Abstract
An anti-fibrotic compound produced by Streptomycesn xiamenensis, found in mangrove sediments, was investigated for possible therapeutic effects against fibrosis. The compound, N-[[3,4-dihydro-3S-hydroxy-2S-methyl-2-(4′R-methyl-3′S-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine (1), was isolated from crude extracts and its structure, including the absolute configuration was determined by extensive spectroscopic data analyses, Mosher’s method, Marfey’s reagent and quantum mechanical calculations. In terms of biological effects, this compound inhibits the proliferation of human lung fibroblasts (WI26), blocks adhesion of human acute monocytic leukemia cells (THP-1) to a monolayer of WI26 cells, and reduces the contractile capacity of WI26 cells in three-dimensional free-floating collagen gels. Altogether, these data indicate that we have identified a bioactive alkaloid (1) with multiple inhibitory biological effects on lung excessive fibrotic characteristics, that are likely involved in fibrosis, suggesting that this molecule might indeed have therapeutic potential against fibrosis.
1. Introduction
Fibrotic diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis, cirrhosis, systemic sclerosis, interstitial nephritis and cardiovascular fibrosis are a threat to public health [1]. Constant high exposure to respirable particles is known to directly cause chronic inflammation-associated pulmonary diseases, including lung fibrosis and lung cancer [2]. These observations have resulted in increased research into mechanisms associated with fibrosis, the excessive fibrous connective tissue that underlies many chronic inflammatory pulmonary pathologies [1]. Indeed, studies have suggested that about 45% of deaths in developed countries are associated with fibrotic diseases of various organs [1].
Fibroblasts, one of the most abundant cells in the interstitial tissues, are known to play an important role in inflammation and fibrogenesis [1,3]. Interactions between fibroblasts and the local microenvironment can induce the formation of self-perpetuating circuits of inflammation [4]. These circuits can maintain the prolonged and elevated excellular matrix (ECM) secreting phenotype of fibroblasts, which is the defining characteristic of fibrotic diseases. Therefore, the search for leading compounds, particularly those obtained from a natural resource, that target fibroblasts represents an emerging pharmacological and therapeutic focus against fibrotic diseases.
Mangrove and its derived actinobacteria strains, are well-known for producing novel secondary metabolites and possessing highly effective bioactive compounds, possibly due to biochemical adaptation to the special intertidal ecosystem [5,6,7,8,9]. For example, in studies of anti-inflammatory compounds, 7-deacetylgedunin from Xylocarpus moluccensis was found to inhibit nitric oxide production in activated macrophages [10]. In another study, diterpenoids from Excoecaria agallocha L. were observed to suppress expression of NF-κB and AP-1 (activating protein-1) targeted genes including TNF-α and IL-6 in mouse macrophages [11]. Surfactin isomers from the mangrove bacterium Bacillus sp. were also tested on the previous two models [12]. Finally, a mixture of Acanthus ilicifolius leaf extract was also shown to exhibit inhibitory activity in rat paw edema [3]. The immense and untapped microbial biodiversity in the mangrove is a promising resource for marine-derived leading therapeutic compounds.
Streptomyces xiamenensis strain 318 was identified as a novel species of actinobacteria from mangrove sediments [13]. During our preliminary screening for anti-fibrotic compounds, a crude extract of S. xiamenensis was tested in an adhesion-bioassay of fibroblasts on monocytes, and showed inhibitory activity. Further studies were then carried out to identify and characterize the active ingredient in this extract. In our work, an alkaloid, N-[[3,4-dihydro-3S-hydroxy-2S-methyl-2-(4′R-methyl-3′S-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine (1), was isolated from crude extracts of S. xiamenensis (Figure 1.) and demonstrated to have considerable bioactivity. Compound 1 was previously isolated from Streptomyces sp. Mer-88, and shown to inhibit binding between LFA-1 and ICAM-1, and suggested to have important anti-inflammatory properties [14]. The absolute configurations of compound 1, including four stereogenic centers, were determined by extensive spectroscopic data analyses, Mosher’s method, Marfey’s reagent and quantum mechanical (QM) calculations. Compound 1 was found to exhibit inhibitory effects on cell proliferation of human lung fibroblasts (WI26), the contractile capacity of WI26 cells in a three-dimensional free-floating collagen gels, and the adhesion of human acute monocytic leukemia cells (THP-1) on a WI26 monolayer. As these properties are thought to contribute to the development of fibrosis, these data suggest that the compound described herein might indeed prove to be of considerable therapeutic benefit against fibrotic pathologies.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Isolation and Structural Elucidation of Compound 1
Crude extracts from S. xiamenensis were assayed for their inhibitory effect on the adhesion of THP-1 cells on a monolayer of WI26 cells. After incubating the crude extract (50 μg/mL) for 3 h, the adhesion of the THP-1 cells was about 15% lower than that with the solvent control (0.01% DMSO). Thus, the extract showed inhibitory adhesion activity and S. xiamenensis was considered as a promising bioactive resource for further chemical analyses. Guided by this bioactivity, a series of alkaloids were detected, using TLC and UPLC-MS, as the main secondary metabolites from the mixture extracted in a solution of ethyl acetate: methanol: formic acid = 80:15:5. The presence of pseudo-molecular ions [M + H]+ at m/z 392.2069 and [M − H]− at m/z 390.1886 in positive and negative ion modes, respectively, in the mass spectra, led to the purification of the main component, compound 1.
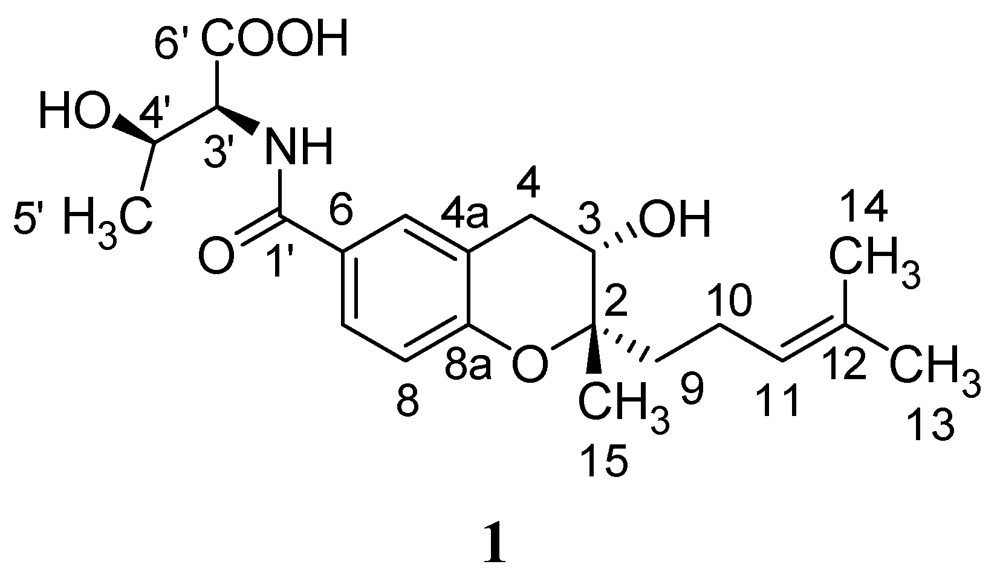
Figure 1.
