Abstract
For a small library of natural products from marine sponges and ascidians, in silico docking to the Lymnaea stagnalis acetylcholine-binding protein (AChBP), a model for the ligand-binding domains of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), was carried out and the possibility of complex formation was revealed. It was further experimentally confirmed via competition with radioiodinated α-bungarotoxin ([125I]-αBgt) for binding to AChBP of the majority of analyzed compounds. Alkaloids pibocin, varacin and makaluvamines С and G had relatively high affinities (Ki 0.5–1.3 μM). With the muscle-type nAChR from Torpedo californica ray and human neuronal α7 nAChR, heterologously expressed in the GH4C1 cell line, no competition with [125I]-αBgt was detected in four compounds, while the rest showed an inhibition. Makaluvamines (Ki ~ 1.5 μM) were the most active compounds, but only makaluvamine G and crambescidine 359 revealed a weak selectivity towards muscle-type nAChR. Rhizochalin, aglycone of rhizochalin, pibocin, makaluvamine G, monanchocidin, crambescidine 359 and aaptamine showed inhibitory activities in electrophysiology experiments on the mouse muscle and human α7 nAChRs, expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Thus, our results confirm the utility of the modeling studies on AChBPs in a search for natural compounds with cholinergic activity and demonstrate the presence of the latter in the analyzed marine biological sources.
1. Introduction
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are among the most comprehensively studied ligand-gated ion channels (see reviews [1,2,3,4]). They are widespread in fish electric organs and mammalian muscles (so-called muscle type of nAChR), central and peripheral nervous systems (neuronal nAChRs) and some non-neuronal tissues (so-called “non-neuronal” nAChRs), where they perform a multitude of functions from conducting nerve-muscle transmission to participation in the different cognitive processes and regulation of inflammatory response. Involvement of distinct nAChR subtypes in different pathologies (muscle dystrophies, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, schizophrenia, nicotinic addiction, chronic pain) dictates the need for potent and highly selective cholinergic ligands to the respective receptor subtypes. In addition, utilization of similar new compounds as drugs in clinics is under intensive development [5].
A huge number of compounds of different chemical nature from various taxa (bacteria, plants, mollusks, chordates) are known to interact with nAChRs. Among them, the most well-known and widely used are α-neurotoxins from snake venoms (see reviews [6,7,8]). The last three decades witnessed the discovery and intensive scientific application of numerous Conus mollusk venom-derived conotoxins of various classes (see reviews [9,10,11]). Other marine creatures were much less studied for presence of cholinergic compounds remaining in the shadow of the latter. Among them, spirolide and gymnodimine phytoplankton toxins [12], nereistoxin from Lumbriconereis heteropoda annelid [13] and two ascidian alkaloids [14] should be mentioned.
Herein, we describe cholinergic properties of 13 natural low molecular weight compounds, isolated at PIBOC from marine sponges and ascidians (Figure 1). A large number of various bioactive compounds were earlier isolated from these two animal taxa, however molecular targets were not identified for the most of them. For some of them, a structural similarity to diverse cholinergic ligands (quaternary ammonium salts, heterocyclic compounds) allowed us to anticipate their possible activity towards nAChRs. To check this, we performed docking of these natural products to Lymnaea stagnalis acetylcholine-binding protein (AChBP) using the available X-ray structures of this protein in complexes with different cholinergic ligands. Several known AChBPs were found to be excellent structural models for the ligand-binding domains of all nAChRs (see reviews [15,16]), and now are widely used from purification of new natural cholinergic ligands [17] to design the libraries of synthetic compounds [18,19]. In the present communication, the conclusions from computer modeling were verified by efficient interaction of the studied compounds with AChBP revealed by radioligand analysis, as well as by their binding to muscle and α7 neuronal nAChRs tested by radioligand analysis and electrophysiology.
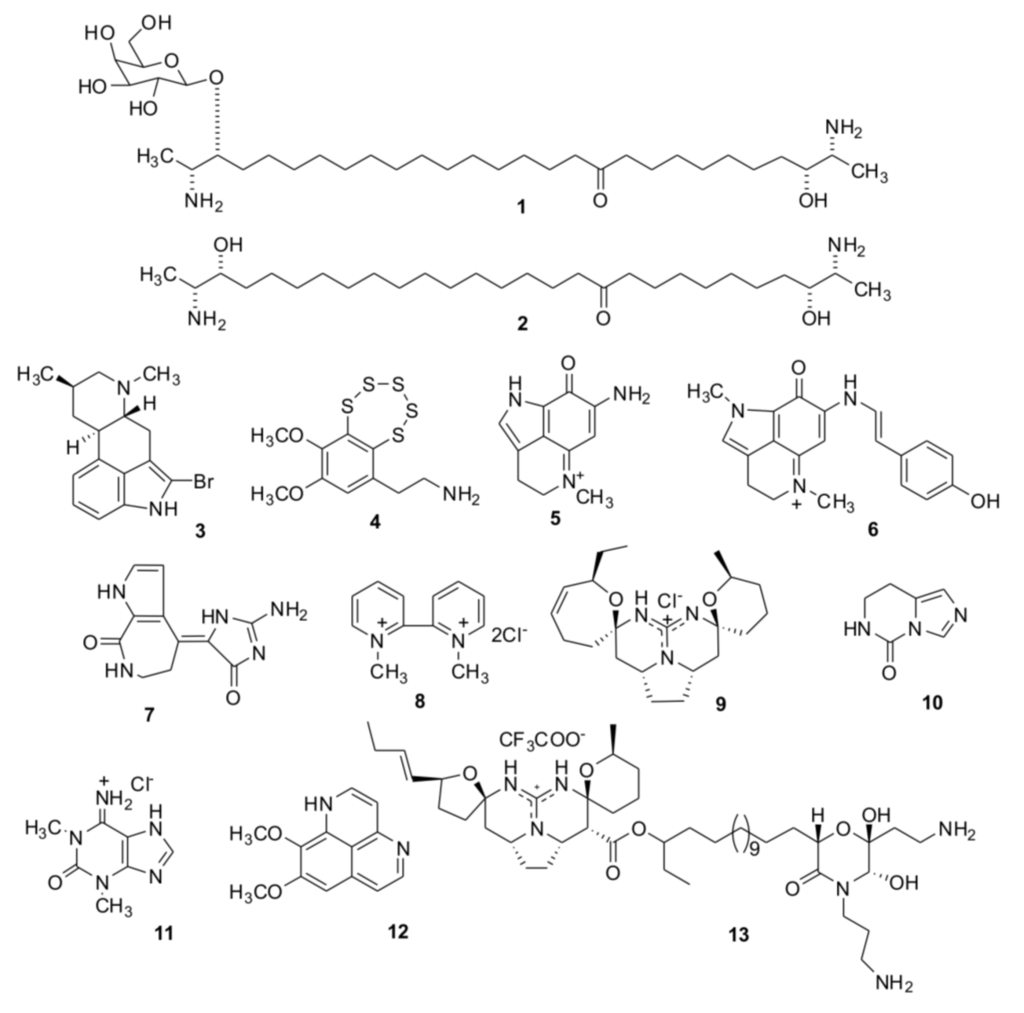
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of compounds from marine sponges and ascidians (1–13), for which putative cholinergic activities were examined by computational and experimental methods.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation of Individual Compounds
Structures of the tested compounds are given on the Figure 1.
