Abstract
The sea cucumber (phylum Echinodermata) body wall is the first line of defense and is well known for its production of secondary metabolites; including vitamins and triterpenoid glycoside saponins that have important ecological functions and potential benefits to human health. The genes involved in the various biosynthetic pathways are unknown. To gain insight into these pathways in an echinoderm, we performed a comparative transcriptome analysis and functional annotation of the body wall and the radial nerve of the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra; to define genes associated with body wall metabolic functioning and secondary metabolite biosynthesis. We show that genes related to signal transduction mechanisms were more highly represented in the H. scabra body wall, including genes encoding enzymes involved in energy production. Eight of the core triterpenoid biosynthesis enzymes were found, however, the identity of the saponin specific biosynthetic pathway enzymes remains unknown. We confirm the body wall release of at least three different triterpenoid saponins using solid phase extraction followed by ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography-quadrupole time of flight-mass spectrometry. The resource we have established will help to guide future research to explore secondary metabolite biosynthesis in the sea cucumber.
1. Introduction
Sea cucumbers belong to the phylum Echinodermata, class Holothuroidea, [1], which are found in benthic areas of marine environments [2]. Currently, commercial fisheries for sea cucumbers are found in the Americas, Europe, Asia, Africa and Australia, but with the highest levels of production in China, Indonesia, Canada and Japan (FAO, 2017 Global Production Statistics 1950–2015, www.FAO.org). In Eastern Asia, their body wall is highly valued as a food source (called trepang) and for its associated pharmacological and nutritional value [3]. Biomolecules, including saponins, produced in the body wall (consisting of a thin cuticle over an epidermis and a thick dermis underneath, composed mostly of collagen [4]) of sea cucumbers are thought to have several beneficial health-related benefits, including cancer prevention, anticoagulant activity, anti-inflammatory activity and wound healing activity [5,6,7].
Saponins are secondary metabolites that are only produced by plants, echinoderms (e.g., starfish, sea cucumbers), marine sponges and octocorals [8,9,10,11]. In plants, triterpenoid and steroid saponins are widely distributed [12] and reported to be present in at least 500 plant species [13]. Many plants produce saponins during normal growth and development. The distribution of saponin differ according to plant species, tissues, organs and seasonal fluctuation [14]. Plant saponins, and their biosynthetic intermediates have been widely studied for their beneficial biological activities within the pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries (28,157 research papers, 8125 patents; SciFinder). Accumulated evidence suggests that saponins have significant neuroprotective effects on attenuation of central nervous system disorders, such as stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease [15,16,17]. Echinoderms secrete a unique set of water-soluble steroidal (found in starfish) and triterpenoid (found in sea cucumbers) saponins that have self-benefit in predator defense, limb regeneration and tissue repair [18]. To date, approximately 59 triterpenoid glycoside saponins have been identified within various sea cucumbers, where different species possess a specific congener mixture [19]. Saponin content also varies depending on the sea cucumber body compartment or tissue, with the highest concentrations found in the Cuvierian tubules (organs that can be ejected for defense) and body wall.
Next-generation transcriptome analysis has proven to be a powerful approach towards the identification of metabolite biosynthetic pathways [20,21]. However, the analysis of RNA expression levels does not necessarily provide an accurate assessment of the amount of the metabolome. Thus, integrating transcriptomics with small molecule analysis (i.e., metabolomics) provides more meaningful insights about the diversity of compounds that can eventually allow deciphering of complex biological systems that define animal phenotypes. To date, there has been little information available regarding the transcriptome or diverse small molecule production in echinoderm species [22,23].
In this study, we have used one of the most economically valuable sea cucumber species, the Holothuria scabra, to help fill the gap in our understanding of secondary metabolite biosynthesis in echinoderms. Our integration of comparative transcriptome data (body wall versus radial nerve tissue) with metabolome data has helped to elucidate the presence of genes involved in secondary metabolite biosynthesis pathways, including core saponin biosynthesis enzymes involved in the production of upstream saponin precursors in the body wall.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Body Wall and Radial Nerve Transcriptome Analysis
The sea cucumber nervous system consists of an anterior circumoral nerve ring with five connecting radial nerves extending posteriorly along the ambulacra [19] (Figure 1A). The system is comprised of several types of nerve and supporting cells that help to coordinate sensory input and control muscles and glands; it is not known to play any direct role in the production of secondary metabolites and no enzymes have been previously discovered that serve a role in their biosynthesis. In contrast, the body wall (also ecotodermic) is a significant contributor to secondary metabolite synthesis [24]. Thus, for this study, the body wall transcriptome was compared to the radial nerve transcriptome, to delineate biosynthesis pathways for secondary metabolites. Illumina platform sequencing yielded a total of 4.6 Gb clean nucleotides from the body wall RNA. Raw reads were assembled into a transcript library containing 107,217 unigenes with a mean length of 901 nucleotides, of which 105,838 encode for open reading frames (>10 amino acids in length) (File S1). Illumina platform sequencing yielded a total of 4.9 Gb clean nucleotides from the radial nerve RNA. Likewise, radial nerve raw reads were assembled into a transcript library, providing a total of 51,874 unigenes with a mean length of 528 nucleotides. Raw sequence reads for both the body wall and radial nerve have been deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (https://submit.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/subs/sra/) under the accession number SRR5713070. These transcriptomes contribute to the increasing number of holothurian transcriptomes available, including those of Apostichopus japonicus combined body wall and intestine [25], hemocytes [26], and developmental stages [27]. In addition, it extends on transcript information obtained from Holothuria glaberrima radial nerve cords, at both regenerative and non-regenerative stages [28].
