Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
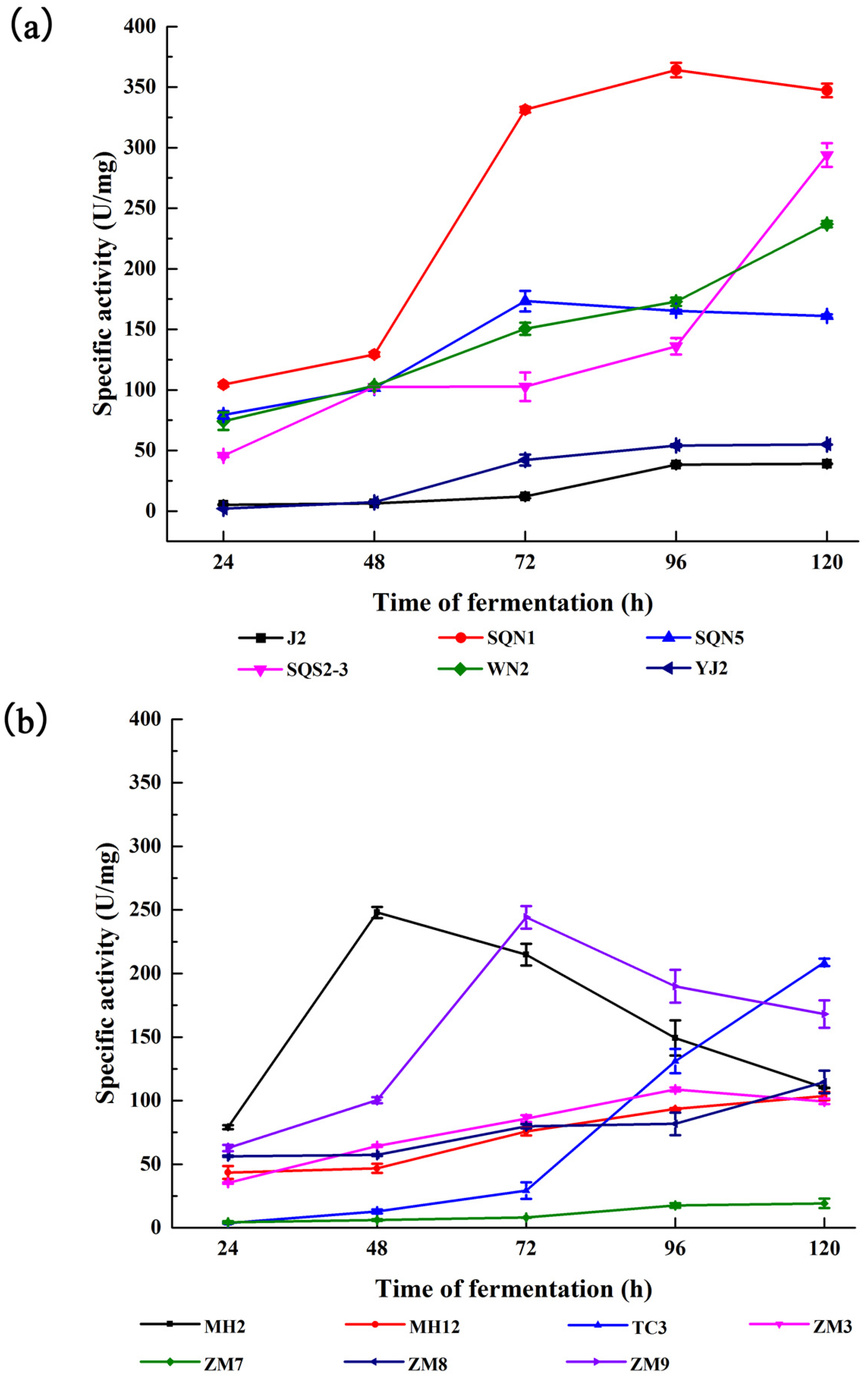
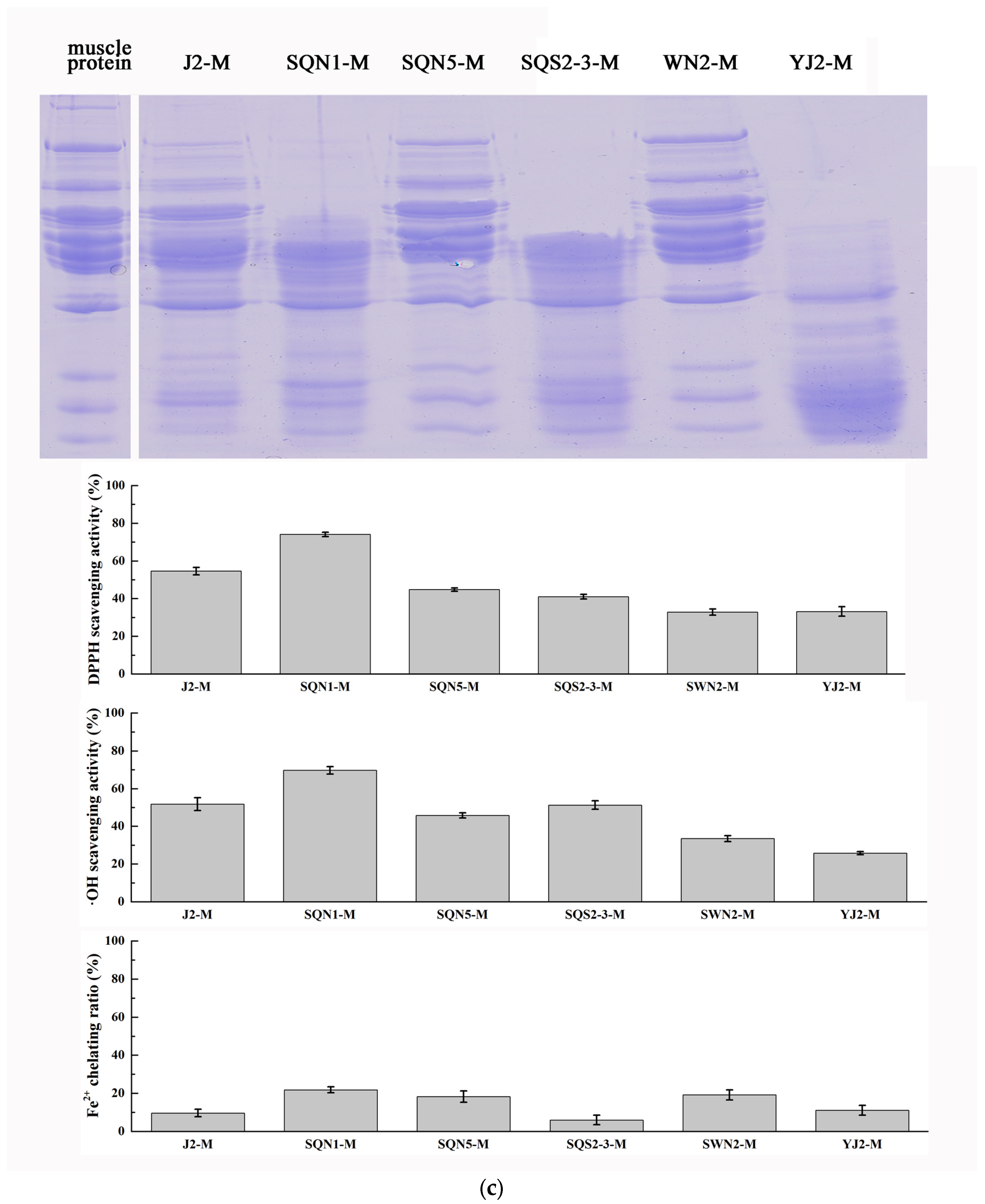
2.1. Substrate-Immersing Zymography of Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
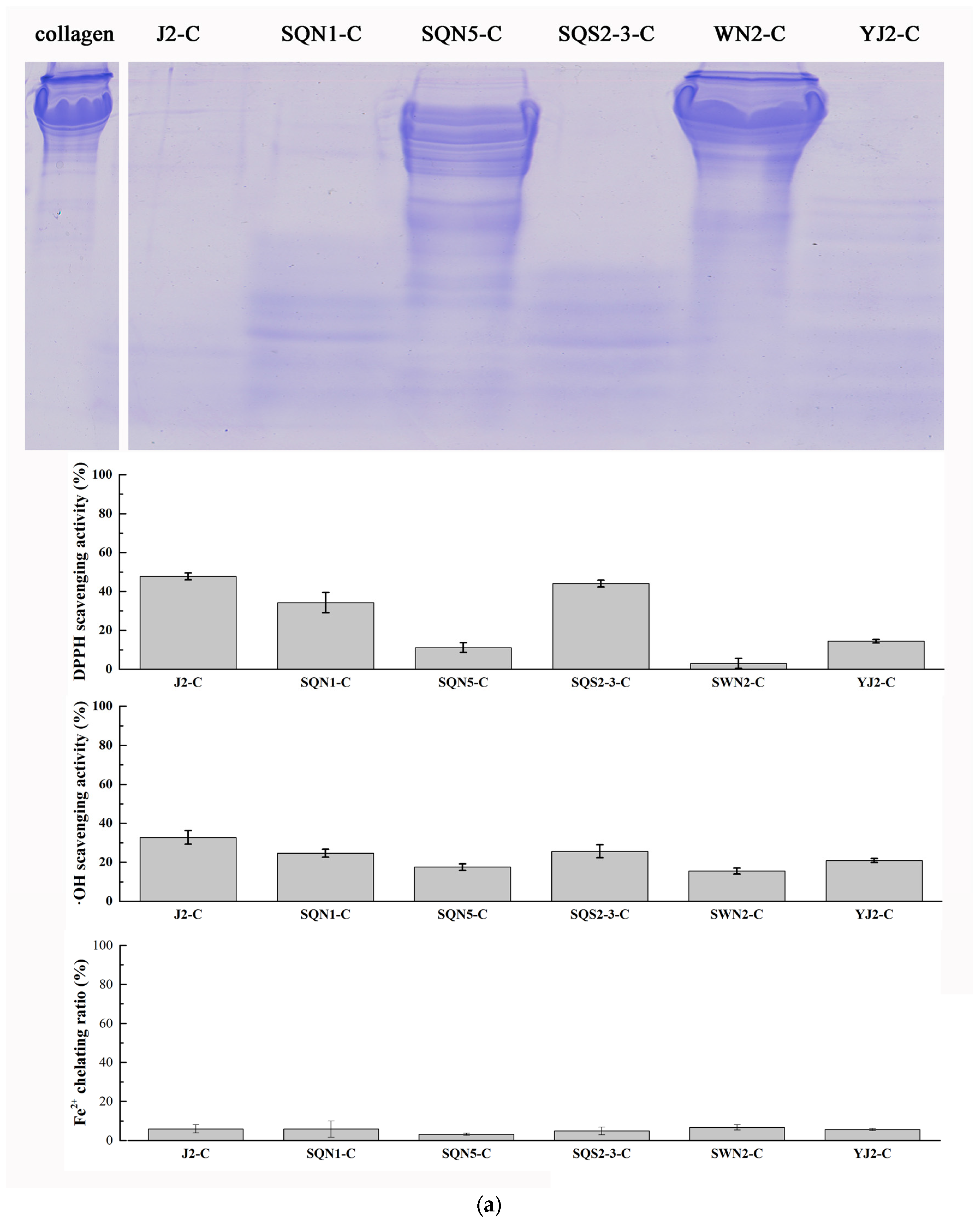
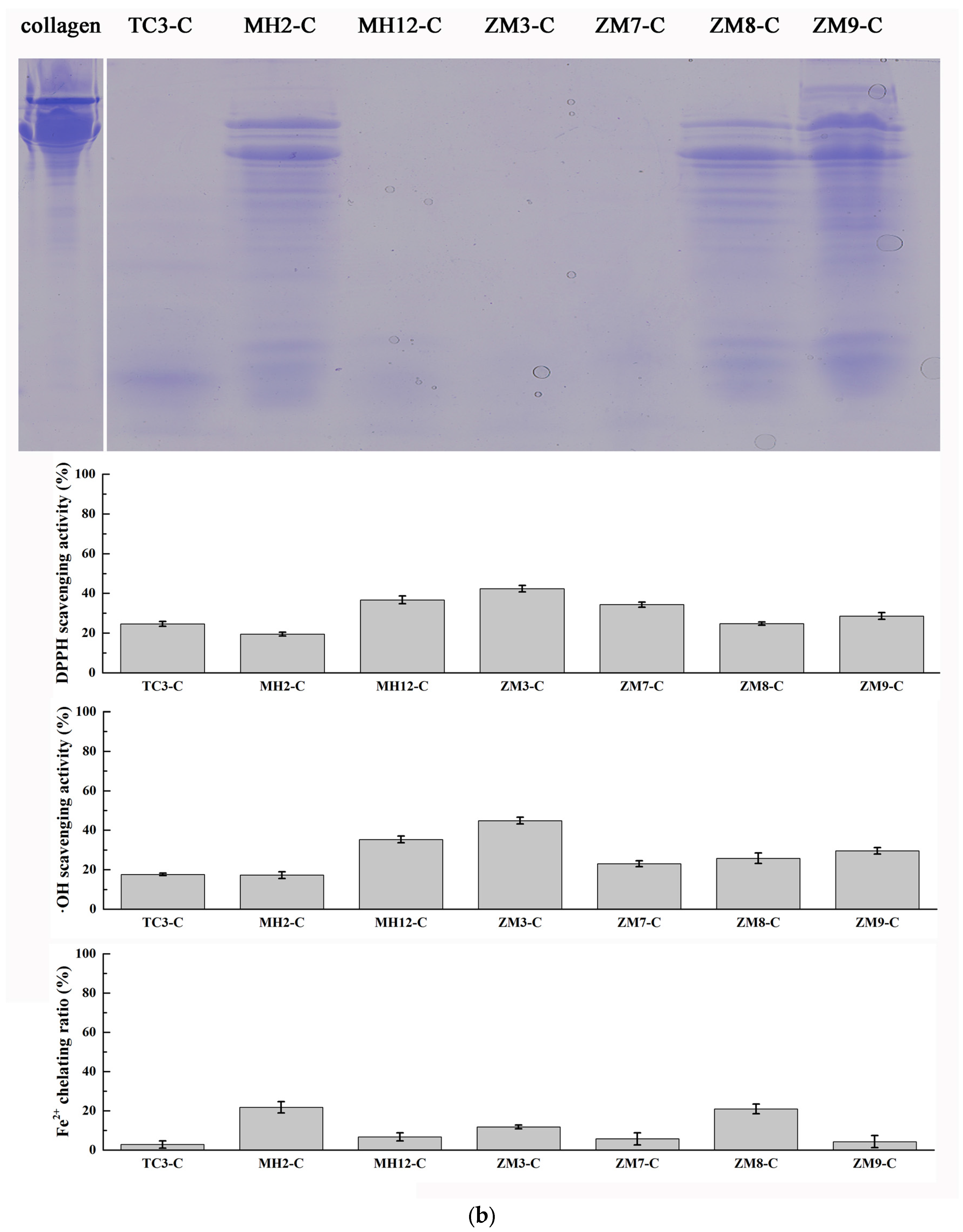
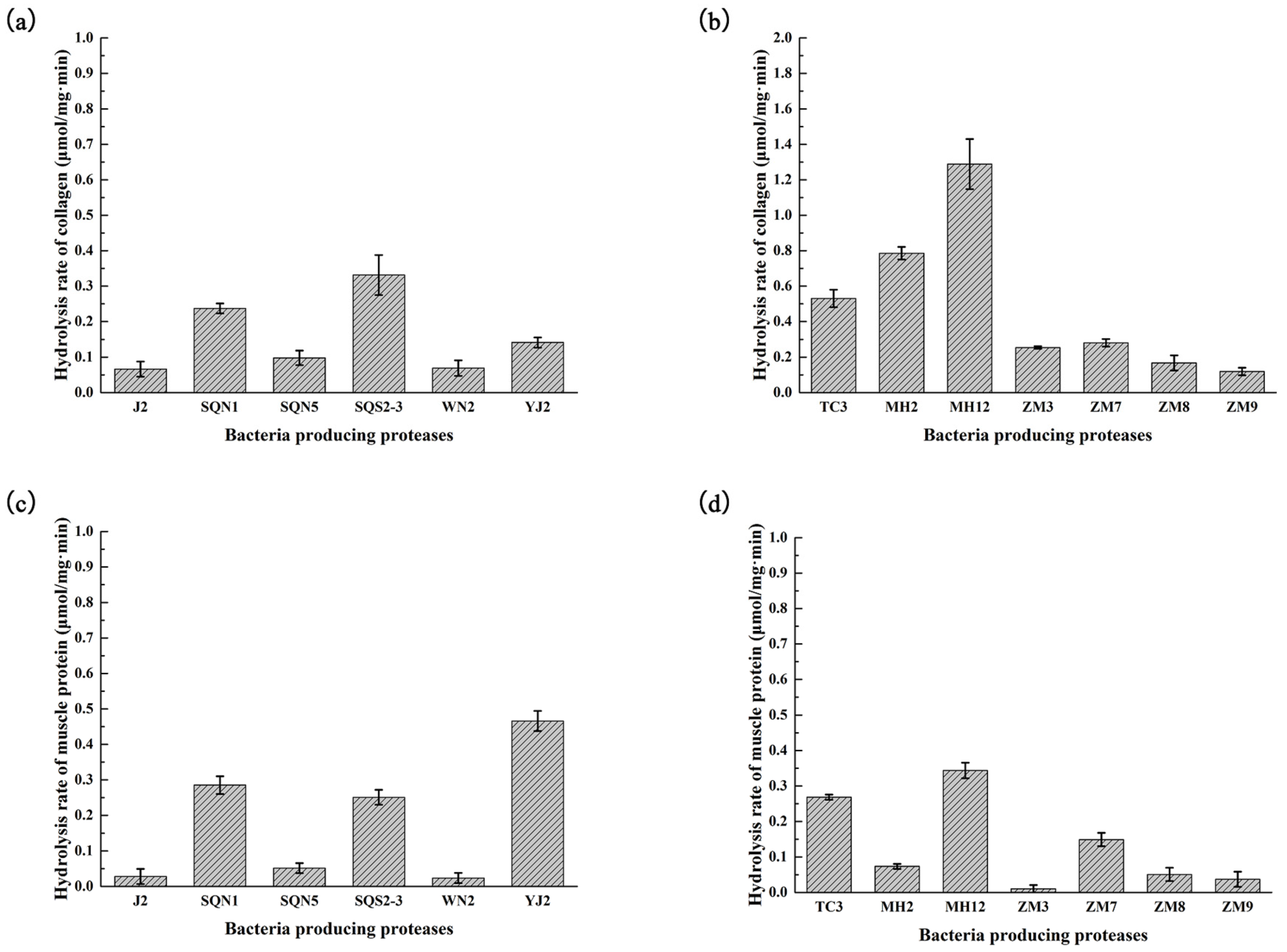
2.2. Hydrolysis of Salmon Protein
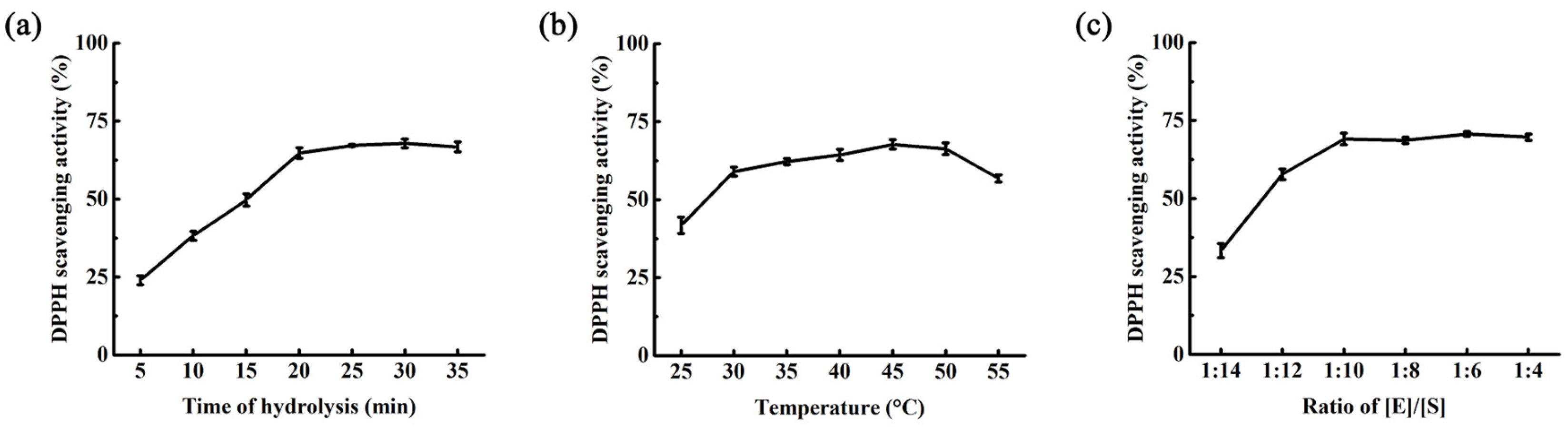
2.3. Optimization of Hydrolysis Condition
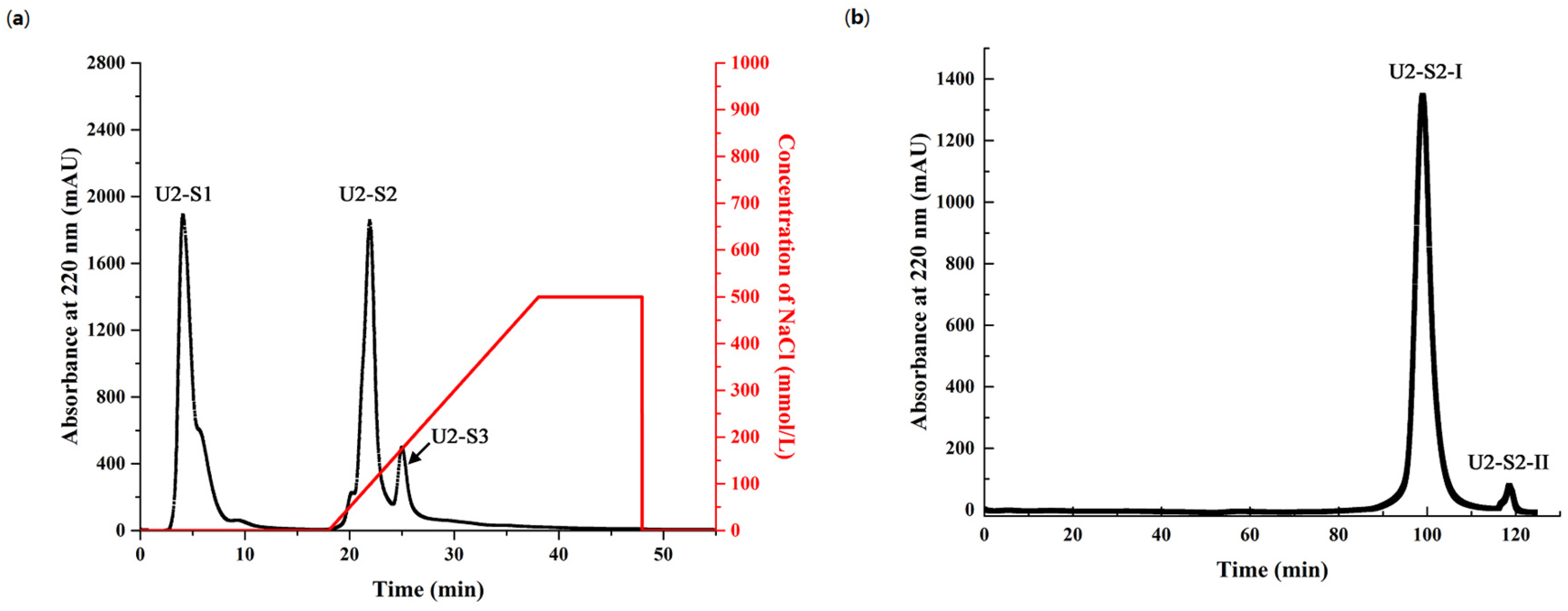
2.4. Purification of Antioxidant Peptides from Hydrolysate of Muscle Proteins
2.5. Oxygen Radical Absorption Capability (ORAC) Assay
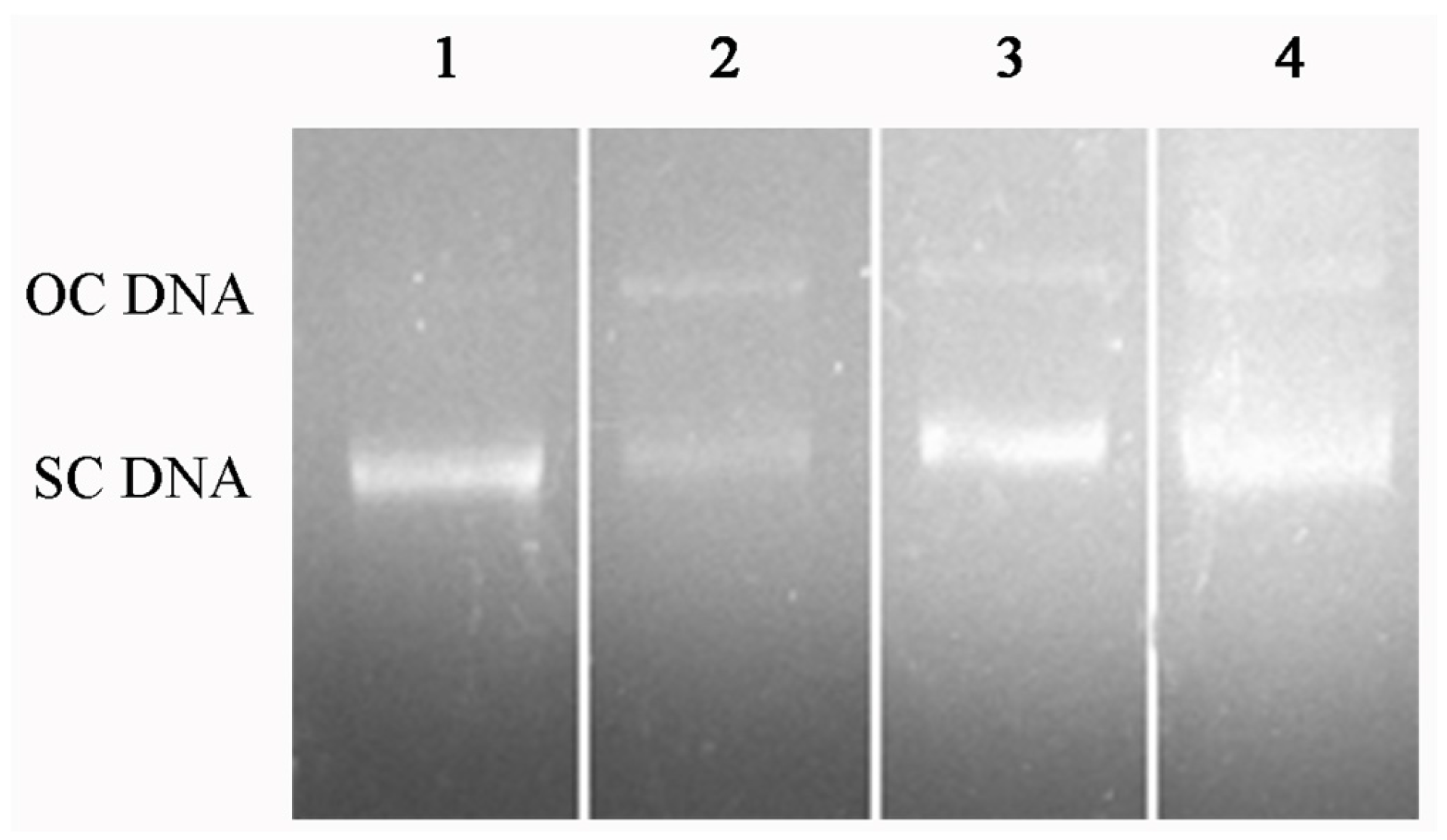
2.6. DNA Protection Effect against Oxidation-Induced Damage
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
3.2.1. Preparation of Bacterial Proteases from Fermentation
3.2.2. Detection of Proteases with Substrate-Immersing Zymography
3.3. Protein Hydrolysis of Salmon Byproducts Using Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
3.3.1. Hydrolysis of Salmon Collagen Using Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
3.3.2. Hydrolysis of Salmon Muscle Using Bacterial Extracellular Proteases
3.4. Isolation of Antioxidant Peptides from Muscle Hydrolysate
3.4.1. Isolation of Muscle Hydrolysate by Ultrafiltration
3.4.2. Cation Exchange Chromatography
3.4.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography
3.5. Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity
3.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
3.5.2. Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity
3.5.3. Ferrous Ion Chelating Assay
3.5.4. Oxygen Radical Absorbance Capability (ORAC) Assay
3.5.5. Protection Effect on Oxidation-Induced DNA Damage
