Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps After Surgery: Risk Factors, Predictive Models, and Treatment Approaches with a Focus on Western and Asian Differences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
- Studies involving adult patients (aged ≥ 18 years) undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) for chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS)
- Reporting recurrence rates, recurrence risk factors, prediction models, or postoperative treatment strategies
- Conducted in or reporting data from Asian or Western populations
- Published in English with full text available
- Pediatric studies (involving patients < 18 years)
- Case reports or case series with <30 patients
- Narrative reviews without systematic methodology, unless cited for background
- Conference abstracts, editorials, and letters
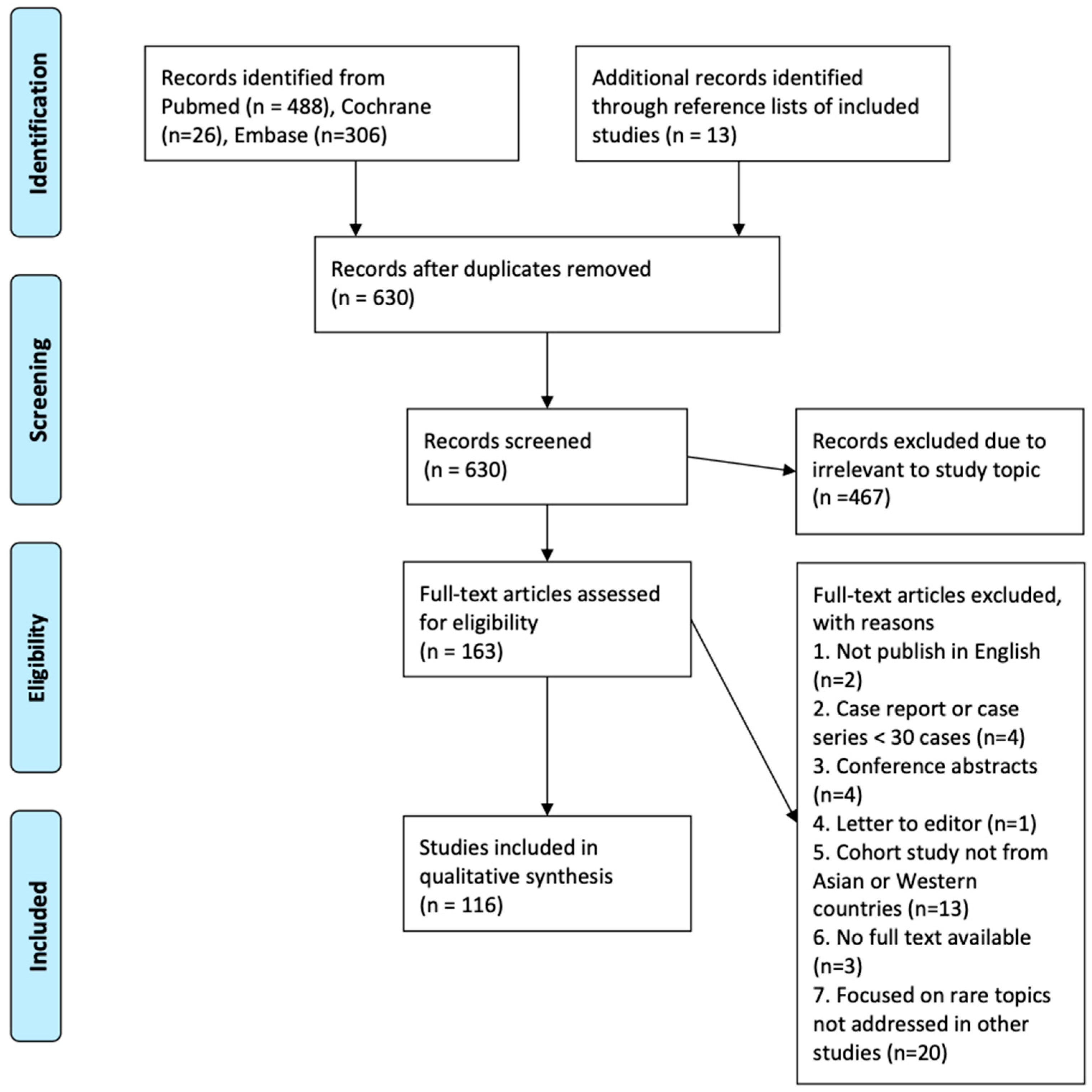
2.3. Study Screening and Selection
3. Recurrence Rates of CRS After Surgery
3.1. Definitions of Recurrence
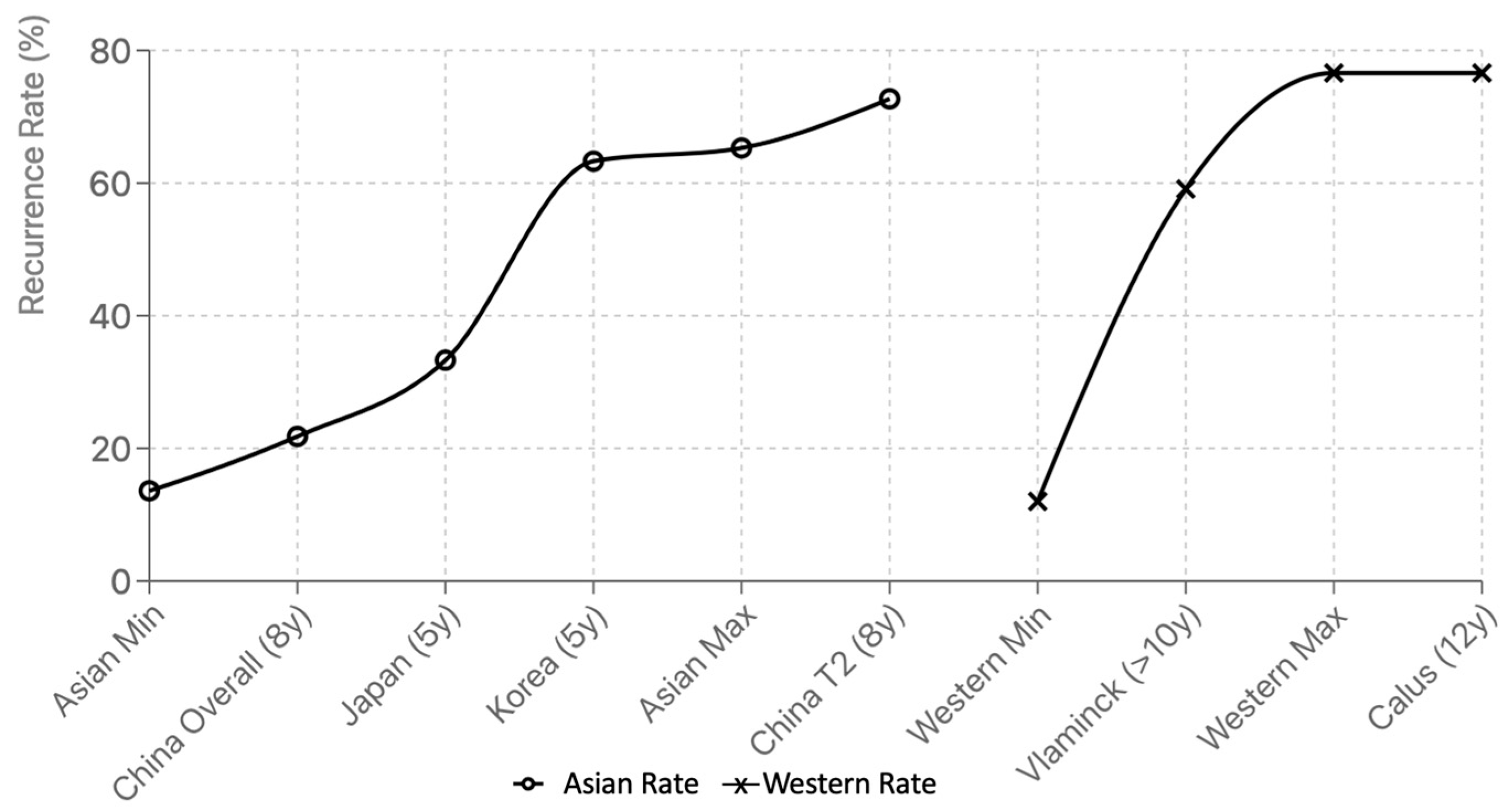
3.2. Recurrence Rates in Western vs. Asia
4. Risk Factors of CRS Recurrence
4.1. Patient Factors
4.2. Disease Characteristics
4.3. Surgical Factors
5. Predictive Models for Recurrence
5.1. Overview of Predictive Modeling Approaches
5.2. Clinical Predictors and Symptom-Based Models
5.3. Serologic and Immunologic Biomarkers
5.4. Histologic Markers of Inflammation
5.5. Radiologic Predictors
5.6. Role of Microbiota in Recurrence Risk
5.7. Integrated and Machine Learning–Based Prediction Models
6. Management of Recurrent CRS
6.1. Medical Treatments
6.2. Surgical Revision Strategies
7. Discussion
7.1. Methodological Limitations
7.2. Regional Differences in Predictors and Models
7.3. Therapeutic Implications
8. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRS | Chronic rhinosinusitis |
| CRSsNP | Chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyp |
| CRSwNP | Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp |
| ESS | Endoscopic sinus surgery |
| SNOT-22 | Sino-Nasal Outcome Test |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| AERD | Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease |
| AR | Allergic rhinitis |
| CF | Cystic Fibrosis |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| JESREC | Japanese Epidemiological Survey of Refractory Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis |
| IgE | Immunoglobulin E |
| ECP | Eosinophil cationic protein |
| CLC | Charcot-Leyden crystals |
| NERD | NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease |
| CCAD | Central Compartment Atopic Disease |
| SES | Steroid-eluting stents |
| ML | Machine learning |
References
- Abuduruk, S.H.; Sabb Gul, B.K.; AlMasoudi, S.M.; Alfattani, E.H.; Mohammad, M.A.; Alshehri, H.M.; Alosaimi, A.D.; Almnjwami, R.F.; Alnafie, J.A.; Jabbari, A.N.; et al. Factors Contributing to the Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e67910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachert, C.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Desrosiers, M.; Khan, A.H. Burden of Disease in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftus, C.A.; Soler, Z.M.; Koochakzadeh, S.; Desiato, V.M.; Yoo, F.; Nguyen, S.A.; Schlosser, R.J. Revision surgery rates in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Meta-analysis of risk factors. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHugh, T.; Snidvongs, K.; Xie, M.; Banglawala, S.; Sommer, D. High tissue eosinophilia as a marker to predict recurrence for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zeng, M.; Liu, Z. Revisiting Asian chronic rhinosinusitis in the era of type 2 biologics. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellings, P.W.; Alobid, I.; Anselmo-Lima, W.T.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Bjermer, L.; Caulley, L.; Chaker, A.; Constantinidis, J.; Conti, D.M.; De Corso, E.; et al. EUFOREA/EPOS2020 statement on the clinical considerations for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps care. Allergy 2024, 79, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gata, A.; Raduly, L.; Budișan, L.; Bajcsi, A.; Ursu, T.M.; Chira, C.; Dioșan, L.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Albu, S. Machine Learning Model Predicts Postoperative Outcomes in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2024, 49, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Lou, H.; Zhang, L. Prognostic factors for post-operative outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A systematic review. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 19, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, H.; Meng, Y.; Piao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2015, 29, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Seet, J.E.; Yap, Q.V.; Chao, S.S.; Thong, M.K.T.; Wang, D.Y.; Ong, Y.K. Latent class analysis of structured histopathology in prognosticating surgical outcomes of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Singapore. Rhinology 2023, 61, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Lou, H.; Meng, Y.; Wang, C. Long-term outcomes of different endoscopic sinus surgery in recurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma. Rhinology 2020, 58, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Liu, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, N.; Bachert, C.; Meng, J. Multivariate analysis of inflammatory endotypes in recurrent nasal polyposis in a Chinese population. Rhinology 2018, 56, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaminck, S.; Acke, F.; Prokopakis, E.; Speleman, K.; Kawauchi, H.; van Cutsem, J.C.; Hellings, P.W.; Jorissen, M.; Seys, S.; Bachert, C.; et al. Surgery in Nasal Polyp Patients: Outcome After a Minimum Observation of 10 Years. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calus, L.; Van Bruaene, N.; Bosteels, C.; Dejonckheere, S.; Van Zele, T.; Holtappels, G.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P. Twelve-year follow-up study after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2019, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, C.; Masieri, S.; Begvarfaj, E.; Loperfido, A.; Baroncelli, S.; Cascone, F.; Ciofalo, A. Long-Term Perspectives on Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Evaluating Recurrence Rates after Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in the Biologics Era-A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeConde, A.S.; Mace, J.C.; Levy, J.M.; Rudmik, L.; Alt, J.A.; Smith, T.L. Prevalence of polyp recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Laryngoscope 2017, 127, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sella, G.C.P.; Tamashiro, E.; Sella, J.A.; Aragon, D.C.; Mendonça, T.N.; Arruda, L.K.P.; Anselmo Lima, W.T.; Valera, F.C.P. Asthma Is the Dominant Factor for Recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lu, Z.; Ma, R.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X. Analysis of recurrent influencing factors of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps. Rev. Psiquiatr. Clin. 2022, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, A.S.; Smith, K.A.; Meeks, H.; Oakley, G.M.; Curtin, K.; LeClair, L.; Howe, H.; Orlandi, R.R.; Alt, J.A. Asthma increases long-term revision rates of endoscopic sinus surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, K.T.; Lee, C.H.; Hsu, W.C.; Ko, J.Y.; Yeh, T.H. Revision of endoscopic sinus surgery in adults: A population-based study in Taiwan. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2023, 48, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.A.; Orlandi, R.R.; Oakley, G.; Meeks, H.; Curtin, K.; Alt, J.A. Long-term revision rates for endoscopic sinus surgery. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Xie, S.; Xie, Z.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H. Hyperuricemia Increases the Risk of Postoperative Recurrence in Chinese Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 2669–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, A.; Salo, R.; Huhtala, H.; Myller, J.; Rautiainen, M.; Kääriäinen, J.; Penttilä, M.; Renkonen, R.; Raitiola, H.; Mäkelä, M.; et al. Factors affecting revision rate of chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2016, 1, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Han, J.S.; Kim, G.J.; Basurrah, M.A.; Hwang, S.H. Clinical predictors of polyps recurring in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rhinology 2023, 61, 482–497. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.N.; Yeh, T.H.; Lin, C.F.; Lin, Y.T. The efficacy of dupilumab as an adjuvant treatment after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A retrospective cohort analysis. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 18, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.A.; Gill, A.S.; Beswick, D.M.; Meeks, H.; Oakley, G.M.; Yim, M.; Curtin, K.; Orlandi, R.R.; Alt, J.A. Cystic Fibrosis Increases Long-Term Revision Rates of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Comorbid Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 36, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.W.; Ting, J.Y.; Platt, M.P.; Tierney, H.T.; Metson, R. Factors affecting time to revision sinus surgery for nasal polyps: A 25-year experience. Laryngoscope 2014, 124, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Jiang, S.; Fan, R.; Gao, K.; Shui, J.; Wang, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Elevated body mass index increased the risk of recurrence in Chinese patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2023, 44, 103841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, A.S.; Meeks, H.; Curtin, K.; Alt, J.A. Tobacco Use Increases the Adjusted Risk of Revision Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2022, 36, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veloso-Teles, R.; Cerejeira, R. Endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Clinical outcome and predictive factors of recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2017, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hox, V.; Delrue, S.; Scheers, H.; Adams, E.; Keirsbilck, S.; Jorissen, M.; Hoet, P.H.; Vanoirbeek, J.A.; Nemery, B.; Hellings, P.W. Negative impact of occupational exposure on surgical outcome in patients with rhinosinusitis. Allergy 2012, 67, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, T.D.; DeConde, A.S.; Manes, R.P. Disease-related expenditures and revision rates in chronic rhinosinusitis patients after endoscopic sinus surgery. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, N.R.; Jafari, A.; DeConde, A.S. Revision rates and time to revision following endoscopic sinus surgery: A large database analysis. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, D.; Jeremic, G.; Wright, E.D.; Rotenberg, B.W. Revision rates after endoscopic sinus surgery: A recurrence analysis. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2011, 120, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, X. Development and validation of a nomogram model for the prediction of recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Front. Surg. 2025, 12, 1581417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, G.; Contro, G.; Ruaro, A.; Barion, U.; Frigo, A.C.; Sfriso, P.; Marioni, G. Sex and age-related differences in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps electing ESS. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Z.; Xie, S.; Jiang, W. Elevated Body Mass Index Aggravates Histopathological Changes and Postoperative Recurrence Risk in Nasal Polyps. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2025, 173, 522–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Bai, Y.; Fang, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Luo, X.; Xiao, Z.; Iyer, R.; Shan, F.; et al. Body mass index’s effect on CRSwNP extends to pathological endotype and recurrence. Rhinology 2024, 62, 370–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Yu, T.; Jiang, L.; Qin, M.; Tong, Z. Metabolic syndrome facilitates histopathological changes and the risk of postoperative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 128, 111540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, R.; Wang, F. Effects of Metabolic Syndrome and its components on the postoperative recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps’ patients. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2024, 90, 101371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Meng, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Xie, S.; Zhong, W.; Jia, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W.; Xie, Z. Hyperglycemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus associate with postoperative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 282, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Zhang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, W. Serum metabolomics identifies uric acid as a possible novel biomarker for predicting recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinology 2023, 61, 541–551. [Google Scholar]
- Loftus, C.A.; Soler, Z.M.; Desiato, V.M.; Koochakzadeh, S.; Yoo, F.; Storck, K.A.; Schlosser, R.J. Factors impacting revision surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2020, 10, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlaminck, S.; Vauterin, T.; Hellings, P.W.; Jorissen, M.; Acke, F.; Van Cauwenberge, P.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P. The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: A 3-year prospective observational study. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 260–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokunaga, T.; Sakashita, M.; Haruna, T.; Asaka, D.; Takeno, S.; Ikeda, H.; Nakayama, T.; Seki, N.; Ito, S.; Murata, J.; et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: The JESREC Study. Allergy 2015, 70, 995–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Huang, J.H.; Price, C.P.E.; Schauer, J.M.; Suh, L.A.; Harmon, R.; Conley, D.B.; Welch, K.C.; Kern, R.C.; Shintani-Smith, S.; et al. Prognostic factors for polyp recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 352–361.e357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corso, E.; Settimi, S.; Montuori, C.; Cantiani, A.; Corbò, M.; Di Bella, G.A.; Sovardi, F.; Pagella, F.; Rigante, M.; Passali, G.C.; et al. How to manage recurrences after surgery in CRSwNP patients in the biologic era: A narrative review. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2023, 43, S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.C.; Lee, T.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, P.H.; Chen, Y.W.; Fu, C.H. Serum eosinophil cationic protein: A prognostic factor for early postoperative recurrence of nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortuaire, G.; Gengler, I.; Carpentier, C.; Szymanski, C.; Chenivesse, C.; Lefevre, G. T helper 2 inflammatory markers are associated with recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps after endoscopic sinus surgery. Rhinology 2020, 58, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riva, G.; Tavassoli, M.; Cravero, E.; Moresco, M.; Albera, A.; Canale, A.; Pecorari, G. Long-term evaluation of nasal polyposis recurrence: A focus on multiple relapses and nasal cytology. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2022, 43, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Guo, D.; Wang, G. The correlation between preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and postoperative recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2024, 38, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Asaka, D.; Kanaya, H.; Kuboki, A.; Haruna, S. Prognostic factors for recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Auris Nasus Larynx 2016, 43, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Englhard, A.S.; Ledderose, G.J. Anatomical findings in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps requiring revision surgery. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 89, 101287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuan, E.C.; Mallen-St Clair, J.; Frederick, J.W.; Tajudeen, B.A.; Wang, M.B.; Harvey, R.J.; Suh, J.D. Significance of undissected retromaxillary air cells as a risk factor for revision endoscopic sinus surgery. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2016, 30, 448–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.J.; Kim, C.; Asghar, M.; Lee, J.M.; Kantarevic, J.; Sibley, L.M.; Chan, Y. Surgeon Case Volume Impacts Revision Rate of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025, 15, e3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, T.L.; Schlosser, R.J.; Mace, J.C.; Alt, J.A.; Beswick, D.M.; DeConde, A.S.; Detwiller, K.Y.; Mattos, J.L.; Soler, Z.M. Long-term outcomes of endoscopic sinus surgery in the management of adult chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Samukawa, Y.; Hoshikawa, H. Early postoperative endoscopic score can predict the long-term endoscopic outcomes in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis (ECRS) patients. Braz. J. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 89, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Han, Y.E.; Seo, Y.; Choe, G.; Kim, M.K.; Huh, G.; Cho, D.; Yang, S.K.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, D.W. Revisiting the Clinical Scoring System for the Prognosis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Lou, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Blood eosinophil count combined with asthma history could predict chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp recurrence. Acta Otolaryngol. 2021, 141, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuzuki, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Okazaki, K.; Nishikawa, H.; Sakagami, M. Predictors of disease progression after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2019, 133, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, C.; Valente, P.; Medeiros, N.; Ribeiro, L.; Lima, N.; Oliveira, P. Predictive factors of revision endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 3265–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, K.; Hamidovic, S.; Besser, G.; Mueller, C.A.; Liu, D.T. Factors Associated with Revision Sinus Surgery in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djukic, V.; Dudvarski, Z.; Arsovic, N.; Dimitrijevic, M.; Janosevic, L. Clinical