Rhizochalin (1), its aglycone (2) [20,21], pibocin (3) [22], and monanchocidin (13) [23] were for the first time isolated and described as new natural products by authors of the paper (T.M. and colleagues) from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata, an ascdian Eudistoma sp. and the sponge Monanchora pulchra, respectively. Varacin (4) was isolated from the far-eastern ascidian Polycitor sp. [24]. Makaluvamines C and G (5, 6) were isolated from the Australian sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa [25] and structurally identified with the corresponding alkaloids previously obtained from Fijian sponges belonging to the same genus [26], and an Indonesian sponge Histodermella sp. [27]. Debromohymenialdesine (7) was isolated from the sponge Acanthella cartery [28] and identified with the alkaloid of the sponge Phakellia flabelata [29]. 1,1′-Dimethyl-[2,2′]-bipyridyldiium salt (8) was isolated from the Far-Eastern ascidian Botrylloides violaceus and identified with the same compound found in the bivalve mollusk Callista chione earlier [30]. Crambescidin 359 (9) was obtained from alcoholic extract of the Australian sponge Monanchora clathrata and identified with the alkaloid previously isolated from the sponge Monanchora unguiculata [31]. 7,8-Dihydroimidazo-[1,5-c]-pyrimidin-5(6H)-one (10) was isolated from the Vietnamese sponge Aplysina sp. [32] and structurally identified with the metabolite of Aplysina fistularis forma fulva [33]. 1,3-Dimethylisoguaniniium hydrochloride (11) was isolated from the Far-Eastern ascidian Syncarpa oviformis and identified with the same compound from the sponge Amphimedon paraviridis [34]. Aaptamine (12) was obtained from extracts of the Vietnamese sponge Aplysina sp. [35] and identified at comparison with that from Aaptos aaptos [36].
2.2. Docking to AChBP and Analysis of Binding Parameters in Competition with [125I]-αBgt
We performed docking of all compounds to Lymnaea stagnalis AChBP using the structure of a protein with a HEPES buffer molecule in the binding site [37], the AChBP structure in complex with competitive antagonist dihydro-β-erythroidine (DHβE) [38], which is a low molecular weight alkaloid, and with the competitive antagonist α-cobratoxin [39], a snake α-neurotoxin close in structure and properties to α-bungarotoxin. In the α-cobratoxin complex, the loop C of each protomer moved away from the central axis of pentameric AChBP in comparison with its position in the HEPES bound protein. On the contrary, in the case of the complex with DHβE, its position is even more close to the central axis and is shifted down in the perpendicular direction. In our opinion, the use of three different spatial forms of AChBP for docking each of the studied compounds increases the significance of such calculations.
The results, presented in the form of calculated inhibition constants (Ki), are summarized in Table 1. For almost all the compounds, the most energy-preferable position was found in the “classical” binding site corresponding to the hydrophobic pocket of nAChRs, where the cholinergic agonists and competitive antagonists are bound. However, computer docking in some cases resulted in the preferred location of the molecule in other (non-classical) binding sites. The most striking example is the 1,3-dimethylisoguaniniium hydrochloride (11), for which the theoretical calculated Ki values for “classical” and another binding sites differed by a factor of 8 (see Table 1).
According to computational data, a high affinity to L. stagnalis AChBP could be expected for some compounds (3–7, 9, 12, 13), and low efficiency of interaction or lack of it—for the others (compounds 1, 2, 8, 10, 11). It should be noted that docking of almost all active compounds (3, 4, 5, 6, 9, 13) to three different forms of AChBP gave similar results with predicted affinities differing by less than 5 μM. Only in case of the moderately active aaptamine (12) and very weak 1,1′-dimethyl-[2,2′]-bipyridyldiium salt (8) the predicted affinities displayed significant discrepancy, which could possibly be explained by differences in distances between the AChBP residues critical to α-cobratoxin binding, as maximal differences are observed in docking to that form of AChBP (Table 1, column C).

Table 1.
The calculated and measured affinities of the studied compounds (see Figure 1) to L. stagnalis acetylcholine-binding protein (AChBP). A—HEPES-bound; B—DHβE-bound and C—α-cobratoxin-bound forms of AChBP respectively; *—only a part of the compound could be docked correctly because of multiple rotatable bonds; **—the binding outside “classical” agonist/competitive antagonist site is predicted; n.d.—not determined (no positive solutions). The measured affinities were obtained as follows: firstly, the respective IC50 values were calculated from inhibition curves (see Figure 2) using ORIGIN 7.5 and then converted into the Kis according to Cheng-Prusoff equation (see Experimental Section) with the mean ± s.e.m. values of duplicate or triplicate measurements for each compound concentration.
| Compounds | Theoretical calculated Ki values (μM) for interaction with L. stagnalis AChBP | Experimental Ki values (μM) at interaction with L. stagnalis AChBP from radioligand assay | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| 1 * | n.d. | n.d. | 39 | 28 ± 4 |
| 2 * | n.d. | n.d. | 39 | 130 ± 10 |
| 3 | 0.98 | 1.7 0.64 ** | 2.0 | 0.83 ± 0.04 |
| 4 | 1.6 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 0.79 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | 2.2 | 0.46 | 5.8 | 1.3 ± 0.1 |
| 6 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.97 | 0.55 ± 0.01 |
| 7 | 8.2 | 0.79 0.50 ** | 1.7 | >1000 |
| 8 | 33 | 12 | 310 | 540 ± 60 |
| 9 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 27 ± 2 |
| 10 | 170 | 120 | n.d. 320 ** | >1000 |
| 11 | 150 | 83 11 ** | 350 | >1000 |
| 12 | 1.5 | 5.3 | 19 | 3.0 ± 0.4 |
| 13 * | 0.53 | 0.43 | 0.11 | 2.5 ± 0.4 |
The interactions, suggested by the calculations, were confirmed in radioligand assay by testing the ability of the compounds to compete with [125I]-αBgt for the L. stagnalis AChBP “classical” binding sites. The inhibition curves of the most active compounds are presented in Figure 2 and the respective Ki values are collected in Table 1. The compounds with the worst in silico docking score showed also a poor ability to compete with [125I]-αBgt (1, 2, 8) or were inactive with Ki > 1000 μM (compounds 10, 11). Moreover, binding activities for some of the most active compounds (3–6, 12, 13) showed good agreement with the results of computer docking.
Thus, the results obtained for the majority of the studied compounds show once again sufficient validity of this computational approach for a preliminary evaluation of affinity of new ligands and even for generating assumptions about intermolecular bonds determining this affinity.
As an example, we can consider a model of the L. stagnalis AChBP complexed with the compound that shows the best binding parameters both in the computer docking and in radioligand assay, namely with makaluvamine G (6) (Figure 3a). In this schematic planar model all the ligand interactions with formation of hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic contacts with definite AChBP amino acid residues can be clearly seen. A high affinity of makaluvamine G (6), deduced from computer calculations, is determined by two hydrogen-bonds and 14 hydrophobic contacts with different L. stagnalis AChBP amino acid residues (Figure 3a).
