Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and Its Effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Composition of Acid Hydrolysis Extract
| Algae (Freeze-Dried) 2 | Proteins | Neutral Sugars | Sulfate Groups | Uronic Acids | Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chondrus crispus | 27.2 ± 1.4 a | 28.8 ± 0.5 a | 17.6 ± 0.1 a | 1.8 ± 0.07 a | 25 ± 0.3 b |
| Codium fragile | 11.7 ± 0.3 b | 31.1 ± 0.4 b | 0.8 ± 0.1 b | 0.6 ± 0.01 b | 49.9 ± 0.2 a |
| P-value | ≤0.0001 | 0.028 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 | ≤0.0001 |
2.2. Biomass Yield
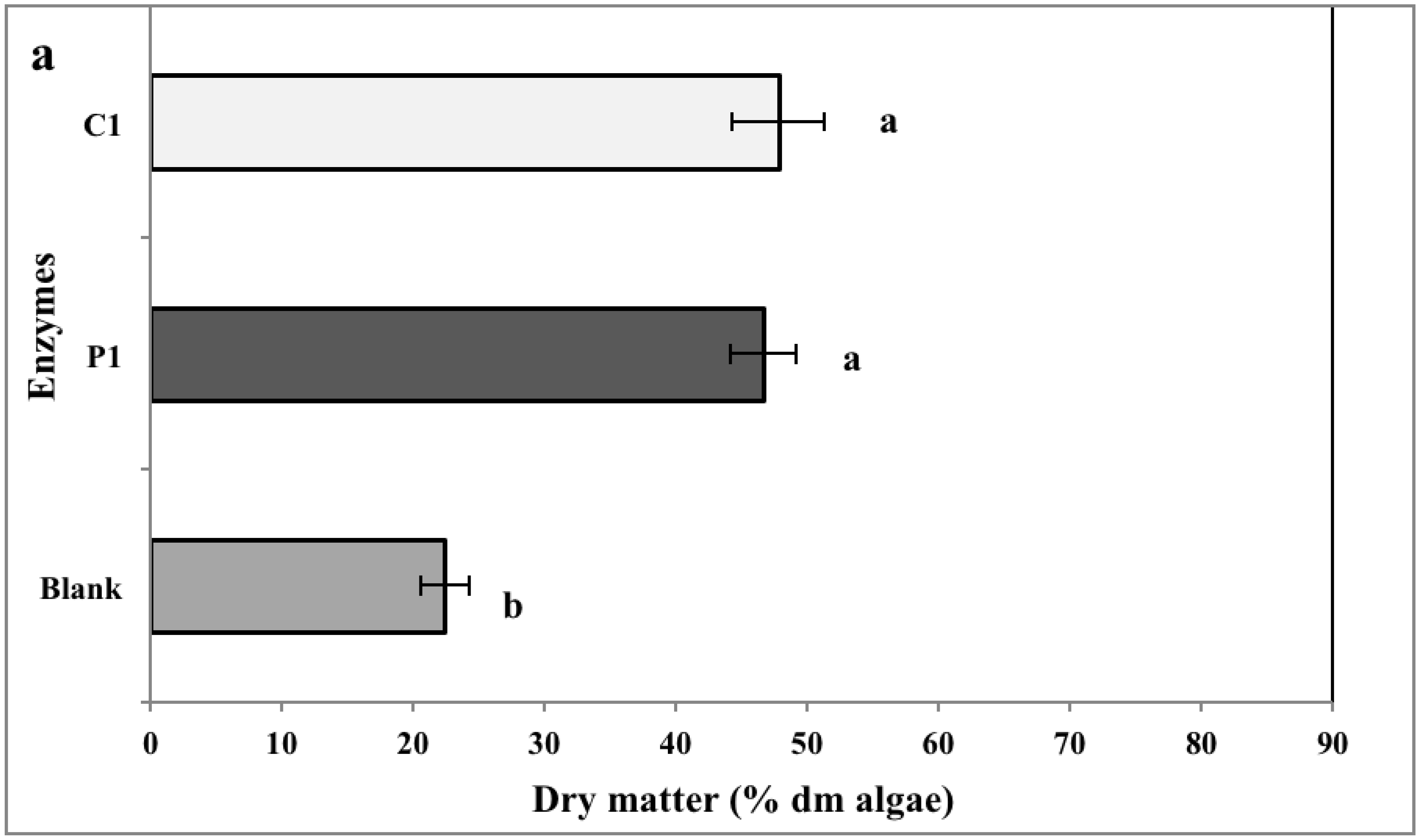
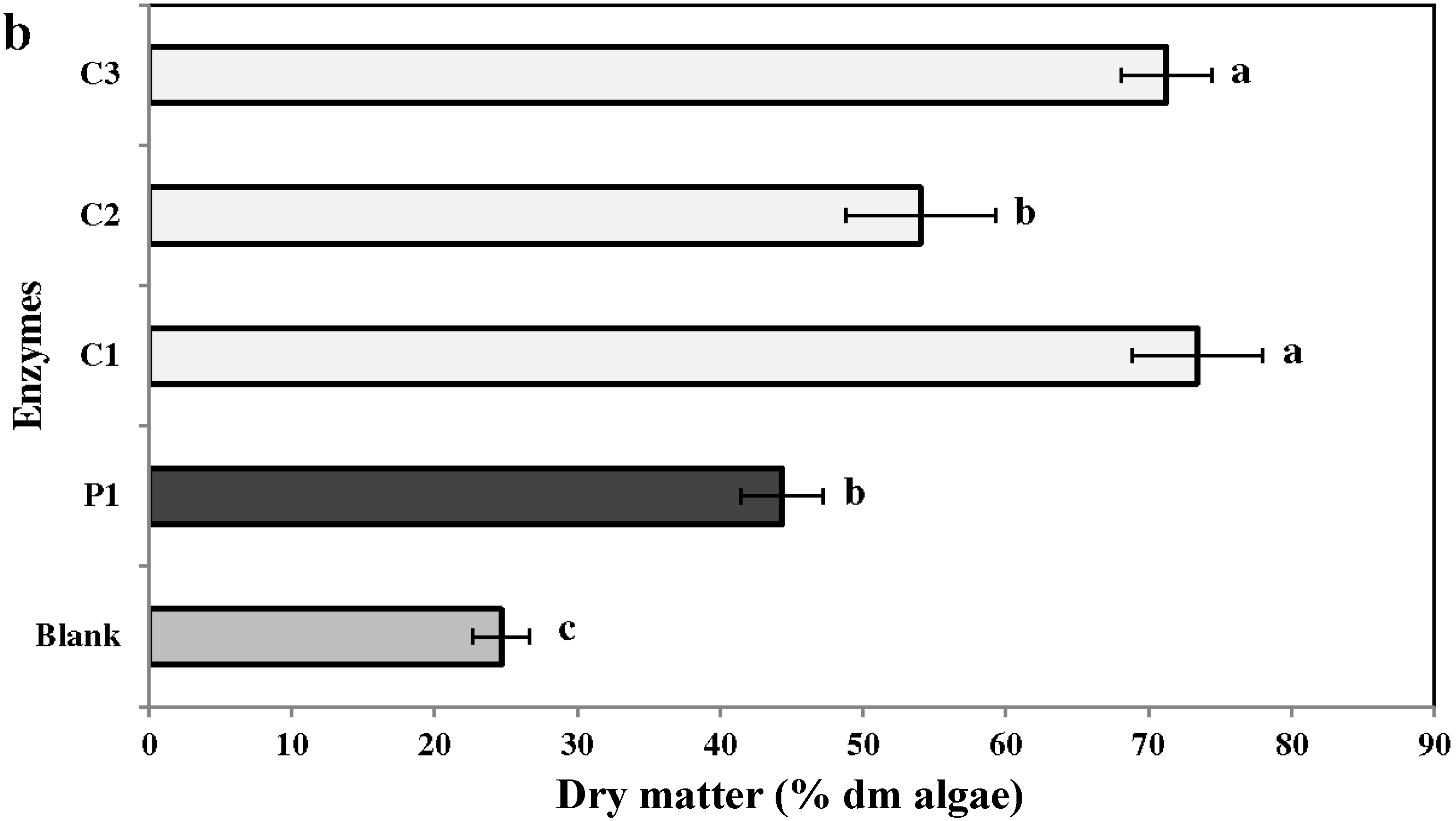
2.3. Chemical Analysis of Enzymatic Hydrolysates
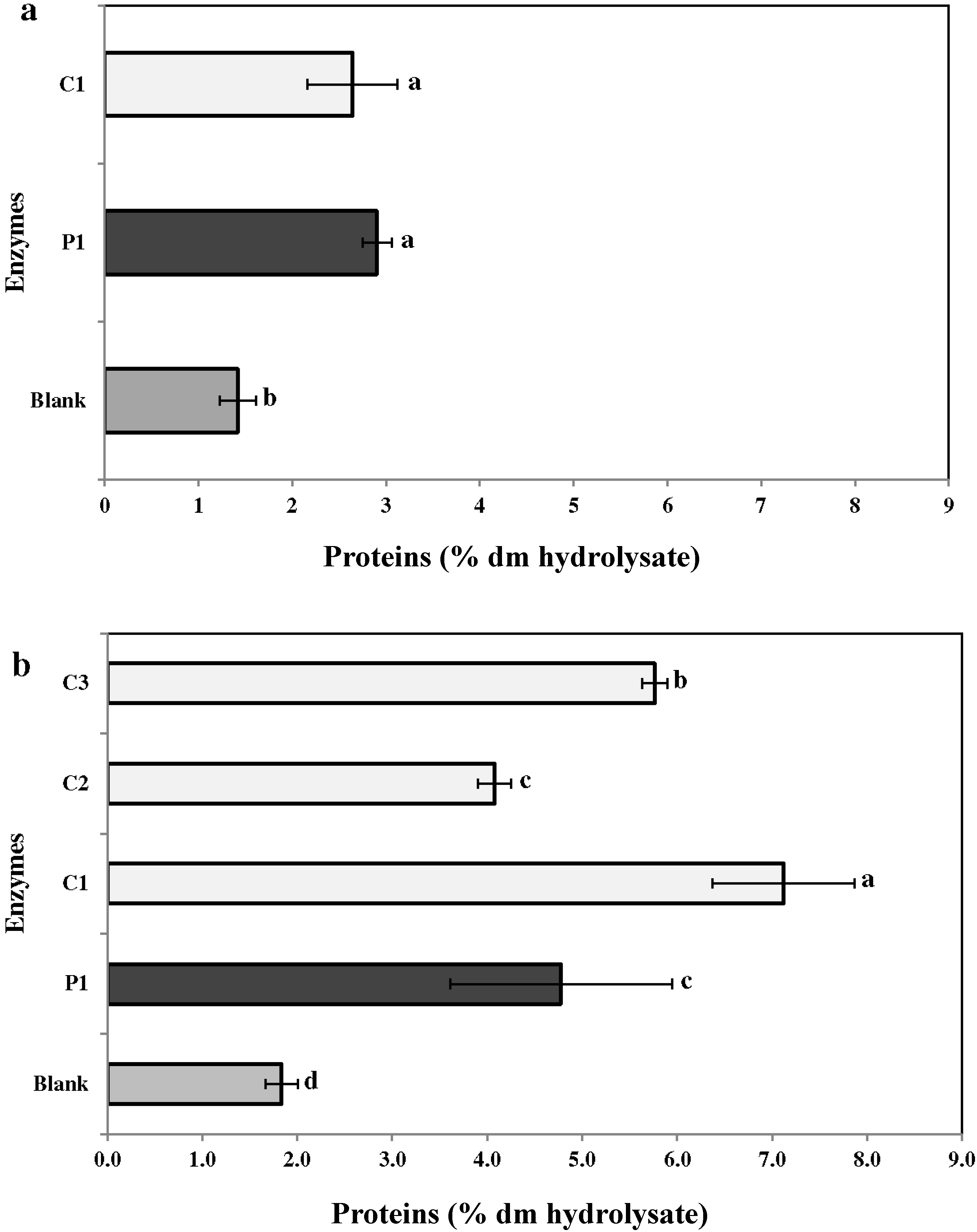
2.3.1. Proteins
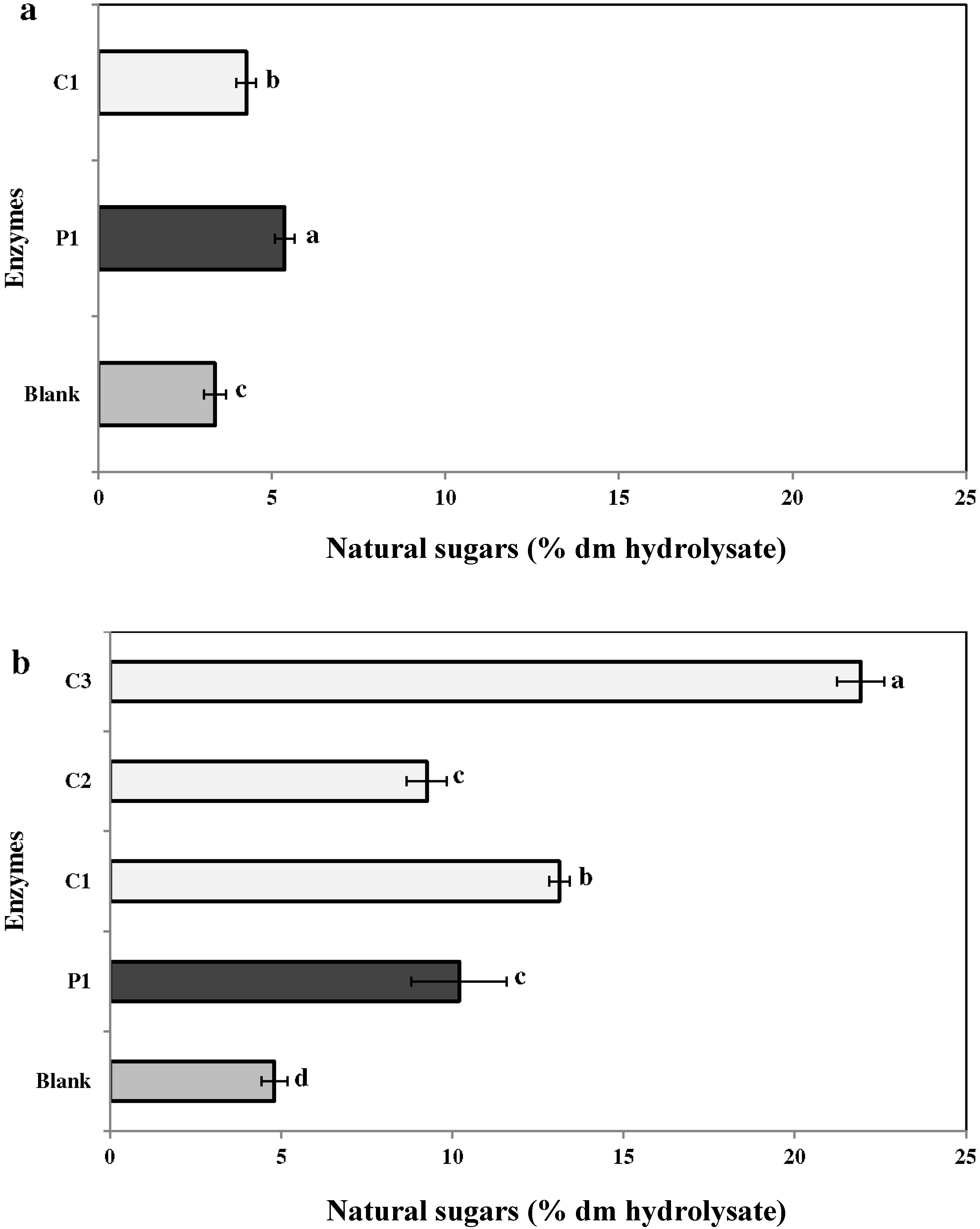
2.3.2. Neutral Sugars
2.3.3. Uronic Acid
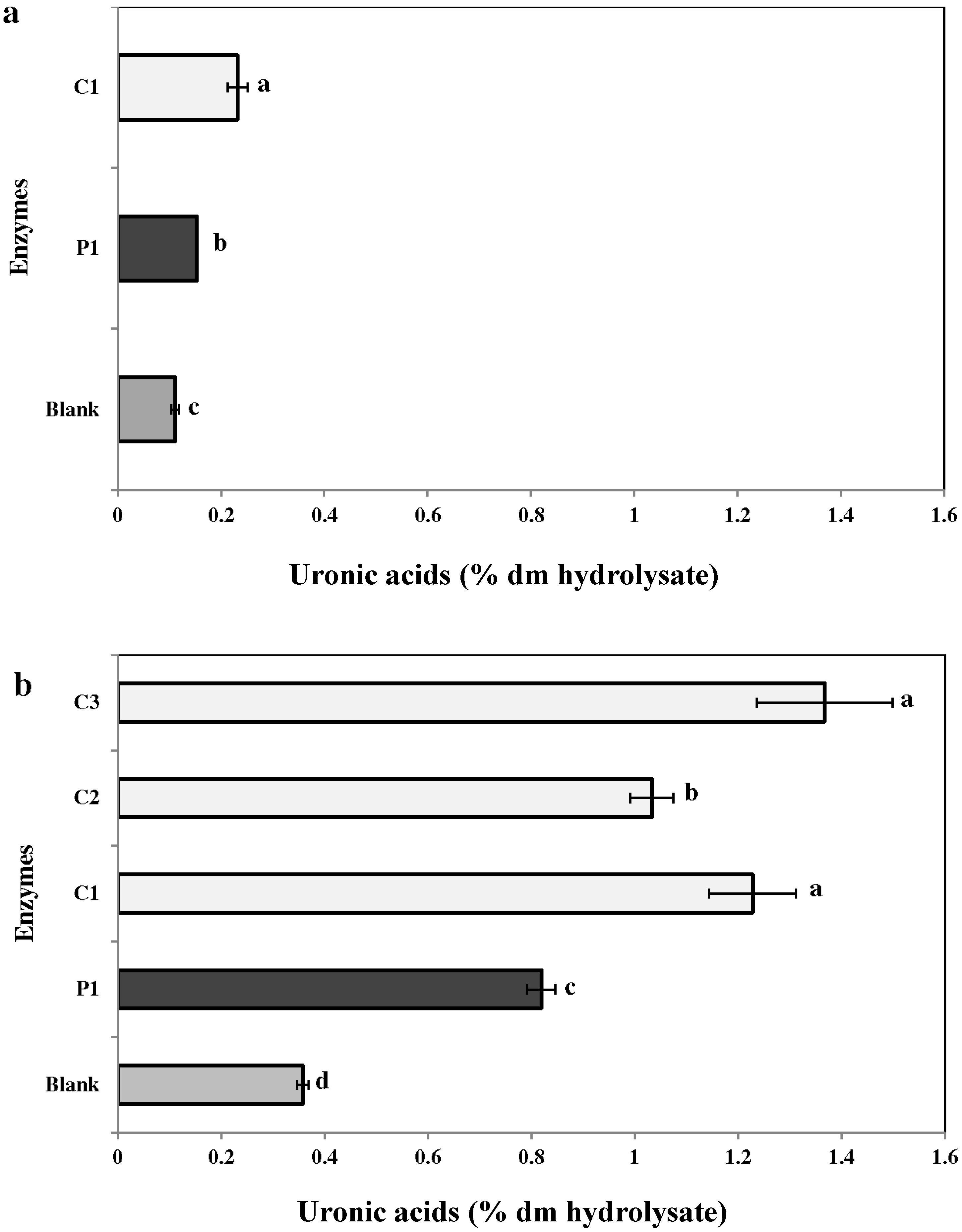
2.3.4. Sulfates
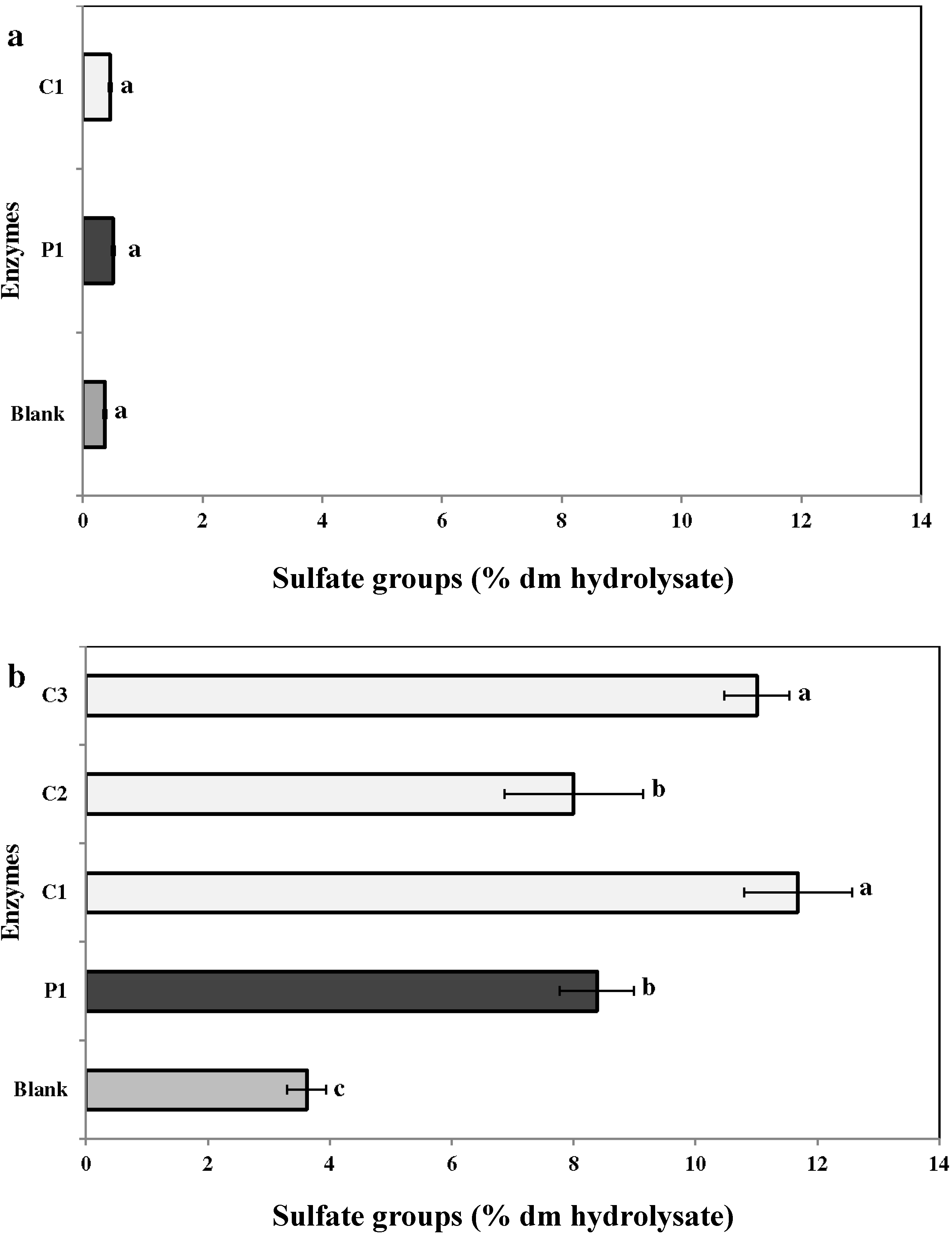
2.3.5. Ash
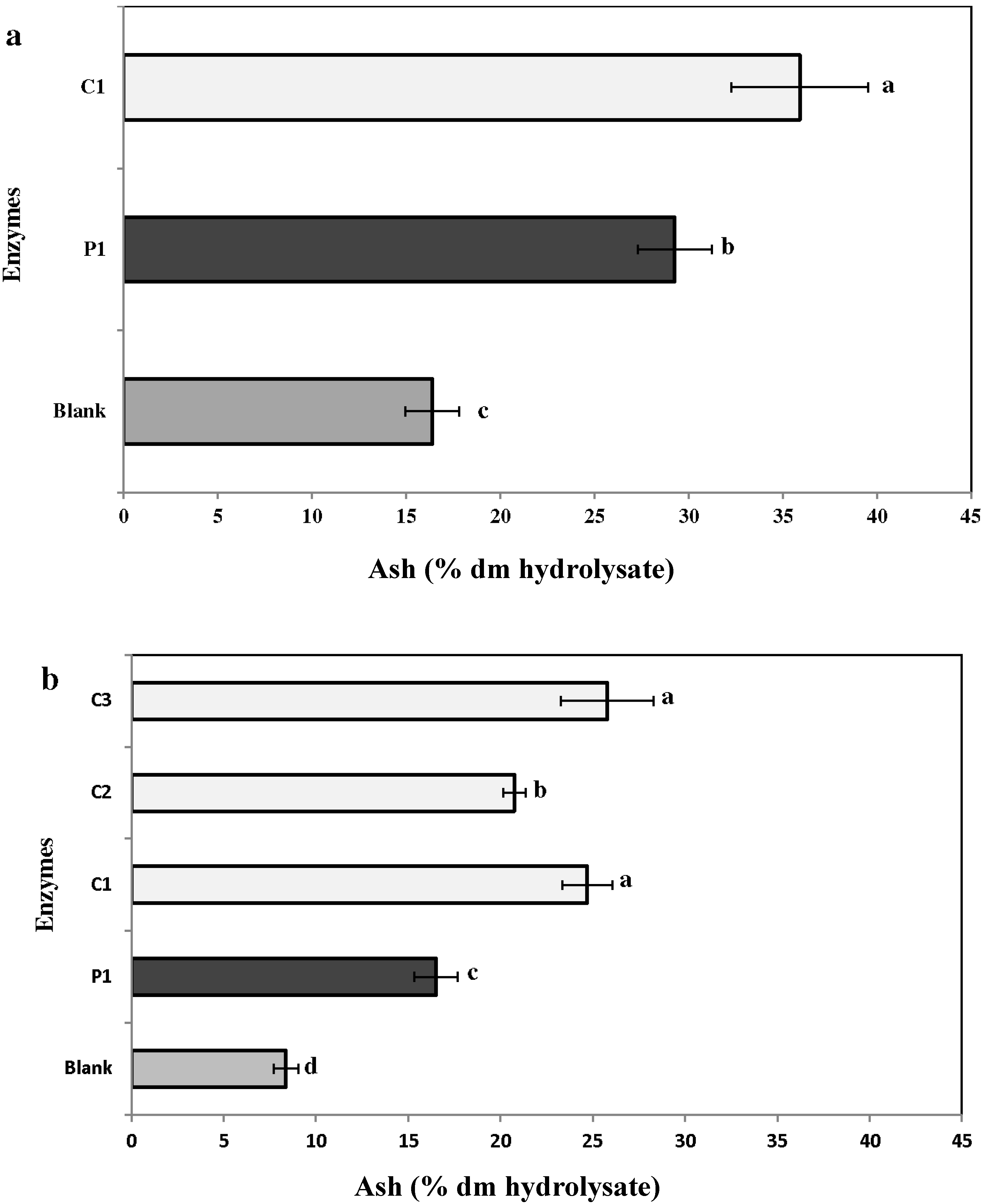
2.4. Carbohydrate Composition
| Treatments | Arabinose | Galactose | Glucose | Mannose | Xylose | Other Sugars |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC (Blank) | 0.00 | 83.63 ± 0.42 | 1.23 ± 0.19 | 1.46 ± 0.04 | 2.57 ± 0.05 | 10.22 ± 0.31 |
| CC (P1) | 0.19 ± 0.01 | 75.24 ± 1.88 | 3.13 ± 0.27 | 1.24 ± 0.71 | 1.64 ± 0.90 | 17.95 ± 1.18 |
| CC (C1) | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 73.11 ± 0.39 | 1.44 ± 0.02 | 1.72 ± 0.03 | 2.48 ± 0.06 | 19.59 ± 0.40 |
| CC (C2) | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 74.87 ± 0.32 | 1.81 ± 0.23 | 1.11 ± 0.08 | 2.45 ± 0.07 | 18.98 ± 0.09 |
| CC (C3) | 3.19 ± 0.44 | 12.94 ± 2.39 | 46.05 ± 8.66 | 11.69 ± 4.93 | 0.00 | 28.50 ± 1.97 |
| CF (Blank) | 4.49 ± 0.04 | 20.06 ± 0.17 | 53.52 ± 0.14 | 15.30 ± 0.16 | 0.00 | 5.85 ± 0.53 |
| CF (P1) | 2.48 ± 0.17 | 10.80 ± 0.77 | 55.92 ± 0.45 | 7.25 ± 1.33 | 0.00 | 23.21 ± 1.90 |
| CF (C1) | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 78.10 ± 0.37 | 1.14 ± 0.09 | 5.45 ± 0.06 | 0.00 | 14.27 ± 0.33 |
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Seaweeds
4.2. Extraction of Seaweeds
4.2.1. Acid Extraction
4.2.2. Enzyme Extraction
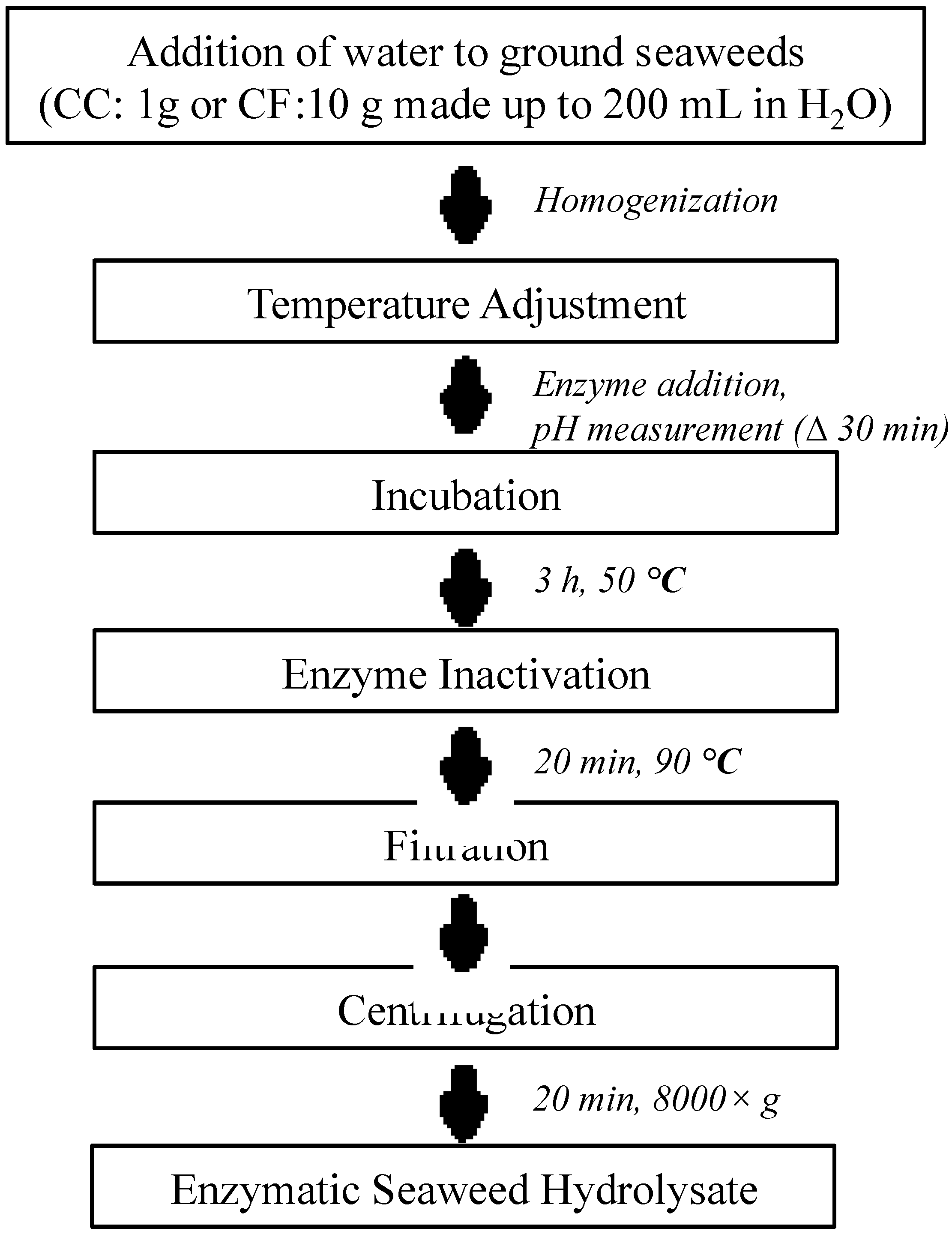
4.2.3. Water Extraction
4.3. Analysis of Chemical Composition of Extracts of Seaweed
4.4. Analysis of Carbohydrates in the Seaweed Hydrolysates
