Natural Products from Marine Fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Secondary Metabolites from Penicillium Species
3. Fungal Diversity in the Marine Environment
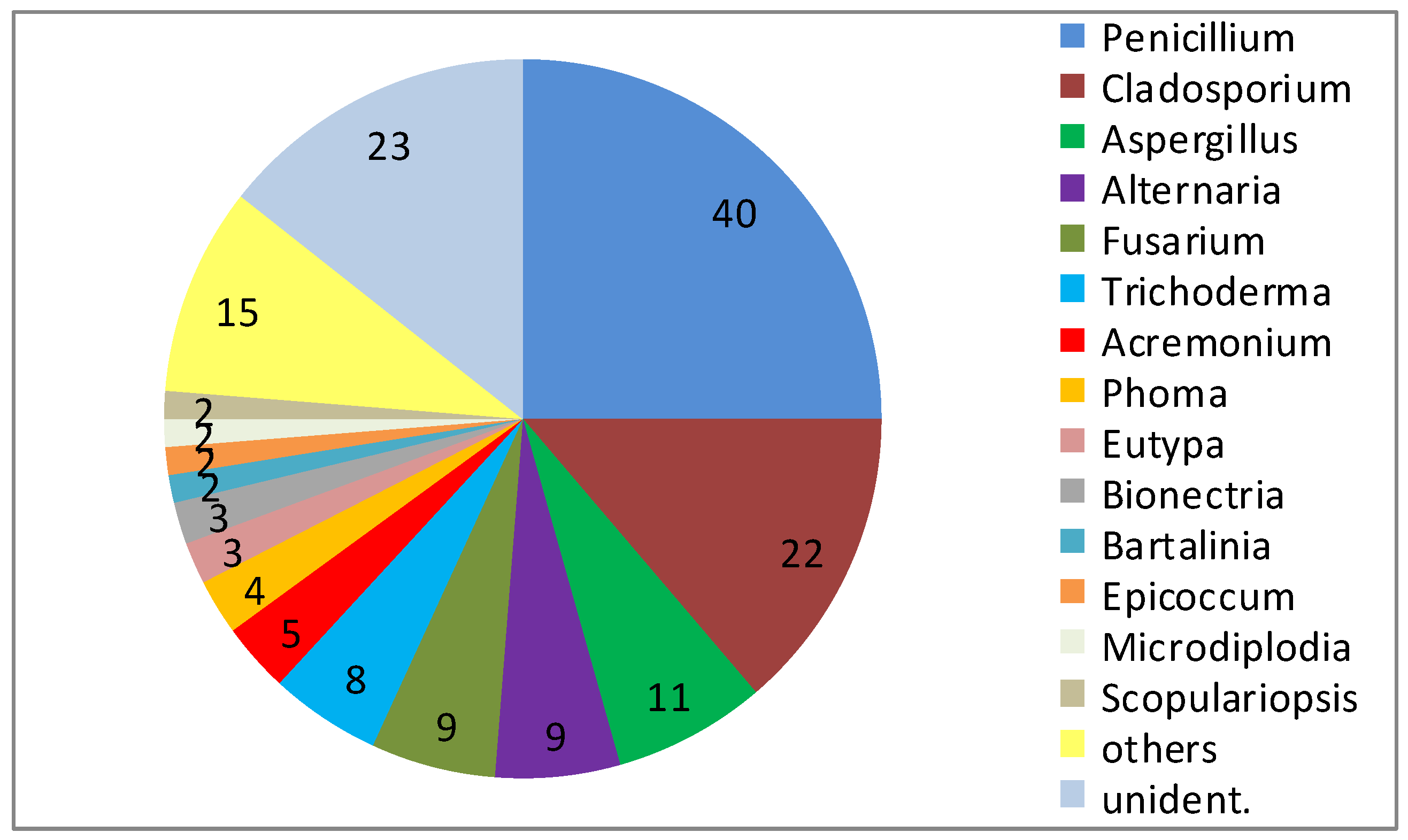

4. New Metabolites from Marine Fungi
4.1. Trichoderma sp. Strain MF106
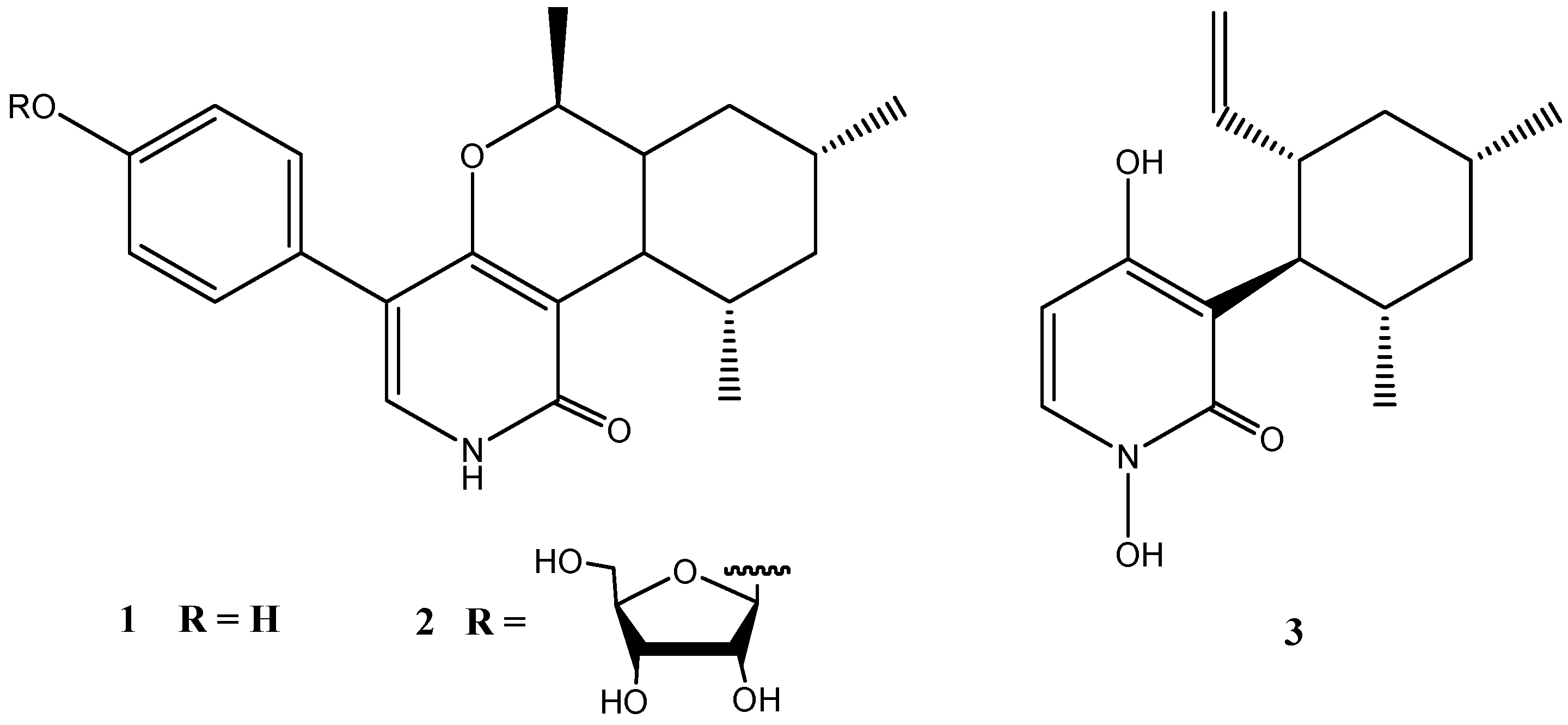
4.2. Stachybotrys sp. Strain MF347

4.3. Talaromyces sp. Strain LF458
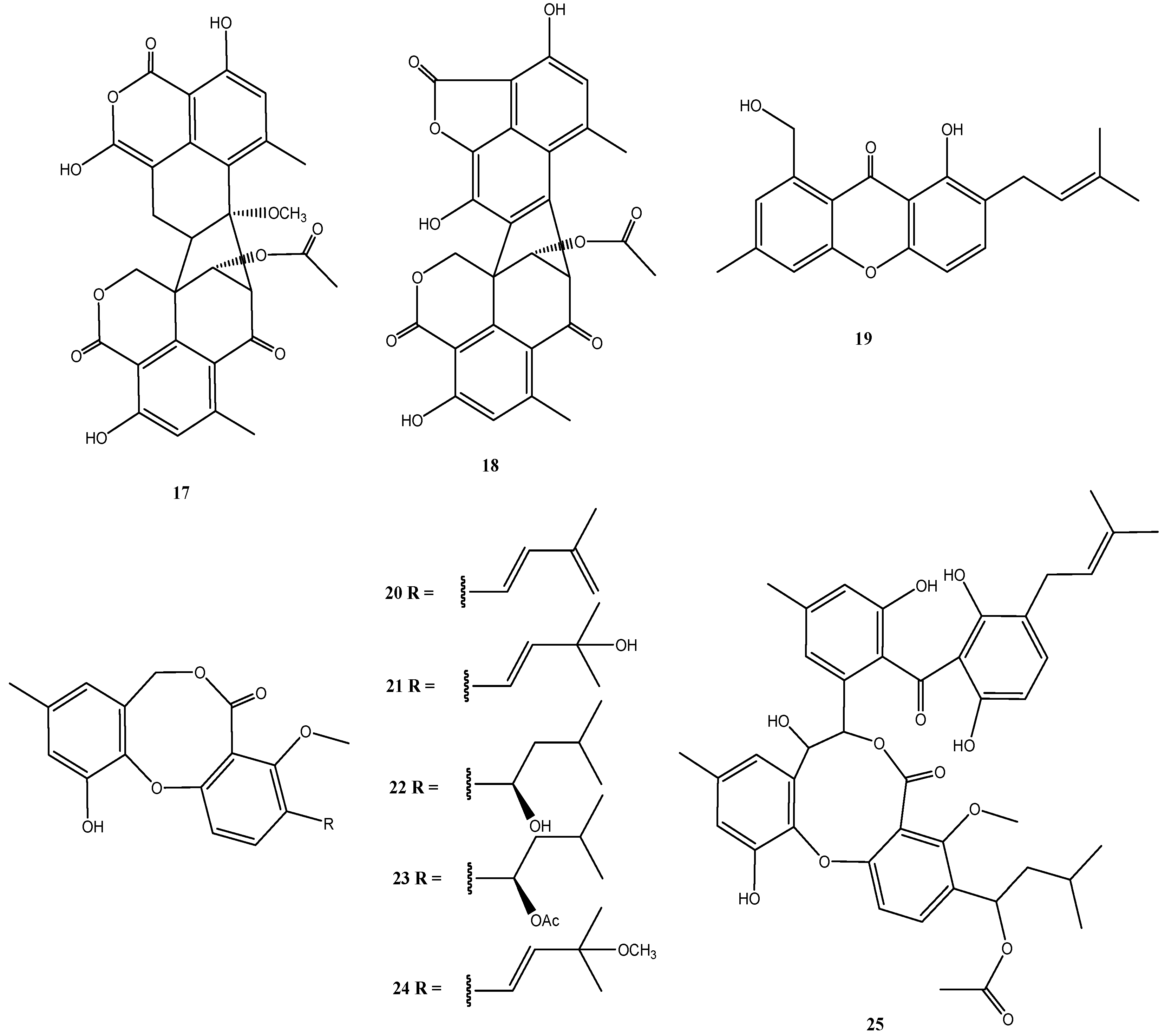
4.4. Calcarisporium sp. Strain KF525
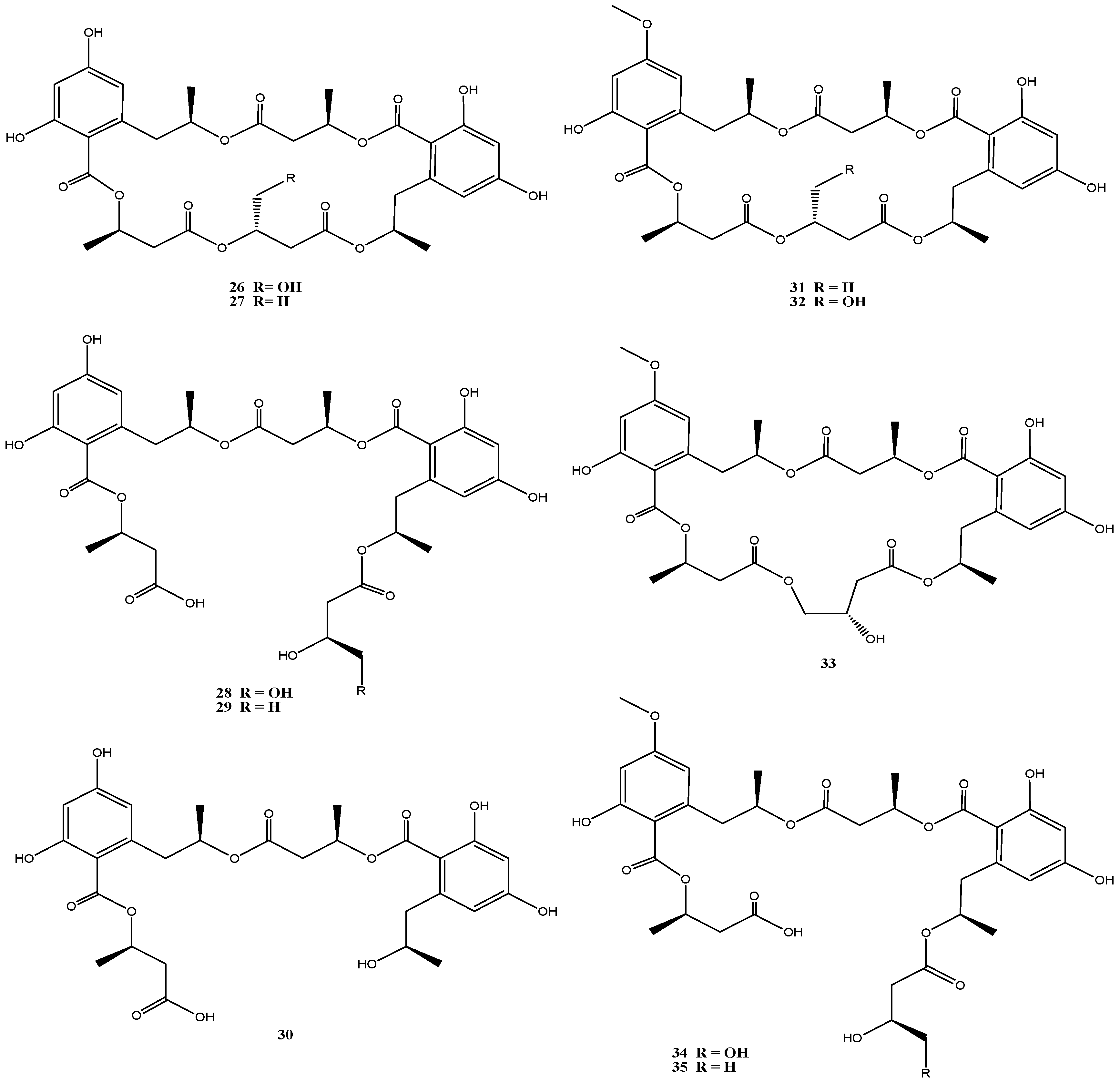
4.5. Bartalinia robillardoides Strain LF550