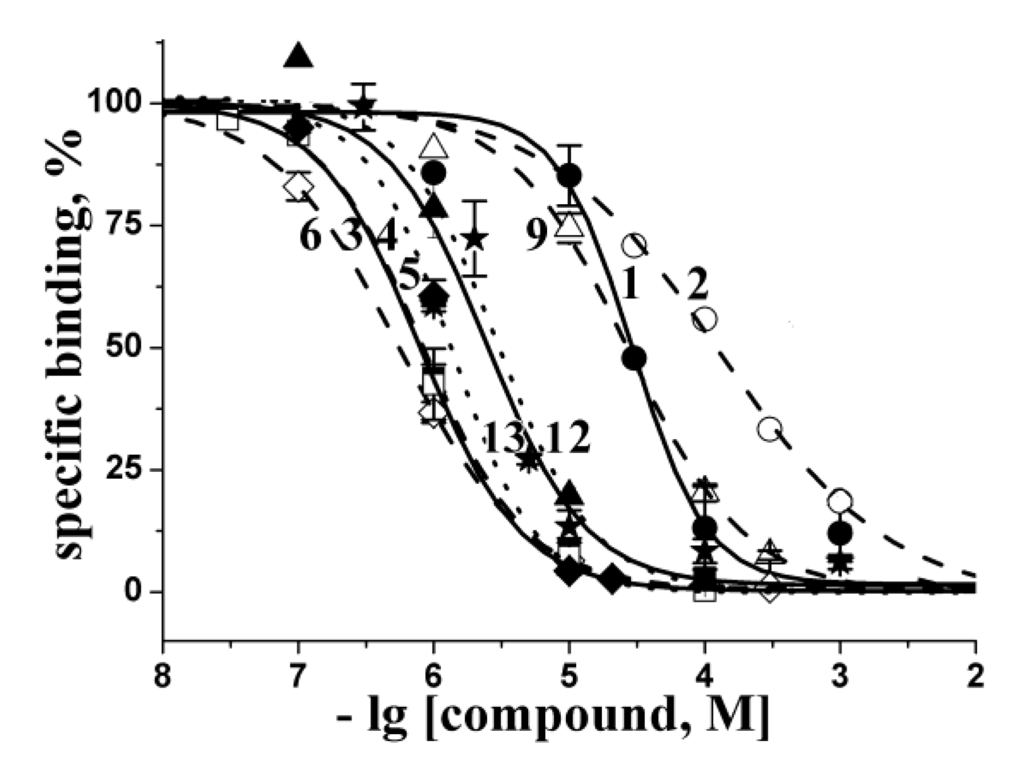
Figure 2.
Inhibition of [125I]-αBgt binding to L. stagnalis AChBP with the most active compounds studied. Numbering the compounds corresponds to the numbering in Figure 1. The corresponding curves are marked with symbols: 1—filled circles; 2—open circles; 3—filled squares; 4—open squares; 5—filled diamonds; 6—open diamonds; 9—open triangles; 12—filled triangles; 13—stars. Each point is a mean ± s.e.m value of two or three measurements for each concentration. The curves were calculated from the means ± s.e.m. using ORIGIN 7.5 program (see Experimental Section). The respective Ki values are listed in Table 1.
We compared this calculated structure with the X-ray structure of the same protein complexed with clothianidin (a neonicotinoid insecticide) (Figure 3b) [40]. In that case, two hydrogen bonds (one of which with the oxygen of bound water molecule) and 10 hydrophobic interactions were revealed, 6 of which are in contacts with the same AChBP amino acid residues as in the complex with makaluvamine G. The similarity of the location of these two molecules in the binding site is obvious. Note that the affinity of clothianidin to L. stagnalis AChBP (Kd 7.3 μM evaluated by quenching of intrinsic tryptophan fluorescence) [40] was lower than that of makaluvamine G (6) (Ki = 0.55 ± 0.01 μM), perhaps because makaluvamine G fits binding site more tightly, forming more of hydrophobic contacts (Figure 3c).
Nevertheless, in two cases (compounds 7, 9) an essential discrepancy between the calculations and experimental data was found (see Table 1). Of course, using computer methods of calculation, one should never forget about false-positive solutions. However, another explanation of the disagreement between the calculated and measured affinities might be the interactions of tested compounds outside the “classical” agonist/competitive antagonist binding site. Such a possibility was simulated for the compound (7) (see Table 1). By comparing the in silico docked debromohymenialdesine (7) and the structure of three-finger toxin α-cobratoxin in their complexes with AChBP (Figure 3d) we could expect poor competition of this compound with α-bungarotoxin (very similar to α-cobratoxin), because of partially overlapping their binding sites on this target. In fact, [125I]-αBgt binding to L. stagnalis AChBP could be observed in radioligand assay even in the presence of debromohymenialdesine (7) as predicted by docking simulations. Analogously, an interaction of compound (9) outside the “classical” binding site could be supposed because of its functional activity towards α7 nAChR subtype (see Section 2.4.) which is the most close in pharmacological profile to L. stagnalis AChBP.
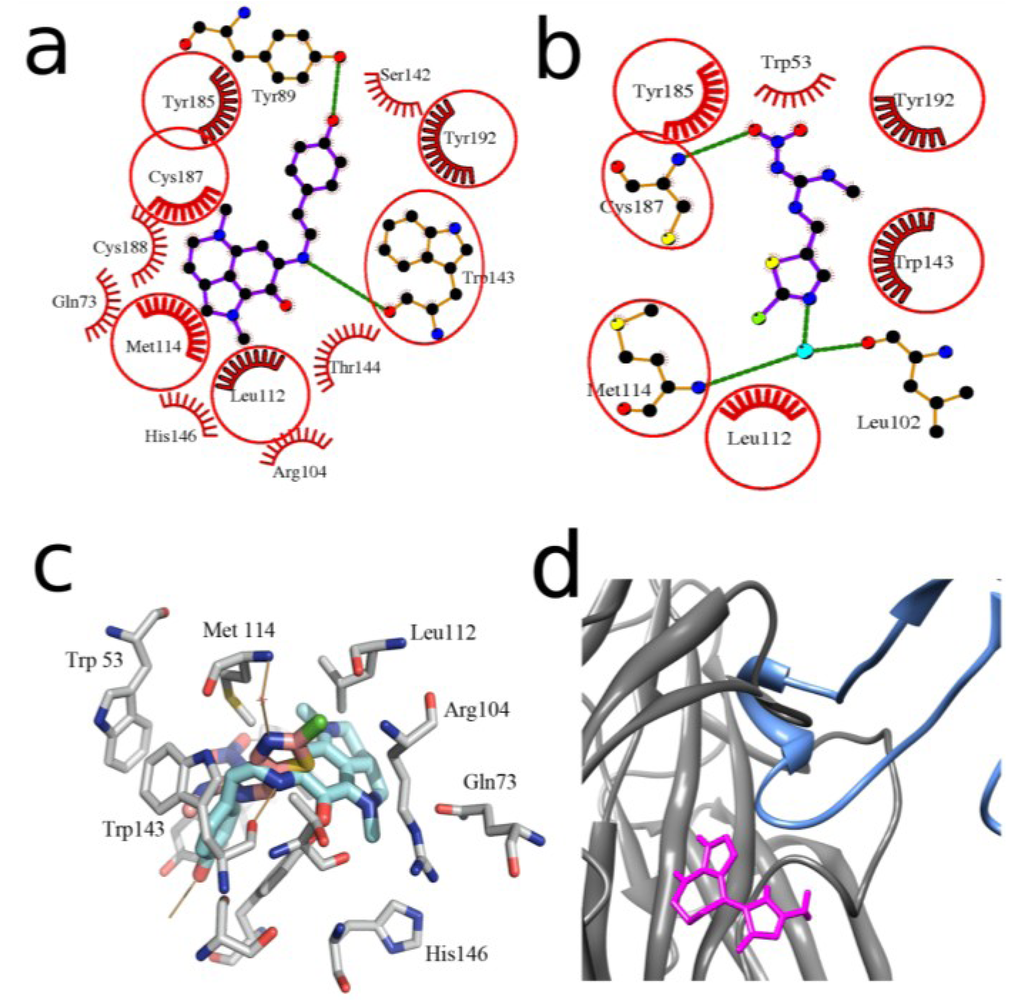
Figure 3.
