The Influence of Spirulina platensis Filtrates on Caco-2 Proliferative Activity and Expression of Apoptosis-Related microRNAs and mRNA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line
2.2. Preparation of Spirulina platensis Filtrate (SPF)
2.3. The Experiment
2.4. Analysis of Caco-2 Proliferation in Cultures with SPF
2.4.1. Metabolic Assay (Alamar Blue)
2.4.2. Analysis of DNA Synthesis (BrdU Incorporation Assay)
2.4.3. Determination of Colony Forming Efficiency (CFE)
2.5. Oxidative Stress Factors in Caco-2 Cultures with SPF
2.6. Morphology of Caco-2 in Cultures with SPF
2.6.1. Inverted and Epifluoresence Microscope
2.6.2. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
2.7. Wound Healing Assay
2.8. Visualization of Mitochondria
2.9. Live/Dead Staining
2.10. Analysis of Cell Cycle
2.11. Analysis of Wnt-10b Concentration in Supernatants after Caco-2 Culture with SPF
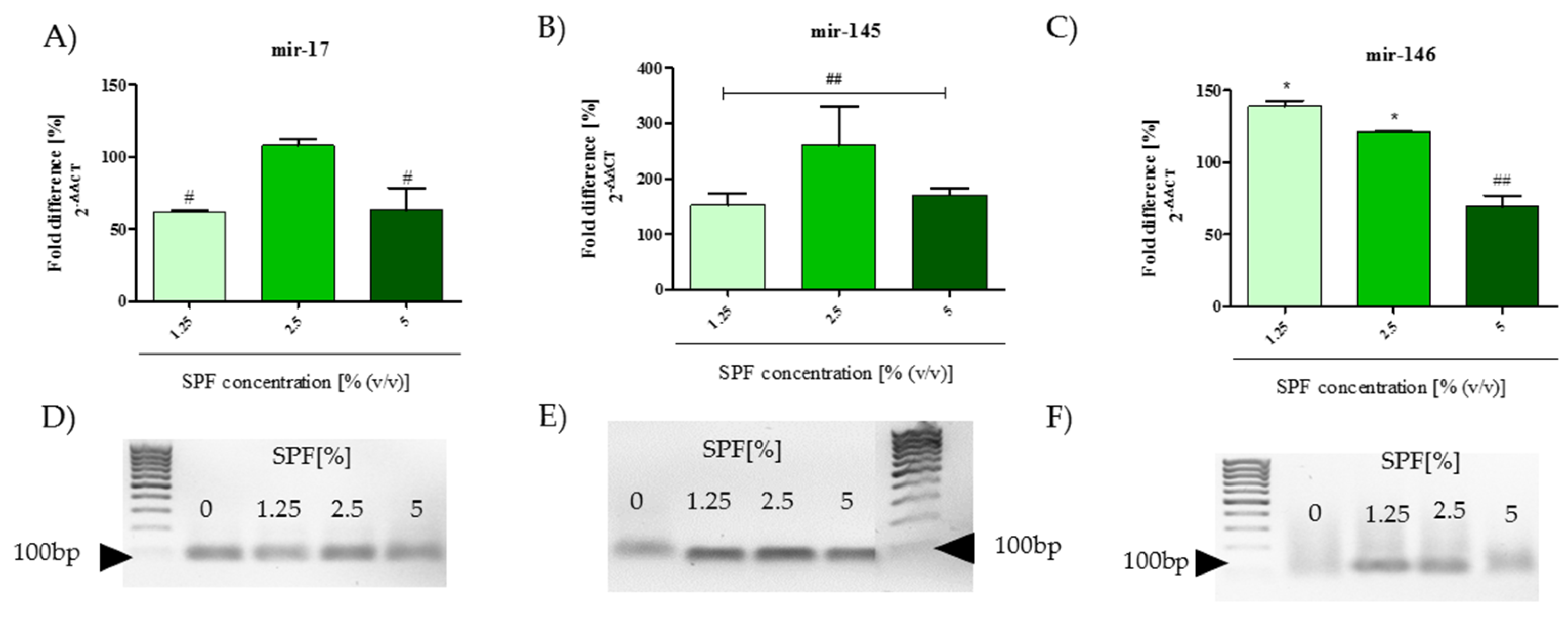
2.12. Analysis of mRNA and miRNA Expression
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
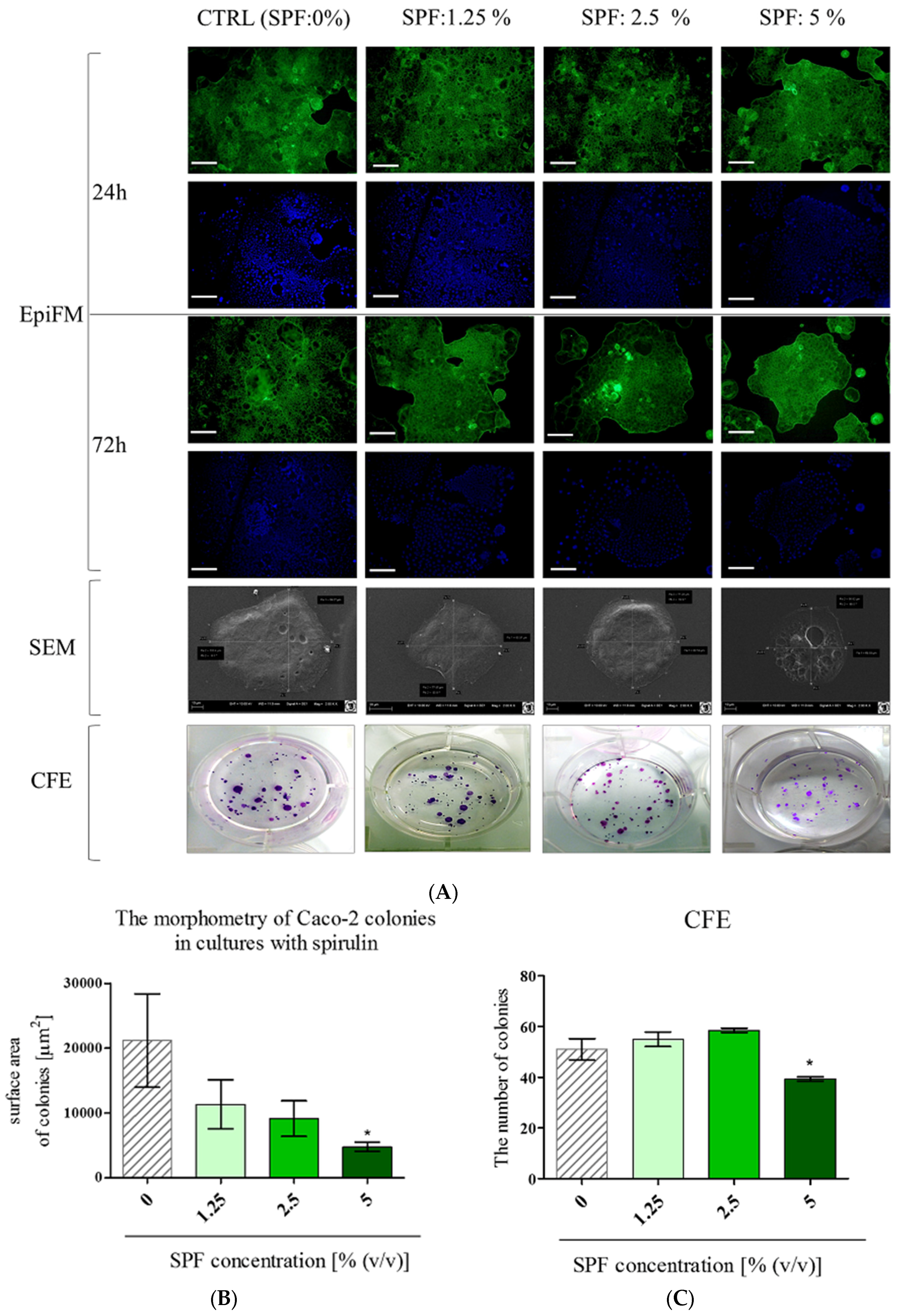
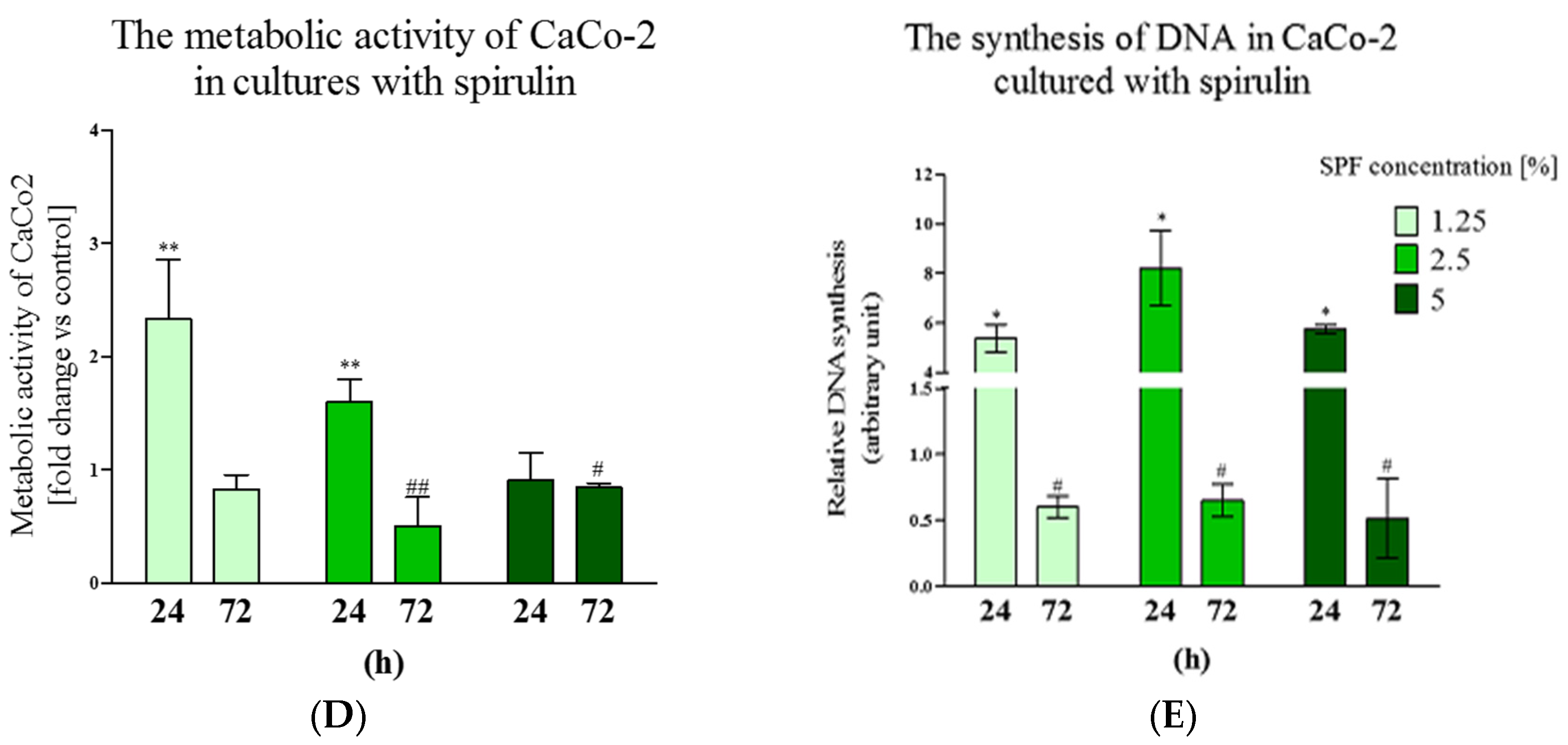
3.1. Spirulina Reduces the Size of Caco-2 Colonies and May Alter Proliferation Activity of Caco-2
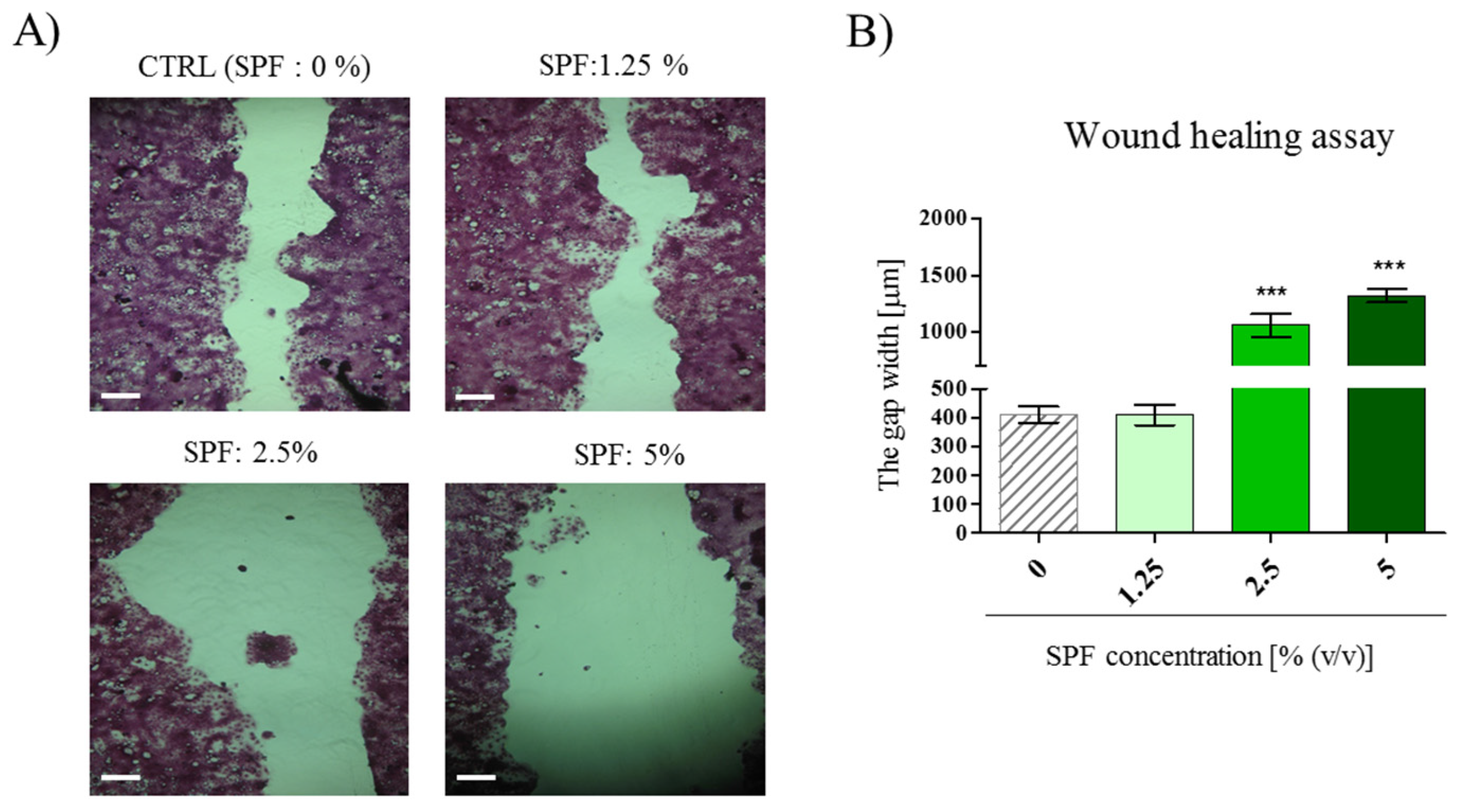
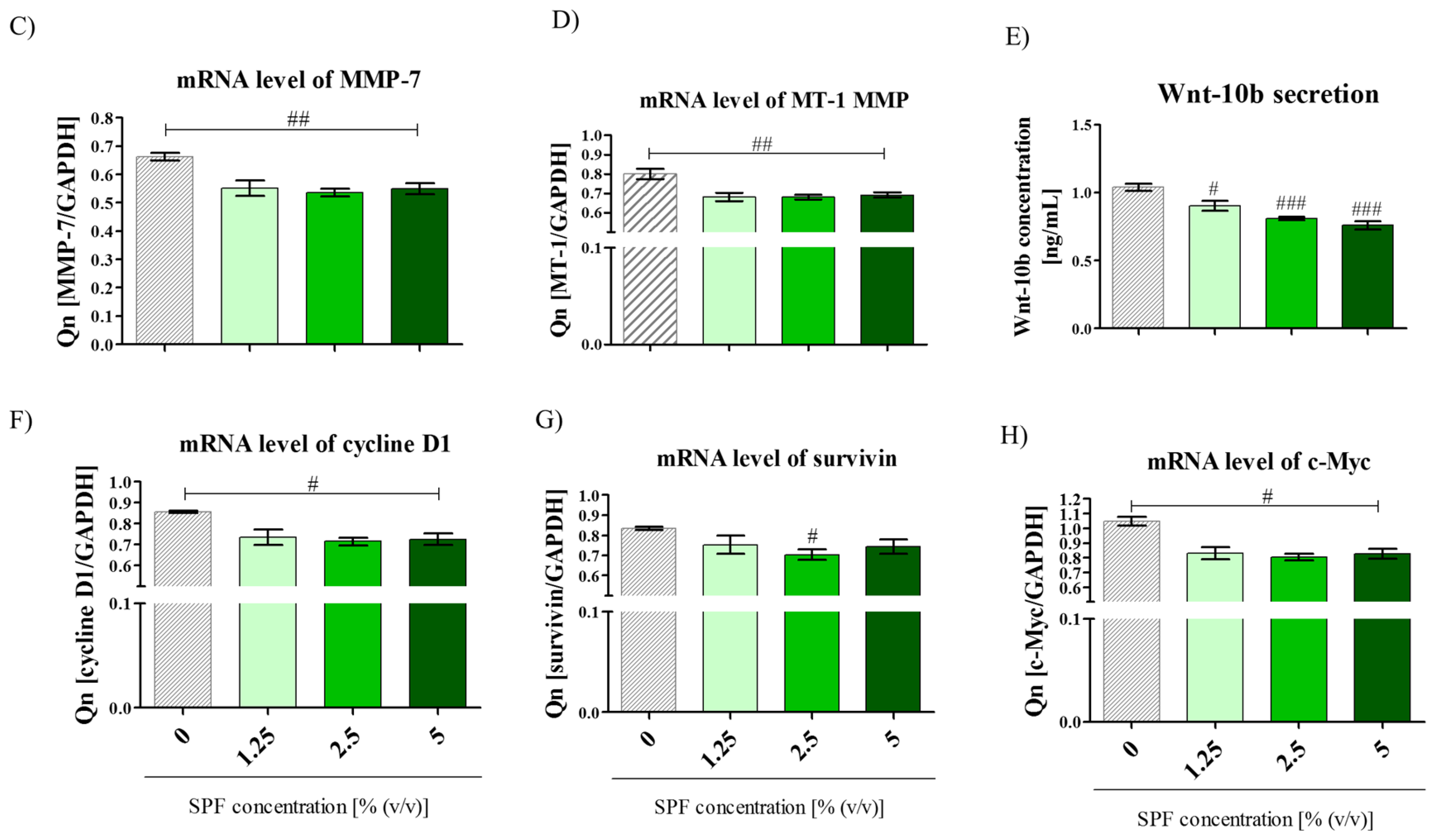
3.2. High Concentration of Spirulina May Inhibit Caco-2 Migration
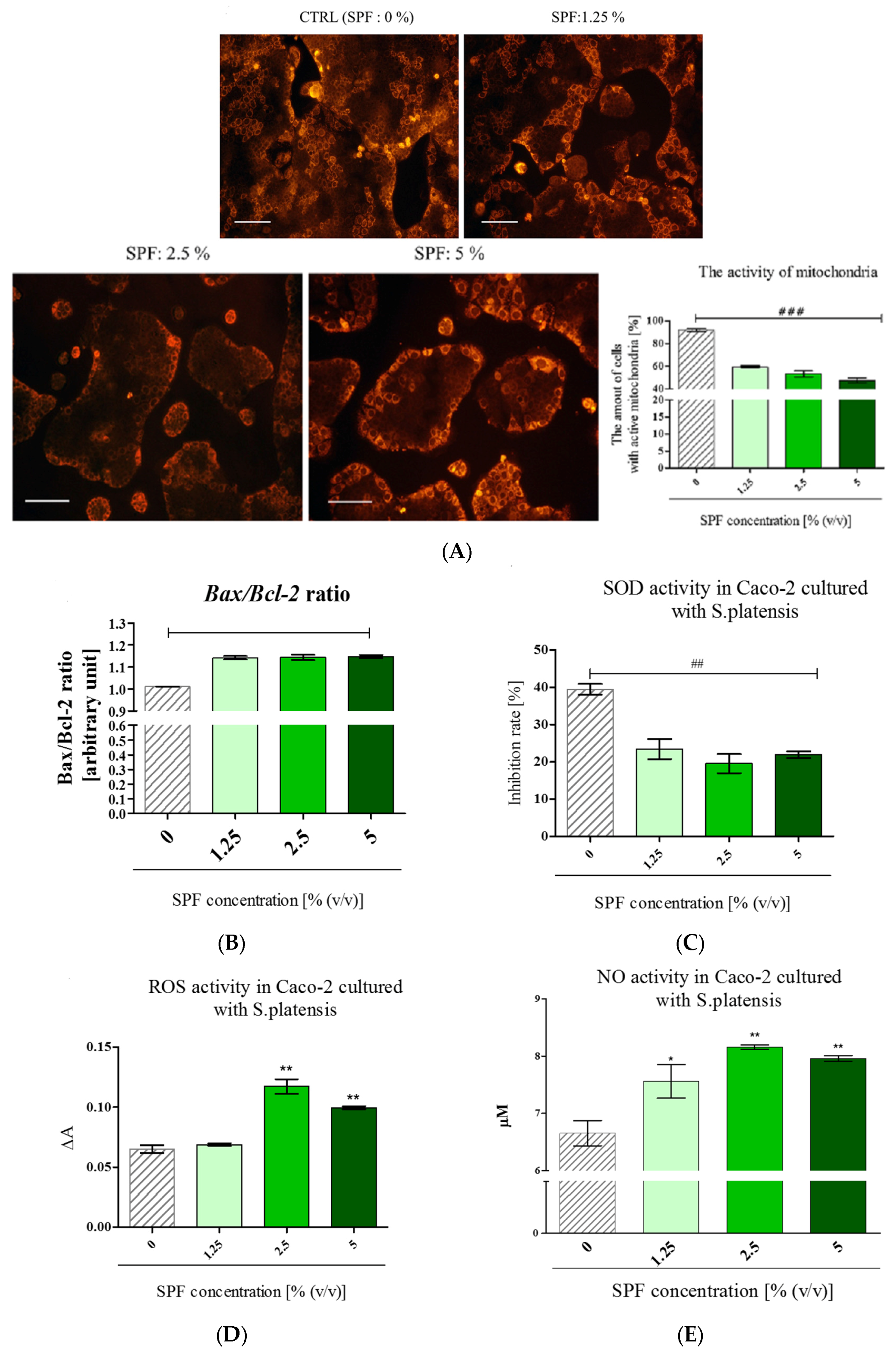
3.3. Spirulina Disturbs on Mitochondrial Activity in Caco-2 and Increases Bax/Bcl-2 Ratio
3.4. The Percentage of PI Stained Cells Increased in Caco-2 Cultures with S. platenis in a Dose-Dependent Manner
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.-K.; Thomas, N.V.; Li, X. Anticancer compounds from marine macroalgae and their application as medicinal foods. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2011, 64, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, E.A. Algae as promising organisms for environment and health. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 1338–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, P.; Fujii, I.; Zhao, J.; Shinohara, M.; Matsukura, M. A novel polysaccharide derived from algae extract induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human gastric carcinoma MKN45 cells via ROS/JNK signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1561–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Pinteus, S.; Horta, A.; Pedrosa, R. High cytotoxicity and anti-proliferative activity of algae extracts on an in vitro model of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Springerplus 2016, 5, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Li, X.