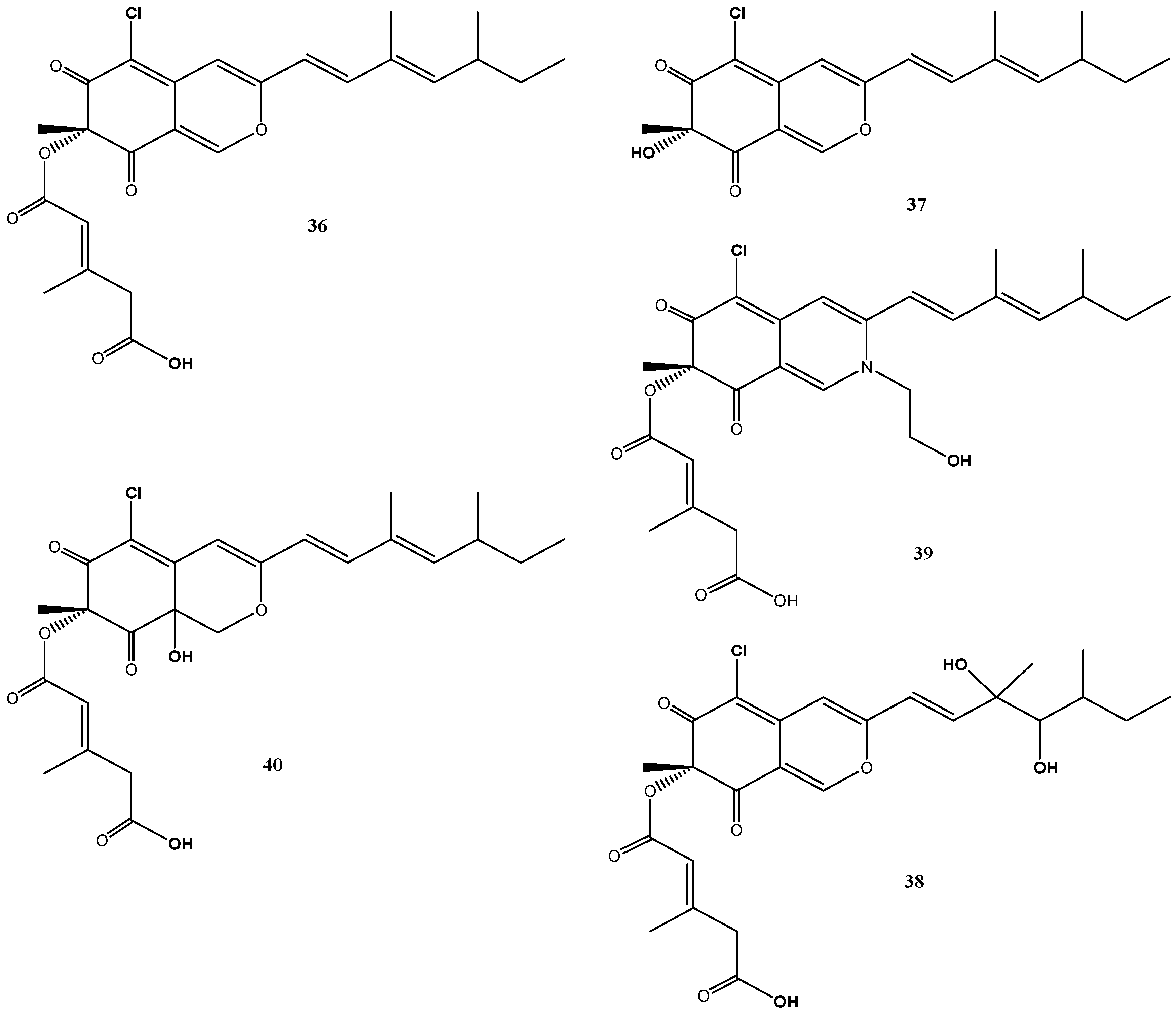
4.6. Cladosporium sp. Strain KF501
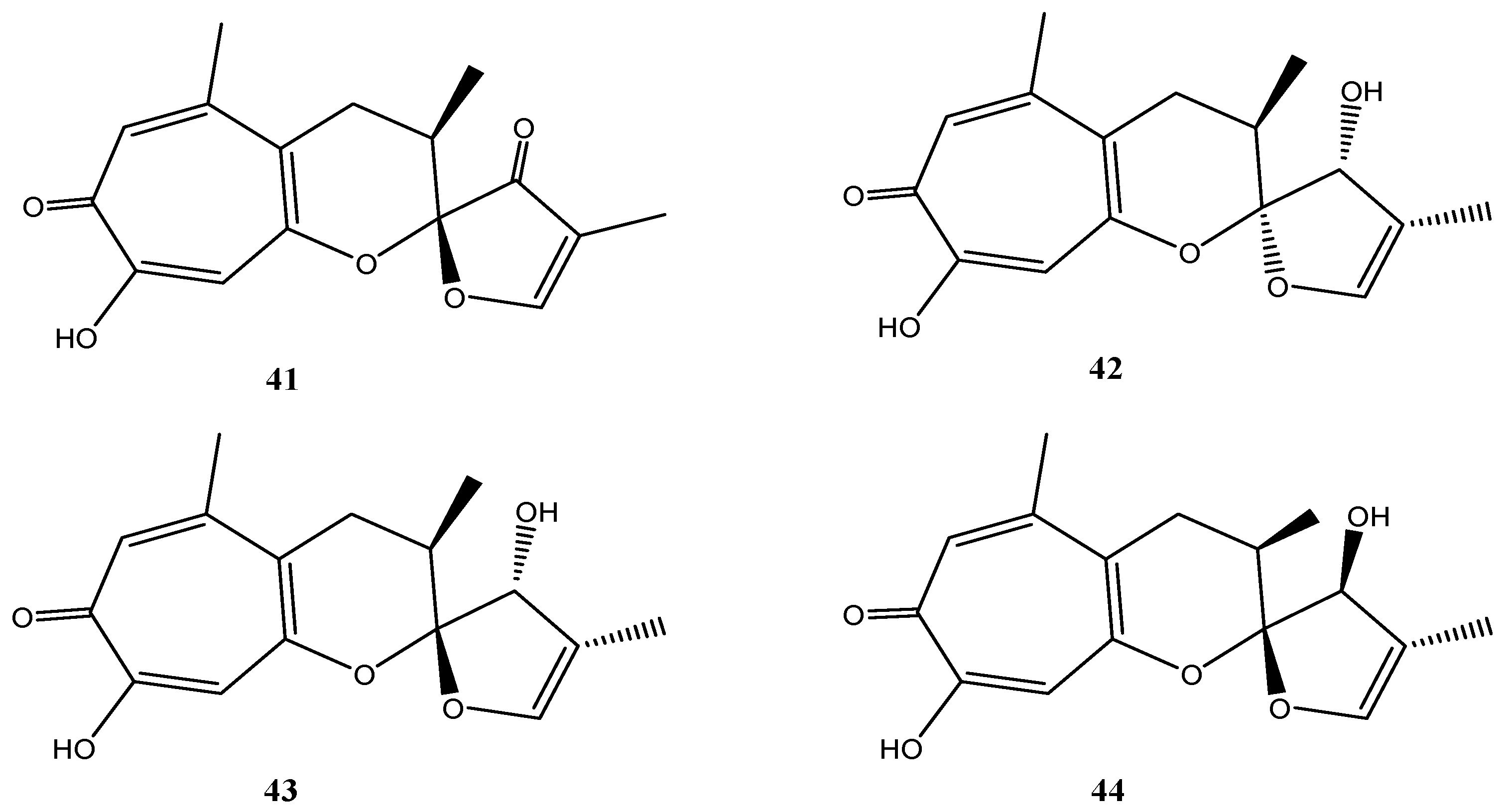
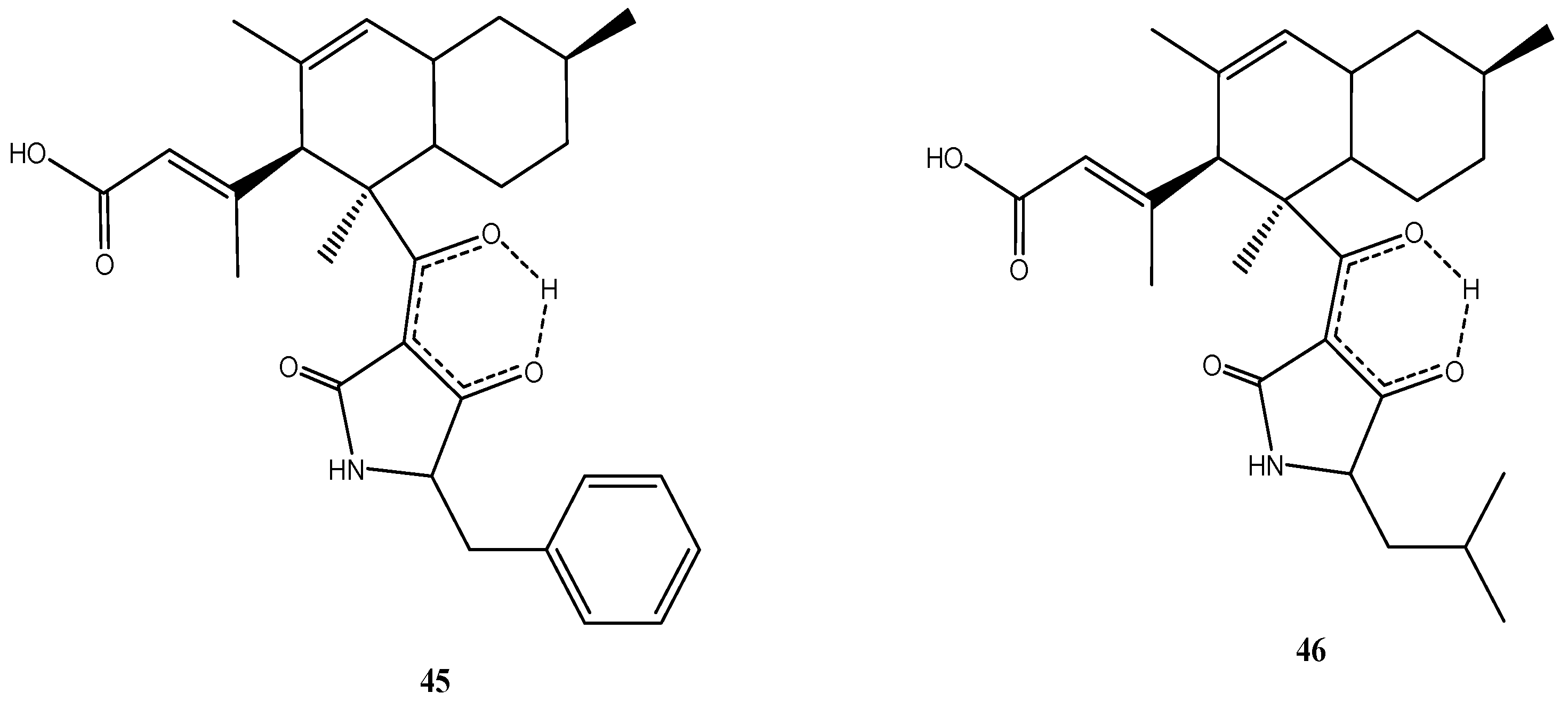
4.7. Massariosphaeria typhicola Strain KF970
5. Conclusions
- -
- Despite the fact that natural products from some fungal genera, in particular Penicillium and Aspergillus, have been often and intensively studied, there is still a great potential of secondary metabolites produced by these fungi, which has not yet been fully explored.
- -