Structure of compound 1 isolated from Streptomyces xiamenensis.
The molecular formula of 1 is C21H29NO6 based on HRESIMS, which is in accordance with the previous literature [14]. In the 1H NMR spectrum of 1, three aromatic protons with signals at δH 7.63 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 6.81 (1H, d, J = 8.4 Hz), 7.76 (1H, s), and 7.78, (1H, d, J = 7.8 Hz), as well as a high-field double-bond proton at δH 5.12 (1H, dd, J = 7.1, 1.3 Hz) were detected (Table 1). Carbon signals in the 13C NMR spectrum consisted of six aromatic carbons, plus two olefinic carbons, two carbonyl groups, two hydroxylated carbon signals at δC 79.8, 66.3, and a methylene at δC 31.2 (Table 1), which is in accordance with the structure of a benzopyran moeity, attached to two side chains, threonine and isoprenylmethyl group. The HMBC correlations (Table 1) further confirmed the planar structure of 1, named N-[[3,4-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-methyl-2-(4′-methyl-3′-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine [14].

Table 1.
1H and 13C NMR spectroscopic data of compound 1 and ΔδRS values of key H-atoms in (R)- and (S)-MPA diesters a.
| Position | 1 | R/S-MPA-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC, type | HMBC | δR | δS | ΔδRS | |
| 1 | -- | -- | ||||
| 2 | -- | 79.8, C | ||||
| 3 | 3.77, t b | 66.3, CH | 4a, 2, 9, 15 | |||
| 4 | 2.71, dd (17.3, 7.4) | 31.2, CH2 | 8a, 5, 4a, 2, 3 | 2.54 | 2.82 | −0.28 |
| 2.98, dd (17.3, 5.2) | 3.09 | 3.23 | −0.14 | |||
| 4a | -- | 120.6, C | ||||
| 5 | 7.67, s | 129.8, CH | 7, 8a, 4, 1′ | |||
| 6 | -- | 126.0, C | ||||
| 7 | 7.63, d (8.4) | 127.2, CH | 5, 8a, 1′ | |||
| 8 | 6.81, d (8.4) | 116.7, CH | 4a, 8a, 6 | |||
| 8a | -- | 156.1, C | ||||
| 9 | 1.60, m | 38.0, CH2 | 11, 12, 2,3 | 1.55 | 1.29 | +0.26 |
| 1.47 | 1.21 | +0.26 | ||||
| 10 | 2.10, m | 21.6, CH2 | 11, 12 | 2.05 | 1.95 | +0.10 |
| 11 | 5.12, dd (7.1, 1.3) | 124.8, CH | 13, 10, 14, 9 | 5.01 | 4.89 | +0.12 |
| 12 | -- | 131.3, C | ||||
| 13 | 1.57, s | 17.9, CH3 | 11 | 1.51 | 1.47 | +0.04 |
| 14 | 1.65, s | 25.9, CH3 | 11 | 1.60 | 1.58 | +0.02 |
| 15 | 1.18, s | 18.7, CH3 | 2, 3, 9 | 1.27 | 0.97 | +0.30 |
| 1′ | -- | 166.6, C | ||||
| 2′ | 7.78, d (7.8) | -- | 1′ | 8.29 | 8.40 | −0.11 |
| 3′ | 4.38, brd | 58.9, CH | 4′, 6′ | 4.81 | 4.84 | −0.03 |
| 4′ | 4.18, brs | 67.1, CH | ||||
| 5′ | 1.12, d (6.0) | 20.9, CH3 | 1.27 | 1.10 | +0.17 | |
| 6′ | -- | 172.8, C | ||||
a Measured in DMSO-d6, Chemical shifts (δ) in ppm; b Measured in [D4]-methanol, δH 3.88, dd (7.4, 5.2).
2.2. Absolute Configurations of Compound 1
The absolute configurations of 1, with four stereogenic centers, were identified by Mosher’s method, Marfey’s reagent, NOESY experiment, and QM calculations. Compound 1 was treated with (R)- and (S)-α-methoxy-α-phenylacetic acid (MPA) to form (R)- and (S)-MPA diesters. Diagnostic ΔδRS sigals of the (R)- and (S)-MPA diesters resulted in negative ΔδRS values for 4-H2 (Table 1), which were in contrast to the positive ΔδRS values for 9-H2, 10-H2, 11-H, 13-H3, 14-H3 and 15-H3, which are all related to the dihydropyran moiety. These data are in accordance with a 3S configuration of 1. The absolute configuration of the neighboring position 2 was then determined by elucidating the relative configuration related to 3S. The NOE correlation between 2-H3 and 4-Ha demonstrated that 2-H3 was in an axial orientation. The other NOE interaction between 2-H3 and 3-H demonstrated that 3-H was equatorially oriented and 3-OH was in a trans configuration to 2-H3 (Figure 2). The relative configuration of 2-H3, 3-H and 4-Ha/e were further confirmed from the values of the coupling constants, which were 4-Ha (2.71, dd, 17.3, 7.4) and 4-He (2.98, dd, 17.3, 5.2).
