Astaxanthin Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and the Antioxidant Responsive Element (Nrf2-ARE) Pathway in the Brain after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats and Attenuates Early Brain Injury
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Observation
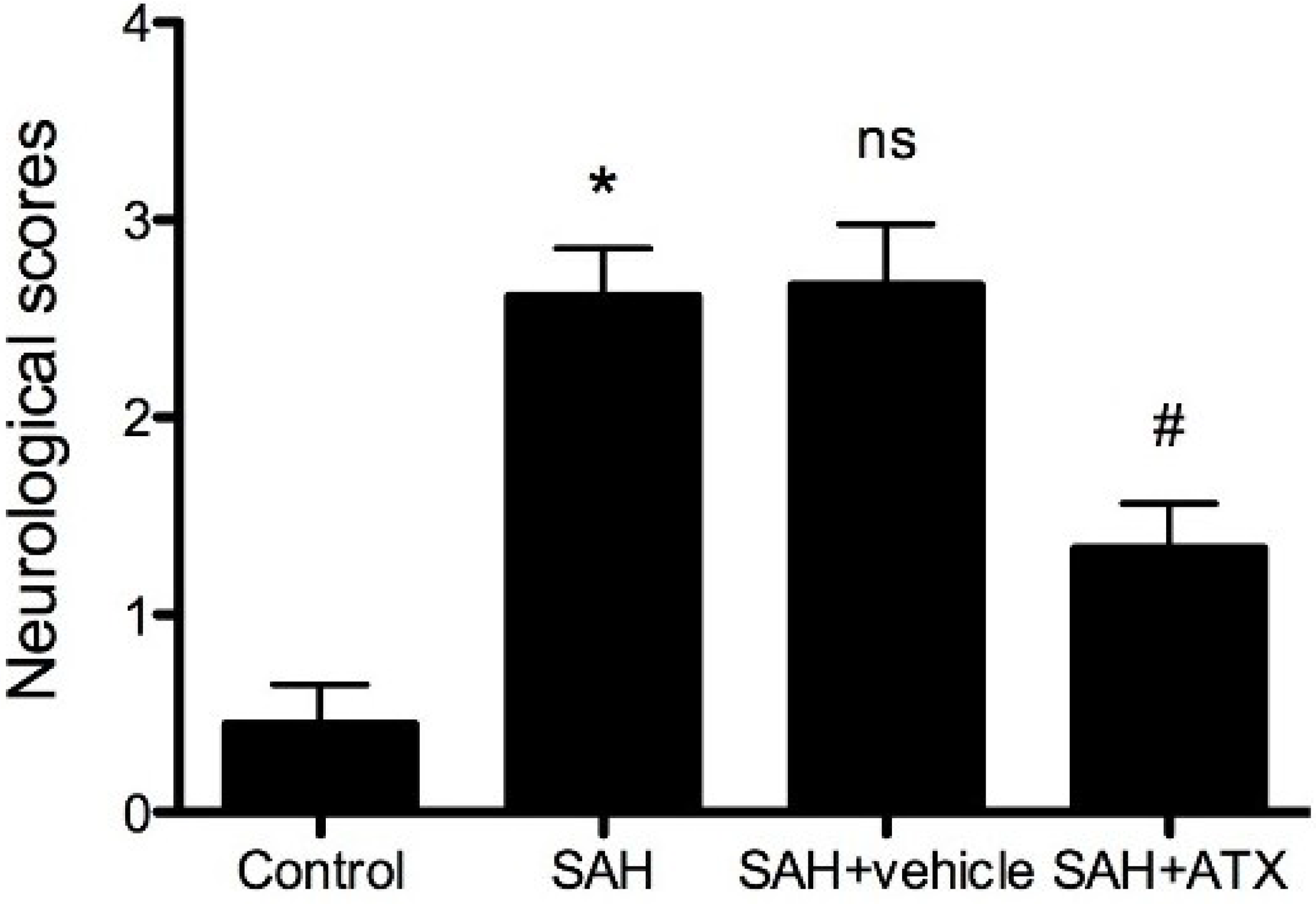
2.2. Neurological Scores
| Category | Behavior | Score |
|---|---|---|
| Appetite | Finished meal | 0 |
| Left meal unfinished | 1 | |
| Scarcely ate | 2 | |
| Activity | Walked and reached at least three corners of the cage | 0 |
| Walked with some stimulation | 1 | |
| Almost always lying down | 2 | |
| Deficits | No deficits | 0 |
| Unstable walk | 1 | |
| Impossible to walk | 2 |
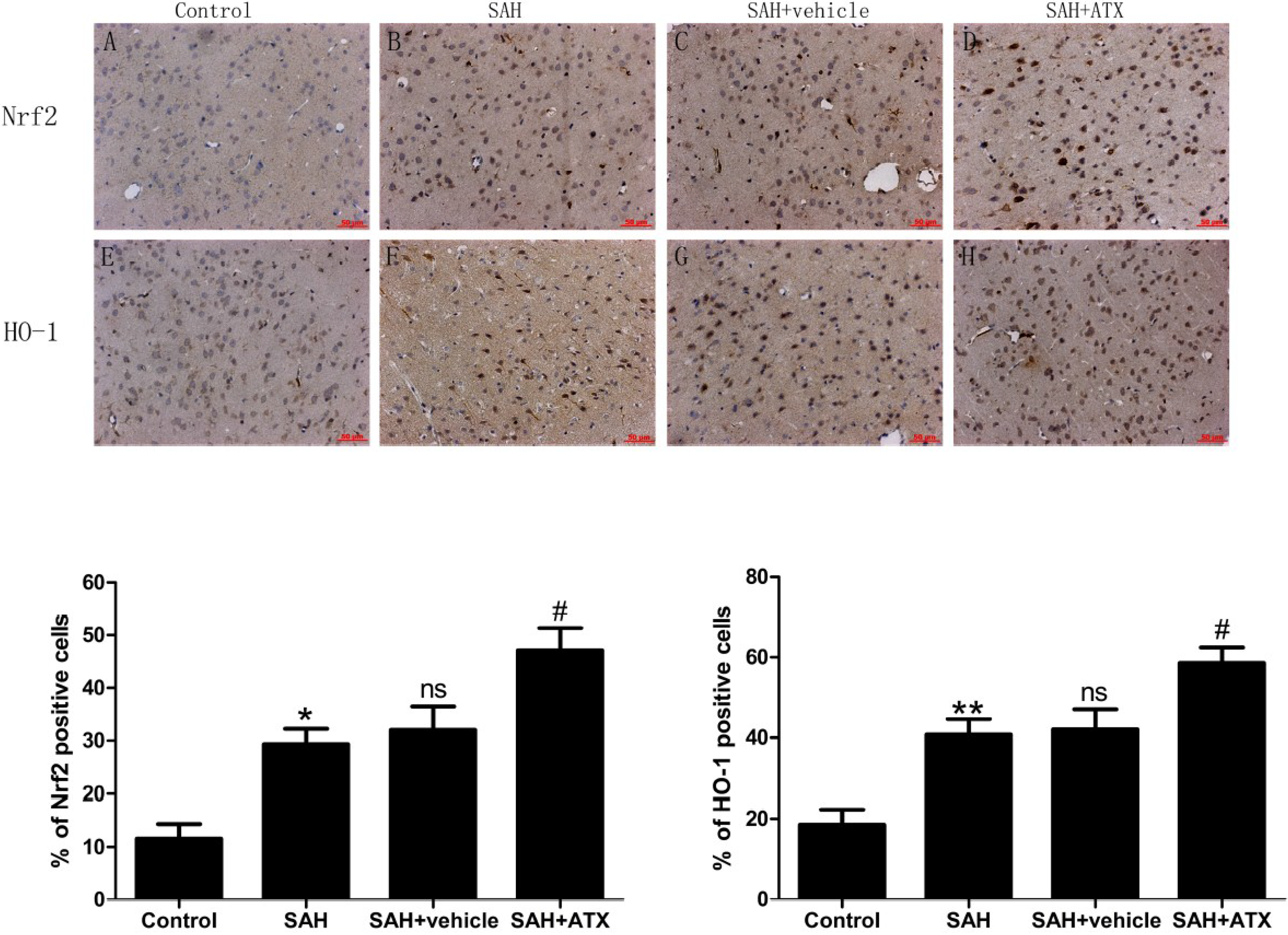
2.3. Immunohistochemistry for Nrf2 and HO-1 Expression
2.4. Western Blot Analysis for Nrf2 and HO-1 Expression

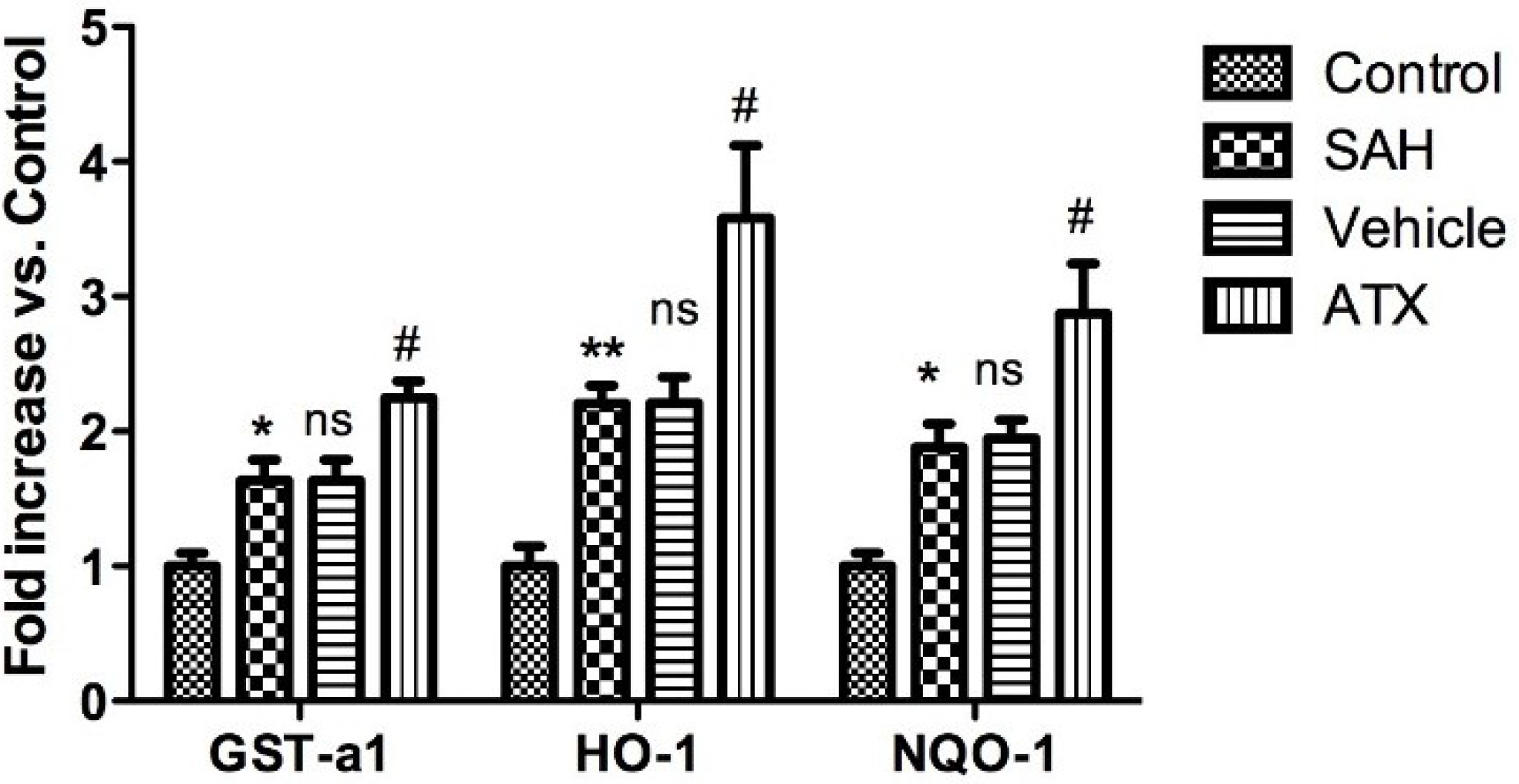
2.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
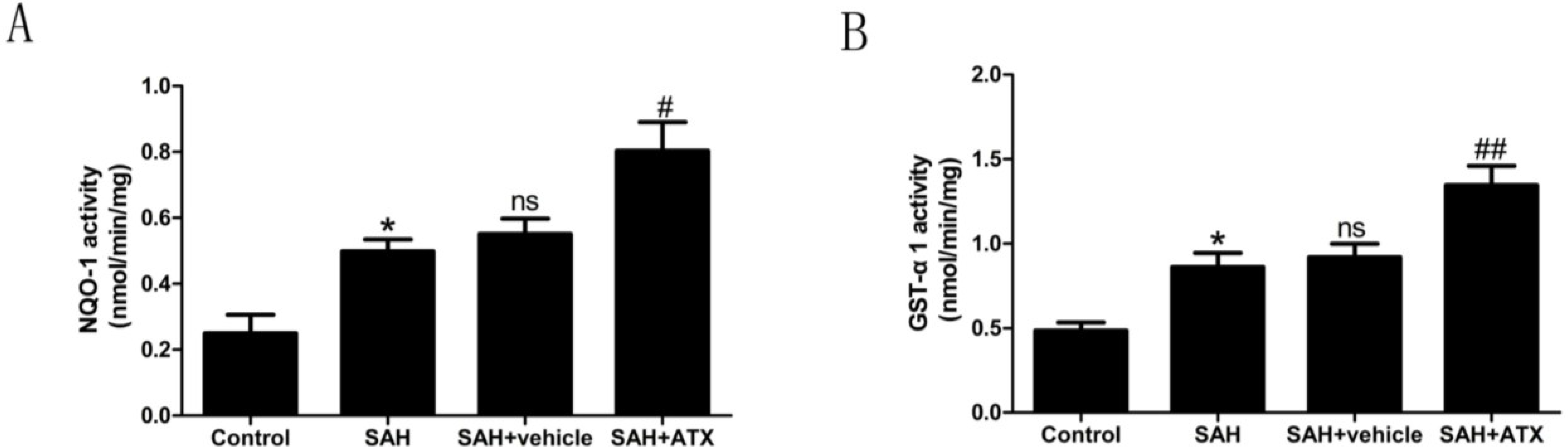
2.6. Enzyme Activity Assay for NQO1 and GST-α1
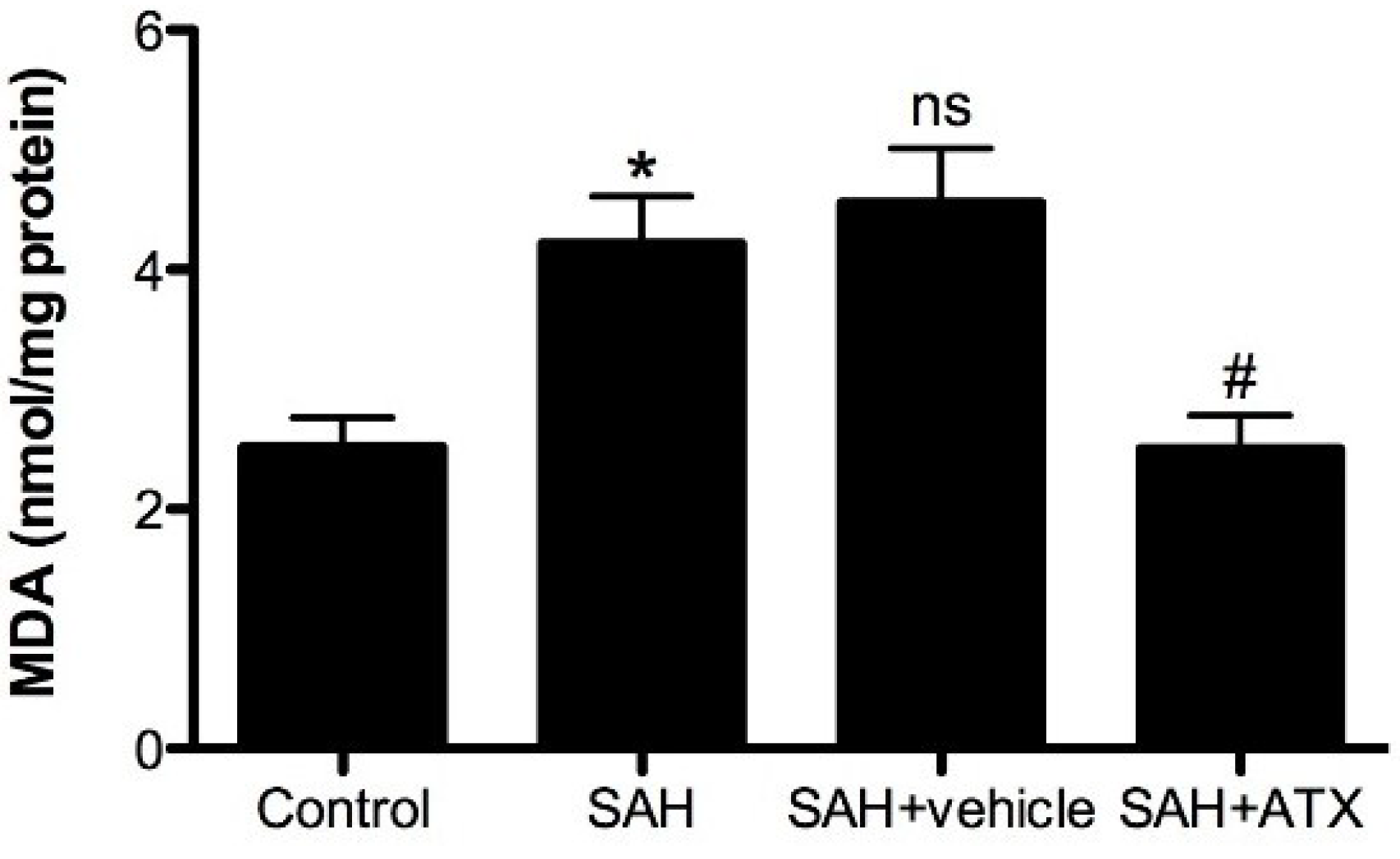
2.7. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Levels
2.8. Brain Water Content

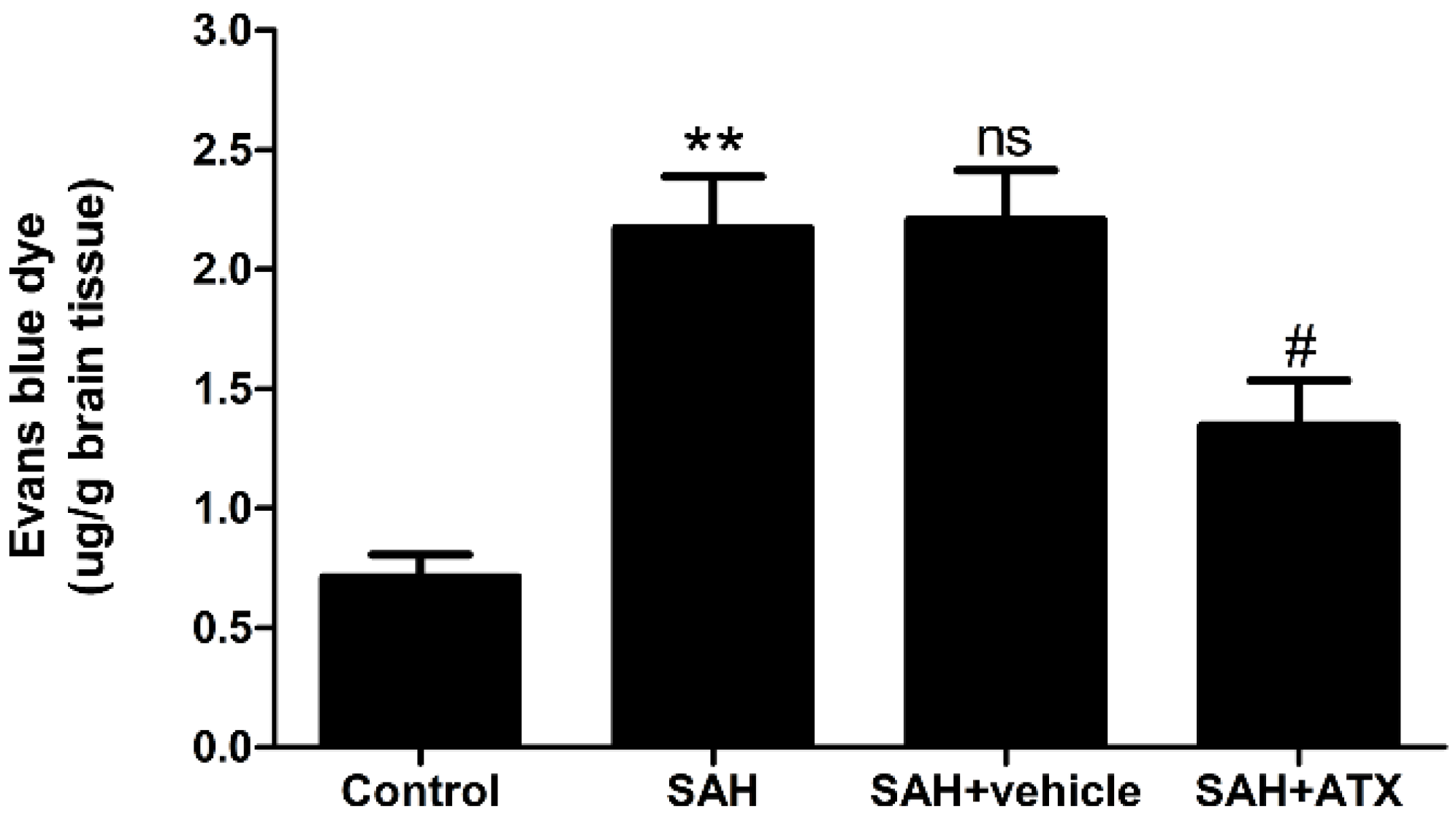
2.9. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability
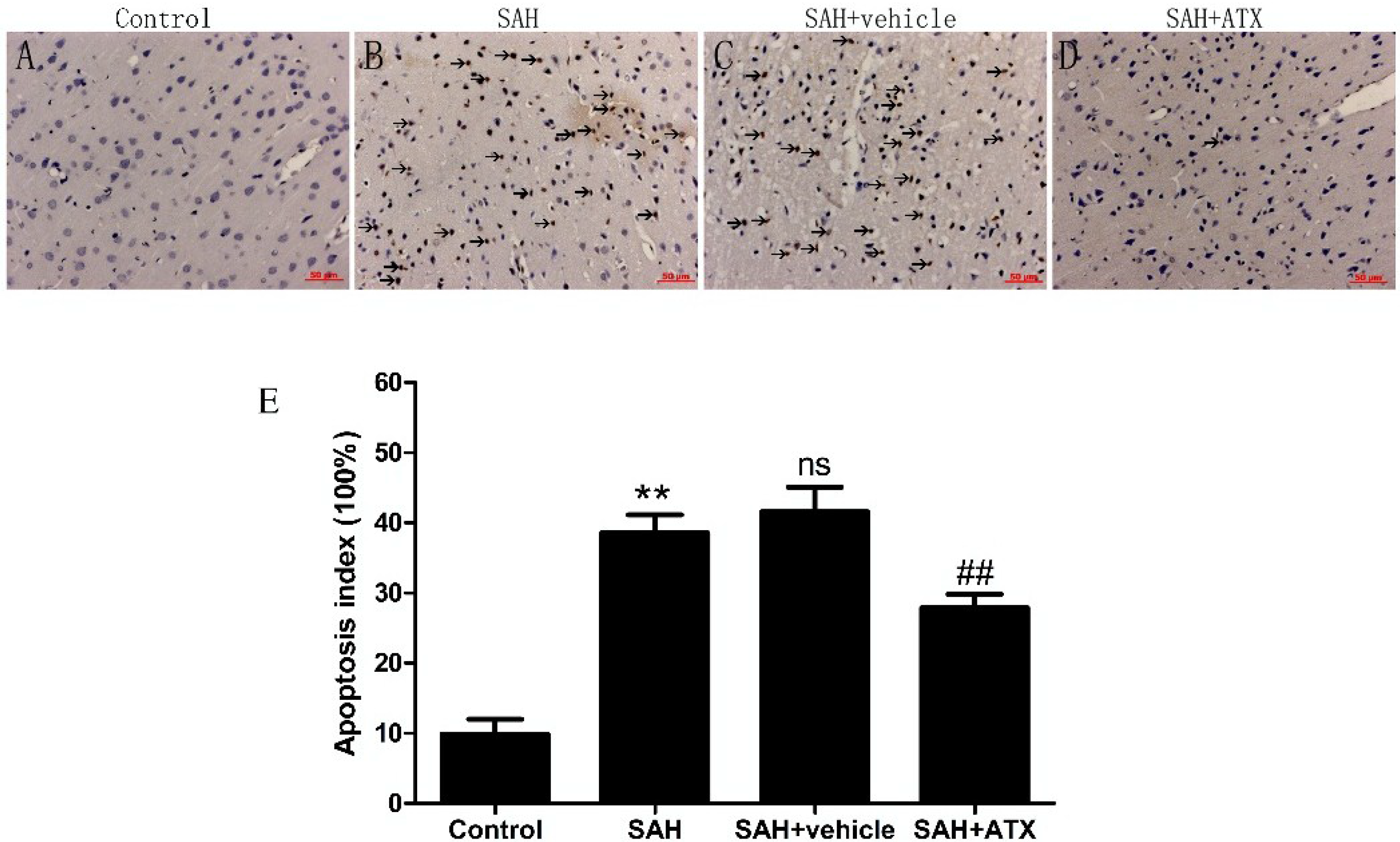
2.10. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase-Mediate dUTP Nick end Labeling Staining (TUNEL) Assay
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
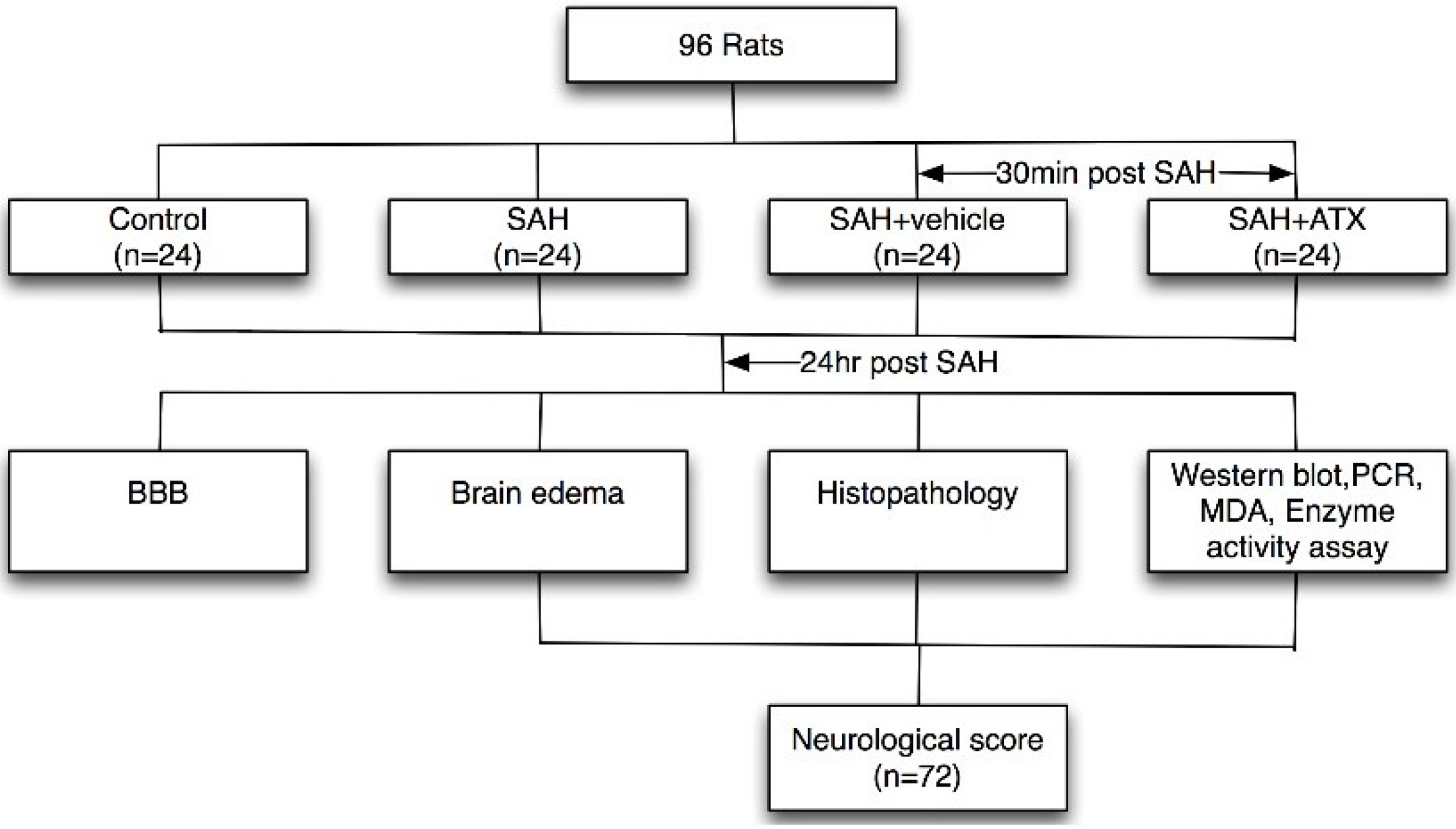
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Prechiasmatic Cistern SAH Model