3.6. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rizzo, A.M.; Berselli, P.; Zava, S.; Montorfano, G.; Negroni, M.; Corsetto, P.; Berra, B. Endogenous antioxidants and radical scavengers. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 698, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spolarics, Z. Endotoxemia, Pentose cycle, and the oxidant/antioxidant balance in the hepatic sinusoid. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1998, 63, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.N.; Frei, B.; Vita, J.A.; Keaney, J.F. Antioxidant and atherosclerotic heart disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 408–416. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stohs, S.J. The role of free radicals in toxicity and disease. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1995, 6, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phanat, K.; Soottawat, B.; Wonnop, V.; Fereidoon, S. Gelatin hydrolysate from blacktip shark skin prepared using papaya latex enzyme: Antioxidant activity and its potential in model systems. Food Chem. 2002, 135, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, L.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Xu, Y.F. Purification and characterisation of a novel antioxidant peptide derived from blue mussel (Mytilus edulis) protein hydrolysate. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, T.G.; He, R.; Fida, M.H.; Chibuike, C.U.; Tom, A.G.; Rotimi, E.A. Evaluation of the in vitro antioxidant properties of a cod (Gadus morhua) protein hydrolysate and peptide fractions. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 652–659. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, D.H.; Ryu, B.; Kim, S.K. Active peptides from skate (Okamejei kenojei) skin gelatin diminish angiotensin-I converting enzyme activity and intracellular free radical-mediated oxidation. Food Chem. 2014, 143, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.K.; Li, W.; He, Y.H.; Ren, D.D.; Felicia, K.; Song, L.L.; Yu, X.J. Novel antioxidative peptides from the protein hydrolysate of oysters (Crassostrea talienwhanensis). Food Chem. 2014, 145, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirari, Y.A.; Ailén, A.; Marta, M.C.; López-Caballero, M.E.; Pilar, M.