The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
2.2. Chemical Synthesis of Peptides
2.3. Oxidative Folding of Analogues Containing Two Disulfide Bonds
2.4. Plasmid Constructions
2.5. Cell Culture and Transient Expression in HEK293 Cells
2.6. Electrophysiology
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Synthesis and Oxidative Folding
3.2. Effect of the Analogues on rNaV1.4 Expressed in HEK293 Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermeling, D.P. Ziconotide, an intrathecally administered N-type calcium channel antagonist for the treatment of chronic pain. Pharmacotherapy 2005, 25, 1084–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callaghan, B.; Haythornthwaite, A.; Berecki, G.; Clark, R.J.; Craik, D.J.; Adams, D.J. Analgesic alpha-conotoxins Vc1.1 and Rg1A inhibit N-type calcium channels in rat sensory neurons via GABAB receptor activation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10943–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstens, B.B.; Clark, R.J.; Daly, N.L.; Harvey, P.J.; Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J. Engineering of conotoxins for the treatment of pain. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 4242–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, O.; McArthur, J.R.; Adams, D.J. Conotoxins targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channel subtypes: Potential analgesics? Toxins (Basel) 2012, 4, 1236–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, K.; Lipkind, G.; Fozzard, H.A.; French, R.J. Electrostatic and steric contributions to block of the skeletal muscle sodium channel by mu-conotoxin. J. Gen. Physiol. 2002, 119, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, Y.; Sato, K.; Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, Y.; Shimonishi, Y. Disulfide pairings in geographutoxin I, a peptide neurotoxin from Conus geographus. FEBS Lett. 1990, 264, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, R.S. Mu-conotoxins as leads in the development of new analgesics. Molecules 2010, 15, 2825–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, T.S.; Radic, Z.; Talley, T.T.; Jois, S.D.; Taylor, P.; Kini, R.M. Protein folding determinants: Structural features determining alternative disulfide pairing in alpha- and chi/lambda-conotoxins. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 3338–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gongora-Benitez, M.; Tulla-Puche, J.; Albericio, F. Multifaceted roles of disulfide bonds. Peptides as therapeutics. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 901–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savarin, P.; Romi-Lebrun, R.; Zinn-Justin, S.; Lebrun, B.; Nakajima, T.; Gilquin, B.; Menez, A. Structural and functional consequences of the presence of a fourth disulfide bridge in the scorpion short toxins: Solution structure of the potassium channel inhibitor HsTX1. Protein Sci. 1999, 8, 2672–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Liang, S.; Martin, L.; Gasparini, S.; Menez, A.; Vita, C. Role of disulfide bonds in folding and activity of leiurotoxin I: Just two disulfides suffice. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11488–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, T.S.; Zhang, M.M.; Walewska, A.; Gruszczynski, P.; Robertson, C.R.; Cheatham, T.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Olivera, B.M.; Bulaj, G. Structurally minimized mu-conotoxin analogues as sodium channel blockers: Implications for designing conopeptide-based therapeutics. ChemMedChem 2009, 4, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price-Carter, M.; Hull, M.S.; Goldenberg, D.P. Roles of individual disulfide bonds in the stability and folding of an omega-conotoxin. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 9851–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Gordon, D.; Heinemann, S.H. Modulation of cloned skeletal muscle sodium channels by the scorpion toxins Lqh II, Lqh III, and Lqh alphaIT. Pflugers Arch. 2000, 439, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leipold, E.; Markgraf, R.; Miloslavina, A.; Kijas, M.; Schirmeyer, J.; Imhof, D.; Heinemann, S.H. Molecular determinants for the subtype specificity of mu-conotoxin SIIIA targeting neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuropharmacology 2011, 61, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartier, G.E.; Yoshikami, D.; Gray, W.R.; Luo, S.; Olivera, B.M.; McIntosh, J.M. A new alpha-conotoxin which targets alpha3beta2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 7522–7528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cummins, T.R.; Aglieco, F.; Dib-Hajj, S.D. Critical molecular determinants of voltage-gated sodium channel sensitivity to mu-conotoxins GIIIA/B. Mol. Pharmacol. 2002, 61, 1192–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.A.; Sato, K.; Kodama, K.; Kohno, T.; Xue, T.; Tomaselli, G.F.; Marban, E. Charge conversion enables quantification of the proximity between a normally-neutral mu-conotoxin (GIIIA) site and the Na+ channel pore. FEBS Lett. 2002, 511, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Ishida, Y.; Wakamatsu, K.; Kato, R.; Honda, H.; Ohizumi, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Ohya, M.; Lancelin, J.M.; Kohda, D.; et al. Active site of mu-conotoxin GIIIA, a peptide blocker of muscle sodium channels. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 16989–16991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Becker, S.; Prusak-Sochaczewski, E.; Zamponi, G.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Gordon, R.D.; French, R.J. Action of derivatives of mu-conotoxin GIIIA on sodium channels. Single amino acid substitutions in the toxin separately affect association and dissociation rates. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 8229–8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakamatsu, K.; Kohda, D.; Hatanaka, H.; Lancelin, J.M.; Ishida, Y.; Oya, M.; Nakamura, H.; Inagaki, F.; Sato, K. Structure-activity relationships of mu-conotoxin GIIIA: Structure determination of active and inactive sodium channel blocker peptides by NMR and simulated annealing calculations. Biochemistry 1992, 31, 12577–12584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudley, S.C., Jr.; Chang, N.; Hall, J.; Lipkind, G.; Fozzard, H.A.; French, R.J. mu-conotoxin GIIIA interactions with the voltage-gated Na(+) channel predict a clockwise arrangement of the domains. J. Gen. Physiol. 2000, 116, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, G.; Aliste, M.P.; Tieleman, D.P.; French, R.J.; Dudley, S.C., Jr. Docking of mu-conotoxin GIIIA in the sodium channel outer vestibule. Channels (Austin) 2007, 1, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, T.; Ennis, I.L.; Sato, K.; French, R.J.; Li, R.A. Novel interactions identified between micro-Conotoxin and the Na+ channel domain I P-loop: Implications for toxin-pore binding geometry. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, S.; Kuyucak, S. Molecular dynamics study of binding of micro-conotoxin GIIIA to the voltage-gated sodium channel Na(v)1.4. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkosh, V.S.; Zhorov, B.S.; Tikhonov, D.B. Folding similarity of the outer pore region in prokaryotic and eukaryotic sodium channels revealed by docking of conotoxins GIIIA, PIIIA, and KIIIA in a NaVAb-based model of NaV1.4. J. Gen. Physiol. 