Cytotoxic Natural Products from Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
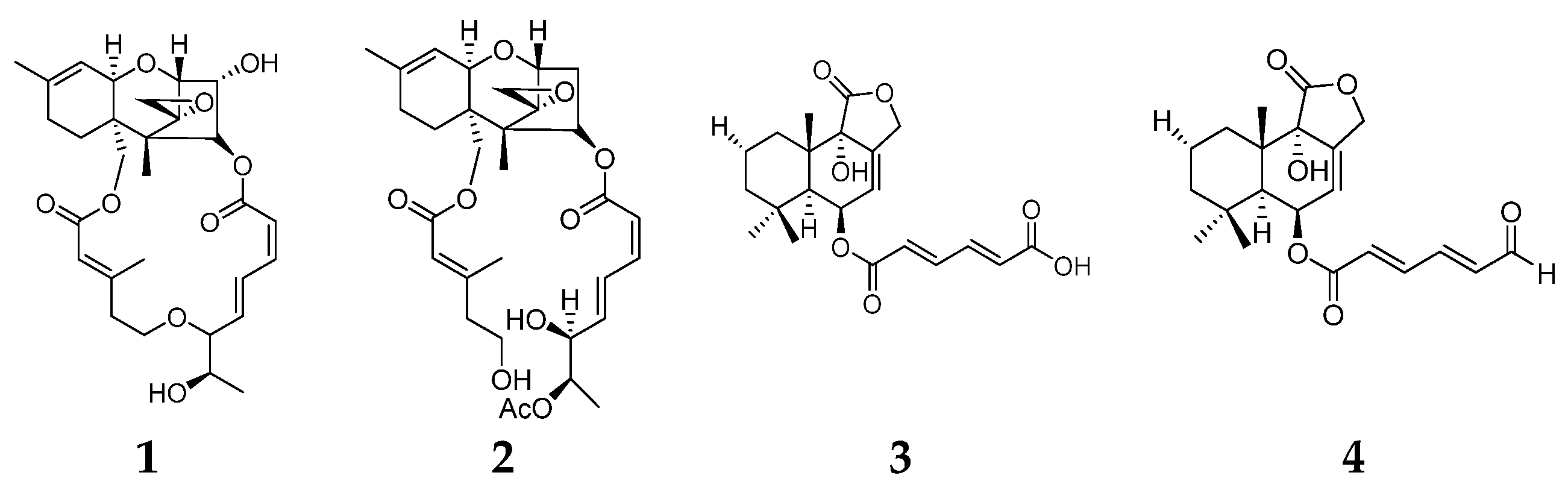
2. Terpenes
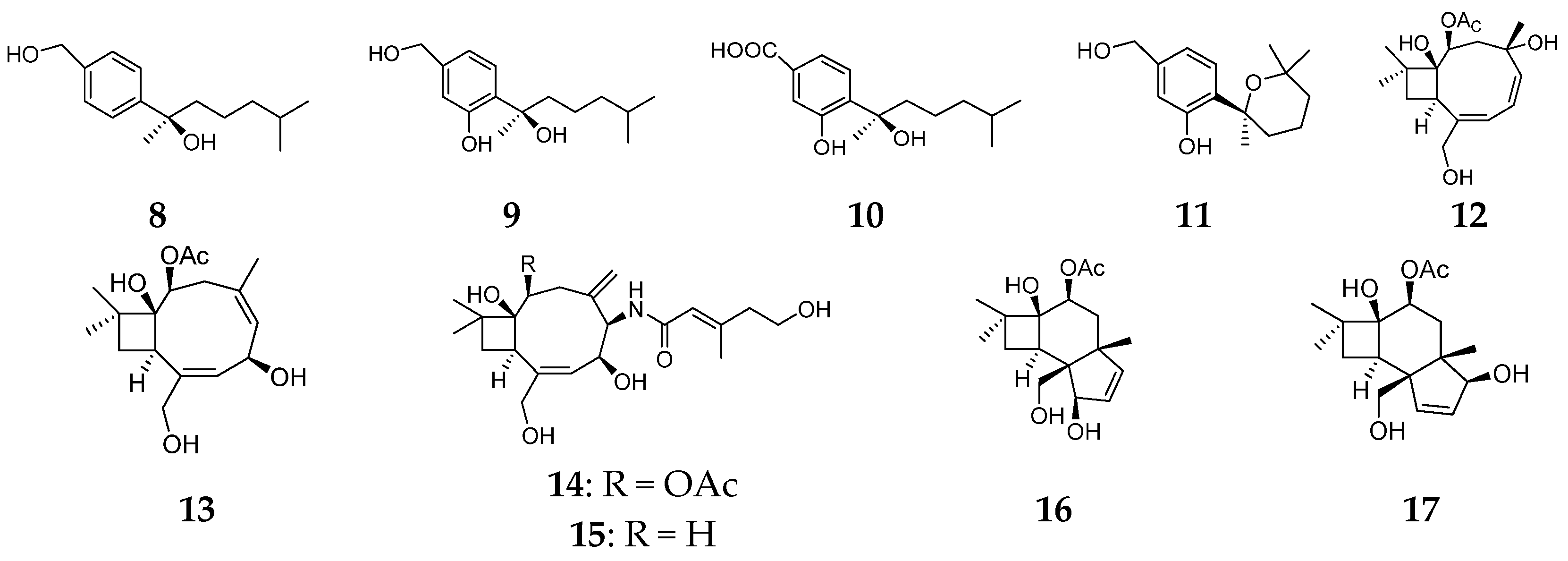
2.1. Sesquiterpenes
2.2. Sesterterpenoids
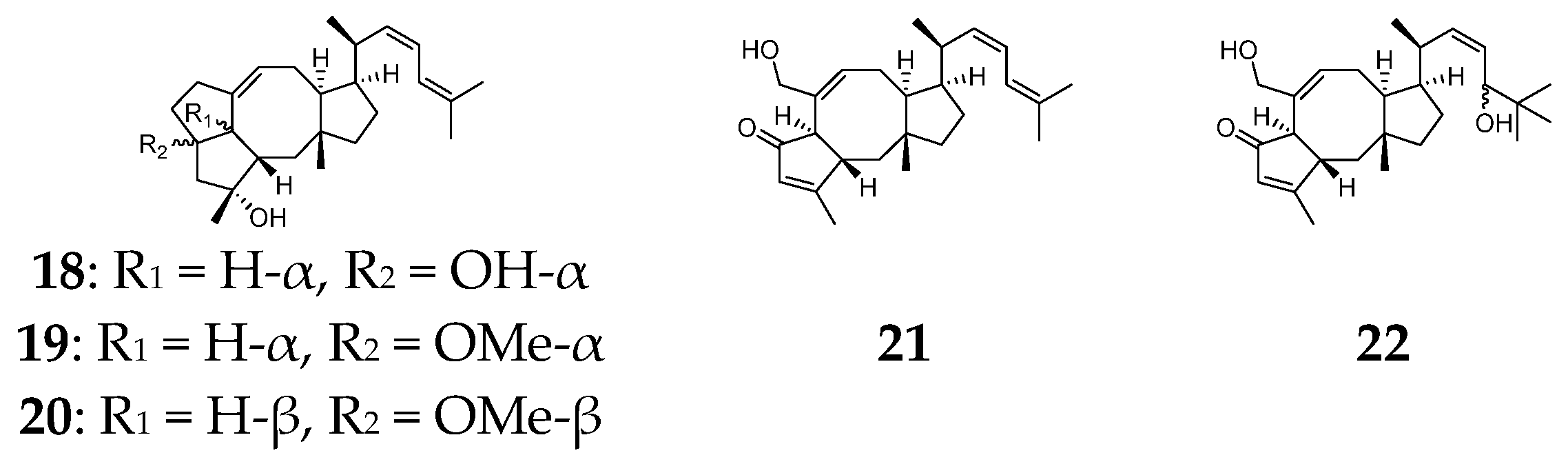
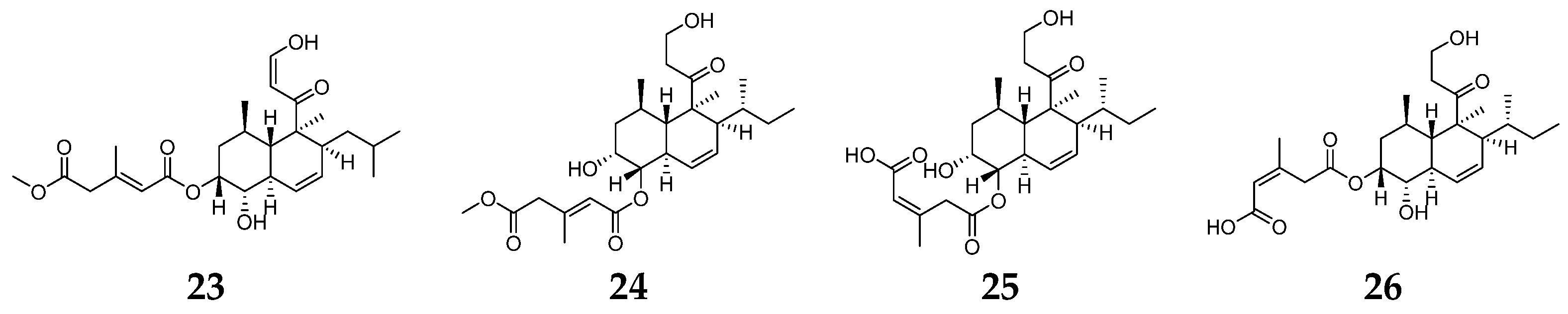
2.3. Diterpenes
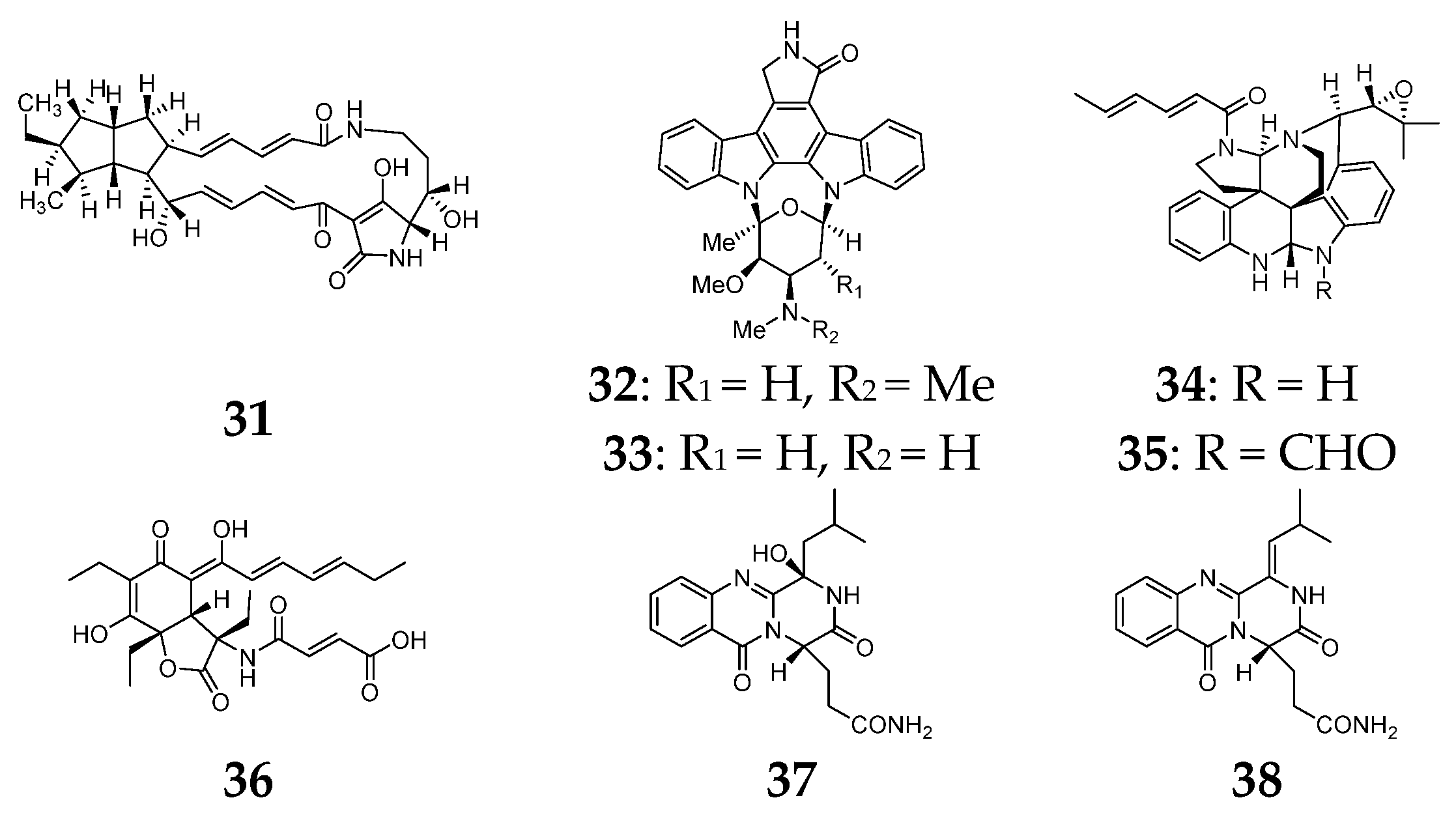
2.4. Meroterpenoids
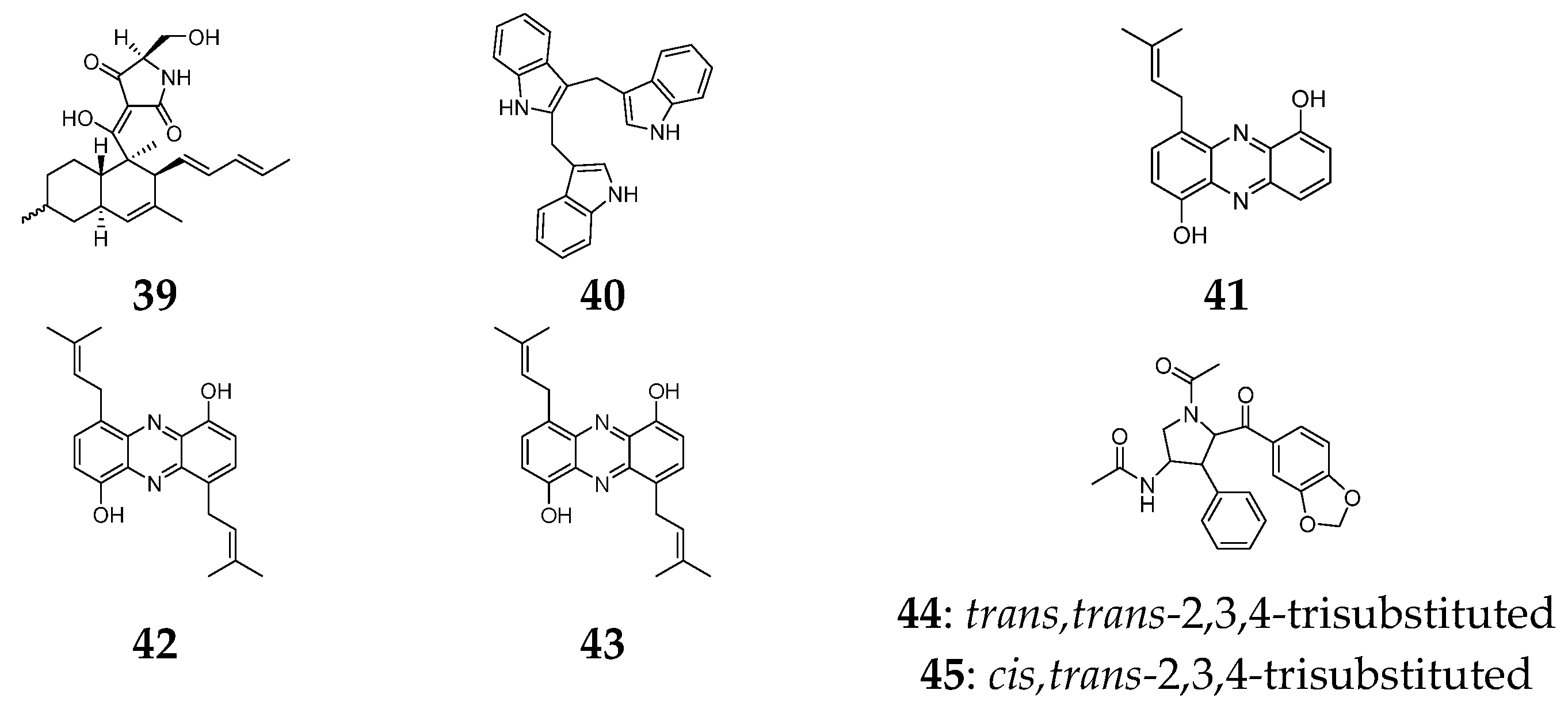
3. Alkaloids
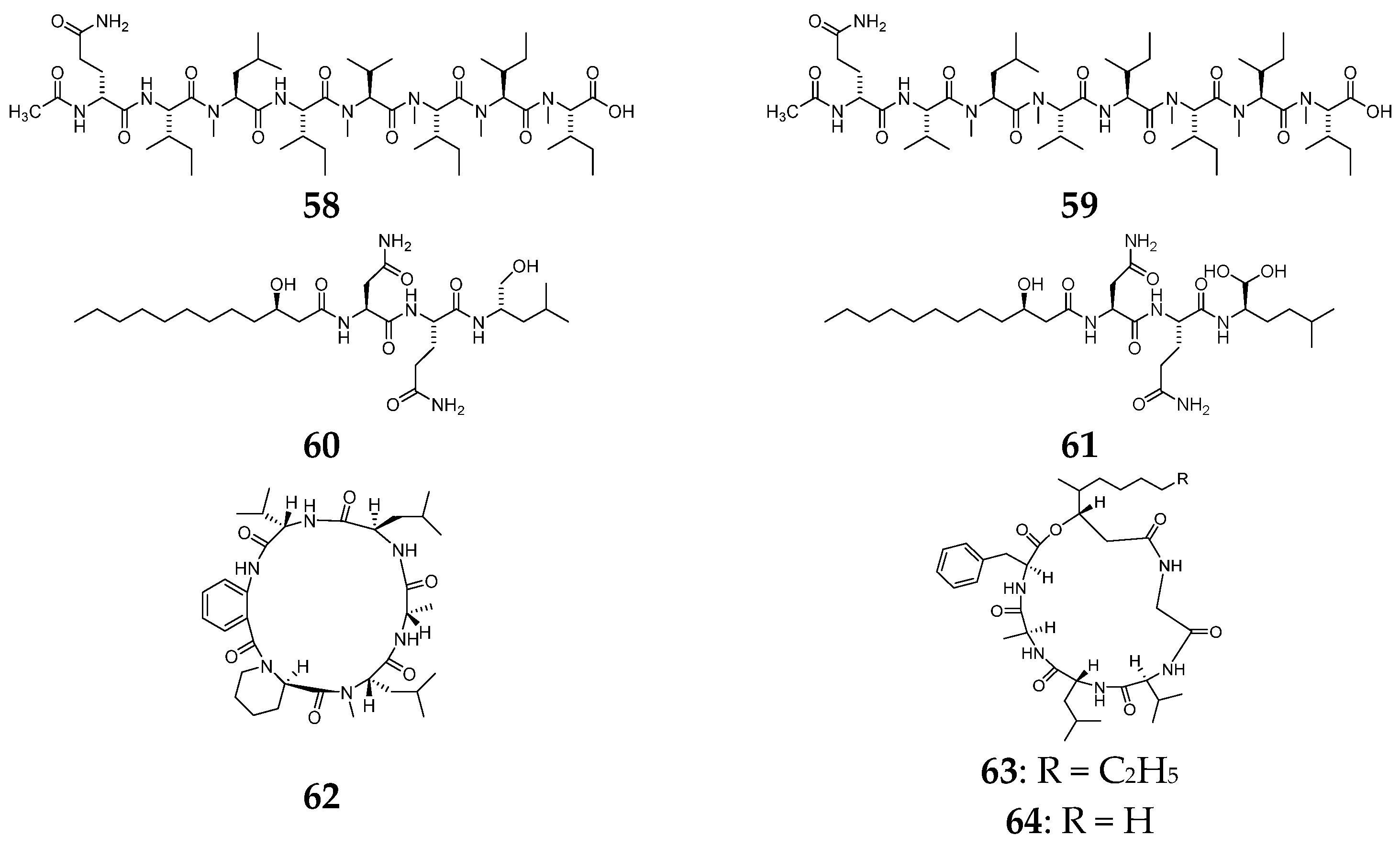
4. Peptides
5. Aromatics
5.1. Polyketides
5.2. α-Pyrone Derivatives
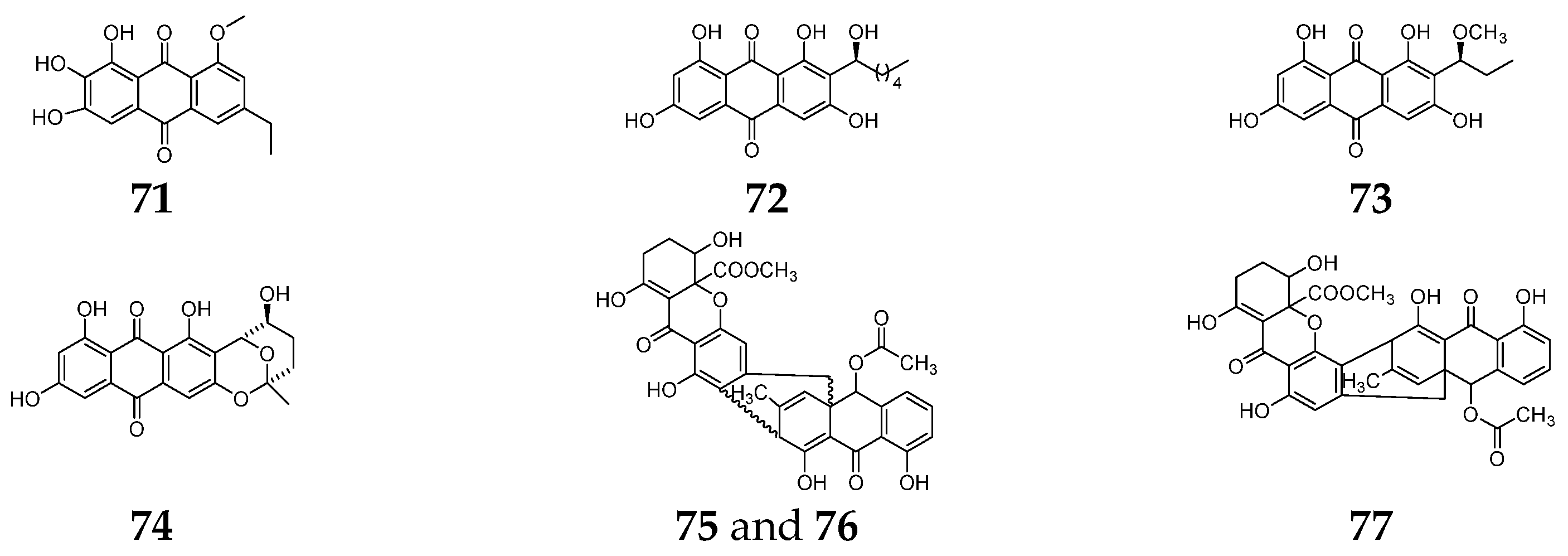
5.3. Anthraquinones
5.4. Bicoumarin
5.5. Ethers
5.6. Xanthones
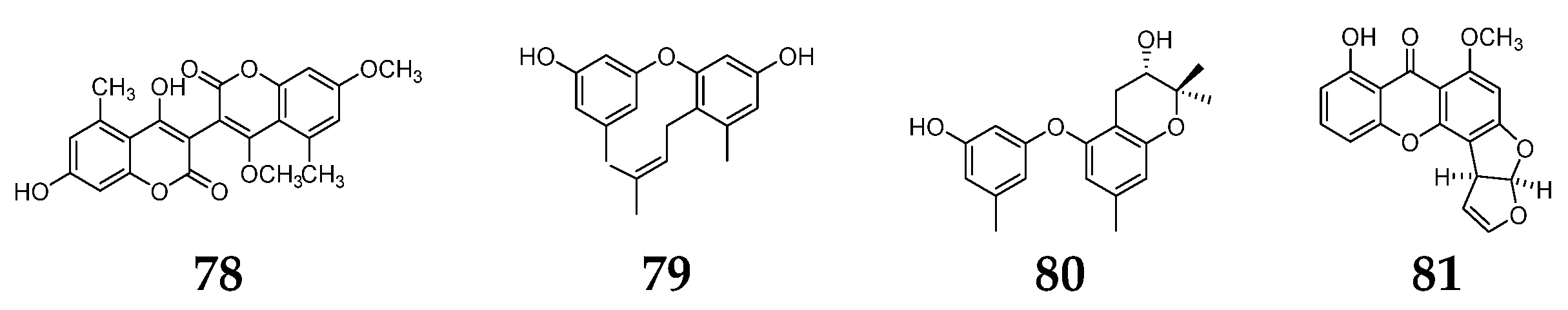
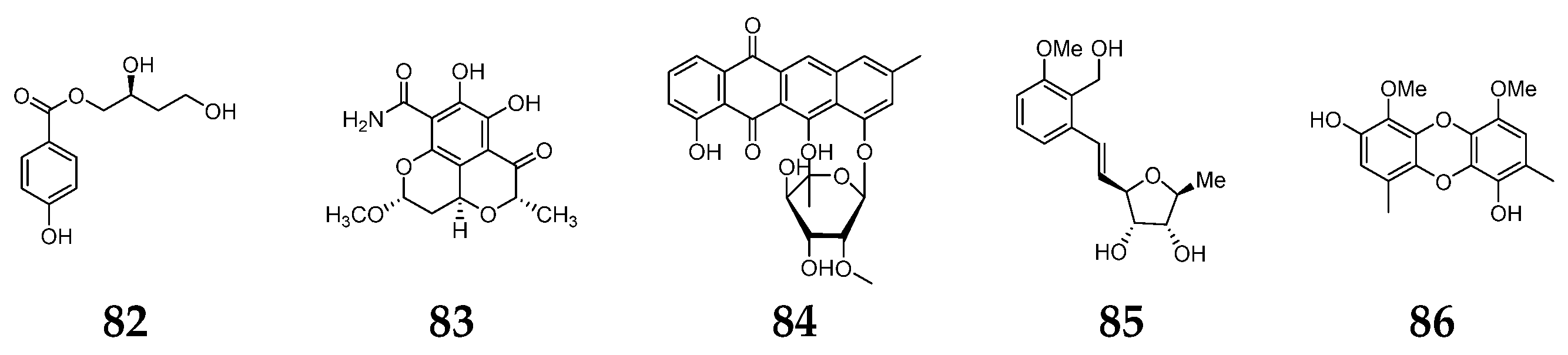
5.7. Other Aromatic Compounds
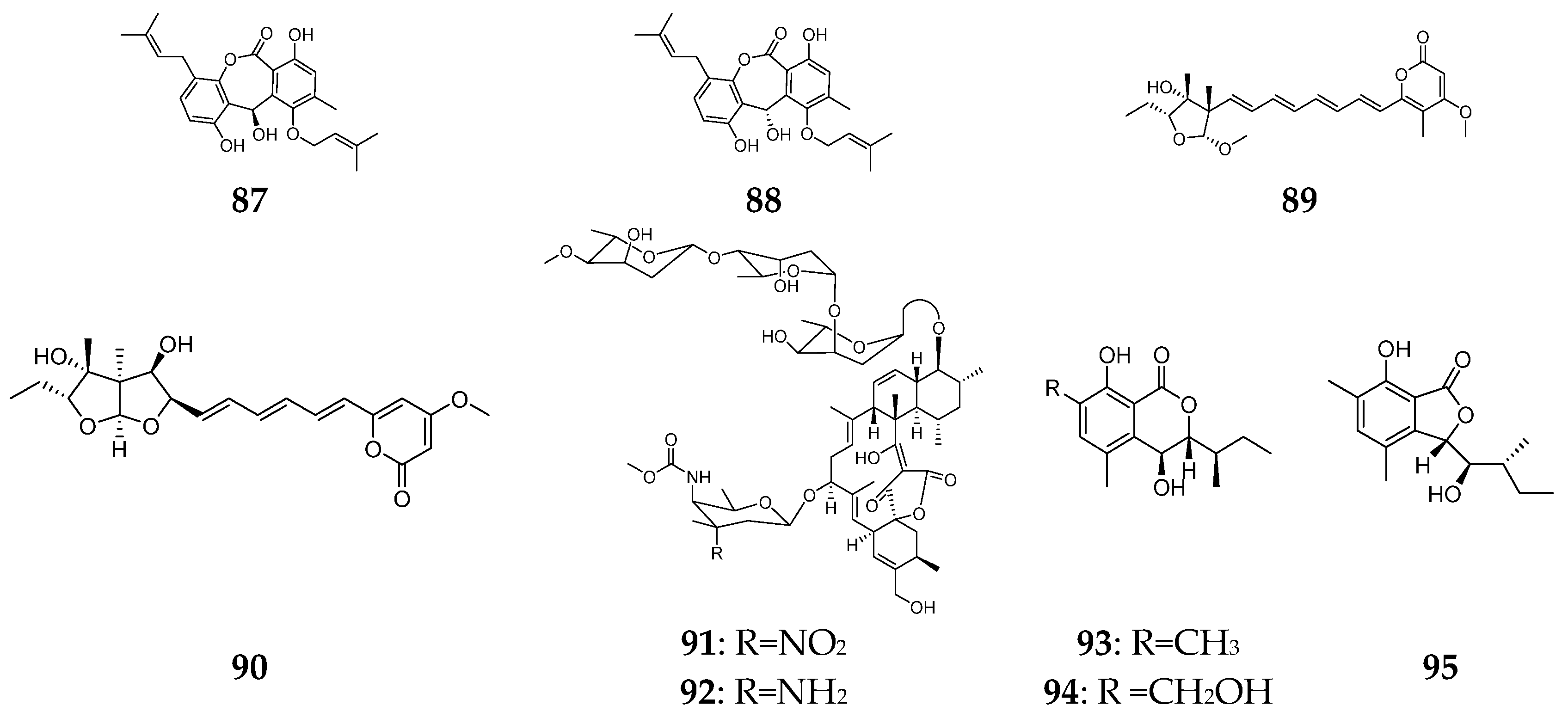
6. Lactones
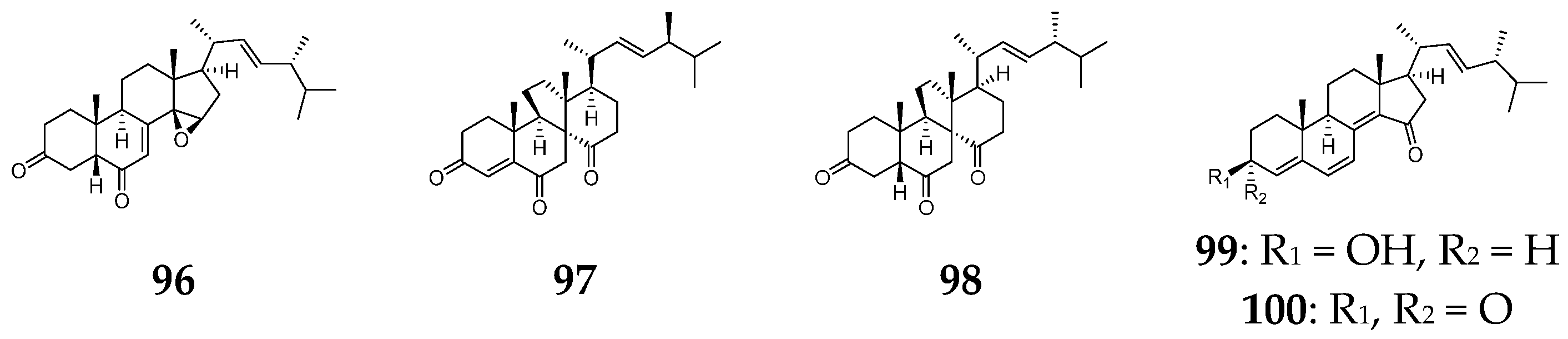
7. Steroids
8. Miscellaneous Compounds
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhanot, A.; Sharma, R.; Noolvi, M.N. Natural sources as potential anti-cancer agents: A review. Int. J. Phytomed. 2011, 3, 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Yan, X.J.; Han, X.T.; Chen, H.M.; Lin, W.; Lee, F.S.C.; Wang, X.R. Identification of norharman as the cytotoxic compound produced by the sponge (Hymeniacidon perleve)-associated marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas piscicida and its apoptotic effect on cancer cells. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2006, 44, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, X.; Jin, M.; Deng, M. Optimizing the formation of in vitro sponge primmorphs from the Chinese sponge Stylotella agminata (Ridley). J. Biotechnol. 2003, 100, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belarbi, E.; Gomez, A.C.; Chisti, Y.; Camacho, F.G.; Grima, E.M. Producing drugs from marine sponges. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 21, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembitsky, V.M.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Poroikov, V.V. Novel antitumor agents: Marine sponge alkaloids, their synthetic analogs and derivatives. Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 2005, 5, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, W.B.; Burke, D.C. Contributions to the study of marineproducts. XXXIX. The nucleosides of sponges. III. Spongothymidine and spongouridine. J. Org. Chem. 1955, 20, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G. Diversity and biotechnological potential of the sponge-associated microbial consortia. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 33, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, T.; Rusch, D.; DeMaere, M.Z.; Yung, P.Y.; Lewis, M.; Halpern, A.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Egan, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Functional genomic signatures of sponge bacteria reveal unique and shared features of symbiosis. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1557–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richelle-Maurer, E.G.; Gomez, R.; Braekman, J.C.; van de Vyver, G.; van Soest, R.W.; Devijver, C. Primary cultures from the marine sponge Xestospongia muta (petrosiidae, haplosclerida). J. Biotechnol. 2003, 100, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Rath, C.; Rigot, J.F.; Tarlov, N.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Structures and cytotoxic properties of trichoverroids and their macrolide analogues produced by saltwater culture of Myrothecium verrucaria. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 4342–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Müller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.; Proksch, P. Drimane sesquiterpenoids from the fungus Aspergillus ustus isolated from the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 1585–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.; Koch, L.; Thu, K.M.; Rahamim, Y.; Aluma, Y.; Ilan, M.; Yarden, O.; Carmeli, S. Novel terpenoids of the fungus Aspergillus insuetus isolated from the Mediterranean sponge Psammocinia sp. collected along the coast of Israel. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 19, 6587–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.L.; Shao, C.L.; Chen, J.F.; Guo, Z.