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C. Antimicrobial and antioxidant chitosan solutions enriched with active shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) waste materials. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 710–717. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Pe, X.; Han, X.; Li, Y. Antioxidant effect of a marine oligopeptide preparation from chum salmon (Oncorhynchus keta) by enzymatic hydrolysis in radiation injured mice. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2304–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, S.; Scott, S.; Witoon, P.; Peter, J.B. Functional and nutritional properties of red salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka) enzymatic hydrolysates. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, C.B.; Kim, J.G.; Je, J.Y. Purification and antioxidant properties of octapeptide from salmon byproduct protein hydrolysate by gastrointestinal digestion. Food Chem. 2014, 147, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, E.M.; Mills, H.J.; Kostka, J.E. Microbial Community diversity associated with carbon and nitrogen cycling in permeable marine sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5689–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Bravo, L.; Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Alemán, A.; Montero, P. Antioxidant properties of tuna-skin and bovine-hide gelatin films induced by the addition of oregano and rosemary extracts. Food Chem. 2009, 112, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Je, J.Y.; Kim, S.K. Purification and characterization of antioxidant peptide from hoki (Johnius belengerii) frame protein by gastrointestinal digestion. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.B.; Wu, C.L.; Liu, D.; Yang, X.H.; Huang, J.F.; Zhang, J.; Liao, B.Q.; He, H.L.; Li, H. Overview of antioxidant peptides derived from marine resources: The sources, characteristic, purification, and evaluation methods. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Y.M.; Chi, C.F.; Luo, H.Y.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of collagen and antioxidant collagen peptides from scales of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea). Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4641–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.I.; Ho, H.Y.; Chu, Y.J.; Chow, C.J. Characteristic and antioxidant activity of retorted gelatin hydrolysates from cobia (Rachycentron canadum) skin. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. Investigation of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin gelatin peptides for their in vitro antioxidant effects. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeer, R.A.; Sampath, K.N.S.; Jai, G.R. In vitro and in vivo studies on the antioxidant activity of fish peptide isolated from the croaker (Otolithes ruber) muscle proteins hydrolysate. Peptides 2012, 35, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferid, A.; Neyssene, A.; Chobert, J.M.; Thomas, H.; Mohamed, N.M. Neutral serine protease from Penicillium italicum. purification, biochemical characterization, and use for antioxidative peptide preparation from Scorpaena notata muscle. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 186–205. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, C.F.; Hu, F.Y.; Wang, B.; Ren, X.J.; Deng, S.G.; Wu, C.W. Purification and characterization of three antioxidant peptides from protein hydrolyzate of croceine croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) muscle. