninčević Gladan, Ž.; Furey, A. Accumulation of Phycotoxins in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Central Adriatic Sea. Croat. Chem. Acta 2006, 79, 291–297. [Google Scholar]
- Ninčević-Gladan, Ž.; Skejić, S.; Bužančić, M.; Marasović, I.; Arapov, J.; Ujević, I.; Bojanić, N.; Grbec, B.; Kušpilić, G.; Vidjak, O. Seasonal Variability in Dinophysis spp. Abundances and Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning Outbreaks Along the Eastern Adriatic Coast. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 449–463. Available online: https://www.degruyter.com/view/j/bot.2008.51.issue-6/bot.2008.067/bot.2008.067.xml (accesssed on 14 September 2017).
- Gladan, Ž.N.; Ujević, I.; Milandri, A.; Marasović, I.; Ceredi, A.; Pigozzi, S.; Arapov, J.; Skejić, S.; Orhanović, S.; Isajlović, I. Is Yessotoxin the Main Phycotoxin in Croatian Waters? Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čustović, S.; Orhanović, S.; Skejić, S.; Pavela-Vrančič, M. The predominant occurrence of YTX in the Eastern-mid Adriatic sea (Vranjic basin, Croatia). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 3453–3458. [Google Scholar]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Royer, F.; Masson, N.; Abadie, E. Report on the first detection of pectenotoxin-2, spirolide-A and their derivatives in French shellfish. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amzil, Z.; Sibat, M.; Royer, F.; Savar, V. First report on azaspiracid and yessotoxin groups detection in French shellfish. Toxicon 2008, 52, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picot, C.; Roudot, A.-C. A Practical Example of Risk Assessment—Risk Assessment to Phycotoxins in a Recreational Shellfish Harvester’s Subpopulation. In Novel Approaches and Their Applications in Risk Assessment; InTech: Lexington, KY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/download/pdf/35499 (accesssed on 2 August 2017).
- Puente, P.F.; Sáez, M.J.F.; Hamilton, B.; Lehane, M.; Ramstad, H.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Rapid determination of polyether marine toxins using liquid chromatography-multiple tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1056, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, E.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Comparative accumulation and composition of lipophilic marine biotoxins in passive samplers and in mussels (M. edulis) on the West Coast of Ireland. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.; McNamee, S.E.; Huet, A.C.; Delahaut, P.; Vilarino, N.; Botana, L.M.; Poli, M.; Elliott, C.T. Evolving to the optoelectronic mouse for phycotoxin analysis in shellfish. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6867–6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciminiello, P.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, S.; Poletti, R.; Satake, M.; Viviani, R.; Yasumoto, T. Yessotoxin in mussels of the northern Adriatic Sea. Toxicon 1997, 35, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draisci, R.; Ferretti, E.; Palleschi, L.; Marchiafava, C.; Poletti, R.; Milandri, A.; Ceredi, A.; Pompei, M. High levels of yessotoxin in mussels and presence of yessotoxin and homoyessotoxin in dinoflagellates of the Adriatic Sea. Toxicon 1999, 37, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draisci, R.; Palleschi, L.; Giannetti, L.; Lucentini, L.; James, K.J.; Bishop, A.G.; Satake, M.; Yasumoto, T. New approach to the direct detection of known and new diarrhoeic shellfish toxins in mussels and phytoplankton by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1999, 847, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Tartaglione, L.; Boschetti, L.; Rubini, S.; Cangini, M.; Pigozzi, S.; Poletti, R. Complex toxin profile