outcomes and quality of life in patients with nasal polyposis after functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2015, 272, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudmik, L.; Soler, Z.M.; Hopkins, C. Using postoperative SNOT-22 to help predict the probability of revision sinus surgery. Rhinology 2016, 54, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hopkins, C.; Lund, V. Does time from previous surgery predict subsequent treatment failure in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps? Rhinology 2021, 59, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brescia, G.; Marioni, G.; Franchella, S.; Ramacciotti, G.; Velardita, C.; Giacomelli, L.; Marino, F.; Martini, A. Can a panel of clinical, laboratory, and pathological variables pinpoint patients with sinonasal polyposis at higher risk of recurrence after surgery? Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2015, 36, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zheng, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, C.; Xu, W.; Hao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. A Nomogram Combing Peripheral Parameters for Estimation of CRSwNP Recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2021, 35, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, K.; Hamidovic, S.; Brkic, F.F.; Besser, G.; Mueller, C.A.; Liu, D.T. Peripheral eosinophil count and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio are associated with revision sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 280, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, G.; Barion, U.; Zanotti, C.; Giacomelli, L.; Martini, A.; Marioni, G. The prognostic role of serum eosinophil and basophil levels in sinonasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2017, 7, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brescia, G.; Pedruzzi, B.; Barion, U.; Cinetto, F.; Giacomelli, L.; Martini, A.; Marioni, G. Are neutrophil-, eosinophil-, and basophil-to-lymphocyte ratios useful markers for pinpointing patients at higher risk of recurrent sinonasal polyps? Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2016, 37, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Alasousi, F.; Okpaleke, C.; Habib, A.R.; Javer, A. Prognosis of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps Using Preoperative Eosinophil/Basophil Levels and Treatment Compliance. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2018, 32, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Xie, D.; Fan, S. Relationship between serum ECP and TIgE levels and the risk of postoperative recurrence in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Front. Surg. 2024, 11, 1516981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztepe, O.F.; Gün, T.; Demir, M.; Gür, Ö.E.; Ozel, D.; Doğru, H. A novel predictive marker for the recurrence of nasal polyposis following endoscopic sinus surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 1439–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, Y.; You, Q.; Chen, H. Prognostic Significance of Serum Complement Component 3 in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2020, 82, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhan, J.; Li, R.; Qi, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zeng, M.; Wei, X. Exploration of Predictive Biomarkers for Postoperative Recurrence in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Based on Serum Multiple-Cytokine Profiling. Mediat. Inflamm. 2022, 2022, 1061658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H. Elevated MIF identified by multiple cytokine analyses facilitates macrophage M2 polarization contributing to postoperative recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinology 2024, 62, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Y. The value of combined detection of specific immunoglobulin E, interleukin-6 and regulatory T cells in predicting the risk of postoperative recurrence in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps. J. Med. Biochem. 