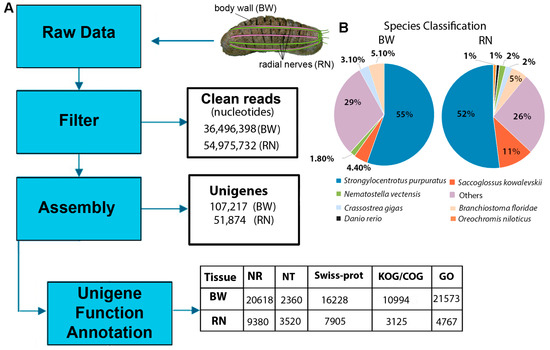
Figure 1.
Overall strategy and outcome of transcriptome sequencing, data analysis and annotation of Holothuria scabra body wall (BW) and radial nerve (RN). (A) Workflow for analysis, including unigene and annotation outcome. NR, protein database; NT, nucleotide database; Swiss-Prot, curated protein sequence database; GO, gene ontology; KOG, Eukaryotic Orthologous Groups ontology. (B) Pie charts showing NR protein database matches.
The H. scabra body wall and radial nerve transcripts were annotated against available databases (NR, NT, Swiss-Prot, KEGG, PFAM, GO and KOG; E-value < 0.00001) where, for example, of the 107,217 consensus body wall unigenes, 20,618 matched with genes within the NR database (Figure 1A). All transcript identification numbers (IDs) and annotation information are provided in File S1. The highest number of matches within the NR protein database were to the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus (55.9%) and the lancelet Branchiostoma floridae (5.0%) (Figure 1B). These annotation results are comparable to those that have been reported in previous de novo transcriptome sequencing studies for echinoderms [26,27]. The reason for the low number of matched genes is likely because transcripts for echinoderms are relatively poorly represented in these databases. Secondly, de novo assembly can sometimes produce artifact sequences that ultimately influence downstream analyses, for instance, reads mapping, sequence clustering, base call error, and number of BLAST hits [29]. Many of the H. scabra genes identified appear to be novel or represent genes containing non-conserved domains, which therefore could not be classified into known protein families.
2.2. Functional Annotation of H. scabra Body Wall and Radial Nerve Transcripts
To help elucidate secondary metabolite biosynthesis genes, we performed a comparison of functional annotation groups between two tissues with distinctly different metabolic functions, the body wall and radial nerve. Functional annotation of body wall transcripts against the KOG database classified 10,994 (10.25%) transcripts into 24 categories as shown in Figure 2A (for details of total number of genes in each category, see File S2a). The largest number of transcripts are represented within the general function prediction category (2365 transcripts; 22%), followed by signal transduction mechanism (2254; 21%), and post-translational modification, protein turnover, chaperones (1060; 10%). Signal transduction mechanisms are processes by which chemical or physical signals are transferred to a series of molecular events, including protein phosphorylation; a regulatory mechanism that controls almost all cellular processes. When compared to the H. scabra radial nerve, 3125 transcripts were annotated into 24 categories (File S2a). Similarly, a large number of transcripts are represented within the general function prediction (1485; 47.52%); however, relatively few annotate within the signal transduction mechanisms (253; 8.09%). Further comparison with another sea cucumber species, Apostichopus japonicus, has noted significant up-regulation of body wall genes involved in signal transduction between animals with healthy skin and ulceration syndrome affected skin [26]. To date, no other sea cucumber species radial nerve has been individually analysed by gene annotation.
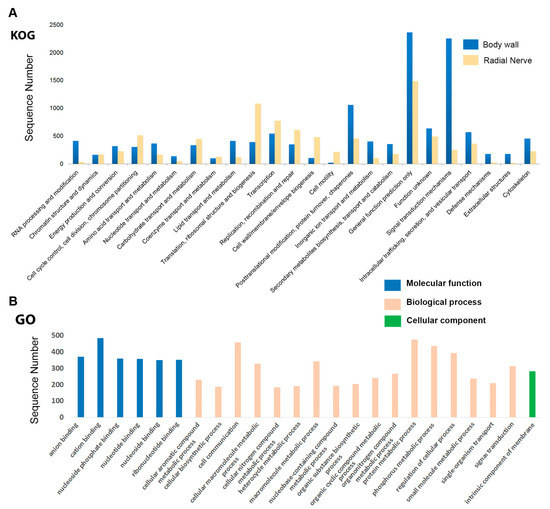
Figure 2.