Schematic planar image of the model of makaluvamine G (6) docked to HEPES-bound form of L. stagnalis AChBP binding site (a) in comparison with the same presentation of the X-ray structure of the complex of the same protein with clothianidin (PDB ID—2ZJV) (b); intermolecular bonds in ligands are colored in magenta; the same links in the AChBP amino acid residues involved in the formation of hydrogen bonds (green lines) are shown in orange. The AChBP amino acid residues forming hydrophobic contacts with ligands are presented as red combs. Those of them that are the same for both ligands are encircled by red lines. Atoms of carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur are colored in black, red, blue and yellow, respectively. Water molecule involved in the formation of hydrogen bonds is shown in cyan; (c) superposition of 3D structures of makaluvamine G (6), docked to AChBP and crystal structure of clothianidine AChBP complex. Carbons of makaluvamine G (6), clothianidine and AChBP are shown in light blue, pink and grey respectively; oxygens are shown red, nitrogens are shown blue; hydrogen bonds are brown; (d) superposition of α-cobratoxin structure (blue) (PDB ID—1YI5) and the best solution for debromohymenialdesine (7) (magenta) in silico docked to L. stagnalis AChBP (gray).
2.3. Analysis of Competition with [125I]-αBgt for Interactions with the Torpedo Californica and α7 nAChRs
The same radioligand assay, based on competition with [125I]-αBgt, was used to evaluate the affinity of tested compounds towards muscle-type nAChR from T. californica ray and to human α7 nAChR heterologously expressed in the GH4C1 cell line. Inhibition curves for the most potent compounds and their Ki values are presented in Figure 4 and Table 2, respectively.
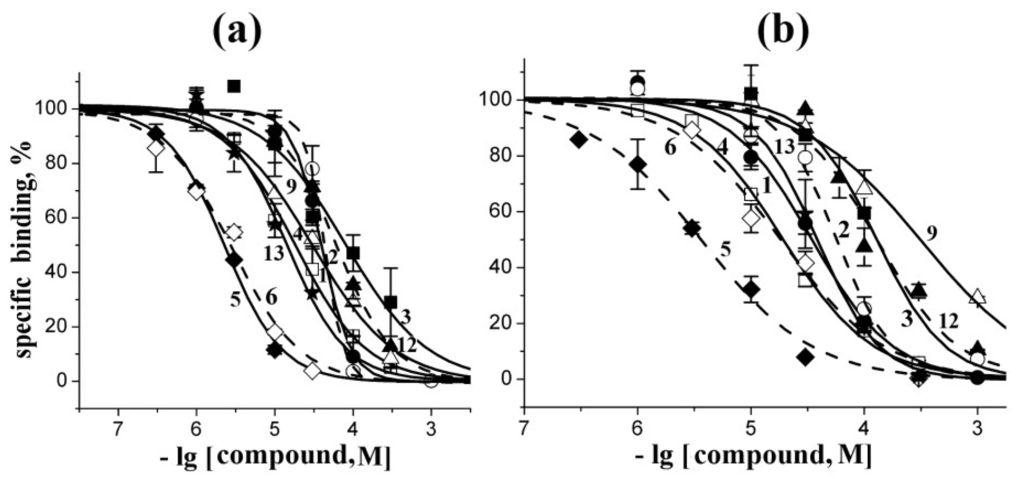
Figure 4.
Inhibition of initial rate for [125I]-αBgt binding to T. californica nAChR (a) or human α7 nAChR (b) with the most active compounds studied. Numbering the compounds and their symbols correspond to the numbering in Figure 1 and symbols in Figure 2, respectively. Each point is a mean ± s.e.m value of two or three measurements for each concentration. The curves were calculated from the means ± s.e.m. using the ORIGIN 7.5 program (see Experimental Section). The respective Ki values are listed in Table 2.

Table 2.
Affinity of all the studied compounds (see Figure 1) tested in competition with [125I]-αBgt for binding to muscle-type nAChR from T. californica and human neuronal α7 nAChR (see respective inhibition curves in Figure 4). The IC50 values were calculated using ORIGIN 7.5 and then converted into the Kis according to Cheng-Prusoff equation (see Experimental Section) with the mean ± s.e.m. values of duplicate or triplicate measurements for each compound concentration.
| Compounds | Ki Values (μM) on… | |
|---|---|---|
| T. californica nAChR | human α7 nAChR | |
| 1 | 22 ± 2 | 33 ± 2 |
| 2 | 24 ± 2 | 56 ± 4 |
| 3 | 44 ± 7 | 130 ± 8 |
| 4 | 10 ± 1 | 19 ± 1 |
| 5 | 1.30 ± 0.05 | 3.6 ± 0.3 |
| 6 | 1.60 ± 0.17 | 18 ± 2 |
| 7 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 8 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 9 | 17 ± 1 | 310 ± 28 |
| 10 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 11 | >1000 | >1000 |
| 12 | 34 ± 1 | 120 ± 15 |
| 13 | 8.0 ± 1.0 | 38 ± 2 |
The compounds 7, 8, 10, and 11 did not show any inhibitory activity (Ki ≥ 1000 μM). A moderate potency (Ki about 20–60 μM) was observed in the case of rhizochalin (1) and its aglycone (2). Somewhat less active towards both T. californica and human α7 nAChRs were pibocin (3) and aaptamine (12). Crambescidin 359 (9) has shown a twenty-fold higher activity on muscle-type receptor; in other words, it has some subtype specificity as revealed in competition with [125I]-αBgt. Makaluvamine G (6) has shown a similar ten-fold preference towards T. californica nAChR. The most potent competitor of [125I]-αBgt for the “classical” binding site on both tested receptors was makaluvamine C (5): it showed Ki = 1.30 ± 0.05 μM on muscle-type receptor and 3.6 ± 0.3 μM on human α7 nAChR.
Summarizing these results on the activity of the studied compounds from sponges and ascidians, we ascertain that there are substances with sound cholinergic properties in these marine sources acting on both muscle-type and α7 neuronal nAChRs. Their mode of action and affinities are close to those for a number of well-known cholinergic ligands from alkaloids (nicotine, lobeline, epibatidine, d-tubocurarine, DHβE) [41], to different α-conotoxins [42,43,44], some snake venoms components (waglerins, weak toxins) [45,46] and native modulators [47] showing similar micromolar potency to the muscle and α7 nAChR subtypes evaluated in competition with [125I]-αBgt.