of Mytilus galloprovincialis from the Adriatic sea revealed by LC-MS. Toxicon 2010, 55, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nincevic Gladan, Z.; Ujevic, I.; Milandri, A.; Marasovic, I.; Ceredi, A.; Pigozzi, S.; Arapov, J.; Skejic, S. Lipophilic Toxin Profile in Mytilus galloprovincialis during Episodes of Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) in the N.E. Adriatic Sea in 2006. Molecules 2011, 16, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, S.; Franzellitti, S.; Poletti, R.; Ceredi, A.; Montanari, G.; Capuzzo, A.; Fabbri, E. Bioaccumulation of algal toxins and changes in physiological parameters in Mediterranean mussels from the North Adriatic Sea (Italy): Effects of Algal Toxins on Marine Mussels. Environ. Toxicol. 2013, 28, 451–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchiocchi, S.; Siracusa, M.; Ruzzi, A.; Gorbi, S.; Ercolessi, M.; Cosentino, M.A.; Ammazzalorso, P.; Orletti, R. Two-year study of lipophilic marine toxin profile in mussels of the North-central Adriatic Sea: First report of azaspiracids in Mediterranean seafood. Toxicon 2015, 108, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; van Olst, E.H.W.; Mulder, P.P.J.; de Boer, J. In-house validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish using matrix-matched calibration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3079–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Top, H.J.; Gerssen, A.; McCarron, P.; van Egmond, H.P. Quantitative determination of marine lipophilic toxins in mussels, oysters and cockles using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Inter-laboratory validation study. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2011, 28, 1745–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.J.; de Boer, J. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish and algae: Development of a library using liquid chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Tangen, K.; Yasumoto, T.; Dahl, E.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins in norwegian mussels. Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 1988, 54, 1953–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstad, H.; Hovgaard, P.; Yasumoto, T.; Larsen, S.; Aune, T. Monthly variations in diarrhetic toxins and yessotoxin in shellfish from coast to the inner part of the Sognefjord, Norway. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torgersen, T.; Sandvik, M.; Lundve, B.; Lindegarth, S. Profiles and levels of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid group toxins and pectenotoxins during toxin depuration. Part II: Blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) and flat oyster (Ostrea edulis). Toxicon 2008, 52, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P. Differential dynamics of dinophysistoxins and pectenotoxins between blue mussel and common cockle: A phenomenon originating from the complex toxin profile of Dinophysis acuta. Toxicon 2004, 44, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, P. Differential dynamics of dinophysistoxins and pectenotoxins, part II: Offshore bivalve species. Toxicon 2006, 47, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Vazquez, J.A.; Thibault, P.; Quilliam, M.A. Simultaneous occurrence of diarrhetic and paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins in Spanish mussels in 1993. Nat. Toxins 1996, 4, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.V.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Botana, L.M. First evidence of spirolides in Spanish shellfish. Toxicon 2006, 48, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar-González, A.; Rodríguez-Velasco, M.L.; Ben-Gigirey, B.; Botana, L.M. Lipophilic toxin profile in Galicia (Spain): 2005 toxic episode. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Iglesia, P.; Gago-Martínez, A. Determination of yessotoxins and pectenotoxins in shellfish by capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2009, 26, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, L.; González, V.; Martínez, A.; Paz, B.; Lago, J.; Cordeiro, V.; Blanco, L.; Vieites, J.M.; Cabado, A.G. Occurrence of Lipophilic Marine Toxins in Shellfish from Galicia (NW of Spain) and Synergies among Them. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1666–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Altares, M.; Casanova, A.; Fernández-Tejedor, M.; Diogène, J.; de la Iglesia, P. Bloom of Dinophysis spp. dominated by D. sacculus and its related diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) outbreak in Alfacs Bay (Catalonia, NW Mediterranean Sea): Identification of DSP toxins in phytoplankton, shellfish and passive samplers. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2016, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobo, L.A.; Lacaze, J.-P.C.; Scott, A.C.; Gallacher, S.; Smith, E.A.; Quilliam, M.A. Liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry—Detection of lipophilic shellfish toxins. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stobo, L.A.; Lacaze, J.-P.C.L.; Scott, A.C.; Petrie, J.; Turrell, E.A. Surveillance of algal toxins in shellfish from Scottish waters. Toxicon 2008, 51, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madigan, T.L.; Lee, K.G.; Padula, D.J.; McNabb, P.; Pointon, A.M. Diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in South Australian shellfish. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, E.; Yu, Q.; Eaglesham, G.; Connell, D.W.; McBroom, J.; Costanzo, S.; Shaw, G.R. Occurrence and seasonal variations of algal toxins in water, phytoplankton and shellfish from North Stradbroke Island, Queensland, Australia. Mar. Environ. Res. 2007, 64, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajani, P.; Harwood, D.; Murray, S. Recent Trends in Marine Phycotoxins from Australian Coastal Waters. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L.; Holland, P.; McNabb, P.; Beuzenberg, V.; Selwood, A.; Suzuki, T. Complex toxin profiles in phytoplankton and Greenshell mussels (Perna canaliculus), revealed by LC-MS/MS analysis. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNabb, P.; Selwood, A.I.; Holland, P.T. Multiresidue method for determination of algal toxins in shellfish: Single-laboratory validation and interlaboratory study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganal, C.A.; Asahina, A.Y.; Hokama, Y.; Miyahara, J.T. Characterization of marine toxin(s) in Myripristis sp. by immunological, mouse toxicity, and guinea pig assays. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1993, 7, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fire, S.E.; Wang, Z.; Byrd, M.; Whitehead, H.R.; Paternoster, J.; Morton, S.L. Co-occurrence of multiple classes of harmful algal toxins in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) stranding during an unusual mortality event in Texas, USA. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Broadwater, M.H.; Ramsdell, J.S. Analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxin-2 in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1416, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.J.; Suzuki, T.; Mok, J.S.; Park, K.; Kwon, J.Y.; Son, K.T.; Song, K.C. First report of contamination of the abalone Haliotis discus hannai by okadaic acid and yessotoxin. J. Shellfish Res. 2012, 31, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.J.; Mok, J.S.; Song, K.C.; Yu, H.