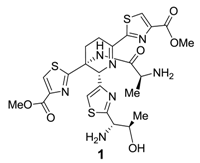
Thiopeptide Antibiotics: Retrospective and Recent Advances
Abstract
:1. Introduction
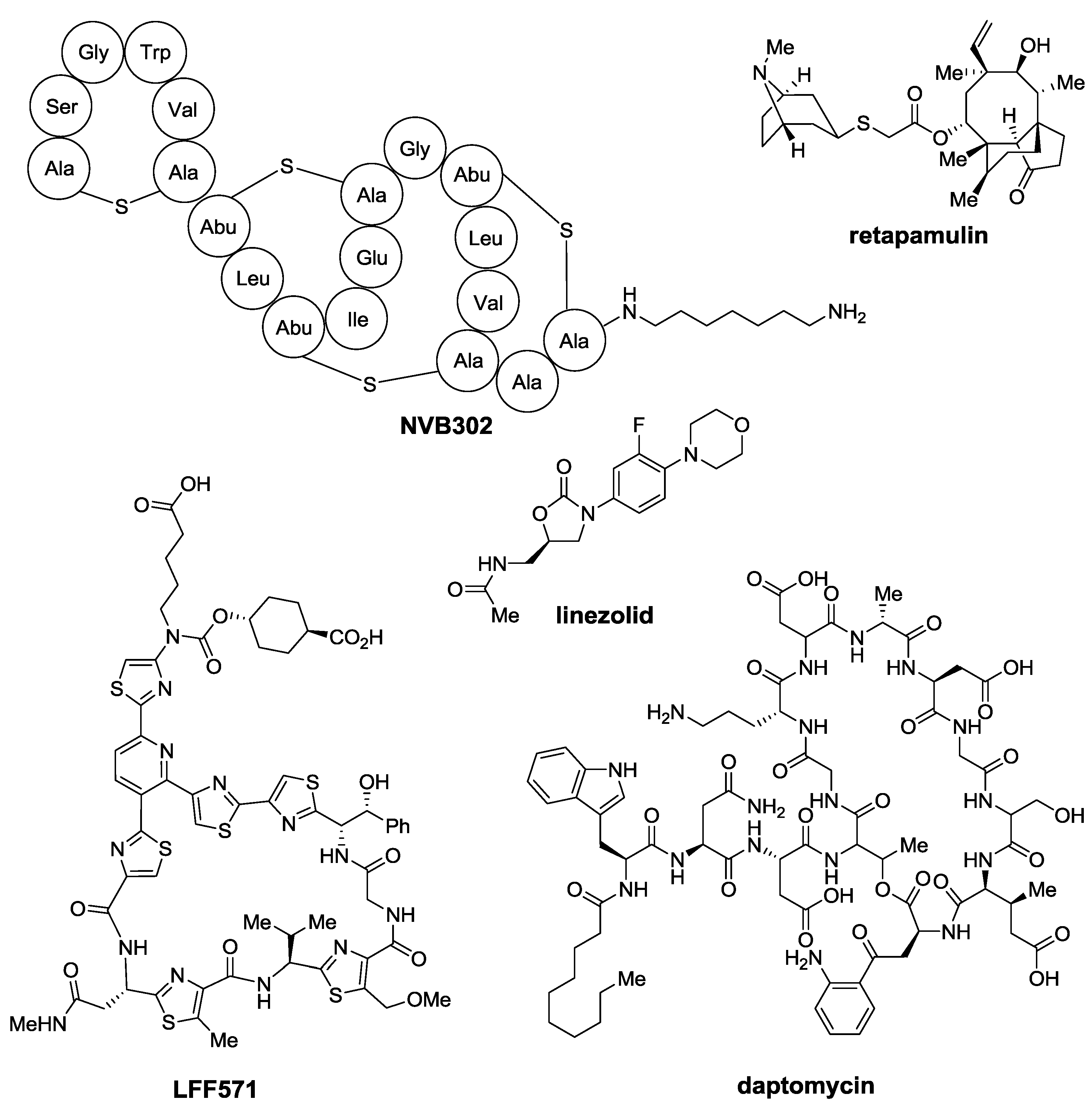
2. Thiopeptides
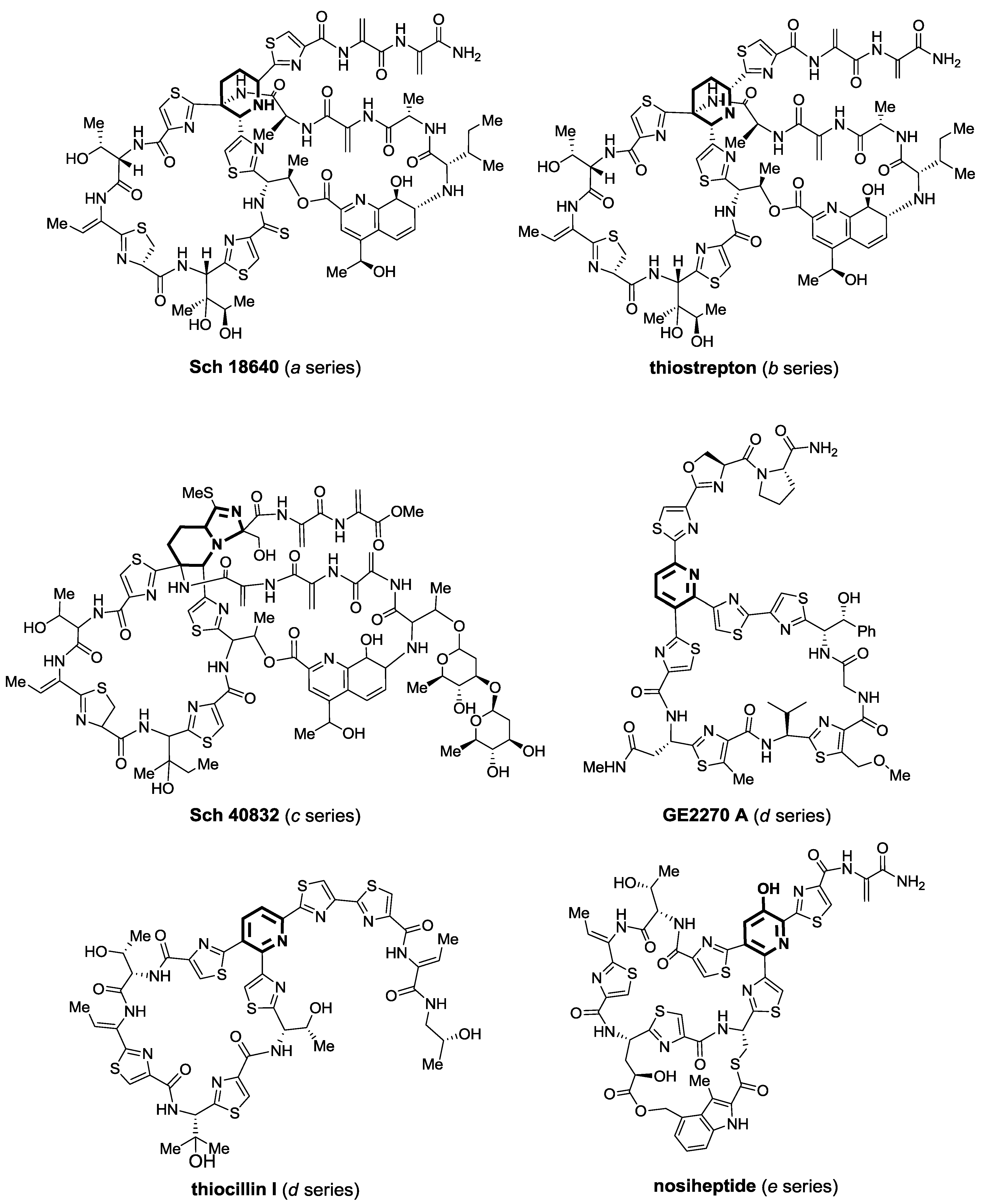
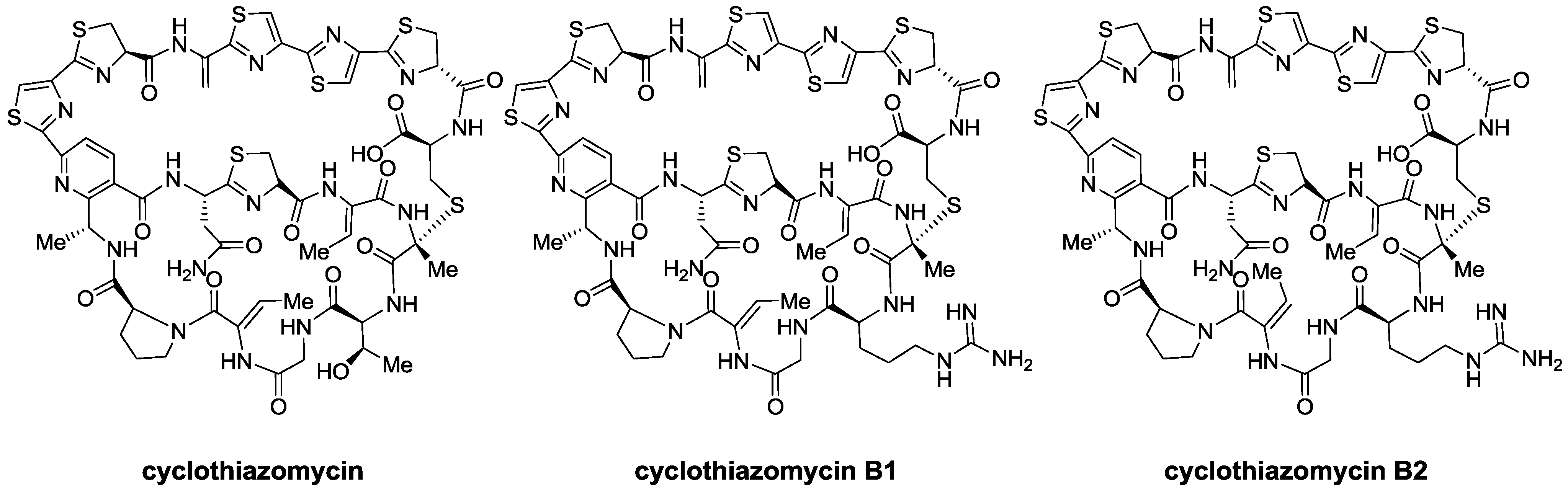
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation
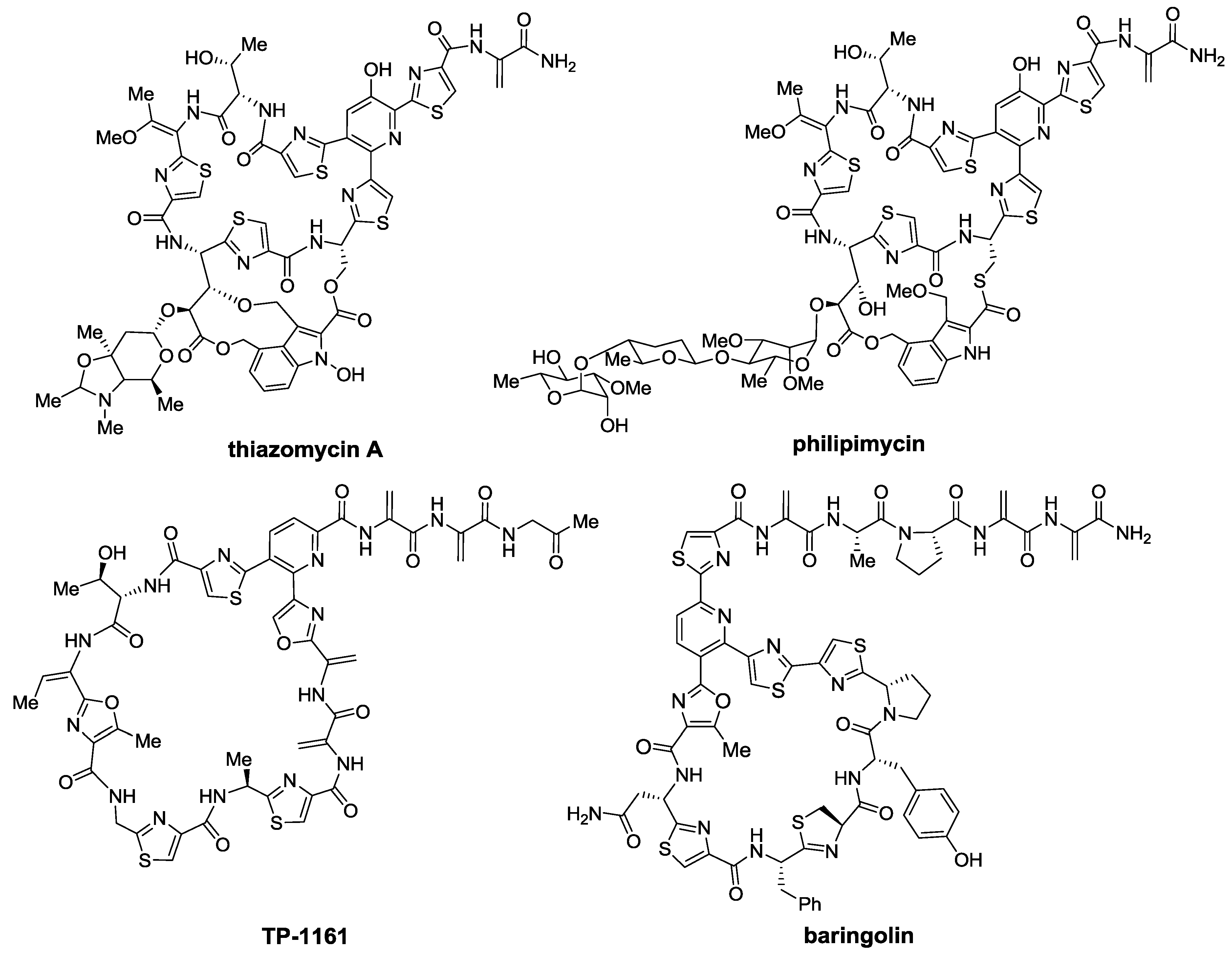
2.2. Biosynthesis

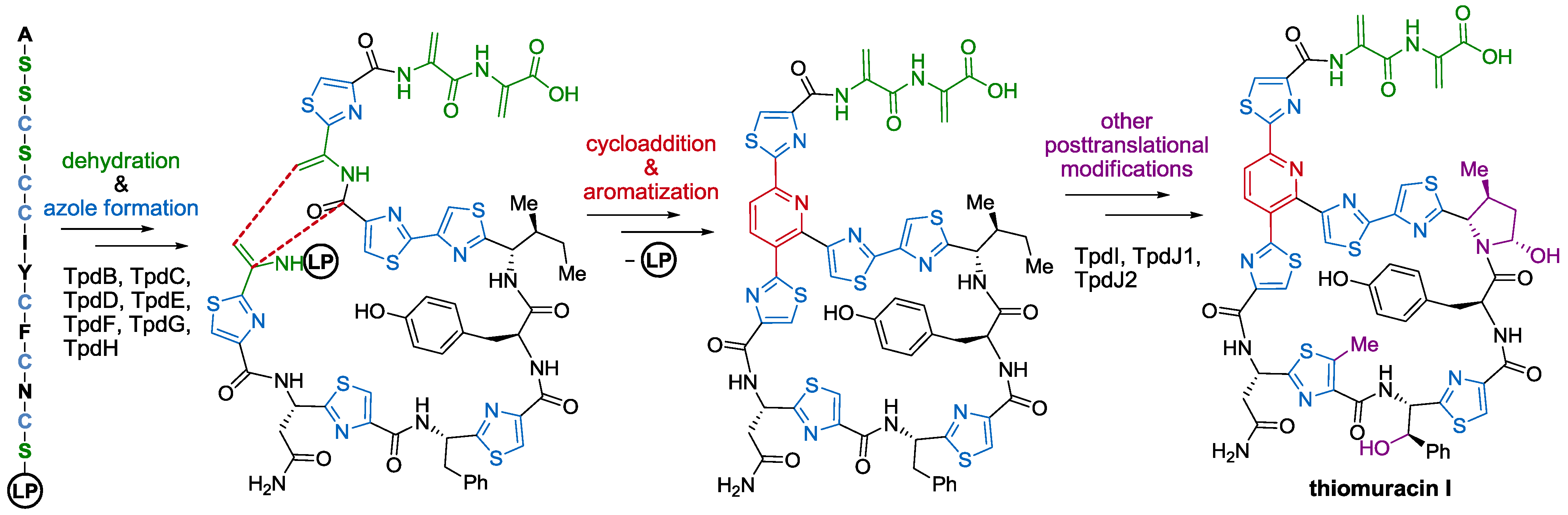
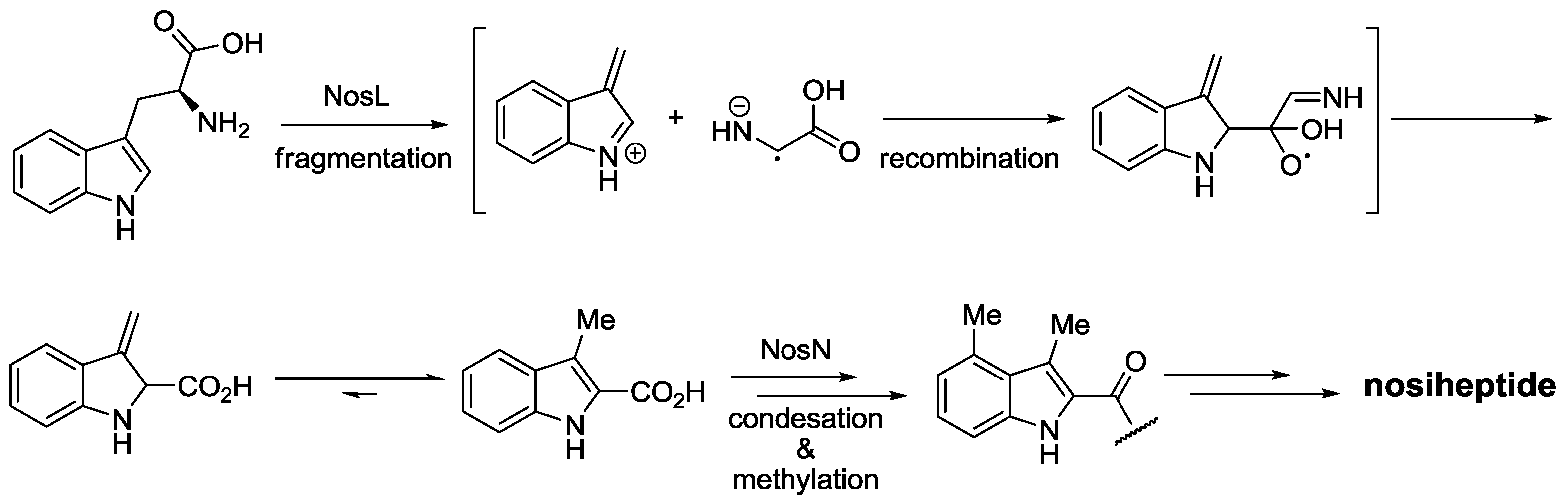
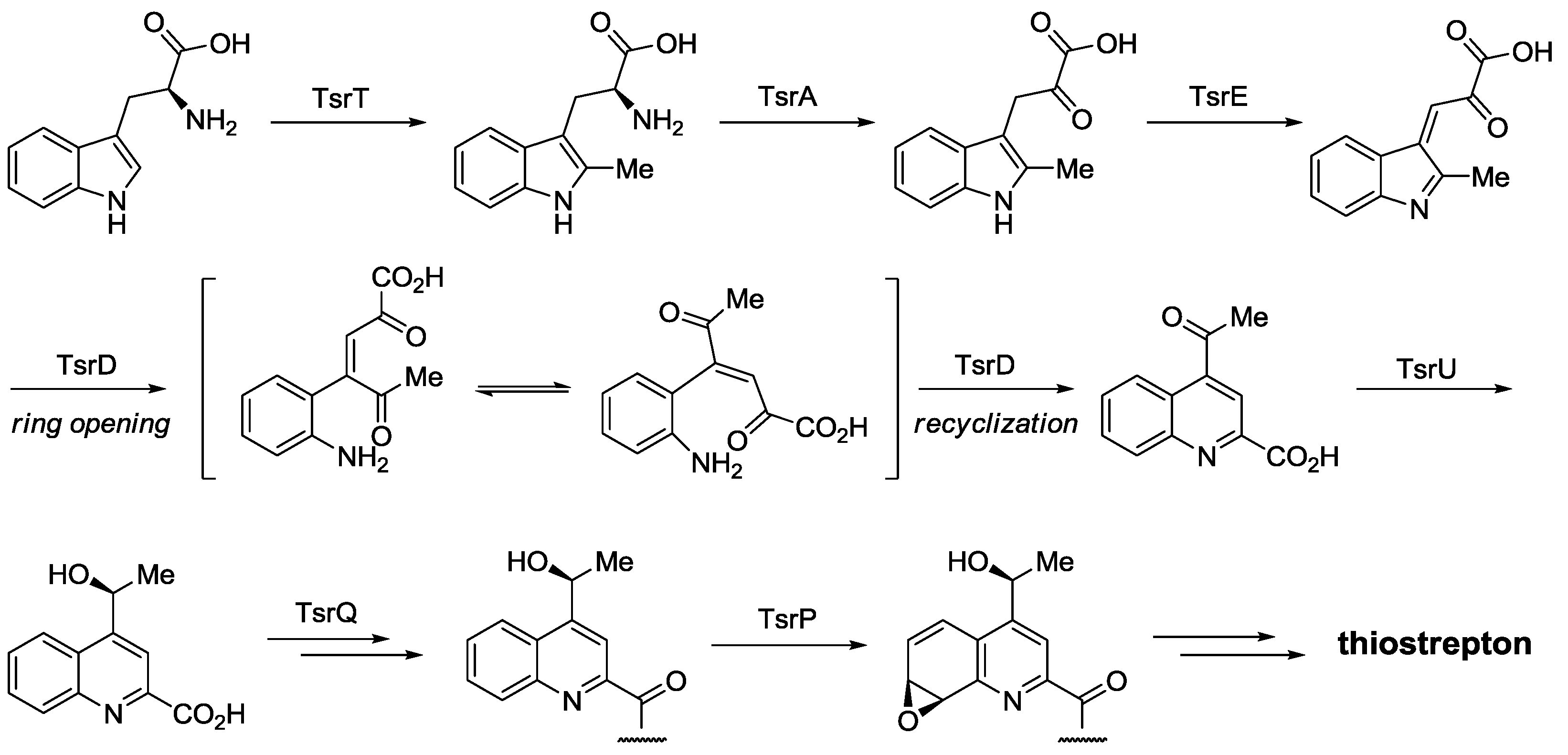
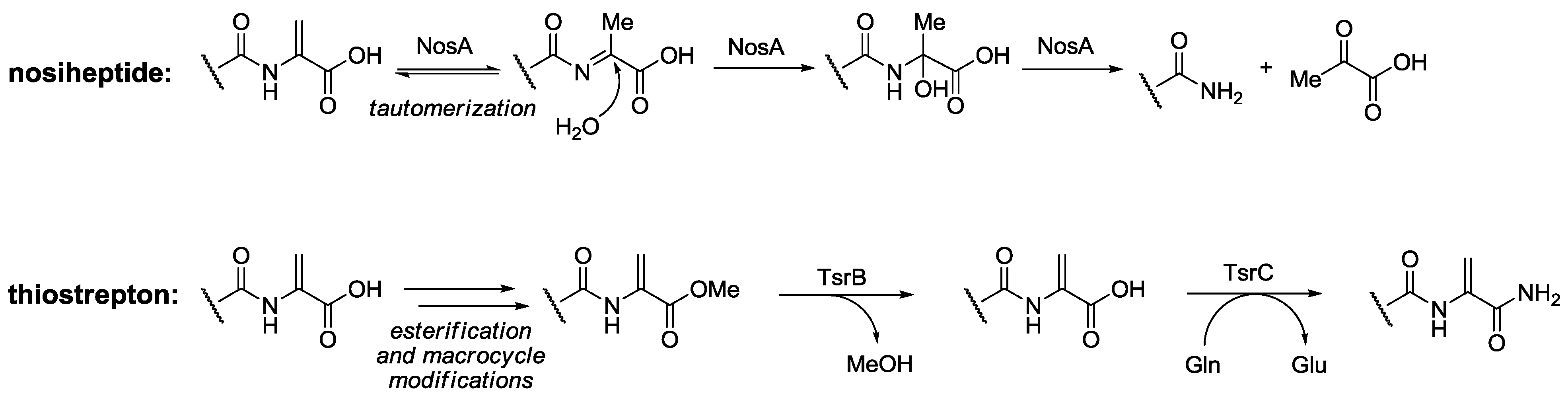
2.3. Biological Activity
2.3.1. Antibacterial Activity
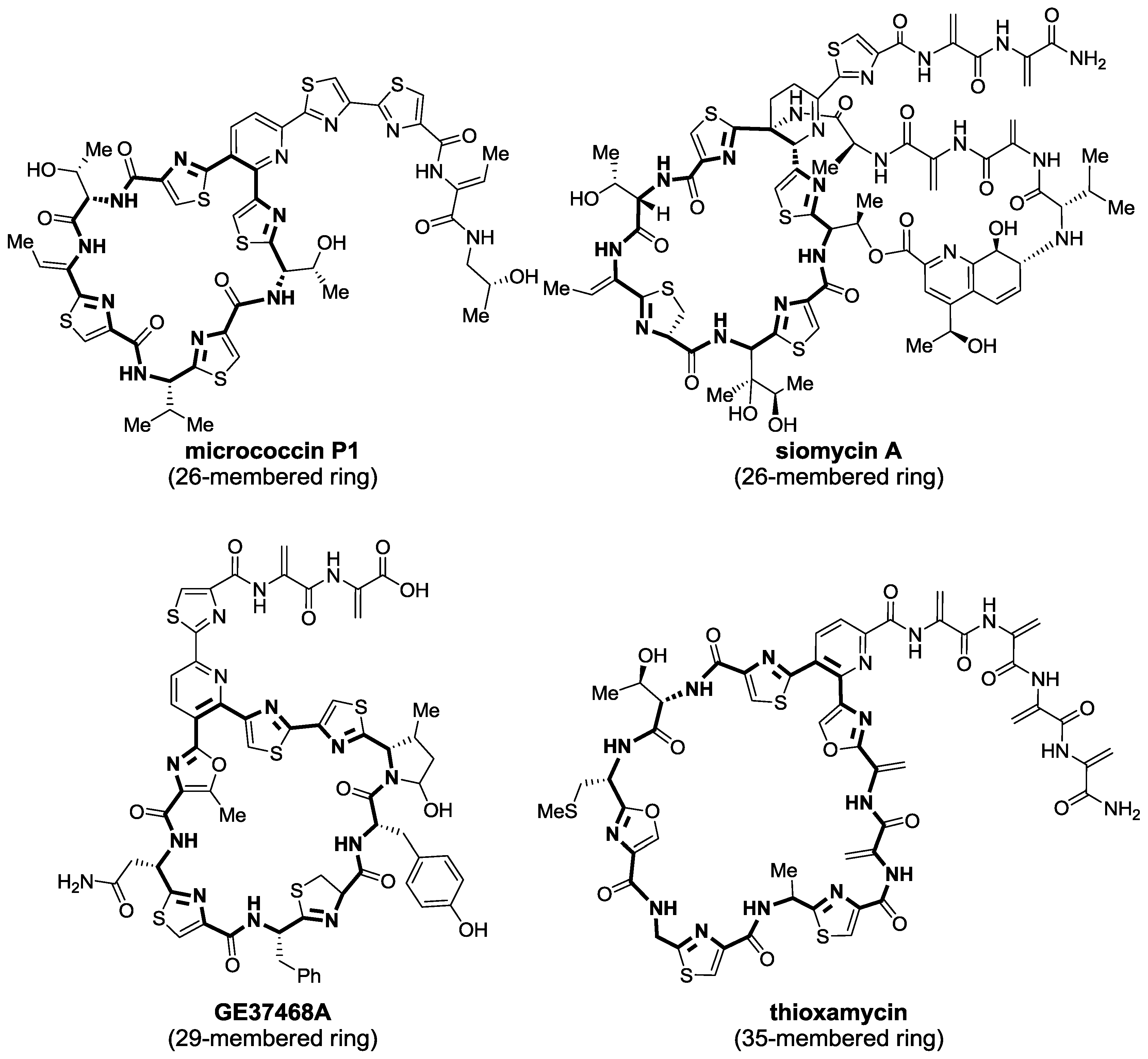
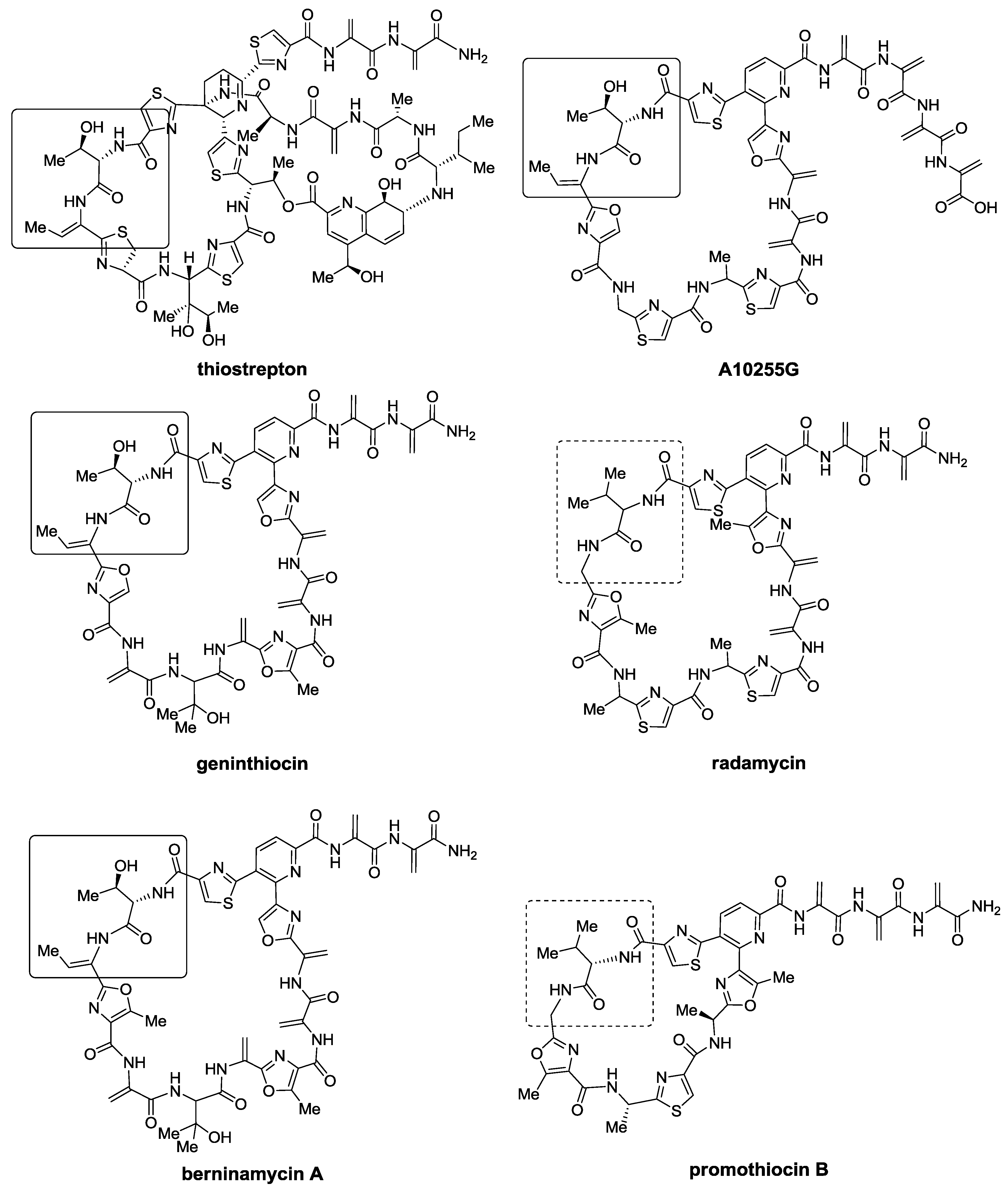

2.3.2. Other Activities
| Compound | LC50 (μM) | IC50 (μM) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCI-H460 | HCT-116 | SK-OV-3 | MCF-7 | K-562 | 1A9 | PTX10 | A8 | AD10 | |
| thiostrepton | 1.5 | 1.6 | 2.8 | 3.8 | 1.7 | 0.96 | 1.1 | 0.9 | 91.0 |
| 1 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.07 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 |
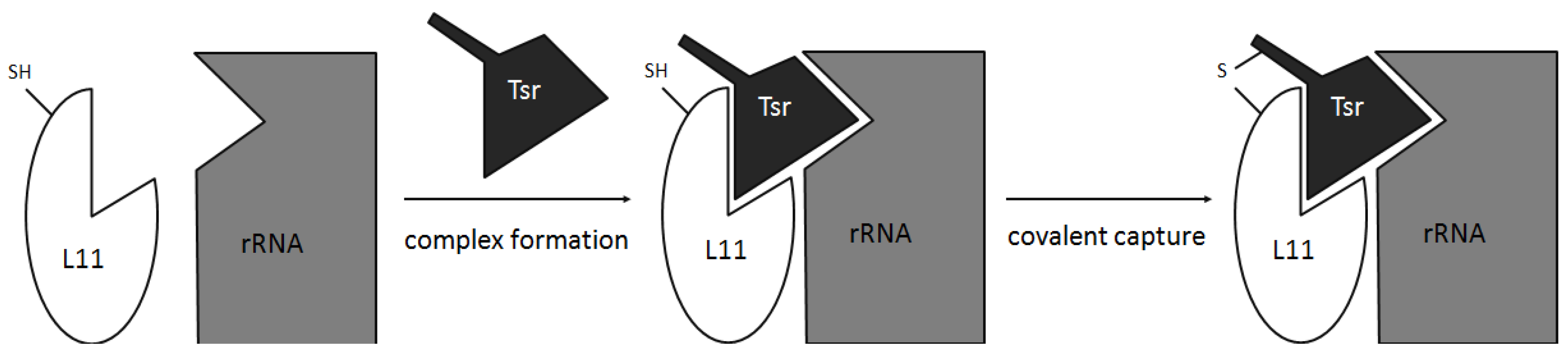
2.4. Conformation and Binding
2.5. Chemical Synthesis
2.5.1. Modification of Pyridine
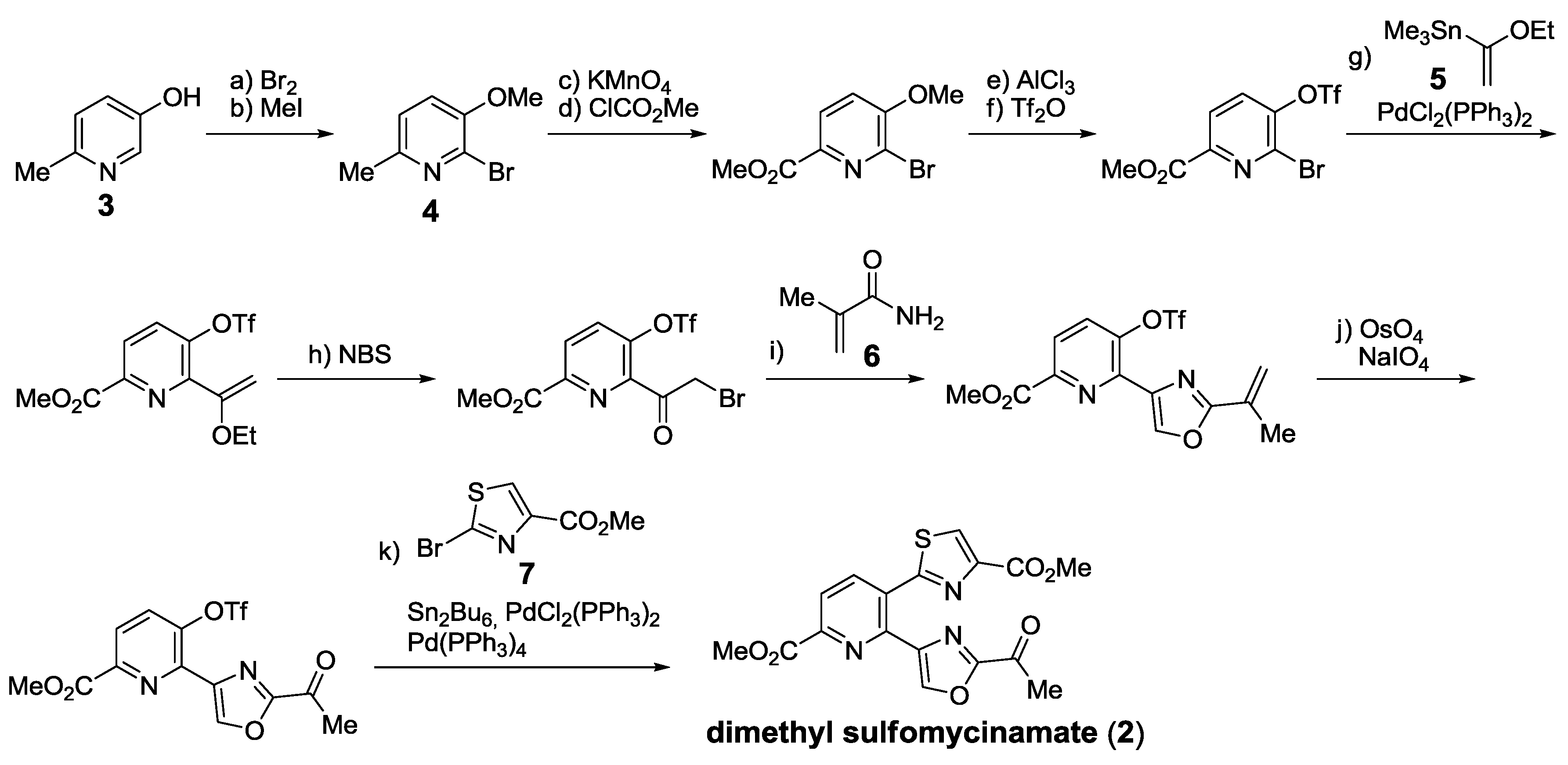
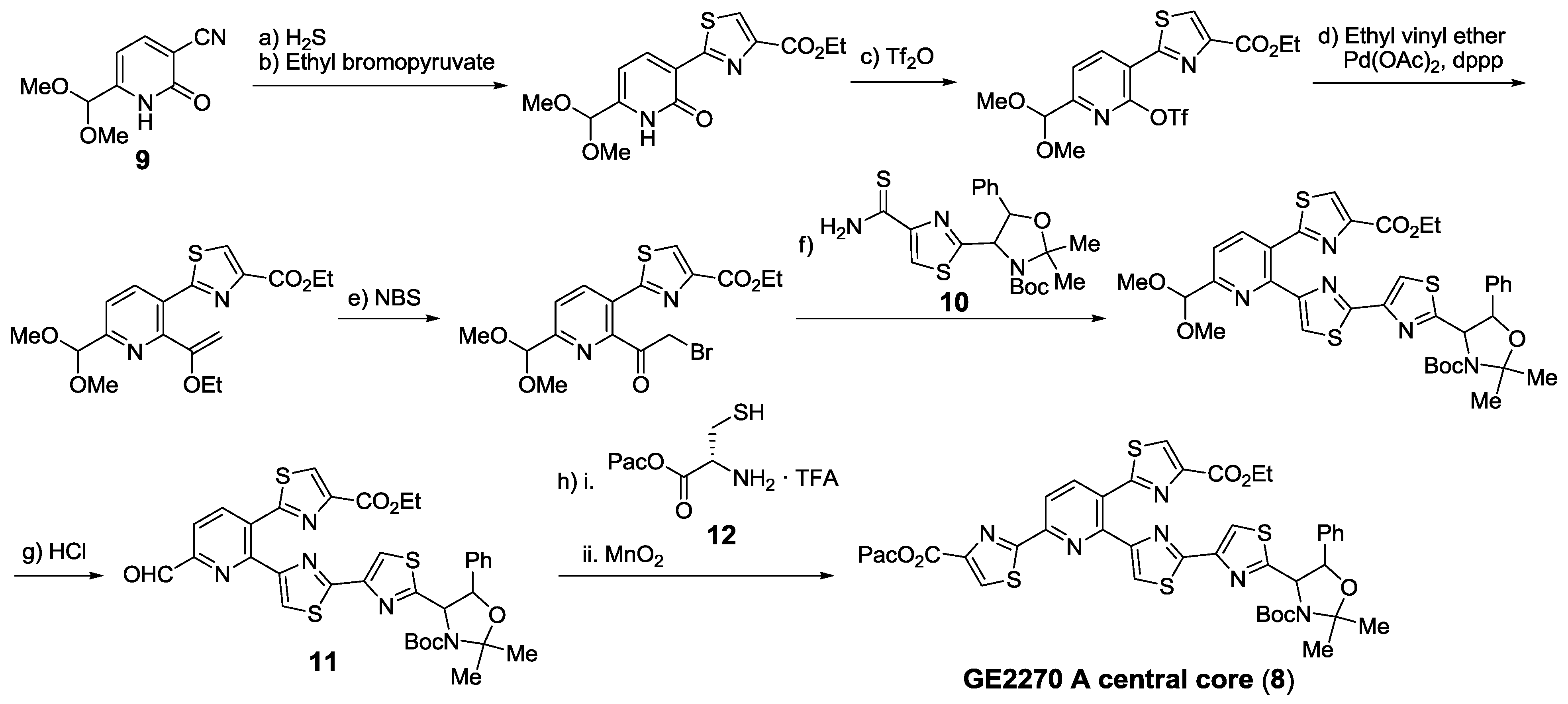
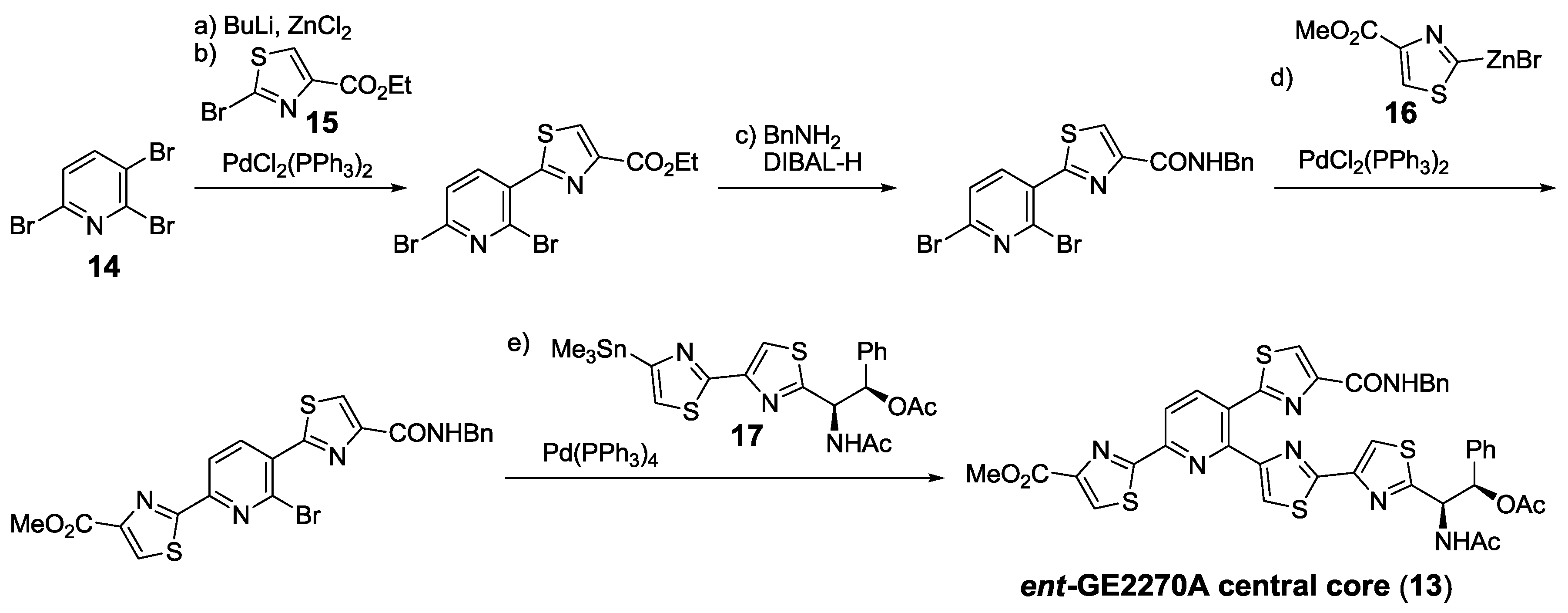
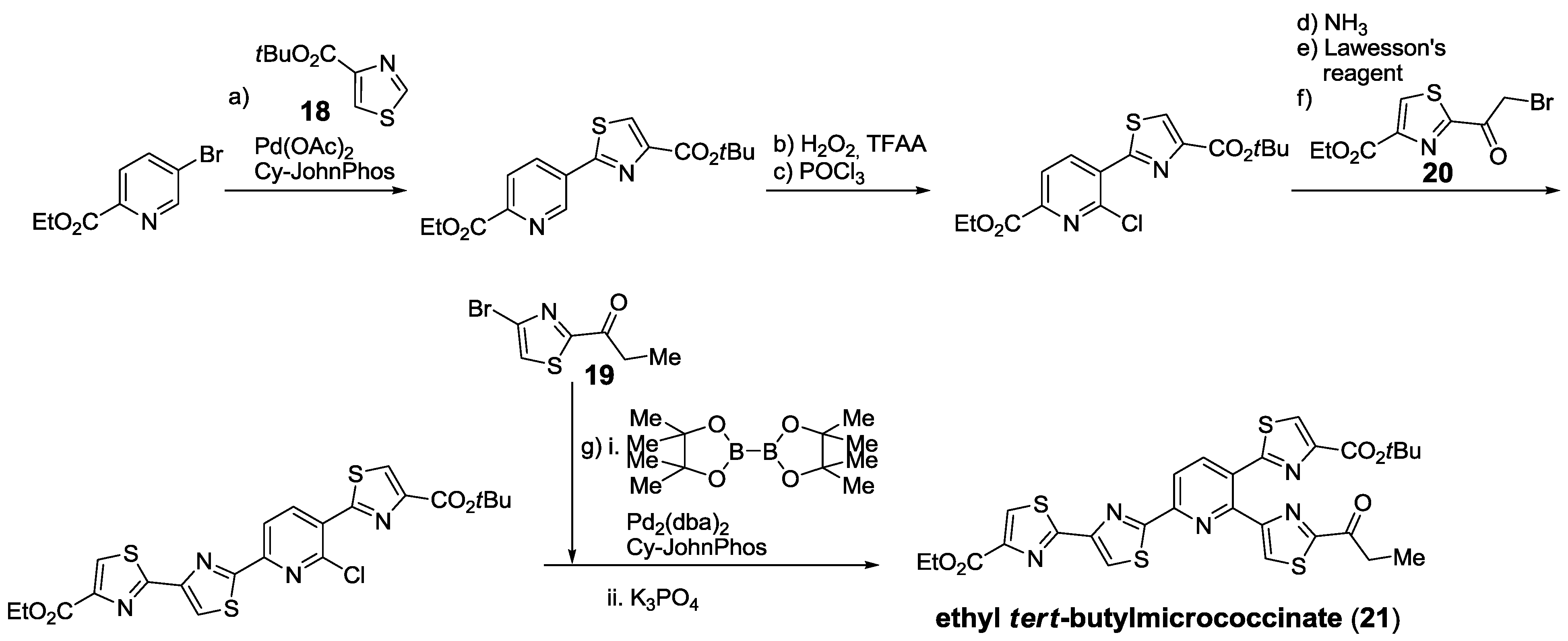
2.5.2. Construction of the Central Ring
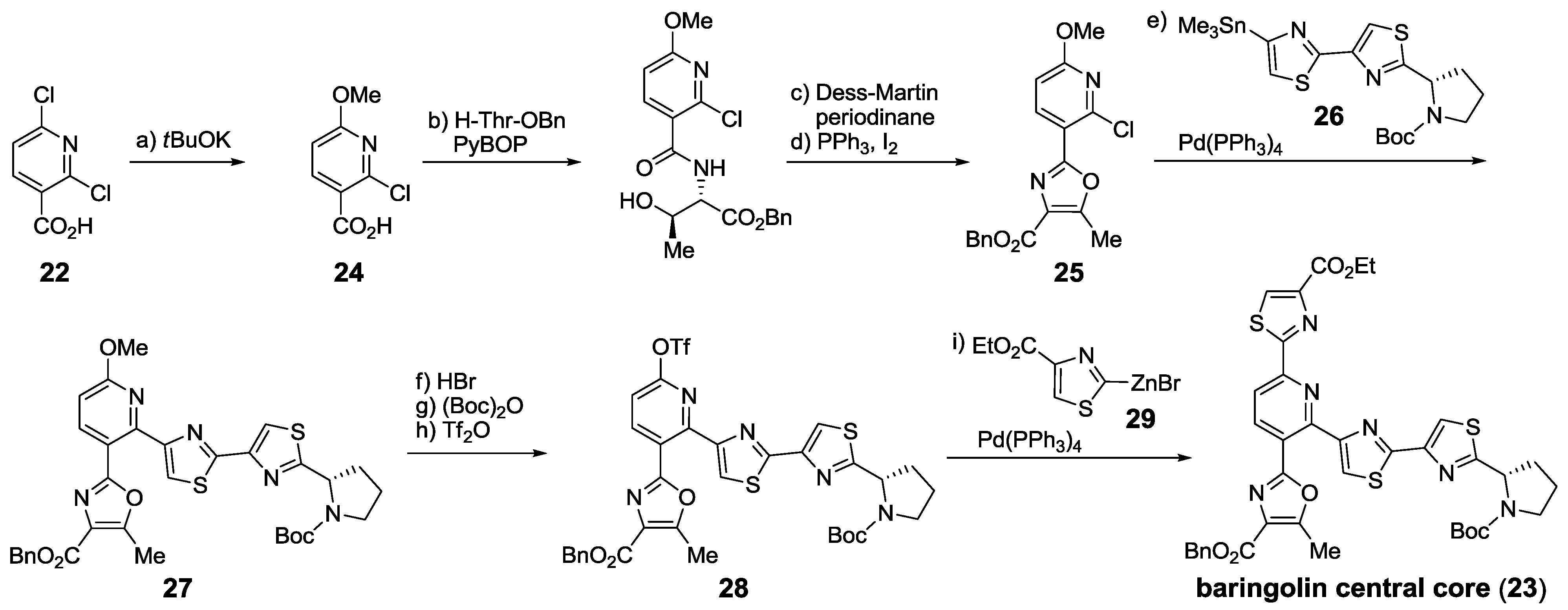
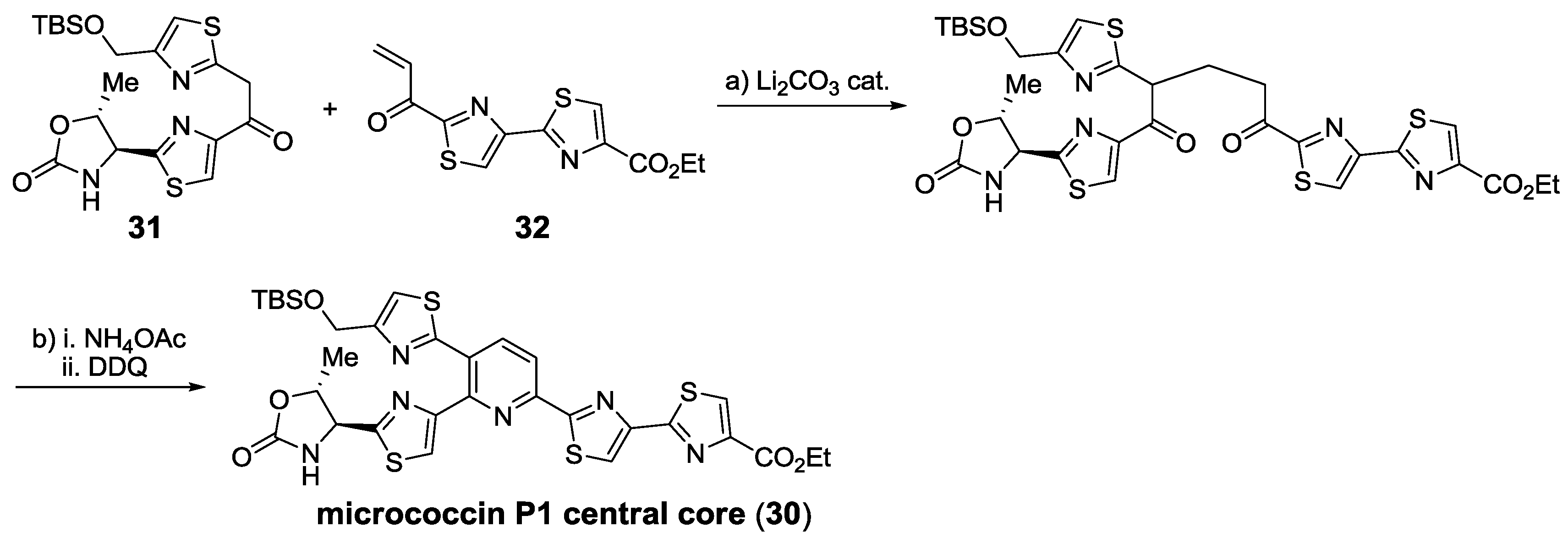
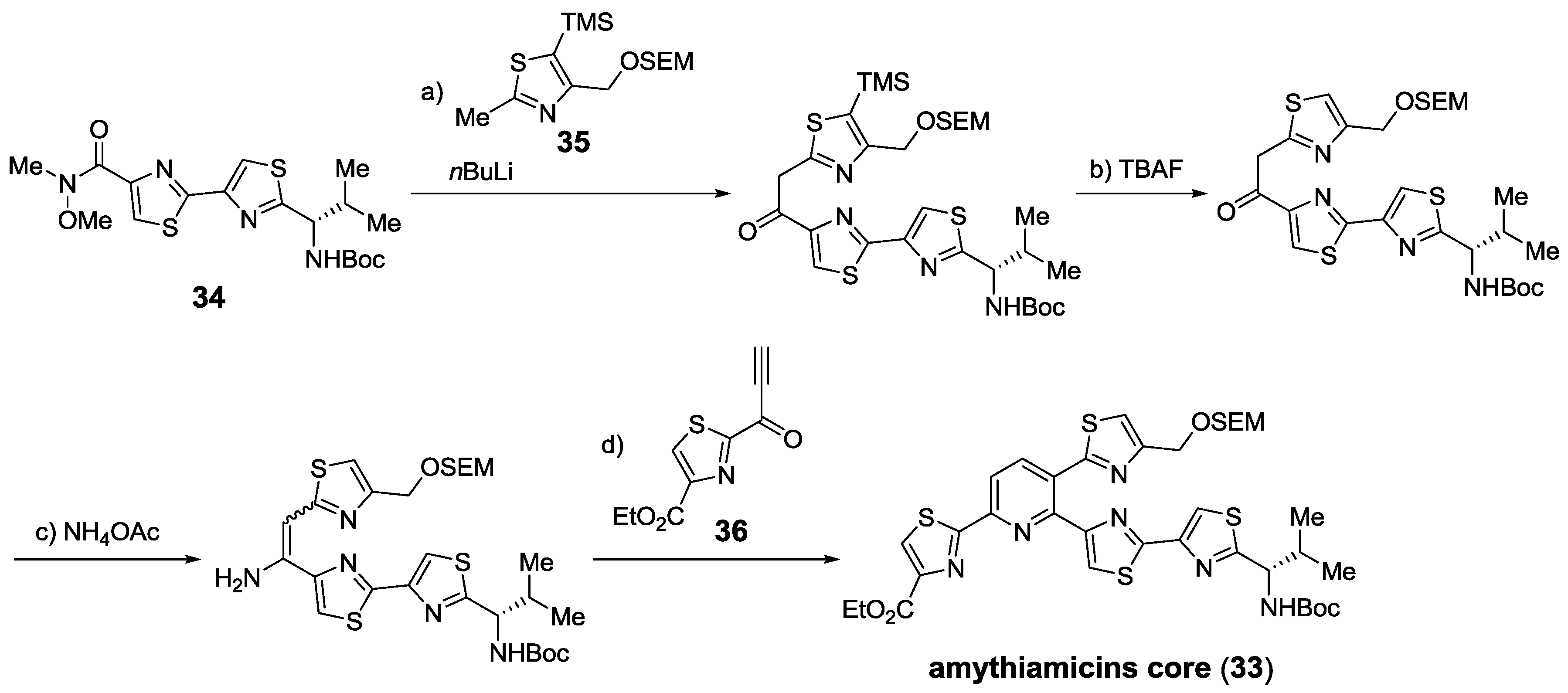

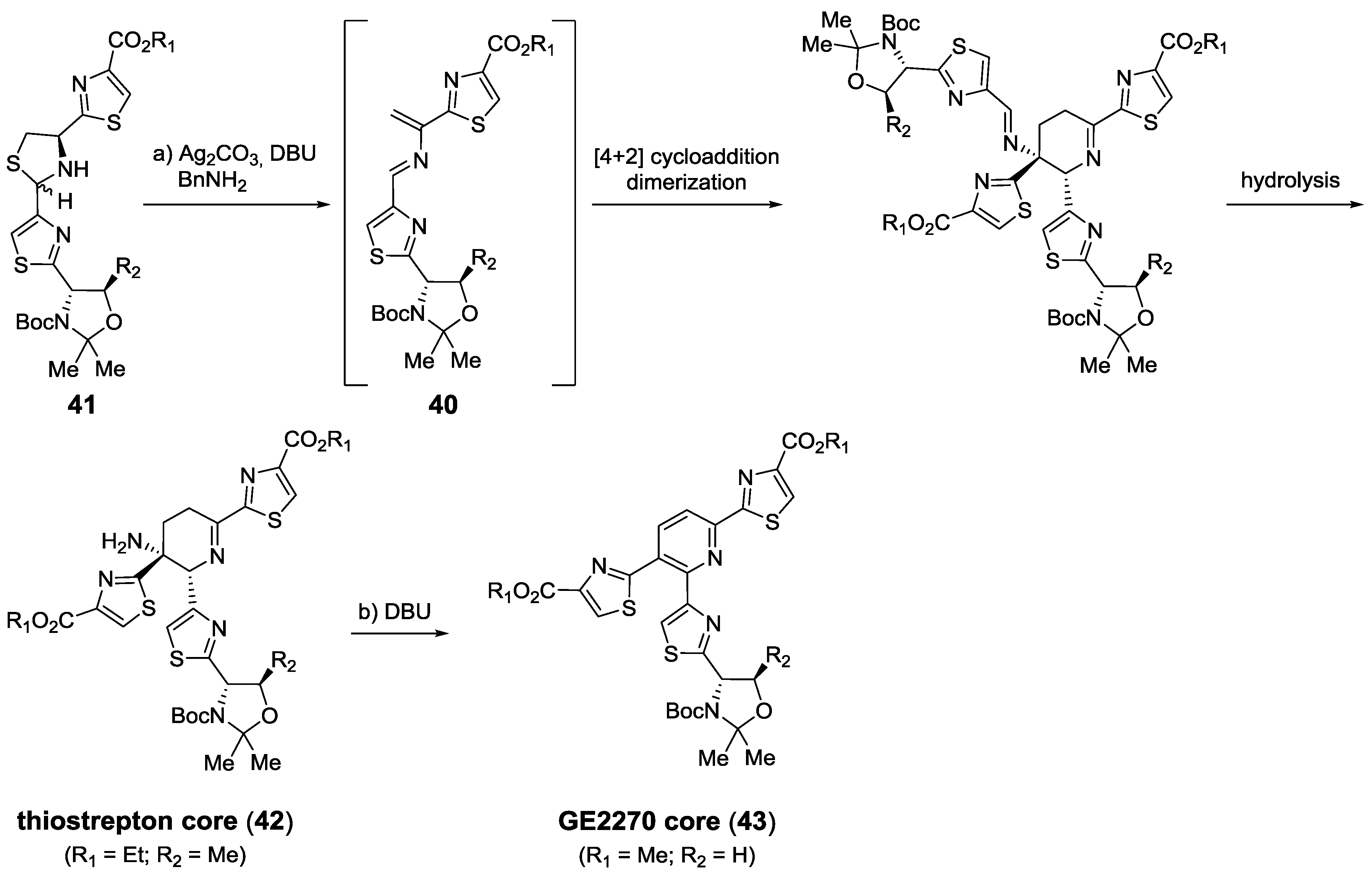
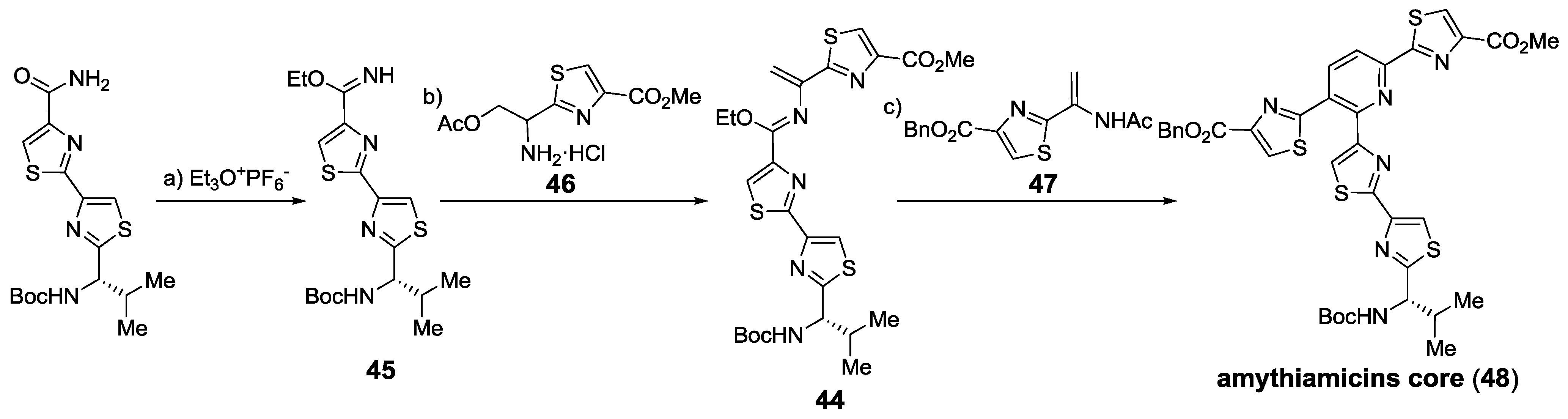
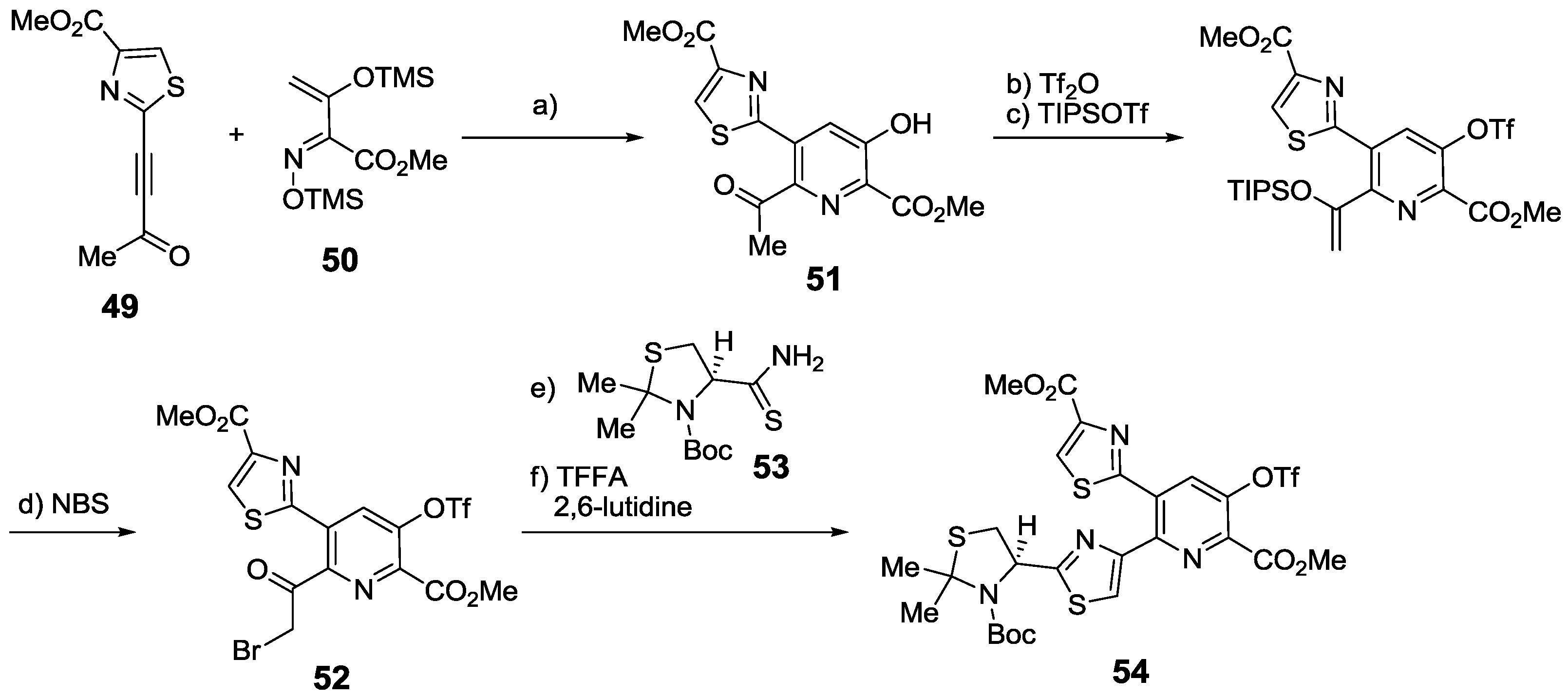
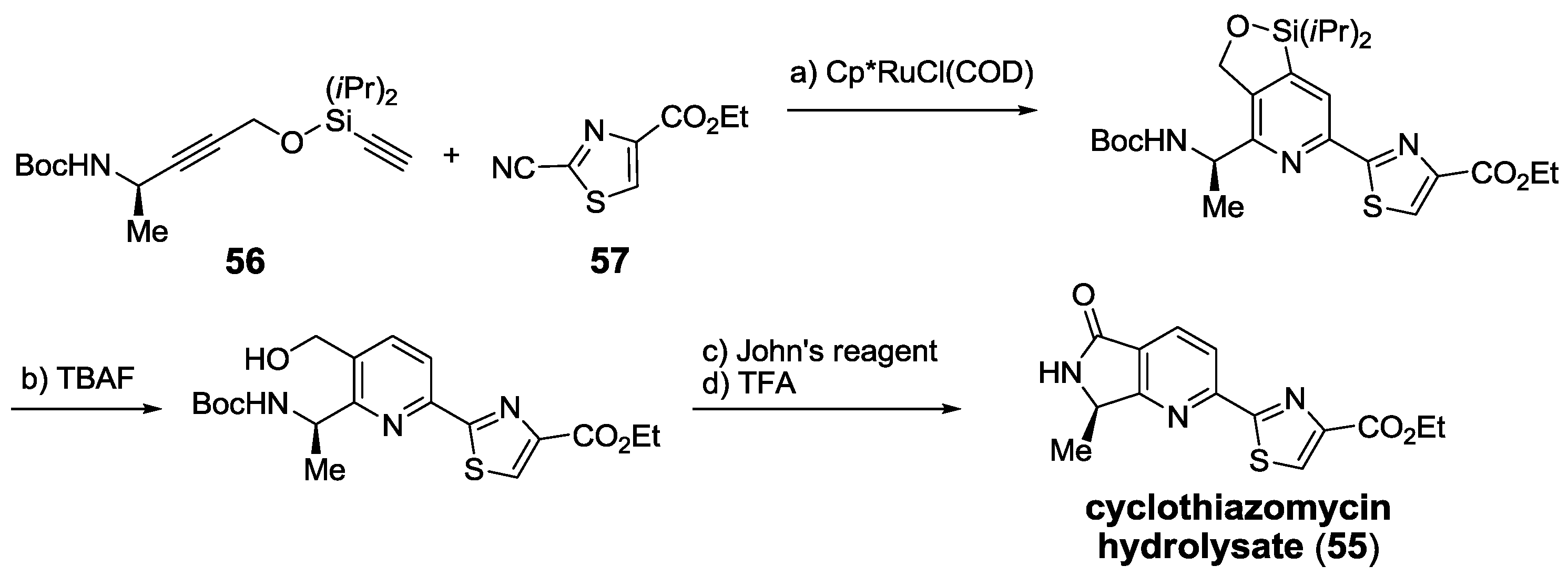
2.6. In the Market
3. Summary
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fischbach, M.A.; Walsh, C.T. Antibiotics for emerging pathogens. Science 2009, 325, 1089–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demain, A.L.; Sanchez, S. Microbial drug discovery: 80 years of progress. J. Antibiot. 2009, 62, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N. Lantibiotics a novel antimicrobial agents: A review. Pharma Sci. Monit. 2012, 3, 2990–3009. [Google Scholar]
- Bagley, M.C.; Dale, J.W.; Merritt, E.A.; Xiong, X. Thiopeptide antibiotics. Chem. Rev. 2005, 105, 685–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMarche, M.J.; Leeds, J.A.; Amaral, A.; Brewer, J.T.; Bushell, S.M.; Deng, G.; Dewhurst, J.M.; Ding, J.; Dzink-fox, J.; Gamber, G.; et al. Discovery of LFF571: An investigational agent for Clostridium difficile infection. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 6, 2376–2387. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.L. Micrococcin, an antibacterial substance formed by a strain of Micrococcus. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 473–481. [Google Scholar]
- Carnio, M.C.; Stachelhaus, T.; Francis, K.P.; Scherer, S. Pyridinyl polythiazole class peptide antibiotic micrococcin P1, secreted by foodborne Staphylococcus equorum WS2733, is biosynthesized nonribosomally. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 6390–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, J.F.; Weinstein, M.J.; Stout, H.A.; Donovick, R. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. I. In vitro studies. Antibiot. Ann. 1955–1956, 3, 554–559. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte, J.; Dutcher, J.D. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. II. Isolation and chemical characterization. Antibiot. Ann. 1955–1956, 3, 560–561. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Jambor, W.P.; Suydam, L.O.; Soriano, A. Thiostrepton, a new antibiotic. III. In vivo studies. Antibiot. Ann. 1955–1956, 3, 562–565. [Google Scholar]
- Cron, M.J.; Whitehead, D.F.; Hooper, I.R.; Heinemann, B.; Lein, J. Bryamycin, a new antibiotic. Antibiot. Chemother. 1956, 6, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Nagai, K.; Kamigiri, K.; Arao, N.; Suzumura, K.-I.; Kawano, Y.; Yamaoka, M.; Zhang, H.; Watanabe, M.; Suzuki, K. YM-266183 and YM-266184, novel thiopeptide antibiotics produced by Bacillus cereus isolated from a marine sponge. I. Taxonomy, fermentation, isolation, physico-chemical properties and biological properties. J. Antibiot. 2003, 56, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasuriya, H.; Herath, K.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Zhang, C.; Zink, D.L.; Brower, M.; Gailliot, F.P.; Greene, J.; Birdsall, G.; Venugopal, J.; et al. Isolation and structure elucidation of thiazomycin, a potent thiazolyl peptide antibiotic from Amycolatopsis fastidiosa. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Occi, J.; Jayasuriya, H.; Herath, K.; Motyl, M.; Dorso, K.; Gill, C.; Hickey, E.; Overbye, K.M.; Barrett, J.F. Antibacterial evaluations of thiazomycin—a potent thiazolyl peptide antibiotic from Amycolatopsis fastidiosa. J. Antibiot. 2007, 60, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zink, D.L.; Ushio, M.; Burgess, B.; Onishi, R.; Masurekar, P.; Barrett, J.F.; Singh, S.B. Isolation, structure, and antibacterial activity of thiazomycin A, a potent thiazolyl peptide antibiotic from Amycolatopsis fastidiosa. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 8818–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Herath, K.; Jayasuriya, H.; Ondeyka, J.G.; Zink, D.L.; Occi, J.; Birdsall, G.; Venugopal, J.; Ushio, M.; Burgess, B.; et al. Thiazomycins, thiazolyl peptide antibiotics from Amycolatopsis fastidiosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 841–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Occi, J.; Masurekar, P.; Barrett, J.F.; Zink, D.L.; Smith, S.; Onishi, R.; Ha, S.; Salazar, O.; Genilloud, O.; et al. Isolation, structure, and antibacterial activity of philipimycin, a thiazolyl peptide discovered from Actinoplanes philippinensis MA7347. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12102–12110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, R.P.; Leeds, J.A.; Naegeli, H.U.; Oberer, L.; Memmert, K.; Weber, E.; LaMarche, M.J.; Parker, C.N.; Burrer, N.; Esterow, S.; et al. Ribosomally synthesized thiopeptide antibiotics targeting elongation factor Tu. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5946–5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.; Degnes, K.F.; Kemmler, M.; Bredholt, H.; Fjaervik, E.; Klinkenberg, G.; Sletta, H.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Zotchev, S.B. Production of a new thiopeptide antibiotic, TP-1161, by a marine Nocardiopsis species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 4969–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, K.; Degnes, K.F.; Zotchev, S.B. Isolation and characterization of the gene cluster for biosynthesis of the thiopeptide antibiotic TP-1161. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7093–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañedo Hernández, L.M.; Romero Millan, F.; Fernández Medarde, A.; Fernández Chimeno, R.I.; Hidalgo Villar, J.C. Peptides as bioactive compounds. Patent WO 2012062906A1, 18 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Palomo, S.; González, I.; de la Cruz, M.; Martín, J.; Tormo, J.R.; Anderson, M.; Hill, R.T.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; Genilloud, O. Sponge-derived Kocuria and Micrococcus spp. as sources of the new thiazolyl peptide antibiotic kocurin. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1071–7086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodanzky, M.; Fried, J.; Sheehan, J.T.; Williams, N.J.; Alicino, J.; Cohen, A.I.; Keeler, B.T.; Birkhimer, C.A. Thiostrepton. degradation products and structural features. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, B.; Hodgkin, D.C.; Viswamitra, M.A. Structure of thiostrepton. Nature 1970, 225, 133–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, G.E.; Sheppard, N.; Walker, J. Chemistry of micrococcin P. X. Proton magnetic resonance spectrum of dimethyl micrococcinate, and the probable mode of biosynthesis of micrococcinic acid. J. Chem. Soc. C 1966, 16, 1371–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Ciufolini, M.A.; Lefranc, D. Micrococcin P: Structure, biology and synthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.; Fuller, A.T.; Walker, J. Chemistry of micrococcin P. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. 1957, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijović, M.P.V.; Walker, J. Chemistry of micrococcin P. Part II. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.; Clark, R.J.; Fuller, A.T.; Mijović, M.P.V.; Walker, J. Chemistry of micrococcin P. Part III. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.; Olesker, A.; Valente, L.; Rabanal, R.; Lukacs, G. Total structure of the polythiazole-containing antibiotic micrococcin P. A carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1977, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, B.W.; Gowland, M.S. The structures of the highly modified peptide antibiotics micrococcin P1 and P2. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1978, 256–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenet, B.; Pierre, F.; Cundliffe, M.; Ciufolini, M.A. The constitution of micrococcin P1: The Bycroft—Gowland hypothesis confirmed. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 2367–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.M.; Mijović, M.P.V.; Walker, J. Chemistry of micrococcin P. Part VI. Racemisation of 2-(l-amino-2-methylpropyl)thiazole-4-carboxylic acid, and related studies. J. Chem. Soc. 1961, 3394–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Okumura, K.; Shigekuni, M.; Nakamura, Y. Total synthesis of antibiotic, micrococcin P, from 2,3,6-polyazolesubstituted pyridine skeleton [fragmentA–C]. Chem. Lett. 1998, 27, 139–140. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, K.; Ito, A.; Yoshioka, D.; Shin, C. Total synthesis of macrocyclic antibiotic, Micrococcin P1. Heterocycles 1998, 48, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufolini, M.A.; Shen, Y.C. Synthesis of the Bycroft-Gowland structure of micrococcin P1. Org. Lett. 1999, 1, 1843–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefranc, D.; Ciufolini, M.A. Total synthesis and stereochemical assignment of micrococcin P1. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4198–4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tori, K.; Tokura, K.; Yoshimura, Y.; Terui, Y.; Okabe, K.; Otsuka, H.; Matsushita, K.; Inagaki, F.; Miyazama, T. Structures of siomycin-B and -C and thiostrepton-B determined by NMR spectroscopy and carbon-13 signal assignments of siomycins, thiostreptons and thiopeptin-Ba. J. Antibiot. 1981, 36, 124–129. [Google Scholar]