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Chen, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Li, R.; de Voogd, N.J.; She, Z.G.; et al. New bisabolane sesquiterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. isolated from the sponge Xestospongia testudinaria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xu, Y.; Shao, C.L.; Yang, R.Y.; Zheng, C.J.; Chen, Y.Y.; Fu, X.M.; Qian, P.Y.; She, Z.G.; de Voogd, N.J.; et al. Antibacterial bisabolane-type sesquiterpenoids from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Punctaporonins H–M: Caryophyllene-type sesquiterpenoids from the sponge-associated fungus Hansfordia sinuosae. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3904–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.B.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Ebel, R.; Wang, Y.; Schulz, B.; Draeger, S.; Müller, W.E.G.; Wray, V.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Ophiobolin sesterterpenoids and pyrrolidine alkaloids from the sponge derived fungus Aspergillus ustus. Helv. Chim. Acta 2011, 94, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Mizutani, Y.; Umebayashi, Y.; Inno, N.; Kawashima, M.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R. Tandyukisin, a novel ketoaldehyde decalin derivative, produced by a marine sponge-derived Trichoderma harzianum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Umebayashi, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Sugiura, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Tanaka, R. Determination of the chemical structures of tandyukisins B–D, isolated from a marine sponge-derived fungus. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cueto, M.; MacMillan, J.B.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Tropolactones A–D, four meroterpenoids from a marine-derived fungus of the genus Aspergillus. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 1826–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemori, H.; Bae, M.A.; Yazawa, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, J. Alteramide A, a new tetracyclic alkaloid from a bacterium Alteromonas sp. associated with the marine sponge Ealhhondria okadai. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4317–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, L.M.; Blanco, J.A.; Baz, J.P.; Puentes, J.L.; Millán, F.R.; Vázquez, F.E.; Fernández-Chimeno, R.I.; Grávalos, D.G. 4′-N-methyl-5′-hydroxystaurosporine and 5′-hydroxystaurosporine, new indolocarbazole alkaloids from a marine Micromonospora sp. strain. J. Antibiot. 2000, 53, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadulco, R.; Edrada, R.A.; Ebel, R.; Berg, A.; Schaumann, K.; Wray, V.; Steube, K.; Proksch, P. New communesin derivatives from the fungus Penicillium sp. derived from the Mediterranean sponge Axinella verrucosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Tsuruta, H.; Mühlbacher, J.; Maksimenka, K.; Steffens, S.; Schaumann, K.; Stöhr, R.; Wiese, J.; et al. The first sorbicillinoid alkaloids, the antileukemic sorbicillactones A and B, from a sponge-derived Penicillium chrysogenum strain. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 7252–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.H.; Fang, Y.; Du, L.; Zhu, T.; Duan, L.; Chen, J.; Gu, Q.Q.; Zhu, W.M. Aurantiomides A–C, quinazoline alkaloids from the sponge-derived fungus Penicillium aurantiogriseum SP0-19. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, K.; Kehraus, S.; Gütschowb, M.; König, G.M. Cytotoxic and HLE-inhibitory tetramic acid derivatives from marine-derived fungi. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Lee, C.O.; Bae, K.S.; Hong, J.; Jung, J.H. Indole oligomers from a marine sponge-associated bacterium Psychrobacter sp. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2010, 38, 839–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.T.; Izumikawa, M.; Motohashi, K.; Mukai, A.; Takagi, M.; Shin-Ya, K. Distribution of the 3-hydroxyl-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene and isoprenoid production in marine-derived Actinobacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 304, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, Y.; Bae, M.; Kim, B.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D.C. A new benzofuran glycoside and indole alkaloids from a sponge-associated rare actinomycete, Amycolatopsis sp. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2326–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagata, T.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Gymnasterones, novel cytotoxic metabolites produced by a fungal strain from a sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 3773–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, A.; Amagata, T.; Minoura, K.; Ito, T. Gymnastatins, novel cytotoxic metabolites produced by a fungal strain from a sponge. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 5675–5678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Gymnastatins F–H, cytostatic metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Gymnascella dankaliensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1384–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, T.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Gymnastatins and Dankastatins, growth inhibitory metabolites of a Gymnascella species from a Halichondria sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, T.; Chen, Y.P.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Additional cytotoxic substances isolated from the sponge-derived Gymnascella dankaliensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 5960–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boot, C.M.; Tenney, K.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Highly N-methylated linear peptides produced by an atypical sponge-derived Acremonium sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M.; Dang, H.T.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.O.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H. A cytotoxic lipopeptide from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Dang, H.T.; Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Hong, J.K.; Lee, C.O.; Jung, J.H. A cytotoxic fellutamide analogue from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, 32, 3817–3820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prompanya, C.; Fernandes, C.; Cravo, S.; Pinto, M.; Dethoup, T.; Silva, A.; Kijjoa, A. A new cyclic hexapeptide and a new isocoumarin derivative from the marine sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus similanensis KUFA 0013. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1432–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Lang, G.; Kajahn, I.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Scopularides A and B, cyclodepsipeptides from a marine sponge-derived fungus, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugni, T.S.; Bernan, V.S.; Greenstein, M.; Janso, J.E.; Maiese, W.M.; Mayne, C.L.; Ireland, C.M. Brocaenols A–C: Novel polyketides from a marine-derived Penicillium brocae. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebel, R.; Riebe, F.; Proksch, P.; Schulz, B.; Müller, W. New cytotoxic α-pyrone derivatives from the sponge-derived fungus Petriella sp. Planta Med. 2007, 73, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Steffens, S.; Günther, E.; Schaumann, K. Evariquinone, isoemericellin, and stromemycin from a sponge derived strain of the fungus Emericella variecolor. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.M.; Li, H.; Hong, J.; Cho, H.Y.; Bae, K.S.; Kim, M.A.; Kim, D.K.; Jung, J.H. Bioactive metabolites from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus versicolor. Arch. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 33, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, J.Y.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. New xanthoquinodin-like compounds, JBIR-97, -98 and -99, obtained from marine sponge-derived fungus Tritirachium sp. SpB081112MEf2. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 615–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiort, J.; Maksimenka, K.; Reichert, M.; Perovic’-Ottstadt, S.; Lin, W.H.; Wray, V.; Steube, K.; Schaumann, K.; Weber, H.; Proksch, P.; et al. New natural products from the sponge-derived fungus Aspergillus niger. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Mou, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Meng, D. Cytotoxic polyphenols from a sponge-associated fungus Aspergillus versicolor Hmp-48. Chem. Biodivers. 