Histograms for KOG and GO functional annotation of Holothuria scabra. (A) Histogram showing KOG functional annotation of H. scabra body wall and radial nerve genes; (B) GO term classifications for those genes represented in the KOG ‘signal transduction mechanisms’ of H. scabra body wall. Division of Molecular, Biological and Cellular categories are shown in GO.
A total of 21,573 (20.12%) body wall transcripts were assigned into GO terms based on BLAST matches with sequences of encoding proteins with known functions that can be categorised into either biological process, molecular function, or cellular component (for details of total number of genes in each category, see File S2b). We were most interested in the GO term classifications for those genes represented in the KOG signal transduction mechanisms (Figure 2B). ‘Binding’ was highly represented, including those terms specific for anion, cation, and nucleotide binding. This is similar to that found in the combined body wall and intestine GO analysis of A. japonicus, particularly during regeneration [25]. Cell communication, as well as metabolic processes associated with protein, macromolecule and small molecule synthesis, were highly represented biological processes. Within the cellular component category, the intrinsic component of the membrane was most highly represented. These include products having some covalently attached portion, for example part of a peptide sequence or some other covalently attached group such as a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein, which spans or is embedded in one or both leaflets of the membrane. These types of processes can be linked with the role of the sea cucumber body wall in the biosynthesis of numerous proteins and secondary metabolites.
2.3. Secondary Metabolite Biosynthesis Pathways in the Body Wall
Here, we integrated the transcriptomic data to better understand the metabolites produced in the sea cucumber body wall. There are about 20 sea cucumber species cultured, particularly in Asian countries [30], primarily due to the nutritional benefits of consuming the body wall. The body wall is rich in high-value nutrients such as vitamin A, vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin), and minerals, especially calcium, magnesium, iron and zinc [31,32]. Also, there are numerous other nutritionally beneficial secondary metabolites such as sulfated polysaccharides, 12-methyltetradecanoic acid, triterpene glycoside compounds, glycosaminoglycan and chondroitin sulfates [3]. Oleic and linoelaidic acids have been found to be prominent unsaturated fatty acids in the sea cucumbers Actinopyga mauritiana, H. scabra, Bohadschia marmorata and Holothuria leucospilota [33]. Raw sea cucumbers are also known to contain high amounts of protein, ranging from 43% to 48% [33]. This compares with the relatively low levels found in other aquaculture species including raw tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (23.06%), raw cat fish Clarias gariepinus (20%) and raw salmon Salmo salar (40%). Further supporting sea cucumbers as an excellent nutritional source is their very low lipid content (4.6% to 5.0%) [34]; relative to levels in salmon (10%), tilapia (12.85%), and catfish (13.86%) [35,36,37].
The availability of a sea cucumber body wall transcriptome enables the investigation of enzyme genes associated with biosynthesis of secondary metabolites. For example, glycine is helpful for the generation of muscle tissue and to convert glucose into energy [33]. It is also the most abundant amino acid in most sea cucumbers, where it may exist at concentrations of between 18.4 and 19.2 g/100 g tissue and comprising 37–39% of the total amino acids [33]. We identified all energy producing enzyme genes for the glycolysis cycle within the H. scabra body wall transcriptome (Figure 3; see Figure S1 for gene annotation), whereas in the radial nerve transcriptome, only 50% are present. These results also suggest that the function of the body wall, in addition to protection, acts as an important fuel reservoir for sea cucumbers. Metabolic activity can be extremely varied in different tissues, where muscle tissues are relatively high in metabolic activity compared to neural tissue, although this should be minimized during sea cucumber aestivation; a complex physiological event that leads to hypometabolism [38]. The sea cucumber body wall consists largely of longitudinal and circular muscles, connective tissue and skin [39]. Still, it is known that the levels of regulatory glycolytic enzymes are higher in rat and fish muscle, compared to sea cucumbers longitudinal muscles, yet is significantly higher than the mollusc, Biomphalaria, foot muscle [40].
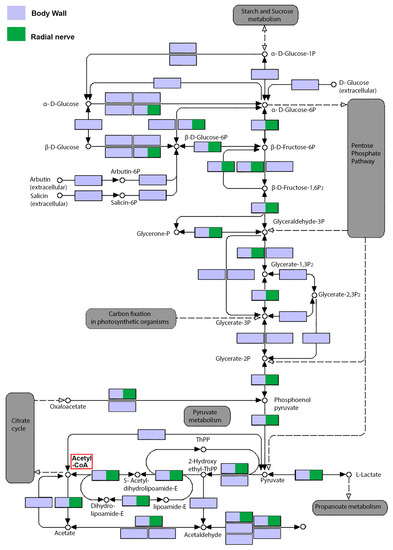
Figure 3.
