NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Spatial Variation in Soft Corals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Spectral Analysis
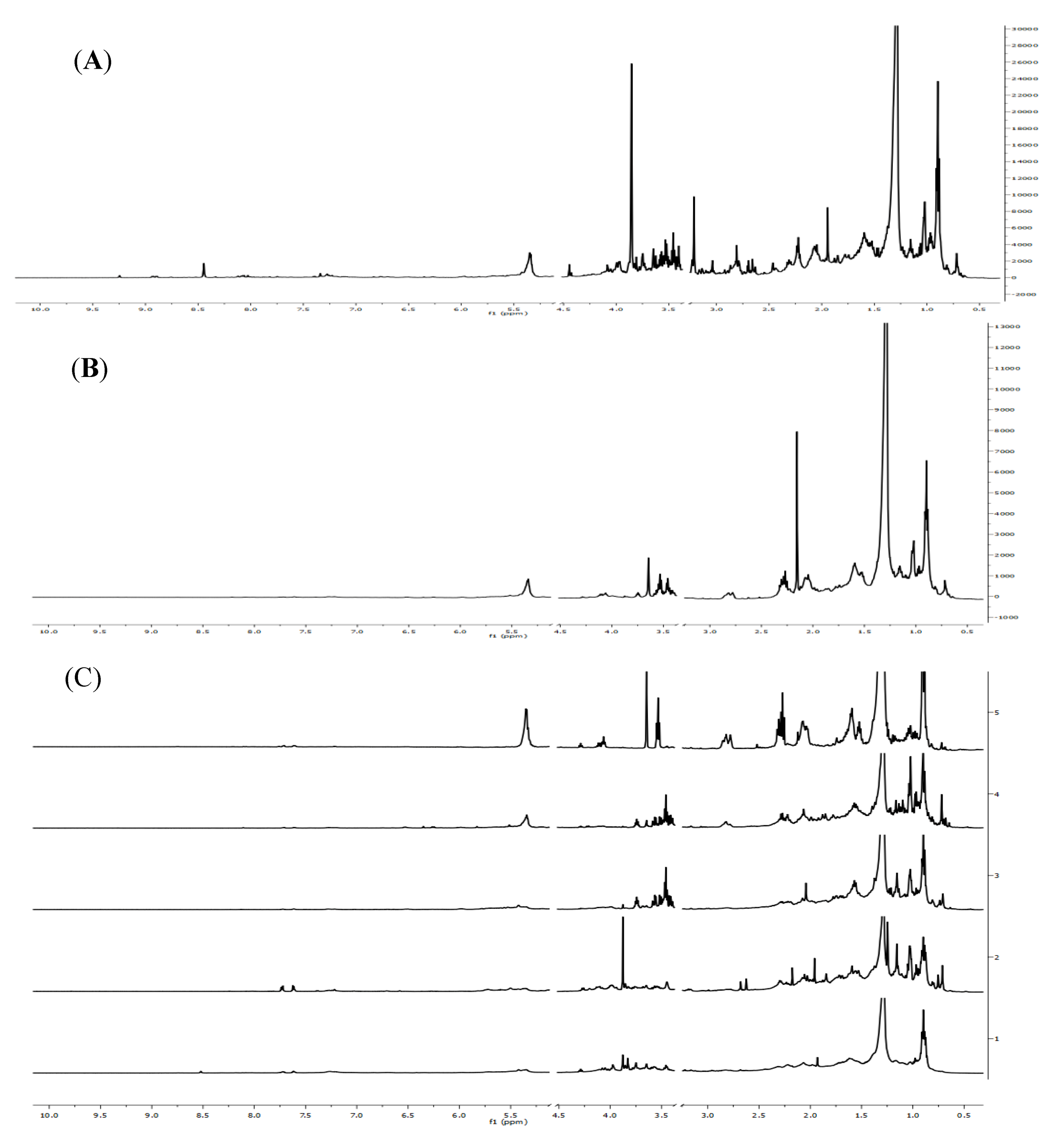
2.2. Statistical Analysis
| Metabolite | Structure | 1H Chemical Shifts (ppm) and Coupling Constants (Hz) |
|---|---|---|
| ∆9(15)-africanene [26] | 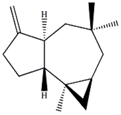 | 0.23 (dd, J = 4.0, 5.0) |
| d-aromadendrane-4β,10α-diol [27,28] | 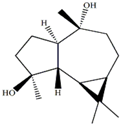 | 0.34 (t, J = 10.5) |
| (+)-aromadendrane-4α,10β-diol [27,28] | 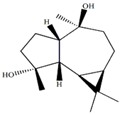 | 0.01 (t, J = 9.5) |
| Alismoxide [29] |  | 5.46 (s) |
| dendronpholide O [21] |  | 6.24 (s), 5.76 (s) |
| 4(15)-eudesmene-1β,6α-diol [30,31] | 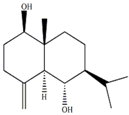 | 4.85 (s), 4.72 (s) |
| Germacra-4(15),5,10(14)-trien-1α-ol [32] | 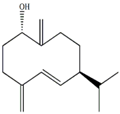 | 5.82 (d, J = 16.2), 4.96 (s), 3.85 (m) |
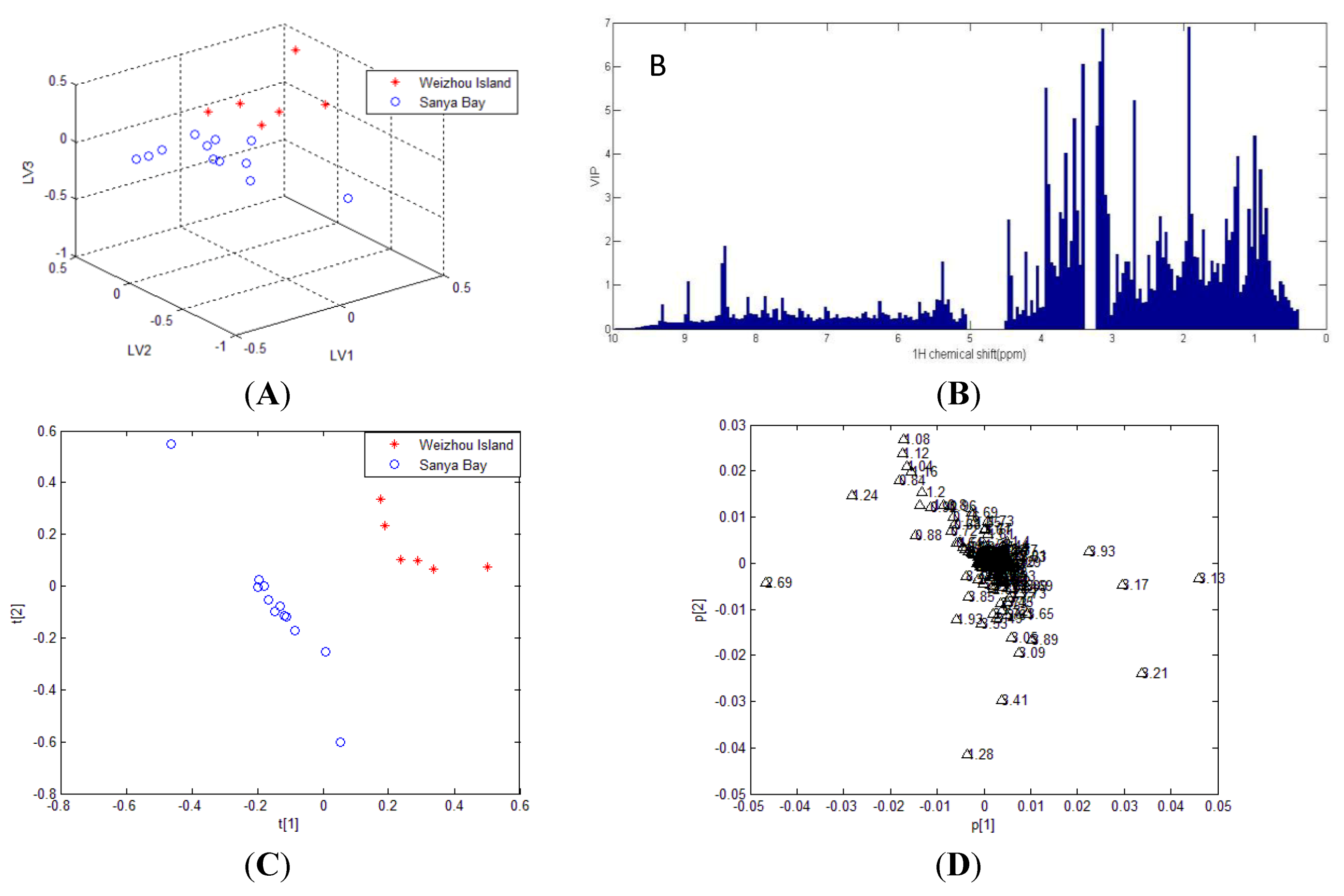
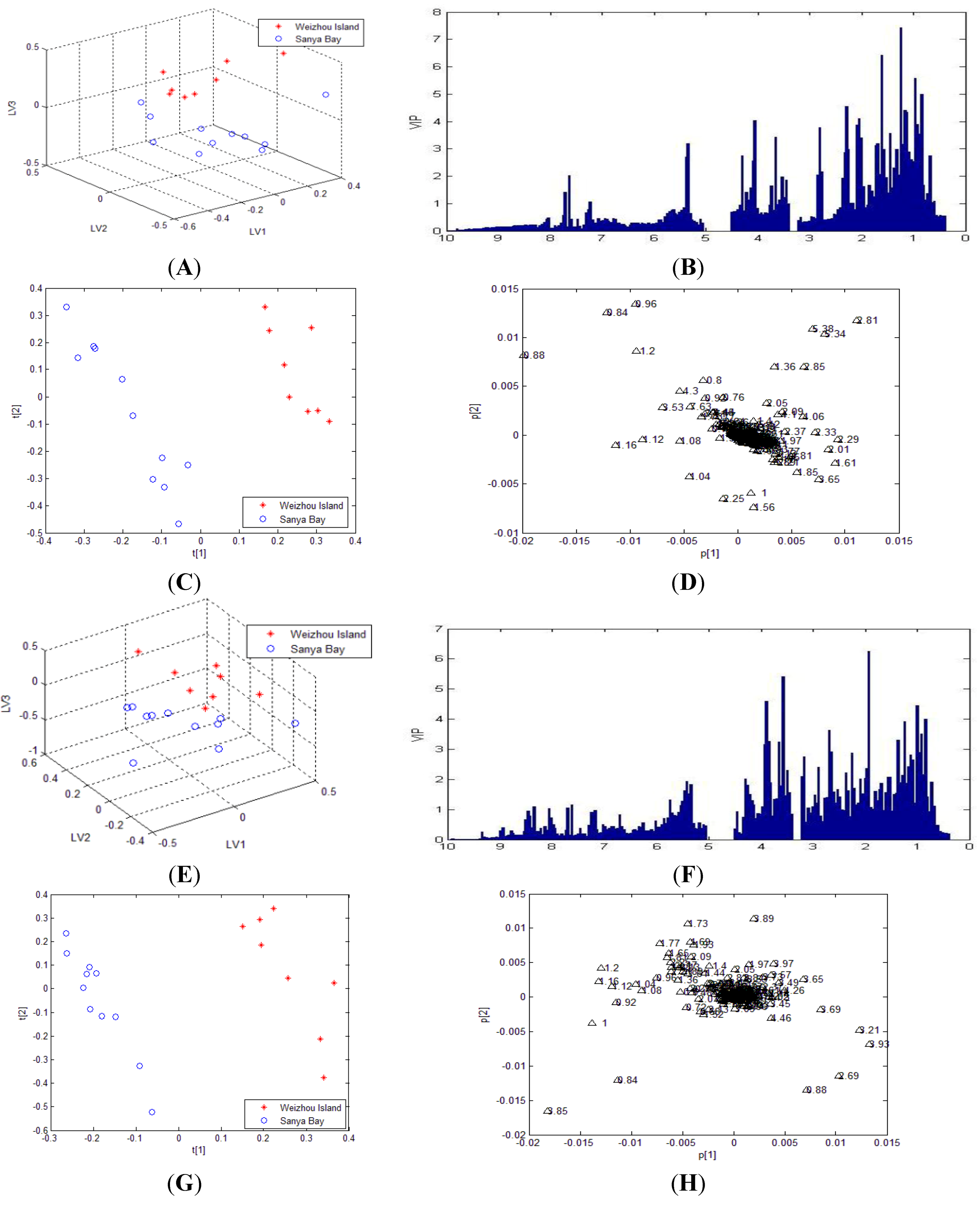
| PLS-DA Model Data | R2X | R2Y | Cross-validated Q2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1H-NMR data of methanol extract | 0.916 | 0.940 | 0.327 |
| 1H-NMR data of ethyl acetate extract Fr.1 | 0.977 | 0.971 | 0.610 |
| 1H-NMR data of ethyl acetate extract Fr.2 | 0.747 | 0.505 | 0.207 |
| 1H-NMR data of ethyl acetate extract Fr.3 | 0.968 | 0.790 | 0.176 |
| 1H-NMR data of ethyl acetate extract Fr.4 | 0.846 | 0.845 | 0.175 |
| 1H-NMR data of ethyl acetate extract Fr.5 | 0.815 | 0.573 | 0.371 |
3. Experimental Section
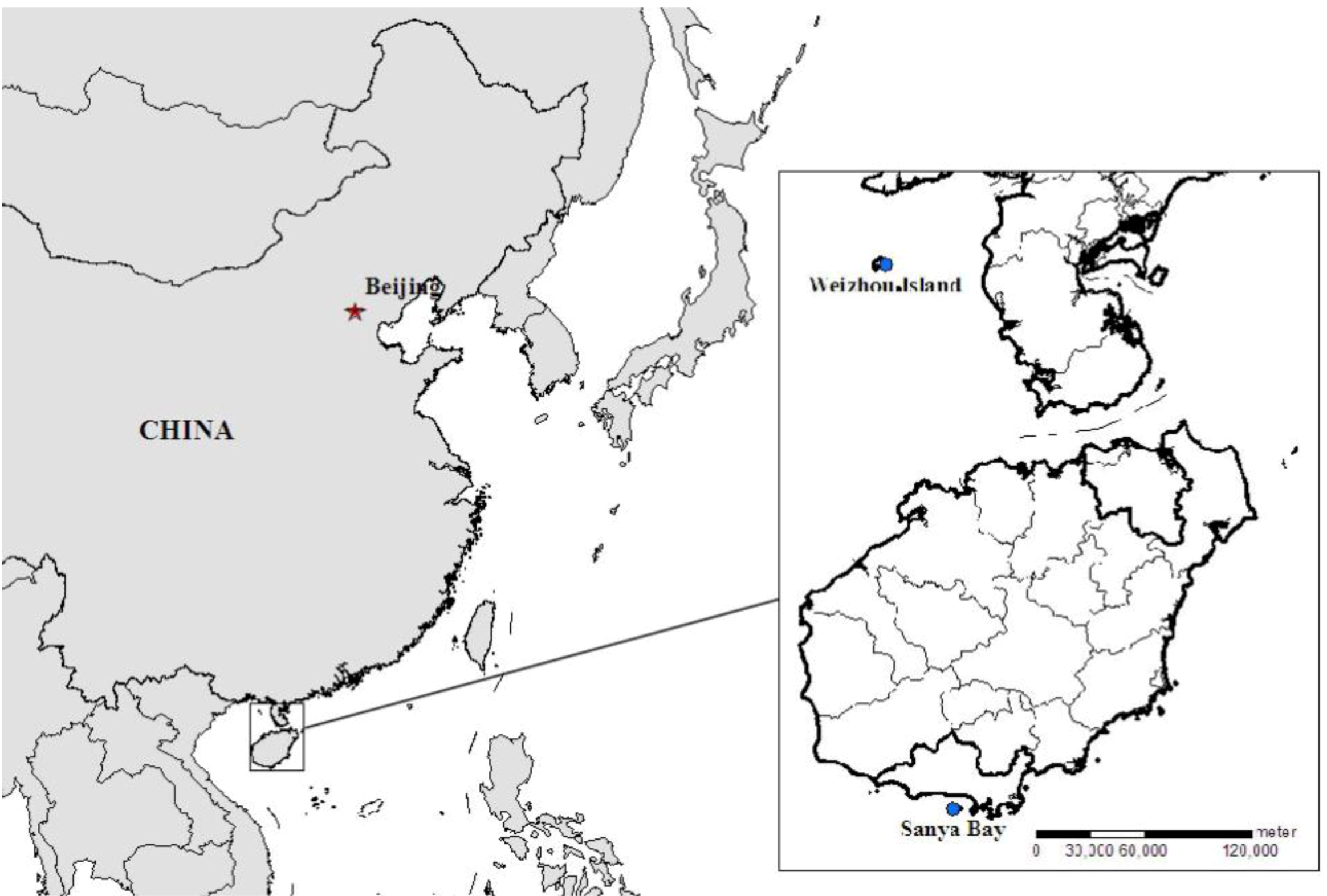
3.1. General Site Description
| Sampling Area | Sanya Bay | Weizhou Island |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature(°C) | 29.2 [46] | 29.6 [48] |
| Salinity (‰) | 33.3 [46] | 32.9 [49] |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 6.72 [50] | 7.31 [48] |
| pH | 8.14 [51] | 8.19 [49] |
| Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (mg/L) | 0.036 [50] | 0.05 [52] |
| Dissolved Inorganic Phosphate(mg/L) | 0.007 [50] | 0.0039 [53] |