- Puar, M.S.; Ganguly, A.K.; Afonso, A.; Brambilla, R.; Mangiaracina, P.; Sarre, O.; MacFarlane, R.D. Sch 18640. A new thiostrepton-type antibiotic. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1981, 36, 5231–5233. [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu, I.; Motoki, Y.; Aoyama, M. Amino acids and derivatives of thiazole-4-carboxylic acid as constituents of thiopeptin B. J. Antibiot. 1977, 30, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puar, M.S.; Chan, T.M.; Hedge, V.; Patel, M.; Bartner, P.; Ng, K.J.; Pramanik, B.N. Sch 40832: A novel thiostrepton from Micromonospora carbonacea. J. Antibiot. 1998, 51, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-S.; Hidaka, T.; Furihata, K.; Seto, H. Microbial metabolites with tipA promoter inducing activity. III. thioxamycin and its novel derivative, thioactin, two thiopeptides produced by Streptomyces sp. DP94. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 1541–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favret, M.E.; Paschal, J.W.; Elzey, T.K.; Boeck, L.D. Biosynthesis of thiopeptide antibiotic A10255, incorporation of isotopically-labeled precursors. J. Antibiot. 1992, 45, 1499–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fate, G.D.; Benner, C.P.; Grode, S.H.; Gilbertson, T.J. The biosynthesis of sulfomycin elucidated by isotopic labeling studies. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 11363–11368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-S.; Seto, H. Promoinducin, a novel thiopeptide produced by Streptomyces sp. SF2741. Biosci. Biotechol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-S.; Hidaka, T.; Furihata, K.; Seto, H. Thiotipin, a novel thiopeptide with a tipA promoter inducing activity produced by Streptomyces sp. DT31. Tetrahedron 1994, 50, 11659–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, K.L.; Mueller, L.; Huang, S.; Abid, S.; Lam, K.S.; Li, W.; Leet, J.E. Conformation and absolute configuration of nocathiacin I determined by NMR spectroscopy and chiral capillary electrophoresis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 7284–7285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavecchia, P.; Gentili, P.; Kurz, M.; Sottani, C.; Bonfichi, R.; Selva, E.; Lociuro, S.; Restelli, E.; Ciabatti, R. Degradation studies of antibiotic MDL 62,879 (GE2270A) and revision of the structure. Tetrahedron 1995, 51, 4867–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Moody, C.J. From amino acids to heteroaromatics—thiopeptide antibiotics, nature’s heterocyclic peptides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 7930–7954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieland Brown, L.C.; Acker, M.G.; Clardy, J.; Walsh, C.T.; Fischbach, M.A. Thirteen posttranslational modifications convert a 14-residue peptide into the antibiotic thiocillin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2549–2553. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, R.; Duan, L.; Lei, C.; Pan, H.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Shen, B.; Yu, Y.; Liu, W. Thiopeptide biosynthesis featuring ribosomally synthesized precursor peptides and conserved posttranslational modifications. Chem. Biol. 2009, 16, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, W.L.; Pan, L.; Li, C. Thiostrepton biosynthesis: Prototype for a new family of bacteriocins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4327–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, H.-D.; Schoof, S.; Lu, J.-Y. Thiopeptide antibiotic biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6770–6773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kelly, W.L. Recent advances in thiopeptide antibiotic biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, C.T.; Acker, M.G.; Bowers, A.A. Thiazolyl peptide antibiotic biosynthesis: A cascade of post-translational modifications on ribosomal nascent proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 27525–27531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Tang, K.; Liu, W.; He, X.; Huang, X.; Deng, Z. Identification and analysis of the biosynthetic gene cluster encoding the thiopeptide antibiotic cyclothiazomycin in Streptomyces hygroscopicus 10–22. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2335–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T.S.; Walsh, C.T. Identification of the thiazolyl peptide GE37468 gene cluster from Streptomyces ATCC 55365 and heterologous expression in Streptomyces lividans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13053–13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Duan, L.; Zhang, Q.; Liao, R.; Ding, Y.; Pan, H.; Wendt-, E.; Tang, G.; Shen, B.; Liu, W. Nosiheptide biosynthesis featuring a unique indole side ring formation on the characteristic thiopeptide framework. ACS Chem Biol. 2009, 4, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Yu, Y.; Pan, H.; Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. Moving posttranslational modifications forward to biosynthesize the glycosylated thiopeptide nocathiacin I in Nocardia sp. ATCC202099. Mol. BioSyst. 2010, 6, 1180–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Q.; Duan, L.; Ding, Y.; Liao, R.; Lei, C.; Shen, B.; Liu, W. NosA catalyzing carboxyl-terminal amide formation in nosiheptide maturation via an enamine dealkylation on the serine-extended precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16324–16326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Liu, W. Thiostrepton maturation involving a deesterification-amidation way to process the C-terminally methylated peptide backbone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2852–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, A.A.; Walsh, C.T.; Acker, M.G. Genetic interception and structural characterization of thiopeptide cyclization precursors from Bacillus cereus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12182–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, D.; Yu, Y.; Duan, L.; Shen, B.; Liu, W. Radical-mediated enzymatic carbon chain fragmentation-recombination. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, N.; Chen, Y. A simple reverse genetics approach to elucidating the biosynthetic pathway of nocathiacin. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, D.; Lin, J.; Liao, R.; Tong, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W. Characterization of NocL involved in thiopeptide nocathiacin I biosynthesis: a [4Fe-4S] cluster and the catalysis of a radical S-adenosylmethionine enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 21287–21294. [Google Scholar]