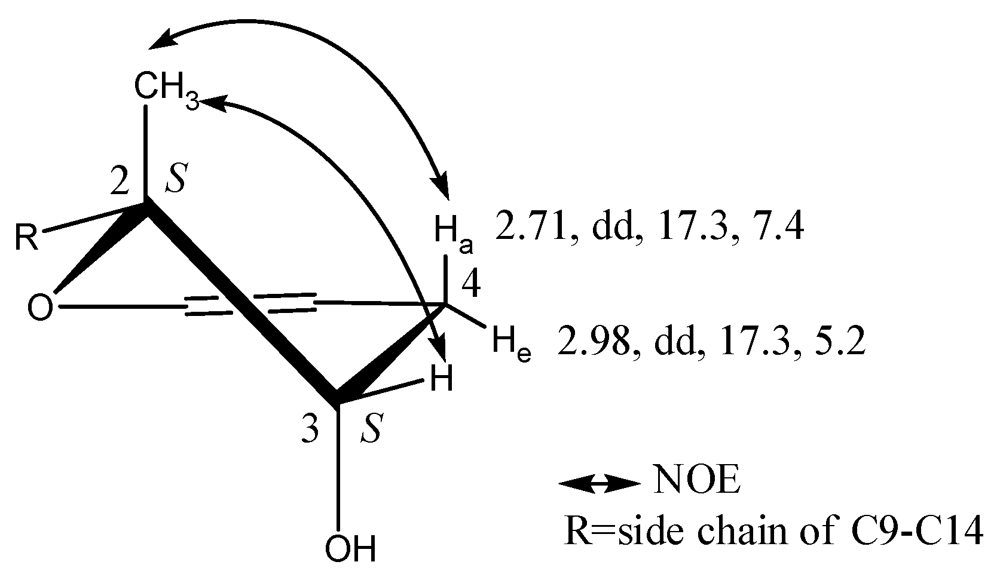
Figure 2.
Key NOE correlations of the dihydropyran moiety in compound 1.
QM calculations on a model molecule of 2,2-dimethyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-3-ol indicate that, compared to that at the equatorial position, the 3-OH group prefers the axial position by about 1.2 kcal/mol both in the gas phase and in DMSO solvent due to the gauche effect [15]. In the gauche conformation, the H-H distances of 2-H3 are as close as 2.55 Å to 3-H, and 2.30 Å to 4-Ha. The results are consistent with the key NOE correlations (Figure 2). Based on the absolute configuration of C-3 and the relative configuration of C-2, we therefore identified the absolute configuration of position 2 to be 2S.
As far as the other two stereocenters in the threonine moiety, diagnostic ΔδRS sigals of the (R)- and (S)-MPA diesters resulted in negative ΔδRS values for 3'-H and 2'-NH (Table 1), which were in contrast to the positive ΔδRS values for 5'-H. The configuration of the position 4' was thus assigned to be R. In order to determine the configuration at the position 3', 1 was hydrolyzed in hydrochloric acid and then derivatized with 1-fluoro-2,4-dinitrophenyl-5-L-alanine (FDAA, Marfey’s reagent) [16]. Based on the results of hydrolyzation of 1 and derivatization with Marfey’s reagent afterwards, the threonine moiety was assigned as the naturally occurring structure of L-threonine [(2S,3R)-2-amino-3-hydroxy butanoic acid]. The absolute configuration of 1 was therefore determined to be N-[[3,4-dihydro-3S-hydroxy-2S-methyl-2-(4′R-methyl-3′S-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine (1).
2.3. Inhibition of Proliferation on Human Diploid Lung Fibroblast (WI26) Cells by Compound 1.
Fibrosis is characterized by the overgrowth, hardening, and/or scarring of various tissues and is attributed to an excess deposition of ECM components including collagen [1]. To combat this, an ability to slow down rapid fibrotic response during typical wound repair and tissue regeneration processes would seem to be a reasonable intervention, with the goal to avoid an accumulation of non-functional fibrotic tissue and thereby enable transformation to more regenerative conditions [3]. We thus investigated the anti-proliferative activity of 1 to this end. Lung fibroblast WI26 cells were exposed to 1, at a concentration of 30 µg/mL, for 0, 2, 3, 4 and 6 days, and the optical density (OD) λ = 450 nm was monitored as a function of time. As illustrated in Figure 3, compound 1 significantly inhibited the proliferation of WI26 cells. The extent of this inhibition increased with time (Figure 3), from a decrease of 7% at day 2 to 27% at day 6, compared with solvent control. Compound 1 therefore indeed exhibits anti-proliferative effects on lung fibroblast cells.
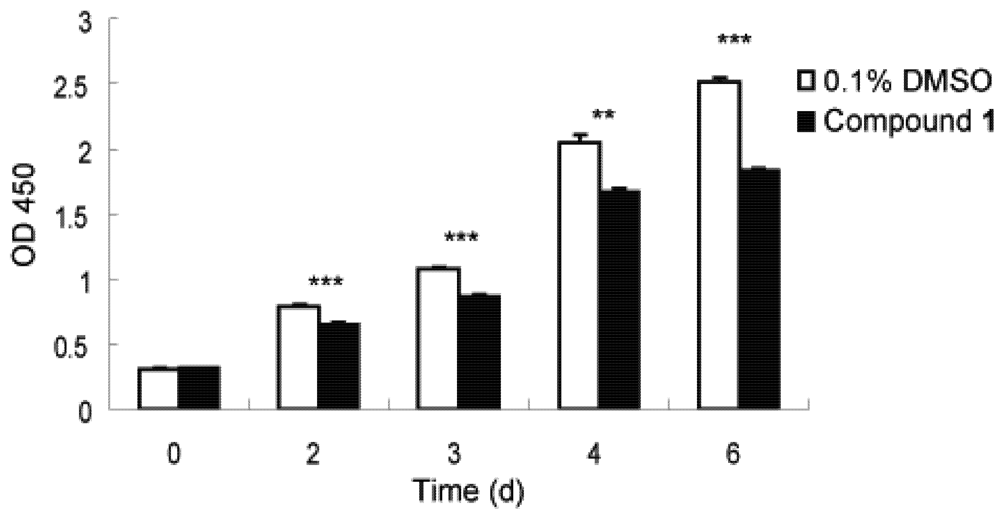
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effect of compound 1 on WI26 cells proliferation. The WI26 cells were exposed to 30 µg/mL of 1 at day 0, 2, 3, 4 and 6. Surviving fraction was determined by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. As illustrated, proliferation of WI26 cells was significantly inhibited by 1 in a time-dependent manner. Data are given as the mean of triplicate values ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences from the value of 0.1% DMSO solvent control were marked **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
2.4. Effect of Compound 1 on the Adhesion of THP-1 Cells to a Monolayer of WI26 Cells
Monocytes and macrophages have been shown to play pivotal roles in inflammation and fibrosis by modulating the secretion of cytokines as well as recruiting and activating fibroblasts and other inflammatory cells [17]. Direct contact between monocytes/macrophages and fibroblasts is important for the initiation, perpetuation, and resolution of fibrosis [18]. We therefore also evaluated the anti-adhesion bioactivity of 1. WI26 cells were first grown as a cell monolayer on a rigid tissue culture support, and then monocytic THP-1 cells were added to this monolayer. The number of adhered cells was then measured by optical microscopy after a 3 h incubation with either 1 (30 μg/mL) or 0.1% DMSO. As shown in Figure 4, there were obvious differences between the experiments with 1 present compared with those of the solvent control (Figure 4). Namely, the adhesion of THP-1 was about 41% lower in the presence of 1 than that in the solvent control. Thus, compound 1 exhibits significant anti-adhesion bioactivity for monocytes on fibroblasts.