- Much of the fungal diversity and the large potential of secondary metabolites of the untapped diversity of fungi in the marine environment still is to be discovered.
- -
- Much of the genomic/genetic potential of secondary metabolites of cultured fungi is not produced under standard culture conditions. In particular, changes in media and culture conditions often change the metabolite profiles and are likely to increase the number of known products from the fungi. In addition, other methods such as cocultivation with other fungi or bacteria or the use of epigenetic modulators may stimulate biosynthesis of the “hidden genomic potential”.
- -
- It has been demonstrated that the production of “families“ of secondary metabolites of structurally related derivatives, which often reveal significant differences in bioactivities, is common to many fungi. Because already small structural changes can be highly effective in regard to the bioactivity, it is important to study the full spectrum of structural variation offered by the fungi in order to unravel their biotechnological potential.
- -
- The multitude of natural derivatives of individual fungi and their bioactivities should be carefully explored.
- -
- Biosynthetic pathways and their regulation need to be studied to conclude on explanations for the formation of multiple derivatives.
- -
- The evolution of biosynthetic pathways of secondary metabolites should be systematically explored in respect to the presence of new biosynthetic gene clusters, in particular by use of the growing resource of fungal genome sequences.
- -
- Genus- and species-specific metabolite profiles need to be elaborated using metabolomic and genomic approaches.
