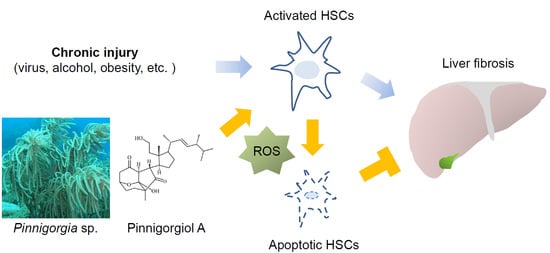
The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
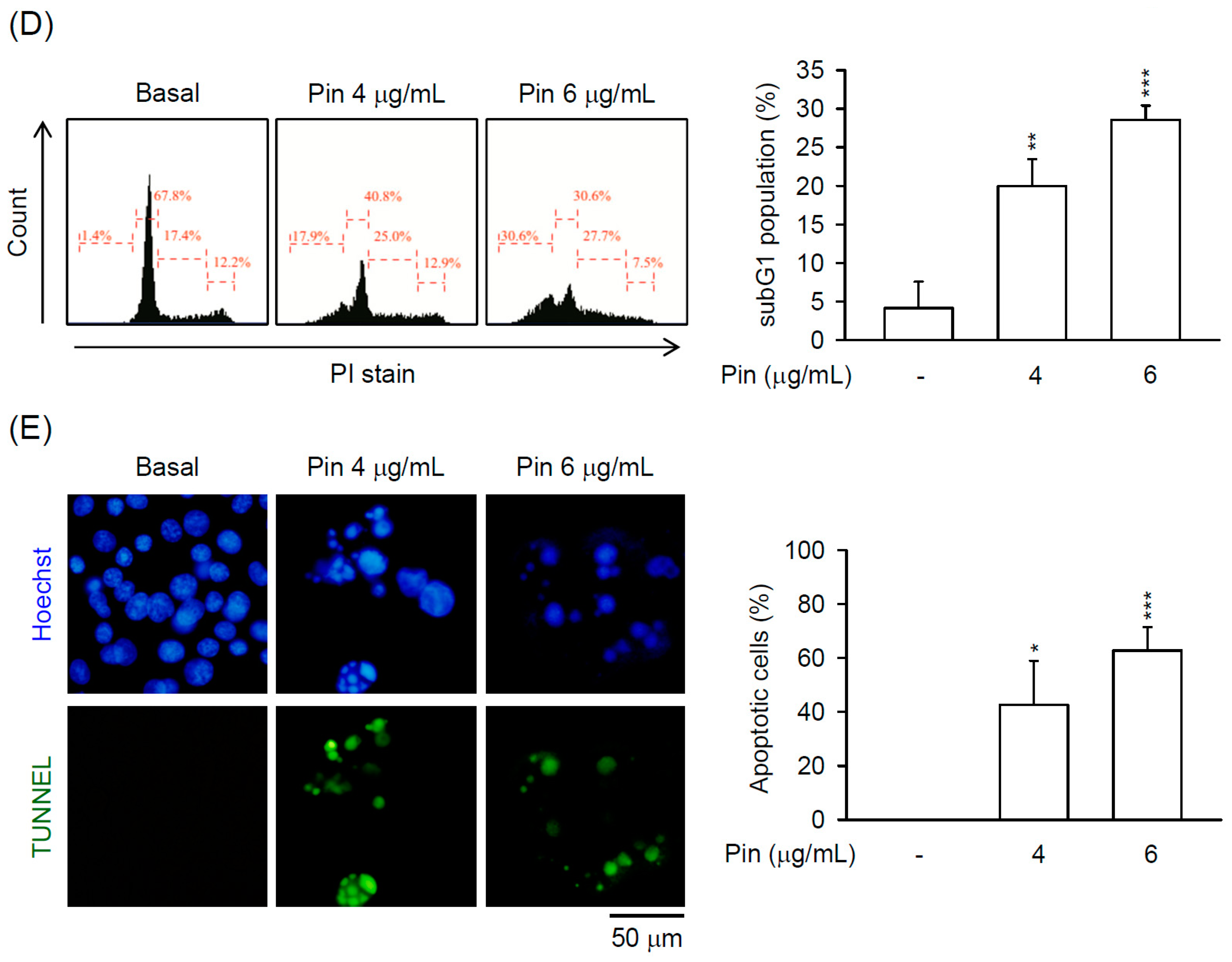
2.1. Pin Exhibits Caspase-3-Dependent Apoptosis in HSC-T6 Cells
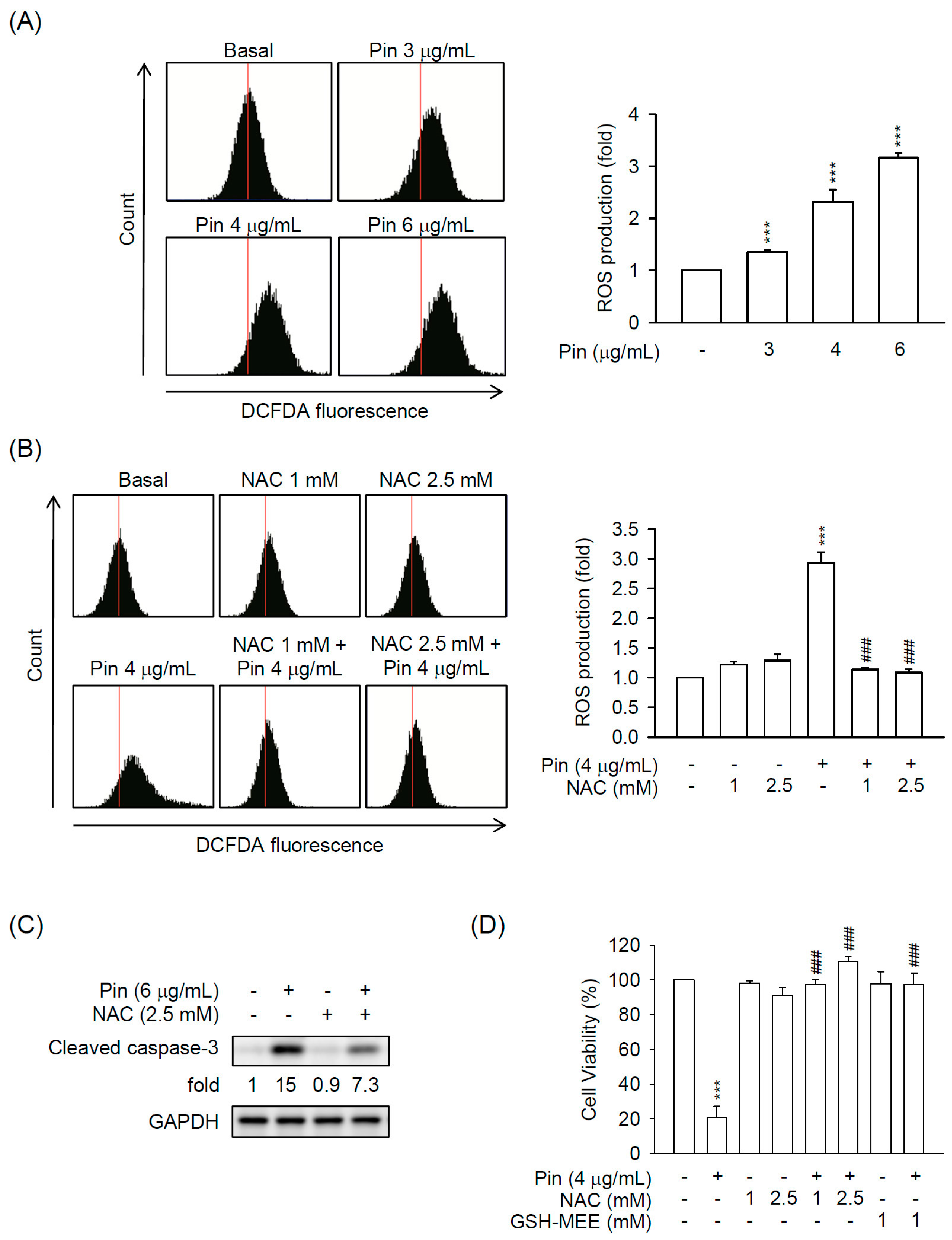
2.2. Pin-Induced Apoptosis Is Dependent on Intracellular ROS Production in HSC-T6 Cells
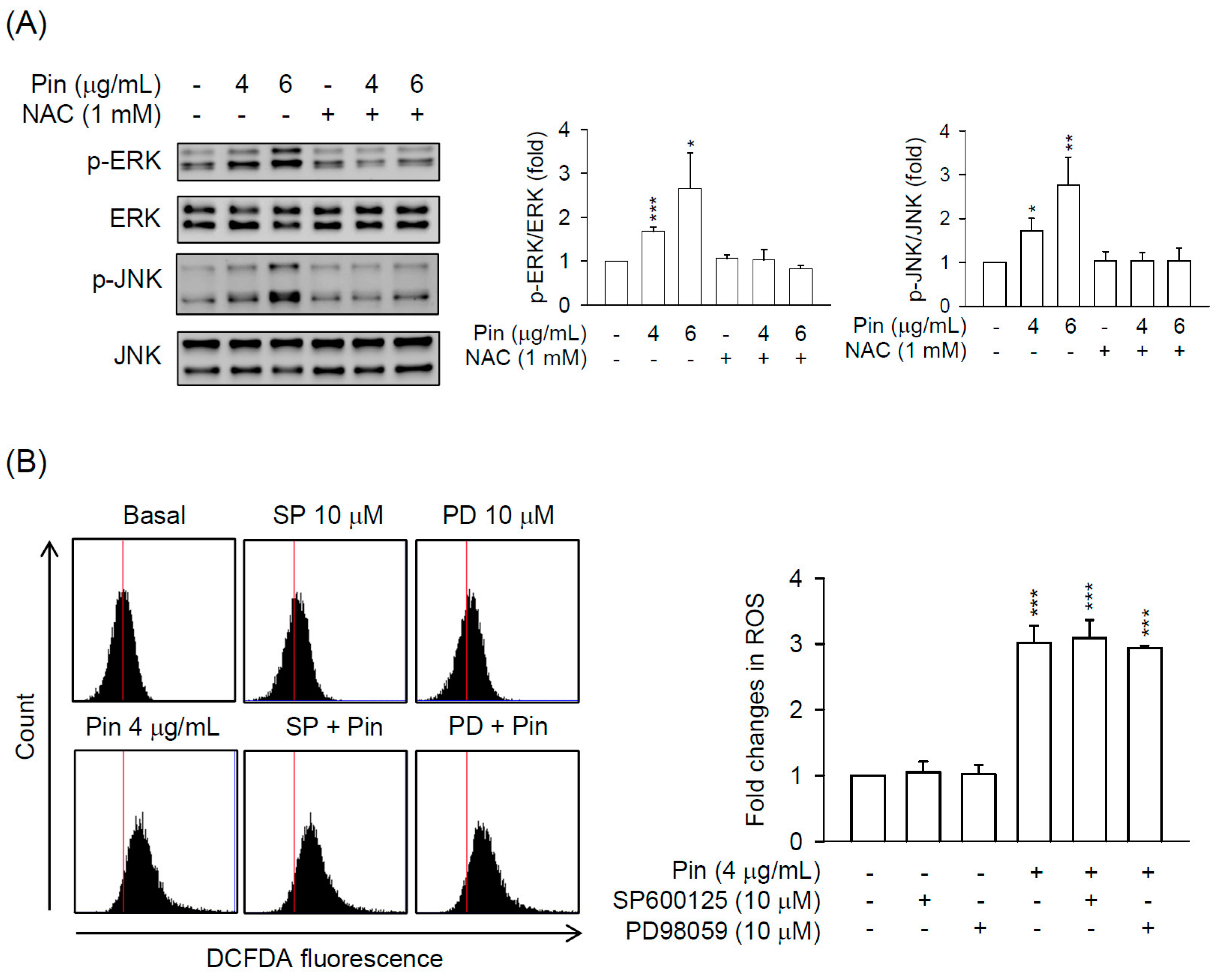
2.3. Pin-Induced Cell Death of HSC-T6 Cells Is through ERK and JNK Pathway
2.4. Pin-Activated ERK and JNK Pathway Act as Downstream Signals of ROS Production in HSC-T6 Cells
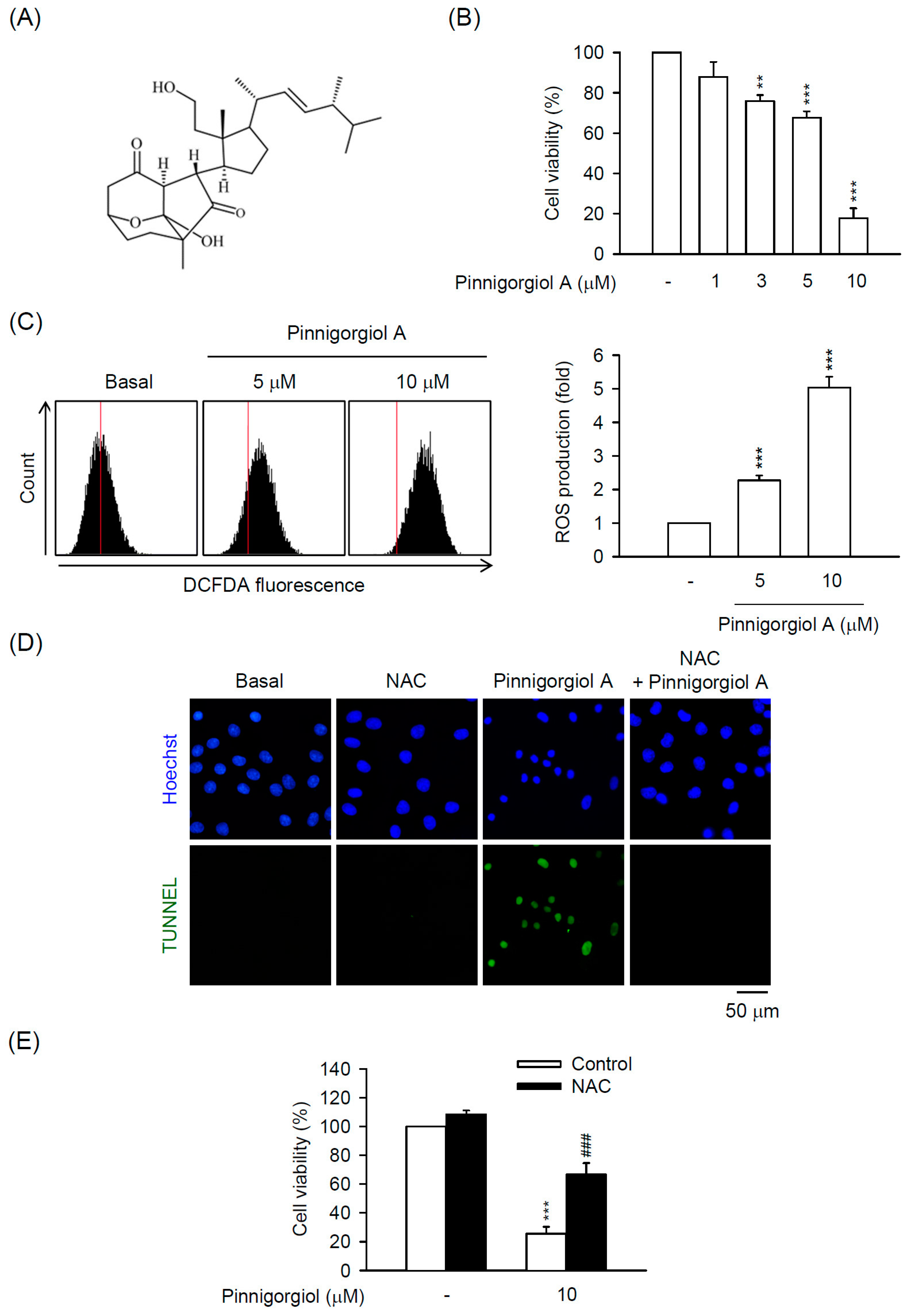
2.5. Pinnigorgiol a Serves as a Bioactive Component of Pin to Trigger the ROS-Dependent Apoptosis in HSC-T6 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Analysis of SubG1 Population
4.5. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Generation
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. TUNEL Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yin, C.; Evason, K.J.; Asahina, K.; Stainier, D.Y. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, T.; Friedman, S.L. Mechanisms of hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, F.; Trautwein, C. Mechanisms of liver fibrosis resolution. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1038–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, S.L. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, X.; Liang, J. Modulation of hepatic stellate cells and reversibility of hepatic fibrosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 352, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yuan, W.G.; He, P.; Lei, J.H.; Wang, C.X. Liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cells: Etiology, pathological hallmarks and therapeutic targets. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10512–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallowfield, J.A. Therapeutic targets in liver fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G709–G715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinski, T.F.; Dalisay, D.S.; Lievens, S.L.; Saludes, J.P. Drug development from marine natural products. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H. Therapies from fucoidan; multifunctional marine polymers. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.G.; Weiskirchen, R.; Al-Musharafi, S.K. The use of marine-derived bioactive compounds as potential hepatoprotective agents. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Kuo, L.M.; Hwang, T.L.; Yeh, J.; Wen, Z.H.; Fang, L.S.; Wu, Y.C.; Lin, C.S.; Sheu, J.H.; Sung, P.J. Pinnisterols A–C, New 9,11-Secosterols from a Gorgonian Pinnigorgia sp. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chen, W.F.; Hwang, T.L.; Fang, L.S.; Wen, Z.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Sung, P.J. Pubinernoid A and Apo-9′-fucoxanthinone, Secondary Metabolites from a Gorgonian Coral Pinnigorgia sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 707–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Sheu, J.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Sung, P.J. New Anti-Inflammatory 9,11-Secosterols with a Rare Tricyclo [5,2,1,1] decane Ring from a Formosan Gorgonian Pinnigorgia sp. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Chao, C.H.; Sung, P.J. New Marine Sterols from a Gorgonian Pinnigorgia sp. Molecules 2017, 22, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hwang, T.L.; Kuo, L.M.; Sung, P.J. Pinnisterols D–J, New 11-Acetoxy-9,11-secosterols with a 1,4-Quinone Moiety from Formosan Gorgonian Coral Pinnigorgia sp. (Gorgoniidae). Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.; Kuo, L.; Su, J.; Hwang, T.; Kuo, Y.; Lin, C.; Wu, Y.; Sheu, J.; Sung, P. Pinnigorgiols A–C, 9,11-secosterols with a rare ring arrangement from a gorgonian coral Pinnigorgia sp. Tetrahedron 2016, 72, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunati, A.M.; Pagano, M.A.; Bindoli, A.; Rigobello, M.P. Thiol redox systems and protein kinases in hepatic stellate cell regulatory processes. Free Radic. Res. 2010, 44, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, S.; Ur Rehman, A.; Tiebosch, M.H.; Hannivoort, R.A.; Haijer, F.W.; Woudenberg, J.; van den Heuvel, F.A.; Buist-Homan, M.; Faber, K.N.; Moshage, H. Glutathione and antioxidant enzymes serve complementary roles in protecting activated hepatic stellate cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Glutathione and apoptosis. Free Radic. Res. 2008, 42, 689–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, L.M.; Kuo, C.Y.; Lin, C.Y.; Hung, M.F.; Shen, J.J.; Hwang, T.L. Intracellular glutathione depletion by oridonin leads to apoptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Molecules 2014, 19, 3327–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Guo, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y. Astragaloside IV synergizes with ferulic acid to suppress hepatic stellate cells activation in vitro. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, C.; Li, J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced hepatic stellate cell apoptosis through calcium-mediated JNK/P38 MAPK and Calpain/Caspase-12 pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 394, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenner, C.; Galluzzi, L.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Naguro, I.; Nishitoh, H.; Matsuzawa, A.; Ichijo, H. Apoptosis signaling kinases: From stress response to health outcomes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 719–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, H.; Lu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yasuda, K.; Wang, H. Berberine inhibits hepatic stellate cell proliferation and prevents experimental liver fibrosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasmuth, H.E.; Tacke, F.; Trautwein, C. Chemokines in liver inflammation and fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puche, J.E.; Saiman, Y.; Friedman, S.L. Hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 1473–1492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ray, K. Liver: Hepatic stellate cells hold the key to liver fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kang, K.L.; Lee, J.C.; Heo, J.S. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 and beta4 subunits contribute nicotine-induced apoptosis in periodontal ligament stem cells. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamenter, M.E.; Perkins, G.A.; Gu, X.Q.; Ellisman, M.H.; Haddad, G.G. DIDS (4,4-diisothiocyanatostilbenedisulphonic acid) induces apoptotic cell death in a hippocampal neuronal cell line and is not neuroprotective against ischemic stress. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posadas, I.; Santos, P.; Cena, V. Acetaminophen induces human neuroblastoma cell death through NFKB activation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, C.; Pastukh, V.; Leonard, J.; Turrens, J.; Wilson, G.; Schaffer, D.; Schaffer, S.W. Mitochondrial DNA damage triggers mitochondrial-superoxide generation and apoptosis. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C413–C422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosas-Molist, E.; Fabregat, I. Role of NADPH oxidases in the redox biology of liver fibrosis. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K. Autophagy and apoptosis in liver injury. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmund, S.V.; Qian, T.; de Minicis, S.; Harvey-White, J.; Kunos, G.; Vinod, K.Y.; Hungund, B.; Schwabe, R.F. The endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoyl glycerol induces death of hepatic stellate cells via mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.A.; Chaudhuri, J.; Biswas, N.; Manna, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Mahato, S.K.; Chaudhuri, U.; Jaisankar, P.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Synergistic apoptosis of CML cells by buthionine sulfoximine and hydroxychavicol correlates with activation of AIF and GSH-ROS-JNK-ERK-iNOS pathway. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wu, L.; Tashiro, S.; Onodera, S.; Ikejima, T. Reactive oxygen species mediate oridonin-induced HepG2 apoptosis through p53, MAPK, and mitochondrial signaling pathways. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2008, 107, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuster-Ciesielska, A.; Mizerska-Dudka, M.; Daniluk, J.; Kandefer-Szerszen, M. Butein inhibits ethanol-induced activation of liver stellate cells through TGF-beta, NFkappaB, p38, and JNK signaling pathways and inhibition of oxidative stress. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabl, B.; Bradham, C.A.; Bennett, B.L.; Manning, A.M.; Stefanovic, B.; Brenner, D.A. TAK1/JNK and p38 have opposite effects on rat hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2001, 34, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameel, N.M.; Thirunavukkarasu, C.; Wu, T.; Watkins, S.C.; Friedman, S.L.; Gandhi, C.R. p38-MAPK- and caspase-3-mediated superoxide-induced apoptosis of rat hepatic stellate cells: Reversal by retinoic acid. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 218, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuo, L.-M.; Chen, P.-J.; Sung, P.-J.; Chang, Y.-C.; Ho, C.-T.; Wu, Y.-H.; Hwang, T.-L. The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010019
Kuo L-M, Chen P-J, Sung P-J, Chang Y-C, Ho C-T, Wu Y-H, Hwang T-L. The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuo, Liang-Mou, Po-Jen Chen, Ping-Jyun Sung, Yu-Chia Chang, Chun-Ting Ho, Yi-Hsiu Wu, and Tsong-Long Hwang. 2018. "The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling" Marine Drugs 16, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010019
APA StyleKuo, L.-M., Chen, P.-J., Sung, P.-J., Chang, Y.-C., Ho, C.-T., Wu, Y.-H., & Hwang, T.-L. (2018). The Bioactive Extract of Pinnigorgia sp. Induces Apoptosis of Hepatic Stellate Cells via ROS-ERK/JNK-Caspase-3 Signaling. Marine Drugs, 16(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16010019