1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to Evaluate the Effects of Caulerpin-Based Diet on Diplodus sargus Lipid Profiles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
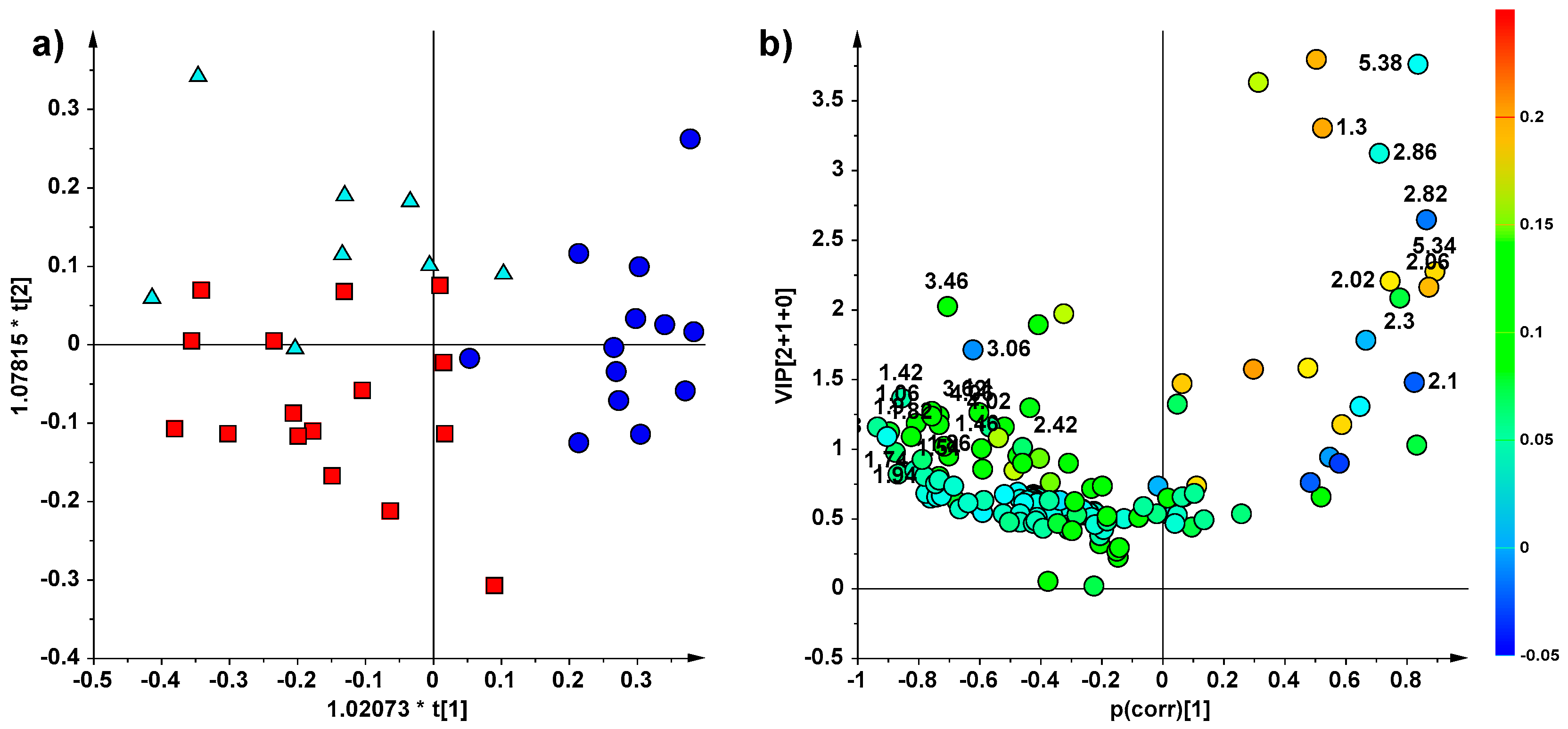
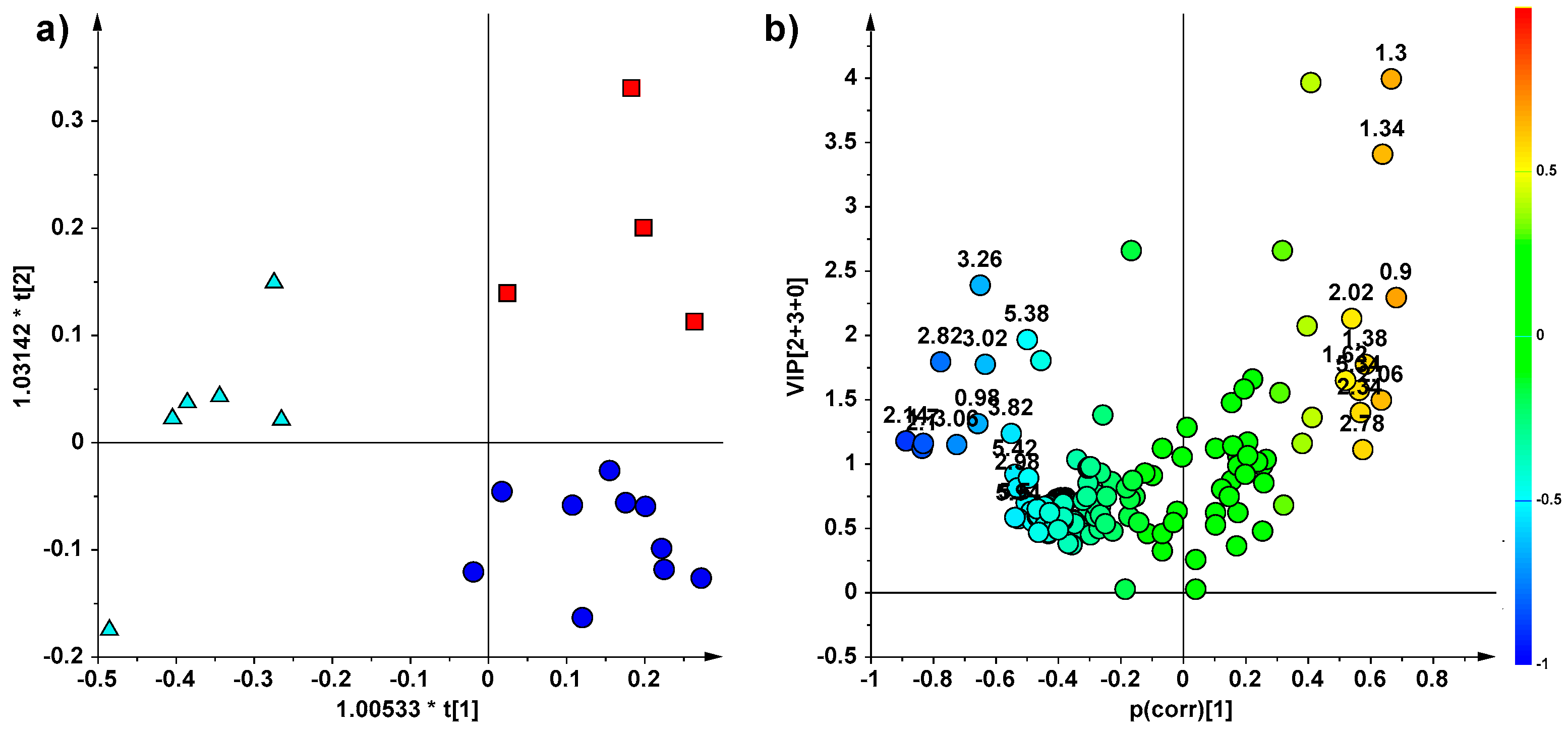
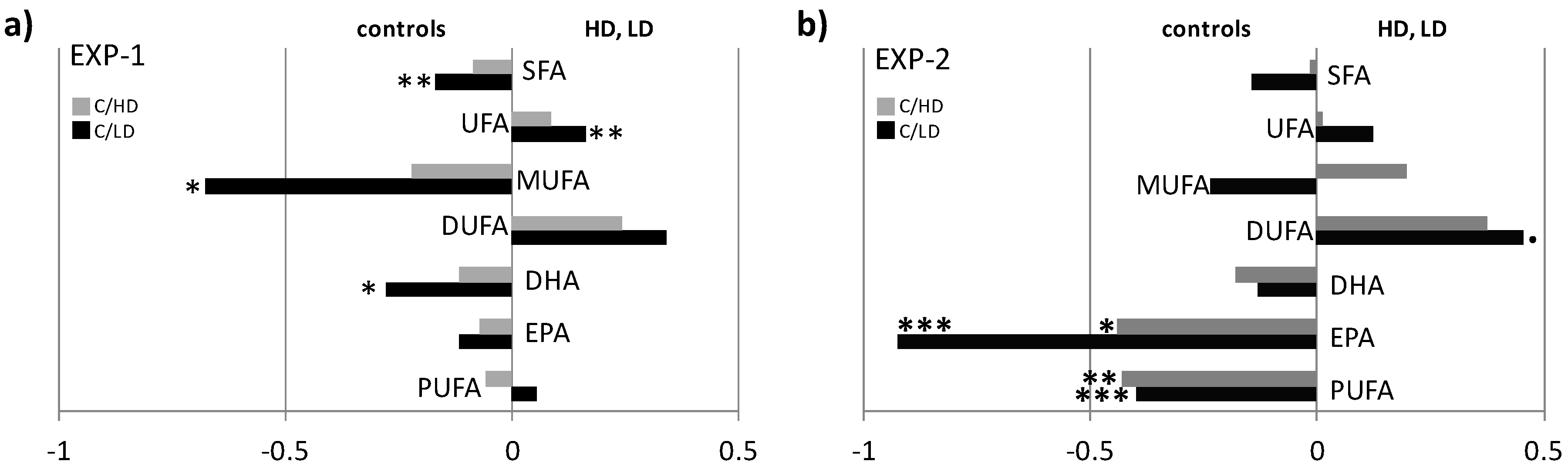
NMR Spectroscopy and Multivariate Statistical Analysis (MVA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Experiment Design
4.2. Sample Preparation for NMR Analysis
4.3. NMR Measurements
4.4. Data Analysis
4.5. Chemicals
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IS | Invasive Species |
| C | Control |
| CAU | Caulerpin |
| CHO | Cholesterol |
| DHA | Docosahexaenoic Acid |
| DUFA | Diunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| EPA | Eicosapentaenoic Acid |
| HD | High Dose |
| LD | Low Dose |
| MVA | Multivariate Analysis |
| MUFA | Monounsaturated Fatty Acids |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC | Phosphatidylcholine |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PUFA | Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids |
| SFA | Saturated Fatty Acids |
| TAGs | Triacilglycerols |
| UFA | Unsaturated Fatty Acids |
References
- Bax, N.; Williamson, A.; Aguero, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Geeves, W. Marine invasive alien species: A threat to global biodiversity. Mar. Policy 2003, 27, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simberloff, D.; Martin, J.-L.; Genovesi, P.; Maris, V.; Wardle, D.A.; Aronson, J.; Courchamp, F.; Galil, B.; García-Berthou, E.; Pascal, M. Impacts of biological invasions: What’s what and the way forward. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollo, E.; Gavagnin, M.; Carbone, M.; Castelluccio, F.; Pozone, F.; Roussis, V.; Templado, J.; Ghiselin, M.T.; Cimino, G. Factors promoting marine invasions: A chemoecological approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mollo, E.; Cimino, G.; Ghiselin, M.T. Alien biomolecules: A new challenge for natural product chemists. Biol. Invasions 2015, 17, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, A.; Felline, S.; Lionetto, M.G.; Caricato, R.; Perfetti, V.; Cutignano, A.; Mollo, E. Detrimental physiological effects of the invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa on the Mediterranean white seabream Diplodus sargus. Aquat. Biol. 2011, 12, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felline, S.; Caricato, R.; Cutignano, A.; Gorbi, S.; Lionetto, M.G.; Mollo, E.; Regoli, F.; Terlizzi, A. Subtle effects of biological invasions: Cellular and physiological responses of fish eating the exotic pest Caulerpa racemosa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorbi, S.; Giuliani, M.; Pittura, L.; d’Errico, G.; Terlizzi, A.; Felline, S.; Grauso, L.; Mollo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Regoli, F. Could molecular effects of Caulerpa racemosa metabolites modulate the impact on fish populations of Diplodus sargus? Mar. Environ. Res. 2014, 96, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Verlaque, M. The Caulerpa racemosa invasion: A critical review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 205–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Žuljević, A.; Thibaut, T.; Despalatović, M.; Cottalorda, J.-M.; Nikolić, V.; Cvitković, I.; Antolić, B. Invasive alga Caulerpa racemosa var. cylindracea makes a strong impact on the Mediterranean sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus. Biol. Invasions 2011, 13, 2303. [Google Scholar]
- Alomar, C.; Deudero, S.; Andaloro, F.; Castriota, L.; Consoli, P.; Falautano, M.; Sinopoli, M. Caulerpa cylindracea Sonder invasion modifies trophic niche in infralittoral rocky benthic community. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 120, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streftaris, N.; Zenetos, A. Alien marine species in the Mediterranean-the 100 ‘Worst Invasives’ and their impact. Mediterr. Mar. Sci. 2006, 7, 87–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohnert, G.; Jung, V. Intracellular compartmentation in the biosynthesis of caulerpenyne: Study on intact macroalgae using stable-isotope-labeled precursors. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 5091–5093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyrniotopoulos, V.; Abatis, D.; Tziveleka, L.-A.; Tsitsimpikou, C.; Roussis, V.; Loukis, A.; Vagias, C. Acetylene sesquiterpenoid esters from the green alga Caulerpa prolifera. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.A.; Paul, V.J.; Van Alstyne, K.L.; Kwiatkowski, L.M. Palatability of macroalgae that use different types of chemical defenses. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raniello, R.; Mollo, E.; Lorenti, M.; Gavagnin, M.; Buia, M.C. Phytotoxic activity of caulerpenyne from the Mediterranean invasive variety of Caulerpa racemosa: A potential allelochemical. Biol. Invasions 2007, 9, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felline, S.; Mollo, E.; Cutignano, A.; Grauso, L.; Andaloro, F.; Castriota, L.; Consoli, P.; Falautano, M.; Sinopoli, M.; Terlizzi, A. Preliminary observations of caulerpin accumulation from the invasive Caulerpa cylindracea in native Mediterranean fish species. Aquat. Biol. 2017, 26, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felline, S.; Mollo, E.; Ferramosca, A.; Zara, V.; Regoli, F.; Gorbi, S.; Terlizzi, A. Can a marine pest reduce the nutritional value of Mediterranean fish flesh? Mar. Biol. 2014, 161, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pascali, S.A.; Del Coco, L.; Felline, S.; Mollo, E.; Terlizzi, A.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR spectroscopy and MVA analysis of Diplodus sargus eating the exotic pest Caulerpa cylindracea. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3550–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ara, J.; Sultana, V.; Qasim, R.; Ahmad, V.U. Hypolipidaemic activity of seaweed from Karachi coast. Phytother. Res. 2002, 16, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghini, V.; Unger, F.T.; Tenori, L.; Turano, P.; Juhl, H.; David, K.A. Metabolomics profiling of pre-and post-anesthesia plasma samples of colorectal patients obtained via Ficoll separation. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1769–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girelli, C.R.; Accogli, R.; Del Coco, L.; Angilè, F.; De Bellis, L.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H-NMR-based metabolomic profiles of different sweet melon (Cucumis melo L.) Salento varieties: Analysis and comparison. Food Res. Int. 2018, 114, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandri, E.; Ahmed, R.; Siddiqui, H.; Choudhary, M.I.; Tsiafoulis, C.G.; Gerothanassis, I.P. High resolution NMR spectroscopy as a structural and analytical tool for unsaturated lipids in solution. Molecules 2017, 22, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannina, L.; Sobolev, A.; Capitani, D.; Iaffaldano, N.; Rosato, M.; Ragni, P.; Reale, A.; Sorrentino, E.; D’amico, I.; Coppola, R. NMR metabolic profiling of organic and aqueous sea bass extracts: Implications in the discrimination of wild and cultured sea bass. Talanta 2008, 77, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, T.; Aursand, M.; Hirata, Y.; Gribbestad, I.S.; Wada, S.; Nonaka, M. Nondestructive quantitative determination of docosahexaenoic acid and n-3 fatty acids in fish oils by high-resolution 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2000, 77, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, G.; Bankefors, J.; Schlechtriem, C.; Brannas, E.; Pickova, J.; Sandstrom, C. High-resolution 1H magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of intact Arctic char (Salvelinus alpinus) muscle. Quantitative analysis of n-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10799–10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tocher, D.R. Fatty acid requirements in ontogeny of marine and freshwater fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 717–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polese, G.; Alaia, R.; Cacace, A.; De Bonis, S.; Pinelli, C.; D’Aniello, B. Effetti della Caulerpina sul Comportamento Trofico del Sarago Maggiore (Diplodus sargus). Available online: https://iris.unicampania.it/handle/11591/212408#.W8fsKyCieUk (accessed on 18 October 2018).
- Magliozzi, L.; Almada, F.; Robalo, J.; Mollo, E.; Polese, G.; Gonçalves, E.J.; Felline, S.; Terlizzi, A.; D’Aniello, B. Cryptic effects of biological invasions: Reduction of the aggressive behaviour of a native fish under the influence of an “invasive” biomolecule. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante-Silva, L.; de Carvalho Correia, A.; Barbosa-Filho, J.; da Silva, B.; de Oliveira Santos, B.; de Lira, D.; Sousa, J.; de Miranda, G.; de Andrade Cavalcante, F.; Alexandre-Moreira, M. Spasmolytic effect of caulerpine involves blockade of Ca2+ influx on guinea pig ileum. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostetler, H.A.; Petrescu, A.D.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) interacts with high affinity and is conformationally responsive to endogenous ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18667–18682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidant stress, antioxidant defense and liver injury. In Drug-Induced Liver Disease, 3rd ed.; Kaplowitz, N., DeLeve, L.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; pp. 71–84. [Google Scholar]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.N. Essential fatty acids—A review. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2006, 7, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasaemle, D.L. Thematic review series: Adipocyte biology. The perilipin family of structural lipid droplet proteins: Stabilization of lipid droplets and control of lipolysis. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2547–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kullgren, A.; Samuelsson, L.M.; Larsson, D.J.; Björnsson, B.T.; Bergman, E.J. A metabolomics approach to elucidate effects of food deprivation in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 299, R1440–R1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Southam, A.D.; Hines, A.; Viant, M.R. High-throughput tissue extraction protocol for NMR-and MS-based metabolomics. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 372, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stabili, L.; Acquaviva, M.; Biandolino, F.; Cavallo, R.; De Pascali, S.; Fanizzi, F.; Narracci, M.; Cecere, E.; Petrocelli, A. Biotechnological potential of the seaweed Cladophora rupestris (Chlorophyta, Cladophorales) lipidic extract. New Biotechnol. 2014, 31, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melis, R.; Cappuccinelli, R.; Roggio, T.; Anedda, R. Addressing marketplace gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) differentiation by 1H NMR-based lipid fingerprinting. Food Res. Int. 2014, 63, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; van der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling and transformations: improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trygg, J.; Wold, S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS). J. Chemom. 2002, 16, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bro, R.; Smilde, A.K. Principal component analysis. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2812–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastment, H.; Krzanowski, W. Cross-validatory choice of the number of components from a principal component analysis. Technometrics 1982, 24, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, E.; Loo, R.L.; Stamler, J.; Bictash, M.; Yap, I.K.; Chan, Q.; Ebbels, T.; De Iorio, M.; Brown, I.J.; Veselkov, K.A. Human metabolic phenotype diversity and its association with diet and blood pressure. Nature 2008, 453, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2013. Available online: https://www.gbif.org/tool/81287/r-a-language-and-environment-for-statistical-computing (accessed on 16 October 2018).