2024, 43, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tojima, I.; Murao, T.; Kawakita, K.; Nakamura, K.; Arai, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Shimizu, S.; Kouzaki, H.; Shimizu, T. A decreased prevalence of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in blood is associated with good postoperative outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2023, 50, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, D.; Rosato, C.; Pagliuca, G.; Cerbelli, B.; Della Rocca, C.; Di Cristofano, C.; Martellucci, S.; Gallo, A. Predictive markers of long-term recurrence in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.; Yan, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L. Predictive significance of Charcot-Leyden Crystal mRNA levels in nasal brushing for nasal polyp recurrence. Rhinology 2020, 58, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Yan, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C. Predictive Significance of Charcot-Leyden Crystal Protein in Nasal Secretions in Recurrent Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longino, E.S.; Labby, A.B.; Wu, J.; Chapurin, N.; Li, P.; Chandra, R.K.; Turner, J.H.; Chowdhury, N.I. Association of cytokine profile with prior treatment failure and revision surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2023, 13, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapurin, N.; Li, P.; Chandra, R.K.; Turner, J.H.; Chowdhury, N.I. Elevated mucus interleukin-17A levels are associated with increased prior sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsky, M.A.; Corredera, E.; Banerjee, H.; Moore, J.; Wang, L.; Kane, L.P.; Lee, S.E. Association of Mast Cell Burden and TIM-3 Expression with Recalcitrant Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2021, 130, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beswick, D.M.; Smith, T.L.; Mace, J.C.; Alt, J.A.; Farrell, N.F.; Ramakrishnan, V.R.; Schlosser, R.J.; Soler, Z.M. Ethmoid-to-maxillary opacification ratio: A predictor of postoperative olfaction and outcomes in nasal polyposis? Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, P.M.; Cabral, D.C.; Barreto, J.; Carção, A.A.; Duarte, D.; Penêda, J.F. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: Predictors of recurrence 5 years after surgery. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024, 144, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilja, M.; Koskinen, A.; Julkunen-Iivari, A.; Mäkitie, A.; Numminen, J.; Rautiainen, M.; Myller, J.P.; Markkola, A.; Suvinen, M.; Mäkelä, M.; et al. Radiological score of computed tomography scans predicts revision surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lou, H.; Wang, C. Predictive value of computed tomography in the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1236–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.L.; Lee, T.J.; Huang, C.C.; Chang, P.H.; Fu, C.H. Clinical predictors of revision surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis within 5-year follow-up. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2020, 41, 102654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steehler, A.J.; Vuncannon, J.R.; Wise, S.K.; DelGaudio, J.M. Central compartment atopic disease: Outcomes compared with other subtypes of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Z.; Lu, A.; Zhang, T. Rectal Staphylococcus aureus Carriage and Recurrence After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: A Prospective Cohort Study. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023, 102, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Hao, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Predicting the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps using nasal microbiota. Allergy 2022, 77, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniakas, A.; Asmar, M.H.; Renteria Flores, A.E.; Nayan, S.; Alromaih, S.; Mfuna Endam, L.; Desrosiers, M.Y. Staphylococcus aureus on Sinus Culture Is Associated With Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilja, M.; Koskinen, A.; Hammarèn-Malmi, S.; Laulajainen-Hongisto, A.; Numminen, J.; Myller, J.; Vento, S.; Penttila, E.; Hytönen, M.; Virkkula, P.; et al. Radiological score, asthma and NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease predict relapsing chronic rhinosinusitis. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2025, 15, e70043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misirovs, R.; Chan, R.; Stewart, K.; Lipworth, B. Phenotypic associations of medical polypectomy and revision surgery following endoscopic sinus surgery: A retrospective study of a single-centre experience in Scotland. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2023, 137, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicandri-Ciufelli, M.; Cantaffa, C.; Galloni, C.; Fernandez, I.J.; Marchioni, D.; Pipolo, C.; Garzaro, M.; Nitro, L.; Dell’Era, V.; Ferella, F.; et al. Impact of single versus multiple surgeries in CRSwNP patients undergoing treatment with dupilumab. Acta Otolaryngol. 