Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of 1
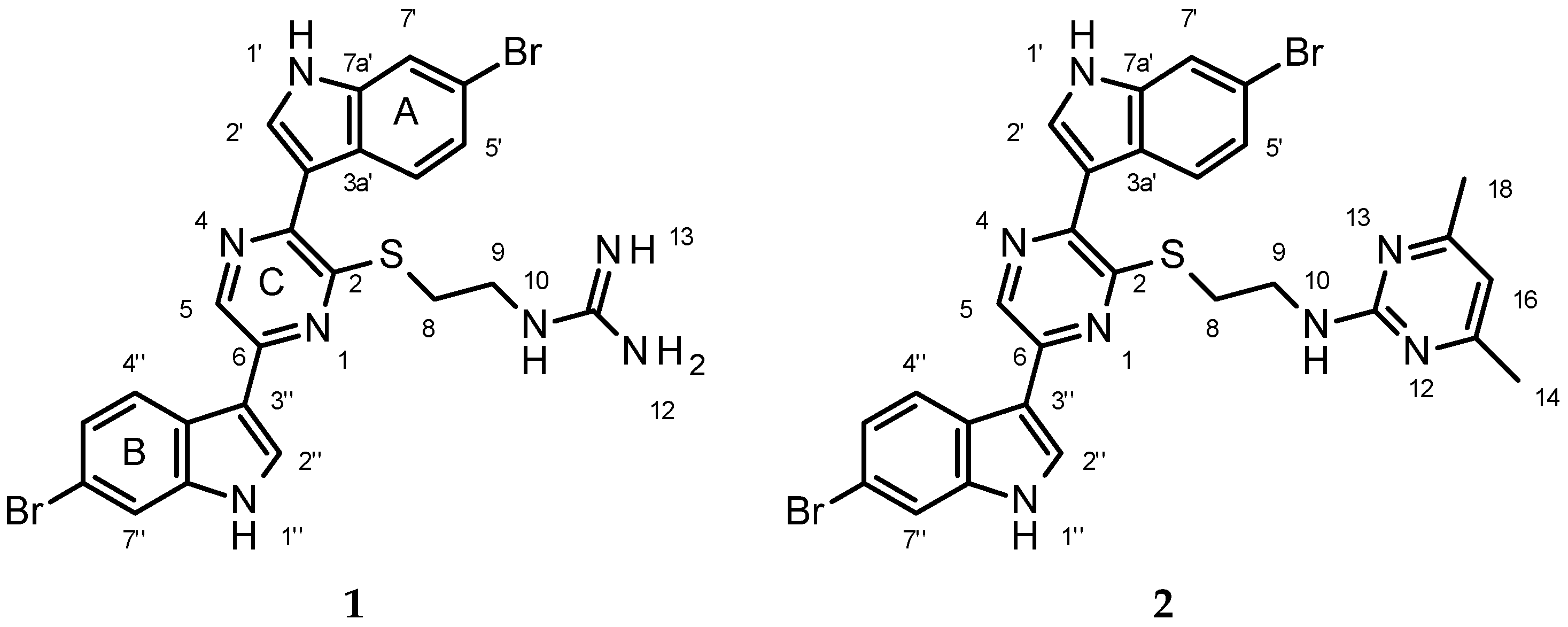
2.2. Structure Elucidation of 1
2.3. Biological Activity Observed for 1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedures
4.2. Biological Material
4.3. Isolation of Dragmacidin G (1)
4.4. Conversion of Dragmacidin G (1) to Pyrimidine Derivative (2)
4.5. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.6. Antibiotic Assays
4.6.1. Staphylococcus aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
4.6.2. M. tuberculosis Bioluminescent Growth Inhibition Assay
4.7. Resazurin-Based Cytotoxicity Assay against J774 Macrophage Cells
4.8. Anti-Plasmodial Assay
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartik, K.; Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Stoller, C.; Huysecom, J.; Vandevyver, G.; Ottinger, R. Topsentins, new toxic bis-indole alkaloids from the marine sponge Topsentia genitrix. Can. J. Chem. 1987, 65, 2118–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, B.; Sun, Q.; Yao, X.; Hong, J.; Lee, C.-O.; Cho, H.Y.; Jung, J.H. Bisindole Alkaloids of the Topsentin and Hamacanthin Classes from a Marine Sponge Spongosorites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujii, S.; Rinehart, K.L.; Gunasekera, S.P.; Kashman, Y.; Cross, S.S.; Lui, M.S.; Pomponi, S.A.; Diaz, M.C. Topsentin, bromotopsentin, and dihydrodeoxybromotopsentin: Antiviral and antitumor bis(indolyl)imidazoles from Caribbean deep-sea sponges of the family Halichondriidae. Structural and synthetic studies. J. Org. Chem. 1988, 53, 5446–5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemi, S.; Sun, H.H. Nortopsentins A, B, and C. Cytotoxic and antifungal imidazolediylbis[indoles] from the sponge Spongosorites ruetzleri. J. Org. Chem. 1991, 56, 4304–4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, S.; Roberts, B.F.; Wright, A.E.; Chakrabarti, D. The bis(indolyl)imidazole alkaloid nortopsentin A exhibits antiplasmodial activity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2362–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; McCarthy, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Hamacanthins A and B, new antifungal bis indole alkaloids from the deep-water marine sponge, Hamacantha sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 1437–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A.; Cross, S.S.; McCarthy, P. A new bis-(indole) alkaloid from a deep-water marine sponge of the genus Spongosorites. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 4772–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capon, R.J.; Rooney, F.; Murray, L.M.; Collins, E.; Sim, A.T.R.; Rostas, J.A.P.; Butler, M.S.; Carroll, A.R. Dragmacidins: New protein phosphatase inhibitors from a Southern Australian deep-water marine sponge, Spongosorites sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutignano, A.; Bifulco, G.; Bruno, I.; Casapullo, A.; Gomez-Paloma, L.; Riccio, R. Dragmacidin F: A new antiviral bromoindole alkaloid from the Mediterranean sponge Halicortex sp. Tetrahedron 2000, 56, 3743–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, D.; Wright, A. Screening Methods for Identifying Anti-Malarial Compounds from Marine Natural Products and Methods of Use Thereof for Treating Malaria. U.S. Patent 9,181,251, 28 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hitora, Y.; Takada, K.; Ise, Y.; Okada, S.; Matsunaga, S. Dragmacidins G and H, Bisindole Alkaloids Tethered by a Guanidino Ethylthiopyrazine Moiety, from a Lipastrotethya sp. Marine Sponge. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2973–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.C.; Pomponi, S.A.; van Soest, R.W.M. A systematic revision of the central west Atlantic halichondrida (Demospongiae, Porifera). Part III: Description of valid species. Sci. Mar. 1993, 57, 283–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kourany-Lefoll, E.; Pais, M.; Sevenet, T.; Guittet, E.; Montagnac, A.; Fontaine, C.; Guenard, D.; Adeline, M.T.; Debitus, C. Phloeodictines A and B: New antibacterial and cytotoxic bicyclic amidinium salts from the new caledonian sponge, Phloeodictyon sp. J. Org. Chem. 1992, 57, 3832–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanovic, M.V. 15N Nuclear magnetic resonance of some pyrazines, 1,2,4-triazines and their N-oxides. Correlation and interrelationship of 15N with 13C chemical shifts of π-deficient heterocyclic systems. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Spectrosc. 1984, 40, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, M.C.; Coburn, W.C., Jr.; Montgomery, J.A. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of some 2-, 6-, and 2,6-substituted purines. J. Magn. Reson. 1974, 15, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Zoraghi, R.; Campbell, S.; Kim, C.; Dullaghan, E.M.; Blair, L.M.; Gillard, R.M.; Reiner, N.E.; Sperry, J. Discovery of a 1,2-bis(3-indolyl)ethane that selectively inhibits the pyruvate kinase of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus over human isoforms. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 5059–5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoraghi, R.; Worrall, L.; See, R.H.; Strangman, W.; Popplewell, W.L.; Gong, H.; Samaai, T.; Swayze, R.D.; Kaur, S.; Vuckovic, M.; et al. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Pyruvate Kinase as a Target for Bis-indole Alkaloids with Antibacterial Activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44716–44725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.S.; Dullaghan, E.M.; Finlay, B.B.; Gong, H.; Reiner, N.E.; Jon Paul Selvam, J.; Thorson, L.M.; Campbell, S.; Vitko, N.; Richardson, A.R.; et al. Discovery and optimization of a new class of pyruvate kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutics for the treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 1708–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.-H.; Chen, C.; Wang, H.; Ye, W.-C.; Zhou, G.-X. Indole alkaloids from Alocasia macrorrhiza. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Soest, R.W.M.; Hooper, J.N.A. Systema Porifera: A Guide to the Classification of Sponges; Hooper, J.N.A., Van Soest, R.W.M., Eds.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2002; pp. 831–832. [Google Scholar]