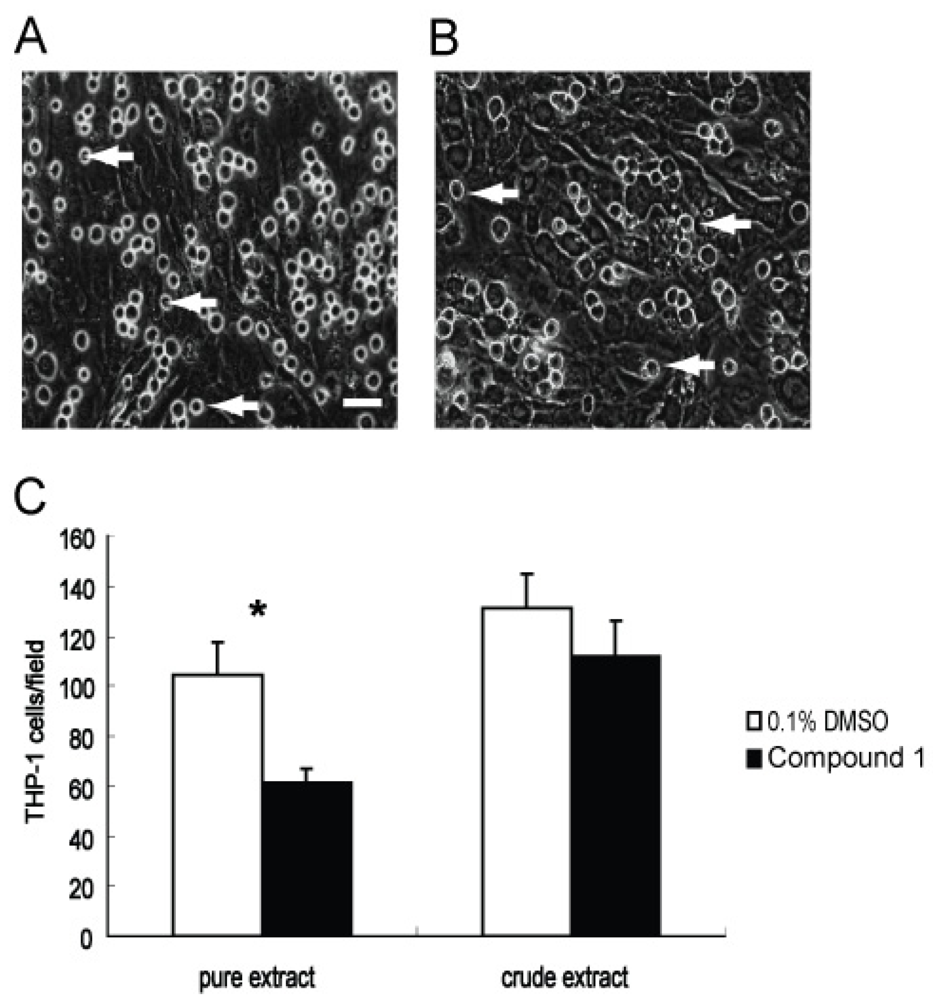
Figure 4.
Blocking adhesion of THP-1 cells onto a monolayer of WI26 cells by compound 1. Representative pictures of the adhering cells taken with 400 fold magnification. Equal numbers of THP-1 cells with 1 (30 μg/mL) or 0.1% DMSO were added to a monolayer of WI26 cells in triplicate wells of 24-well plates, respectively. Adhering THP-1 cells after 3-h-incubation were counted in four random visual fields of each well. (A) The attachment of THP-1 cells (marked by arrows) onto confluent WI26 cells, treated with 0.1% DMSO; (B) The attachment of THP-1 cells onto confluent WI26 cells, treated with 1 (30 μg/mL). It is clear from these images that adhesion of THP-1 cells was significantly blocked by 1. Bar = 25 μm. Each point represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant difference from the value of 0.1% DMSO solvent control was marked, *p < 0.05.
2.5. Effects of Compound 1 on Contraction of WI26 Cells in 3D Collagen Lattices
It is widely known that mechanical force plays a contributing role in inflammation and fibrotic processes [19,20]. Not surprisingly, the contractible force generated by fibroblasts is a focus of much research [21]. Activated fibroblasts express many stress fibers which can facilitate wound repair [3] and fibrogenesis [22], while at the same time mechanical stress can promote inflammation and fibrosis by activating fibroblasts and inflammation cells [19,23]. In order to evaluate the anti-contractility activity of 1, three-dimensional collagen lattices were used as a richer, perhaps more physiologically relevant physical environment, that can enable direct investigation of the interactive process of fibroblast-collagen matrix remodeling [24]. WI26 cells were seeded in free-floating collagen gel lattices, followed by the application of 1 or solvent control. As shown in Figure 5A, the presence of compound 1 significantly delayed contraction of the collagen gel. After 1, 2, 3 and 6 h, the contraction was markedly decreased compared to solvent control by 21%, 22%, 18% and 8%, respectively (Figure 5B).
