Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fatty Acids and Lactones
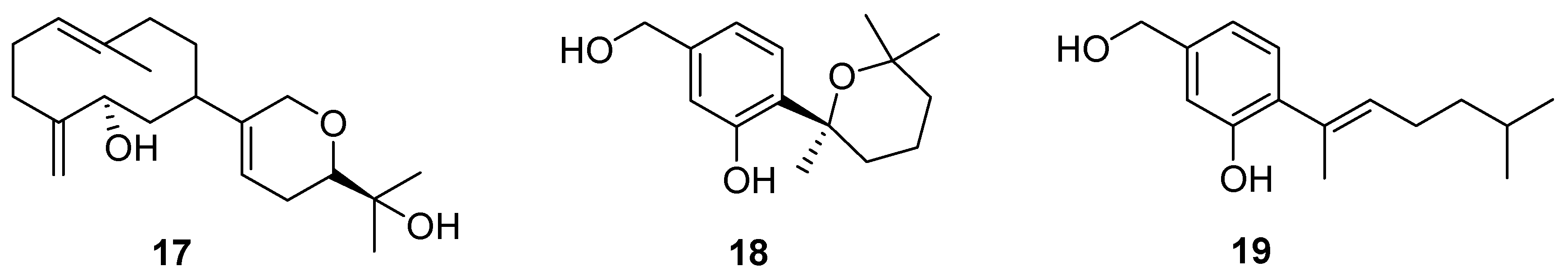
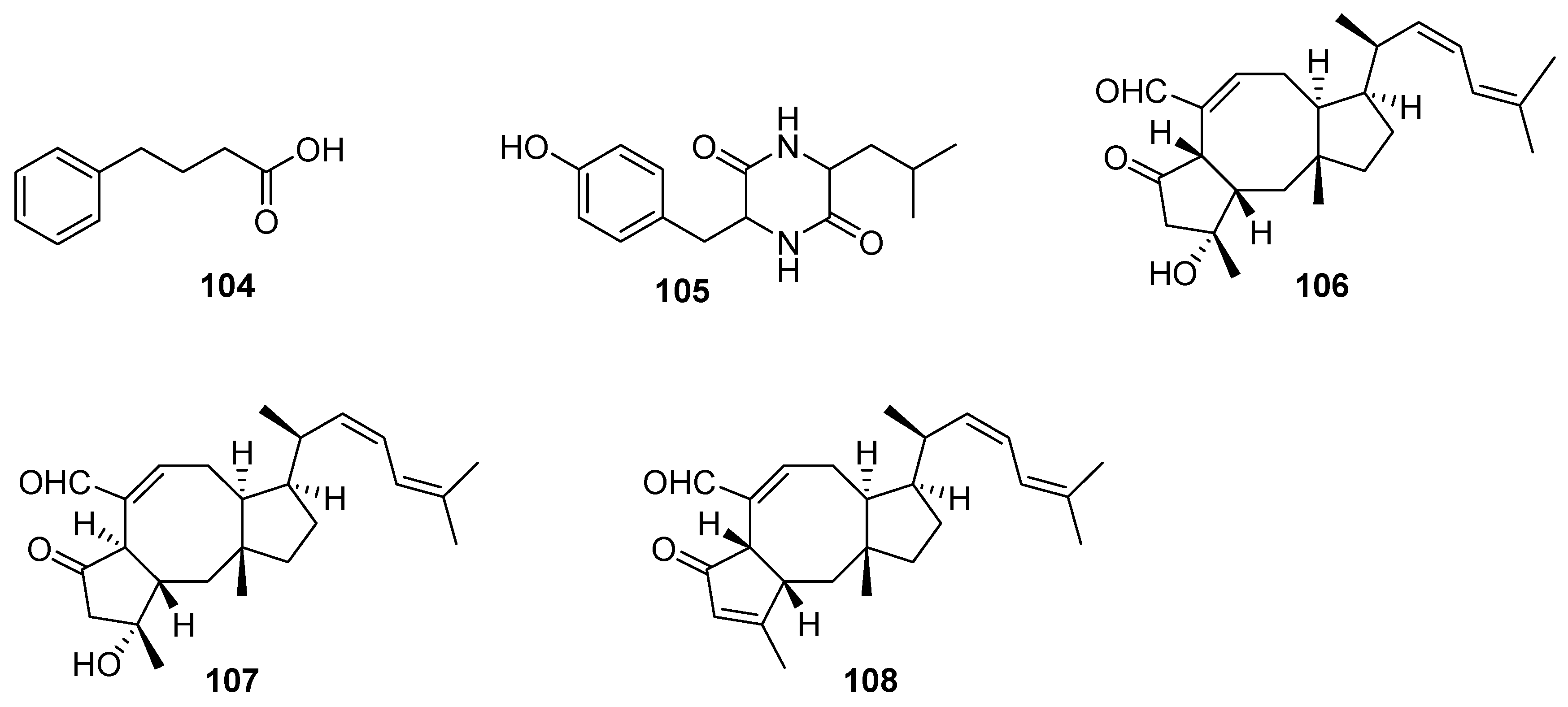
3. Terpenes and Steroids
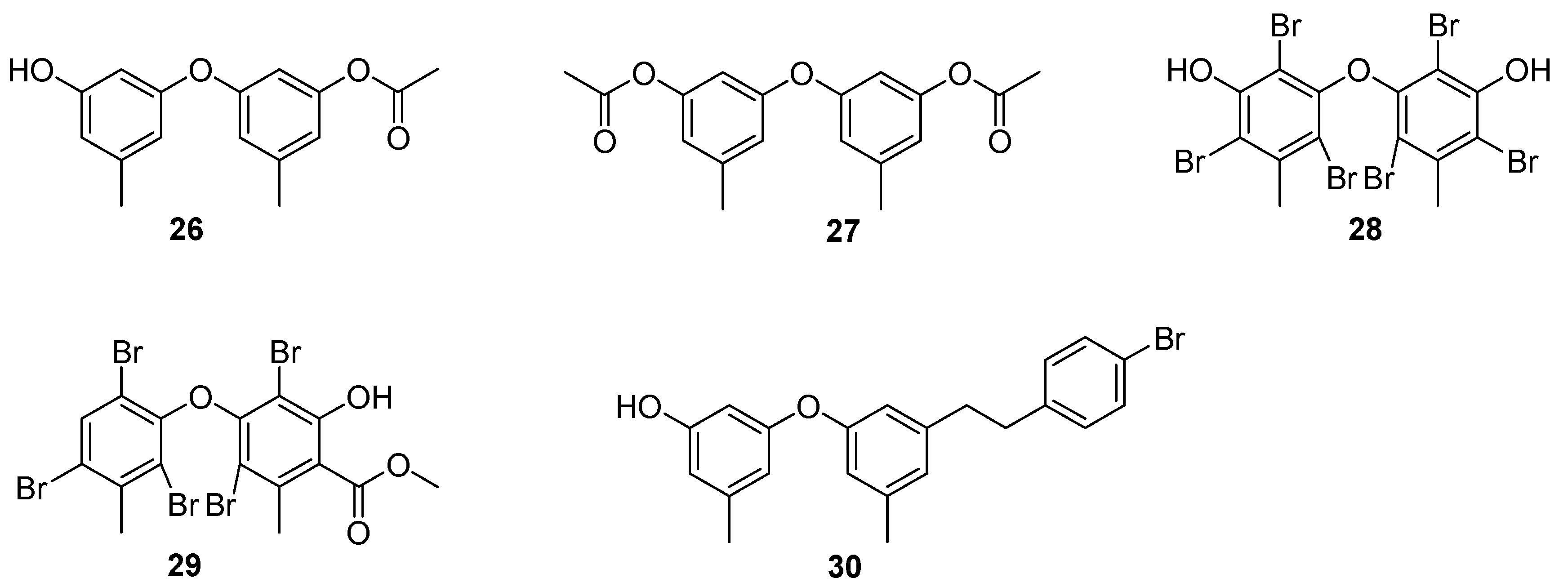
4. Benzenoids and Phenyl Ethers
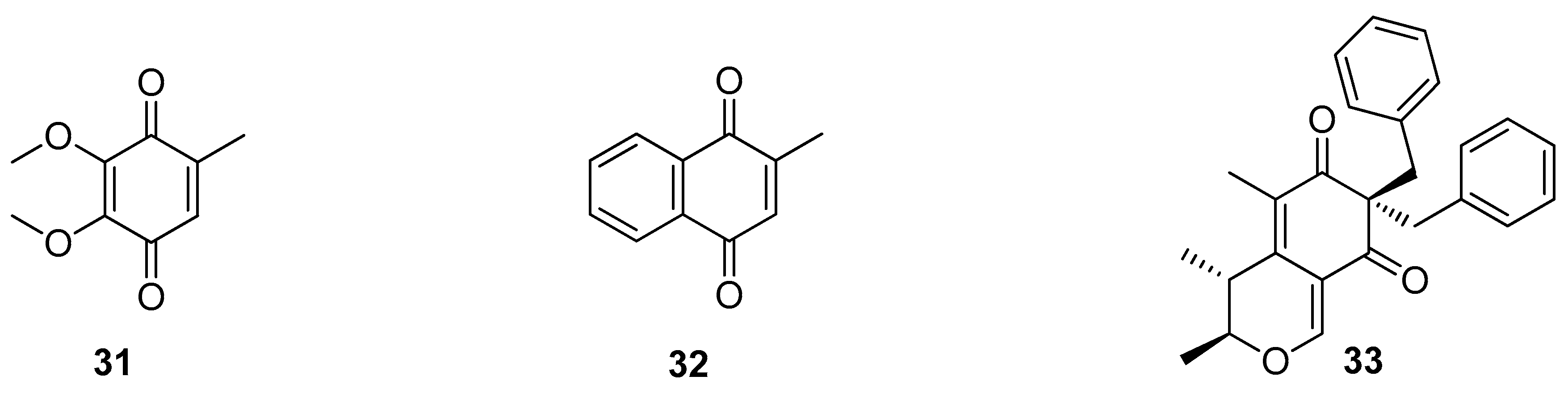
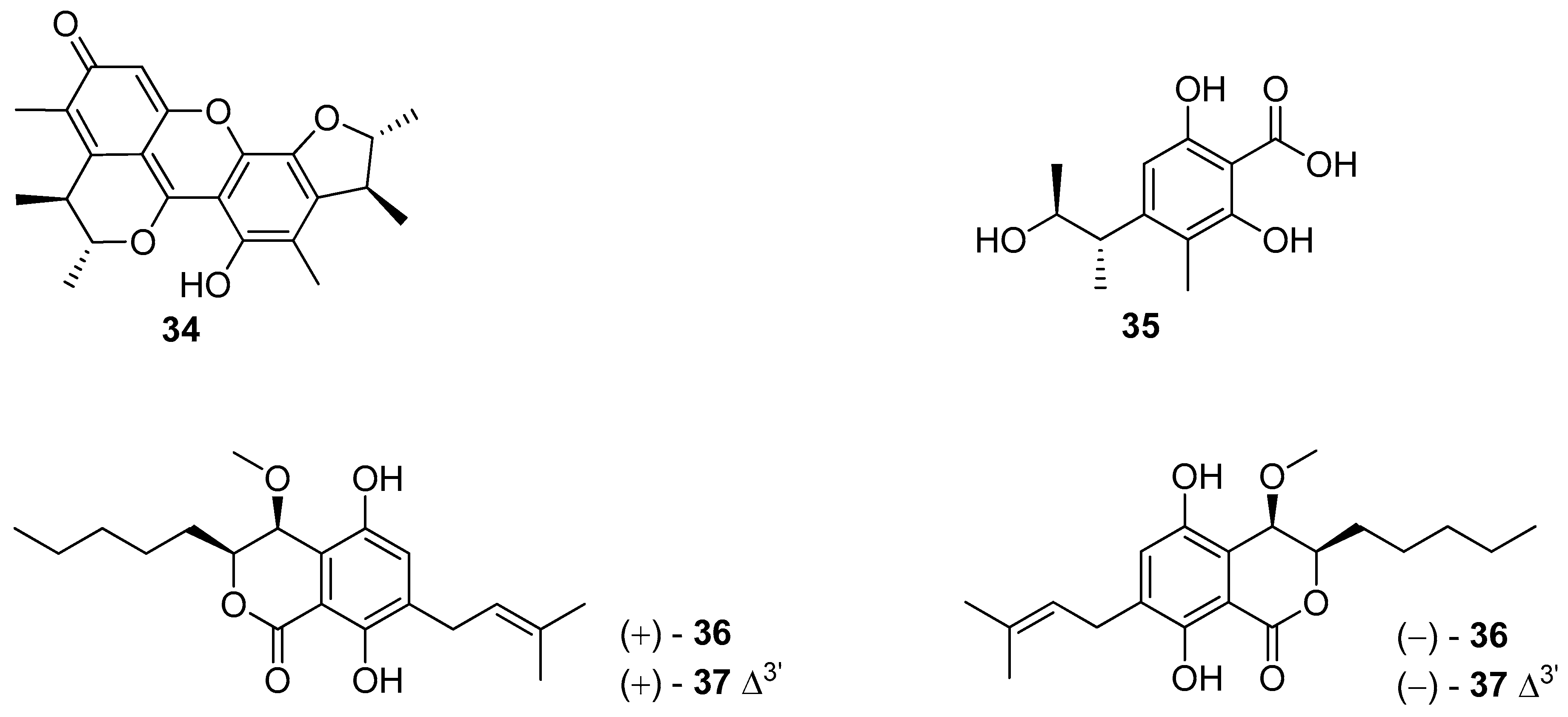
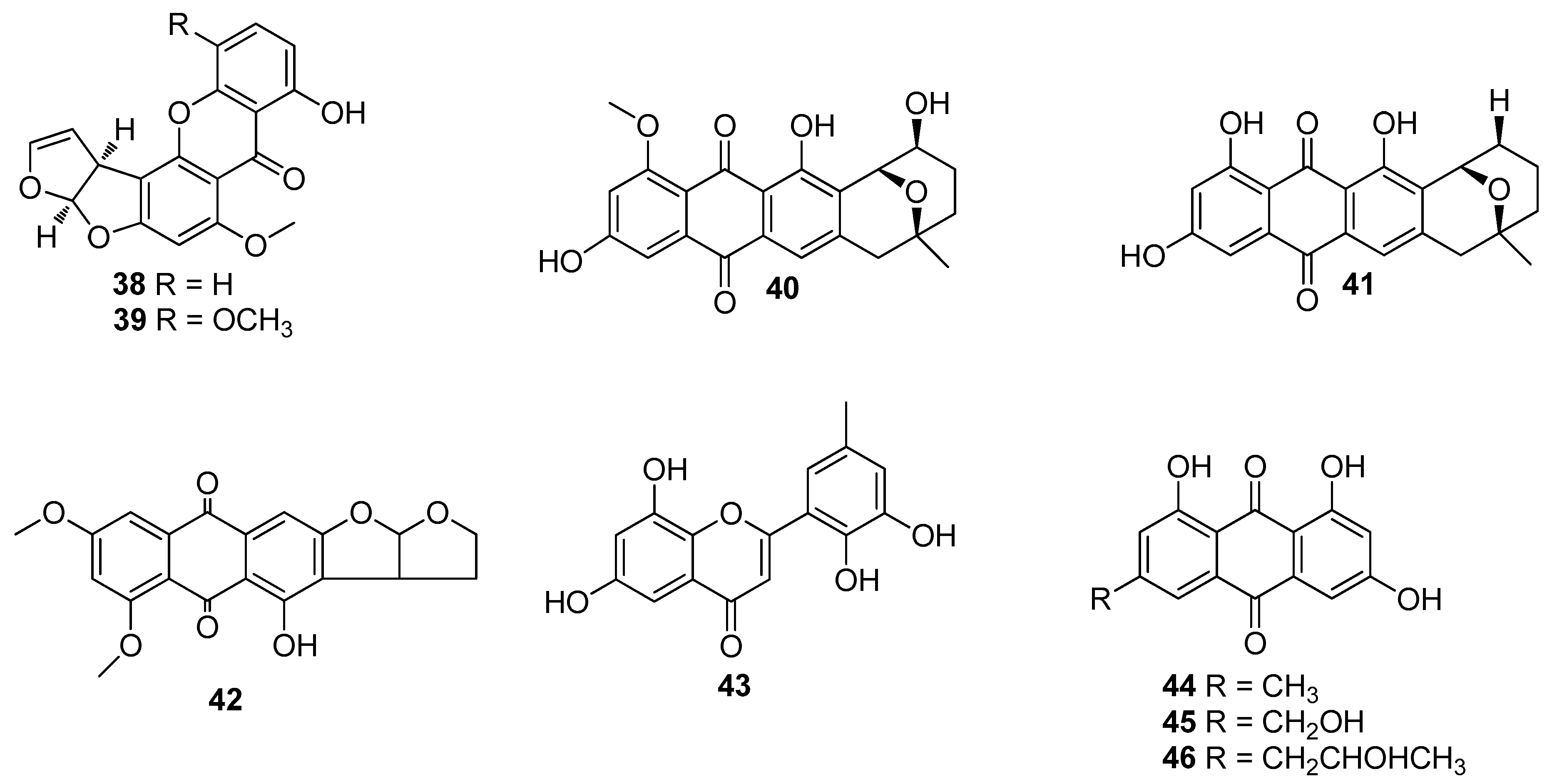
5. Polyketides
6. Alkaloids
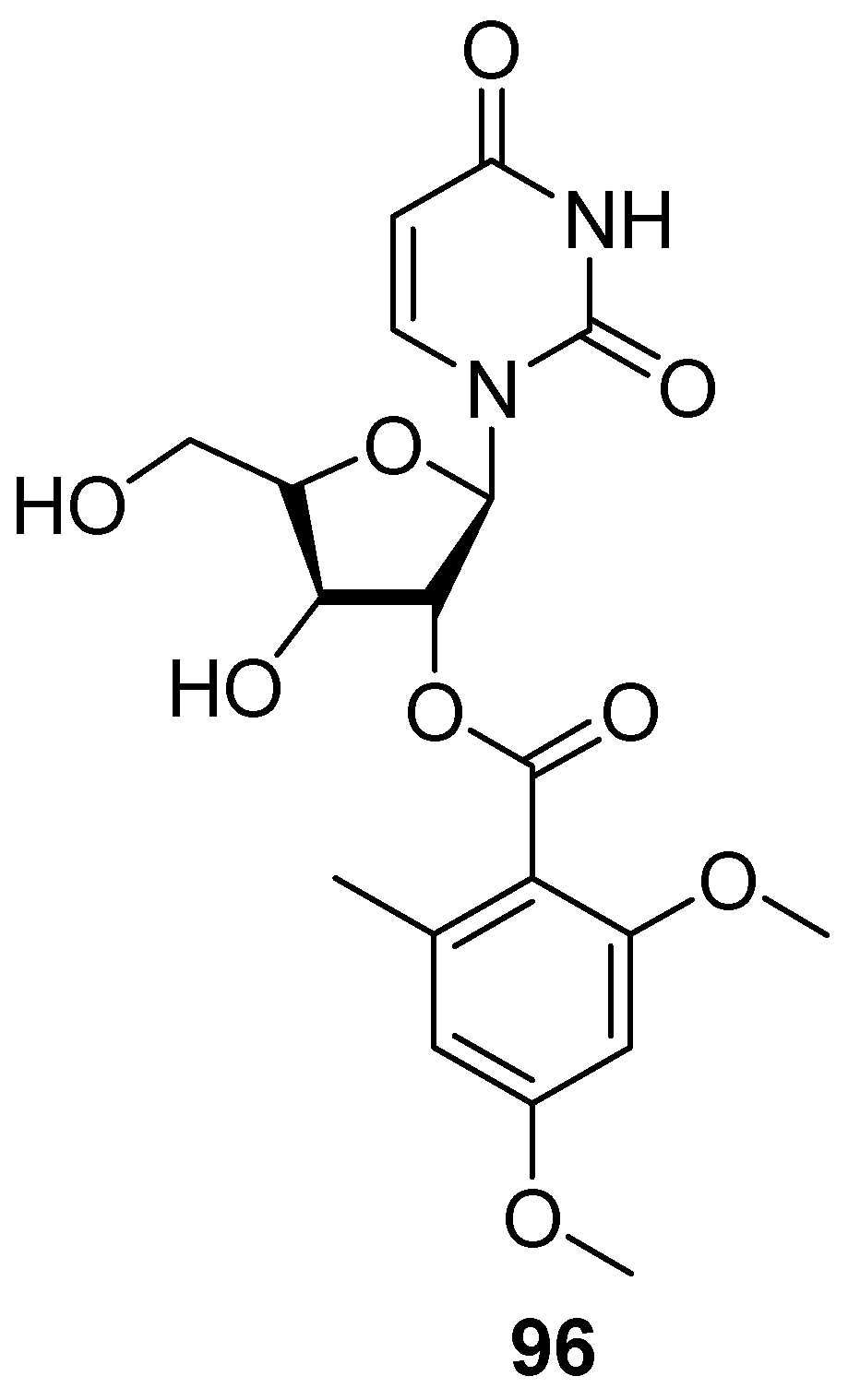
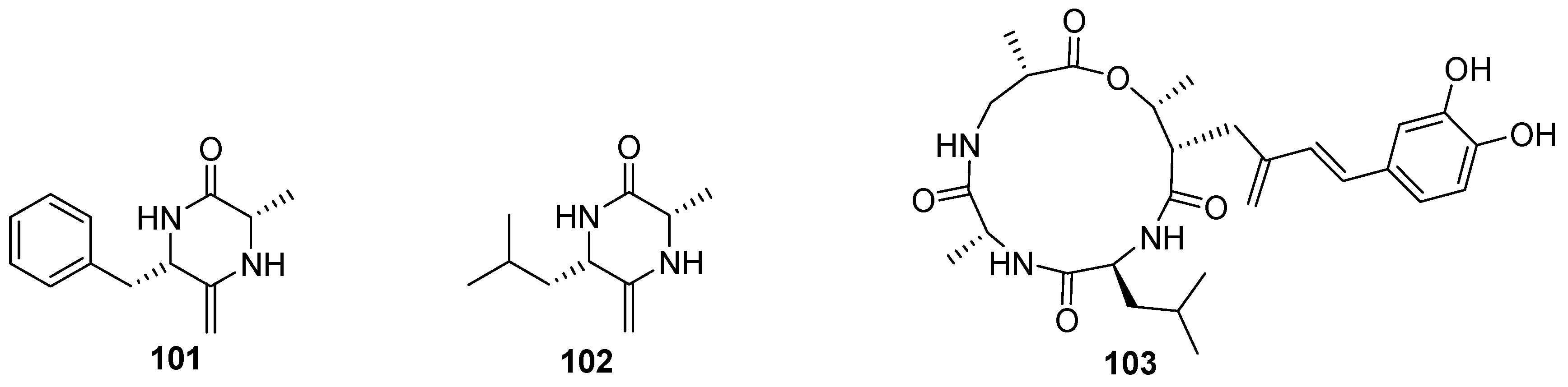
7. Nucleosides and Peptides
8. Enzymes
9. Biofilm Inhibitors
10. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Callow, M.E.; Callow, J.E. Marine biofouling: A sticky problem. Biologist 2002, 49, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wahl, M. Marine epibiosis. 1. fouling and antifouling-some basic aspects. Mar. Ecol.-Prog. Ser. 1989, 58, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P.; Bendick, J.A.; Holm, E.R.; Hertel, W.M. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yebra, D.M.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Antifouling technology-past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2004, 50, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadury, P.; Wright, P.C. Exploitation of marine algae: Biogenic compounds for potential antifouling applications. Planta 2004, 219, 561–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, I.C.; Brown, C.W.; Sytsma, M.D.; Ruiz, G.M. The role of containerships as transfer mechanisms of marine biofouling species. Biofouling 2009, 25, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Mini-review: Molecular mechanisms of antifouling compounds. Biofouling 2013, 29, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. Worldwide occurrence and effects of antifouling paint booster biocides in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Int. 2004, 30, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N. Antifouling paint booster biocides: Occurrence and partitioning in water and sediments. Handb. Environ. Chem. 2006, 50, 155–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell, T.; Richards, J.P.; Glegg, G.A.; Readman, J.W. The impact of legislation on the usage and environmental concentrations of Irgarol 1051 in UK coastal waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, I.; Martinez Bueno, M.J.; Agueera, A.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R. Environmental and human health risk assessment of organic micro-pollutants occurring in a Spanish marine fish farm. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, J.R. Marine invertebrate chemical defenses. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.S. Marine natural product antifoulants: Status and potential. Biofouling 1996, 9, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusetani, N. Biofouling and antifouling. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Xu, Y.; Fusetani, N. Natural products as antifouling compounds: Recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 2010, 26, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusetani, N. Antifouling marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009–2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Dahms, H.U.; Qian, P.Y. Inhibition of biofouling by marine microorganisms and their metabolites. Biofouling 2006, 22, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobretsov, S.; Abed, R.M.M.; Teplitski, M. Mini-review: Inhibition of biofouling by marine microorganisms. Biofouling 2013, 29, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satheesh, S.; Ba-akdah, M.A.; Al-Sofyani, A.A. Natural antifouling compound production by microbes associated with marine macroorganisms—A review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 21, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konya, K.; Shimidzu, N.; Otaki, N.; Yokoyama, A.; Adachi, K.; Miki, W. Inhibitory effect of bacterial ubiquinones on the setting of barnacle, Balanus amphitrite. Experientia 1995, 51, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.D.; Ganti, V.S.; Paudel, B.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, H.K.; Hong, Y.K.; Shin, H.W. Isolation of antifouling compounds from the marine bacterium, Shewanella oneidensis SCH0402. World. J. Microb. Biot. 2007, 23, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Xiao, X.; Qian, P.Y. Inhibitory effects of a branched-chain fatty acid on larval settlement of the polychaete hydroides elegans. Mar. Biotechnol. 2009, 11, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Lateff, A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Fouad, M.A.; Okino, T. Aureobasidin, new antifouling metabolite from marine-derived fungus Aureobasidium sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; He, H.; Schulz, S.; Liu, X.; Fusetani, N.; Xiong, H.; Xiao, X.; Qian, P.Y. Potent antifouling compounds produced by marine Streptomyces. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1331–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickschat, J.S.; Martens, T.; Brinkhoff, T.; Simon, M.; Schulz, S. Volatiles released by a Streptomyces species isolated from the North Sea. Chem. Biodivers. 