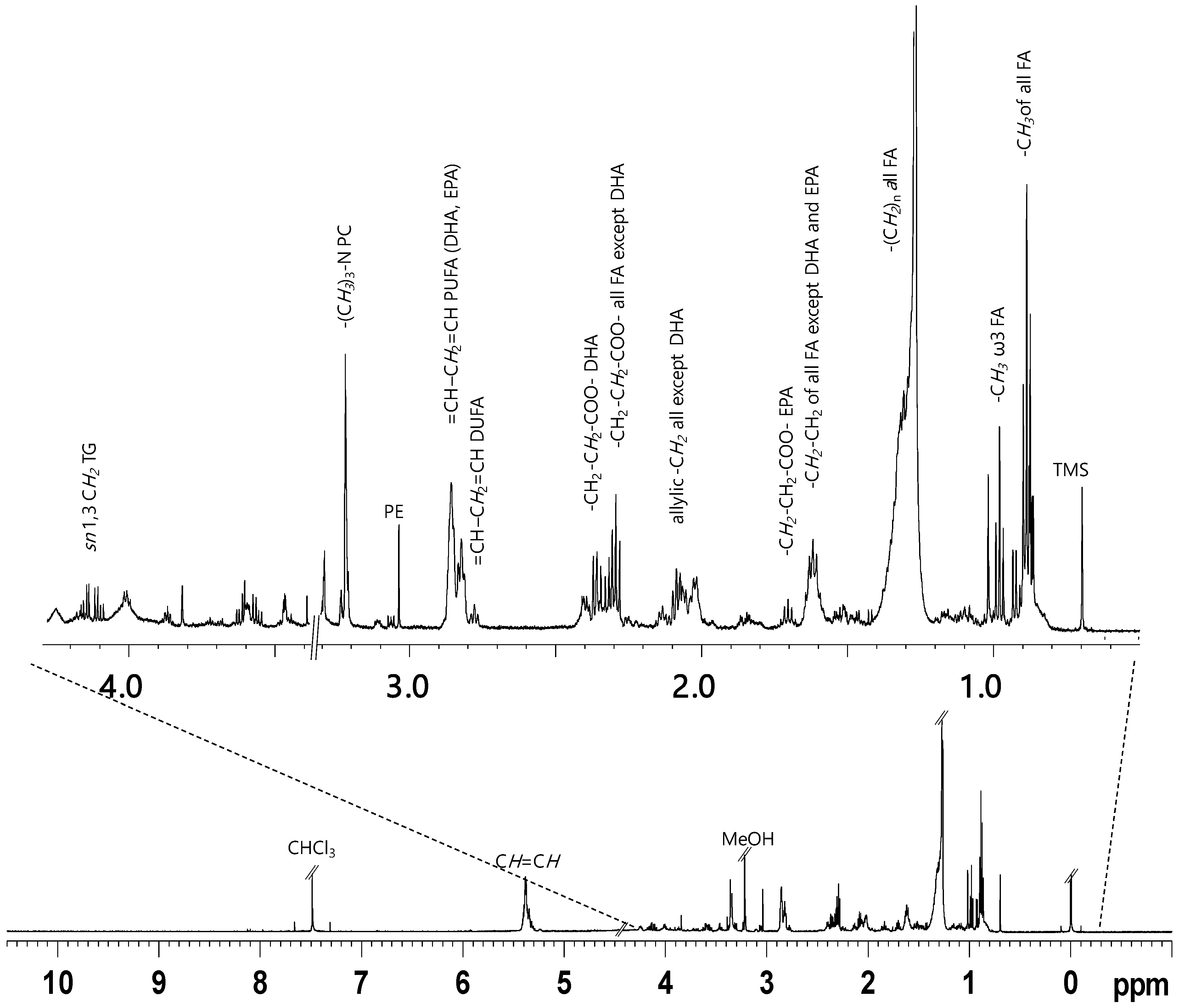
| Compound | Assignment | 1H (ppm, multiplicity) |
|---|---|---|
| CHO | -CH3-18 -CH3-21 -CH3-19 | 0.68–0.69 (s) 0.92 (d) 1.01 (s) |
| All FA (SFA, MUFA, DUFA) except ω3 FA | -CH3 | 0.87–0.88 (t) * |
| ω3 PUFA | -CH3 | 0.98 (t) * |
| All fatty acids | -(CH2)n | 1.22–1.34 (m) |
| All fatty chains except DHA and EPA | COOCH2CH2 | 1.57–1.66 (m) |
| EPA | COOCH2CH2 | 1.67–1.74 (m) * |
| All fatty acids except DHA | -CH=CH-CH2 | 1.99–2.17 (m) * |
| All fatty acids except DHA | COOCH2 | 2.27–2.35 (t) * |
| DHA | COOCH2CH2 | 2.38 (dd) * |
| DUFA | CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH | 2.77 (t) * |
| PUFA (DHA, EPA) | CH=CH-CH2-CH=CH | 2.80–2.85 (t) |
| PE | -CH2-N | 3.03 (s) |
| PC | -(CH3)3-N | 3.22 (s) |
| TAGs | CH2 (sn1,3) CH (sn2) | 4.11–4.14 (dd) 5.24 (m) |
| All FA | CH=CH | 5.28–5.43 (m) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Coco, L.; Felline, S.; Girelli, C.R.; Angilè, F.; Magliozzi, L.; Almada, F.; D’Aniello, B.; Mollo, E.; Terlizzi, A.; Fanizzi, F.P. 1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to Evaluate the Effects of Caulerpin-Based Diet on Diplodus sargus Lipid Profiles. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100390
Del Coco L, Felline S, Girelli CR, Angilè F, Magliozzi L, Almada F, D’Aniello B, Mollo E, Terlizzi A, Fanizzi FP. 1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to Evaluate the Effects of Caulerpin-Based Diet on Diplodus sargus Lipid Profiles. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(10):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100390
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Coco, Laura, Serena Felline, Chiara Roberta Girelli, Federica Angilè, Laura Magliozzi, Frederico Almada, Biagio D’Aniello, Ernesto Mollo, Antonio Terlizzi, and Francesco P. Fanizzi. 2018. "1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to Evaluate the Effects of Caulerpin-Based Diet on Diplodus sargus Lipid Profiles" Marine Drugs 16, no. 10: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100390
APA StyleDel Coco, L., Felline, S., Girelli, C. R., Angilè, F., Magliozzi, L., Almada, F., D’Aniello, B., Mollo, E., Terlizzi, A., & Fanizzi, F. P. (2018). 1H NMR Spectroscopy and MVA to Evaluate the Effects of Caulerpin-Based Diet on Diplodus sargus Lipid Profiles. Marine Drugs, 16(10), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16100390