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bringmann, G.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Lang, G.; Schmitt, S.; Stöhr, R.; Wiese, J.; Nagel, K.; Imhoff, J.F. Large scale biotechnological production of the antileukemic marine natural product sorbicillactone A. Mar. Drugs 2007, 5, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiese, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Blümel, M.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Phylogenetic identification of fungi isolated from the marine sponge Tethya aurantium and identification of their secondary metabolites. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 561–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, G.; Wiese, J.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. New pentaenes from the sponge-derived marine fungus Penicillium rugulosum: Structure determination and biosynthetic studies. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 11844–11849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Mu, J.; Feng, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gu, P.J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.F.; Zhu, Y.H. Broad-spectrum antimicrobial epiphytic and endophytic fungi from marine organisms: Isolation, bioassay and taxonomy. Mar. Drugs 2009, 7, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz, Z.; Komon-Zelazowska, M.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Aveskamp, M.M.; Schnaiderman, A.; Aluma, A.; Carmeli, S.; Ilan, M.; Yarden, O. Diversity and potential antifungal properties of fungi associated with a Mediterranean sponge. Fung. Divers. 2010, 42, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rateb, M.E.; Ebel, R. Secondary metabolites of fungi from marine habitats. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 290–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugni, T.S.; Ireland, C.M. Marine-derived fungi: A chemically and biologically diverse group of microorganisms. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Calvez, T.; Burgaud, G.; Mahe, S.; Barbier, G.; Vandenkoornhuyse, P. Fungal diversity in deep-sea hydrothermal ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6415–6421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenical, W.; Jensen, P.R. Marine microorganisms: A new biomedical resource. In Marine Biotechnology; Attaway, D.H., Zaborsky, O.R., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; Volume 1, pp. 419–457. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.; Ali, M.S.; Hussain, S.; Asharaf, M.; Lee, Y.S. Marine natural products of fungal origin. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2007, 24, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munro, M.H.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 116–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J. Biomining the microbial treasures of the ocean: New natural products. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-T.; Xue, Y.-R.; Liu, C.-H. A brief review of bioactive metabolites derived from deep-sea fungi. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4594–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Gulder, T.A.M.; Tsurata, H.; Mühlbacher, J.; Maksimenka, K.; Steffens, S.; Schaumann, K.; Stöhr, R.; Wiese, J.; et al. The first sorbicillinoid alkaloids, sorbicillacton A and B, from a sponge-derived Penicillium chrysogenum. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 7252–7265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Lang, G.; Bruhn, T.; Schäffler, K.; Steffens, S.; Schmaljohann, R.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Sorbifuranones A–C, sorbicillinoid metabolites from Penicillium strains isolated from Mediterranean sponges. Tetrahedron 2010, 66, 9894–9901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, D.; Ohlendorf, B.; Zinecker, H.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Eutypoids B−E produced by a Penicillium sp. strain from the North Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coghlan, M.P.; Culbert, A.A.; Cross, D.A.; Corcoran, S.L.; Yates, J.W.; Pearce, N.J.; Rausch, O.L.; Murphy, G.J.; Carter, P.S.; Cox, L.R.; et al. Selective small molecule inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 modulate glycogen metabolism and gene transcription. Chem. Biol. 2000, 7, 793–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P. Phylogenetic diversity of culturable fungi associated with the Hawaiian sponges Suberites zeteki and Gelliodes fibrosa. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2008, 93, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höller, U.; Wright, A.D.; Matthée, G.F.; König, G.M.; Draeger, S.; Aust, H.J.; Schulz, B. Fungi from marine sponges: Diversity, biological activity and secondary metabolites. Mycol. Res. 2000, 104, 1354–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indriani, I.D. Biodiversity of Marine-Derived Fungi and Identification of their Metabolites. Ph.D. Thesis, University Düsseldorf, Düsseldorf, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Van den Berg, M.A.; Albang, R.; Albermann, K.; Badger, J.H.; Daran, J.-M.; Driessen, A.J.M.; Garcia-Estrada, C.; Fedorova, N.D.; Harris, D.M.; Heijne, W.H.M.; et al. Genome sequencing and analysis of the filamentous fungus Penicillium chrysogenum. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.F.; Somoza, A.D.; Keller, N.P.; Wang, C.C.C. Advances in Aspergillus secondary metabolite research in the post-genomic era. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulder, T.A.M.; Hong, H.; Correa, J.; Egereva, E.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F.; Gross, H. Isolation, structure elucidation and total synthesis of lajollamides A–D from the marine fungus Asteromyces cruciatus. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2912–2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imhoff, J.F.; Schmaljohann, R.; Wiese, J. GEOMAR Helmholtz Center for Ocean Research, Kiel, Germany. Unpublished work. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Thiel, V.; Neulinger, S.C.; Staufenberger, T.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Spatial distribution of sponge-associated bacteria in the Mediterranean sponge Tethya aurantium. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007, 59, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Lang, G.; Kajahn, I.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Scopularides A and B, cyclodepsipeptides from a marine sponge-derived fungus, Scopulariopsis brevicaulis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1052–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, N.; Ohlendorf, B.; Erhard, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Helicusin E, Isochromophilone X and isochromophilone XI: New chloroazaphilones produced by the fungus Bartalinia robillardoides strain LF550. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 800–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Oesker, V.; Wiese, J.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Two new pyridones produced by a marine fungus Trichoderma sp. strain MF106. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Oesker, V.; Wiese, J.; Malien, S.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Spirocyclic drimanes from the marine fungus Stachybotrys sp. strain MF347. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1924–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Ohlendorf, B.; Oesker, V.; Wiese, J.; Schmaljohann, R.; Malien, S.; Imhoff, J.F. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the marine fungus Talaromyces sp. strain LF458. Mar. Biotechnol. 