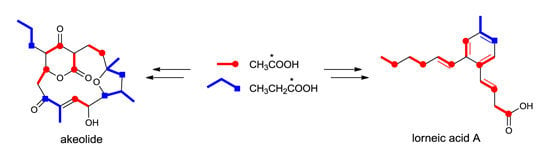
Biosynthesis of Akaeolide and Lorneic Acids and Annotation of Type I Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in the Genome of Streptomyces sp. NPS554
Abstract
:1. Introduction
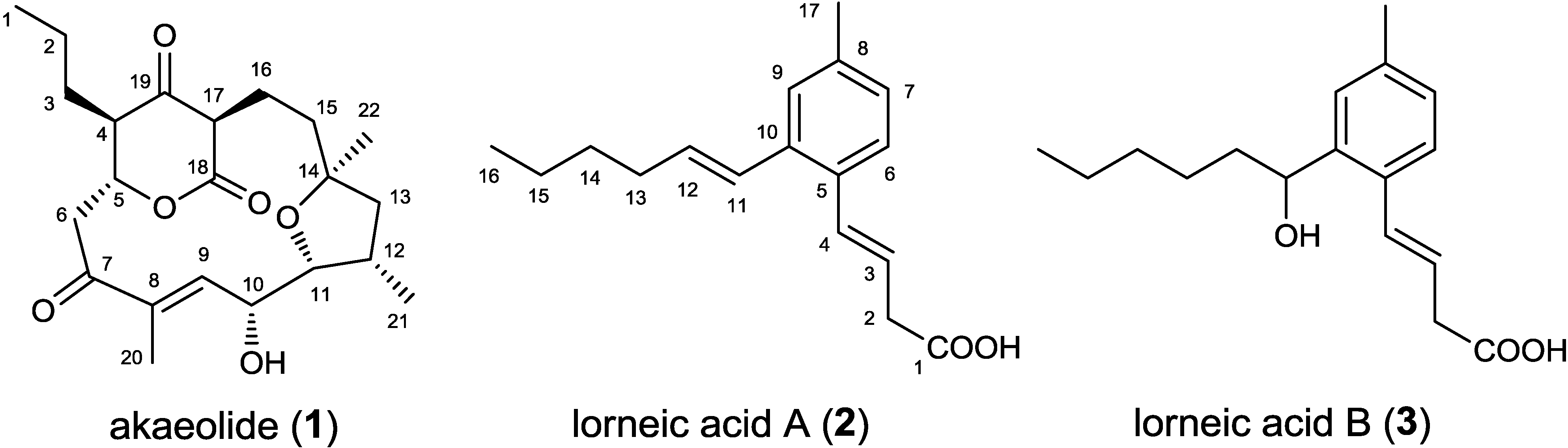
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Incorporation of 13C-Labeled Precursors
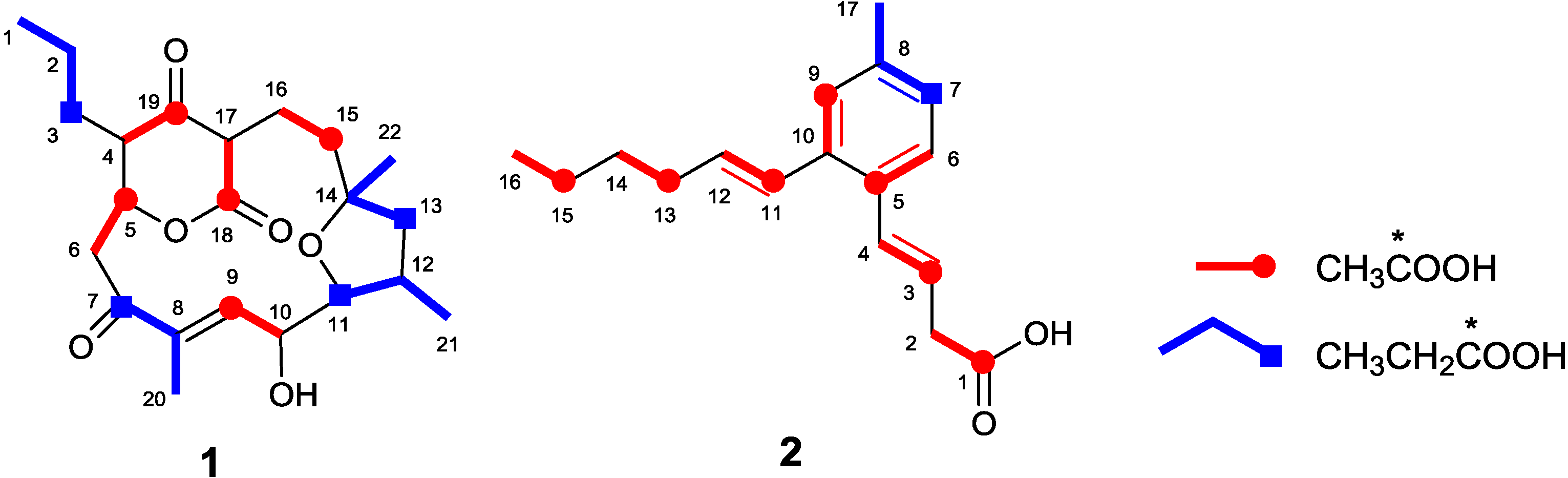
| Position | 17-chloroakaeolide (4) | Lorneic Acid A (2) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative Enrichments α | |||||||
| δC | [1-13C]acetate | [2-13C]acetate | [1-13C]propionate | δC | [1-13C]acetate | [1-13C]propionate | |
| 1 | 14.5 | 1.01 | 0.88 | 0.83 | 177.7 | 7.25 | 0.88 |
| 2 | 19.0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 38.3 | 1.04 | 1.02 |
| 3 | 28.8 | 1.00 | 1.69 | 32.90 | 121.8 | 6.71 | 1.03 |
| 4 | 46.8 | 0.99 | 4.44 | 0.99 | 131.9 | 0.99 | 1.01 |
| 5 | 75.4 | 5.01 | 1.06 | 0.81 | 131.7 | 6.53 | 0.83 |
| 6 | 43.5 | 1.14 | 4.83 | 0.90 | 126.4 | 0.97 | 1.01 |
| 7 | 203.1 | 1.17 | 2.11 | 40.33 | 127.8 | 1.03 | 42.61 |
| 8 | 138.9 | 0.94 | 0.77 | 0.58 | 137.3 | 0.93 | 0.73 |
| 9 | 140.6 | 4.60 | 1.02 | 0.84 | 127.0 | 6.49 | 1.13 |
| 10 | 69.0 | 1.04 | 4.47 | 0.61 | 136.1 | 0.80 | 0.81 |
| 11 | 84.1 | 0.96 | 1.60 | 30.19 | 127.4 | 6.13 | 1.13 |
| 12 | 34.7 | 4.88 | 1.03 | 0.87 | 133.7 | 0.90 | 1.00 |
| 13 | 49.1 | 0.99 | 1.61 | 31.63 | 33.0 | 6.35 | 1.07 |
| 14 | 83.1 | 0.99 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 31.6 | 1.02 | 1.00 |
| 15 | 34.7 | 1.00 | 1.03 | 0.87 | 22.3 | 6.32 | 1.04 |
| 16 | 30.1 | 1.00 | 4.33 | 1.02 | 13.9 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 17 | 63.7 | 0.96 | 3.77 | 1.12 | 21.2 | 1.01 | 0.99 |
| 18 | 164.5 | 4.79 | 0.94 | 0.79 | |||
| 19 | 196.4 | 4.41 | 1.02 | 1.07 | |||
| 20 | 14.5 | 1.01 | 0.88 | 0.83 | |||