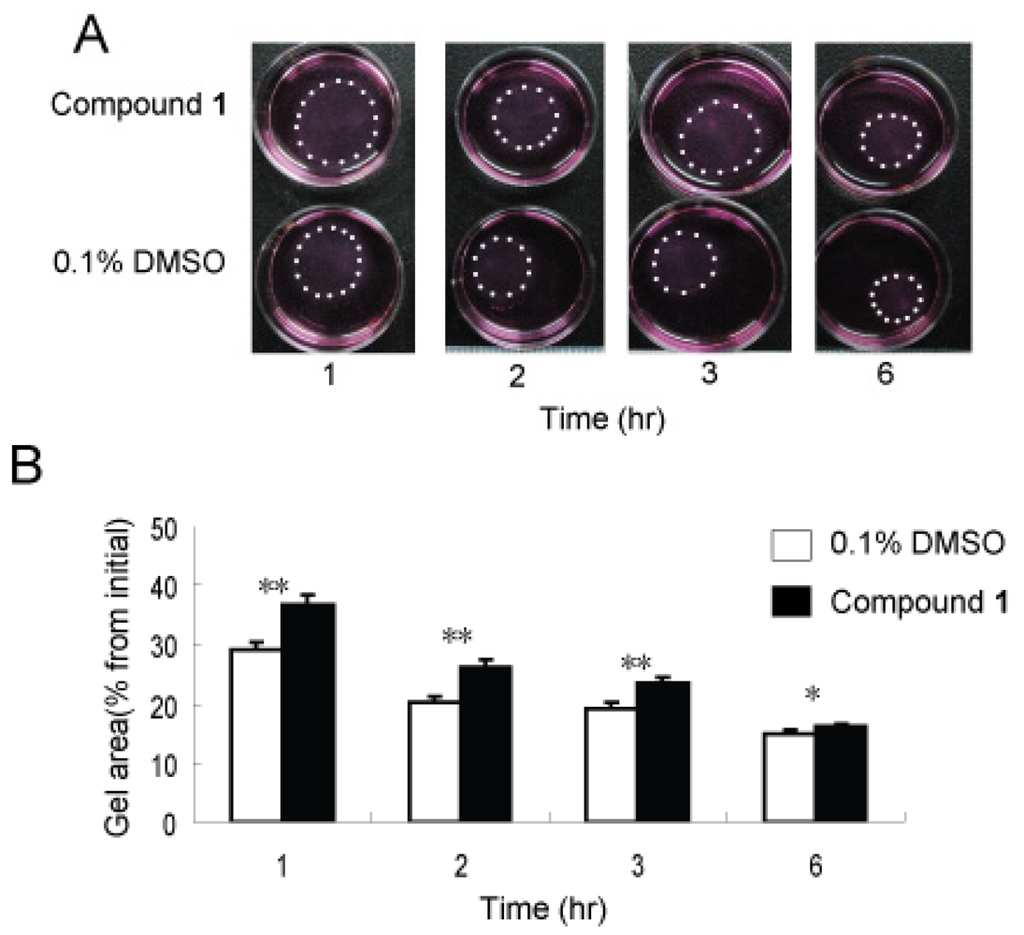
Figure 5.
Compound 1 inhibited contractile ability of WI26 cells in 3D collagen lattices. Equal numbers of WI26 cells were seeded in triplicate gels of collagen I with compound 1 (30 μg/mL) or 0.1% DMSO. The contraction of collagen gel was monitored by photographing the gels at appointed time intervals. (A) As illustrated, contraction of collagen gel was attenuated by compound 1 compared to 0.1% DMSO at different time points. The edge of gel was marked with dots. (B) The area of the gel was measured and plotted as a percentage of the original area at the onset of the experiments. Each point represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significant differences from the value of 0.1% DMSO solvent control were marked, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
2.6. Discussion
Today, fibrotic diseases are becoming more threathening than ever, due to enviromental pollution. It has been reported that high levels of air pollutant paticles can induce chronic fibrotic responses in airways [25]. Identification of bioactive molecules that affect fibrosis is thus becoming a promising theraputic area and also an urgent task. For example, the synthetic drug TAS-301, a constrictive remodeling regulator, was shown to have high inhibitory potency on coronary artery stenosis, mainly due to inhibition of adventitial fibroblast proliferation and the contractile ability of myofibroblasts [26]. During excessive fibrogenesis, it is well known that self-perpetuating circuits of inflammation and ECM accumulation, and constriction by inflammation and mechanical force, directly influence the development of fibrotic diseases [4]. Hence, the development of leading compounds aimed at these circuits may target the effects on these diseases, while avoiding severely disturbing physiological processes induced by steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Fibroblasts play pivotal roles in establishing and maintaining these circuits and are in fact the main ECM generating cells in fibrotic diseases [27]. During these diseases, resident fibroblasts proliferate and are activated as a result of stimulation by injury or inflammation. The activated fibroblasts contribute to ECM production and inflammatory modulation [28]. Radiotherapy and chemotherapeutics are useful for treating hypertrophic scar and keloid development by inducing apoptosis of fibroblasts [29]. Compound 1 showed inhibitory effects on fibroblast proliferation, and thus may contribute to the alleviation of excessive fibrotic accumulation.
Activated fibroblasts may also convert into myofibroblasts, which express many more stress fibers and generate much more mechanical tension [1]. The mechanical force generated by endogenous fibroblasts has been found to play important roles in the activation and secretion of inflammatory cells [19,23,30]. It has been demonstrated that reduction of mechanical stress can alleviate inflammation and fibrosis in vivo [12]. Therefore, mechanical force and local inflammation together comprise one of the most important self-perpetuating inflammatory circuits that, underlies many fibrotic diseases. Compound 1 can reduce the contractile capability of fibroblasts, thus indicating a potential to inhibit this key aspect of fibrogenesis.
The interaction of monocytes and fibroblasts is known to play an important role in inflammation [17,31]. Direct contact between monocytes and fibroblasts can faciliate the activation of both cells [32]. Compound 1 blocked the adhesion of fibroblasts and monocytes, which may ameliorate excessive inflammatory processes in fibrotic diseases. In previous investigation, 1 was reported as an antagonist of the LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction [14]. Since LFA-1/ICAM-1 can mediate direct contact of inflammatory cells and fibroblasts [33], the LFA-1/ICAM-1 binding inhibitory effect may explain the results of the adhesion experiment.
In conclusion, 1 has multiple biological effects on lung fibroblast properties, including proliferation, contractile capacity and interaction with monocytes, which are likely to be involved in the establishment of positive feedback circuits that lead to excessive fibrosis.
Although pathological fibrosis of different organs is common in many diseases [1], there are presently very few therapeutic options [34]. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids can prevent pathological fibrosis [29,35], but long-term use and high dosage are unsuitable owing to their extensive adverse effects [36,37]. Superficial compression is useful for preventing the development of skin hypertrophic scars [29], but this procedure cannot be used in visceral organs. The “vicious cycle” of fibroproliferation is one of the most important characteristics of pathological fibrosis [19,23]. Hence, small molecules that target the positive feedback circuits may prove tremendously effective in exhibiting antifibrotic activities without severe side effects. The results presented herein illustrate that compound 1 may serve as a useful antifibrotic leading compound for treating pulmonary fibrosis and other pathological fibrotic diseases.