2.4. Electrophysiological Analysis of Effects on Functional Activity of Nicotinic Receptors
To compare the affinity found in binding studies with possible functional activity, electrophysiological measurements were performed. We applied 10 μM solutions of tested compounds to murine muscle nAChR and to human α7 nAChR expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Figure 5 represents the inhibition activities of tested compounds in percents of maximal inhibition achieved by 15 min application of 1 μM α-bungarotoxin.
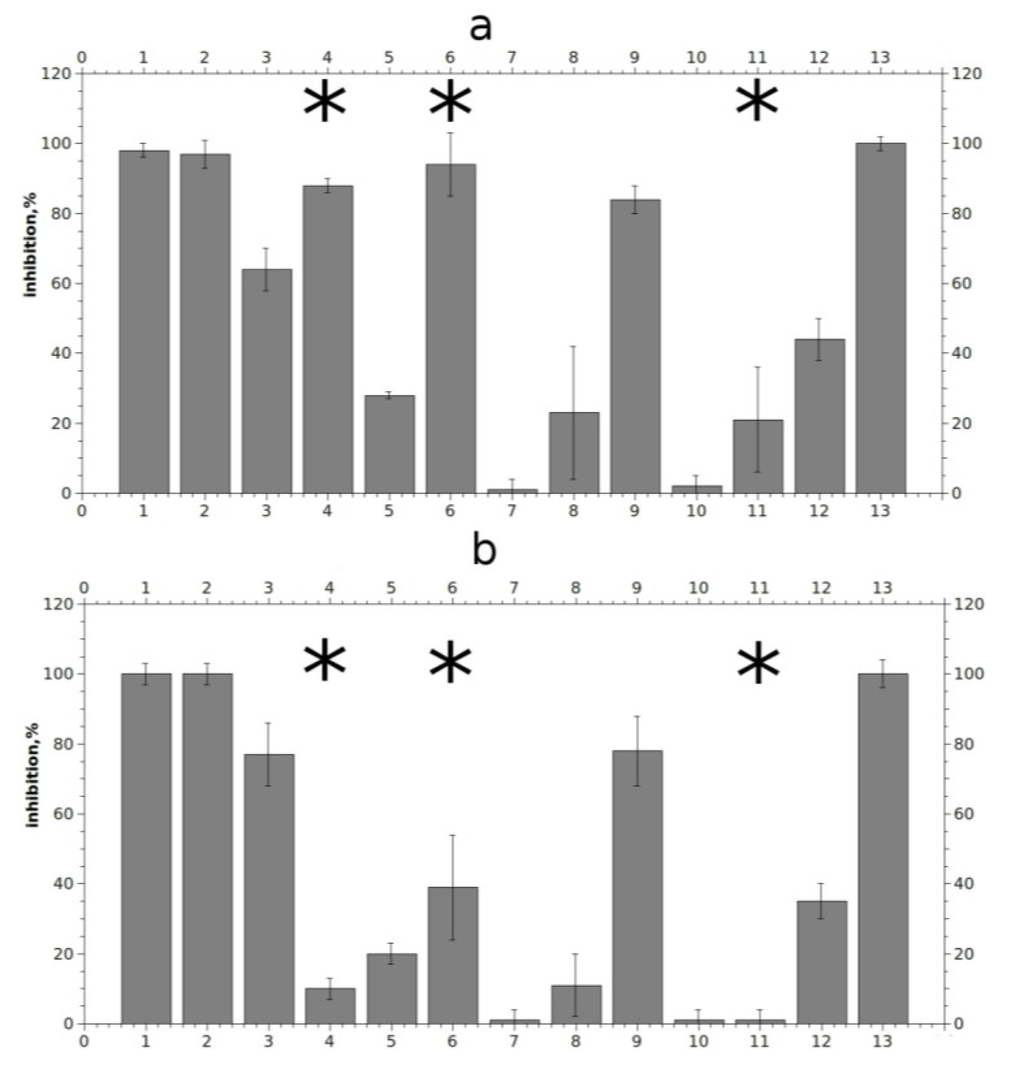
Figure 5.
Relative inhibition of agonist-evoked current by 10 μM compounds on murine muscle-type nAChR (a) and on human α7 nAChR (b). Numbering the compounds in x axis corresponds to the numbering in Figure 1. Asterisks indicate significant (p < 0.05, according to Student’s test) differences between inhibition effects on murine muscle- and human α7 nAChRs for compounds (4), (6) and (11).
Compounds 1, 2, 6, and 13 blocked muscle nAChR at given concentration almost completely, while compounds 3, 4, 9, and 12 showed moderate activity. A weaker but still reproducible effect was shown by compound 5, whereas only extremely weak, if any, activity was observed for compounds 7, 8, 10 and 11. It is noticeable that the effects of compounds with a long non-polar carbon chain (1, 2 and 13) were very slowly reversible, despite their relatively good solubility in water as seen in Figure 6a for rhizochalin (1) (for compounds 2 and 13 data not shown). All the tested compounds, with the exception of makaluvamine G (6), varacin (4) and to a lesser extent compound (11), showed similar effects both on α7 and muscle nAChR at a given concentration. Although 10 μM makaluvamine G (6) blocked muscle nAChR almost completely, like slowly-reversible rhizochalin and its aglycone (1, 2) and monanchocidin (13), its inhibition has a fast off-set rate and the receptor recovered in 5 min from the end of compound application (Figure 6b). Interestingly, 10 μM varacin showed a strong inhibition of muscle nAChR, but not α7 nAChR. A difference in rates of inhibition of muscle and α7 nAChRs was observed also for compounds (6) and (11). However, even statistically significant differences in rates of inhibition should not be interpreted as a sign of selectivity towards one or another receptor subtype without further and more thorough studies.
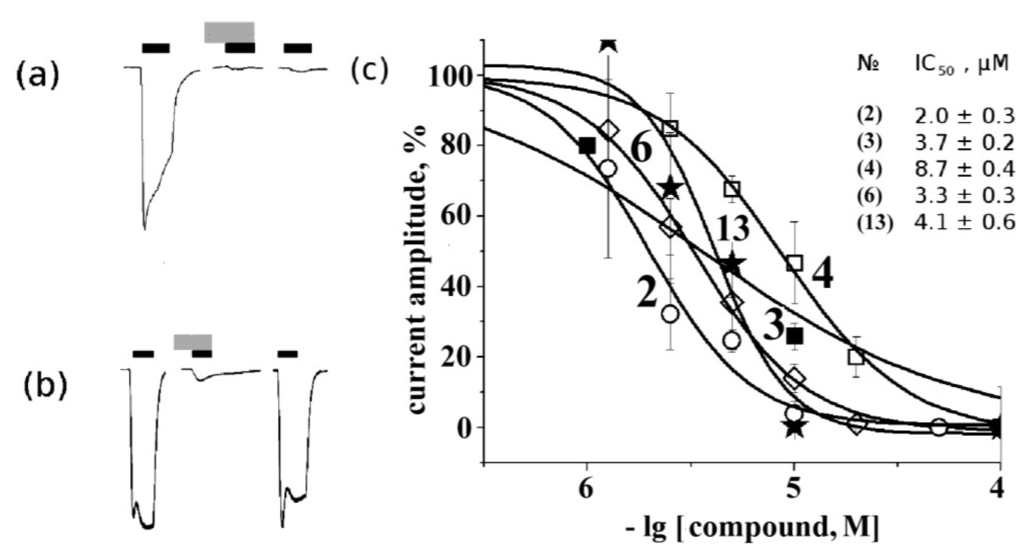
Figure 6.