2014, 11, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Z.H.; Zhu, W.M.; Gu, Q.Q.; Fang, Y.C.; Duan, L.; Cui, C.B. A new cytotoxic compound from Penicillium auratiogriseum symbiotic or epiphytic fungus of sponge Mycale plumose. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2005, 16, 1227–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Ueda, J.Y.; Khan, S.T.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-58, a new salicylamide derivative, isolated from a marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SpD081030ME-02. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, K.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. Tetracenoquinocin and 5-iminoaranciamycin from a sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. Sp080513GE-26. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 755–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrøm, J.; Christophersen, C.; Barrero, A.F.; Oltra, J.E.; Justicia, J.; Rosales, A. Bioactive metabolites from a marine-derived strain of the fungus Emericella. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Long, H.L.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W.H. Varioxiranols I–L, new lactones from a sponge-associated Emericella variecolor fungus. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 17, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.B.; Xi, T.; Li, J.; Wang, P.; Li, F.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Qin, S. Lobophorin C and D, new kijanimicin derivatives from a marine sponge-associated actinomycetal strain AZS17. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.E.; Julianti, E.; Oh, H.; Park, W.; Oh, D.C.; Oh, K.B.; Shin, J. Stereochemistry of hydroxy-bearing benzolactones: Isolation and structural determination of chrysoarticulins A–C from a marine-derived fungus Chrysosporium articulatum. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 3111–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Doi, M.; Tohgo, M.; Minoura, K.; Numata, A. Dankasterone, a new class of cytotoxic steroid produced by a Gymnascella species from a marine sponge. Chem. Commun. 