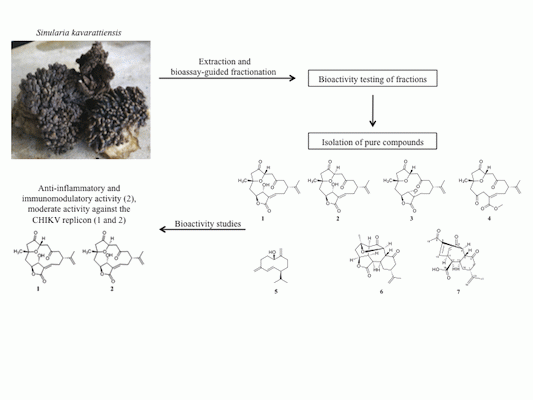
Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bioassay-Guided Fractionation of S. kavarattiensis Extract
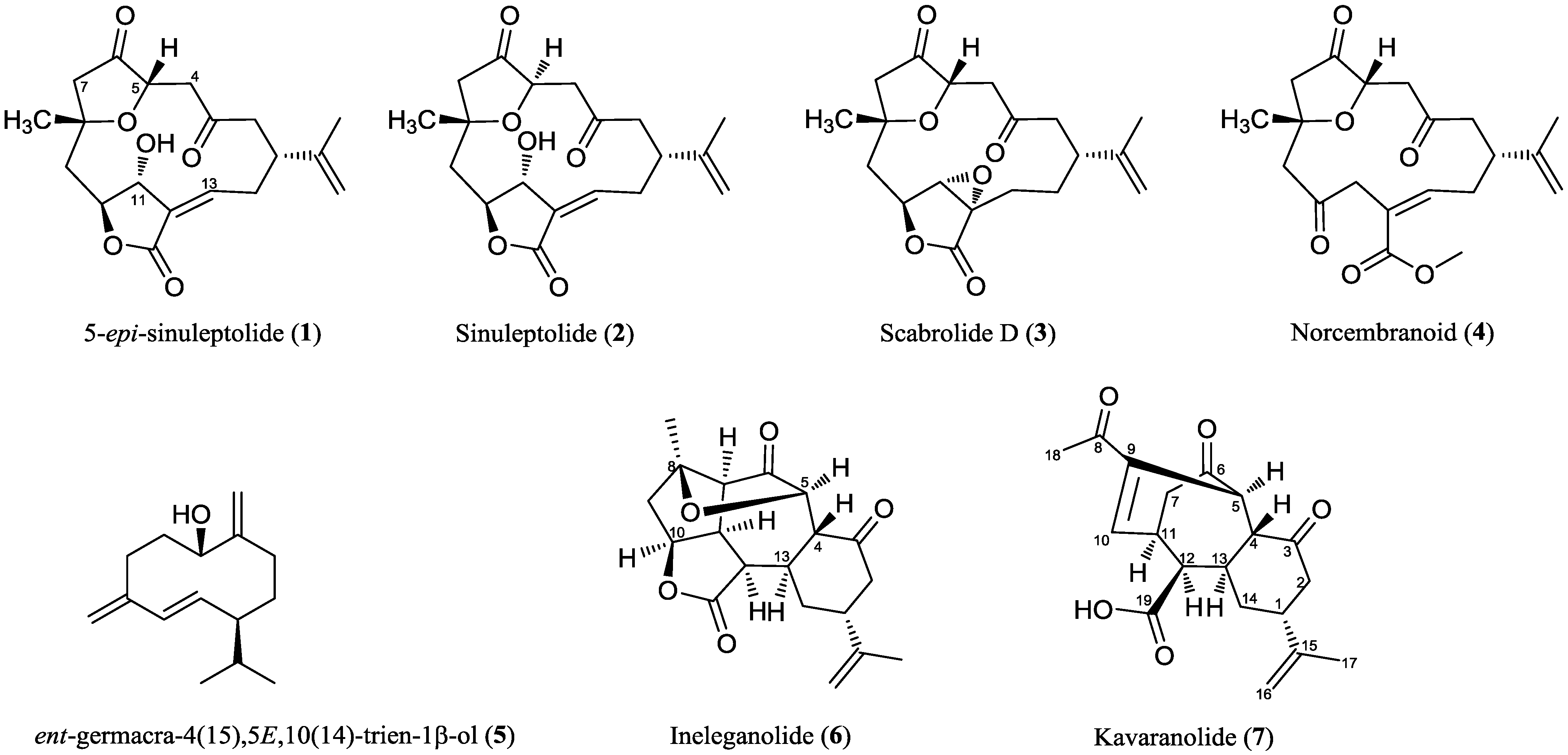
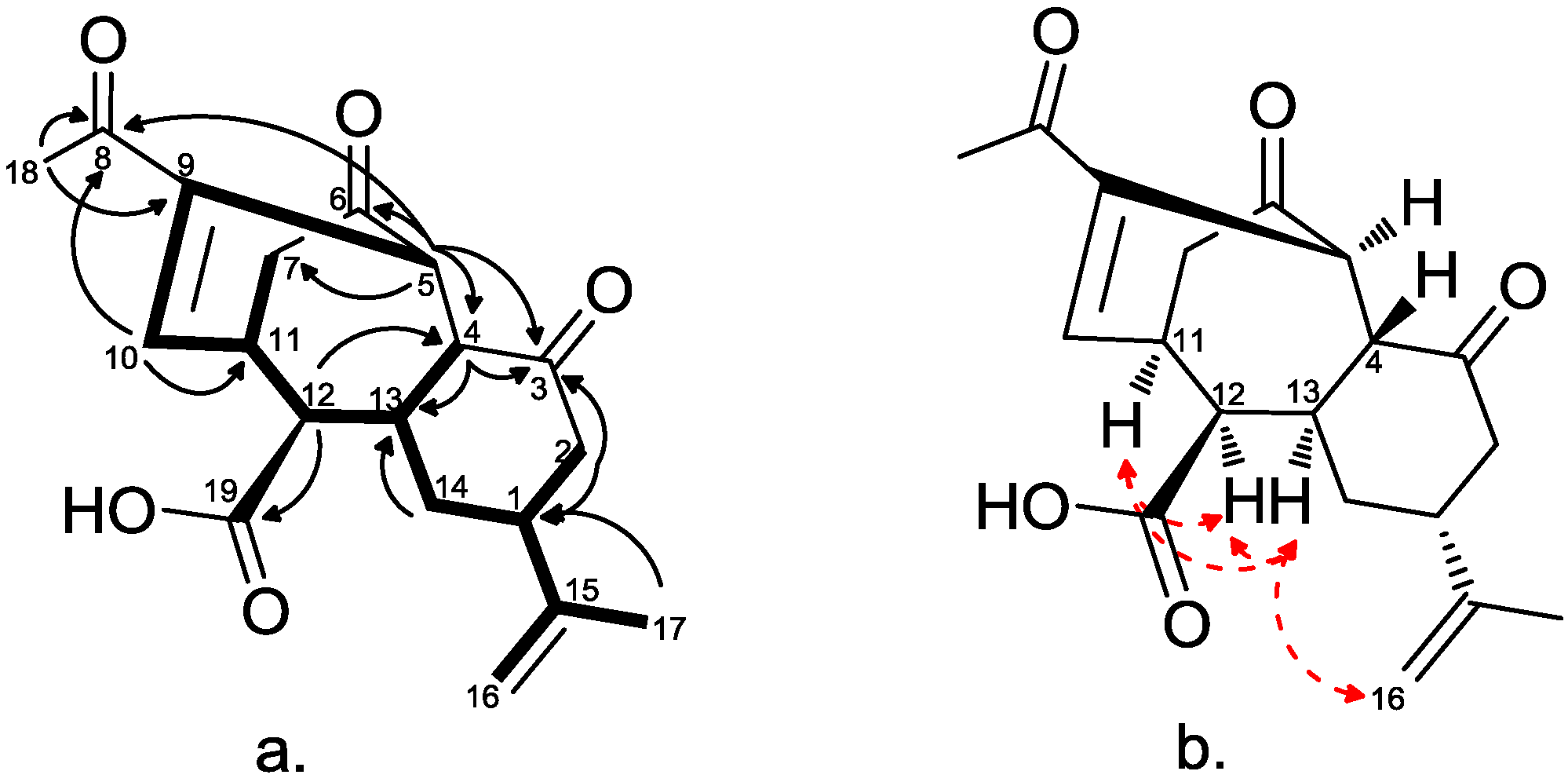
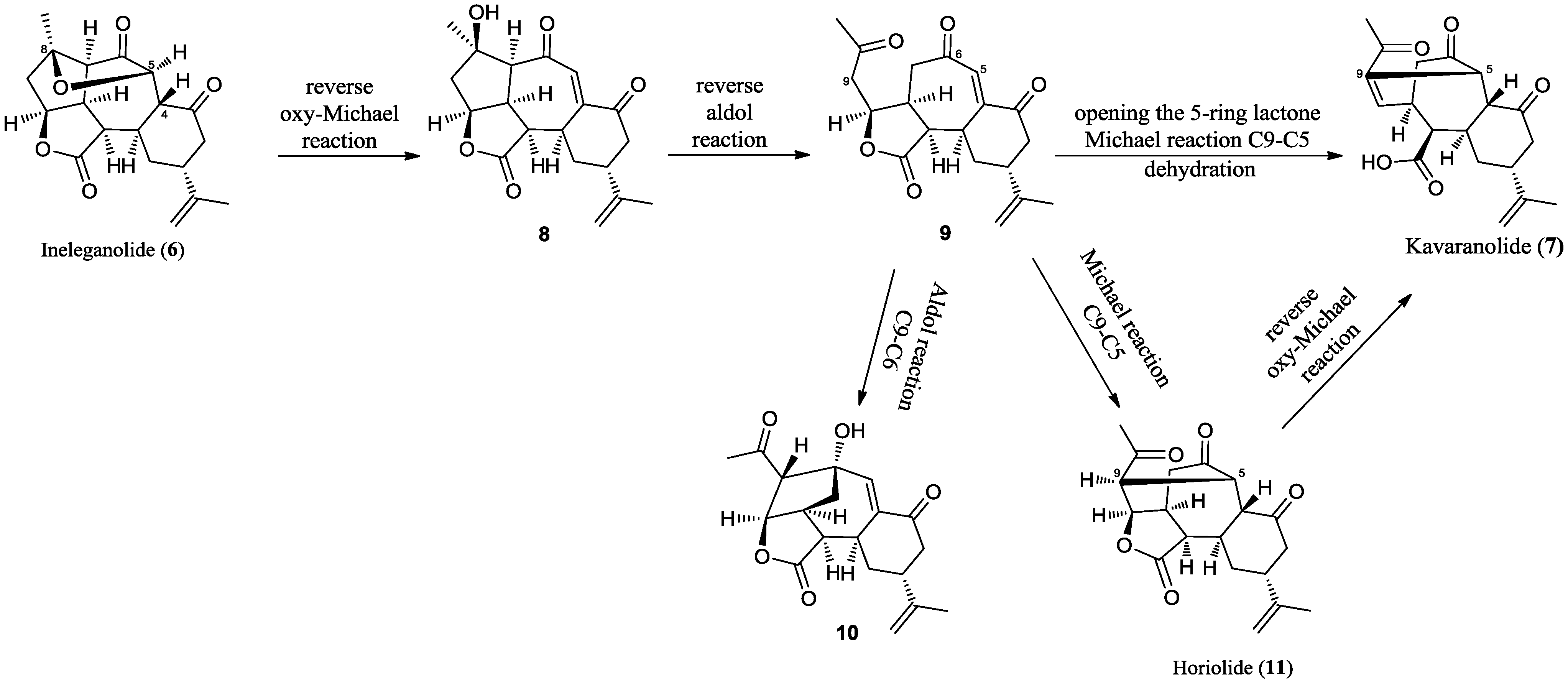
2.2. Chemical Characterization
| δH a | δC | HMBC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.62 m | 39.9 | |
| 2α | 2.50 b | 43.9 | C1, C3, C15 |
| 2β | 2.36 m | C3, C14 | |
| 3 | - | 207.9 | |
| 4 | 3.12 d (12.6) | 50.5 | C3, C5, C6, C13 |
| 5 | 4.30 br s | 43.3 | C3, C4, C6, C7, C8, C9, C10, C13 |
| 6 | - | 211.3 | |
| 7α | 2.19 c | 39.2 | C6, C10, C11, C12 |
| 7β | 2.24 m | C6, C12 | |
| 8 | - | 195.7 | |
| 9 | - | 139.5 | |
| 10 | 7.36 br d (7.5) | 149.0 | C5, C7, C8, C11 |
| 11 | 3.17 m | 34.7 | |
| 12 | 2.29 dd (5.2, 7.5) | 48.8 | C4, C10, C13, C19 |
| 13 | 1.84 m | 36.1 | |
| 14α | 1.55 m | 31.7 | |
| 14β | 2.44 m | C13, C15 | |
| 15 | - | 147.2 | |
| 16 | 4.75 br s | 111.2 | C1, C15, C17 |
| 4.43 br s | C1, C17 | ||
| 17 | 1.63 s | 21.8 | C1, C15, C16 |
| 18 | 2.21 s | 24.8 | C8, C9 |
| 19 | - | 174.1 |
2.3. Inhibition of CHIKV Replicon by Compounds Isolated from S. kavarattiensis
2.3.1. Primary Evaluation by Rluc Detection and ATP Quantitation
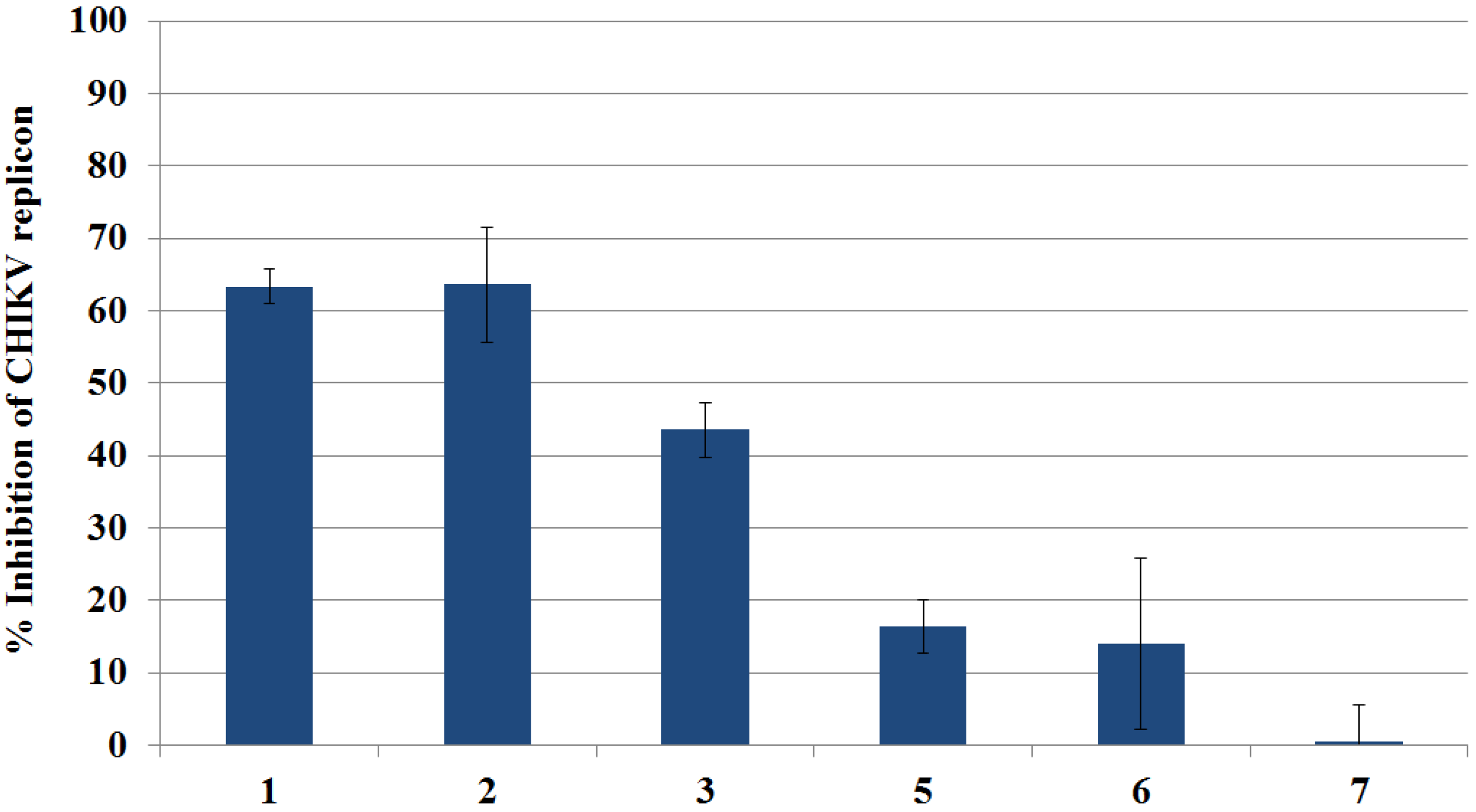
2.3.2. Live Cell Imaging
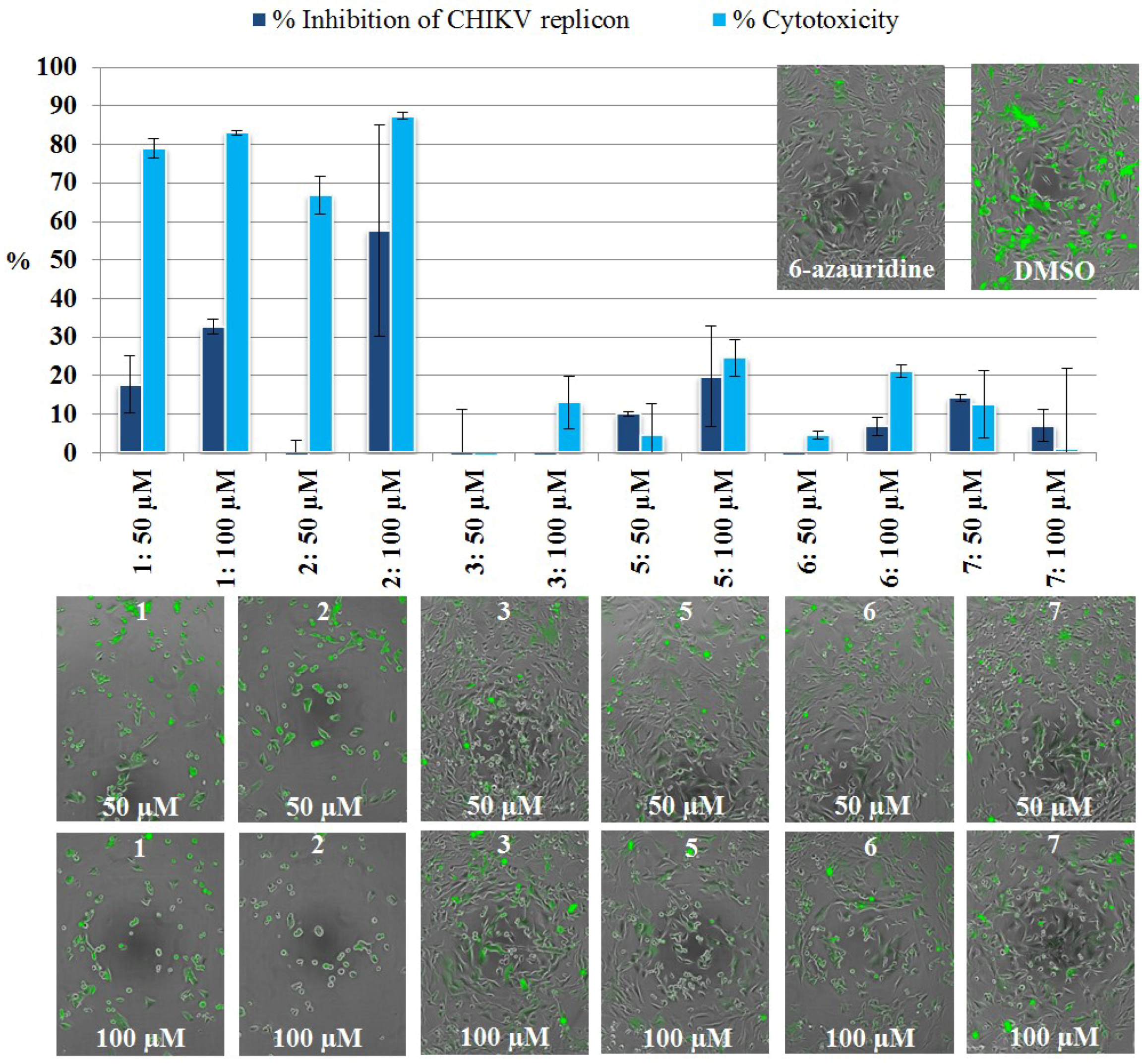
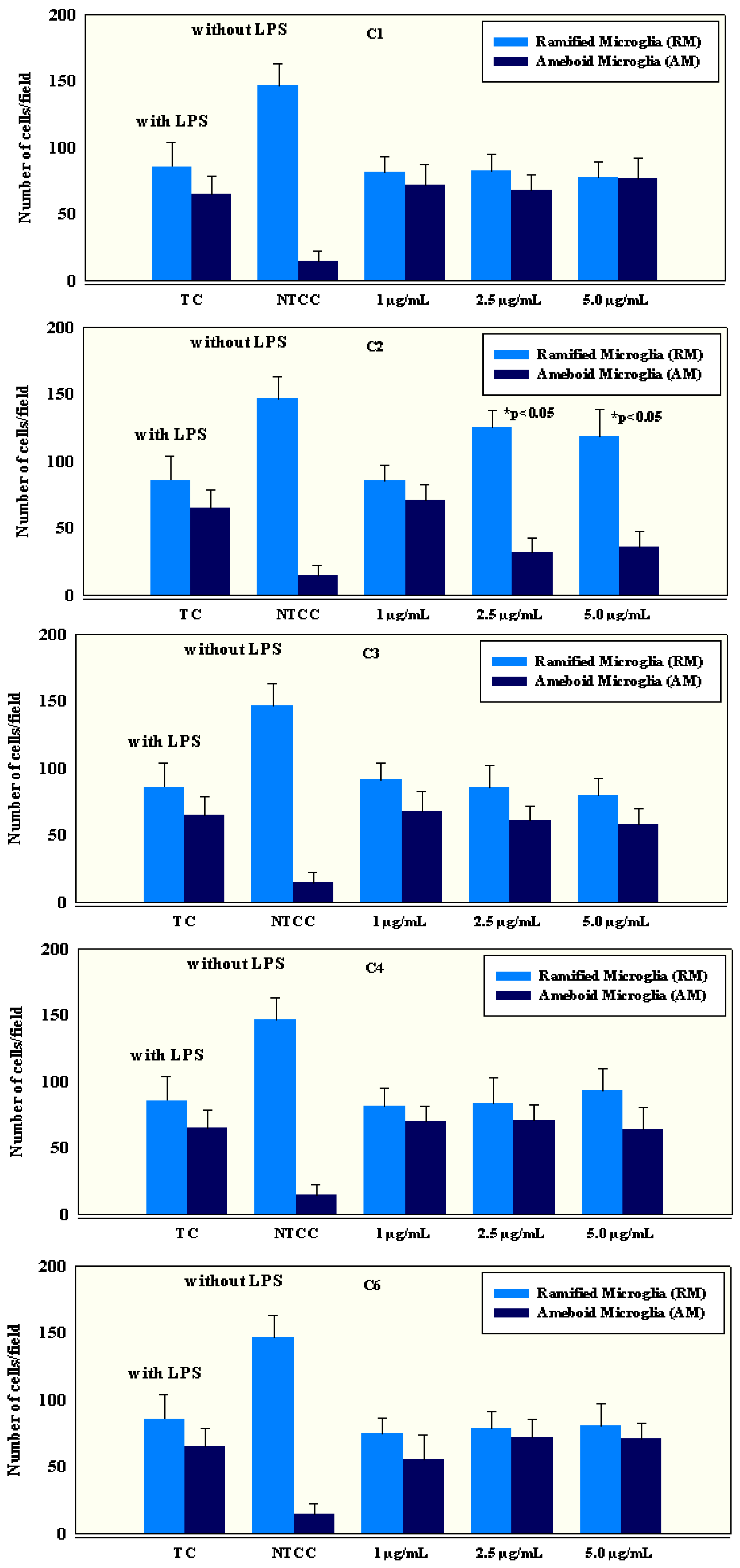
2.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Isolated Compounds
| IL-1β | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-18 | TNF-α | IL-4 | IL-10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LPS-treated (TC) (1 μg/mL) | 1.05 ± 0.06 | 13.5 ± 1.2 | 257 ± 5.7 | 325 ± 8.4 | 34.5 ± 12.2 | 1.4 ± 2.4 | 1.6 ± 2.1 |
| Non-treated (NTCC) (Medium) | 0.05 ± 0.02 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 7 ± 1.1 | 8 ± 1.3 | 5 ± 1.8 | 7.3 ± 0.05 | 8.1 ± 0.08 |
| 1(C1) | 1.04 ± 0.08 | 14.2 ± 1.8 | 256 ± 12 | 319 ± 8.1 | 33.5 ± 11.2 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 7.6 ± 1.6 |
| 1(C2) | 1.09 ± 0.1 | 11.7 ± 1.2 | 239 ± 5 | 318 ± 7.5 | 31.2 ± 9.2 | 2.1 ± 0.8 | 8.2 ± 1.8 |
| 1(C3) | 1.08 ± 0.05 | 13.5 ± 1.4 | 241 ± 7 | 315 ± 8.1 | 33.6 ± 11.1 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 8.7 ± 2.1 |
| 2(C1) | 1.08 ± 0.02 | 12.1 ± 0.9 | 249±13 | 326 ± 4.9 | 34.1 ± 9.1 | 2.1 ± 0.9 | 7.9 ± 3.4 |
| 2(C2) | 0.07 ± 0.04 * | 7.8 ± 1.4 * | 123 ± 11 * | 187 ± 14 * | 12.3 ± 3.4 * | 15.5 ± 2.3 * | 17.4 ± 2.3 * |