2005, 2, 837–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Matsumura, K.; Han, Z.; Liu, L.; Lin, W.; Jia, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Structural optimization and evaluation of butenolides as potent antifouling agents: Modification of the side chain affects the biological activities of compounds. Biofouling 2012, 28, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.K.; Cho, J.Y. Effect of seaweed epibiotic bacterium Streptomyces violaceoruber SCH-09 on marine fouling organisms. Fish. Sci. 2013, 79, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Arellano, S.M.; Xiao, K.; Qian, P.Y. Comparative proteome and phosphoproteome analyses during cyprid development of the Barnacle Balanus (=Amphibalanus) amphitrite. J. Proteome. Res. 2010, 9, 3146–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Wong, Y.H.; Zhang, Y. Changes in the proteome and phosphoproteome expression in the bryozoan Bugula neritina larvae in response to the antifouling agent butenolide. Proteomics 2010, 10, 3435–3446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, G.D.; Wong, H.F.; Hutchinson, N.; Lee, S.C.; Chan, B.K.K.; Williams, G.A. Chemistry and biology of maculalactone A from the marine cyanobacterium Kyrtuthrix maculans. Phytochem. Rev. 2004, 3, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kim, M.S. Induction of antifouling diterpene production by Streptomyces cinnabarinus PK209 in co-culture with marine-derived Alteromonas sp. KNS-16. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Qian, P.Y.; She, Z.G.; de Voogd, N.J.; et al. Antibacterial bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y. Antifouling steroids isolated from red alga epiphyte filamentous bacterium Leucothrix mucor. Fish. Sci. 2012, 78, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, T.F.N.; Miao, L.; Li, X.; Qian, P.Y. Novel antifouling and antimicrobial compound from a marine-derived fungus Ampelomyces sp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2006, 8, 634–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Q.; Gan, L.S.; Mou, X.F.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Shao, C.L. Isolation, resolution and biological evaluation of pestalachlorides E and F containing both point and axial chirality. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22653–22658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Qian, P.Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Zheng, J.J.; Liu, M.