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, C.F.; Wang, B.; Deng, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.M.; Deng, S.G.; Ma, J.Y. Isolation and characterization of three antioxidant pentapeptides from protein hydrolysate of monkfish (Lophius litulon) muscle. Food Res. Int. 2014, 55, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Mohamed, H.; Rafik, B.; Imen, L.; Yosra, T.E.; Moncef, N. Antioxidant and free radical-scavenging activities of smooth hound (Mustelus mustelus) muscle protein hydrolysates obtained by gastrointestinal proteases. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; He, G.Y. Preparation and evaluation of antioxidant peptide from papain hydrolysate of Sphyrna lewini muscle protein. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, R.J.; Kellerby, S.S.; Decker, E.A. Antioxidant activity of proteins and peptides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2008, 48, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheih, I.C.; Wu, T.K.; Fang, T.J. Antioxidant properties of a new antioxidative peptide from algae protein waste hydrolysate in different oxidation systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karawita, R.; Senevirathne, M.; Athukorala, Y.; Affan, A.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.B.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effect of enzymatic extracts from microalgae against DNA damage induced by H2O2. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Yang, X.H.; Huang, J.F.; Wu, R.B.; Wu, C.L.; He, H.L.; Li, H. In situ demonstration and characteristic analysis of the protease components from marine bacteria using substrate immersing zymography. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 175, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.L.; Guo, J.; Chen, X.L.; Xie, B.B.; Zhang, X.Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhou, B.C. Structural and functional characterization of mature forms of metalloprotease E495 from arctic sea-ice bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. SM495. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, K.; Fujikawa, K.; Yahara, K.; Nakamura, T. Antioxidative properties of xanthan on the antioxidation of soybean oil in cyclodextrin emulsion. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Z.R.; Chi, C.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Luo, H.Y. Preparation and evaluation of antioxidant peptides from ethanol-soluble proteins hydrolysate of Sphyrna lewini Muscle. Peptides 2012, 36, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiansilakul, Y.; Benjakul, S.; Shahidi, F. Compositions functional properties and antioxidative activity of protein hydrolysates prepared from round scad (Decapterus maruadsi). Food Chem. 2007, 103, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, D.; Carmen, G.C.; Begona, B. Extending applicability of the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC-fluorescein) assay. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, Z.J.; Jung, W.K.; Byun, H.G.; Kim, S.K. protective effect of an antioxidative peptide purified from gastrointestinal digests of oyster (Crassostrea gigas) against free radical induced DNA damage. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3365–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
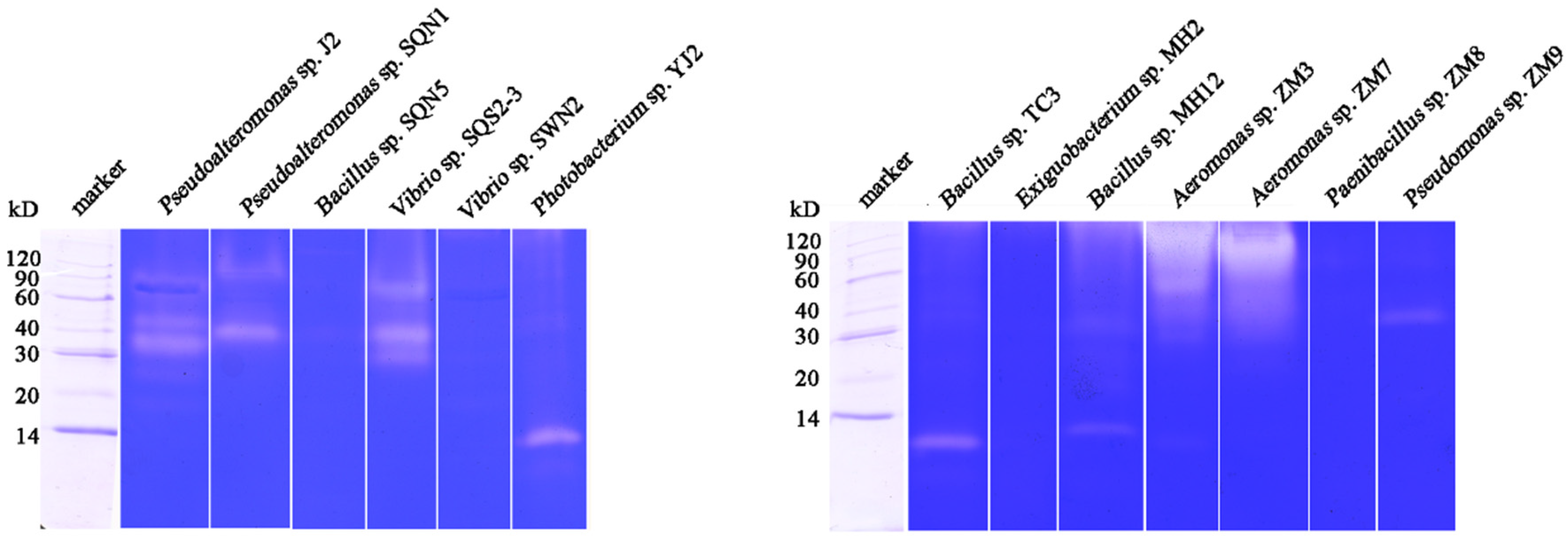


| Bacteria Strain | Concentration of Total Protein (mg/mL) | Specific Activity (U/mg) | Amount of Proteases | Molecular Weight (kD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria from sea water | ||||
| Pseudoalteromonas sp. J2 | 2.63 | 39.06 | 3 | 90, 40, 30~40 |
| Pseudoalteromonas sp. SQN1 | 1.26 | 347.27 | 2 | 90~120, 40 |
| Bacillus sp. SQN5, | 1.98 | 161.06 | ||
| Vibrio sp. SQS2-3 | 1.18 | 293.95 | 3 | 60, 40, 30 |
| Vibrio sp. SWN2 | 1.65 | 236.92 | ||
| Photobacterium sp. YJ2 | 2.00 | 54.93 | 1 | 14 |
| Bacteria from fresh water | ||||
| Bacillus sp. TC3 | 1.03 | 110.04 | 1 | <14 |
| Exiguobacterium sp. MH2 | 2.20 | 103.67 | ||