3.2. Biological Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. 1H-NMR Data Acquisition and Multivariate Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.-W.; Gu, Y. Secondary metabolites from the South China Sea invertebrates: Chemistry and biological activity. Curr. Med. Chem. 2006, 13, 2041–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Hatanaka, M.; Nakano, A.; Morihara, K.; Takemura, K. Distribution of sarcophytol A in soft coral of the Sarcophyton genus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2000, 64, 858–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Chao, C.H.; Su, J.H.; Tsai, C.W.; Wang, W.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Huang, C.Y.; Sung, P.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Sheu, J.H. Klysimplexins I–T, eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011, 9, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Su, J.H.; Wang, W.H.; Fan, T.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Eunicellin-based diterpenoids from the cultured soft coral Klyxum simplex. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 7016–7022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.L.; Su, J.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, B.W.; Dai, C.F.; Kuo, Y.H.; Sheu, J.H. Simplexins A–I, Eunicellin-Based Diterpenoids from the Soft Coral Klyxum simplex. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 994–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. 5,8-Epidioxysterols and related derivatives from a Chinese Soft Coral Sinularia flexibilis. Steroids 2006, 71, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundy, J.G.; Davey, M.P.; Viant, M.R. Environmental metabolomics: A critical review and future perspectives. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroujerdi, A.F.; Vizcaino, M.I.; Meyers, A.; Pollock, E.C.; Huynh, S.L.; Schock, T.B.; Morris, P.J.; Bearden, D.W. NMR-based microbial metabolomics and the temperature-dependent coral pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7658–7664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremaroli, V.; Workentine, M.L.; Weljie, A.M.; Vogel, H.J.; Ceri, H.; Viti, C.; Tatti, E.; Zhang, P.; Hynes, A.P.; Turner, R.J.; et al. Metabolomic investigation of the bacterial response to a metal challenge. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, M.