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brady, R.C.; Bernstein, D.I. Treatment of Herpes simplex virus infections. Anti-Viral Res. 2004, 61, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, K.; Burlot, A.; Umami, A.; Tanniou, A.; Stiger-Pouvreau, V.; Widowati, I.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N. Biochemical and anti-viral activities of enzymatic hydrolysates from different invasive french seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1029–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spear, P.G. Herpes simplex virus: Receptors and ligands for cell entry. Cell. Microbiol. 2004, 6, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campadelli-Fiume, G.; Amasio, M.; Avitabile, E.; Cerretani, A.; Forghieri, C.; Gianni, T.; Menotti, L. The multipartite system that mediates entry of Herpes simplex virus into the cell. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Astani, A.; Ghosh, T.; Schnitzler, P.; Ray, B. Polysaccharides from Sargassum tenerrimum: Structural features, chemical modification and anti-viral activity. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, S.H.; Kanth, A. Disseminated cutaneous Herpes simplex virus Type-1 with interstitial pneumonia as a first presentation of AIDS. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 1999, 91, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chretien, F.; Belec, L.; Hilto, D.; Flament-Saiilour, M.; Guillon, F.; WingertsmanrT, L.; Baudrimonf, M.; Truchis, P.D.; Keochane, C.; Vital, C. Herpes simplex virus Type 1 encephalitis in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1996, 22, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, Y.; Lee, J.; Hayashi, K.; Hayashi, T. Isolation of sulfated galactan from Codium fragile and its anti-viral effect. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 32, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corey, L.; Wald, A. Maternal and neonatal Herpes simplex virus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, Z.A.; Benedetti, J.; Ashley, R.; Burchett, S.; Selke, S.; Berry, S.; Vontver, L.A.; Corey, L. Neonatal Herpes simplex virus infection in relation to asymptomatic maternal infection at the time of labor. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, J.; Flournoy, N.; Thomas, E. Infection with Herpes-simplex virus and cell-mediated immunity after marrow transplant. J. Infect. Dis. 1980, 142, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenberg, M.; Friedman, H.; Cohen, S.; Oh, S.; Laster, L.; Starr, S. A comparative-study of Herpes-simplex infections in renal-transplant and leukemic patients. J. Infect. Dis. 1987, 156, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Park, S.M.; Kim, B.H. Synthesis of 5-Isoxazol-5-Yl-2′-deoxyuridines exhibiting anti-viral activity against HSV and several RNA viruses. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strand, M.; Islam, K.; Edlund, K.; Oberg, C.T.; Allard, A.; Bergstrom, T.; Mei, Y.; Elofsson, M.; Wadell, G. 2-[4,5-Difluoro-2-(2-Fluorobenzoylamino)-Benzoylamino]Benzoic Acid, an anti-viral compound with activity against acyclovir-resistant isolates of Herpes simplex virus Types 1 and 2. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 5735–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, L.; Zibetti, R.; Faria, P.; Scolaro, L.; Duarte, M.; Noseda, M.; Pujol, C.; Damonte, E. Anti-herpes simplex virus activity of sulfated galactans from the red seaweeds Gymnogongrus griffithsiae and Cryptonemia crenulata. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2004, 34, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.R.; Robaina, M.C.S.; Mendes, G.S.; Silva, T.S.L.; Gestinari, L.M.S.; Pamplona, O.S.; Yoneshigue-Valentin, Y.; Kaiser, C.R.; Villela Romanos, M.T. Anti-viral activity of extracts from brazilian seaweeds against Herpes simplex virus. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. Braz. J. Pharmacogn. 2012, 22, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, D. Biotechnology and the red seaweed polysaccharide industry: Status, needs and prospects. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, S.L.; Kraan, S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: Functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 2011, 23, 543–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafting, J.T.; Critchley, A.T.; Cornish, M.L.; Hubley, S.A.; Archibald, A.F. On-land cultivation of functional seaweed products for human usage. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banskota, A.H.; Stefanova, R.; Sperker, S.; Lall, S.; Craigie, J.S.; Hafting, J.T. Lipids isolated from the cultivated red alga Chondrus crispus inhibit nitric oxide production. J. Appl. Phycol. 