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y. Antifouling phenyl ethers and other compounds from the invertebrates and their symbiotic fungi collected from the South China Sea. AMB Express 2016, 6, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; She, Z.G.; Qian, P.Y.; Lin, Y.C. Aspergilones A and B, two benzylazaphilones with an unprecedented carbon skeleton from the gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nong, X.H.; Zheng, Z.H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Lu, X.H.; Qi, S.H. Polyketides from a marine-derived fungus Xylariaceae sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1718–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, K.L.; Xu, Y.; She, Z.G.; Wang, C.Y. Dihydroisocoumarin derivatives with antifouling activities from a gorgonian-derived Eurotium sp. fungus. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 9132–9138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Han, Z.; Gao, H.C.; He, F.; Qian, P.Y.; Qi, S.H. Antifouling and antibacterial polyketides from marine gorgonian coral-associated fungus Penicillium sp. SCSGAF 0023. J. Antibiot. 2013, 66, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Wu, H.X.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, P.Y. Antifouling activity of secondary metabolites isolated from Chinese marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.; She, Z.; Guo, Z.; Peng, H.; Cai, X.; Zhou, S.; Gu, Y.; Lin, Y. H-1 and C-13 NMR assignments for two anthraquinones and two xanthones from the mangrove fungus (ZSUH-36). Magn. Reson. Chem. 2007, 45, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Li, H.; Hong, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H. Bioactive metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.L.; Wu, H.X.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Q.A.; Xu, Y.; Wei, M.Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Gu, Y.C.; Zheng, C.J.; She, Z.G.; Lin, Y.C. Potent antifouling resorcylic acid lactones from the gorgonian-derived fungus Cochliobolus lunatus. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.A.; Shao, C.L.; Gu, Y.C.; Blum, M.; Gan, L.S.; Wang, K.L.; Chen, M.; Wang, C.Y. Antifouling and fungicidal resorcylic acid lactones from the Sea Anemone-derived fungus Cochliobolus lunatus. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2014, 62, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Zhang, G.; Sun, J.; Xu, Y.; Han, Z.; Liu, L.L.; Shao, C.L.; Liu, Q.A.