Electrophysiological measurements of 10 μM rhizochalin (1) (a) and makaluvamine G (6) (b) activity on muscle nAChR. Black and grey rectangles represent application of acetylcholine and tested compound, respectively. From left to right: control acetylcholine-evoked current, acetylcholine-evoked current in the presence of tested compound and acetylcholine-evoked current after 15 min of wash out. Current inhibition dose-response curves (c): concentrations of tested compounds from 1 to 100 μM were used to evaluate IC50 (values placed on figure according to numbering from Figure 1). The symbols used for the respective compounds are the same as in Figure 2 and Figure 4.
We obtained IC50 values on muscle nAChR for some of the most potent compounds (Figure 6c). As can be seen, aglycone of rhizochalin (2) and makaluvamine G (6) are the most potent inhibitors of mouse muscle-type nAChR. The differences in the affinity and specificity for some compounds (1, 2, 3, 5) found in comparison of the data obtained by radioligand analysis and electrophysiology might depend on the intrinsic features of these two methods. For the former, a crucial factor is potent and virtually irreversible binding of [125I]-αBgt to 2 binding sites on muscle-type nAChR and to 5 sites on α7 nAChR. On the other hand, in electrophysiology experiments the choice and concentration of agonist are of importance.
Summarizing the results of electrophysiology experiments, we can conclude that a number of analyzed compounds from marine sponges and ascidians possess functional (inhibitory) activities at micromolar concentrations. The majority of active compounds are not selective in respect to the muscle or neuronal α7 nAChRs, but some of them appear to be relatively selective towards studied receptor subtypes. However, further experiments will reveal whether they might act on heteromeric neuronal nAChRs or other Cys-loop receptors.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Isolation of Individual Compounds
Purity of all the obtained samples were confirmed by TLC, HPLC, as well as by measurements of physical constants, while their structures were established mainly using NMR and MS data at comparison with those reported in literature [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
3.2. Computer Modeling
Avogadro software was used to generate energy minimized structures of ligands [48]. Molecular dockings were performed using Autodock 4.2/Adt software [49]. Keeping in mind that some recent studies [50] discussed spatial rearrangements in the Cys-loop proteins bound to diverse types of ligands, including partial and full agonists and antagonists, we decided to perform docking to those AChBP structures which were observed in complexes with HEPES, α-cobratoxin and dihydro-β-erythroidine (PDB 1UX2, 1YI5 and 4ALX, respectively), after removing these ligands. Initially, only those in silico structures involving the binding sites for agonists and competitive antagonists were taken into account. Search space was centered at the C-loop, x/y/z dimensions were 120/70/50 where x is collinear with symmetry axis of the receptor and y is tangential to C-loop. The following Autodock Lamarckian genetic algorithm parameters were set: 200 dockings, evaluation number—long. Results were analyzed in respect of predicted affinity and compatibility with the αBgt binding site. LigPlot+ software [51] and PyMOL™ 1.2r2 (Molecular Graphics System, DeLano Scientific LLC, San Carlos, CA, USA) were used to analyze docked structures.
For rhizochalin, aglycon of rhizochalin and monanchocidin (1, 2, 13, respectively) we decided to dock only part of the molecule to overcome Autodock’s limitations to the number of flexible bonds. For rhizochalin and its aglycon the part from the oxo-group to the closest sphingosine head was used. The pentacyclic (crambescidine-like) part of monanchocidin represented this ligand in the docking.
3.3. Radioligand Assay
In competition experiments with [125I]-αBgt, all the compounds (in concentration range of 0.03–1000 μM) were pre-incubated 2-3 h at room temperature with the L. stagnalis AChBP (the final concentration of 2.4 nM) in 50 μL of buffer A (phosphate-buffered saline, 0.7 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 7.5) or with the GH4C1 cells (6.5 μg of total protein with final concentration of 0.4 nM of toxin-binding sites) or Torpedo californica electric organ membranes (final concentration 1.25 nM of toxin-binding sites) in 50 μL of buffer B (20 mM Tris-HCl buffer, 1 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin, pH 8.0). After that [125I]-αBgt was added to L. stagnalis AChBP, GH4C1 cells or membranes to final concentration 0.1–0.2 nM and the mixtures were additionally incubated for 5 min. Binding was stopped by rapid filtration on double DE-81 filters (Whatman, Maidstone, UK) pre-soaked in buffer A (for AChBP) or on GF/C filters (Whatman) pre-soaked in 0.25% polyethylenimine (for GH4C1 cells or membranes), unbound radioactivity being removed from the filters by washout (3 × 3 mL) with the buffers A and B, respectively. Non-specific binding was determined in all cases using 2–3 h pre-incubation with 10 μM α-cobratoxin.
The binding results were analyzed using ORIGIN 7.5 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) fitting to a one-site dose-response curve by Equation:
where IC50 is the concentration at which 50% of the binding sites are inhibited and n is the Hill coefficient. The Ki values were calculated from the experimentally measured IC50s by the method of Cheng & Prusoff according to Equation:
where L is concentration of free radioligand and Kd is dissociation constant for [125I]-αBgt to the respective target measured under similar assay conditions. Under radioligand assay conditions used the measured Kd values were 0.032 ± 0.003 nM for T. californica nAChR, 0.88 ± 0.19 nM for human α7 nAChR and 3.5 ± 0.6 nM for L. stagnalis AChBP.
% response = 100/{1 + ([toxin]/IC50)n}
Ki = IC50/(1 + L/Kd)
3.4. Electrophysiology Measurements
Oocytes were obtained from benzocaine anesthetized Xenopus by surgically removing a part of the ovarium. Single oocytes were isolated and transferred to ND96 electrophysiology buffer. To achieve nAChR expression, each oocyte was injected with 1–5 ng of plasmid DNA containing the respective subunit genes (CHRNA1, CHRNB1, CHRND, CHRNE and CHRNA7) under control of CMV-promoter. Current recordings were performed after 36–48 h of incubation at 18 °C in ND96 solution.