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.H.; Verpoorte, R. Metabolomic response of Brassica rapa submitted to pre-harvest bacterial contamination. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shulaev, V.; Cortes, D.; Miller, G.; Mittler, R. Metabolomics for plant stress response. Physiol. Plant. 2008, 132, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasulo, S.; Iacono, F.; Cappello, T.; Corsaro, C.; Maisano, M.; D’Agata, A.; Giannetto, A.; de Domenico, E.; Parrino, V.; Lo Paro, G.; et al. Metabolomic investigation of Mytilus galloprovincialis (Lamarck 1819) caged in aquatic environments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 84, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, T.; Mauceri, A.; Corsaro, C.; Maisano, M.; Parrino, V.; Lo Paro, G.; Messina, G.; Fasulo, S. Impact of environmental pollution on caged mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis using NMR-based metabolomics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, L.M.; Björlenius, B.; Förlin, L.; Larsson, D.J. Reproducible 1H-NMR-based metabolomic responses in fish exposed to different sewage effluents in two separate studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schock, T.B.; Stancyk, D.A.; Thibodeaux, L.; Burnett, K.G.; Burnett, L.E.; Boroujerdi, A.F.; Bearden, D.W. Metabolomic analysis of Atlantic blue crab, Callinectes sapidus, hemolymph following oxidative stress. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochfort, S.J.; Ezernieks, V.; Yen, A.L. NMR-based metabolomics using earthworms as potential indicators for soil health. Metabolomics 2009, 5, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R. Recent developments in environmental metabolomics. Mol. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics—The link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viant, M.R. Environmental metabolomics using 1H-NMR spectroscopy. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 410, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, E.S.; Viant, M.R.; Braid, B.M.; Moore, J.D.; Friedman, C.S.; Tjeerdema, R.S. Characterizing the metabolic actions of natural stresses in the California red abalone, Haliotis rufescens using 1H-NMR metabolomics. Metabolomics 2005, 1, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Bayer, M.