-F.; Kang, K.-H.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Stigmasterol isolated from marine microalgae Navicula incerta induces apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erfani, N.; Nazemosadat, Z.; Moein, M. Cytotoxic activity of ten algae from the Persian Gulf and Oman Sea on human breast cancer cell lines; MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, and T-47D. Pharmacogn. Res. 2015, 7, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, S.S. Effects of seaweed supplementation on blood glucose concentration, lipid profile, and antioxidant enzyme activities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2008, 2, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anitha, L.; Chandralekha, K. Effect of Supplementation of Spirulina on Blood Glucose, Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Lipid Profile of Male Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetics. Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 36–46. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadi, A.; Zorofchian Moghadamtousi, S.; Abubakar, S.; Zandi, K. Antiviral Potential of Algae Polysaccharides Isolated from Marine Sources: A Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 825203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpore, J.; Zongo, F.; Kabore, F.; Dansou, D.; Bere, A.; Nikiema, J.-B.; Pignatelli, S.; Biondi, D.M.; Ruberto, G.; Musumeci, S. Nutrition rehabilitation of HIV-infected and HIV-negative undernourished children utilizing spirulina. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2005, 49, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, M.; Hossain, M.F.; Tanu, A.R.; Shekhar, H.U. Effect of Spirulina Intervention on Oxidative Stress, Antioxidant Status, and Lipid Profile in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 486120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashandy, S.A.E.; El Awdan, S.A.; Ebaid, H.; Alhazza, I.M. Antioxidant Potential of Spirulina platensis Mitigates Oxidative Stress and Reprotoxicity Induced by Sodium Arsenite in Male Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 7174351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Miron, A.; Klímová, B.; Wan, D.; Kuča, K. The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activities of Spirulina: An overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1817–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jibri, S.M.; Jakada, B.H.; Umar, H.Y.; Ahmad, T.A. Importance of Some Algal Species as a Source of Food and Supplement. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Bhadouria, P.; Bisen, P.S. Nutritional and therapeutic potential of Spirulina. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2005, 6, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Assis, L.M.; Machado, A.R.; Motta, A.S.; Costa, J.A.V.; de Souza-Soares, L.A. Development and Characterization of Nanovesicles Containing Phenolic Compounds of Microalgae Spirulina Strain LEB-18 and Chlorella pyrenoidosa. Adv. Mater. Phys. Chem. 2014, 4, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koníčková, R.; Vaňková, K.; Vaníková, J.; Váňová, K.; Muchová, L.; Subhanová, I.; Zadinová, M.; Zelenka, J.; Dvořák, A.; Kolář, M.; et al. Anti-Cancer effects of blue-green alga Spirulina platensis, a natural source of bilirubin-like tetrapyrrolic compounds. Ann. Hepatol. 2014, 13, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ou, C.; Deng, Z.; Chen, M.; Huang, W.; Li, L. MicroRNA-145 inhibits tumour growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting fascin-1. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2300–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dews, M.; Homayouni, A.; Yu, D.; Murphy, D.; Sevignani, C.; Wentzel, E.; Furth, E.E.; Lee, W.M.; Enders, G.H.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrane, I.; Kourda, N.; Stambouli, N.; Privat, M.; Medimegh, I.; Arfaoui, A.; Uhrhammer, N.; Bougatef, K.; Baroudi, O.; Bouzaienne, H.; et al. MicroRNAs 146a and 147b Biomarkers for Colorectal Tumor’s Localization. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, e584852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, Q. Inhibitive effects of spirulina on aberrant crypts in colon induced by dimethylhydrazine. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi 1995, 29, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-González, I.; Islas-Islas, V.; Chamorro-Cevallos, G.; Barrios, J.P.; Paniagua, N.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Villa-Treviño, S.; Madrigal-Santillán, O.; Morales-González, J.A.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E. Inhibitory Effect of Spirulina maxima on the Azoxymethane-induced Aberrant Colon Crypts and Oxidative Damage in Mice. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, S619–S624. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smieszek, A.; Donesz-Sikorska, A.; Grzesiak, J.; Krzak, J.; Marycz, K. Biological effects of sol-gel derived ZrO2 and SiO2/ZrO2 coatings on stainless steel surface—In vitro model using mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 29, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornicka, K.; Marycz, K.; Tomaszewski, K.A.; Marędziak, M.; Śmieszek, A. The Effect of Age on Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation Potential of Human Adipose Derived Stromal Stem Cells (hASCs) and the Impact of Stress Factors in the Course of the Differentiation Process. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, e309169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Śmieszek, A.; Czyrek, A.; Basinska, K.; Trynda, J.; Skaradzińska, A.; Siudzińska, A.; Marędziak, M.; Marycz, K. Effect of Metformin on Viability, Morphology, and Ultrastructure of Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Balb/3T3 Embryonic Fibroblast Cell Line. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, e769402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-Step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, B.-J.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Zhu, D.-J.; Ju, Y.-L.; Wu, J.-H.; Ouyang, M.-Z.; Chen, X.-W.; Zhou, S.-F. Alisertib Induces Cell Cycle Arrest, Apoptosis, Autophagy and Suppresses EMT in HT29 and Caco-2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussavou, G.; Kwak, D.H.; Obiang-Obonou, B.W.; Ogandaga Maranguy, C.A.; Dinzouna-Boutamba, S.-D.; Lee, D.H.; Manvoudou Pissibanganga, O.G.; Ko, K.; Seo, J.I.; Choo, Y.K. Anticancer Effects of Different Seaweeds on Human Colon and Breast Cancers. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, A.M.; Burrington, C.M.; Gillaspie, E.A.; Lynch, D.T.; Horsman, M.J.; Greene, M.W. High-Fat Western diet-induced obesity contributes to increased tumor growth in mouse models of human colon cancer. Nutr. Res. 2016, 36, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Huang, H.-W.; Chang, F.-R.; Yeh, C.-C.; Tang, J.-Y.; Chang, H.-W. Marine algal natural products with anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Béliveau, R.; Gingras, D. Role of nutrition in preventing cancer. Can. Fam. Phys. 2007, 53, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Subhashini, J.; Mahipal, S.V.K.; Reddy, M.C.; Mallikarjuna Reddy, M.; Rachamallu, A.; Reddanna, P. Molecular mechanisms in C-Phycocyanin induced apoptosis in human chronic myeloid leukemia cell line-K562. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 68, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouhtit, A.; Gaur, R.L.; Abdraboh, M.; Ireland, S.K.; Rao, P.N.; Raj, S.G.; Al-Riyami, H.; Shanmuganathan, S.; Gupta, I.; Murthy, S.N.; et al. Simultaneous Inhibition of Cell-Cycle, Proliferation, Survival, Metastatic Pathways and Induction of Apoptosis in Breast Cancer Cells by a Phytochemical Super-Cocktail: Genes That Underpin Its Mode of Action. J. Cancer 2013, 4, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambato, G.; Baroni, É.G.; Garcia, C.S.C.; Frassini, R.; Frozza, C.O.S.; Moura, S.; Pereira, C.M.P.; Fujii, M.T.; Colepicolo, P.; Lambert, A.P.F.; et al. Brown Algae Himantothallus grandifolius (Desmarestiales, Phaeophyceae) Suppresses Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis-Mediated Cell Death in Tumor Cells. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2014, 4, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Woo, H.C.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, G.-D. The Extracts of Sargassum fulvellum Induce Pro-Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest on MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2010, 15, 52–59. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Fucoidan inhibits the migration and proliferation of HT-29 human colon cancer cells via the phosphoinositide-3 kinase/Akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 3446–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.-W.; Choi, H.-J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Jeong, H.-S.; Kim, C.-H.; Joo, M.; Choi, J.-Y.; Han, C.-W.; Kim, S.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; et al. Marine algal fucoxanthin inhibits the metastatic potential of cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 439, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagoutte, E.; Villeneuve, C.; Lafanechère, L.; Wells, C.M.; Jones, G.E.; Chavrier, P.; Rossé, C. LIMK Regulates Tumor-Cell Invasion and Matrix Degradation through Tyrosine Phosphorylation of MT1-MMP. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.H.; Raufman, J.-P.; Xie, G. The Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2014, 6, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, M.T.; Tsao, P.N.; Lin, H.L.; Tung, C.C.; Change, M.C.; Chang, Y.T.; Wong, J.M.; Wei, S.C. Hes1 Increases the Invasion Ability of Colorectal Cancer Cells via the STAT3-MMP14 Pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholer-Dahirel, A.; Schlabach, M.R.; Loo, A.; Bagdasarian, L.; Meyer, R.; Guo, R.; Woolfenden, S.; Yu, K.K.; Markovits, J.; Killary, K.; et al. Maintenance of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC)-mutant colorectal cancer is dependent on Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17135–17140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloshanenko, O.; Erdmann, G.; Dubash, T.D.; Augustin, I.; Metzig, M.; Moffa, G.; Hundsrucker, C.; Kerr, G.; Sandmann, T.; Anchang, B.; et al. Wnt secretion is required to maintain high levels of Wnt activity in colon cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-Q.; Lu, Z.