Biosynthetic routes of glycolysis cycle showing genes annotated from Holothuria scabra body wall and radial nerve transcriptomes. Violet squares represent genes detected in the body wall transcriptome, while green squares represent genes detected in the radial nerve transcriptome. All energy producing cycles, including starch and sucrose metabolism, pyruvate metabolism and propanoate metabolism, pentose phosphate pathway, carbon fixation and citric cycle are marked as grey (modified from KEGG Pathway Database). Location of Acetyl-CoA is highlighted by a red box.
Saponins are retained in cooked sea cucumber body wall and may contribute to its proposed health properties [41]. Besides the body wall, saponins are found in the animal’s digestive organs and gonads (ovary and testis) [42,43], and have also been found in the surrounding seawater to warn off predators, and to facilitate species communication [44]. It is understood that a primary source tissue for these exogenous saponins is the body wall [22]. Saponin types can be shared by many species, such as the holothurins A and B [5], or be very specific, such as the Griseaside A that has so far, only been found in Holothuria grisea [45]. In our study, we had identified the biosynthesis pathway in the production of Acetyl-CoA (see Figure 3), which is a critical metabolite for production of saponins. We further identified by BLASTp the core biosynthetic genes known for saponin biosynthesis within the H. scabra body wall transcriptome open reading frames, including thiolase, hydroxymethylglutaryl (HMG) CoA synthase, HMG CoA reductase, mevalonate kinase, phosphomevalonate kinase, farnesyl pyrophosphate, squalene synthase, and squalene epoxidase enzymes (Figure 4A) (for details of protein sequences, see File S3) [14]. The homology of core saponin biosynthetic enzymes in the sea cucumber, comparable to those of plants (domain conservation and E-value cut-off 10−3), indicates that the plant and echinoderm biosynthetic pathways are highly conserved, despite over 1 billion years since divergence. The ability for triterpene cyclization is critical in the formation of a wide array of different triterpene structures, all derived from the simple and ubiquitous linear isoprenoid substrate 2,3-oxidosqualene. The cyclisation of 2,3-oxidosqualene, which involves two main steps: (i) cyclisation of 2,3-oxidosqualene catalysed by oxidosqualene cyclase; and (ii) oxidative modification at various positions of the skeleton mediated by cytochrome P450s enzymes, represents the start of saponin biosynthesis pathway (Figure 4A). In the radial nerve, only thiolase, HMG CoA reductase and phosphomevalonate kinase were present. One explanation for the presence of only these three enzymes in the radial nerve, may be their role in synthesizing other secondary metabolites.
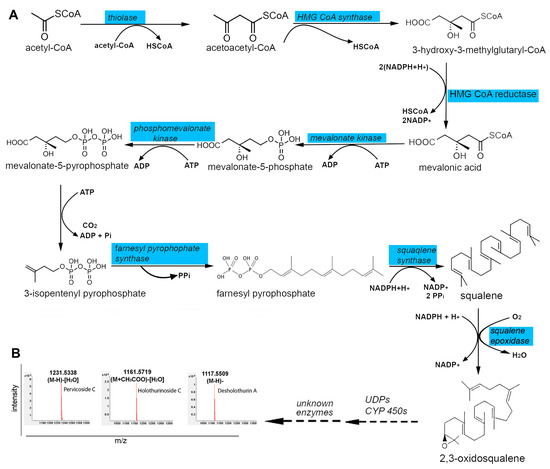
Figure 4.
Saponin biosynthesis pathway and LC-MS identification of saponin types in Holothuria scabra. (A) Saponin biosynthesis pathway showing enzyme genes annotated from the H. scabra body wall. All genes found in H. scabra are highlighted in blue. UDPs, uridine diphosphate; CYP450 cytochrome P450; (B) LC-MS chromatograms showing saponins identified from H. scabra body wall eluate. m/z, mass to charge ratio.
We have identified upstream core enzymes required to produce saponins, yet the downstream triterpene-modifying (or tailoring) enzymes (e.g., cytochrome P450s, sugar transferases, and acyltransferases) that facilitate the enormous structural diversity of saponins, remain unknown. Various approaches may be exploited towards revealing the tailoring enzyme genes required for sea cucumber triterpenoid saponin synthesis, including more in-depth comparative transcriptomics and targeted gene knock-down. To assist with this, it is important to know the types of saponins produced in the experimental animal. For H. scabra, saponins including the holothurinoside C, desholothurin A, pervicoside C, holothurinoside G, holothurinoside D, scabraside A and scabraside B have previously been identified in the body wall and other organs at concentrations of ~1 g/kg tissue [19,41]. Additional saponins that have been found in the conditioned water of H. scabra are holothurin A3 and holothurin A4 [46]. In our study, we used LC-MS to identify saponins in the conditioned water of H. scabra; LC-MS is a very effective and powerful technique to differentiate isomeric saponins as they exhibit different MSn fingerprint spectra that provide strong confirmatory evidence [47,48,49]. We can also report the presence of holothurinoside C, desholothurin A, and pervicoside C in H. scabra eluate (Figure 4B), while an additional 13 saponins may be present although their structures are yet to be confirmed by LC-MS/MS or nuclear magnetic resonance (Table 1).

Table 1.