- Pierre, S.; Guillot, A.; Benjdia, A.; Sandström, C.; Langella, P.; Berteau, O. Thiostrepton tryptophan methyltransferase expands the chemistry of radical SAM enzymes. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 957–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Wang, S.; Liao, R.; Liu, W. Insights into quinaldic acid moiety formation in thiostrepton biosynthesis facilitating fluorinated thiopeptide generation. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolmson, S.J.; Young, T.S.; Ruby, J.G.; Skewes-Cox, P.; Walsh, C.T. The posttranslational modification cascade to the thiopeptide berninamycin generates linear forms and altered macrocyclic scaffolds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 8483–8488. [Google Scholar]
- Houck, D.R.; Chen, L.; Keller, P.J.; Beale, J.M.; Floss, H.G. Biosynthesis of the modified peptide antibiotic nosiheptide in Streptomyces actuosus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 5800–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocek, U.; Zeng, Z.; O’Hagan, D.; Zhou, P.; Fan, L.D.G.; Beale, J.M.; Floss, H.G. Biosynthesis of the modified peptide antibiotic thiostrepton in Streptomyces azureus and Streptomyces laurentii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7992–8001. [Google Scholar]
- Mocek, U.; Knaggs, A.R.; Tsuchiya, R.; Nguyen, T.; Beale, J.M.; Floss, H.G. Biosynthesis of the modified peptide antibiotic nosiheptide in Streptomyces actuosus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7557–7558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, N.D.; Smith, T.M.; Shipley, P.R.; Floss, H.G. Studies on the biosynthesis of thiostrepton: Intermediate on the pathway to the quinaldic acid moiety. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996, 4, 1135–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, T.; Zhou, P.; Floss, H.G. Formation of 2-methyltryptophan in the biosynthesis of thiostrepton: Isolation of S-adenosylmethionine: Tryptophan 2-methyltransferase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1990, 278, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, T.M.; Priestley, N.D.; Knaggs, A.R.; Nguyen, T.; Floss, H.G. 3,4-Dimethylindole-2-carboxylate and 4-(1-hydroxyethyl)quinoline-2-carboxylate activating enzymes from the nosiheptide and thiostrepton producers, Streptomyces actuosus and Streptomyces laurentii. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 1612–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.I.; van der Donk, W.A.; Liu, W. Radical-mediated enzymatic methylation: A tale of two SAMS. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Zak, M.; Rahimipour, S.; Estrada, A.A.; Lee, S.H.; O’Brate, A.; Giannakakou, P.; Ghadiri, M.R. Discovery of a biologically active thiostrepton fragment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15042–15044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, S.K.; Bhat, U.G.; Hughes, D.E.; Wang, I.-C.; Costa, R.H.; Gartel, A.L. Identification of a chemical inhibitor of the oncogenic transcription factor forkhead box M1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9731–9735. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, J.M.-M.; Myatt, S.S.; Marson, C.M.; Coombes, R.C.; Constantinidou, D.; Lam, E.W.-F. Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2022–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowling, B.D.; Doudican, N.; Manga, P.; Orlow, S.J. Inhibition of mitochondrial protein translation sensitizes melanoma cells to arsenic trioxide cytotoxicity via a reactive oxygen species dependent mechanism. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2008, 63, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, U.G.; Zipfel, P.A.; Tyler, D.S.; Gartel, A.L. Novel anticancer compounds induce apoptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 1851–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, U.G.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, N.S.; Sanders, D.A.; Rodriguez, R.; Balasubramanian, S. The transcription factor FOXM1 is a cellular target of the natural product thiostrepton. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 725–731. [Google Scholar]