-H.; Fang, Y.-J.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Pan, Z.-Z.; Wan, D.-S. Expression and clinical significance of survivin and matrix metalloproteinase-7 in colon cancer. Ai Zheng 2009, 28, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xia, J.-F.; Lin, J.-J.; Li, R.-Z.; Yang, D.-Q.; Xu, M.-Y.; Li, X.-Y. Ellagic acid regulates Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and CDK8 in HCT 116 and HT 29 colon cancer cells. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, B.-E.; Wang, M.-X.; Li, R. Quercetin inhibit human SW480 colon cancer growth in association with inhibition of cyclin D1 and survivin expression through Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Investig. 2009, 27, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, J.H.Y. Fucoidan present in brown algae induces apoptosis of human colon cancer cells. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, M.J.; Kim, A.D.; Kang, K.A.; Chung, H.S.; Kim, H.S.; Suh, I.S.; Chang, W.Y.; Hyun, J.W. The green algae Ulva fasciata Delile extract induces apoptotic cell death in human colon cancer cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2013, 49, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, Q. Anticancer properties and mechanisms of fucoidan on mouse breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, W.-L.; Lim, Y.-W.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Lim, P.-E. Protective effect of aqueous extract from Spirulina platensis against cell death induced by free radicals. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2010, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karawita, R.; Senevirathne, M.; Athukorala, Y.; Affan, A.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, J.-B.; Jeon, Y.-J. Protective effect of enzymatic extracts from microalgae against DNA damage induced by H2O2. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-L.; Wu, S.-L.; Liao, H.-F.; Jiang, C.-M.; Huang, R.-L.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-J. Induction of apoptosis by three marine algae through generation of reactive oxygen species in human leukemic cell lines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1776–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardhasaradhi, B.V.V.; Ali, A.M.; Kumari, A.L.; Reddanna, P.; Khar, A. Phycocyanin-Mediated apoptosis in AK-5 tumor cells involves down-regulation of Bcl-2 and generation of ROS. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2003, 2, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z. Increased Oxidative Stress as a Selective Anticancer Therapy. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2015, 2015, 294303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, R.; Niu, J.; Cui, D.; Xie, B.; Zhang, B.; Lu, K.; Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Oxidative Stress Mediated-Alterations of the MicroRNA Expression Profile in Mouse Hippocampal Neurons. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 16945–16960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Zhou, D. MicroRNAs in colorectal carcinoma—from pathogenesis to therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schee, K.; Boye, K.; Abrahamsen, T.W.; Fodstad, Ø.; Flatmark, K. Clinical relevance of microRNA miR-21, miR-31, miR-92a, miR-101, miR-106a and miR-145 in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.; Dong, Y.; Tsoi, H.; Yu, J. Detection of miRNA as non-invasive biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 2810–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knudsen, K.N.; Nielsen, B.S.; Lindebjerg, J.; Hansen, T.F.; Holst, R.; Sørensen, F.B. microRNA-17 Is the Most Up-Regulated Member of the miR-17-92 Cluster during Early Colon Cancer Evolution. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, S.E.; Simões, A.E.S.; Pereira, D.M.; Castro, R.E.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Borralho, P.M. miR-143 or miR-145 overexpression increases cetuximab-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human colon cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9368–9387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]

| Gene | Primer | Sequence 5′-3′ | Loci | Ta [°C] | Amplicon Length [bp] | Accesion No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bax | F: | ACCAAGAAGCTGAGCGAGTGTC | 235–256 | 59.6 | 365 | NM_001291428.1 |
| R: | ACAAAGATGGTCACGGTCTGCC | 627–648 | ||||
| Bcl-2 | F: | ATCGCCCTGTGGATGACTGAG | 1010–1030 | 58.6 | 129 | NM_000633.2 |
| R: | CAGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACAGAGG | 1115–1138 | ||||
| p21 | F: | AGAAGAGGCTGGTGGCTATTT | 21–41 | 57.9 | 169 | NM_001220777.1 |
| R: | CCCGCCATTAGCGCATCAC | 171–189 | ||||
| p53 | F: | AGATAGCGATGGTCTGGC | 868–885 | 57.8 | 381 | NM_001126118.1 |
| R: | TTGGGCAGTGCTCGCTTAGT | 1229–1248 | ||||
| c-Myc | F: | CTTCTCTCCGTCCTCGGATTCT | 1215–1236 | 58.2 | 204 | NM_002467.4 |