2015, 17, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silber, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Labes, A.; Näther, C.; Imhoff, J.F. Calcaripeptides A–C, cyclodepsipeptides from a Calcarisporium strain. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silber, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Labes, A.; Erhard, A.; Imhoff, J.F. Calcarides A–E, antibacterial macrocyclic and linear polyesters from a Calcarisporium strain. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 3309–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silber, J.; Ohlendorf, B.; Labes, A.; Erhard, A.; Näther, C.; Imhoff, J.F. Malettinin E, an antimicrobial tropolone produced by a marine Cladosporium strain. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wiese, J.; Labes, A.; Kramer, A.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Lindgomycin, an unusual antibiotic polyketide from a marine fungus of the Lindgomycetaceae. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4617–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, F.; Dai, H.; Tong, Y.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Sun, N.; Liu, X.; Bian, J.; Liu, M.; Gao, H.; et al. Trichodermaketones A–D and 7-O-methylkoninginin D from the marine fungus Trichoderma koningii. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 806–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruksakorn, P.; Arai, M.; Kotoku, N.; Vilchèze, C.; Baughn, A.D.; Moodley, P.; Jacobs, W.R., Jr.; Kobayashi, M. Trichoderins, novel aminolipopeptides from a marine sponge-derived Trichoderma sp., are active against dormant mycobacteria. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3658–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garo, E.; Starks, C.M.; Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, J. Trichodermamides A and B, cytotoxic modified dipeptides from the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma virens. J. Nat. Prod. 2003, 66, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamthong, N.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Tadpetch, K.; Kaewpet, M.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J. Tetrahydroanthraquinone and xanthone derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Trichoderma aureoviride PSU-F95. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, N.; Roullier, C.; Petit, K.; Sallenave-Namont, C.; Grovel, O.; Pouchus, Y.F. Marine-Derived Trichoderma: A source of new bioactive metabolites. In Trichoderma: Biology and Applications; Mukherjee, P.K., Horwitz, B.A., Singh, U.S., Mukherjee, M., Schmoll, M., Eds.; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2013; pp. 247–279. [Google Scholar]
- Crous, P.W.; Gams, W.; Stalpers, J.A.; Robert, V.; Stegehuis, G. MycoBank: An online initiative to launch mycology into the 21st century. Stud. Mycol. 2004, 50, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Das, S.; Sabat, J.; Basak, U.C. Isolation, identification and growth of Stachybotrys sp. obtained from mangrove ecosystem of Bhitarkanika, Orissa. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 2, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis, B.B.; Salemme, J.; Morais, A. Stachybotrys toxins. 1. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaise, H.; Shinohara, M.; Miyazaki, W.; Izawa, T.; Nakano, Y.; Sugawara, M.; Sugiura, K. Structure of K-76, a complement inhibitor produced by Stachybotrys complementi nov. sp. K-76. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1979, 16, 726–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, K.; Nakamura, M.; Hayashi, M.; Yaginuma, S.; Yamamoto, S.; Furihara, K.; Shiin-Ya, K.; Seto, H. Stachybocins, novel endothelin receptor antagonists, produced by Stachybotrys sp. M6222. II. Structure determination of stachybocins A, B and C. J. Antibiot. 1995, 48, 1396–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vázqueza, M.J.; Vegad, A.; Rivera-Sagredoe, A.; Jiménez-Alfarob, M.D.; Dı́ezb, E.; Hueso-Rodrı́guezc, J.A. Novel sesquiterpenoids as tyrosine kinase inhibitors produced by Stachybotrys chartarum. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domsch, K.-H.; Gams, W.; Anderson, T.-H. Compendium of Soil Fungi; IHW-Verlag: Eching, Gemany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Seydametova, E.; Salihon, J.; Zainol, N.; Convey, P. Production of Lovastatin by Penicillium spp. soil microfungi. Int. J. Chem. Eng. Appl. 2012, 3, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reenen-Hoekstra, E.S.; Frisvad, J.C.; Samson, R.A.; Stolk, A.C. The Penicillium funiculosum complex—Well defined species and problematic taxa. In Modern Concepts in Penicillium and Aspergillus Classification; Samson, R.A., Pitt, J.I., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 173–192. [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger, W.; Hauser, D. Isolierung und Strukturaufklärung von 11-Desacetoxy-wortmannin. Helv. Chim. Acta 1973, 56, 2901–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shope, R.E. An antiviral substance from Penicillium funiculosum. I. Effect upon injection in mice with swine influenza virus and Columbia SK encephalomyelitis virus. J. Exp. Med. 1953, 97, 601–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoletti, R.; de Stefano, M.; de Stefano, S.; Trincone, A.; Marziano, F. Antagonism against Rhizoctonia solani and fungitoxic metabolite production by some Penicillium isolates. Mycopathologia 2004, 158, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.-H.; Li, X.-M.; Li, C.-S.; Ji, N.-Y.; Wang, B.-G. Secondary metabolites from Penicillium pinophilum SD-272, a marine sediment-derived fungus. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2230–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, K.; Abe, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Mori, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Shiomi, K.; Omura, S.; Masuma, R. Enhancement of metabolites productivity of Penicillium pinophilum FKI-5653, by co-culture with Trichoderma harzianum FKI-5655. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Okuyama, E. Isolation and structures of oxaphenalenone dimers from Talaromyces bacillosporus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1980, 28, 3649–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsebai, M.F.; Kehraus, S.; Lindequist, U.; Sasse, F.; Shaaban, S.; Cütscho, M.; Josten, M.; Sahl, H.G.; König, G.M. Antimicrobial phenalenone derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Coniothyrium cereal. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomoda, H.; Tabata, N.; Masuma, R.; Si, S.Y.; Omura, S. Erabulenols, inhibitors of cholesteryl ester transfer protein produced by Penicillium sp. FO-5637. I. Production, isolation and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Yang, J.; Miao, C.-P.; Yan, Y.; Ma, Y.-T.; Li, X.-N.; Zhao, L.-X.; Huang, S.-X. New duclauxamide from Penicillium manginii YIM PH30375 and structure revision of the duclauxin family. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, B.C. Hyphomycetes from Manitoba and Saskatchewan, Canada; Commonwealth Mycological Institute: Surrey, UK, 1973; pp. 1–143. [Google Scholar]
