Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Structural Elucidation of the Stress Metabolite

| Position | δC a,b, multiplicities | δH c, multiplicities (J in Hz) | Position | δC a,b, multiplicities | δH c, multiplicities (J in Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ile 1 | Leu2 | ||||
| 1 | 170.2, C | 22 | 171.2, C | ||
| 2 | 58.3, CH | 4.04, dd (8.2, 3.0) | 23 | 51.5, CH | 4.31, m |
| 3 | 35.5, CH | 1.88, m | 24 | 41.5, CH2 | 1.46, m |
| 4 | 24.2, CH2 | 25 | 24.3, CH d | 1.48, overlap | |
| 5 | 11.3, CH3 | 0,82, overlap | 26 | 22.8, CH3e | 0.87, overlap |
| 6 | 15.6, CH3 | 0.83, overlap | 27 | 22.2, CH3 | 0.87, overlap |
| 7 | NH | 8.22, d (8.7) | 28 | NH | 7.30, d (8.3) |
| Ile 2 | Leu3 | ||||
| 8 | 172.6, C | 29 | 172.0, C | ||
| 9 | 62.9, CH | 3.34, m | 30 | 50.3, CH | 4.41, m |
| 10 | 33.2, CH | 2.29, m | 31 | 38.8, CH2 | 1.46, m |
| 11 | 25.1, CH2 | 1.48, overlap | 32 | 24.6, CH d | 1.48, overlap |
| 12 | 9.8, CH3 | 0.79, t (7.5) | 33 | 22.4, CH3e | 0.87, overlap |
| 13 | 15.4, CH3 | 0.83, overlap | 34 | 22.2, CH3 | 0.87, overlap |
| 14 | NH | 8.35, d (8.4) | 35 | NH | 7.87, d (8.4) |
| Leu 1 | |||||