List of saponins identified in Holothuria scabra eluate.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Animals and Tissue Collection
Adult H. scabra used in this study were cultured animals obtained from the Tasmanian Seafoods’ broodstock facility, Darwin, Australia. H. scabra body wall tissue was washed in 70% ethanol and a 1 cm2 section removed from the dorsal side and immediately stored in RNAlater (Ambion, Waltham, MA, USA). The radial nerves were isolated by making a longitudinal incision along the center of the bivium, then digestive organs, gonad and respiratory trees were discarded before the radial nerve-longitudinal muscle band complex was excised using sterile scalpel and forceps. Muscle bands and excess muscle tissue were separated from the radial nerve over ice and under a stereoscopic dissecting microscope. Separated radial nerves were then stored in RNAlater at −20 °C.
3.2. Total RNA Isolation, Transcriptome Analysis and Pathway Analysis
Total RNA was prepared from H. scabra body wall and radial nerve tissue using Trizol Reagent (Invitrogen, CA, USA), following the manufacturer’s protocol, and stored at −80 °C until use. The purity and quantity of each RNA sample was measured by a Nanodrop spectrophotometer 2000c (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) at 260 and 280 nm. High quality total RNA (RIN > 6) was sent to Novogene (Beijing, China), for cDNA synthesis using a cDNA Rapid Library Preparation Kit (Roche, Mannhem, Germany) and subjected to Illumina HiSeq 2500 sequencing (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). Raw reads were initially subjected to quality filtering based on (1) discard reads with adaptor contamination; (2) discard reads when uncertain nucleotides constitute more than 10% of either read (N > 10%); and (3) discard reads when low quality nucleotides (base quality less than 20) constitute more than 50% of the read. Quality reads were de novo assembled using SOAPdevono2 (CLC genomics workbench, version 9.5.3, Quigen, Hilden, Germany) with parameters set as follows: seqType, fq; minimum kmer coverage = 4; minimum contig length of 100 bp; group pair distance = 250. Estimation of transcript expression was performed using the de novo RNA-Seq analysis tool on the CLC Genomic workbench software with default parameters. The raw sequence dataset was deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under the accession number: SRR5713070. BLASTx homology searches of the GenBank non-redundant (NR) database hosted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) were performed on all transcripts. All BLAST searches were conducted using Blast2GO software (blast2go pro, BioBam Bioinformatics, Valencia, Spain) [63] with an E-value cut-off of 10−3. The Blast2GO software suite was also used to predict functions of individual transcripts, assigned gene ontology (GO) terms and their parents associated with the top 50 BLAST hits for each sequence. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis was performed to predict enzymatic functions in the context of the metabolic pathways (E-value cutoff of 10−6). Protein sequences for plant saponin biosynthesis-related genes were obtained from NCBI (NCBI; www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov), and then used as queries for tBLASTp searches (E-value cut-off 10−3) of the assembled H. scabra assembled body wall and radial nerve transcriptome.
3.3. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomic (LC-MS) Analysis
H. scabra body wall was gently pinched to facilitate the release of compounds into a small volume (1 mL) of filtered seawater. After collection of the ‘conditioned water’ eluate (n = 3), samples were passed through pre-equilibrated Sep-Pak C18 cartridges (Waters, Milford, MA, USA) to extract compounds of interest. Cartridges were eluted with 70% acetonitrile (Sigma-Aldrich, Castle Hill, Australia), then freeze-dried. Lyophilised samples were stored at −80 °C until subsequent analysis.
Freeze-dried samples were resuspended to 15% of the original volume by adding 30 μL methanol and then 120 μL of MilliQ (Millipore Corporation, Bedford, MA, USA) water to produce a 20:80 methanol:water solution. The extract solution was stored at −80 °C until chemical analysis. Before LC-MS analysis, samples were thawed and kept on ice prior to injection. The chromatographic separation of compounds and extracts was performed using Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) on an Agilent 1290 series system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The UHPLC was coupled to an Agilent 6520 high-resolution accurate mass (HRAM) qToF mass spectrometer equipped with a multimode source (Agilent) and controlled using MassHunter acquisition software (B. 02.01 SP3; Agilent). Separation was achieved using a 4.6 150 mm, 2.7 µm Poroshell 120 EC-C18 column (Agilent). The chromatographic analysis was performed using 0.1% (v/v) aqueous formic acid (mobile phase A) and acetonitrile +0.1% (v/v) formic acid (mobile phase B) at a flow rate of 0.20 mL/min. The column was pre-equilibrated for 15 min with 20% mobile phase B. After injection, the composition of mobile phase was changed from 20% mobile phase B to 100% mobile phase B over a period of 25 min, the composition was held at 100% mobile phase B for 2 min, and then returned to the starting composition of 20% mobile phase B over the next 2 min. The column was re-equilibrated using 20% mobile phase B for 6 min prior to the next injection. The total chromatographic run time was 35 min. Each chromatographic sequence included initial blank injections intercalated throughout the UHPLC sequence to control for any acquisition-dependent variation. The injection volume was 20 µL. LC-MS parameters were those as used in previous studies [20,64].