- Blunt, J.W.; Calder, V.L.; Fenwick, G.D.; Lake, R.J.; McCombs, J.D.; Munro, M.H.G.; Perry, N.B. Reverse phase flash chromatography: A method for the rapid partitioning of natural product extracts. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 290–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekera, S.P.; Zuleta, I.A.; Longley, R.E.; Wright, A.E.; Pomponi, S.A. Discorhabdins S, T, and U, new cytotoxic pyrroloiminoquinones from a deep-water Caribbean sponge of the genus Batzella. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Atom | δC, Multiplicity | δN | δH (J in Hz) | COSY | 1H-13C HMBC b | 1H-15N HMBC c | NOESY |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 324 a | ||||||
| 2 | 150.1, C | ||||||
| 3 | 143.3, C | ||||||
| 4 | 299 a | ||||||
| 5 | 135.4, CH | 8.98, s | C2 (w), C3, C6, C3″ | N1, N4 | H2″, H4″ | ||
| 6 | 145.9, C | ||||||
| 8 | 28.7, CH2 | 3.56, m | C2, C9 | N10 | |||
| 9 | 40.2, CH2 | 3.54, m | H10 | C8, C11 | |||
| 10 | 80 | 7.93, bt (4.8) | H9ab | C8, C9, C11 | N12, N13 | H9ab | |
| 11 | 156.8, C | ||||||
| 12, 13 | 72 | ||||||
| 1′ | - | 136 | 11.82, bs | H2′ | C2′, C3′, C3a′, C7a′ | H2′, H7′ | |
| 2′ | 127.9, CH | 8.08, d (2.7) | H1′ | C3, C3′, C3a′, C7a′ | N1′ | H1′ | |
| 3′ | 111.8, C | ||||||
| 3a′ | 125.4, C | ||||||
| 4′ | 123.1, CH | 8.10, d (8.9) | H5′ | C6′, C7a′ | H5′ | ||
| 5′ | 122.8, CH | 7.25, dd (8.9 1.4) | H4′, H7′ | C3a′, C7′ | H4′ | ||
| 6′ | 114.83, C | ||||||
| 7′ d | 114.4, CH | 7.70, d (1.4) | H5′ | C3a′, C5′, C7a′ | N1′ | ||
| 7a′ | 137.1, C | ||||||
| 1″ | - | 138 | 11.95, bs | H2″ | C2″, C3″, C3a″, C7a″ | H2″, H7″ | |
| 2″ | 127.7, CH | 8.33, d (2.7) | H1″ | C6, C3″, C3a″, C7a″ | N1″ | H1″ | |
| 3″ | 112.6, C | ||||||
| 3a″ | 124.0, C | ||||||
| 4″ | 122.6, CH | 8.22, d (8.9) | H5″ | C3″, C6″, C7a″ | H5, H5″, H8ab | ||
| 5″ | 123.3, CH | 7.31, dd (8.9, 1.4) | H4″, H7″ | C3a″, C7″ | H4″ | ||
| 6″ | 114.78, C a | ||||||
| 7″ d | 114.74, CH a | 7.71, d (1.4) | H5″ | C3a″, C5″, C7a″ | N1″ | ||
| 7a″ | 137.9, C |
© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wright, A.E.; Killday, K.B.; Chakrabarti, D.; Guzmán, E.A.; Harmody, D.; McCarthy, P.J.; Pitts, T.; Pomponi, S.A.; Reed, J.K.; Roberts, B.F.; et al. Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010016
Wright AE, Killday KB, Chakrabarti D, Guzmán EA, Harmody D, McCarthy PJ, Pitts T, Pomponi SA, Reed JK, Roberts BF, et al. Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites. Marine Drugs. 2017; 15(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleWright, Amy E., K. Brian Killday, Debopam Chakrabarti, Esther A. Guzmán, Dedra Harmody, Peter J. McCarthy, Tara Pitts, Shirley A. Pomponi, John K. Reed, Bracken F. Roberts, and et al. 2017. "Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites" Marine Drugs 15, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010016
APA StyleWright, A. E., Killday, K. B., Chakrabarti, D., Guzmán, E. A., Harmody, D., McCarthy, P. J., Pitts, T., Pomponi, S. A., Reed, J. K., Roberts, B. F., Rodrigues Felix, C., & Rohde, K. H. (2017). Dragmacidin G, a Bioactive Bis-Indole Alkaloid from a Deep-Water Sponge of the Genus Spongosorites. Marine Drugs, 15(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/md15010016