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.H. First Detection and Seasonal Variation of Lipophilic Toxins Okadaic Acid, Dinophysistoxin-1, and Yessotoxin in Korean Gastropods. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 2000–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacKenzie, L.A.; Selwood, A.I.; McNabb, P.; Rhodes, L. Benthic dinoflagellate toxins in two warm-temperate estuaries: Rangaunu and Parengarenga Harbours, Northland, New Zealand. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasen, J.A.B.; Espenes, A.; Miles, C.O.; Samdal, I.A.; Hess, P.; Aune, T. Combined oral toxicity of azaspiracid-1 and yessotoxin in female NMRI mice. Toxicon 2011, 57, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aune, T.; Espenes, A.; Aasen, J.A.B.; Quilliam, M.A.; Hess, P.; Larsen, S. Study of possible combined toxic effects of azaspiracid-1 and okadaic acid in mice via the oral route. Toxicon 2012, 60, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa, S.; Ardizzone, M.; Beltramo, D.; Vita, F.; Dell’Ovo, V.; Barreras, A.; Yasumoto, T.; Tubaro, A. Repeated oral co-exposure to yessotoxin and okadaic acid: A short term toxicity study in mice. Toxicon 2013, 76, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franchini, A.; Marchesini, E.; Poletti, R.; Ottaviania, E. Swiss mice CD1 fed on mussels contaminated by okadaic acid and yessotoxins: Effects on thymus and spleen. Eur. J. Histochem. 2005, 49, 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Sala, G.L.; Ronzitti, G.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Yasumoto, T.; Bigiani, A.; Rossini, G.P. Proteomic Analysis Reveals Multiple Patterns of Response in Cells Exposed to a Toxin Mixture. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2009, 22, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferron, P.-J.; Dumazeau, K.; Beaulieu, J.-F.; Le Hégarat, L.; Fessard, V. Combined Effects of Lipophilic Phycotoxins (Okadaic Acid, Azapsiracid-1 and Yessotoxin) on Human Intestinal Cells Models. Toxins 2016, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.-C. Theoretical Basis, Experimental Design, and Computerized Simulation of Synergism and Antagonism in Drug Combination Studies. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 621–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
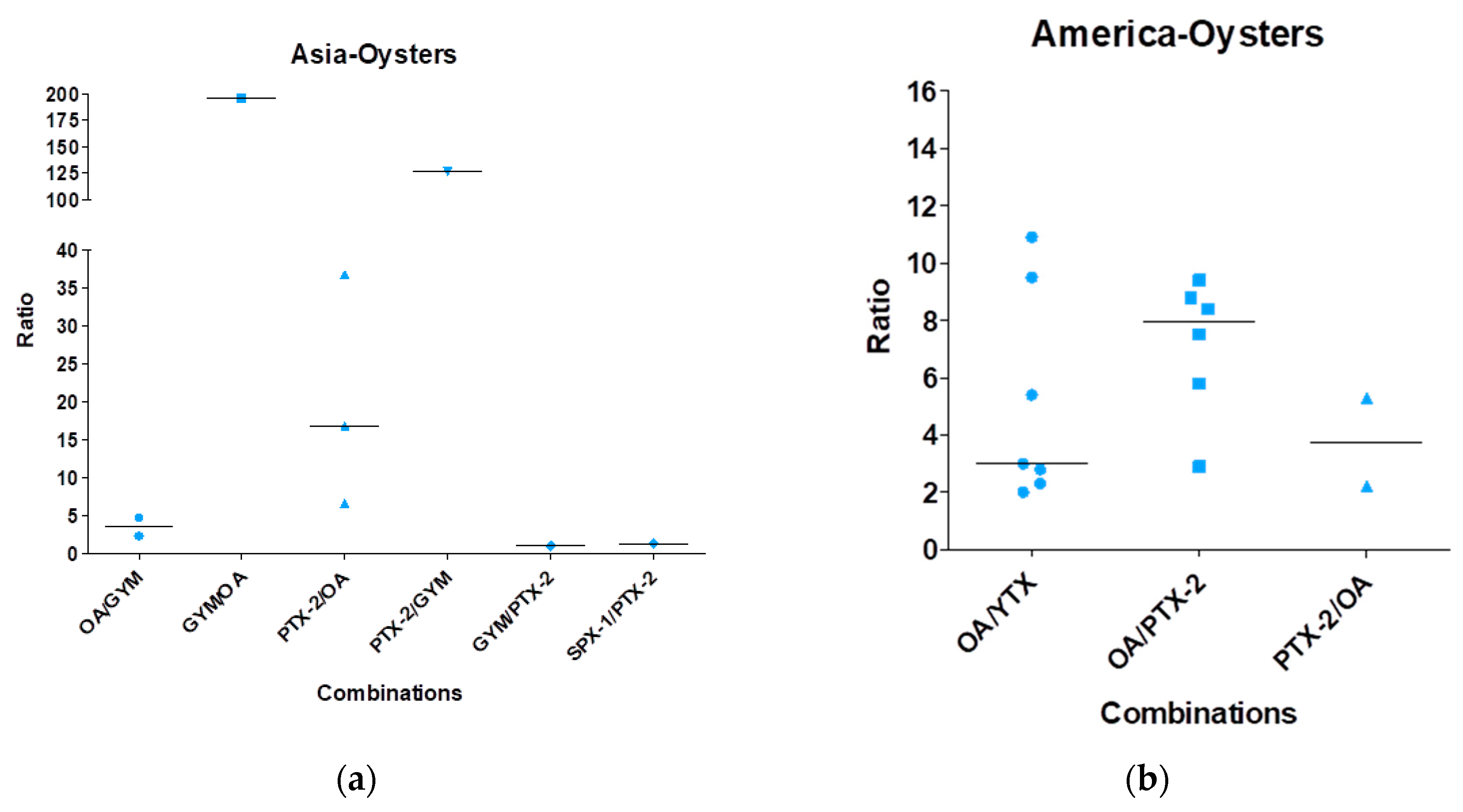
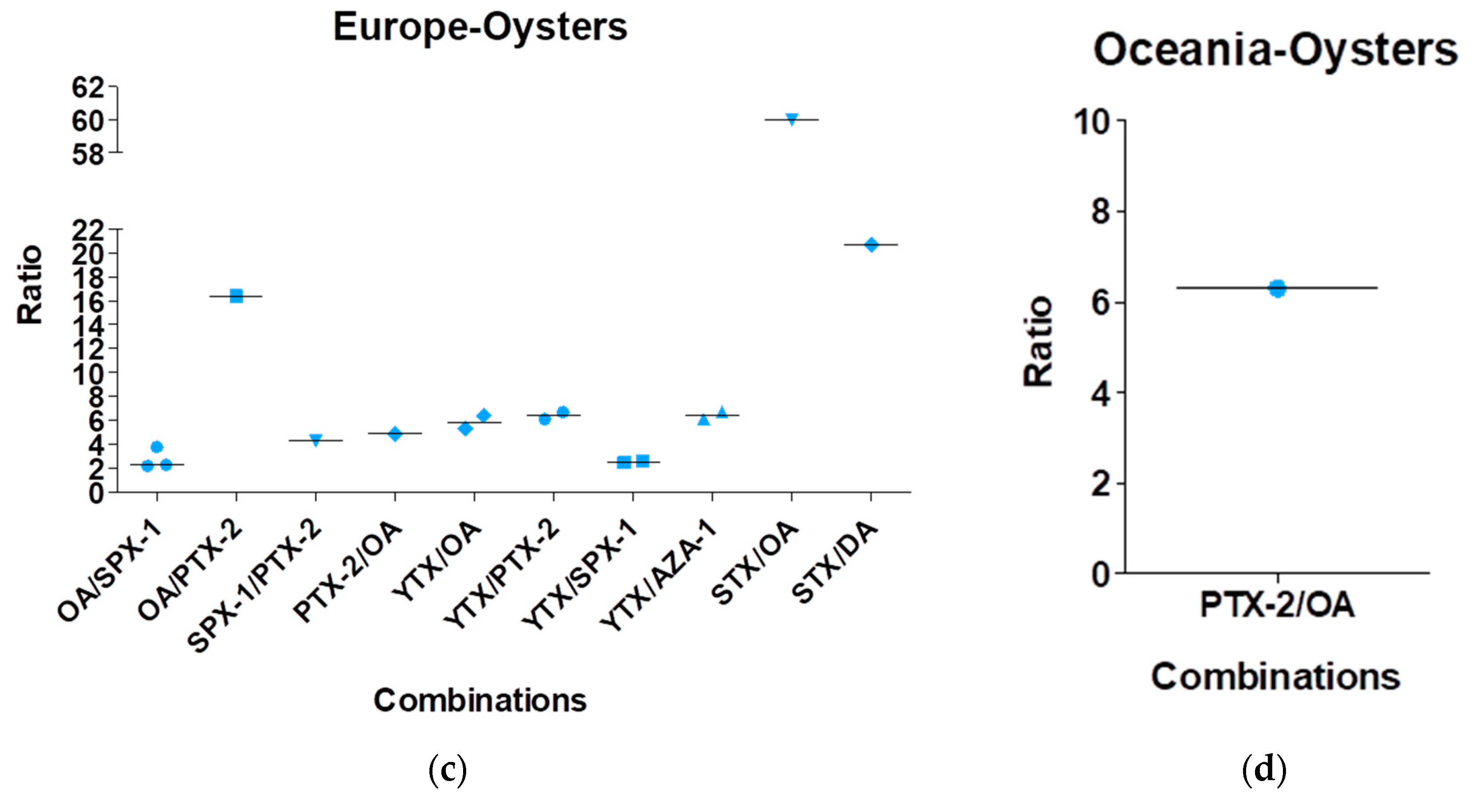
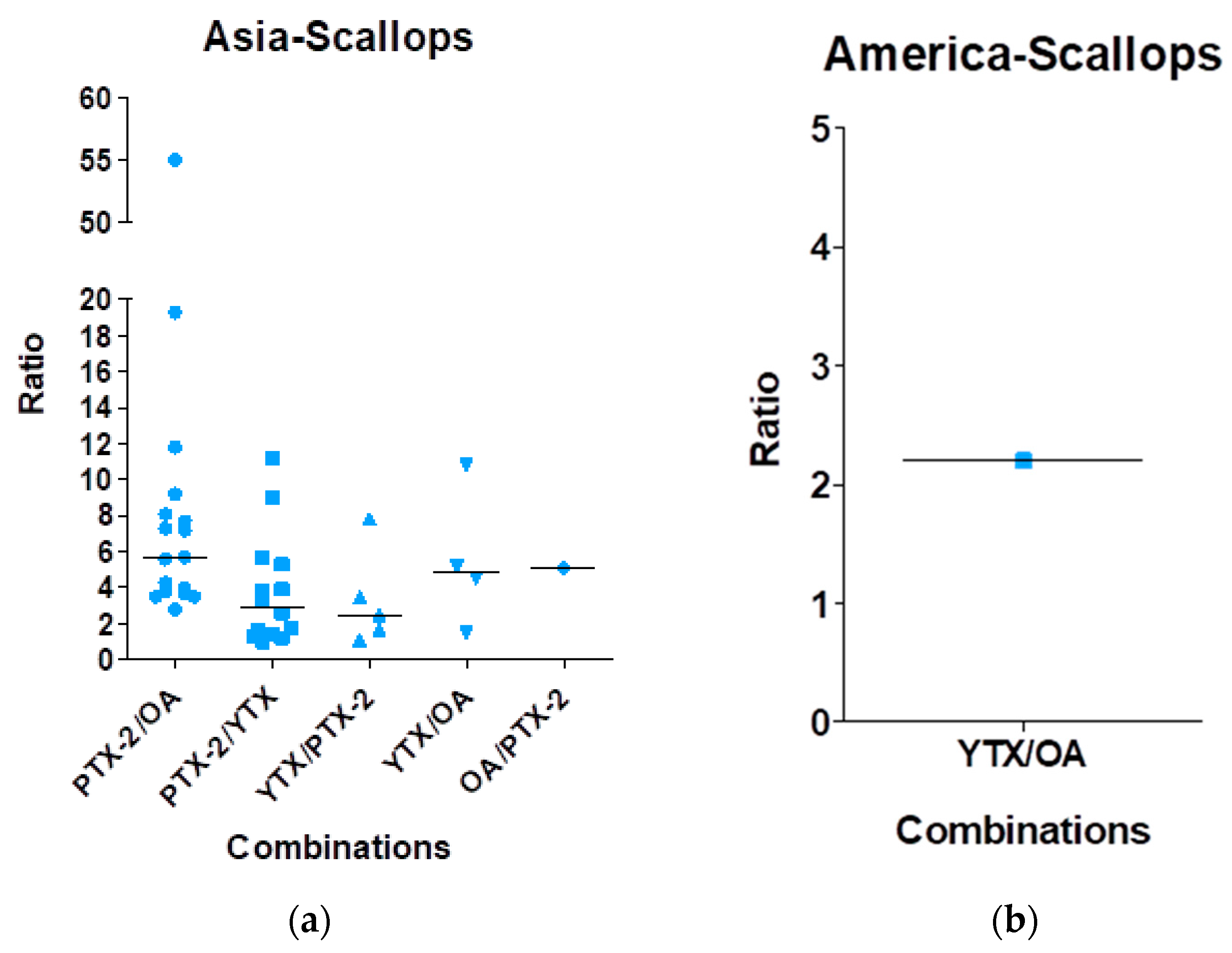
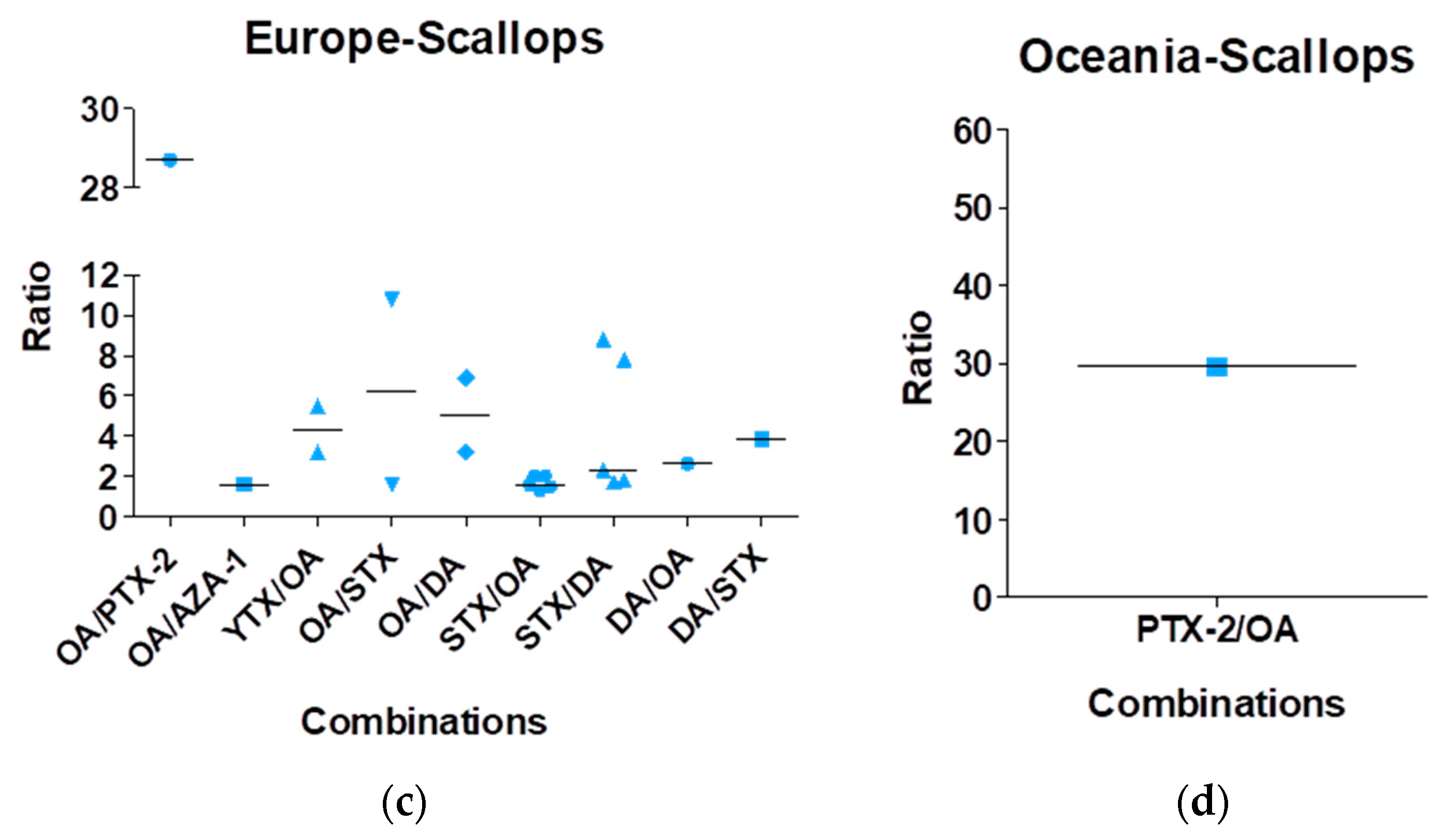

| Toxin Group | Current EU Limits in Shellfish Meat | Exposure by Eating a 400-g Portion at the EU Limit | ARfD |
|---|---|---|---|
| OA and analogues | 160 µg OA eq./kg SM | 64 µg OA eq./person | 0.3 µg OA eq./kg b.w. |
| AZA | 160 µg AZA eq./kg SM | 64 µg AZA1 eq./person | 0.2 µg AZA1 eq./kg b.w. |
| PTX | 160 µg OA eq./kg SM | 64 µg PTX2 eq./person | 0.8 µg PTX2 eq./kg b.w. |
| YTX | 1 mg YTX eq./kg SM | 400 µg YTX eq./person | 25 µg YTX eq./kg b.w. |
| STX | 800 µg PSP/kg SM | 320 µg STX eq./person | 0.5 µg STX eq./kg b.w. |
| DA | 20 mg DA/kg SM | 8 mg DA/person | 30 µg DA/kg b.w. |
| Phycotoxins | Species | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| OA/DTXs | Dinophysis mitra, Dinophysis tripos, Prorocentrum lima, Prorocentrum concavum | [4,5] |
| OA/DTXs and PTXs | Dinophysis fortii, Dinophysis acuta, Dinophysis acuminata, Dinophysis norvegica, Dinophysis rotundata | [4,6,7,8,9] |
| YTXs | Protoceratium reticulatum, Lingulodinium polyedrum, Gonyaulax spinifera | [10,11] |
| AZAs | Azadinium spinosum | [12] |
| SPXs | Alexandrium ostenfeldii, Alexandrium peruvianum | [13,14] |
| Authors | Ref. | Area | Toxins Investigated | Toxins Mixtures Reported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taleb et al., 2006 | [33] | Morocco | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3 | mixtures of OA, DTX-2, AZA-2 and AZA-1 |