| Bacillus sp. MH12 | 3.84 | 208.78 | 2 | <14 |
| Aeromonas sp. ZM3 | 5.35 | 99.47 | Proteases cannot be separated | |
| Aeromonas sp. ZM7 | 5.26 | 19.25 | Proteases cannot be separated | |
| Paenibacillus sp. ZM8 | 1.02 | 114.68 | ||
| Pseudomonas sp. ZM9 | 1.06 | 168.12 | 1 | 30~40 |
| Group | Time (min) | Temperature (°C) | Ratio of [E]/[S] (g/g) | DPPH Scavenging Activity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 29.2 | 45 | 1:50 | 68.13 |
| 2 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 68.70 |
| 3 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 69.27 |
| 4 | 22.5 | 47.5 | 1.5:50 | 71.19 |
| 5 | 20.8 | 45 | 1:50 | 72.91 |
| 6 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 70.80 |
| 7 | 25 | 40.8 | 1:50 | 69.46 |
| 8 | 27.5 | 42.5 | 0.5:50 | 70.99 |
| 9 | 25 | 45 | 1.8:50 | 74.44 |
| 10 | 27.5 | 42.5 | 1.5:50 | 76.54 |
| 11 | 25 | 49.2 | 1:50 | 69.66 |
| 12 | 27.5 | 47.5 | 0.5:50 | 67.93 |
| 13 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 73.67 |
| 14 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 71.95 |
| 15 | 25 | 45 | 1:50 | 73.48 |
| 16 | 22.5 | 42.5 | 1.5:50 | 73.29 |
| 17 | 22.5 | 47.5 | 0.5:50 | 69.08 |
| 18 | 22.5 | 42.5 | 0.5:50 | 70.42 |
| 19 | 27.5 | 47.5 | 1.5:50 | 70.80 |
| 20 | 25 | 45 | 0.2:50 | 70.43 |
| Source | Sum of Square | df | Mean Square | F Value | p-Value (Prob > F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.390 × 10−3 | 3 | 1.230 × 10−3 | 6.53 | 0.0043 |
| A-Time | 9.880 × 10−5 | 1 | 9.880 × 10−5 | 0.52 | 0.4793 |
| B-Temperature | 3.781 × 10−4 | 1 | 3.781 × 10−4 | 2.01 | 0.1756 |
| C-Ratio of [E]/[S] | 3.213 × 10−3 | 1 | 3.213 × 10−3 | 17.07 | 0.0008 |
| Residual | 3.013 × 10−3 | 16 | 1.883 × 10−4 | ||
| Lack of Fit | 2.197 × 10−3 | 11 | 1.998 × 10−4 | 1.23 | 0.4375 |
| Pure Error | 8.152 × 10−4 | 5 | 1.630 × 10−4 | ||
| Cor Total | 6.703 × 10−3 | 19 |
| Preparation Step | Fractions | IC50 Value (mg/mL) | Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DPPH | ●OH | |||