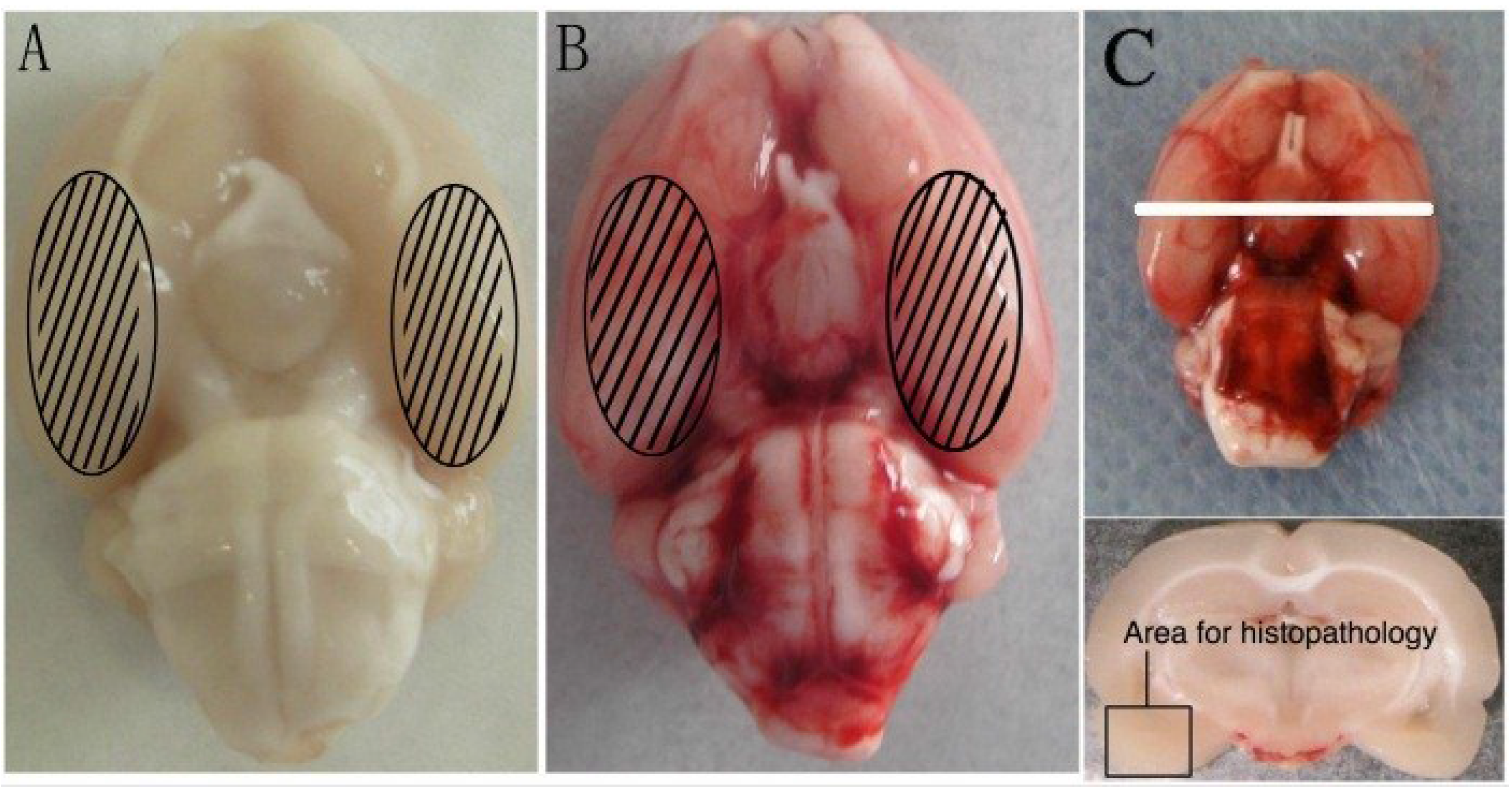
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. TUNEL Assay
4.6. Cell Counting
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.9. Enzyme Activity Assay
4.10. MDA Level Determination
4.11. Brain Water Content
4.12. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tripathi, D.N.; Jena, G.B. Astaxanthin intervention ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced oxidative stress, DNA damage and early hepatocarcinogenesis in rat: Role of Nrf2, p53, p38 and phase-II enzymes. Mutat. Res. 2010, 696, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Kuo, C.C.; Chou, J.; Delvolve, A.; Jackson, S.N.; Post, J.; Woods, A.S.; Hoffer, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Harvey, B.K. Astaxanthin reduces ischemic brain injury in adult rats. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1958–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Shibata, T.; Hisaka, S.; Osawa, T. Astaxanthin inhibits reactive oxygen species-mediated cellular toxicity in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells via mitochondria-targeted protective mechanism. Brain Res. 2009, 1254, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Tsuji, S.; Satoh, A.; Ishikura, M.; Shirasawa, T.; Shimizu, T. Protective effects of astaxanthin on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. J. Neurochem. 2008, 107, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.S.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.L.; Zhou, X.M.; Li, N.; Li, W.; Cong, Z.X.; Sun, Q.