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Dendronpholides A–R, cembranoid diterpenes from the Chinese Soft Coral Dendronephthya sp. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraccaroli, M.; Nicoletti, S.; Maltese, F.; Choi, Y.H.; Guzzo, F.; Levi, M.; Verpoorte, R. Pre-analytical method for metabolic profiling of plant cell cultures of Passiflora garckei. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 2031–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-S.; Yao, L.-G.; di Pascale, A.; Irace, C.; Mollo, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Guo, Y.-W. Polyoxygenated diterpenoids of the eunicellin-type from the Chinese soft coral Cladiella krempfi. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, M.; Carroll, A.; Coll, J. Variability of terpene content in the soft coral Sinularia flexibilis (Coelenterata: Octocorallia), and its ecological implications. J. Chem. Ecol. 1993, 19, 2285–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Ding, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Sinulaflexiolides A–K, Cembrane-type diterpenoids from the Chinese soft coral sinularia flexibilis. J. Nat. Prod. 2008, 71, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashman, Y.; Bodner, M.; Finer-Moore, J.S.; Clardy, J. Δ9 (15)-Africanene, a new sesquiterpene hydrocarbon from the soft coral Sinularia erecta. Experientia 1980, 36, 891–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, A.S.; Sagar, K.S.; Venugopal, M.J. Terpenoid and steroid constituents of the Indian ocean soft coral Sinularia maxima. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 10997–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.H.G.; Roque, N.F. Estudo fitoquímico da madeira de Guarea macrophylla (Meliaceae). Quim. Nova 2009, 32, 2351–2354. [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa, I.; Kobayashi, M.; Cui, Z.; Kiyota, Y.; Ohnishi, M. Marine natural products. XV: Chemical constituents of an Okinawan soft coral of Xenia sp. (Xeniidae). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1986, 34, 4590–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.Y.; Su, J.H.; Liu, Y.C.; Wen, Z.