| 21 | 25.1 | 1.00 | 0.82 | 0.99 | |||
| 22 | 14.6 | 1.01 | 0.88 | 0.83 | |||
2.2. Genome Analysis and Annotation of Biosynthetic Genes
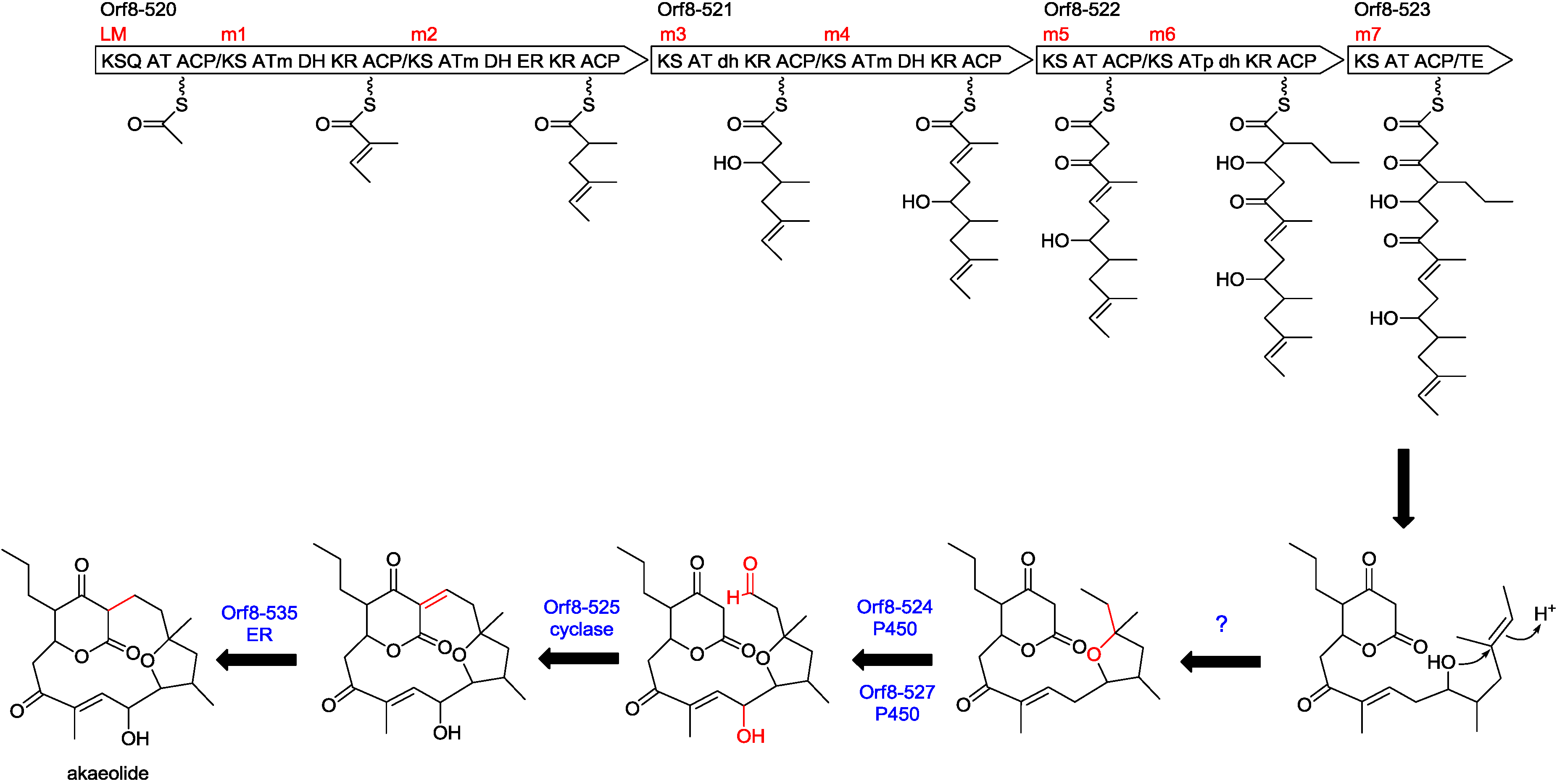
2.3. Biosynthetic Gene Cluster for Akaeolide
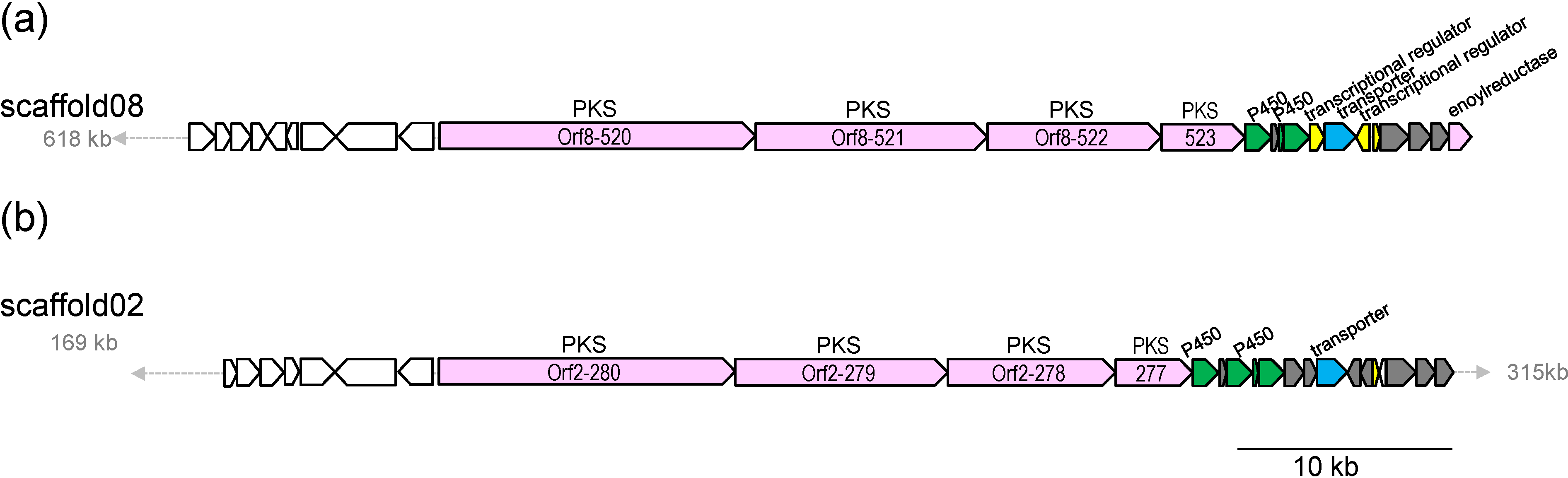
| Orf8- | Size a | Proposed Function | Protein Homolog, Origin, Accession Number | % b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 511 | 413 | ligase | ligase, Streptomyces sp. NRRL S-118, WP_031071281 | 86/92 |
| 512 | 242 | glutamine amidotransferase | glutamine amidotransferase, Streptomycetaceae bacterium MP113-05, EST22401 | 86/91 |
| 513 | 315 | unknown | membrane protein, S. hygroscopicus, WP_030828871 | 76/83 |
| 514 | 248 | type II thioesterase | thioesterase, S. mobaraensis, EME98724 | 64/76 |
| 515 c | 294 | methyltransferase | methyltransferase type 12, S. bingchenggensis, ADI12483 | 70/82 |
| 516 c | 180 | unknown | GCN5 family acetyltransferase, Streptomyces sp. NRRL S-87, WP_030200822 | 68/78 |
| 517 | 532 | acyl CoA carboxylase α-subunit | carboxyl transferase, S. rimosus, ELQ79111 | 82/89 |
| 518 c | 947 | transcriptional regulator | hypothetical protein, Lechevalieria aerocolonigenes, WP_030473578 | 45/57 |
| 519 c | 532 | oxidoreductase | hypothetical protein, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030473579 | 64/76 |
| 520 | 4917 | type I PKS | putative type I polyketide synthase, S. bingchenggensis, ADI04502 | 53/64 |
| 521 | 3601 | type I PKS | polyketide synthase, S. rapamycinicus, AGP57755 | 53/64 |
| 522 | 2771 | type I PKS | type I polyketide synthase, S. flaveolus, ACY06287 | 52/63 |
| 523 | 1322 | type I PKS | hypothetical protein, partial, S. novaecaesareae, WP_033330653 | 52/61 |
| 524 | 408 | cytochrome P450 | cytochrome P450, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470230 | 72/84 |