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, C.X.; et al. Amelioration of oxidative stress and protection against early brain injury by astaxanthin after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluta, R.M.; Hansen-Schwartz, J.; Dreier, J.; Vajkoczy, P.; Macdonald, R.L.; Nishizawa, S.; Kasuya, H.; Wellman, G.; Keller, E.; Zauner, A.; et al. Cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage: Time for a new world of thought. Neurol. Res. 2009, 31, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.D.; Zhou, Y.T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.L.; Qi, W.; Zhuang, Z.; Su, X.F.; Shi, J.X. Expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in the basilar artery after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits: A preliminary study. Brain Res. 2010, 1358, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, W.; Wang, H.; Ji, Y.; Hu, Q.; Yan, W.; Chen, G.; Yin, H. Increased intestinal inflammatory response and gut barrier dysfunction in Nrf2-deficient mice after traumatic brain injury. Cytokine 2008, 44, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, H.; Liu, Y. Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2009, 1282, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Z. Role of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.E.; Hu, L.; Zhao, L.; Huang, J. Carotenoids inhibit proliferation and regulate expression of peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in K562 cancer cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 512, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ma, C.; Meng, C.J.; Zhu, G.Q.; Sun, X.B.; Huo, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, H.X.; He, W.C.; Shen, X.M.; et al. Melatonin activates the Nrf2-ARE pathway when it protects against early brain injury in a subarachnoid hemorrhage model. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claassen, J.; Carhuapoma, J.R.; Kreiter, K.T.; Du, E.Y.; Connolly, E.S.; Mayer, S.A. Global cerebral edema after subarachnoid hemorrhage: frequency, predictors, and impact on outcome. Stroke 2002, 33, 1225–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, J.; Zhang, J.H. Subarachnoid hemorrhage: Is it time for a new direction? Stroke 2009, 40, S86–S87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, R.E.; Zhang, J.H. Oxidative stress in subarachnoid haemorrhage: Significance in acute brain injury and vasospasm. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2008, 104, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ostrowski, R.P.; Colohan, A.R.; Zhang, J.H. Molecular mechanisms of early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol. Res. 2006, 28, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Huang, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X. Astaxanthin protects against MPP(+)-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells via the HO-1/NOX2 axis. BMC Neurosci. 2012, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.C.; Mong, M.C.; Yin, M.C. Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory neuroprotective effects of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in nerve growth factor differentiated PC12 cells. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, H225–H231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fassett, R.G.; Coombes, J.S. Astaxanthin, oxidative stress, inflammation and cardiovascular disease. Future Cardiol. 2009, 5, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauver, D.A.; Lockwood, S.F.; Lucchesi, B.R. Disodium Disuccinate Astaxanthin (Cardax) attenuates complement activation and reduces myocardial injury following ischemia/reperfusion. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 314, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, G.J.; Lockwood, S.F. Cardioprotection and myocardial salvage by a disodium disuccinate astaxanthin derivative (Cardax). Life Sci. 2004, 75, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Wang, H.; Zhu, L.; Mao, L.; Qiao, L.; Su, X. Depletion of Nrf2 enhances inflammation induced by oxyhemoglobin in cultured mice astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 2434–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Muiswinkel, F.L.; Kuiperij, H.B. The Nrf2-ARE Signalling pathway: Promising drug target to combat oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Curr. Drug Targets CNS Neurol. Disord. 2005, 4, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Dor, A.; Steiner, M.; Gheber, L.; Danilenko, M.; Dubi, N.; Linnewiel, K.; Zick, A.; Sharoni, Y.; Levy, J. Carotenoids activate the antioxidant response element transcription system. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Radjendirane, V.; Joseph, P.; Lee, Y.H.; Kimura, S.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Jaiswal, A.K. Disruption of the DT diaphorase (NQO1) gene in mice leads to increased menadione toxicity. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 7382–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, A.Y.; Johnson, D.A.; Wong, G.; Kraft, A.D.; Jiang, L.; Erb, H.; Johnson, J.A.; Murphy, T.H. Coordinate regulation of glutathione biosynthesis and release by Nrf2-expressing glia potently protects neurons from oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3394–3406. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ku, B.M.; Joo, Y.; Mun, J.; Roh, G.S.; Kang, S.S.; Cho, G.J.; Choi, W.S.; Kim, H.J. Heme oxygenase protects hippocampal neurons from ethanol-induced neurotoxicity. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 405, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipper, L.M.; Mulcahy, R.T. Erk activation is required for Nrf2 nuclear localization during pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate induction of glutamate cysteine ligase modulatory gene expression in HepG2 cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2003, 73, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Q.; Sun, X.B.; Xu, Y.X.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Q.Y.; Zhu, C.Q. Astaxanthin upregulates heme oxygenase-1 expression through ERK1/2 pathway and its protective effect against beta-amyloid-induced cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Brain Res. 2010, 1360, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, B.W.; Kim, W.J.; Choi, Y.H. Astaxanthin improves the proliferative capacity as well as the osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation potential in neural stem cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 1741–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunell, G.F.; Mathiesen, T.; Svendgaard, N.A. A