All recordings were performed using the Turbo TEC-03X amplifier (npi electronic GmbH, Tamm, Germany). 3M KCl-filled recording electrodes with a resistance of about 0.1–0.5 MΩ were used. To achieve a minimum of compound consumption we used a hand-made recording chamber with approximately 25 μL volume. Membrane potential was clamped at 50–70 mV. During the experiment each oocyte was perfused with ND96 solution until the resting current reached a steady state. Then short pulses (approximately 10 s) of agonist (50 μM nicotine in the case of α7 or 10 μM acetylcholine in the case of muscle nAChR) were applied to the oocyte and then washed out with control buffer until the current returned to baseline. If the amplitude of agonist-evoked currents did not change after 5 min wash, oocytes were considered suitable for further experiments. Applications of agonist were performed every five minutes. Amplitudes of current responses to agonist in the presence of tested marine compounds were compared to the preceding agonist-induced current response. Each compound was tested on three different oocytes expressing each type of receptor (muscle or α7). In preliminary experiments the marine compounds were tested at a concentration of 10 μM, and QtiPlot software was used to display the results. For the most active compounds further measurements with concentrations of tested ligand in the range 1.25–20 μM were done, and IC50 values were calculated using Origin 7.5 software (OriginLab, Northampton, MA, USA).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we described the interaction between nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and several low molecular weight naturally-occurring compounds from marine sponges and ascidians. Molecular docking, radioligand binding and functional electrophysiological tests were done to determine potency of these products. Makaluvamines C (5) and G (6) were the most active in radioligand binding assay, and makaluvamine G (6) as well as crambescidine 359 (9) revealed most evident selectivity towards muscle-type nAChR. In electrophysiological tests rhizochalin (1), aglycone of rhizochalin (2), pibocin (3), varacin (4), makaluvamine G (6), crambescidine 359 (9) and monanchocidin (13) demonstrated highest potency (in the low micromolar range) on mouse muscle nAChR. The same compounds, with the exception of (4) and (6), showed the similar affinities on human α7 nAChR. Our results indicate that some of the earlier described pleiotropic activities of the analyzed marine products may be associated with their action on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. On the other hand, the activities revealed here by radioligand analysis and electrophysiology, as well as computer modeling in comparison with the crystalline structures of complexes of nicotinic ligands, may be useful for designing drugs against diseases associated with malfunctioning of the cholinergic system (myasthenia gravis, psychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to T. Sixma (Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) for AChBP, to F. Hucho (Free University of Berlin, Berlin, Germany) for T. californica electric organ preparation, to R.J. Lukas (Division of Neurobiology, Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, USA) for α7 nAChR clone, to Veit Witzemann (Department of Molecular Neurobiology, Max Planck Institute for Medical Research, Heidelberg, Germany) for muscle nAChR clones, and to EliLilly (London, UK) for GH4C1 cells transfected with human α7 nAChR. The work was supported by Russian Foundation for Basic Research (RFBR) grant No. 12-04-01746-а and No. 13-04-40377-Н, and the program of the Russian Academy of Sciences “Molecular and cellular biology”.
Author Contributions
Isolation and structure identification of marine natural compounds: Makarieva T. [rhizochalin (1), aglycone of rhizochalin (2), pibocin (3), varacin (4), monanchocidin (13)]; Utkina N. [makaluvamines C (5) and G (6), debromohymenialdisine (7), aaptamine (12)]; Santalova E. [1,1′-dimethyl-[2,2′]-bipyridyldiium salt (8), crambescidin 359 (9), 7,8-dihydroimidazo-[1,5-c]-pyrimidin-5(6H)-one (10), 1,3-dimethylisoguaniniium hydrochloride (11)].
In silico docking: Kudryavtsev D.
Radioligand binding assay: Kasheverov I., Kudryavtsev D.
Electrophysiological measurements: Kudryavtsev D., Kryukova E., Methfessel C.
Writing of the paper (alphabetical order): Kasheverov I., Kudryavtsev D., Makarieva T., Methfessel C., Stonik V., Tsetlin V.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Changeux, J.P. The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: The founding father of the pentameric ligand-gated ion channel superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40207–40215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamida, D.; Poulas, K.; Avramopoulou, V.; Fostieri, E.; Lagoumintzis, G.; Lazaridis, K.; Sideri, A.; Zouridakis, M.; Tzartos, S.J. Muscle and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Structure, function and pathogenicity. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 3799–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsetlin, V.; Hucho, F. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at atomic resolution. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sine, S.M.; Engel, A.G. Recent advances in Cys-loop receptor structure and function. Nature 2006, 440, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prickaerts, J.; van Goethem, N.P.; Chesworth, R.; Shapiro, G.; Boess, F.G.; Methfessel, C.; Reneerkens, O.A.; Flood, D.G.; Hilt, D.; Gawryl, M.; et al. EVP-6124, a novel and selective α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor partial agonist, improves memory performance by potentiating the acetylcholine response of α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C. Looking back on the discovery of α-bungarotoxin. J. Biomed. Sci. 1999, 6, 368–375. [Google Scholar]
- Tsetlin, V. Snake venom α-neurotoxins and other ‘three-finger’ proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Structure, function and evolution of three-finger toxins: Mini proteins with multiple targets. Toxicon 2010, 56, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halai, R.; Craik, D.J. Conotoxins: Natural product drug leads. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2009, 26, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichert, R.W.; Olivera, B.M. Natural products and ion channel pharmacology. Future Med. Chem. 2010, 2, 731–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Dutertre, S.; Vetter, I.; Christie, M.J. Conus venom peptide pharmacology. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 259–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, Y.; Radic, Z.; Aráoz, R.; Talley, T.T.; Benoit, E.; Servent, D.; Taylor, P.; Molgó, J.; Marchot, P. Structural determinants in phycotoxins and AChBP conferring high affinity binding and nicotinic AChR antagonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6076–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.W.; Kang, J.J.; Liu, S.H.; Jeng, C.R.; Cheng, Y.W.; Hu, C.M.; Tsai, S.F.; Wang, S.C.; Pang, V.F. Effects of cartap on isolated mouse phrenic nerve diaphragm and its related mechanism. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 55, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneki, H.; You, Y.; Toyooka, N.; Sasaoka, T.; Nemoto, H.; Dani, J.A.; Kimura, I. Marine alkaloids(−)-pictamine and (−)-lepadin B block neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rucktooa, P.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Insight in nAChR subtype selectivity from AChBP crystal structures. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakel, J.L. Gating of nicotinic ACh receptors: Latest insights into ligand binding and function. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, S.; Ulens, C.; Büttner, R.; Fish, A.; van Elk, R.; Kendel, Y.; Hopping, G.; Alewood, P.F.; Schroeder, C.; Nicke, A.; et al. AChBP-targeted α-conotoxin correlates distinct binding orientations with nAChR subtype selectivity. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 3858–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulens, C.; Akdemir, A.; Jongejan, A.; van Elk, R.; Bertrand, S.; Perrakis, A.; Leurs, R.