2014, 144, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, S.; Kuyucak, S. Systematic study of binding of mu-conotoxins to the sodium channel NaV1.4. Toxins (Basel) 2014, 6, 3454–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietze, A.A.; Tietze, D.; Ohlenschlager, O.; Leipold, E.; Ullrich, F.; Kuhl, T.; Mischo, A.; Buntkowsky, G.; Gorlach, M.; Heinemann, S.H.; et al. Structurally diverse mu-conotoxin PIIIA isomers block sodium channel NaV1.4. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2012, 51, 4058–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shon, K.J.; Olivera, B.M.; Watkins, M.; Jacobsen, R.B.; Gray, W.R.; Floresca, C.Z.; Cruz, L.J.; Hillyard, D.R.; Brink, A.; Terlau, H.; et al. mu-Conotoxin PIIIA, a new peptide for discriminating among tetrodotoxin-sensitive Na channel subtypes. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4473–4481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Green, B.R.; Zhang, M.M.; Chhabra, S.; Robinson, S.D.; Wilson, M.J.; Redding, A.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Bulaj, G.; Norton, R.S. Interactions of disulfide-deficient selenocysteine analogs of mu-conotoxin BuIIIB with the alpha-subunit of the voltage-gated sodium channel subtype 1.3. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 2885–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.; Zhang, M.M.; Gupta, K.; Gajewiak, J.; Gulyas, J.; Balaram, P.; Rivier, J.E.; Olivera, B.M.; Yoshikami, D.; Bulaj, G.; et al. Mammalian neuronal sodium channel blocker mu-conotoxin BuIIIB has a structured N-terminus that influences potency. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1344–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


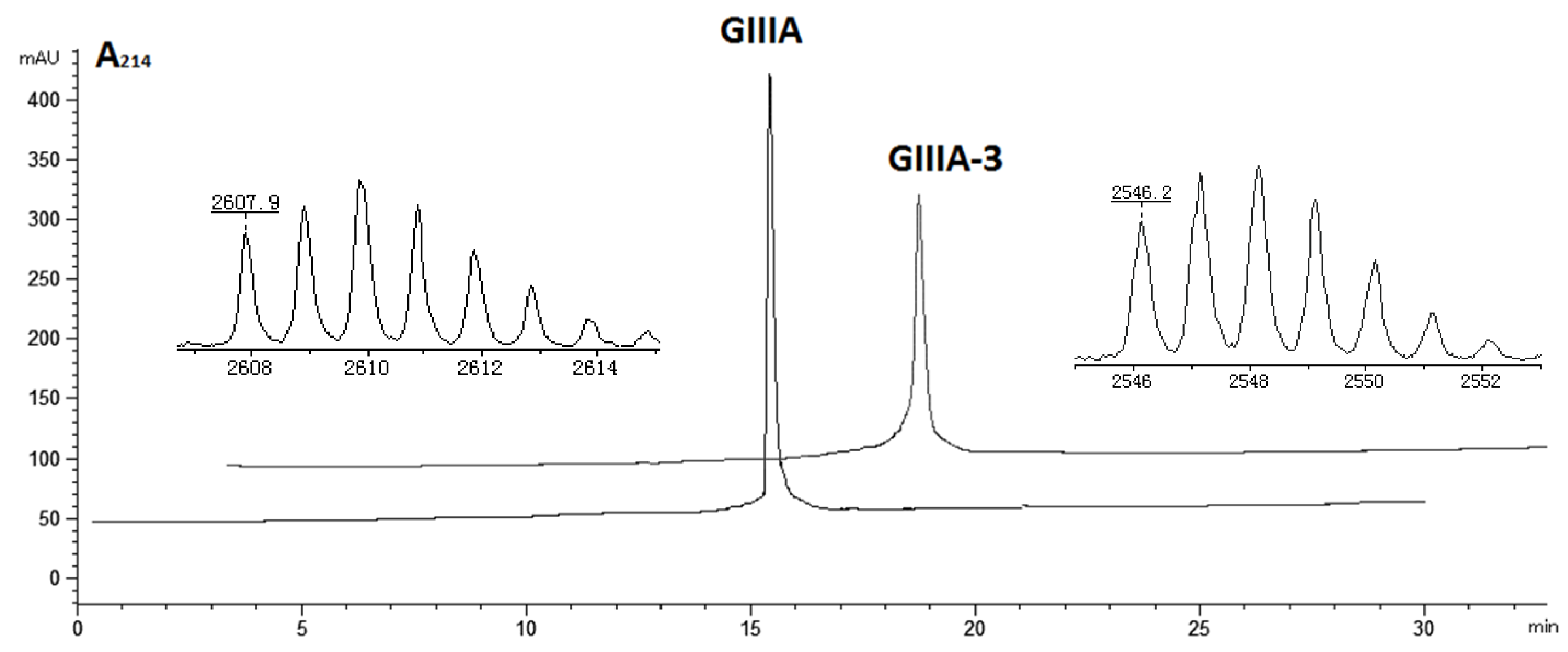

| Peptide # | Sequence | Cysteine Frame |
|---|---|---|
| GIIIA | RDCCTOOKKCKDRQCKOQRCCA * |  |
| GIIIA-1 | RDACTOOKKCKDRQAKOQRCCA * |  |
| GIIIA-2 | RDCATOOKKCKDRQCKOQRACA * |  |
| GIIIA-3 | RDCCTOOKKAKDRQCKOQRCAA * |  |
| GIIIA-12 | RDAATOOKKCKDRQAKOQRACA * |  |
| GIIIA-13 | RDACTOOKKAKDRQAKOQRCAA * |  |
| GIIIA-23 | RDCATOOKKAKDRQCKOQRAAA * |  |
| GIIIA-123 | RDAATOOKKAKDRQAKOQRAAA * |  |
| Peptides | IC50 (μM) * | Inhibitory Potency |
|---|---|---|
| GIIIA | 0.069 ± 0.005 | 1 |
| GIIIA-1 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | 0.033 |
| GIIIA-2 | 3.3 ± 0.2 | 0.021 |
| GIIIA-3 | 15.8 ± 0.8 | 0.005 |
| GIIIA-12 | >100 | <0.0007 |
| GIIIA-13 | >100 | <0.0007 |
| GIIIA-23 | >100 | <0.0007 |
| GIIIA-123 | >100 | <0.0007 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, P.; Wang, K.; Dai, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H.; Fan, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, J. The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110213
Han P, Wang K, Dai X, Cao Y, Liu S, Jiang H, Fan C, Wu W, Chen J. The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(11):213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110213
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Penggang, Kang Wang, Xiandong Dai, Ying Cao, Shangyi Liu, Hui Jiang, Chongxu Fan, Wenjian Wu, and Jisheng Chen. 2016. "The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4" Marine Drugs 14, no. 11: 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110213
APA StyleHan, P., Wang, K., Dai, X., Cao, Y., Liu, S., Jiang, H., Fan, C., Wu, W., & Chen, J. (2016). The Role of Individual Disulfide Bonds of μ-Conotoxin GIIIA in the Inhibition of NaV1.4. Marine Drugs, 14(11), 213. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14110213