| Elgarch et al., 2008 | [34] | Morocco | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, AZAs | mixtures of OA, DTX-2 and traces of AZA-2. OA found in highest concentrations |
| Ben Haddouch et al., 2015 | [35] | Morocco | OA, DTXs, PTXs, AZAs, GYMs, SPXs, YTXs | mixtures of OA, DTXs, YTX, PTXs, AZA-2 and sometimes GYM |
| Pitcher et al., 2011 | [36] | South Africa | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, AZA-1, GYM, SPXs, YTX, DA | mixtures of OA, DTX-1 and traces of PTXs |
| Turner et al., 2015 | [37] | Argentina | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-11, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, 20 Me SPX-G, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | YTX/OAs |
| McCarron et al., 2014 | [38] | Canada | DA, OA, DTXs, AZAs, PTXs, YTXs, GYMs, SPXs, PnTXs. | mixtures of high levels of DTX-1, PTXs, YTXs and trace levels of cyclic imines |
| Alvarez et al., 2010 | [39] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, AZA-1, SPX-1, YTX | mixtures of AZA-1 and SPX-1; levels were below LOQ |
| Garcia et al., 2012 | [40] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, YTX, AZA-1 | DTX-1/PTX-2/YTX |
| Zamorano et al., 2013 | [41] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, STX, neo-STX, GTXs | OAs/PTX-2/AZA-1/YTX/STXs |
| Alves de Souza et al., 2014 | [42] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, PTX-2, YTX, 45-OH-YTX | mixture of 45-OH-YTX and traces of PTX-2 |
| García et al., 2015 | [43] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, STX, neo-STX, GTXs | mixtures of STXs and OA/DTX-1; hydrophilic toxins were subjected to shellfish metabolism |
| Garcia et al., 2016 | [44] | Chile | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, homoYTX, COOH-YTX | OAs/PTX-2/YTX and OAs/YTX |
| García-Mendoza et al., 2014 | [45] | Mexico | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-11, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | mixtures mainly of OA, PTX-2, YTX and low levels of SPX-1 and AZA-1 |
| Trainer et al., 2013 | [46] | U.S. | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX | OA/YTX/PTX-2 and OA/PTX-2 and OA/YTX and OA/PTX-2/AZA-2 and OA/YTX/PTX-2/AZA-2 |
| Hattenrath-Lehmann et al., 2013 | [47] | U.S. | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-11 | OAs/PTXs |
| Eberhart et al., 2013 | [48] | U.S. | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, YTX | mixtures of DTX-1 and YTX |
| Wu et al., 2005 | [49] | China | OA, DTX-1, STX, neo-STX, GTXs | mixtures of OA and GTX-2/3 |
| Liu et al., 2011 | [50] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, SPX-A, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | GYM/OA and PTX-2s/OA |
| Li et al., 2012 | [51] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX, 45-OH-YTX | OAs/PTX-2s |
| Guo et al., 2012 | [52] | China | OA, DTX-1, PTX-2, YTX | OAs/PTX-2 |
| Zhang et al., 2012 | [53] | China | OA, DTX-1, PTXs | mixture of OA, DTX-1, 7-epi-PTX-2sa and PTX-2sa |
| Li et al., 2014 | [54] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-3, PTXs, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX | PTX-2s/GYM and PTX-2s/GYM/OAs and PTX-2s/OAs |
| Fang et al., 2014 | [55] | China | PTX-2, AZA-2, GYM, SPX-1 | SPX-1/PTX-2 |
| Wu et al., 2014 | [56] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX, PbTXs | mixtures of OA, SPX-1, PTX-2, AZAs, PbTx-3 and traces of YTX |
| Wang et al., 2015 | [57] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX | mixtures of OA, DTX-1, PTX-2 and GYM |
| Wu et al., 2015 | [58] | China | OA, PTX-2, AZA-1, GYM, SPX-1 | OA/PTX-2/GYM/SPX-1 and OA/AZA-1/PTX-2/GYM/SPX-1 and OA/PTX-2/GYM |