| 15 | 171.2, C | ||||
| 16 | 52.1, CH | 4.31, m | |||
| 17 | 40.1, CH2 | 1.51, m | |||
| 18 | 24.6, CH d | 1.49, overlap | |||
| 19 | 22.4, CH3e | 0.87, overlap | |||
| 20 | 22.2, CH3 | 0.87, overlap | |||
| 21 | NH | 8.63, d (8.2) |

2.2. Clavatustide B Inhibits Growth of Cancer Cells
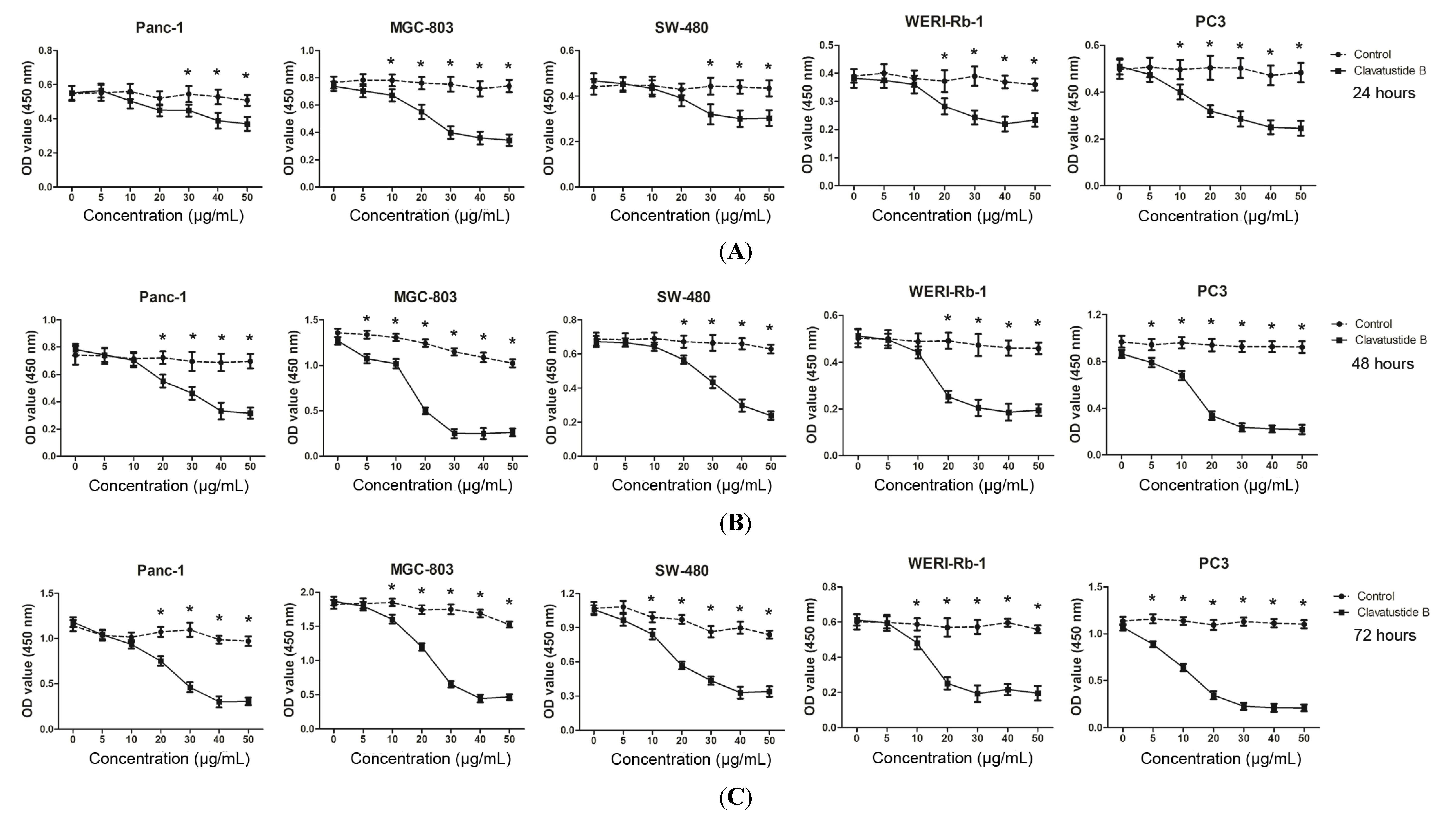
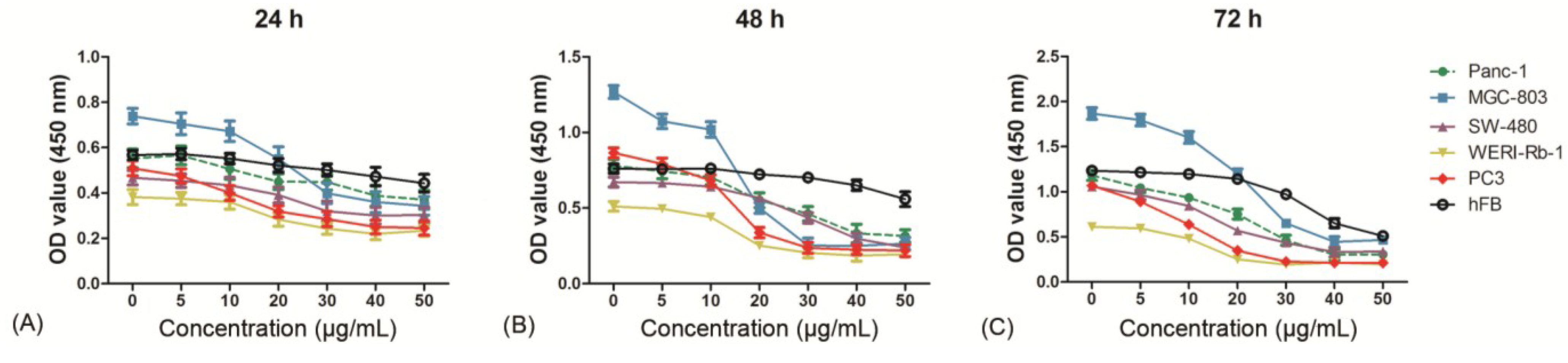
2.3. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity
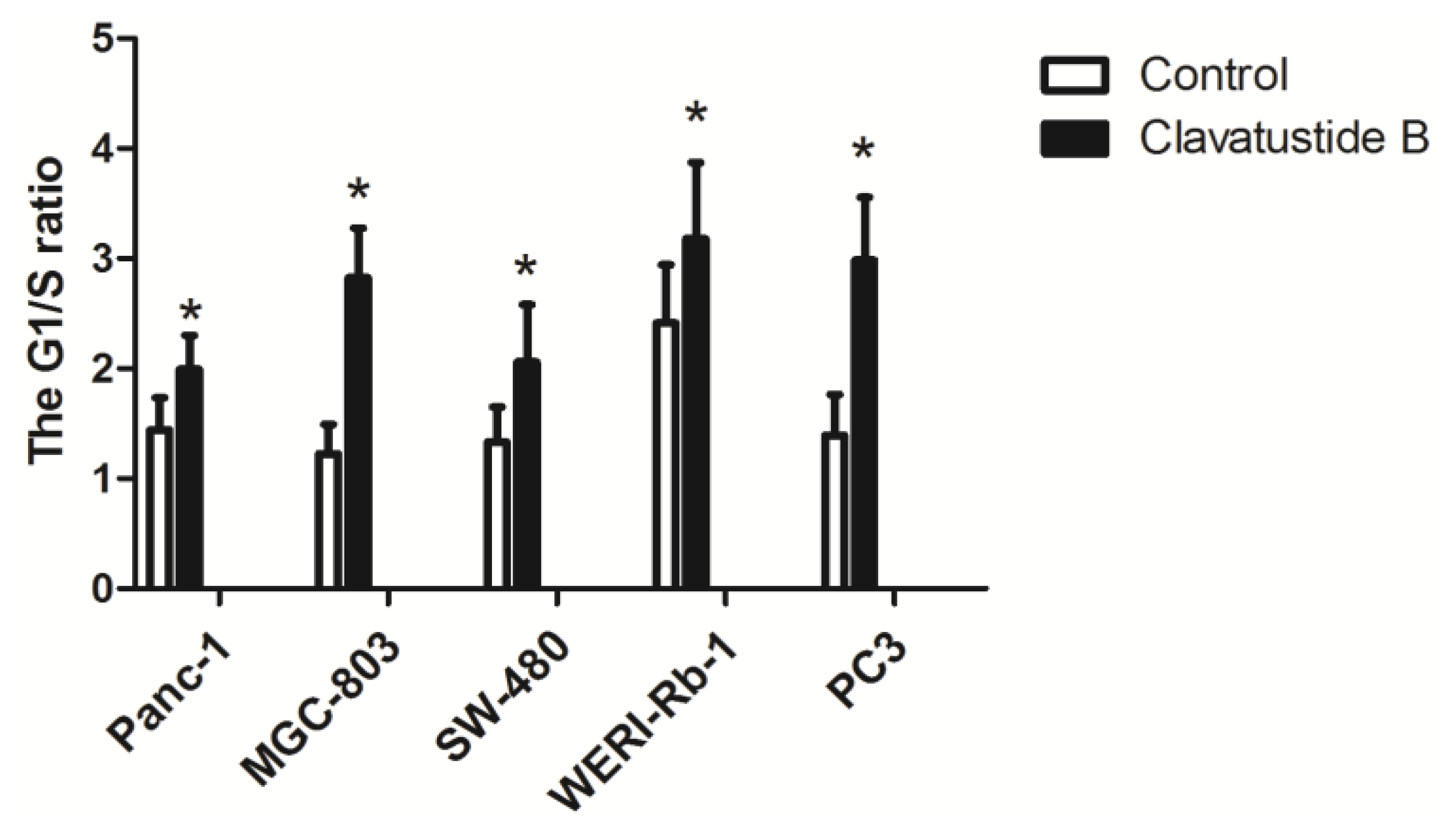
2.4. Clavatustide B Delays G1-S Cell Cycle Transition
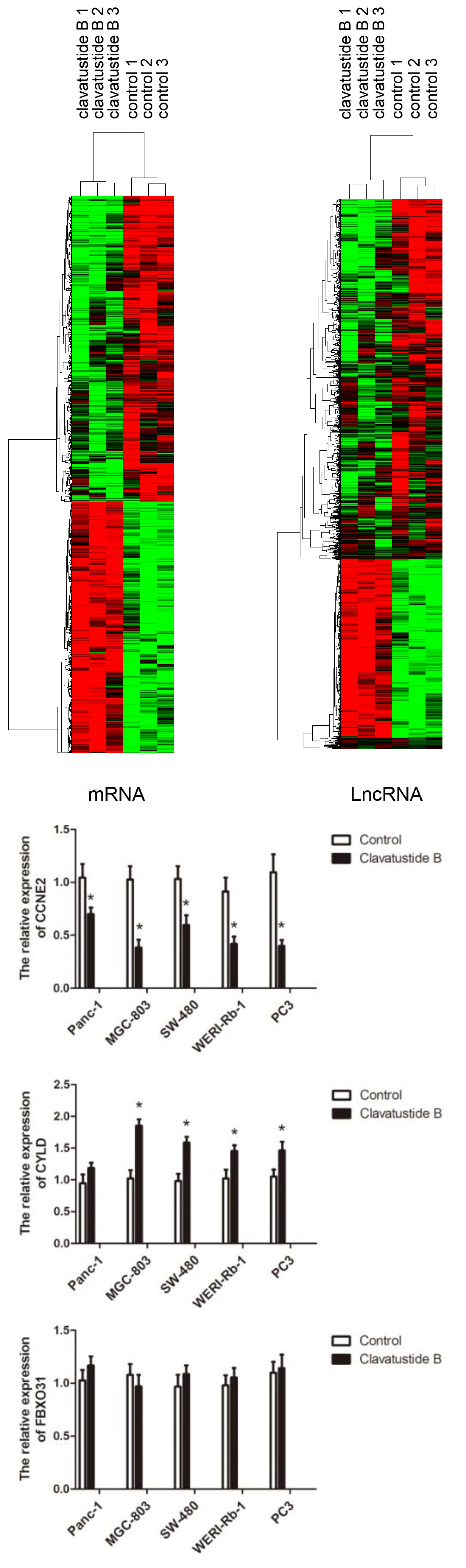
2.5. Clavatustide B Regulates G1-S Transition Genes
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Fungal Cultivation and Stress Applications
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Cell Culture and Proliferation Assay
3.5. Cell Cycle Assay
3.6. Microarray Assay
3.7. Real-Time PCR
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holden, J.F.; Adams, M.W.W. Microbe-metal interactions in marine hydrothermal environments. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2003, 7, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Ye, P.; Chen, C.T.A.; Wang, K.; Liu, P.; He, S.; Wu, X.; Gan, L.; Wu, B. Two novel hepatocellular carcinoma cycle inhibitory cyclodepsipeptides from a hydrothermal vent crab-associated fungus Aspergillus clavatus C2WU. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4761–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, M.S.; Ng, N.K.; Ng, P.K.L. Hydrothermal vent crabs feast on sea “snow”. Nature 2004, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Wu, X.; Sun, M.; Li, M. Two novel tyrosinase inhibitory sesquiterpenes induced by CuCl2 from a marine-derived fungus Pestalotiopsis sp. Z233. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2713–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Oesker, V.; Wiese, J.; Schmaljohann, R.; Imhoff, J.F. Two new antibiotic pyridones produced by a marine fungus Trichoderma sp. Strain MF106. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1208–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.R.; Fenical, W. Strategies for the discovery of secondary metabolites from marine bacteria: Ecological perspectives. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1994, 48, 559–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cueto, M.; Jensen, P.R.; Kauffman, C.; Fenical, W.; Lobkovsky, E.; Clardy, K. Pestalone, a new antibiotic produced by a marine fungus in response to bacterial challenge. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 1444–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.B.; Kwon, H.C.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, H.O. Glionitrin A, an antibiotic-antitumor metabolite derived from competitive interaction between abandoned mine microbes. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Jiang, W.; Wu, B. Methodological aspects about determination of plant defensive phenolics in response to stress. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2013, 9, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterfield, D.A.; Jonasson, I.R.; Massoth, G.J.; Feely, R.A.; Roe, K.K.; Embley, R.E.; Holden, J.F.; McDuff, R.E.; Lilley, M.D.; Delaney, J.R. Seafloor eruptions and evolution of hydrothermal fluid chemistry. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A 1997, 355, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/all.html (accessed on 5 April 2014).