- Somrithipol, S.; Jones, E.B.G. Calcarisporium phaeopodium sp. nov., a new hyphomycete from Thailand. Sydowia 2006, 58, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.L.; Song, Y.C.; Tan, R.X. A potent feed preservative candidate produced by Calcarisporium sp., an endophyte residing in stargrass (Cynodon dactylon). J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, C.L.; Pady, S.M.; Rogerson, C.T.; Ouye, L.G. Kansas aeromycology II. Materials, methods, and general results. Trans. Kans. Acad. Sci. 1959, 62, 184–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P. Calcarisporium arbuscula living as an endophyte in apparently healthy sporophores of Russula and Lactarius. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1955, 38, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlingmann, G.; Milne, L.; Carter, G.T. Isolation and identification of antifungal polyesters from the marine fungus Hypoxylon oceanicum LL-15G256. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6825–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinholt, J.; Jensen, G.W.; Nielsen, R.I.; Olsen, C.E.; Frisvad, J.C. Antifungal macrocyclic polylactones from Penicillium verruculosum. J. Antibiot. 1993, 46, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Maruhashi, M.; Sakai, N.; Mizoue, K.; Hanada, K. NG-011 and NG-012, novel potentiators of nerve growth factor. I. Taxonomy, isolation, and physico-chemical and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 1992, 45, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Vijayakumar, E.K.S.; Ganguli, B.N.; Fehlhaber, H.-W. Orbuticin, a new secondary metabolite from Acremonium butyri. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 1186–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Tomoda, H.; Okuda, T.; Wang, H.; Tabata, N.; Masuma, R.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Omura, S. Funicone-related compounds, potentiators of antifungal miconazole activity, produced by Talaromyces flavus FKI-0076. J. Antibiot. 2002, 55, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.-Y.; Liu, R.; Jiang, M.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Niu, Y.; Zhu, Y.-C.; Dong, Z.-J.; Liu, J.-K. Two new cleistanthane diterpenes and a new isocoumarine from cultures of the basidiomycete Albatrellus confluens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 975–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangadevi, V.; Muthumary, J. Taxol, an anticancer drug produced by an endophytic fungus Bartalinia robillardoides Tassi, isolated from a medicinal plant, Aegle marmelos Correa ex Roxb. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, E.; Fujimoto, H.; Baba, M.; Yamazaki, M. Four new chlorinated azaphilones, helicusins A–D, closely related to 7-epi-sclerotiorin, from an ascomycetous fungus, Talaromyces helicus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 43, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Takayanagi, H.; Matsuzaki, K.; Tanaka, H.; Furuhata, K.; Omura, S. Synthesis and inhibitory activities of isochromophilone analogues against gp120-CD4 binding. J. Antibiot. 1996, 49, 689–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmanova, N.; Schultze, W.; Ayoub, N. Azaphilones: A class of fungal metabolites with diverse biological activities. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 315–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bensch, K.; Braun, U.; Groenewald, J.Z.; Crous, P.W. The genus Cladosporium. Stud. Mycol. 2012, 72, 1–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoe, T.; Okada, H.; Itabashi, T.; Nozawa, K.; Okada, K.; de Campos Takaki, G.M.; Fukushima, K.; Miyaji, M.; Kawai, K. A new pentanorlanostane derivative, cladosporide A, as a characteristic antifungal agent against Aspergillus fumigatus, isolated from Cladosporium sp. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoe, T.; Okamoto, S.; Nozawa, K.; Kawai, K.-I.; Okada, K.; de Campos Takaki, G.M.; Fukushima, K.; Miyaji, M. New pentanorlanostane derivatives, cladosporide B–D, as characteristic antifungal agents against Aspergillus fumigatus, isolated from Cladosporium sp. J. Antibiot. 2001, 54, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sassa, T. Cotylenins, leaf growth substances produced by a fungus. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1971, 35, 1415–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassa, T.; Togashi, M.; Kitaguchi, T. The structures of cotylenins A, B, C, D and E. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1975, 39, 1735–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.; Ando, K.; Nakano, H.; Iida, T.; Ohno, H.; Morimoto, M.; Karaoki, T. Calphostins (UCN-1028), novel and specific inhibitors of protein kinase C.I. Fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological activities. J. Antibiot. 1989, 42, 1470–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, P.M.; van Walbeek, W.; MacLean, W.M. Cladosporin, a new antifungal metabolite from Cladosporium cladosporioides. J. Antibiot. 1971, 24, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anke, H.; Zähner, H.; König, W.A. Metabolic products of microorganisms. 170. On the antibiotic activity of cladosporin. Arch. Microbiol. 1978, 116, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grove, J.F.; Pople, M. The insecticidal activity of some fungal dihydroisocoumarins. Mycopathologia 1981, 76, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, J.P.; Cutler, H.G.; Crumley, F.G.; Cox, R.H.; Davis, E.E.; Thean, J.E. Plant growth regulatory effects and stereochemistry of cladosporin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1981, 29, 853–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, H.; Fujimaki, T.; Okuyama, E.; Yamazaki, M. Immunomodulatory constituents from an ascomycete, Microascus tardifaciens. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1999, 47, 1426–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angawi, R.F.; Swenson, D.C.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T. Malettinin A: A new antifungal tropolone from an unidentified fungal colonist of Hypoxylon stromata (NRRL 29110). Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 7593–7596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angawi, R.F.; Swenson, D.C.; Gloer, J.B.; Wicklow, D.T. Malettinins B–D: New polyketide metabolites from an unidentified fungal colonist of Hypoxylon stromata (NRRL 29110). J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onydeka, J.G.; Smith, S.K.; Zink, D.L.; Vicente, F.; Basilio, A.; Bills, G.F. Isolation, structure elucidation and antibacterial activity of a new tetramic acid, ascosetin. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royles, B.J.L. Naturally occurring tetramic acids: Structure, isolation, and synthesis. Chem. Rev. 1995, 95, 1981–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfori, E.C.; Bamba, T.; Kajiyama, S.; Fukusaki, E.; Kobayashi, A. Biosynthetic studies of the tetramic acid antibiotic trichosetin. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6655–6658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowery, C.A.; Park, J.; Gloeckner, C.; Meijler, M.M.; Mueller, R.S.; Boshoff, H.I.; Ulrich, R.L.; Barry, C.E., III; Bartlett, D.H.; Kravchenko, V.V.; et al. Defining the mode of action of tetramic acid antibacterials derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing signals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 14473–14479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Imhoff, J.F. Natural Products from Marine Fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010019
Imhoff JF. Natural Products from Marine Fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource. Marine Drugs. 2016; 14(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleImhoff, Johannes F. 2016. "Natural Products from Marine Fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource" Marine Drugs 14, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010019
APA StyleImhoff, J. F. (2016). Natural Products from Marine Fungi—Still an Underrepresented Resource. Marine Drugs, 14(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/md14010019