| Li et al., 2016 | [59] | China | OA, DTX-1, PTXs, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTXs | STXs/SPXs/YTXs and PTX-2/SPXs and STX/SPXs and OA/didesMe-SPX-C |
| Jiang et al., 2017 | [60] | China | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTXs, DA | PTX-2s/OA/GYM and DTX-1/GYM |
| Suzuki et al., 2000 | [61] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, PTX-6 | PTX-6/OAs |
| Ito et al., 2001 | [62] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, PTX-6, YTX | mixtures constituted of OA, DTX-1, YTX and PTX-6 |
| Suzuki et al., 2005 | [63] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, YTXs | PTX-2s/OAs/YTXs and OAs/YTXs |
| Hashimoto et al., 2006 | [64] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, DTX-3, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-6, YTX, 45-OH-YTX | PTX-2s/YTXs/OAs |
| Suzuki et al., 2011 | [65] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, YTXs | PTX-2s/OAs/YTXs and OAs/YTXs |
| Matsushima et al., 2015 | [66] | Japan | OA, DTX-1, DTX-3, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-3, PTX-6 | mixtures mainly of PTX-6 and DTX-3 |
| Kim et al., 2010 | [67] | Korea | OA, DTX-1, PTX-2, YTX | mixtures of OA, DTX-1 and traces of PTX-2, YTX |
| Lee et al., 2011 | [68] | Korea | OA, DTX-1, PTX-2, YTX | mixtures mainly constituted of OA and DTX-1; DSP toxin content 10-times higher in mussels than in oysters |
| Vershinin et al., 2006 | [69] | Russia | OA, DTX-1, PTXs, YTXs, AZAs, SPX-1 | OAs/PTXs/YTXs |
| Morton et al., 2009 | [70] | Russia | OA, DTX-1, PTXs | mixtures of OA, DTX-1, PTX-2 and PTX-2 sa |
| Orellana et al., 2017 | [71] | Belgium | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, SPX-1, YTX | mixtures of OA, DTX-2, SPXs and their ester metabolites |
| Pavela-Vrancic et al., 2001 | [72] | Croatia | OA, DTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa | mixtures of OA and 7-epi-PTX-2sa |
| Pavela-Vrancic et al., 2002 | [73] | Croatia | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa | OA/7-epi-PTX-2SA |
| Pavela-Vrancic et al., 2006 | [74] | Croatia | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa | OA/7-epi-PTX-2SA |
| Ninčević Gladan et al., 2008 | [75] | Croatia | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, PTX-6, AZAs, GYM, SPX, YTX, COOHYTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | YTXs/OA and OA/YTXs |
| Ninčević Gladan et al., 2010 | [76] | Croatia | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, YTXs, GYM, SPX-1 | YTXs/OA and OA/YTXs/PTX-2s and OA/PTX-2s |
| Čustović et al., 2014 | [77] | Croatia | OA, DXT-3, YTX, PSP | YTX/OAs |
| Amzil et al., 2007 | [78] | France | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, PTXs, AZAs, YTXs, SPXs, GYMs | OA/PTX-2/SPXs and OA/SPXs and PTX-2/OA |
| Amzil et al., 2008 | [79] | France | OA, DTXs, PTXs, PTX-6, AZAs, GYMs, SPXs, YTXs | mixtures of OA, AZA-1 and AZA-2 |
| Picot et al., 2012 | [80] | France | OA, SPX-1 | OA/SPX-1 |
| Fernandez Puente et al., 2004 | [81] | Ireland | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa | OAs/PTX-2s |
| Fux et al., 2009 | [82] | Ireland | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, YTX, SPX, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3 | AZAs/OAs and OAs/AZAs and OAs/AZAs/YTX |
| Campbell et al., 2014 | [83] | Ireland | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DA, STX, palytoxin | PSP/OAs/DA |
| Ciminiello et al., 1997 | [84] | Italy | OA, YTX | YTX/OA |
| Draisci et al., 1999 | [85] | Italy | OA, YTX, homoYTX | OA/YTX |
| Draisci et al., 1999 | [86] | Italy | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, YTX | mixture of YTX, PTXs and OA |
| Ciminiello et al., 2010 | [87] | Italy | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTXs, SPXs, DA | SPXs/PTX-2sa |