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K.; Bertrand, D.; et al. Use of acetylcholine binding protein in the search for novel α7 nicotinic receptor ligands. In silico docking, pharmacological screening, and X-ray analysis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdemir, A.; Rucktooa, P.; Jongejan, A.; van Elk, R.; Bertrand, S.; Sixma, T.K.; Bertrand, D.; Smit, A.B.; Leurs, R.; de Graaf, C.; et al. Acetylcholine binding protein (AChBP) as template for hierarchical in silico screening procedures to identify structurally novel ligands for the nicotinic receptors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6107–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Stonik, V.A.; Milgrom, Y.M.; Rashkes, Y.V. Rhizochalin, a novel secondary metabolite of mixed biosynthesis from the sponge Rhizochalina incrustata. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 6581–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinski, T.F.; Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A. (−)-Rhizochalin is a dimeric enantiomorphic (2R)-sphingolipid. Absolute configuration on pseudo-C2V-symmetric bic-2-amino-3-alkanols by CD. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2000, 39, 4076–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Ilyin, S.G.; Stonik, V.A.; Lyssenko, K.A.; Denisenko, V.A. Pibocin, the first ergoline marine alkaloid from the far-eastern ascidian Eudistoma sp. Tetrahedron Lett. 1999, 40, 1591–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzii, A.G.; Makarieva, T.N.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Kuzmich, A.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. Monanchocidin: A new apoptosis-inducing polycyclic guanidine alkaloid from the marine sponge Monanchora pulchra. Org. Lett. 2010, 12, 4292–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarieva, T.N.; Stonik, V.A.; Dmitrenok, A.S.; Grebnev, B.B.; Isakov, V.V.; Rebachyk, N.M. Varacin and three new marine antimicrobial polysulfides from the Far-Eastern ascidian Polycitor sp. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Makarchenko, A.E.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S. Zyzzyanone A, a novel pyrrolo[3,2-f]indole alkaloid from the Australian marine sponge Zyzzya fuliginosa. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 7491–7494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisky, D.C.; Radisky, E.S.; Barrows, L.R.; Copp, B.R.; Kramer, R.A.; Ireland, C.M. Novel cytotoxic topoisomerase-II inhibiting pyrroloiminoquinones from Fijian sponges of the genus Zyzzya. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 1632–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carney, J.R.; Scheuer, P.J.; Kelly-Borges, M. Makaluvamine-G, a cytotoxic pigment from an Indonesian sponge Histodermella sp. Tetrahedron 1993, 49, 8483–8486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkina, N.K.; Fedoreev, S.A.; Maximov, O.B. Nitrogen-containing metabolites from marine sponge Acanthella cartery. Chem. Nat. Comp. 1984, 20, 511–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.M.; Buyer, J.S.; Pomerantz, M.W. Characterization of a yellow compound isolated from the marine sponge Phakellia flabellata. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1980, 10, 435–436. [Google Scholar]
- Vagias, C.; Tsitsimpikow, C.; Rapti, T.; Roussis, V. 1,1-Dimethyl-[2,2′]bipyridyldium salt from bivalve Callista chione. Nat. Prod. Lett. 2000, 14, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Braekman, J.C.; Daloze, D.; Tavares, R.; Hajdu, E.; van Soest, R.W.M. Novel polycyclic guanidine alkaloids from two marine sponges of the genus Monanchora. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalova, E.A.; Denisenko, V.A.; Stonik, V.A. Dibromotyrosine and histamine derivatives from the tropical marine sponge Aplysina sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 377–382. [Google Scholar]
- Ciminiello, P.; Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Magno, S.; Mangoni, A.; Pansini, M. Chemistry of Verongida sponges. Constituents of the Caribbean sponge Aplysina fistularis forma fulva. J. Nat. Prod. 1994, 57, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.-J.; Inagaki, M.; Higuchi, R.; Miyamoto, T.; Ono, M.; Kuwano, M.; van Soest, R.W.M. 1,3-Dimethylisoguaninium, an antiangiogenic purine analog from the sponge Amphimedon paraviridis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. Chem, 51, 731–733. [Google Scholar]
- Shubina, L.K.; Kalinovsky, A.I.; Fedorov, S.A.; Radchenko, O.S.; Denisenko, V.A.; Dmitrenok, P.S.; Dyshlovoy, S.A.; Krasokhin, V.B.; Stonik, V.A. Aaptamine alkaloids from the Vietnamese sponge Aaptos sp. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, H.; Kobayashi, J.; Ohizumi, H. Isolation and structure of aaptamine a novel heteroaromatic substance possessing alpha-blocking activity from the sea sponge Aaptos aaptos. Tetrahedron Lett. 1982, 23, 5555–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celie, P.H.; van Rossum-Fikkert, S.E.; van Dijk, W.J.; Brejc, K.; Smit, A.B.; Sixma, T.K. Nicotine and carbamylcholine binding to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors as studied in AChBP crystal structures. Neuron 2004, 41, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahsavar, A.; Kastrup, J.S.; Nielsen, E.O.; Kristensen, J.L.; Gajhede, M.; Balle, T. Crystal structure of Lymnaea stagnalis AChBP complexed with the potent nAChR antagonist DHβE suggests a unique mode of antagonism. PLoS One 2012, 7, e40757. [Google Scholar]
- Bourne, Y.; Talley, T.T.; Hansen, S.B.; Taylor, P.; Marchot, P. Crystal structure of a Cbtx-AChBP complex reveals essential interactions between snake α-neurotoxins and nicotinic receptors. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, M.; Okajima, T.; Yamashita, A.; Oda, T.; Hirata, K.; Nishiwaki, H.; Morimoto, T.; Akamatsu, M.; Ashikawa, Y.; Kuroda, S.; et al. Crystal structures of Lymnaea stagnalis AChBP in complex with neonicotinoid insecticides imidacloprid and clothianidin. Invertebr. Neurosci. 2008, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonnacott, S.; Barik, J. Nicotinic ACh Receptors; Tocris Bioscience Scientific Review Series Tocris Reviews NO. 28; Tocris Bioscience: Bristol, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Vulfius, C.A.; Gorbacheva, E.V.; Mordvintsev, D.Y.; Utkin, Y.N.; van Elk, R.; Smit, A.B.; Tsetlin, V.I. α-Conotoxin analogs with additional positive charge show increased selectivity towards Torpedo californica and some neuronal subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 4470–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Fish, A.; Rucktooa, P.; Khruschov, A.Yu.; Osipov, A.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; D’hoedt, D.; Bertrand, D.; Sixma, T.K.; et al. Interaction of α-conotoxin ImII and its analogs with nicotinic receptors and acetylcholine-binding proteins: Additional binding sites on Torpedo receptor. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Zhmak, M.N.; Khruschov, A.Y.; Tsetlin, V.I. Design of new α-conotoxins: From computer modeling to synthesis of potent cholinergic compounds. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1698–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Naturally occurring and synthetic peptides acting on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2430–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N.; Kukhtina, V.V.; Kryukova, E.V.; Chiodini, F.; Bertrand, D.; Methfessel, C.; Tsetlin, V.I. “Weak toxin” from Naja kaouthia is a nontoxic antagonist of α7 and muscle-type nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 15810–15815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyukmanova, E.N.; Shulepko, M.A.; Buldakova, S.L.; Kasheverov, I.E.; Shenkarev, Z.O.; Reshetnikov, R.V.; Filkin, S.Y.; Kudryavtsev, D.S.; Ojomoko, L.O.; Kryukova, E.V.; et al. Water-soluble LYNX1 residues important for interaction with muscle-type and/or neuronal nicotinic receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 15888–15899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An advanced semantic chemical editor, visualization, and analysis platform. J. Cheminform. 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexiblity. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 16, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar]
- Brams, M.; Pandya, A.; Kuzmin, D.; van Elk, R.; Krijnen, L.; Yakel, J.L.; Tsetlin, V.; Smit, A.B.; Ulens, C. A structural and mutagenic blueprint for molecular recognition of strychnine and d-tubocurarine by different Cys-loop receptors. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).