| 525 | 115 | cyclase | hypothetical protein, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470229 | 63/79 |
| 526 | 78 | ferredoxin | hypothetical protein BN6_14320, Saccharothrix espanaensis DSM 44229, CCH28755 | 61/73 |
| 527 | 402 | cytochrome P450 | cytochrome P450, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470226 | 73/84 |
| 528 | 229 | transcriptional regulator | NmrA family transcriptional regulator, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470224 | 76/84 |
| 529 | 498 | transporter | Puromycin resistance protein pur8, partial, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470223 | 66/76 |
| 530c | 216 | transcriptional regulator | NmrA family transcriptional regulator, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470222 | 70/82 |
| 531 | 109 | transcriptional regulator | HxlR family transcriptional regulator, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470221 | 69/83 |
| 532 | 457 | enoyl-CoA reductase/carboxylase | NADPH:quinone reductase, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470219 | 79/87 |
| 533 | 340 | 3-oxoacyl ACP synthase | 3-oxoacyl-ACP synthase, S. olivaceus, WP_031035846 | 70/82 |
| 534 | 286 | 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase | 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase, L. aerocolonigenes, WP_030470217 | 63/80 |
| 535 | 339 | enoylreductase | putative succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating), S. afghaniensis, EPJ38274 | 68/77 |
| 536 | >213 d | transposase | transposase, Streptomyces sp. NRRL B-24484, WP_030264850 | 78/87 |
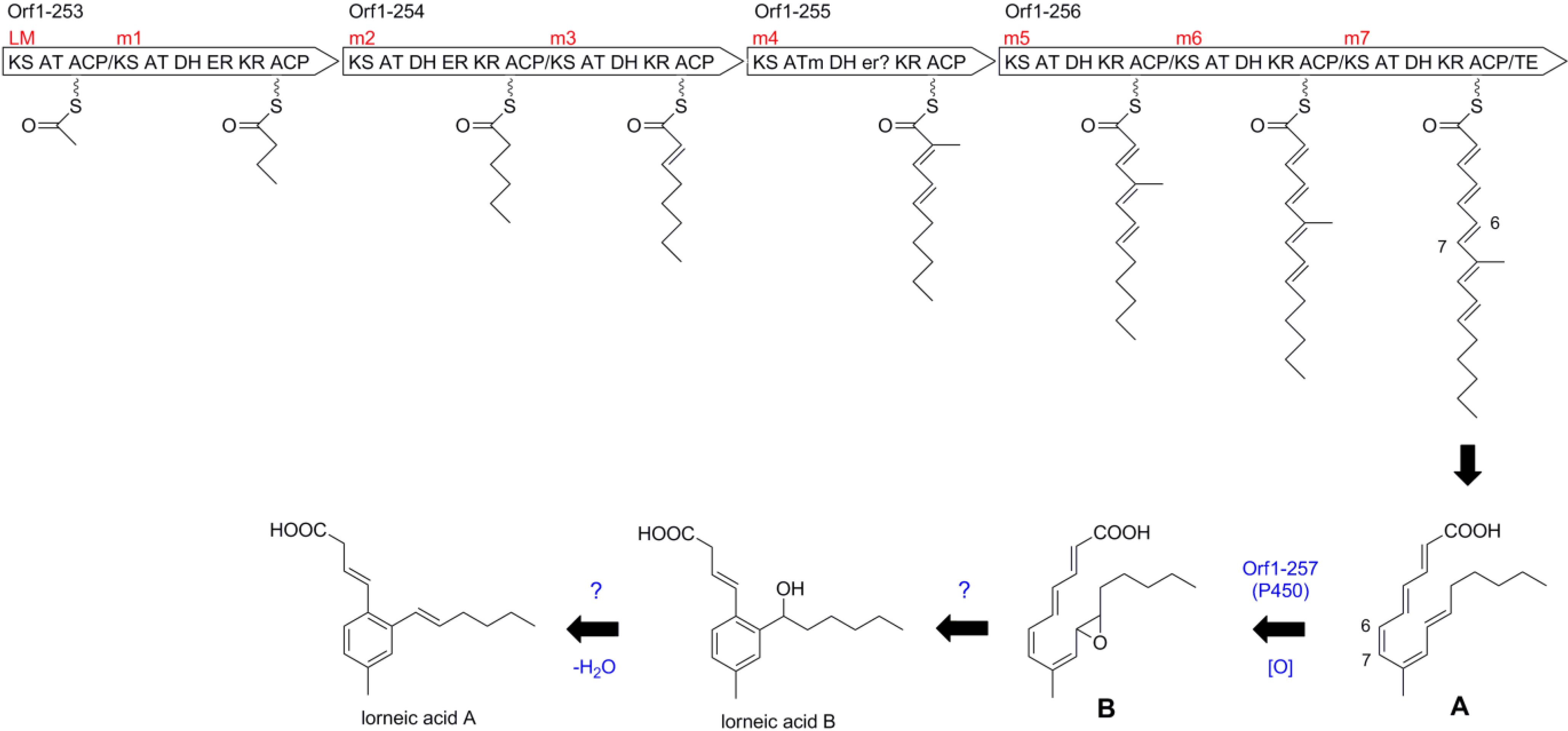
2.4. Biosynthetic Gene Cluster for Lorneic Acid
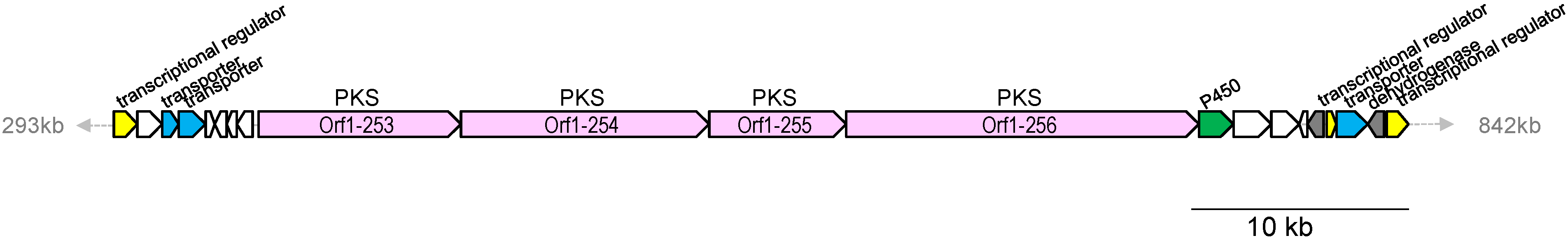
| Orf1- | Size a | Proposed Function | Protein Homolog, Origin, Accession Number | % b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 245 | 372 | transcriptional regulator | transcriptional regulator, Cellulosimicrobium cellulans, WP_024839151 | 80/89 |