Data processing was performed using Agilent MassHunter Qualitative software (Version B.05.00, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The Molecular Feature Extractor algorithm within MassHunter Qualitative analysis software (version 05.00, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA was used to extract chemically qualified molecular features from the LC-QToF-MS data files (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). For empirical formula generation, the Molecular Formula Generator algorithm was used. To aid the data-mining process, the LC-QToF-MS data file of the blank sample was also analysed to extract features and to use as a background reference. Data analysis and compound identification was performed according to our published work [20,65]. Briefly, molecular formulas were generated after extracting the compounds from the samples. Finally, an in-house database was used to identify metabolites present in the sea cucumber sample. The elemental composition of ions was estimated based on the m/z values registered with ~5 ppm accuracy.
4. Conclusions
Our investigation of the H. scabra body wall transcriptome, and comparison with the radial nerve transcriptome, has provided a foundation resource for the identification of biosynthetic pathway genes responsible for the production of secondary metabolites which contribute to the animal’s nutritional properties. For example, we reveal the functional annotation of upstream biosynthetic genes encoding enzymes involved in the triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis pathway. This resource could ultimately be exploited towards biotechnological applications, focused on production of nutritionally beneficial secondary metabolites.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/1660-3397/15/11/349/s1. File S1: The body wall transcriptome of H scabra where raw reads were assembled into a transcript library containing 107,217 unigenes, of which 105,838 encode for open reading frames (>10 amino acids in length). File S2: Classification of body wall and radial nerve transcripts. (a) Functional annotation of body wall and radial nerve transcripts against the KOG database, where total number of genes in each category are accessible. (b) GO term classifications for body wall genes presented in the KOG signal transduction mechanisms, where total number of genes in each category are accessible. File S3: Identified core enzyme Pfam domains (table) and sequences for proposed saponin biosynthesis pathway of H. scabra. Figure S1: Biosynthetic routes of glycolysis cycle from H. scabra body wall and radial nerve transcriptomes with gene annotation number. Violet squares represent genes detected in the body wall transcriptome, while green squares represent genes detected in the radial nerve transcriptome.
Acknowledgments
This research was undertaken with the assistance of resources from the National Computational Infrastructure (NCI), which is supported by the Australian Government. We acknowledge the Australian Seafood Cooperative Research Centre and industry partner Tasmanian Seafood’s P/L for funding the radial nerve transcriptome.
Author Contributions
Shahida Akter Mitu prepared RNA and performed transcriptome analysis of the body wall and constructed figures. Shahida Akter Mitu, Utpal Bose and Paul Nicholas Shaw performed sample preparation and analysis of LC-MS. Luke H. Turner performed transcriptome analysis of the radial nerve. Shahida Akter Mitu, Saowaros Suwansa-ard and Utpal Bose undertook the biosynthesis pathway analysis. Min Zhao performed gene and protein annotation. Abigail Elizur, Steven M. Ogbourne and Scott F. Cummins conceived the idea and obtained funding. All authors contributed to writing and drafting of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Jia, B.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Ding, J.; Xiao, X. Differentiation of dried sea cucumber products from different geographical areas by surface desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9356–9364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conand, C. Harvest and trade: Utilization of sea cucumbers; sea cucumber fisheries; current international trade; illegal, unreported and unregulated trade; bycatch; socio-economic characteristics of the trade in sea cucumbers. In The Proceedings of the Technical Workshop on the Conservation of Sea Cucumbers in the Families Holothuridae and Stichopodidae; NOAA Technical Memorandum: Seattle, WA, USA, 2005; pp. 47–69. [Google Scholar]
- Janakiram, N.B.; Mohammed, A.; Rao, C.V. Sea cucumbers metabolites as potent anti-cancer agents. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Kumiko, K.; Yasuzawa, T.; Matsui, M.; Suzuki, S.; Kitagawa, I. Marine natural products. XXVII. Distribution of lanostane-type triterpene oligoglycosides in ten kinds of Okinawan sea cucumbers. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1991, 39, 2282–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyakov, G.; Kuznetsova, T.; Stonik, V.; Levin, V.; Albores, R. Glycosides of marine invertebrates—IV. A comparative study of the glycosides from Cuban sublittoral holothurians. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1975, 52, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods—A review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, R.G.; Chen, Z. In vivo and in vitro biosynthesis of saponins in sea cucumbers. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewi, A.S.; Tarman, K.; Uria, A.R. Marine natural products: Prospects and impacts on the sustainable development in Indonesia. In Proceedings of the Indonesian Student Scientific Meeting (ISSM) on Sustainable Development in Indonesia: An Interdisciplinary Approach, Delft, The Netherlands, 13–15 May 2008; pp. 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Stonik, V.A. Marine polar steroids. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2001, 70, 673–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skropeta, D. Deep-sea natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2008, 25, 1131–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, J.-P.; Heng, L.; de Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negi, J.; Negi, P.; Pant, G.; Rawat, M.; Negi, S. Naturally occurring saponins: Chemistry and biology. J. Poisonous Med. Plant Res. 2013, 1, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity ofsaponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nah, S.-Y. Ginseng ginsenoside pharmacology in the nervous system: Involvement in the regulation of ion channels and receptors. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Sobolewska, D. Saponins as cytotoxic agents: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 425–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skene, C.D.; Sutton, P. Saponin-adjuvanted particulate vaccines for clinical use. Methods 2006, 40, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, M.S. Biological activities of sulfated glycosides from echinoderms. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2008, 35, 311–354. [Google Scholar]