| 2(C3) | 0.08 ± 0.06 * | 8.5 ± 1.3 * | 108 ± 9 * | 155 ± 11 * | 9.8 ± 3.3 * | 18.4 ± 1.8 * | 18.5 ± 1.9 * |
| 3(C1) | 1.1 ± 0.05 | 12.9 ± 1.1 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 33.6 ± 11.2 | 1.5 ± 0.9 | 7.5 ± 1.4 |
| 3(C2) | 1.3 ± 0.06 | 11.5 ± 1.3 | 237 ± 4 | 321 ± 7.8 | 24.5 ± 6.9 | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 6.8 ± 1.5 |
| 3(C3) | 1.2 ± 0.05 | 13.2 ± 1.2 | 244 ± 11 | 318 ± 7.6 | 35.4 ± 12.4 | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 6.9 ± 1.5 |
| 4(C1) | 1.01 ± 0.04 | 12.1 ± 1.3 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 33.2 ± 2.8 | 2.2 ± 0.2 | 8.4 ± 2.6 |
| 4(C2) | 1.02 ± 0.04 | 14.1 ± 1.1 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 29.8 ± 2.5 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 7.9 ± 2.5 |
| 4(C3) | 1.01 ± 0.02 | 12.1 ± 1.3 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 32.5 ± 3.7 | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 7.8 ± 3.2 |
| 6(C1) | 1.07 ± 0.07 | 13.2 ± 0.2 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 31.2 ± 2.9 | 1.8 ± 0.6 | 8.5 ± 3.2 |
| 6(C2) | 1.1 ± 0.05 | 12.1 ± 0.9 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 30.6 ± 2.6 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 7.8 ± 2.2 |
| 6(C3) | 1.09 ± 0.02 | 11.8 ± 1.2 | 247 ± 8 | 312 ± 8.2 | 32.3 ± 3.2 | 1.9 ± 0.9 | 7.5 ± 2.1 |
| Sample | Cytotoxicity | IL-1β | IL-6 | IL-8 | IL-18 | TNF-α | IL-4 | IL-10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (μg/mL) | ||||||||
| 1 | >100 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 |
| 2 | >100 | 0.5 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.9 | 1.7 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| 3 | >100 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 |
| 4 | >100 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 |
| 6 | >100 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 | >12.5 |
| Tamoxifen | 3.60 | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| Prednisolone | ND | 12 | 13 | 15 | 16 | 10 | 20 | 15 |
2.5. Bioactivity Potential and Structure-Activity Relationships of Metabolites from S. kavarattiensis
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Chemical Characterization
3.4. Characteristic Data for Natural Compounds
3.5. Evaluation of Anti-CHIKV Replicon Properties
3.5.1. BHK-CHIKV-NCT Cell Culture
3.5.2. CHIKV Replicon Assay, Rluc Detection
3.5.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
3.5.4. CHIKV Replicon Assay, Live Cell Imaging