- Li, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Chang, J.; Sun, X.; Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Traditional Chinese medicine in cancer care: A review of controlled clinical studies published in chinese. PLoS One 2013, 8, e60338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Xu, X.; Wei, X.; Wang, W.; Zhou, B.; Wang, B.; Zheng, S. Oxymatrine induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP families, and releasing of cytochrome c. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, Y.; Sakurai, A. Chemical studies on the mistleteo. II. The structure of viscumamide, anew cyclic peptide isolated from Viscum album Linn. var. coloratum Ohwi. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1973, 46, 2190–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, A.; Okumura, Y. Synthesis of viscumamide and its analogs. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1979, 52, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Q.; Xu, X.; Zheng, S.S.; Kalthoff, H. The diversity between pancreatic head and body/tail cancers: Clinical parameters and in vitro models. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2013, 12, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimeault, M.; Johansson, S.L.; Batra, S.K. Marked improvement of cytotoxic effects induced by docetaxel on highly metastatic and androgen-independent prostate cancer cells by downregulating macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar]
- Malumbres, M.; Barbacid, M. Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Shao, Y.; Hou, G.; Bai, J.; Yuan, W.; Hu, L.; Cheng, T.; Zetterberg, A.; Zhang, J. QM-FISH analysis of the genes involved in the G1/S checkpoint signaling pathway in triple-negative breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 1847–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Barraclough, J.; Stone, A.; Sutherland, R.L. Cyclin D as a therapeutic target in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, F.H.; Yao, D.; Quinn, J.A.; Greenhalgh, D.A. PTEN ablation in Ras/Fos skin carcinogenesis invokes p53-dependent p21 to delay conversion while p53-independent p21 limits progression via cyclin D1/E2 inhibition. Oncogene 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstrom, S.A.; Masoumi, K.C.; Khochbin, S.; Fassler, R.; Massoumi, R. CYLD negatively regulates cell-cycle progression by inactivating HDAC6 and increasing the levels of acetylated tubulin. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.W.; Simon, R.M. A random variance model for detection of differential gene expression in small microarray experiments. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 2448–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Liu, J.; He, F.; Xu, W.; Yao, K. Hypoxia-Induced deregulation of miR-126 and its regulative effect on VEGF and MMP-9 expression. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 11, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, P.; Shen, L.; Jiang, W.; Ye, Y.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wu, X.; Wang, K.; Wu, B. Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 3203-3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063203
Ye P, Shen L, Jiang W, Ye Y, Chen C-TA, Wu X, Wang K, Wu B. Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(6):3203-3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063203
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Panpan, Ling Shen, Wei Jiang, Ying Ye, Chen-Tung Arthur Chen, Xiaodan Wu, Kuiwu Wang, and Bin Wu. 2014. "Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B" Marine Drugs 12, no. 6: 3203-3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063203
APA StyleYe, P., Shen, L., Jiang, W., Ye, Y., Chen, C.-T. A., Wu, X., Wang, K., & Wu, B. (2014). Zn-Driven Discovery of a Hydrothermal Vent Fungal Metabolite Clavatustide C, and an Experimental Study of the Anti-Cancer Mechanism of Clavatustide B. Marine Drugs, 12(6), 3203-3217. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12063203