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, P.Y. Cochliomycin A inhibits the larval settlement of Amphibalanus amphitrite by activating the NO/cGMP pathway. Biofouling 2016, 32, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OlguinUribe, G.; AbouMansour, E.; Boulander, A.; Debard, H.; Francisco, C.; Combaut, G. 6-bromoindole-3-carbaldehyde, from an Acinetobacter sp. bacterium associated with the ascidian Stomozoa murrayi. J. Chem. Ecol. 1997, 23, 2507–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blom, J.F.; Brutsch, T.; Barbaras, D.; Bethuel, Y.; Locher, H.H.; Hubschwerlen, C.; Gademann, K. Potent algicides based on the cyanobacterial alkaloid nostocarboline. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Xu, Y.; Lu, L.; Li, Y.; Han, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shao, C.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, P.Y. Low-toxicity diindol-3-ylmethanes as potent antifouling compounds. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Han, Z.; Peng, J.; Qian, P.Y.; Qi, S.H. Antifouling indole alkaloids from two marine derived Fungi. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burgess, J.G.; Boyd, K.G.; Armstrong, E.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, L.M.; Berggren, M.; May, U.; Pisacane, T.; Granmo, A.; Adams, D.R. The development of a marine natural product-based antifouling paint. Biofouling 2003, 19, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.; Fu, P.; Peng, J.; Zhu, W.M.; Qi, S.H. A novel antifouling alkaloid from halotolerant fungus Penicillium sp. OUCMDZ-776. Tetrahedron Lett. 2012, 53, 2280–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.J.; Shao, C.L.; Wu, L.Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, K.L.; Zhao, D.L.; Sun, X.P.; Chen, G.Y.; Wang, C.Y. Bioactive phenylalanine derivatives and cytochalasins from the soft coral-derived fungus, Aspergillus elegans. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2054–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, C.L.; Xu, R.F.; Wang, C.Y.; Qian, P.Y.; Wang, K.L.; Wei, M.Y. Potent Antifouling marine dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one-containing alkaloids from the gorgonian coral-derived fungus Scopulariopsis sp. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredimoses, M.; Zhou, X.; Ai, W.; Tian, X.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Xian, J.Y.; Liu, Y. Westerdijkin A, a new hydroxyphenylacetic acid derivative from deep sea fungus Aspergillus westerdijkiae SCSIO 05233. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Fu, X.M.; Kong, C.J.; Wang, C.Y. Nucleoside derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Nat. Prod. Res. 2014, 28, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.T.; Goh, B.P.L.; Tripathi, A.; Lim, M.G.; Dickinson, G.H.; Lee, S.S.C.; Teo, S.L.M. Natural antifoulants from the marine cyanobacterium Lyngbya majuscula. Biofouling 2010, 26, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalme, L.O.; Yamauchi, A.; Sato, A.; Petitbois, J.G.; Nogata, Y.; Yoshimura, E.; Okino, T.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F. Total synthesis and biological activity of dolastatin 16. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1140–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, J.Y.; Kang, J.Y.; Hong, Y.K.; Baek, H.H.; Shin, H.W.; Kim, M.S. Isolation and structural determination of the antifouling diketopiperazines from marine-derived Streptomyces praecox 291-11. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2012, 76, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xu, X.Y.; He, F.; Nong, X.H.; Qi, S.H. New cyclic tetrapeptides and asteltoxins from gorgonian-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSGAF 0076. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.M.; Pedersen, L.T.; Laursen, M.H.; Kiil, S.; Dam-Johansen, K. Enzyme-based antifouling coatings: A review. Biofouling 2007, 23, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvig, T.A.; Leavitt, R.I.; Powers, W.P. Marine Antifouling Methods and Compositions. U.S. Patent 5,919,689, 29 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Polsenski, M.J.; Leavitt, R.I. Coatings with Enhanced Microbial Performance. U.S. Patent 7,041,285, 9 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Dobretsov, S.; Xiong, H.; Xu, Y.; Levin, L.A.; Qian, P.Y. Novel antifoulants: Inhibition of larval attachment by proteases. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clare, A.S.; Rittschof, D.; Gerhart, D.J.; Maki, J.S. Molecular approaches to nontoxic antifouling. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1992, 22, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Lau, S.C.K.; Dahms, H.U.; Dobretsov, S.; Harder, T. Marine biofilms as mediators of colonization by marine macroorganisms: Implications for antifouling and aquaculture. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stowe, S.D.; Richards, J.