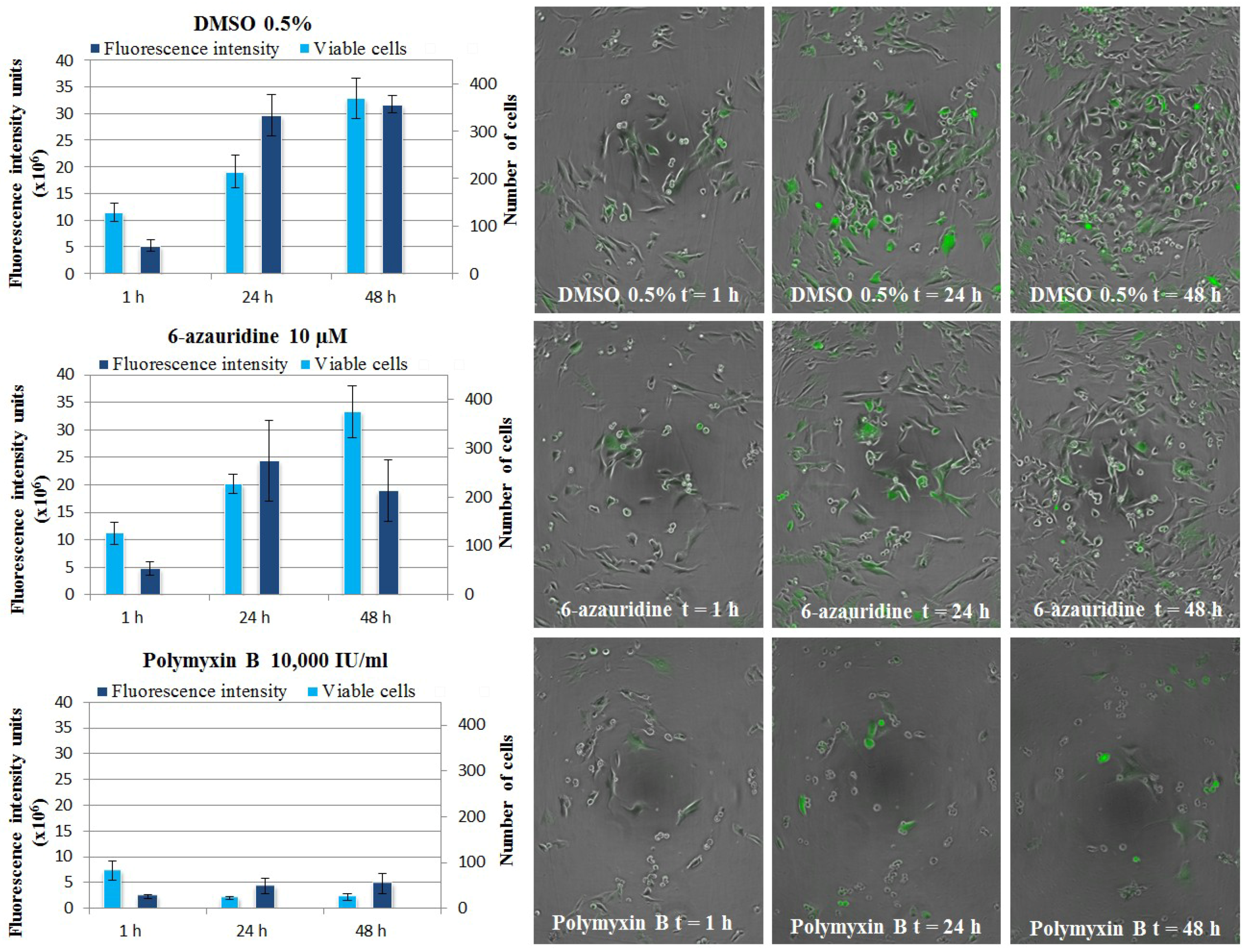
3.6. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Properties
3.6.1. Preparation of Microglial Primary Cell Cultures
3.6.2. Cell Count
3.6.3. Determination of Cytokine Concentration
3.6.4. Determination of IC50 Values by Quantitation of Cytokine Release and Colorimetric Methyl Thiazol Tetrazolium (MTT) Cytotoxicity Assay
3.6.5. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Files
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borgherini, G.; Poubeau, P.; Staikowsky, F.; Lory, M.; le Moullec, N.; Becquart, J.P.; Wengling, C.; Michault, A.; Paganin, F. Outbreak of Chikungunya on Reunion island: Early clinical and laboratory features in 157 adult patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, A.M.; Logue, C.H. Changing patterns of chikungunya virus: Re-emergence of a zoonotic arbovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 2363–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, F.; Parola, P.; Grandadam, M.; Fourcade, S.; Oliver, M.; Brouqui, P.; Hance, P.; Kraemer, P.; Mohamed, A.A.; de Lamballerie, X.; et al. Chikungunya Infection: An emerging rheumatism among travelers returned from Indian Ocean islands. Medicine 2007, 86, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, M.L.; Grilli, E.; Corvetta, A.; Silvi, G.; Angelini, R.; Mascella, F.; Miserocchi, F.; Sambo, P.; Finarelli, A.C.; Sambri, V.; et al. Long-term Chikungunya infection clinical manifestations after an outbreak in Italy: A prognostic cohort study. J. Infect. 2012, 65, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pialoux, G.; Gaüzère, B.A.; Jauréguiberry, S.; Strobel, M. Chikungunya, an epidemic arbovirosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratz, N.G. Critical review of the vector status of Aedes albopictus. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2004, 18, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetsarkin, K.A.; Chen, R.; Leal, G.; Forrester, N.; Higgs, S.; Huang, J.; Weaver, S.C. Chikungunya virus emergence is constrained in Asia by lineage-specific adaptive landscapes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7872–7877. [Google Scholar]