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Oppositane-type sesquiterpenoids from the Formosan soft coral Sinularia leptoclados. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 83, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, A. 7-epi-Eudesmanes from Teucrium polium. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Mayol, L.; Amico, V.; Piattelli, M.; Tringali, C. Isolation of (2R, 8R)-germacra-1 (11), 5 (12), E6-trien-2-ol acetate from the brown alga dilophusfasciola. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 4149–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erikson, L.; Johansson, E.; Kettaneh-Wold, N.; Wold, S. Multi-and Megavariate Data Analysis; Umetyrics AB: Malmö, Sweden, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, V.; Kumar, R. Metabolites from Sinularia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 801–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, R.; Kuang, Y.; Zeng, L. A new cembranolide from the soft coral Sinularia capillosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1543–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, Z.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Cytotoxic cembranoid diterpenes from a soft coral Sinularia gibberosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-X.; Yan, S.-J.; Zhang, G.-W.; Lu, W.-G.; Su, J.-Y.; Zeng, L.-M.; Gu, L.-Q.; Yang, X.-P.; Lian, Y.-J. Cytotoxic diterpenoids from the soft coral sinularia microclavata. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1087–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Shao, C.-L.; Qi, X.; Li, X.-B.; Li, J.; Sun, L.-L.; Wang, C.-Y. Polyoxygenated sterols from the South China Sea Soft Coral Sinularia sp. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 1422–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.-Y.; Li, X.-B.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Tang, H.; Liu, B.-S.; Yi, Y.-H. Bioactive constituents from Sinularia sp. J. Pharm. Pract. 2010, 28, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Tang, X.; Li, P.; Li, G. Studies on chemical constituents of Sinularia sp. Chin. J. Mar. Drugs 2012, 31, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R.; Kurtán, T.; Mándi, A.; Yan, X.-H.; Zhang, W.; Guo, Y.