- Caulier, G.; Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P. Review of saponin diversity in sea cucumbers belonging to the family Holothuriidae. Secr. Pac. Community Beche-De-Mer Inf. Bull. 2011, 31, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, U.; Centurion, E.; Hodson, M.; Shaw, P.; Storey, K.; Cummins, S. Global metabolite analysis of the land snail Theba pisana hemolymph during active and aestivated states. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2016, 19, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, U.; Kruangkum, T.; Wang, T.; Zhao, M.; Ventura, T.; Mitu, S.A.; Hodson, M.P.; Shaw, P.N.; Sobhon, P.; Cummins, S.F. Biomolecular changes that occur in the antennal gland of the giant freshwater prawn (Machrobrachium rosenbergii). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, G.; Mezali, K.; Soualili, D.L.; Decroo, C.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Chemical characterization of saponins contained in the body wall and the cuvierian tubules of the sea cucumber Holothuria (Platyperona) sanctori (Delle Chiaje, 1823). Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2016, 68, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Yi, Y.; Xu, Q.; La, M.; Zhang, H. Two new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Planta Med. 2009, 75, 1608–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proksch, P. Defensive roles for secondary metabolites from marine sponges and sponge-feeding nudibranchs. Toxicon 1994, 32, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Chen, M.; Yang, H.; Wang, T.; Liu, B.; Shu, C.; Gardiner, D.M. Large scale gene expression profiling during intestine and body wall regeneration in the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2011, 6, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Zhu, L.; Su, X.; Li, Y.; Jin, C.; Li, T. De novo assembly of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus hemocytes transcriptome to identify miRNA targets associated with skin ulceration syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, H.; Bao, Z.; Hou, R.; Wang, S.; Su, H.; Yan, J.; Tian, M.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Lu, W. Transcriptome sequencing and characterization for the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus (Selenka, 1867). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San Miguel-Ruiz, J.E.; Maldonado-Soto, A.R.; Garcia-Arraras, J.E. Regeneration of the radial nerve cord in the sea cucumber Holothuria glaberrima. BioMed Cent. Dev. Biol. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Madrigal, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gomez-Cabrero, D.; Cervera, A.; McPherson, A.; Szczesniak, M.W.; Gaffney, D.J.; Elo, L.L.; Zhang, X. A survey of best practices for RNA-seq data analysis. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Present Status and Prospects of Sea Cucumber Industry in China; Food and Agricultural Organization Fisheries and Technical Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005; pp. 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Overview of sea cucumber farming and sea ranching practices in China. Secr. Pac. Community Beche-De-Mer Inf. Bull. 2003, 18, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadizadeh, F.; Ehsanpor, M.; Afkhami, M.; Mokhlesi, A.; Khazaali, A.; Montazeri, S. Antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic effects of a sea cucumber Holothuria leucospilota, from the north coast of the Persian Gulf. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2013, 93, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, N.E.-S.E.-S. Nutritional value of some Egyptian sea cucumbers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 5466–5472. [Google Scholar]
- Sroyraya, M.; Hanna, P.J.; Siangcham, T.; Tinikul, R.; Jattujan, P.; Poomtong, T.; Sobhon, P. Nutritional components of the sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2017, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar]
- Adeniyi, S.; Orjiekwe, C.; Ehiagbonare, J.; Josiah, S. Nutritional composition of three different fishes (Clarias gariepinus, Malapterurus electricus and Tilapia guineensis). Pak. J. Nutr. 2012, 11, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, O. Influences of drying methods on nutritional properties of tilapia fish (Oreochromis nilotieus). World J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 5, 256–258. [Google Scholar]
- Waagbo, R.; Sandnes, K.; Torrissen, O.J.; Sandvin, A.; Lie, O. Chemical and sensory evaluation of fillets from Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fed three levels of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids at two levels of vitamin E. Food Chem. 1993, 46, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Storey, K.B. High-throughput sequencing reveals differential expression of miRNAs in intestine from sea cucumber during aestivation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binyon, J. Physiology of Echinoderms: International Series of Monographs in Pure and Applied Biology Zoology; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 49. [Google Scholar]
- Berg, J.M.; Tymoczko, J.L.; Stryer, L. Each Organ Has a Unique Metabolic Profile Available Biochemistry, 5th ed.; W H Freeman Co. Ltd.: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 851–854. [Google Scholar]