2014, 26, 1565–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgougnon, N.; Lahaye, M.; Chermann, J.; Kornprobst, J. Composition and anti-viral activities of a sulfated polysaccharide from Schizymenia-dubyi (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 1993, 3, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgougnon, N.; Lahaye, M.; Quemener, B.; Chermann, J.; Rimbert, M.; Cormaci, M.; Furnari, G.; Kornprobst, J. Annual variation in composition and in vitro Anti-HIV-1 activity of the sulfated glucuronogalactan from Schizymenia dubyi (Rhodophyta, Gigartinales). J. Appl. Phycol. 1996, 8, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhlal, R.; Haslin, C.; Chermann, J.; Colliec-Jouault, S.; Sinquin, C.; Simon, G.; Cerantola, S.; Riadi, H.; Bourgougnon, N. Anti-viral activities of sulfated polysaccharides isolated from Sphaerococcus coronopifolius (Rhodophytha, Gigartinales) and Boergeseniella thuyoides (Rhodophyta, Ceramiales). Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1187–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witvrouw, M.; Este, J.; Mateu, M.; Reymen, D.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R.; Ikeda, S.; Pauwels, R.; Bianchini, N.; Desmyter, J.; et al. Activity of a sulfated polysaccharide extracted from the red seaweed Aghardhiella-tenera against Human-immunodeficiency-virus and other enveloped viruses. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1994, 5, 297–303. [Google Scholar]
- Pujol, C.; Estevez, J.; Carlucci, M.; Ciancia, M.; Cerezo, A.; Damonte, E. Novel DL-galactan hybrids from the red seaweed Gymnogongrus torulosus are potent inhibitors of Herpes simplex virus and dengue Virus. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2002, 13, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scheibling, R.E.; Gagnon, P. Competitive interactions between the invasive green alga Codium fragile ssp. Tomentosoides and native canopy-forming seaweeds in Nova Scotia (Canada). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 325, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romarís-Hortas, V.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Pineiro, A. Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic hydrolysis for iodinated amino acid extraction from edible seaweed before reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1309, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M.; Sharma, D.; Barrow, C.J. Enzyme-assisted extraction of bioactives from plants. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Jeon, Y. Enzyme-assistant extraction (EAE) of bioactive components: A useful approach for recovery of industrially important metabolites from seaweeds: A review. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jonsdottir, R.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Hreggvidsson, G.O.; Jonsson, J.O.; Thorkelsson, G.; Olafsdottir, G. Enzyme-enhanced extraction of antioxidant ingredients from red algae Palmaria palmata. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cian, R.E.; Fajardo, M.A.; Alaiz, M.; Vioque, J.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Drago, S.R. Chemical composition, nutritional and antioxidant properties of the red edible seaweed Porphyra columbina. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 65, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.C.; Wright, J.L.C.; Simpson, F.J. Review of chemical-constituents of the red alga Palmaria-palmata (Dulse). Econ. Bot. 1980, 34, 27–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurence, J. Seaweed proteins: Biochemical, nutritional aspects and potential uses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho-Soriano, E.; Fonseca, P.C.; Carneiro, M.A.A.; Moreira, W.S.C. Seasonal variation in the chemical composition of two tropical seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2402–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.; Cheung, P.C. Nutritional evaluation of some subtropical red and green seaweeds: Part I—proximate composition, amino acid profiles and some physico-chemical properties. Food Chem. 2000, 71, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaich, H.; Garna, H.; Besbes, S.; Paquot, M.; Blecker, C.; Attia, H. Chemical composition and functional properties of Ulva lactuca seaweed collected in Tunisia. Food Chem. 2011, 128, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, J.M.; Fernandez, P.V.; Kasulin, L.; Dupree, P.; Ciancia, M. Chemical and in situ characterization of macromolecular components of the cell walls from the green seaweed Codium fragile. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 212–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Smith, A.; Hossain, M. Extraction of phenolics from citrus peels II. enzyme-assisted extraction method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2006, 48, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, B.; Sahin, S.; Sumnu, G. Solvent-free microwave extraction of essential oil from oregano. J. Food Eng. 2008, 88, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uysal, B.; Sozmen, F.; Kose, E.O.; Deniz, I.G.; Oksal, B.S. Solvent-free microwave extraction and hydrodistillation of essential oils from endemic origanum husnucanbaseri H. Duman, Aytac A. Duran: Comparison of antibacterial activity and contents. Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 24, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.; Park, E.; Lee, K.; Jeon, Y. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from brown seaweeds. Bioresour. Technol. 2005, 96, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, P.; Shahidi, F.; Jeon, Y. Antioxidant activities of enzymatic extracts from an edible seaweed Sargassum horneri using ESR spectrometry. J. Food Lipids 2004, 11, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, K.; Bedoux, G.; Burlot, A.; Nyvall-Collen, P.; Bourgougnon, N. Enzymatic recovery of metabolites from seaweeds: Potential applications. Sea Plants 2014, 71, 279–320. [Google Scholar]
- Fleurence, J.; Massiani, L.; Guyader, O.; Mabeau, S. Use of enzymatic cell-wall degradation for improvement of protein extraction from Chondrus-crispus, Gracilaria-verrucosa and Palmaria-palmata. J. Appl. Phycol. 1995, 7, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.F.; Craigie, J.S. Sulfohydrolase activity and carrageenan biosynthesis in Chondrus-crispus (Rhodophyceae). Plant Physiol. 1978, 61, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, C.; le Jeune, H.; Gaudin, P.; Fleurence, J. An evaluation of methods for quantifying the enzymatic degradation of red seaweed Grateloupia turuturu. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, L.B.; Damonte, E.B. Interference in dengue virus adsorption and uncoating by carrageenans. Virology 2007, 363, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlucci, M.J.; Scolaro, L.A.; Noseda, M.D.; Cerezo, A.S.; Damonte, E.B. Protective effect of a natural carrageenan on genital Herpes simplex virus infection in mice. Anti-viral Res. 2004, 64, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, P.; Yu, G.; Li, C.; Hao, C.; Qi, X.; Zhang, L.; Guan, H. Preparation and anti-influenza A virus activity of κ-carrageenan oligosaccharide and its sulfated derivatives. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.B.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.K.; DeWreede, R.E.; Hong, Y.K. Anti-viral compounds in extracts of Korean seaweeds: Evidence for multiple activities. J. Appl. Phycol. 1998, 10, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, K.D.; Dragar, C. Anti-viral activity of Undaria pinnatifida against Herpes simplex virus. Phytother. Res. 2004, 18, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damonte, E.; Matulewicz, M.; Cerezo, A. Sulfated seaweed polysaccharides as anti-viral agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 2399–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blough, H.A. 2-Deoxy Glucose as an anti-Viral Agent against Herpes simplex. U.S. Patent No. 4,315,001, 9 Feburay 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Jung, M.; Mar, W. In vitro anti-viral activity of 1,2,3,4,6-penta-O-galloyl-beta-d-glucose against Hepatitis B virus. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 2131–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Pei, Y.; Qu, C.; Lai, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yang, K.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, D. In vitro anti-Herpes simplex virus activity of 1,2,4,6-Tetra-O-galloyl-β-d-glucose from Phyllanthus emblica L. (Euphorbiaceae). Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spivack, J.; Prusoff, W.; Tritton, T. A study of the anti-viral mechanism of action of 2-Deoxy-d-glucose—Normally glycosylated proteins are not strictly required for Herpes-simplex virus attachment but increase viral penetration and infectivity. Virology 1982, 123, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Defer, D.; Bourgougnon, N.; Fleury, Y. Screening for antibacterial and anti-viral activities in three bivalve and two gastropod marine molluscs. Aquaculture 2009, 293, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, M.; Gilles, K.A.; Hamilton, J.K.; Rebers, P.T.; Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal. Chem. 1956, 28, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenkrantz, N.; Asboe-Hansen, G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic Acids. Anal. Biochem. 