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded with Bruker DRX-500 and Avance III-600 NMR spectrometers with the solvent as an internal standard (DMSO-d6 δ = 2.51 and 40.0 ppm, respectively). Chemical shifts (δ) expressed in parts per million (ppm) and coupling constants (J) are reported in Hertz (Hz). LC-HRMS was performed on a Waters ACQUITY UPLC system equipped with a binary solvent delivery manager and a sample manager, coupled with a Waters Micromass Q-TOF Premier Mass Spectrometer equipped with an electrospray interface (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA). Column chromatography was performed with silica gel (200–300 mesh, Qingdao Marine Chemical, Inc., Qingdao, China), silica gel H (10–40 μm, Qingdao), Sephadex LH-20 (40–70 μm, Amersham Pharmacia Biotech AB, Uppsala, Sweden) and Lichroprep reversed-phase RP-18 silica gel (40–63 μm, Merck, Darmstadt, Germany). The chemical reagents used for chromatography were purchased from Shanghai Chemical Works Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Optical rotations were recorded on a JASCO P-2000 polarimeter. CD spectra were taken on a J-815 spectropolarimeter (JASCO, Gross-Umstadt, Germany) at room temperature. An Agilent 1200 series system was used for the analytical scale method. Analytical HPLC was carried out on an Welch XB-C18 column (4.6 × 150 mm, 5 μm, Welch Materials, Inc., USA), flow 1 mL/min. Organic solvents for HPLC were analytical grade and were purchased from Shanghai ANPEL Scientific Instrument Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
3.2. Strain Cultivation
Streptomyces xiamenensis strain 318 was isolated from a mangrove sediment sample collected in the national mangrove reserve in Fujian province of China [13]. Spores of strain 318 were inoculated on GYM (Glucose 4 g, Yeast extract 4 g, Malt extract 10 g, CaCO3 2 g, Agar 12 g, Distilled water 1 L, adjusted to pH 7.2 with KOH before adding agar.) plates were then incubated at 28 ± 1 °C for 12 days before harvesting.
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
The 30 L plate culture of S. xiamenisis was extracted with a solvent mixture of ethyl acetate/methanol/acetic acid (80:15:5, v:v:v) at room temperature overnight. The supernatant was filtered and the residue was then extracted twice as described above. The total supernatants were combined and concentrated under vacuum at 37 °C in order to remove the organic part to afford a crude extract (12 g). Half of the crude extract was subjected to column chromatography on silica gel, eluted by CH2Cl2:MeOH (gradient from methanol, 100:1, 50:1, 20:1, 10:1, 5:1 to MeOH). The fraction [eluted with CH2Cl2:MeOH (10:1, v:v)] was collected and purified by repeated column chromatography on Sephadex LH-20, which was washed by MeOH. The fractions were collected and guided by HPLC fingerprints to find peaks containing the target UV profile (λmax 206, 260 nm). Finally, the combination was separated by ODS column (eluted with MeOH:H2O = 75:25) to obtain compound 1 (15 mg).
N-[[3,4-dihydro-3S-hydroxy-2S-methyl-2-(4′R-methyl-3S-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine (1): Yellow amorphous powder (MeOH); [α]22D +39.5° (c 0.044, MeOH); UV λmax (MeOH) 206, 260 nm; CD (MeOH) Δε201 +0.15, Δε202 +0.55, Δε205 +0.3, Δε207.5 +0.5, Δε229 −0.05, Δε259 +0.28; 1H and 13C NMR data, see Table 1; HRESIMS m/z 392.2069 [M + H]+, (calcd for C21H30NO6, m/z 392.2073), 390.1886 [M − H]−, (calcd for C21H29NO6, m/z 390.1917).
3.4. (R)- and (S)-MPA Esterification
(R)-MPA (4.0 mg), dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC), and catalytic N,N-dimethylpyridin-4-amine (DMAP) were added to a CHCl3 solution of compound 1. The mixture was stirred for 2 h to yield (R)-MPA ester of 1. The (S)-MPA ester (1.1 mg) was obtained by the same protocol as for (R)-MPA ester (1.2 mg).
3.5. Hydrolysis of Compound 1, Derivatization with Marfey’s Reagent
Compound 1 (1.0 mg) was hydrolyzed in 1:1 hydrochloric acid-acetic acid at 100 °C for 18 h, 500 μL H2O was added and the mixture was lyophilized overnight [16]. Then 200 μL of 1 M NaHCO3 and 400 μL of 38.7 μM FDAA (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louise, MO, USA) in acetone were added to the mixture for derivatization. The solution was vortexed and incubated at 40 °C for 60 min. Reactions were quenched by addition of 100 μL of 2M HCl. Samples were diluted 1:2 with HPLC initial mobile phase. The derivatization of L-Threonine (Sangon, Shanghai, China) and D-Threonine (Sangon, Shanghai, China) were prepared in the same way. Then the samples were analyzed by HPLC with UV detection at 340 nm and further confirmed by UPLC-MS.
3.6. Cell Culture
The WI26-SV40 transformed human lung fibroblast [American Type Culture Collection (ATCC) CCL 95.1] cells were maintained in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM, Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Solarbio, Beijing, China). THP-1 (human acute monocytic leukemia cell line) cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 meted with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, GIBCO-BRL, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Solarbio, Beijing, China). THP-1 (human acute monocytic leukemia cell line) cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA), supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 0.5 mM/L β-mercaptoethanol (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA). Both kinds of cells were incubated at 37 °C humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 in air.
3.7. Cell Proliferation Assay
The effect of compound 1 on cell proliferation was determined using a standard Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan) assay according to the manufacturer’s instruction. WI26 cells at 70%–80% confluent were trysinized by 0.25% trypsin-0.02% EDTA solution, centrifuged and re-suspended in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and antibiotics and seeded in 96-well plates (100 μL/well) at an initial density of 2.5 × 104 cells/mL. The medium was replaced 24 h later by fresh DMEM with 10% FBS and antibiotics containing 30 μg/mL compound 1 or 0.1% DMSO (AppliChem, Darmstadt, Germany), then the medium was refreshed and the cells viability was measured by using CCK-8 solution at day 0, 2, 3, 4 and 6, respectively. Proliferation measurement was applied by adding 10 μL CCK-8 solutions to each well and incubating at 37 °C for 1 h. The OD values of each well were measured at the primary wavelength λ = 450 nm by using a Microplate Spectrophotometer (PowerWaveXS, BioTek, Seattle, WA, USA). Data are shown as means ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.