| Enzymatic hydrolysis | Hydrolysate | 0.721 ± 0.024 | 1.371 ± 0.178 | 100 |
| Ultrafiltration | U1 | 0.972 ± 0.151 | 1.495 ± 0.214 | 35.18 |
| U2 | 0.377 ± 0.013 | 0.882 ± 0.127 | ||
| Cation exchange chromatography | U2-S1 | 1.781 ± 0.048 | 1.689 ± 0.118 | 12.81 |
| U2-S2 | 0.289 ± 0.022 | 0.681 ± 0.078 | ||
| U2-S3 | 0.972 ± 0.053 | 0.920 ± 0.093 | ||
| Size exclusion chromatography | U2-S2-I | 0.263 ± 0.018 | 0.512 ± 0.055 | 12.68 |
| U2-S2-II | 4.832 ± 0.552 | 3.191 ± 0.323 | ||
| Source | Enzyme | Antioxidant Activity (DPPH) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salmon muscle | Protease from Pseudoalteromonas sp. SQN1 | IC50 = 0.51 mg/mL | |
| Scorpaena notata muscle | neutral serine protease | IC50 = 0.60 mg/mL | [22] |
| Croceine croaker muscle | pepsin and alcalase | IC50 = 1.35 mg/mL | [23] |
| Monkfish muscle | trypsin | IC50 = 1.40 mg/mL | [24] |
| Smooth hound muscle | gastrointestinal proteases | IC50 = 0.60 mg/mL | [25] |
| Sphyrna ewini muscle | papain | IC50 = 3.06 mg/mL | [26] |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, R.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, X.; Lei, M.; Chen, Y.; He, H. Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010004
Wu R, Chen L, Liu D, Huang J, Zhang J, Xiao X, Lei M, Chen Y, He H. Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Ribang, Leilei Chen, Dan Liu, Jiafeng Huang, Jiang Zhang, Xiao Xiao, Ming Lei, Yuelin Chen, and Hailun He. 2017. "Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases" Marine Drugs 15, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010004
APA StyleWu, R., Chen, L., Liu, D., Huang, J., Zhang, J., Xiao, X., Lei, M., Chen, Y., & He, H. (2017). Preparation of Antioxidant Peptides from Salmon Byproducts with Bacterial Extracellular Proteases. Marine Drugs, 15(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010004