1973, 54, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaques, L.; Balueux, R.; Dietrich, C.P.; Kavanagh, L. A Microelectrophoresis method for heparin. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1968, 46, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.; Mallia, A.; Gartner, F.; Provenzano, M.; Fujimoto, E.; Goeke, N.; Olson, B.; Klenk, D. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langlois, M.; Allard, J.; Nugier, F.; Aymard, M. A rapid and automated colorimetric assay for evaluating the sensitivity of Herpes simplex strains to anti-viral drugs. J. Biol. Stand. 1986, 14, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaren, C.; Ellis, M.; Hunter, G. A colorimetric assay for the measurement of the sensitivity of Herpes simplex viruses to anti-viral agents. Anti-viral Res. 1983, 3, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kulshreshtha, G.; Burlot, A.-S.; Marty, C.; Critchley, A.; Hafting, J.; Bedoux, G.; Bourgougnon, N.; Prithiviraj, B. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and Its Effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 558-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010558
Kulshreshtha G, Burlot A-S, Marty C, Critchley A, Hafting J, Bedoux G, Bourgougnon N, Prithiviraj B. Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and Its Effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1). Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(1):558-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010558
Chicago/Turabian StyleKulshreshtha, Garima, Anne-Sophie Burlot, Christel Marty, Alan Critchley, Jeff Hafting, Gilles Bedoux, Nathalie Bourgougnon, and Balakrishnan Prithiviraj. 2015. "Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and Its Effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1)" Marine Drugs 13, no. 1: 558-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010558
APA StyleKulshreshtha, G., Burlot, A.-S., Marty, C., Critchley, A., Hafting, J., Bedoux, G., Bourgougnon, N., & Prithiviraj, B. (2015). Enzyme-Assisted Extraction of Bioactive Material from Chondrus crispus and Codium fragile and Its Effect on Herpes simplex Virus (HSV-1). Marine Drugs, 13(1), 558-580. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010558