3.8. Cell Adhesion Assay
Two days before adhesion assay, WI26 cells were seeded in 24-well plates (500 μL/well) at a density of 3 × 105 cells/mL and allowed to grow 24 h to confluence. The medium of THP-1 and WI26 cells was replaced by DMEM supplemented with 0.5% FBS and antibiotics 24 h before the adhesion experiment. The culture of THP-1 cells was centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant was discarded. The THP-1 cells were re-suspended in DMEM with 10% FBS and antibiotics, then diluted to 5 × 105 cells/mL. The medium of WI26 cells in 24-well plates was discarded to get a monolayer of WI26 cells in each well, then 500 μL THP-1 suspension was added into each well as previously published [38,39]. For the biotest groups, 30 μg/mL compound 1 or 50 μg/mL crude extract of S. xiamenensis culture was added in each well, respectively. For the control groups, 0.1% DMSO was used as solvent control for 1 and 0.01% DMSO as solvent control of crude extract, respectively, according to the different final DMSO concentration of 1 and crude extract. Two kinds of cells were co-cultured for 3 h, then the medium and the non-adherent THP-1 cells were removed by washing with PBS three times. Adherent THP-1 cells were quantified microscopically at 400-fold magnification in 4 random visual fields of each well and photographed with a digital camera (LY-WN-HPCCD, China) mounted on a microscope (Olympus, CKX31, Japan). Data are shown as means ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.
3.9. Fibroblast Contraction Assay
WI26 cells at 70%–80% confluent were trysinized by 0.25% trypsin-0.02% EDTA solution and seeded at a density of 4 × 105 cells/mL into 32 mm bacteriological plates (2 mL/dish) in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, antibiotics, sodium ascorbate (50 μg/mL), and containing 0.3 mg/mL of acid-extracted collagen I from newborn calf skin (IBFB, Leipzig, Germany) as previously described [40]. For the biotest groups, 30 μg/mL pure extract of compound 1 was added in each well; for the control groups, 0.1% DMSO was used as solvent control. The cultures were placed at 37 °C for 60 min to allow collagen polymerization, and then the gels from plates were released by tilting the plates slightly. Gradual lattice contraction was monitored by measuring the gel area of triplicate setups at successive time points up to 6 h. Data are shown as means ± standard deviation (SD) of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate.
3.10. Statistical Analysis
Statistic differences were calculated using student’s paired t-test at a significance level of p < 0.05 to 0.001.
3.11. Computational Methods
The QM calculations were carried out with the M06-2X hybrid meta DFT functional with the 6 − 31 + G(d,p) basis set using Gaussian 09. Conformations were fully optimized and characterized by harmonic vibrational frequency analysis. The solvation energies in DMSO were calculated with Truhlar’s SMD solvation model [41,42,43].
4. Conclusions
The investigation of anti-fibrosis small molecules derived from S. xiamenensis may represent an emerging pharmacological and therapeutic area for fibrotic diseases. The structure and absolute configurations of N-[[3,4-dihydro-3S-hydroxy-2S-methyl-2-(4′R-methyl-3′S-pentenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-6-yl]carbonyl]-threonine (1) was fully elucidated by extensive spectroscopic data analyses, Mosher’s method, Marfey’s reagent and QM calculations. The multiple biological effects of 1 on lung fibroblast behavior were investigated, including proliferation, anti-contractile capacity and anti-adhesion with monocytes. These three bioactive aspects are involved in the construction of positive feedback circuits of excessive fibrosis. Developing leading compounds from marine natural products, aiming at these circuits may have targeted effects on fibrotic diseases.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Zhiwei Deng in Analytical and Testing Center of Beijing Normal University, and Jieli Wu in Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for technical support during the NMR measurement. We are also grateful to Lei Feng and Na Zhu in Instrumental Analysis Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University for the HRESIMS and UPLC-MS measurements. I am very thankful to Daniel M. Czajkowsky for the English correction. The work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation of China (30901845, 91029738, 3082105), the National Basic Research Program of China “973” 2012CB72100 and the grants from the State Key Laboratory of Oncogenes and Related Genes (No. 90-10-11). The project was also sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM SHSTC (10PJ1405200), SHEC (SOS-0900000171) and by Research Fund for the New Teacher Program of Higher Education of China (20090001120047).