| 246 | 376 | unknown | hypothetical protein, C. cellulans, WP_024839150 | 76/84 |
| 247 | 255 | ABC transporter | sugar ABC transporter ATP-binding protein, C. cellulans, WP_024839149 | 79/86 |
| 248 | 418 | ABC transporter | ABC transporter permease, C. cellulans, WP_024839148 | 74/82 |
| 249 | 138 | unknown | hypothetical protein AOR_1_82014, Aspergillus oryzae, XP_003189833 | 50/60 |
| 250 c | 185 | unknown | hypothetical protein, Streptomyces sp. CNQ766, WP_018834862 | 24/43 |
| 251 c | 158 | unknown | hypothetical protein, Jiangella gansuensis, WP_026874523 | 56/66 |
| 252 c | 239 | unknown | hypothetical protein, Actinopolymorpha alba, WP_020576671 | 60/70 |
| 253 | 3128 | type I PKS | hypothetical protein, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024802962 | 59/70 |
| 254 | 3893 | type I PKS | hypothetical protein, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024802962 | 58/69 |
| 255 | 2176 | type I PKS | hypothetical protein, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024802960 | 68/78 |
| 256 | 5477 | type I PKS | hypothetical protein, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024802963 | 62/72 |
| 257 | 534 | cytochrome P450 | cytochrome P450, Micromonospora sp. ATCC 39149, EEP70569 | 73/84 |
| 258 | 588 | unknown | hypothetical protein (glycosidase), Streptomyces sp. CNY243, WP_018851787 | 79/87 |
| 259 | 435 | unknown | beta-lactamase, Catenulispora acidiphila, ACU74739 | 80/87 |
| 260 c | 118 | unknown | PDZ and LIM domain protein 1, partial, Columba livia, EMC79925 | 31/52 |
| 261 c | 254 | methyltransferase | methyltransferase, S. avermitilis, BAC68374 | 84/89 |
| 262 | 148 | transcriptional regulator | Rrf2 family transcriptional regulator, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024804268 | 78/86 |