- Clough, B.; Strath, M.; Preiser, P.; Denny, P.; Wilson, I.R.J.M. Thiostrepton binds to malarial plastid rRNA. FEBS Lett. 1997, 406, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clough, B.; Rangachari, K.; Strath, M.; Preiser, P.R.; Iain Wilson, R.J.M. Antibiotic inhibitors of organellar protein synthesis in Plasmodium falciparum. Protist 1999, 150, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.; Li, J.; Kumar, S.; Rogers, M.J.; McCutchan, T.F. Effects of interruption of apicoplast function on malaria infection, development, and transmission. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2000, 109, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlitzer, M. Malaria chemotherapeutics part I: History of antimalarial drug development, currently used therapeutics, and drugs in clinical development. ChemMedChem 2007, 2, 944–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, C.D.; Su, V.; McFadden, G.I. The effects of anti-bacterials on the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 152, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoof, S.; Pradel, G.; Aminake, M.N.; Ellinger, B.; Baumann, S.; Potowski, M.; Najajreh, Y.; Kirschner, M.; Arndt, H.-D. Antiplasmodial thiostrepton derivatives: Proteasome inhibitors with a dual mode of action. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 3317–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoi, U.; Furukawa, S.; Abe, F.; Ushioda, M.; Fujine, K.; Johki, S.; Hatori, H.; Ueda, J. Suppressive effect of antibiotic siomycin on antibody production. J. Antibiot. 2004, 57, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, M.; Ohtsuka, T.; Yamada, M.; Ohba, Y.; Yoshizaki, H.; Yasuno, H.; Sano, T.; Watanabe, J.; Yokose, K.; Roche, N. Cyclothiazomycin, a novel polythiazole-containing peptide with renin inhibitory activity: taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and physico-chemical characterization. J. Antibiot. 1991, 44, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Murakami, T.; Funahashi, K.; Tokunaga, T.; Nihei, K.; Okuno, T.; Kimura, T.; Naoki, H.; Himeno, H. An RNA polymerase inhibitor, cyclothiazomycin B1, and its isomer. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8259–8270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuhara, N.; Kuroda, M.; Ogita, A.; Tanaka, T.; Usuki, Y.; Fujita, K.-I. Antifungal thiopeptide cyclothiazomycin B1 exhibits growth inhibition accompanying morphological changes via binding to fungal cell wall chitin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 5300–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Schoof, S.; Harkal, S.D.; Arndt, H.-D. Mapping the binding site of thiopeptide antibiotics by proximity-induced covalent capture. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 5664–5666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, J.M.; Wilson, D.N.; Schluenzen, F.; Connell, S.R.; Stachelhaus, T.; Zaborowska, Z.; Spahn, C.M.T.; Fucini, P. Translational regulation via L11: Molecular switches on the ribosome turned on and off by thiostrepton and micrococcin. Mol. Cell 2008, 30, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.D.; Hunter, M.; Cobb, M.; Traeger, G.; Spiegel, P.C. Thiostrepton inhibits stable 70S ribosome binding and ribosome-dependent GTPase activation of elongation factor G and elongation factor 4. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selva, E.; Montanini, N.; Stella, S.; Sofiientini, A.; Gastaldo, L.; Denaro, M. Targeted screening of elonfation Factor Tu binding antibiotics. J. Antibiot. 1997, 50, 22–26. [Google Scholar]
- Heffron, S.E.; Jurnak, F. Structure of an EF-Tu complex with a thiazolyl peptide antibiotic determined at 2.35 A resolution: Atomic basis for GE2270A inhibition of EF-Tu. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmeggiani, A.; Nissen, P. Elongation factor Tu-targeted antibiotics: four different structures, two mechanisms of action. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 4576–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Holt, T.G.; Thompson, C.J. Thiostrepton-induced gene expression in Streptomyces lividans. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, B.-S.; Hidaka, T.; Furihata, K.; Seto, H. Microbial metabolites with tipA promoter inducing activity. II. Geninthiocin, a novel thiopeptide produced by Streptomyces sp. DD84. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-S.; Hidaka, T.; Furihata, K.; Seto, H. Promothiocins A and B, novel thiopeptides with tipA promoter inducing activity produced by Streptomyces sp. SF2741. J. Antibiot. 1994, 47, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentzen, G.; Klinck, R.; Matassova, N.; Aboul-ela, F.; Murchie, A.I.H. Structural basis for contrasting activities of ribosome binding thiazole antibiotics. Chem. Biol. 2003, 10, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.L.; Folcher, M.; Katoh, T.; Puglia, A.M.; Vohradsky, J.; Yun, B.S.; Seto, H.; Thompson, C.J. Broad spectrum thiopeptide recognition specificity of the Streptomyces lividans TipAL protein and its role in regulating gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 20578–20586. [Google Scholar]
- Young, T.S.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Walsh, C.T. Codon randomization for rapid exploration of chemical space in thiopeptide antibiotic variants. Chem. Biol. 2012, 19, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Hughes, R.A.; Alcaraz, L.; Thompson, S.P.; Moody, C.J. Solution structures of thiopeptide antibiotics. Chem. Commun. 2006, 4215–4217. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J. Cancer therapeutic agent comprising thiopeptide with multiple thiazole rings. Patent WO02066046, 29 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, R.A.; Wurst, J.M.; Tan, D.S. Expanding the range of “druggable” targets with natural product-based libraries: An academic perspective. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, A.N. A complex task? Direct modulation of transcription factors with small molecules. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2010, 14, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubey, S.; Kumar, A.; Singh, D.; Habib, S. The apicoplast of Plasmodium falciparum is translationally active. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, P.; Yusuf, S. New evidence on the importance of the renin-angiotensin system in the treatment of higher-risk patients with hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, S.S. Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system: Implications for diabetes control and prevention. J. Invest. Med. 2013, 61, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki, M.; Katayama, Y. Involvement of RAS in clinical pathophysiology. Alzheime’s disease. Angiotensin Res. 2013, 10, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, R.; Truumees, I.; Barrett, T.; Patel, M.; Schwartz, J.; Puar, M.; Das, P.; Pramanik, B. Saramycetin, a thiazolyl peptide from a Streptomyces sp., chemical characterization and molecular weight determination. J. Antibiot. 1990, 43, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, A.A.; Acker, M.G.; Koglin, A.; Walsh, C.T. Manipulation of thiocillin variants by prepeptide gene replacement: Structure, conformation, and activity of heterocycle substitution mutants. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7519–7527. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, B.-S.; Fujita, K.-I.; Furihata, K.; Seto, H. Absolute stereochemistry and solution conformation of promothiocins. Tetrahedron 2001, 57, 9683–9687. [Google Scholar]
- LaMarche, M.J.; Leeds, J.A.; Amaral, K.; Brewer, J.T.; Bushell, S.M.; Dewhurst, J.M.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Gangl, E.; Goldovitz, J.; Jain, A.; et al. Antibacterial optimization of 4-aminothiazolyl analogues of the natural product GE2270 A: Identification of the cycloalkylcarboxylic acids. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 8099–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaMarche, M.J.; Leeds, J.A.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Gangl, E.; Krastel, P.; Neckermann, G.; Palestrant, D.; Patane, M.A.; Rann, E.M.; Tiamfook, S.; et al. Antibiotic optimization and chemical structure stabilization of thiomuracin A. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6934–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, J.; Drysdale, M.; Hebdon, R.; Jordan, A.; Lentzen, G.; Matassova, N.; Murchie, A.; Powles, J.; Roughley, S. Structure-based design of agents targeting the bacterial ribosome. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2455–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonker, H.R.A.; Baumann, S.; Wolf, A.; Schoof, S.; Hiller, F.; Schulte, K.W.; Kirschner, K.N.; Schwalbe, H.; Arndt, H.-D. NMR structures of thiostrepton derivatives for characterization of the ribosomal binding site. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3308–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, S.; Schoof, S.; Bolten, M.; Haering, C.; Takagi, M.; Shin-ya, K.; Arndt, H.-D. Molecular determinants of microbial resistance to thiopeptide antibiotics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 6973–6981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Echevarren, A.; Chandrakumar, N.S.; Köksal, Y. Synthesis of berninamycinic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1984, 25, 2127–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Jagoe, C.T.; Gu, Z. Synthesis of micrococcinic acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 1991, 32, 4263–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, T.R.; Lang, F. Total synthesis of dimethyl sulfomycinamate. Tetrahedron Lett. 1995, 36, 5319–5322. [Google Scholar]
- Kelly, T.R.; Lang, F. Total synthesis of dimethyl sulfomycinamate. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 4623–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Bashford, K.E.; Hesketh, C.L.; Moody, C.J. Total synthesis of the thiopeptide promothiocin A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3301–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Thompson, S.P.; Alcaraz, L.; Moody, C.J. Total synthesis of the thiopeptide antibiotic amythiamicin D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 15644–15651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Safina, B.S.; Zak, M.; Estrada, A.A.; Lee, S.H. Total synthesis of thiostrepton, part 1: Construction of the dehydropiperidine/thiazoline-containing macrocycle. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5087–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Zak, M.; Safina, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Estrada, A.A. Total synthesis of thiostrepton, part 2: Construction of the quinaldic acid macrocycle and final stages of the synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 5092–5097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.M.; Delgado, O.; Bach, T. Total synthesis of the thiazolyl peptide GE2270 A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4771–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, O.; Müller, H.M.; Bach, T. Concise total synthesis of the thiazolyl peptide antibiotic GE2270 A. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 2322–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciufolini, M.A.; Shen, Y.C. Studies toward thiostrepton antibiotics : assembly of the central pyridine-thiazole cluster of micrococcins. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 3263, 3804–3805. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, C.J.; Hughes, R.A.; Thompson, S.P.; Alcaraz, L. Biosynthesis inspired Diels-Alder route to pyridines: Synthesis of the 2,3-dithiazolylpyridine core of the thiopeptide antibiotics. Chem. Commun. 