| Nincevic Gladan et al., 2011 | [88] | Italy | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa, PTX-6, GYM, SPX-1, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | OA/homoYTX and OA/homoYTX/PTX-2sa and OA/PTX-2sa |
| Buratti et al., 2011 | [89] | Italy | OA, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, COOH-YTX | mixtures mainly of YTX and homoYTX. HomoYTX found in highest concentrations |
| Bacchiocchi et al., 2015 | [90] | Italy | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | mixtures mainly of OA and YTX plus traces of AZA-2 |
| Gerssen et al., 2010 | [91] | The Netherlands | OA, PTX-2, AZA-1, YTX, SPX-1 | YTX/OA/AZA-1/PTX-2/SPX-1 |
| Van den Top et al., 2011 | [92] | The Netherlands | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, 45-OH-YTX | OAs/AZAs/YTXs/PTX-2 and YTXs/OAs and YTXs/OAs/AZAs |
| Gerssen et al., 2011 | [93] | The Netherlands | OA, DTXs, PTXs, AZAs, YTXs | OAs/AZAs/PTX-2s and OAs/AZAs/YTXs/PTX-2s and PTX-2s/OAs/YTXs |
| Lee et al., 1988 | [94] | Norway | OA, DTX-1, PTX-2, YTX | mixtures of DTX-1 and YTX |
| Ramstad et al., 2001 | [95] | Norway | OA, DTX-1, YTX | mixtures constituted of OA/DTX-1 and YTX |
| Torgersen et al., 2008 | [96] | Norway | OA, DTXs, PTXs | mixtures of PTXs, OA and DTXs |
| Vale et al., 2004 | [97] | Portugal | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa | mixtures of OA/DTX-2 and PTX-2/PTX-2sa |
| Vale et al., 2006 | [98] | Portugal | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, 7-epi-PTX-2 sa | mixtures of OA/DTX-2 and PTX-2/PTX-2sa |
| Gago-Martinez et al., 1996 | [99] | Spain | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, STXs, GTXs, neo-STXs | mixtures mainly of OA, DTX-2, GTXs and traces of STX |
| Villar Gonzalez et al., 2006 | [100] | Spain | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, SPX-1 | mixtures of OA, DTX-2 and traces of SPX-1 |
| Villar Gonzalez et al., 2007 | [101] | Spain | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, AZA-1, YTX, SPX-1 | OA/PTX-2sa and OA/PTX-2sa/SPX-1 |
| de la Iglesia et al., 2009 | [102] | Spain | PTX-6, YTX, 45-OH-YTX | mixtures of PTX-6 and YTXs |
| Rodriguez et al., 2015 | [103] | Spain | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | YTX/OA and OAs/YTX and YTXs/OA/PTX-2 |
| García-Altares et al., 2016 | [104] | Spain | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, GYM, SPX-1, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | mixtures of OA and PTX-2 |
| Stobo et al., 2005 | [105] | UK | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | YTX/OA and OA/AZA-1 and OA/YTX/PTX-2 and OA/PTX-2 and OA/YTX |
| Stobo et al., 2008 | [106] | UK | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, DTX-3, PTX-1, PTX-2, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, 45-OH-homoYTX | mixtures of OA, DTXs, PTXs and DA |
| Madigan et al., 2006 | [107] | Australia | OA, PTX-2, GYM, YTX, DA | PTX-2s/OA |
| Takahashi et al., 2007 | [108] | Australia | OA, DTXs, PTX-2, PTX-2 sa, GYM, DA | GYM/DA/PTX-2 and PTX-2s/OA/DA/GYM and PTX-2/OA |
| Ajani et al., 2017 | [109] | Australia | OA, PTX-2, GYM, YTX, DA | PTX-2s/OA |
| MacKenzie et al., 2002 | [110] | New Zealand | OA, DTX-1, PTXs, AZA-1, GYM, YTX, 45-OH-YTX, homoYTX, DA | YTXs/OA/PTX-2s/GYM/DA |
| McNabb et al., 2005 | [111] | New Zealand | OA, DTX-1, DTX-2, PTXs, AZA-1, AZA-2, AZA-3, YTXs, GYM, SPXs, DA | PTX-2s/OA/YTXs/GYM and DA/OAs/PTX-2 and OAs/GYM/PTX-2/AZA-1/YTX |
| Authors | Area | Toxin Mixtures | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zamorano et al., 2013 | Chile | OAs/PTX-2/AZA-1/YTX/STXs | Gastropods | [41] |
| García et al., 2015 | Chile | STXs/OA/DTX-1 | Gastropods | [43] |
| García et al., 2016 | Chile | OAs/PTX-2/YTX and OAs/YTX | Gastropods | [44] |
| Ganal et al., 1993 | Hawaii | OA/CTX | Fish | [112] |