| 263 | 486 | transporter | MFS transporter, Nocardia sp. BMG51109, WP_024804269 | 68/80 |
| 264 c | 250 | short-chain dehydrogenase | short-chain dehydrogenase, A. alba, WP_020577481 | 92/94 |
| 265 | 331 | transcriptional regulator | AraC family transcriptional regulator, A. alba, WP_020577482 | 92/94 |
2.5. Distribution of Biosynthetic Gene Clusters for Akaeolide and Lorneic Acid in Other Strains
2.6. Other Type I PKS Gene Clusters in Streptomyces sp. NPS554

3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Isolation of Akaeolide (1) and Lorneic Acid A (2)
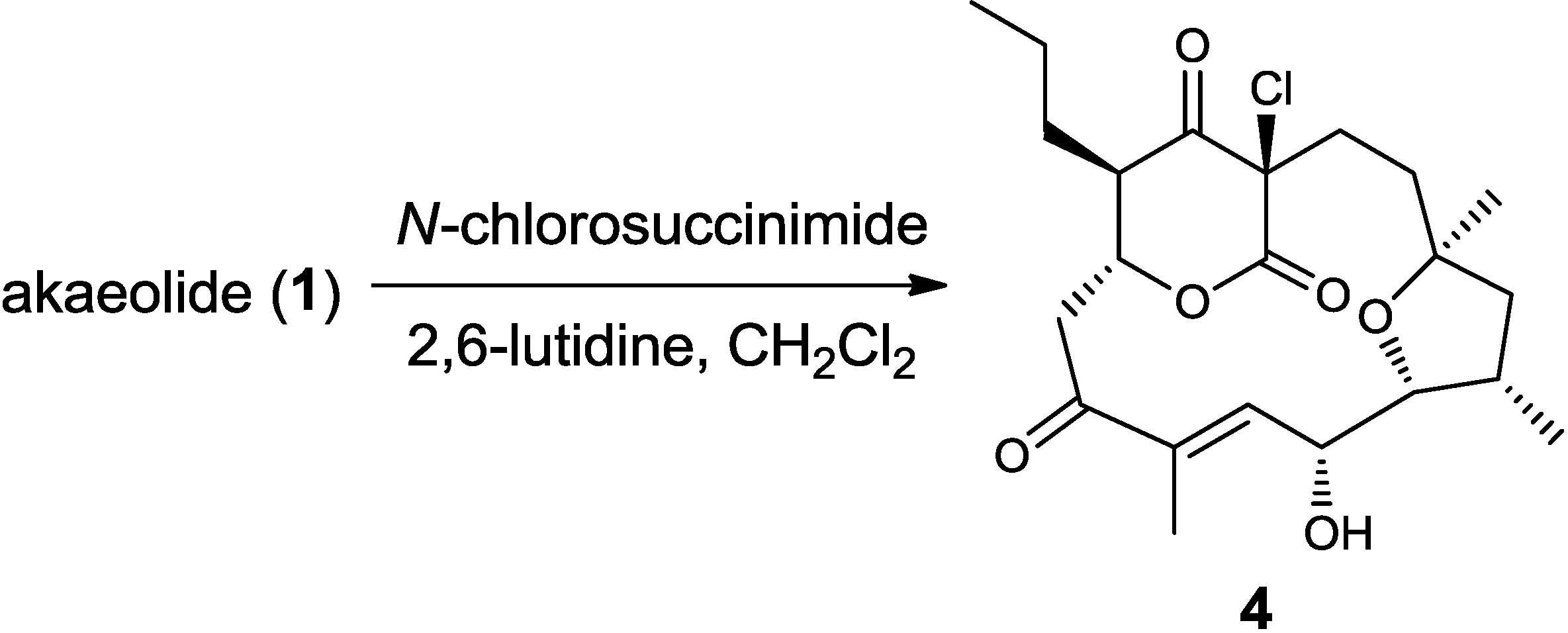
3.3. Chlorination of 1 to Yield 17-Chloroakaeolide (4)
3.4. Preparation of 13C-Labeled Akaeolide (1)
3.5. Preparation of 13C-Labeled Lorneic Acid A (2)
3.6. Whole Genome Shotgun Sequencing
3.7. Annotation of PKS Gene Clusters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cragg, G.M.; Newman, D.J. Natural products: A continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3670–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debbab, A.; Aly, A.H.; Lin, W.H.; Proksch, P. Bioactive compounds from marine bacteria and fungi. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 544–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manivasagan, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Sivakumar, K.; Kim, S.-K. Pharmaceutically active secondary metabolites of marine actinobacteria. Microbial. Res. 2014, 169, 262–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewick, P.M. Medicinal Natural Products. A Biosynthetic Approach, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Assembly-line enzymology for polyketide and nonribosomal peptide antibiotics: Logic, machinery, and mechnisms. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 3468–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boddy, C.N. Bioinformatics tools for genome mining of polyketide and non-ribosomal peptides. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachmann, B.O.; van Lanen, S.G.; Baltz, R.H. Microbial genome mining for accelerated natural products discovery: Is a renaissance in the making? J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 41, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igarashi, Y.; Zhou, T.; Sato, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Yu, L.; Oku, N. Akaeolide, a carbocyclic polyketide from marine-derived Streptomyces. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 5678–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, F.; Sato, S.; Mukai, T.; Yamada, S.; Takeo, J.; Abe, A.; Okita, T.; Kawahara, H. Lorneic acids, trialkyl-substituted aromatic acids from a marine-derived actinomycete. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 2046–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Komatsu, H.; Kozone, I.; Kawaide, H.; Abe, H.; Natsume, M. Biosynthetic origin of the carbon skeleton and nitrogen atom of pamamycin-607, a nitrogen-containing polyketide. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2005, 69, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.A.; Sidebottom, P.J.; Cannell, R.J.P.; Noble, D.; Rudd, B.A.M. The squalestatins, novel inhibitors of squalene synthase produced by a species of Phoma. III. Biosynthesis. J. Antibiot. 1992, 45, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, F.; Petkovic, H.; Kendrew, S.G.; Low, L.; Wilkinson, B.; Lill, R.; Cortes, J.; Rudd, B.A.; Staunton, J.; Leadlay, P.F. Active-site residue, domain and module swaps in modular polyketide synthases. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 30, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakavas, S.J.; Katz, L.; Stassi, D. Identification and characterization of the niddamycin polyketide synthase genes from Streptomyces caelestis. J. Bacteriol. 1997, 179, 7515–7522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eustaquio, A.S.; McGlinchey, R.P.; Liu, Y.; Hazzard, C.; Beer, L.L.; Florova, G.; Alhamadsheh, M.M.; Lechner, A.; Kale, A.J.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Biosynthesis of the salinosporamide A polyketide synthase substrate chloroethylmalonyl-coenzyme A from S-adenosyl-L-methionine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12295–12300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hazzard, C.; Eustáquio, A.S.; Reynolds, K.A.; Moore, B.S. Biosynthesis of salinosporamides from α,β-unsaturated fatty acids: Implications for extending polyketide synthase diversity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 10376–10377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goranovic, D.; Kosec, G.; Mrak, P.; Fujs, S.; Horvat, J.; Kuscer, E.; Kopitar, G.; Petkovic, H. Origin of the allyl group in FK506 biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 14292–14300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keatinge-Clay, A. A tylosin ketoreductasereveals how chirality is determined in polyketides. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 898–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwan, D.H.; Sun, Y.; Schulz, F.; Hong, H.; Popovic, B.; Sim-Stark, J.C.C.; Haydock, S.F.; Leadlay, P.F. Prediction and manipulation of the stereochemistry of enoylreduction in modular poyketide synthases. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- InterProScan Sequence Search. Available online: http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/search/sequence-search (accessed on 1 December 2014).