-W. Biscembranoids formed from an α, β-unsaturated γ-lactone ring as a dienophile: Structure revision and establishment of their absolute configurations using theoretical calculations of electronic circular dichroism spectra. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 78, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.-X.; He, X.-X.; Zhang, J.; Guo, Q.; Lei, L.-F.; Su, J.-Y.; Zeng, L.-M. New precursor of tetraterpenoids from the soft coral Sarcophyton glaucum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Wang, P.; Gong, W.; Xue, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Liu, B.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, W. Bioactive polyoxygenated steroids from the South China Sea soft coral, Sarcophyton sp. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, N.S.; Krishna, M.S.; Pasha, S.G.; Rao, T.S.P.; Venkateswarlu, Y.; Parameswaran, P.S. Marine metabolites: The sterols of soft coral. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 2803–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tan, Y.; Song, X.; Huang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Dong, J.; Chen, R. The status of the ecological environment and a proposed protection strategy in Sanya Bay, Hainan Island, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Shao Wang, Y.; Wu, M.L.; Zhang, S.; Cai, C.H. Chemometry use in the evaluation of the sanya bay water quality. Braz. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 58, 339–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.S.; Huang, H.; Huang, L.M.; Wang, D.R. Sanya Coral Reefs and Biodiversity; China Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 2010; pp. 25–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, G.Z. The status and prospect of researches on coral reef in Weizhou Island. J. Guangxi Acad. Sci. 2009, 25, 72–75. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.Y. Monitoring and Evaluation of Ecological Environment of Coral Reef Areas in Weizhou Island, Beihai, Guangxi. Master Thesis, Ocean University of China, Shandong, China, 2 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.X.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Li, P.S. Evaluation of water quality status of coastal water in Sanya Bay in sunmmer. Trans. Oceanol. Limnol. 