| Fire et al., 2011 | U.S. | OA/DA/PbTx-3 | Bottlenose dolphin | [113] |
| Wang et al., 2015 | U.S. | OA/DTXs/PTX-2 | Bottlenose dolphin | [114] |
| Kim et al., 2012 | Korea | OA/YTX | Gastropods | [115] |
| Lee et al., 2012 | Korea | OA/YTX | Gastropods | [116] |
| MacKenzie et al., 2011 | New Zealand | OA/PnTxs | Gastropods | [117] |
| Ref. | Animal | Treatment | Toxin (mg/kg b.w.) | Results Toxins alone | Results Mixtures | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distribution in Internal Organs a,b | Macro- and Micro-Scopical Examination | Distribution in Internal Organs | Macro- and Micro-Scopical Examination | ||||
| Aasen et al., 2011 [118] | Female NMRI mice | single intake by gavage | YTX: 1 or 5 AZA-1: 200 YTX/AZA-1: 1/200 or 1/500 |
| YTX: no effects AZA-1: retention of material in the stomach and dilatation of the upper 1/3 of the small intestine with increased fluidity; contraction and bluntness of villi from duodenum, extension of cryptal compartments and extensive infiltration of neutrophils in lamina propria |
| No mixture effect |
| Aune et al., 2012 [119] | Female NMRI mice | single intake by gavage | OA: 0.6; 0.82; 0.9; 0.98 or 1.14 AZA-1: 0.42; 0.54; 0.6; 0.66 or 0.78 OA/AZA-1 *: LD10/LD10 or LD50/LD10 |
| OA: dilatation of stomach; shortened villi in the duodenum and jejunum and infiltration of neutrophils in lamina propria AZA-1: severe increase amount of content in stomach and dilatation of small intestine; shortened villi in the duodenum and infiltration of neutrophils in lamina propria | lower level for both toxins | No mixture effect |
| Sosa et al., 2013 [120] | Female CD-1 mice | repeated intake for 7 days by gavage | YTX: 1 OA: 0.185 YTX/OA: 1/0.185 | Not investigated | YTX: ultrastructural changes in cardiomyocytes/OA: inflammation of the forestomach submucosa and ultrastructural changes in cardiomyocytes | Not investigated | No mixture effect |
| Cell Model | Treatment | Endpoint | Toxin Mixture (nM) | Mixture Effect | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixture | Molar Ratio * | ||||
| Caco-2 | 24-h incubation | Neutral red uptake | AZA-1/YTX | 1:0.8 | additive |
| 1:1.3 | synergistic | ||||
| 1:2.4 | |||||
| 1:3.6 | |||||
| AZA-1/OA | 1:51 | antagonistic | |||
| 1:27.2 | |||||
| 1:15.3 | |||||
| 1:8.2 | |||||
| YTX/OA | 1:26.5 | antagonistic | |||
| 1:14.1 | additive | ||||
| 1:7.9 | |||||
| 1:4.2 | |||||
| Human intestinal epithelial crypt-like HIEC | 24-h incubation | Neutral red uptake | AZA-1/YTX | 1:0.8 | synergistic |
| 1:1.3 | |||||
| 1:2.4 | |||||
| 1:3.6 | additive | ||||
| AZA-1/OA | 1:51 | antagonistic | |||
| 1:27.2 | additive | ||||
| 1:15.3 | |||||
| 1:8.2 | antagonistic | ||||
| YTX/OA | 1:26.5 | synergistic | |||
| 1:14.1 | antagonistic | ||||
| 1:7.9 | additive | ||||
| 1:4.2 | |||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alarcan, J.; Biré, R.; Le Hégarat, L.; Fessard, V. Mixtures of Lipophilic Phycotoxins: Exposure Data and Toxicological Assessment. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020046
Alarcan J, Biré R, Le Hégarat L, Fessard V. Mixtures of Lipophilic Phycotoxins: Exposure Data and Toxicological Assessment. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(2):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlarcan, Jimmy, Ronel Biré, Ludovic Le Hégarat, and Valérie Fessard. 2018. "Mixtures of Lipophilic Phycotoxins: Exposure Data and Toxicological Assessment" Marine Drugs 16, no. 2: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020046
APA StyleAlarcan, J., Biré, R., Le Hégarat, L., & Fessard, V. (2018). Mixtures of Lipophilic Phycotoxins: Exposure Data and Toxicological Assessment. Marine Drugs, 16(2), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16020046