References
- Wynn, T.A. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar]
- Borm, P. Toxicity of Selected: Toxicology of Fibers and Particles; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, C.; Ding, A.H. Nonresolving Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 871–882. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.; Grabley, S.; Groth, I.; Lin, W.; Christner, A.; Guo, D.; Sattler, I. Structure determination of germacrane-type sesquiterpene alcohols from an endophyte Streptomyces griseus subsp. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, 1028–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.H.; Sattler, I.; Lin, W.H.; Guo, D.A.; Grabley, S. p-Aminoacetophenonic acids produced by a mangrove endophyte: Streptomyces griseus subsp. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1198–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Li, L.; Fu, H.; Sattler, I.; Huang, X.; Grabley, S. New cyclopentenone derivatives from an endophytic Streptomyces sp. isolated from the mangrove plant Aegiceras comiculatum. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 2005, 58, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xu, M.; Li, Q.; Sattler, I.; Lin, W. p-Aminoacetophenonic acids produced by a mangrove endophyte Streptomyces sp. (strain HK10552). Molecules 2010, 15, 2782–2790. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Gessner, G.; Groth, I.; Lange, C.; Christner, A.; Bruhn, T.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Heinemann, S.H.; Grabley, S.; et al. Shearinines D-K, new indole triterpenoids from an endophytic Penicillium sp. (strain HKI0459) with blocking activity on large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 435–444. [Google Scholar]
- Ravangpai, W.; Sommit, D.; Teerawatananond, T.; Sinpranee, N.; Palaga, T.; Pengpreecha, S.; Muangsin, N.; Pudhom, K. Limonoids from seeds of Thai Xylocarpus moluccensis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 4485–4489. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, S.; Proksch, P.; Gu, J.; Lin, W. TNF-alpha inhibitory diterpenoids from the Chinese mangrove plant Excoecaria agallocha L. Phytochemistry 2010, 71, 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Dauskardt, R.H.; Wong, V.W.; Bhatt, K.A.; Wu, K.; Vial, I.N.; Padois, K.; Korman, J.M.; Longaker, M.T. Improving cutaneous scar formation by controlling the mechanical environment: Large animal and phase I studies. Ann. Surg. 2011, 254, 217–225. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, S.J.; Xu, J.; Xiao, J.; Ruan, J.S. Streptomyces xiamenensis sp. nov., isolated from mangrove sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 472–476. [Google Scholar]
- Kawamura, N.; Tsuji, E.; Watanabe, Y.; Tsuchihashi, K.; Takako, T. Benzopyran derivatives, their manufacture with Streptomyces species, and their use for treatment of asthma and rheumatoid arthritis. Mercian Corp.: Kyoto, Japan, 2000 March 7; Daiichi Seiyaku Co., Ltd. [Google Scholar]
- Plavec, J.; Tong, W.; Chattopadhyaya, J. How do the gauche and anomeric effects drive the pseudorotational equilibrium of the pentofuranose moiety of nucleosides? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 9734–9746. [Google Scholar]
- Goodlett, D.R.; Abuaf, P.A.; Savage, P.A.; Kowalski, K.A.; Mukherjee, T.K.; Tolan, J.W.; Corkum, N.; Goldstein, G.; Crowther, J.B. Peptide chiral purity determination: Hydrolysis in deuterated acid, derivatization with Marfey’s reagent and analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 1995, 707, 233–244. [Google Scholar]
- Wynn, T.A.; Barron, L. Macrophages: Master regulators of inflammation and fibrosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 245–257. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, L.; Wynn, T.A. Fibrosis is regulated by Th2 and Th17 responses and by dynamic interactions between fibroblasts and macrophages. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G723–G728. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Rustad, K.C.; Akaishi, S.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Januszyk, M.; Nelson, E.R.; Levi, K.; Paterno, J.; Vial, I.N.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase links mechanical force to skin fibrosis via inflammatory signaling. Nat. Med. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Oakes, P.W.; Patel, D.C.; Morin, N.A.; Zitterbart, D.P.; Fabry, B.; Reichner, J.S.; Tang, J.X. Neutrophil morphology and migration are affected by substrate elasticity. Blood 2009, 114, 1387–1395. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Akaishi, S.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Pushing back: Wound mechanotransduction in repair and regeneration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 2186–2196. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, D.J.; Eckes, B.; Rajkumar, V.; Krieg, T. New developments in fibroblast and myofibroblast biology: Implications for fibrosis and scleroderma. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2007, 9, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.W.; Paterno, J.; Sorkin, M.; Glotzbach, J.P.; Levi, K.; Januszyk, M.; Rustad, K.C.; Longaker, M.T.; Gurtner, G.C. Mechanical force prolongs acute inflammation via T-cell-dependent pathways during scar formation. FASEB J. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell, F. Fibroblast biology in three-dimensional collagen matrices. Trends Cell Biol. 2003, 13, 264–269. [Google Scholar]
- Churg, A.; Brauer, M. Ambient atmospheric particles in the airways of human lungs. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2000, 24, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki, E.; Tanahashi, Y.; Yamasaki, Y.; Oda, N.; Nozawa, Y.; Terakawa, H.; Miyoshi, K.; Muranaka, Y.; Miyake, H.; Matsuura, N. Inhibitory effect of TAS-301, a new synthesized constrictive remodeling regulator, on renarrowing after balloon overstretch injury of porcine coronary artery. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 295, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Eckes, B.; Nischt, R.; Krieg, T. Cell-matrix interactions in dermal repair and scarring. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2010, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Strieter, R.M.; Gomperts, B.N.; Keane, M.P. The role of CXC chemokines in pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 549–556. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfram, D.; Tzankov, A.; Pulzl, P.; Piza-Katzer, H. Hypertrophic scars and keloids—A review of their pathophysiology, risk factors, and therapeutic management. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, G.J.; Chambers, R.C.; Hill, M.R.; McAnulty, R.J. Regulation of matrix turnover: Fibroblasts, forces, factors and fibrosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delavary, B.M.; van der Veer, W.M.; van Egmond, M.; Niessen, F.B.; Beelen, R.H. Macrophages in skin injury and repair. Immunobiology 2011, 216, 753–762. [Google Scholar]
- Holt, D.J.; Chamberlain, L.M.; Grainger, D.W. Cell-cell signaling in co-cultures of macrophages and fibroblasts. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9382–9394. [Google Scholar]
- Long, E.O. ICAM-1: Getting a grip on leukocyte adhesion. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5021–5023. [Google Scholar]
- Kelemen, O.; Kollar, L. Current methods of treatment and prevention of pathologic scars. Magy. Seb. 2007, 60, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa, R. The most current algorithms for the treatment and prevention of hypertrophic scars and keloids. Plast. Reconstruct. Surg. 2010, 125, 557–568. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Ashby, D.; Smyth, R.L. Oral steroids for long-term use in cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hunzelmann, N.; Moinzadeh, P.; Genth, E.; Krieg, T.; Lehmacher, W.; Melchers, I.; Meurer, M.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Olski, T.M.; Pfeiffer, C.; et al. High frequency of corticosteroid and immunosuppressive therapy in patients with systemic sclerosis despite limited evidence for efficacy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Pfaff, A.W.; Georges, S.; Candolfi, E. Different effect of Toxoplasma gondii infection on adhesion capacity of fibroblasts and monocytes. Parasite Immunol. 2008, 30, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Taub, D.D.; Lloyd, A.R.; Conlon, K.; Wang, J.M.; Ortaldo, J.R.; Harada, A.; Matsushima, K.; Kelvin, D.J.; Oppenheim, J.J. Recombinant human interferon-inducible protein 10 is a chemoattractant for human monocytes and T lymphocytes and promotes T cell adhesion to endothelial cells. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Bothe, I.; Hirche, F.; Zweers, M.; Gullberg, D.; Pfitzer, G.; Krieg, T.; Eckes, B.; Aumailley, M. Interactions of primary fibroblasts and keratinocytes with extracellular matrix proteins:Contribution of α2β1 integrin. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar]
- Gaussian 9, Revision A.02; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. Density functionals with broad applicability in chemistry. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 157–167. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar]
- Sample Availability: Sample of compound 1 is available from authors.
Supplementary Files
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).