new experimental model in rats for study of the pathophysiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 2553–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prunell, G.F.; Mathiesen, T.; Svendgaard, N.A. Experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage: Cerebral blood flow and brain metabolism during the acute phase in three different models in the rat. Neurosurgery 2004, 54, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wang, H.D.; Zhu, L.; Feng, X.M.; Qiao, L.; Jin, W.; Tang, K. Traumatic brain injury induces the activation of the Nrf2-ARE pathway in the lung in rats. Brain Injury 2008, 22, 802–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, W.; Wang, H.D.; Feng, X.M.; Ding, Y.S.; Jin, W.; Tang, K. The expression of NF-E2-related factor 2 in the rat brain after traumatic brain injury. J. Trauma 2009, 66, 1431–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Chen, G.; Zhu, W.; Dong, W.; Wang, Z. Influence of melatonin on cerebrovascular proinflammatory mediators expression and oxidative stress following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rabbits. Mediat. Inflamm. 2009, 2009, 426346. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, W.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Zhu, L.; Hu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Tang, K. Role of Nrf2 in protection against traumatic brain injury in mice. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.-S.; Wang, H.-D.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, W.; Zhou, M.-L.; Wang, X.-L. Astaxanthin Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and the Antioxidant Responsive Element (Nrf2-ARE) Pathway in the Brain after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats and Attenuates Early Brain Injury. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 6125-6141. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126125
Wu Q, Zhang X-S, Wang H-D, Zhang X, Yu Q, Li W, Zhou M-L, Wang X-L. Astaxanthin Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and the Antioxidant Responsive Element (Nrf2-ARE) Pathway in the Brain after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats and Attenuates Early Brain Injury. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(12):6125-6141. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qi, Xiang-Sheng Zhang, Han-Dong Wang, Xin Zhang, Qing Yu, Wei Li, Meng-Liang Zhou, and Xiao-Liang Wang. 2014. "Astaxanthin Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and the Antioxidant Responsive Element (Nrf2-ARE) Pathway in the Brain after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats and Attenuates Early Brain Injury" Marine Drugs 12, no. 12: 6125-6141. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126125
APA StyleWu, Q., Zhang, X.-S., Wang, H.-D., Zhang, X., Yu, Q., Li, W., Zhou, M.-L., & Wang, X.-L. (2014). Astaxanthin Activates Nuclear Factor Erythroid-Related Factor 2 and the Antioxidant Responsive Element (Nrf2-ARE) Pathway in the Brain after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage in Rats and Attenuates Early Brain Injury. Marine Drugs, 12(12), 6125-6141. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12126125