| R: | GAAGGTGATCCAGACTCTGACCTT | 1395–1418 | ||||
| cyclinD1 | F: | GATGCCAACCTCCTCAACGA | 264–283 | 58.2 | 211 | NM_053056.2 |
| R: | GGAAGCGGTCCAGGTAGTTC | 455–474 | ||||
| survivin | F: | ACCGCATCTCTACATTCAAG | 171–190 | 58.2 | 113 | NM_001012271.1 |
| R: | CAAGTCTGGCTCGTTCTC | 266–283 | ||||
| MMP7 | F: | TGTATGGGGAACTGCTGACA | 494–513 | 58.2 | 151 | NM_002423.4 |
| R: | GCGTTCATCCTCATCGAAGT | 625–644 | ||||
| MT1-MMP | F: | TCGGCCCAAAGCAGCAGCTTC | 364–384 | 58.2 | 180 | NM_004995.3 |
| R: | CTTCATGGTGTCTGCATCAGC | 523–543 | ||||
| GAPDH | F: | GTCAGTGGTGGACCTGACCT | 894–913 | 59.1 | 256 | NM_001289746.1 |
| R: | CACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGC | 1130–1149 |
| Gene | Primer | Sequence 5′-3′ | Location | Ta [°C] | Amplicon Length [bp] | Accesion No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hsa-miR-17-5p | F: | CAAAGTGCTTACAGTGCAGGTAG | 13q31.3 | 57.4 | * | MIMAT0000070 |
| Hsa-miR-145-5p | F: | GTCCAGTTTTCCCAGGAATCCCT | 5q32 | 58.8 | * | MIMAT0000437 |
| Hsa-miR-146a-5p | F: | TGAGAACTGAATTCCATGGGTT | 5q33.3 | 61 | * | MIMAT0000449 |
| U6 | F: | GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT | 16q21 | 60 | * | NR_125730.1 |
| R: | CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Śmieszek, A.; Giezek, E.; Chrapiec, M.; Murat, M.; Mucha, A.; Michalak, I.; Marycz, K. The Influence of Spirulina platensis Filtrates on Caco-2 Proliferative Activity and Expression of Apoptosis-Related microRNAs and mRNA. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030065
Śmieszek A, Giezek E, Chrapiec M, Murat M, Mucha A, Michalak I, Marycz K. The Influence of Spirulina platensis Filtrates on Caco-2 Proliferative Activity and Expression of Apoptosis-Related microRNAs and mRNA. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(3):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030065
Chicago/Turabian StyleŚmieszek, Agnieszka, Ewa Giezek, Martyna Chrapiec, Martyna Murat, Aleksandra Mucha, Izabela Michalak, and Krzysztof Marycz. 2017. "The Influence of Spirulina platensis Filtrates on Caco-2 Proliferative Activity and Expression of Apoptosis-Related microRNAs and mRNA" Marine Drugs 15, no. 3: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030065
APA StyleŚmieszek, A., Giezek, E., Chrapiec, M., Murat, M., Mucha, A., Michalak, I., & Marycz, K. (2017). The Influence of Spirulina platensis Filtrates on Caco-2 Proliferative Activity and Expression of Apoptosis-Related microRNAs and mRNA. Marine Drugs, 15(3), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15030065