2010, 3, 100–106. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.T.; Shan, X.J.; Liu, S.M.; Ye, H.B.; Yang, C.Y.; Xu, C.; Dong, J.D. Spatial and temporal distribution of pH in Sanya Bay in recent 10 years and its effects on coral reef. South China Fish. Sci. 2013, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.M.; Chen, B.; Ma, Z.Y.; Yu, W.W. Assessment and cause analysis of eutrophication in the adjancent sea areas of south subtropical islands. Mar. Sci. Bull. 2010, 29, 572–576. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.X.; Li, G.Z.; He, B.M.; Li, Z.; Tan, Q.Z.; Wang, X. Seasonal variation of different forms of phosphorous and the influential factors in coral reef ecoregion of Weizhou Island. J. Appl. Oceanogr. 2013, 32, 258–264. [Google Scholar]
- Moberg, F.; Folke, C. Ecological goods and services of coral reef ecosystems. Ecol. Econ. 1999, 29, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
He, Q.; Sun, R.; Liu, H.; Geng, Z.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Han, J.; Lin, W.; Du, S.; Deng, Z. NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Spatial Variation in Soft Corals. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 1876-1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041876
He Q, Sun R, Liu H, Geng Z, Chen D, Li Y, Han J, Lin W, Du S, Deng Z. NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Spatial Variation in Soft Corals. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(4):1876-1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041876
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Qing, Ruiqi Sun, Huijuan Liu, Zhufeng Geng, Dawei Chen, Yinping Li, Jiao Han, Wenhan Lin, Shushan Du, and Zhiwei Deng. 2014. "NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Spatial Variation in Soft Corals" Marine Drugs 12, no. 4: 1876-1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041876
APA StyleHe, Q., Sun, R., Liu, H., Geng, Z., Chen, D., Li, Y., Han, J., Lin, W., Du, S., & Deng, Z. (2014). NMR-Based Metabolomic Analysis of Spatial Variation in Soft Corals. Marine Drugs, 12(4), 1876-1890. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12041876