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Thompson, R.; Melander, C.; Cavanagh, J. Anti-biofilm compounds derived from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2010–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buommino, E.; Scognamiglio, M.; Donnarumma, G.; Fiorentino, A.; D’Abrosca, B. Recent advances in natural product-based anti-biofilm approaches to control infections. Mini-Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1169–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rane, R.A.; Sahu, N.U.; Shah, C.P. Synthesis and antibiofilm activity of marine natural product-based 4-thiazolidinones derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 7131–7134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, T.; Lee, B.W.K.; Cannon, L.M.; Ritter, K.A.; Dai, S.; Ren, D.; Wood, T.K.; Zhou, Z.S. A naturally occurring brominated furanone covalently modifies and inactivates LuxS. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6200–6204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusane, D.H.; Pawar, V.S.; Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Venugopalan, V.P.; Kumar, A.R.; Zinjarde, S.S. Anti-biofilm potential of a glycolipid surfactant produced by a tropical marine strain of Serratia marcescens. Biofouling 2011, 27, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nithya, C.; Devi, M.G.; Pandian, S.K. A novel compound from the marine bacterium Bacillus pumilus S6-15 inhibits biofilm formation in gram-positive and gram-negative species. Biofouling 2011, 27, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scopel, M.; Abraham, W.R.; Henriques, A.T.; Macedo, A.J. Dipeptide cis-cyclo(Leucyl-Tyrosyl) produced by sponge associated Penicillium sp. F37 inhibits biofilm formation of the pathogenic Staphylococcus epidermidis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 624–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Niikawa, H.; Kobayashi, M. Marine-derived fungal sesterterpenes, ophiobolins, inhibit biofilm formation of Mycobacterium species. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maréchal, J.P.; Hellio, C. Challenges for the development of new non-toxic antifouling solutions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4623–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.S.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Lee, O.O.; Matsumura, K.; Qian, P.Y. The regulatory role of the NO/cGMP signal transduction cascade during larval attachment and metamorphosis of the barnacle Balanus (=Amphibalanus) amphitrite. J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 3813–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, H.; He, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Butenolide inhibits marine fouling by altering the primary metabolism of three target organisms. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; He, F.; Xu, Y.; Matsumura, K.; He, L.S.; Qiu, J.W.; Qi, S.H.; Qian, P.Y. iTRAQ-based proteomic profiling of the barnacle Balanus amphitrite in response to the antifouling compound meleagrin. J. Proteome Res. 2013, 12, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wong, Y.H.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Arellano, S.M.; Ravasi, T.; Qian, P.Y. Quantitative proteomics identify molecular targets that are crucial in larval settlement and metamorphosis of Bugula neritina. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson Clarke Shipping Pty. Ltd.; CTI Consultants Pty. Ltd.; Lewis, J.A. Antifouling Performance Standards for the Maritime Industry. Available online: http://www.environment.gov.au/marine/publications/antifouling-performance-standards-maritime-industry (accessed on 21 July 2007).
- Leroy, C.; Delbarre-Ladrat, C.; Ghillebaert, F.; Compere, C.; Combes, D. Effects of commercial enzymes on the adhesion of a marine biofilm-forming bacterium. Biofouling 2008, 24, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harder, T.; Lam, C.; Qian, P.Y. Induction of larval settlement in the polychaete Hydroides elegans by marine biofilms: An investigation of monospecific diatom films as settlement cues. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2002, 229, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.C.K.; Harder, T.; Qian, P.Y. Induction of larval settlement in the serpulid polychaete Hydroides elegans (Haswell): Role of bacterial extracellular polymers. Biofouling 2003, 19, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.-L.; Wu, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Xu, Y. Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090266
Wang K-L, Wu Z-H, Wang Y, Wang C-Y, Xu Y. Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(9):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090266
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kai-Ling, Ze-Hong Wu, Yu Wang, Chang-Yun Wang, and Ying Xu. 2017. "Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs" Marine Drugs 15, no. 9: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090266
APA StyleWang, K.-L., Wu, Z.-H., Wang, Y., Wang, C.-Y., & Xu, Y. (2017). Mini-Review: Antifouling Natural Products from Marine Microorganisms and Their Synthetic Analogs. Marine Drugs, 15(9), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15090266