2002, 1760–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Dale, J.W.; Xiong, X.; Bower, J. Synthesis of dimethyl sulfomycinamate. Org. Lett. 2003, 5, 4421–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Chapaneri, K.; Dale, J.W.; Xiong, X.; Bower, J. One-pot multistep Bohlmann-Rahtz heteroannulation reactions: Synthesis of dimethyl sulfomycinamate. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1389–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckmann, G.; Bach, T. Synthesis of the heterocyclic core of the GE 2270 antibiotics and structure elucidation of a major degradation product. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Arndt, H.-D. Hetero Diels-Alder synthesis of 3-hydroxypyridines: Access to the nosiheptide core. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 4205–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Verrier, C.; Hoarau, C.; Marsais, F. Direct C-2 arylation of alkyl 4-thiazolecarboxylates: New insights in synthesis of heterocyclic core of thiopeptide antibiotics. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2909–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Laguerre, C.; Hoarau, C.; Marsais, F. Highly efficient borylation Suzuki coupling process for 4-bromo-2-ketothiazoles: Straightforward access to micrococcinate and saramycetate esters. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3690–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Takaishi, T.; Okuda, T.; Aoe, K.; Date, T. Methanolysis products of sulfomycin I. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 2791–2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Shigekuni, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Shin, C. Useful synthesis of 2,3,6-polythiazolesubstituted pyridine skeleton [Fragment A–C] of peptide antibiotic, micrococcin P. Chem. Lett. 1996, 25, 1025–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Umemura, K.; Shin, I.; Yoshimura, J.; Okumura, K.; Saito, H.; Shin, C. Synthesis of the central heterocyclic skeleton of an antibiotic, A10255. Chem. Lett. 1997, 26, 1203–1204. [Google Scholar]
- Umemura, K.; Noda, H.; Yoshimura, J.; Konn, A.; Yonezawa, Y.; Shin, C. The synthesis of fragment a of an antibiotic, nosiheptide. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 3539–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Saito, H.; Shin, C.; Umemura, K.; Yoshimura, J. Convenient synthesis of the central 3,6-di(2-thiazolyl)-2-(4-thiazolyl)pyridine skeleton of a macrocyclic antibiotic, GE2270 A. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1998, 71, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Okabe, A.; Ito, A.; Ito, A.; Yonezawa, Y. Novel synthesis of the main central 2,3,6-trisubstituted pyridine skeleton [Fragment A–B–C] of a macrobicyclic antibiotic, cyclothiazomycin. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2002, 75, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, C.; Saito, H.; Yonezawa, Y. Useful synthesis of the main central 2,3,6-trisubstituted pyridine skeleton of various thiostrepton-type macrocyclic antibiotics. Heterocycles 2003, 61, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endoh, N.; Yonezawa, Y.; Shin, C. Asymmetric synthesis of the main pyridine skeleton for a macrobicyclic antibiotic, cyclothiazomycin. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2003, 76, 643–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Yonezawa, Y.; Shin, C. Useful synthesis of fragment A–C–D of a thiostrepton-type macrocyclic antibiotic, thiocilline I. Chem. Lett. 2004, 33, 814–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammer, C.; Bach, T. Total syntheses of the thiopeptides amythiamicin C and D. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 14083–14093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just-Baringo, X.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. From 2,6-dichloronicotinic acid to thiopeptide cores. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2013, 6404–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirokawa, Y.; Fujiwara, I.; Suzuki, K.; Harada, H.; Yoshikawa, T. Synthesis and structure-affinity relationships of novel potent serotonin 5-HT 3 and dopamine D2 receptor antagonistic activity. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just-Baringo, X.; Bruno, P.; Ottesen, L.K.; Cañedo, L.M.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. Total synthesis and stereochemical assignment of baringolin. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7818–7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just-Baringo, X.; Bruno, P.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. Highly efficient, multigram and enantiopure synthesis of (S)-2-(2,4′-bithiazol-2-yl)pyrrolidine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 5435–5437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulakh, V.S.; Ciufolini, M.A. Total synthesis and complete structural assignment of thiocillin I. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5900–5904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.J.; Bagley, M.C. Studies on thiopeptide antibiotics: synthesis of an oxazole-thiazole-pyridine fragment related to promothiocin A. Synlett 1998, 1998, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Dale, J.W.; Hughes, D.D.; Ohnesorge, M.; Phillips, N.G.; Bower, J. Synthesis of pyridines and pyrido[2,3-d]pyrimidines by the Lewis acid catalyzed Bohlmann-Rahtz heteroannulation reaction. Synlett 2001, 2001, 1523–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Bagley, M.C.; Chapaneri, K. A new mild method for the one-pot synthesis of pyridines. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 6121–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Dale, J.W.; Jenkins, R.L.; Bower, J. First synthesis of an amythiamicin pyridine cluster. Chem. Commun. 2004, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Xiong, X. Stereoselective Synthesis of the β-lactam hydrolysate of the thiopeptide cyclothiazomycin. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3401–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, E.; Bagley, M. Convergent synthesis of the central heterocyclic domain of micrococcin P1. Synlett 2007, 2007, 954–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, C.J.; Bagley, M.C. The first synthesis of promothiocin A. Chem. Commun. 1998, 4, 2049–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, M.C.; Moody, C.J. Synthesis of bioactive cyclic peptides. In Proceedings of 216th ACS National Meeting, Boston, MA, USA, 23–27 August 1998.
- Higashibayashi, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakata, M. Synthetic studies on the thiostrepton family of peptide antibiotics: synthesis of the tetrasubstituted dehydropiperidine and piperidine cores. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashibayashi, S.; Kohno, M.; Goto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Mori, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakata, M. Synthetic studies on thiostrepton family of peptide antibiotics: synthesis of the pentapeptide segment containing dihydroxyisoleucine, thiazoline and dehydroamino acid. Tetrahedron Lett. 2004, 45, 3707–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Tohmiya, H.; Satouchi, Y.; Higashibayashi, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Nakata, M. Synthetic studies on thiostrepton family of peptide antibiotics: synthesis of the cyclic core portion containing the dehydropiperidine, dihydroquinoline, l-valine, and masked dehydroalanine segments. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005, 46, 6423–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Higashibayashi, S.; Goto, T.; Kohno, M.; Satouchi, Y.; Shinko, K.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Tohmiya, H.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Total synthesis of siomycin A. Tetrahedron Lett. 2007, 48, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Higashibayashi, S.; Goto, T.; Kohno, M.; Satouchi, Y.; Shinko, K.; Suzuki, K.; Suzuki, S.; Tohmiya, H.; Hashimoto, K.; et al. Total synthesis of siomycin A: Construction of synthetic segments. Chem. Asian J. 2008, 3, 984–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Nevalainen, M.; Safina, B.S.; Zak, M.; Bulat, S. A biomimetically inspired synthesis of the dehydropiperidine domain of thiostrepton. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1941–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C. How thiostrepton was made in the laboratory. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 12414–12436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Zou, B.; Dethe, D.H.; Li, D.B.; Chen, D.Y.-K. Total synthesis of antibiotics GE2270A and GE2270T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 7786–7792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaou, K.C.; Dethe, D.H.; Chen, D.Y.-K. Total syntheses of amythiamicins A, B and C. Chem. Commun. 2008, 2632–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.A.; Thompson, S.P.; Alcaraz, L.; Moody, C.J. Total synthesis of the thiopeptide amythiamicin D. Chem. Commun. 2004, 946–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Riedrich, M.; Mikyna, M.; Arndt, H.-D. Aza-Wittig-supported synthesis of the A ring of nosiheptide. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 8137–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Deiters, A. Synthesis of the pyridine core of cyclothiazomycin. Org. Lett. 2011, 13, 4352–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keppens, L.; De Groote, G. Effect of a new antibiotic “nosiheptide” in broiler feeds. Rev. l’Agric. 1979, 32, 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Trzasko, A.; Leeds, J.A.; Praestgaard, J.; LaMarche, M.J.; McKenney, D. Efficacy of LFF571 in a hamster model of Clostridium difficile infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4459–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeds, J.A.; Sachdeva, M.; Mullin, S.; Dzink-Fox, J.; LaMarche, M.J. Mechanism of action of and mechanism of reduced susceptibility to the novel anti-Clostridium difficile compound LFF571. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4463–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Just-Baringo, X.; Albericio, F.; Álvarez, M. Thiopeptide Antibiotics: Retrospective and Recent Advances. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 317-351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010317
Just-Baringo X, Albericio F, Álvarez M. Thiopeptide Antibiotics: Retrospective and Recent Advances. Marine Drugs. 2014; 12(1):317-351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010317
Chicago/Turabian StyleJust-Baringo, Xavier, Fernando Albericio, and Mercedes Álvarez. 2014. "Thiopeptide Antibiotics: Retrospective and Recent Advances" Marine Drugs 12, no. 1: 317-351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010317
APA StyleJust-Baringo, X., Albericio, F., & Álvarez, M. (2014). Thiopeptide Antibiotics: Retrospective and Recent Advances. Marine Drugs, 12(1), 317-351. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12010317