- Schuffenecker, I.; Iteman, I.; Michault, A.; Murri, S.; Frangeul, L.; Vaney, M.; Lavenir, R.; Pardigon, N.; Reynes, J.; Pettinelli, F.; et al. Genome microevolution of Chikungunya viruses causing the Indian Ocean outbreak. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Grandadam, M.; Caro, V.; Plumet, S.; Thiberge, J.; Souarès, Y.; Failloux, A.; Tolou, H.J.; Budelot, M.; Cosserat, D.; Leparc-Goffart, I.; et al. Chikungunya virus, southeastern France. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 910–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezza, G.; Nicoletti, L.; Angelini, R.; Romi, R.; Finarelli, A.; Panning, M.; Cordioli, P.; Fortuna, C.; Boros, S.; Magurano, F.; et al. Infection with Chikungunya virus in Italy: An outbreak in a temperate region. Lancet 2007, 370, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Rua, A.; Zouache, K.; Caro, V.; Diancourt, L.; Delaunay, P.; Grandadam, M.; Failloux, A. High efficiency of temperate Aedes albopictus to transmit Chikungunya and Dengue viruses in the southeast of France. PLoS One 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.H.; Strauss, E.G. The alphaviruses: Gene expression, replication, and evolution. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 491–562. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, P.; Chu, J.J.H. Chikungunya virus: An update on antiviral development and challenges. Drug Discov. Today 2013, 18, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, V.; Kumar, R. Metabolites from Sinularia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 801–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Chen, S.P.; Lu, C.K.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Sinularianins A and B, novel Sesquiterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 2006, 47, 5889–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.J.; Shen, K.P.; Lin, H.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Dai, C.F.; Sheu, J.H. Lochmolins A–G, new Sesquiterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia lochmodes. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.N.; Slattery, M. Terpenoids of Sinularia: Chemistry and biomedical applications. Pharm. Biol. 2005, 43, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.; Pasha, S.G.; Rao, T.S.P.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.S. Marine metabolites: The sterols of soft coral. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.F.; Tai, S.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Wu, Y.C.; Hu, W.P.; Sheu, J.H. A C-3 Methylated isocembranoid and 10-oxocembranoids from a Formosan soft coral, Sinularia grandilobata. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Chuang, C.T.; Wen, Z.H.; Wang, S.K.; Chiou, S.F.; Hsu, C.H.; Dai, C.F.; Duh, C.Y. Bioactive norditerpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia gyrosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 3379–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.C.; Yen, W.H.; Su, J.H.; Chiang, M.Y.N.; Wen, Z.H.; Chen, W.F.; Lu, T.J.; Chang, Y.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, W.H.; et al. Cembrane derivatives from the soft corals, Sinularia gaweli and Sinularia flexibilis. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2154–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, Y.F.; Wen, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia querciformis and Sinularia granosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Su, J.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Sheu, J.H. Cembranoids from the soft corals Sinularia granosa and Sinularia querciformis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 58, 464–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.C.; Sung, P.J.; Duh, C.Y.; Chen, B.W.; Sheu, J.H.; Yang, N.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of natural products isolated from soft corals of Taiwan between 2008 and 2012. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4083–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Chuang, C.; Wang, S.; Wen, Z.; Chiou, S.; Hsu, C.; Dai, C.; Duh, C. Antiviral and anti-inflammatory diterpenoids from the soft coral Sinularia gyrosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.J.; Chen, Y.C.; El-Shazly, M.; Du, Y.C.; Su, J.H.; Tsao, C.W.; Yen, W.H.; Chang, W.B.; Su, Y.D.; Yeh, Y.T.; et al. 5-Episinuleptolide Acetate, a norcembranoidal diterpene from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia sp. induces leukemia cell apoptosis through Hsp90 inhibition. Molecules 2013, 18, 2924–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Cytotoxic cembranoid diterpenes from a soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoh, C.A.; Wang, R.Y.L.; Din, Z.H.; Su, J.H.; Chen, Y.K.; Tsai, F.J.; Weng, S.H.; Wu, Y.J. Induction of apoptosis by Sinulariolide from soft coral through mitochondrial-related and p38MAPK pathways on human bladder carcinoma cells. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 2893–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, B.F.; Coll, J.C.; Mitchell, S.J.; Mulder, J.; Stokie, G.J. Studies of Australian Soft Corals. IX. A novel nor-diterpene from the soft coral Sinularia leptoclados. Aust. J. Chem. 1978, 31, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoji, N.; Umeyama, A.; Arihara, S.A. Novel norditerpenoid from the Okinawan soft coral Sinularia sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1993, 56, 1651–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitman, A.; Rulliere, P.; Sullivan, S.D.E.; Theodorakis, E.A. Total synthesis of Norcembrenolide B and Scabrolide D. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 5854–5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, J.H.; Ahmed, A.F.; Shiue, R.T.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H. Scabrolides A–D, four new norditerpenoids isolated from the soft coral Sinularia scabra. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 1904–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Fenical, W.; Qi-tai, Z.; Clardy, J. Norcembrene diterpenoids from Pacific soft-corals of the genus Sinularia (Alcyonacea; Octocorallia). Tetrahedron 1985, 41, 4303–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, F.; Toyota, M.; Asakawa, Y. Terpenoids from some Japanese liverworts. Phytochemistry 1990, 29, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duh, C.Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chia, M.C.; Chiang, M.Y. A novel cytotoxic norditerpenoid from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia inelegans. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 6033–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Perry, V.H. Microglial physiology: Unique stimuli, specialized responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, V.H.; Nicoll, J.A.R.; Holmes, C. Microglia in neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubanek, J.; Jensen, P.R.; Keifer, P.A.; Sullards, M.C.; Collins, D.O.; Fenical, W. Seaweed resistance to microbial attack: A targeted chemical defense against marine fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6916–6921. [Google Scholar]
- Radhika, P.; Subba Rao, P.V.; Anjaneyulu, V.; Asolkar, R.N.; Laatsch, H. Horiolide, a novel norditerpenoid from Indian Ocean soft coral of the Genus Sinularia. J. Nat. Prod. 2002, 65, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pattenden, G. Novel macrocyclic and polycyclic norcembranoid diterpenes from Sinularia. species of soft coral: Structural relationships and biosynthetic speculations. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pattenden, G. Biomimetic syntheses of ineleganolide and sinulochmodin C from 5-episinuleptolide via sequences of transannular Michael reactions. Tetrahedron 2011, 67, 10045–10052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhamifar, L.; Wu, L.; Andersen, H.; Moghimi, S.M. Live-cell fluorescent microscopy platforms for real-time monitoring of polyplex-cell interaction: Basic guidelines. Methods 2014, 68, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.H.; Wang, G.H.; Chou, T.H.; Wang, S.H.; Lin, R.J.; Chan, L.P.; So, E.C.; Sheu, J.H. 5-epi-Sinuleptolide induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through tumor necrosis factor/mitochondria-mediated Caspase signaling pathway in human skin cancer cells. BBA Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1149–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, W.; Hu, L.; Su, J.; Lu, M.; Twan, W.; Yang, S.; Kuo, Y.; Weng, C.; Lee, C.; Kuo, Y.; et al. Norcembranoidal diterpenes from a Formosan soft coral Sinularia sp. Molecules 2012, 17, 14058–14066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledeboer, A.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Poole, S.; Tilders, F.J.H.; van Dam, A. Interleukin-10, interleukin-4, and transforming growth factor-beta differentially regulate lipopolysaccharide-induced production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide in co-cultures of rat astroglial and microglial cells. Glia 2000, 30, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Grencis, R.; Rothwell, N.J. Actions of exogenous and endogenous IL-10 on glial responses to bacterial LPS/Cytokines. Glia 2001, 33, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, H.; Koganemaru, R.; Iwakawa, Y.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T. Inhibitory effect of norditerpenes on LPS-induced TNF-alpha; Production from the Okinawan soft coral, Sinularia sp. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 26, 380–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avonto, C.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Pollastro, F.; Minassi, A.; di-Marzo, V.; de-Petrocellis, L.; Appendino, G. An NMR spectroscopic method to identify and classify thiol-trapping agents: Revival of Michael acceptors for drug discovery? Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, J.C.; Asgian, J.L.; Ekici, O.D.; James, K.E. Irreversible inhibitors of Serine, Cysteine, and Threonine proteases. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4639–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amslinger, S. The tunable functionality of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds enables their differential application in biological systems. Chem. Med. Chem. 2010, 5, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohjala, L.; Utt, A.; Varjak, M.; Lulla, A.; Merits, A.; Ahola, T.; Tammela, P. Inhibitors of alphavirus entry and replication identified with a stable Chikungunya replicon cell line and virus-based assays. PLoS One 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollini, S.; Herbst, J.J.; Gaughan, G.T.; Verdoorn, T.A.; Ditta, J.; Dubowchik, G.M.; Vinitsky, A. High-throughput fluorescence polarization method for identification of FKBP12 ligands. J. Biomol. Screen. 2002, 7, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, K.; Kitamura, Y.; Tsuchiya, D.; Kawasaki, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Shimohama, S. High mobility group Box Protein-1 inhibits microglial Aβ clearance and enhances Aβ neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 78, 880–891. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.K.; Koppula, S.; Suk, K. Inhibitors of microglial neurotoxicity: Focus on natural products. Molecules 2011, 16, 1021–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Lillsunde, K.-E.; Festa, C.; Adel, H.; De Marino, S.; Lombardi, V.; Tilvi, S.; Nawrot, D.A.; Zampella, A.; D'Souza, L.; D'Auria, M.V.; et al. Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis . Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 4045-4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074045
Lillsunde K-E, Festa C, Adel H, De Marino S, Lombardi V, Tilvi S, Nawrot DA, Zampella A, D'Souza L, D'Auria MV, et al. Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis . Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(7):4045-4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074045
Chicago/Turabian StyleLillsunde, Katja-Emilia, Carmen Festa, Harshada Adel, Simona De Marino, Valter Lombardi, Supriya Tilvi, Dorota A. Nawrot, Angela Zampella, Lisette D'Souza, Maria Valeria D'Auria, and et al. 2014. "Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis " Marine Drugs 12, no. 7: 4045-4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074045
APA StyleLillsunde, K.-E., Festa, C., Adel, H., De Marino, S., Lombardi, V., Tilvi, S., Nawrot, D. A., Zampella, A., D'Souza, L., D'Auria, M. V., & Tammela, P. (2014). Bioactive Cembrane Derivatives from the Indian Ocean Soft Coral, Sinularia kavarattiensis . Marine Drugs, 12(7), 4045-4068. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12074045