1999, 14, 1321–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagata, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yamada, T.; Doi, M.; Minoura, K.; Ohishi, H.; Yamori, T.; Numata, A.; Makhloufi, G. Variation in cytostatic constituents of a sponge-derived Gymnascella dankaliensis by manipulating the carbon source. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amagata, T.; Usami, Y.; Minoura, K.; Ito, T.; Numata, A. Cytotoxic substances produced by a fungal strain from a sponge: Physico-chemical properties and structures. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, J.Y.; Hashimoto, J.; Inaba, S.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K. JBIR-59, a new sorbicillinoid, from a marine-derived fungus Penicillium citrinum SpI080624G1f01. J. Antibiot. 2010, 63, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, L.; Kaufmann, K.; Garcia, R.; Schwär, G.; Huch, V.; Müller, R. Bendigoles D–F, bioactive sterols from the marine sponge-derived Actinomadura sp. SBMs009. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6570–6575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
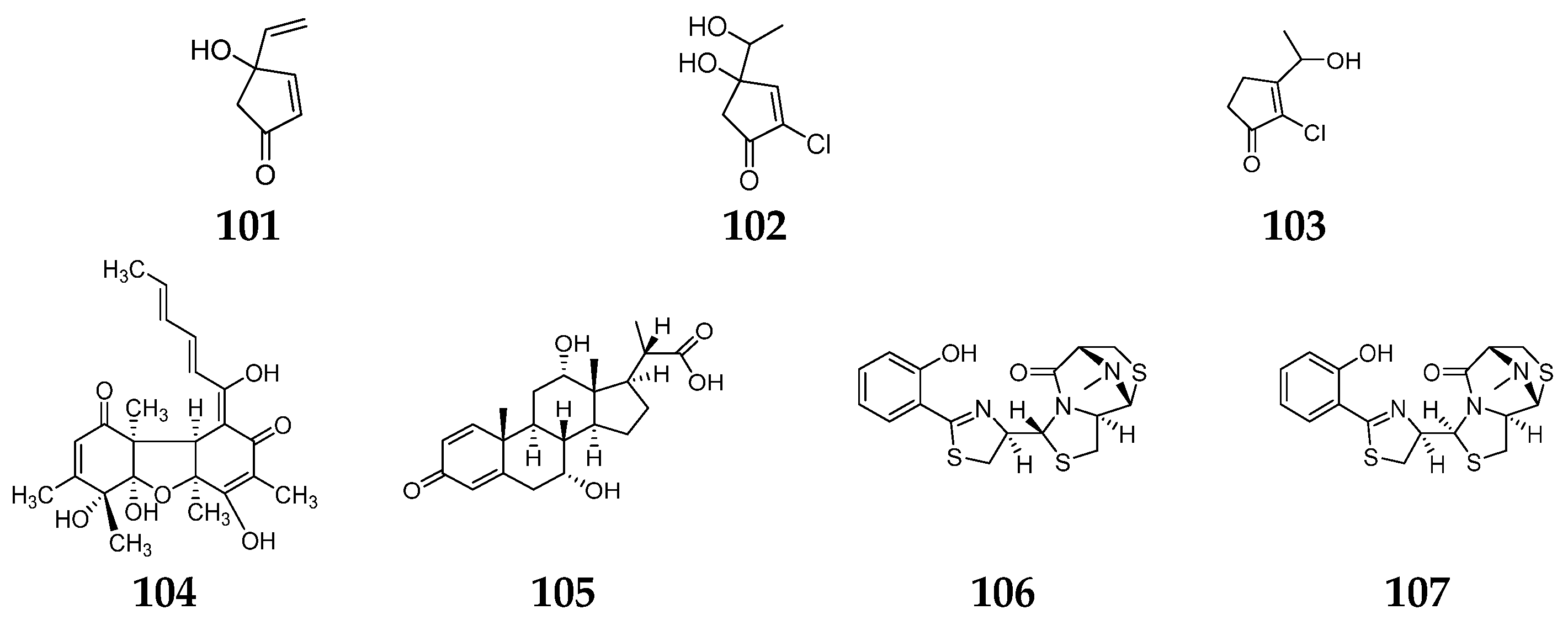
- Igarashi, Y.; Asano, D.; Sawamura, M.; In, Y.; Ishida, T.; Imoto, M. Ulbactins F and G, polycyclic thiazoline derivatives with tumor cell migration inhibitory activity from Brevibacillus sp. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 1658–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 629–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H. Cytotoxic Natural Products from Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030068
Zhang H, Zhao Z, Wang H. Cytotoxic Natural Products from Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(3):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030068
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Huawei, Ziping Zhao, and Hong Wang. 2017. "Cytotoxic Natural Products from Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms" Marine Drugs 15, no. 3: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030068
APA StyleZhang, H., Zhao, Z., & Wang, H. (2017). Cytotoxic Natural Products from Marine Sponge-Derived Microorganisms. Marine Drugs, 15(3), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030068