- Caulier, G.; Flammang, P.; Rakotorisoa, P.; Gerbaux, P.; Demeyer, M.; Eeckhaut, I. Preservation of the bioactive saponins of Holothuria scabra through the processing of trepang. Cah. Biol. Mar. 2013, 54, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Elucidation of molecular diversity and body distribution of saponins in the sea cucumber Holothuria forskali (Echinodermata) by mass spectrometry. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 152, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinin, V.I.; Aminin, D.L.; Avilov, S.A.; Silchenko, A.S.; Stonik, V.A. Triterpene glycosides from sea cucucmbers (holothurioidea, echinodermata). Biological activities and functions. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2008, 35, 135–196. [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyck, S.; Caulier, G.; Todesco, M.; Gerbaux, P.; Fournier, I.; Wisztorski, M.; Flammang, P. The triterpene glycosides of Holothuria forskali: Usefulness and efficiency as a chemical defense mechanism against predatory fish. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.Q.; Li, L.; Yi, Y.H.; Yuan, W.H.; Liu, B.S.; Weng, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z.L. Two new cytotoxic nonsulfated pentasaccharide holostane (= 20-hydroxylanostan-18-oic acid γ-lactone) glycosides from the sea cucumber Holothuria grisea. Helv. Chim. Acta 2008, 91, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, N.H.; Van Thanh, N.; Van Kiem, P.; Huong, L.M.; Van Minh, C.; Kim, Y.H. Two new triterpene glycosides from the Vietnamese sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. Metabolite profiling of polar steroid constituents in the far eastern starfish Aphelasterias japonica using LC–ESI MS/MS. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 1153–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. LC-ESI MS/MS profiling of polar steroid metabolites of the far eastern starfish Patiria (= Asterina) pectinifera. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, R.S.; Ivanchina, N.V.; Kicha, A.A.; Malyarenko, T.V.; Grebnev, B.B.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Stonik, V.A. LC–MS-based metabolome analysis on steroid metabolites from the starfish Patiria (= Asterina) pectinifera in conditions of active feeding and stresses. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.S.; Yi, Y.H.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Han, H.; Sun, G.Q.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Z.L. Argusides D and E, two new cytotoxic triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Bohadschia argus Jaeger. Chem. Biodivers. 2008, 5, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Hori, M.; Kyogoku, Y. Structures of four new triterpenoidal oligoglycosides, bivittoside A, B, C, and D, from the sea cucumber Bohadschia bivittata Mitsukuri. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1981, 29, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silchenko, A.S.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Avilov, S.A.; Andryjaschenko, P.V.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Yurchenko, E.A.; Dolmatov, I.Y.; Savchenko, A.M.; Kalinin, V.I. Triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Cladolabes schmeltzii. II. Structure and biological action of cladolosides A1-A6. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elbandy, M.; Rho, J.R.; Afifi, R. Analysis of saponins as bioactive zoochemicals from the marine functional food sea cucumber Bohadschia cousteaui. Eur. Food Res. Technol 2014, 238, 937–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C. Discovery of novel saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lessoni. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2633–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniain, C.; Centurion, R.; Careaga, V.; Maier, M. Chemical ecology and bioactivity of triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Psolus patagonicus (Dendrochirotida: Psolidae). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2008, 88, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Xu, L.; Shi, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lou, Q.; Xue, C. Eicosapentaenoic acid-enriched phosphatidylcholine isolated from Cucumaria frondosa exhibits anti-hyperglycemic effects via activating phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal pathway. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegami, S.; Okano, K.; Muragaki, H. Structure of glycoside B2, a steroidal saponin in the ovary of the starfish, Asterias amurensis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979, 20, 1769–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, I.; Sugawara, T.; Yosioka, I.; Kuriyama, K. Saponin and Sapogenol. XIV. Antifugal glycosides from the sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus Selenka.(1). Structure of Stichopogenin A4, the genuine aglycone of Holotoxin A. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1976, 24, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.; Riguera, R. Lefevreiosides: Four novel triterpenoid glycosides from the sea cucumber Cucumaria lefevrei. J. Chem. Res. Synop. 1989, 11, 342–343. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.-J.; Zhu, Q.-K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, H.-W. New cytotoxic triterpene glycoside from the East China Sea cucumber Holothuria nobilis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Yi, Y.-H.; Tang, H.-F. Bioactive triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Holothuria fuscocinerea. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 1492–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.-L.; Li, L.; Yi, Y.-H.; Sun, P. Philinopsides E and F, two new sulfated triterpene glycosides from the sea cucumber Pentacta quadrangularis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2006, 20, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, U.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Ng, Y.K.; Shaw, P.N.; Fuerst, J.A.; Hodson, M.P. LC-MS-Based metabolomics study of marine bacterial secondary metabolite and antibiotic production in Salinispora arenicola. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, U.; Hewavitharana, A.K.; Vidgen, M.E.; Ng, Y.K.; Shaw, P.N.; Fuerst, J.A.; Hodson, M.P. Discovering the recondite secondary metabolome spectrum of Salinispora species: A study of inter-species diversity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).