- Torkkell, S.; Kunnari, T.; Palmu, K.; Hakala, J.; Mäntsälä, P.; Ylihonko, K. Identification of a cyclase gene dictating the C-9 stereochemistry of anthracyclines from Streptomyces nogalater. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sultana, A.; Kallio, P.; Jansson, A.; Wang, J.S.; Niemi, J.; Mäntsälä, P.; Schneider, G. Structure of the polyketide cyclase SnoaL reveals a novel mechanism for enzymatic aldol condensation. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 1911–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichikawa, N.; Sasagawa, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Komaki, H.; Yoshida, Y.; Yamazaki, S.; Fujita, N. DoBISCUIT: A database of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D408–D414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhamadsheh, M.M.; Palaniappan, N.; DasChouduri, S.; Reynolds, K.A. Modular polyketide synthases and cis double bond formation: Establishment of activated cis-3-cyclohexylpropenoic acid as the diketide intermediate in phoslactomycin biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1910–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BLAST Assembled Genomes. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 1 December 2014).
- Nakashima, T.; Iwatsuki, M.; Ochiai, J.; Kamiya, Y.; Nagai, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Ishiyama, A.; Otoguro, K.; Shiomi, K.; Takahashi, Y.; et al. Mangromicins A and B: Structure and antitrypanosomal activity of two new cyclopentadecane compounds from Lechevalieria aerocolonigenes K10-0216. J. Antibiot. 2014, 67, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsubo, Y.; Maruyama, F.; Mitsui, H.; Nagata, Y.; Tsuda, M. Complete genome sequence of Acidovorax sp. strain KKS102, a polychlorinated-biphenyl degrader. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6970–6971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.L.; Locascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinformatics 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komaki, H.; Ichikawa, N.; Oguchi, A.; Hanamaki, T.; Fujita, N. Genome-wide survey of polyketide synthase and nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene clusters in Streptomyces turgidiscabies NBRC 16081. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, T.; Komaki, H.; Ichikawa, N.; Hosoyama, A.; Sato, S.; Igarashi, Y. Biosynthesis of Akaeolide and Lorneic Acids and Annotation of Type I Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in the Genome of Streptomyces sp. NPS554. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 581-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010581
Zhou T, Komaki H, Ichikawa N, Hosoyama A, Sato S, Igarashi Y. Biosynthesis of Akaeolide and Lorneic Acids and Annotation of Type I Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in the Genome of Streptomyces sp. NPS554. Marine Drugs. 2015; 13(1):581-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010581
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Tao, Hisayuki Komaki, Natsuko Ichikawa, Akira Hosoyama, Seizo Sato, and Yasuhiro Igarashi. 2015. "Biosynthesis of Akaeolide and Lorneic Acids and Annotation of Type I Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in the Genome of Streptomyces sp. NPS554" Marine Drugs 13, no. 1: 581-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010581
APA StyleZhou, T., Komaki, H., Ichikawa, N., Hosoyama, A., Sato, S., & Igarashi, Y. (2015). Biosynthesis of Akaeolide and Lorneic Acids and Annotation of Type I Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters in the Genome of Streptomyces sp. NPS554. Marine Drugs, 13(1), 581-596. https://doi.org/10.3390/md13010581