2025, 145, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangl, K.; Liu, D.T.; Bartosik, T.; Campion, N.J.; Vyskocil, E.; Mueller, C.A.; Knerer, B.; Eckl-Dorna, J.; Schneider, S. Real-Life Study of Patient Preference for Dupilumab or Revision Surgery for Recurrent Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviano, G.; Saccardo, T.; Roccuzzo, G.; Bernardi, R.; Chicco, A.D.; Pendolino, A.L.; Scarpa, B.; Mairani, E.; Nicolai, P. Effectiveness of Dupilumab in the Treatment of Patients with Uncontrolled Severe CRSwNP: A “Real-Life” Observational Study in Naïve and Post-Surgical Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, A.; Endam, L.M.; Gonzalez, E.; Jannat, S.; Irani, T.; Desrosiers, M. Perioperative adjuvant therapy with short course of dupilumab with ESS for recurrent CRSwNP. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025, 15, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutphin, J.; Okafor, S.; Reed, S.D.; Deb, A.; Silver, J.; Wallace, M.J.; Yang, J.C.; Abi Hachem, R.; Jang, D.W. Patient preferences for treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Rhinology 2025, 63, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fujieda, S.; Matsune, S.; Takeno, S.; Asako, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Fujita, H.; Takahashi, Y.; Amin, N.; Deniz, Y.; Rowe, P.; et al. The Effect of Dupilumab on Intractable Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps in Japan. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, E1770–E1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Fushimi, K.; Hirose, T.; Haruna, T.; Tsuzuki, K. Predictors of the Need for Additional Postoperative Treatment for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis. ORL J. Otorhinolaryngol. Relat. Spec. 2025, 87, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Jimenez, D.; Moreno-Luna, R.; Gago-Torres, C.; Maza-Solano, J.; Sanchez-Gomez, S. Relevance of anatomical remnants for revision sinus surgery. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2025, 142, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, F.; Pace, G.M.; Giombi, F.; Heffler, E.; Paoletti, G.; Nappi, E.; Sanità, W.; Giulietti, G.; Giunta, G.; Ferreli, F.; et al. Outcomes of Non-Mucosa Sparing Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (Partial Reboot) in Refractory Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis: An Academic Hospital Experience. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 1584–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentati, F.; Kim, J.; Hoying, D.; D’Anza, B.; Rodriguez, K. Revision Rates and Symptom Trends Following Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: Impact of Race on Outcomes. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 2878–2884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes Orozco, F.; Gao, J.; Hur, K. Treatment decision-making among Asian Americans with chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2022, 12, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senior, B.A.; Ow, R.A.; Major, M.S.; Silvers, S.L.; Rosenbloom, J.S.; Luong, A.U.; Soler, Z.M.; Naclerio, R.; Kern, R.C.; Brayton, L.; et al. Evaluation of LYR-220 Mometasone Sinonasal Implants in Patients With Chronic Rhinosinusitis and Prior Ethmoid Surgery: Results From the Randomized, Blinded, Controlled BEACON Phase 2 Study. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2025, 15, e23567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Welch, K.; Kern, R. Mometasone furoate sinus implant—A new targeted approach to treating recurrent nasal polyp disease. Expert. Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshtasbi, K.; Abouzari, M.; Abiri, A.; Yasaka, T.; Sahyouni, R.; Bitner, B.; Tajudeen, B.A.; Kuan, E.C. Efficacy of steroid-eluting stents in management of chronic rhinosinusitis after endoscopic sinus surgery: Updated meta-analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavigne, F.; Miller, S.K.; Gould, A.R.; Lanier, B.J.; Romett, J.L. Steroid-eluting sinus implant for in-office treatment of recurrent nasal polyposis: A prospective, multicenter study. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolovitzky, J.P.; Kern, R.C.; Han, J.K.; Forwith, K.D.; Ow, R.A.; Wright, S.K.; Gould, A.; Matheny, K.E.; Karanfilov, B.; Huang, S.; et al. In-office Placement of Mometasone Furoate Sinus Implants for Recurrent Nasal Polyps: A Pooled Analysis. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2019, 33, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.K.; Forwith, K.D.; Smith, T.L.; Kern, R.C.; Brown, W.J.; Miller, S.K.; Ow, R.A.; Poetker, D.M.; Karanfilov, B.; Matheny, K.E.; et al. RESOLVE: A randomized, controlled, blinded study of bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus implants for in-office treatment of recurrent sinonasal polyposis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernst, F.R.; Imhoff, R.; Minshall, M.; DeConde, A.S.; Manes, R.P. Steroid-Eluting Sinus Implant Versus Revision Surgery for Patients with Recurrent Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSWNP): An Economic Evaluation Model. Value Health 2018, 21, S165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forwith, K.D.; Han, J.K.; Stolovitzky, J.P.; Yen, D.M.; Chandra, R.K.; Karanfilov, B.; Matheny, K.E.; Stambaugh, J.W.; Gawlicka, A.K. RESOLVE: Bioabsorbable steroid-eluting sinus implants for in-office treatment of recurrent sinonasal polyposis after sinus surgery: 6-month outcomes from a randomized, controlled, blinded study. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2016, 6, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, B.S.; Nelson, J.; Deng, X.; McKenzie, K.; Kallman, J.E. Equivalent healthcare resource use following either a long-acting steroid-eluting implant or repeat endoscopic surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis patients with nasal polyp recurrence: A real-world evidence study. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2025, 41, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Van Strahlen, C.; Arancibia, C.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I. Systematic Review of Long Term Sinonasal Outcomes in CRSwNP after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A call for Unified and Standardized Criteria and Terms. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024, 24, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Risk Factor/Description | |
|---|---|
| Patient Factors | Asthma and AERD are common and strong predictors for CRS recurrence [3,4,18,19,20,21] |
| Allergic rhinitis (AR), often combined with asthma, increases recurrence risk via mucosal edema and eosinophilia [18,22,23,24] | |
| Smoking increases risk, especially among asthmatic patients; also predicts postoperative inflammation [25,26,27,28,29] | |
| Environmental and occupational exposures (e.g., dust, chemicals) independently raise recurrence and revision surgery risk [31] | |
| Demographics: female sex and age (either younger or older, region-dependent) may influence recurrence risk [32,33,34,35,36] | |
| Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a strong predictor of revision, especially in Western cohorts [26] | |
| Metabolic comorbidities (obesity, metabolic syndrome, T2DM): higher BMI, MetS components, and T2DM linked to recurrence [28,37,38,39,40,41] | |
| Serum uric acid (hyperuricemia) identified as an independent risk biomarker for recurrence [22,42] | |
| Disease Characteristics | CRSwNP carries a higher recurrence risk than CRSsNP; pan-European study shows 3× higher revision with polyps [20,21,32,43] |
| Eosinophilic inflammation (tissue/blood eosinophilia, high ECP, high IgE, high IL-5) is a consistent predictor of relapse [1,4,44,45] | |
| Inflammatory endotype (type 2 inflammation, high IL-5/IL-13) is associated with more severe, recurrent disease [24,35,46,47,48,49,50] | |
| Non-type 2 or mixed inflammation (eosinophilic-neutrophilic) is more prevalent in Asian cohorts, with variable prognosis [8,11,51] | |
| Surgical Factors | Incomplete/opening of key sinuses and residual disease (missed cells, structures) increase recurrence risk [21,32,33,52,53,54] |
| Surgeon’s experience: high-volume surgeons have lower recurrence rates post-ESS [40,55] | |
| Insufficient postoperative management and inflammation control (poor healing, inadequate steroids) raise recurrence rates [7,22,47,48] | |
| High postoperative endoscopy scores (e.g., Lund-Mackay) within 3–6 months signal higher likelihood of relapse [7,9,57] |
| Model | Parameters | Highlights | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Predictors and Symptom-Based Models | Comorbidities: Asthma, allergic rhinitis, NSAID-exacerbated respiratory disease (NERD), previous surgery Symptom Trajectory: SNOT-22 change over 3–12 months Surgery Interval: Shorter interval between surgeries | Strong, consistent clinical predictors for recurrence and revision surgery Dynamic symptom tracking (e.g., SNOT-22) offers added prognostic value | Often region and tool- dependent; symptoms alone have moderate accuracy [7,30,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67] |
| Serologic & Immunologic Biomarkers | Peripheral eosinophil, basophil counts, ELR, NLR, serum ECP Cytokines: Interleukins (e.g., IL-5, IL-13), eotaxin, complement proteins Immune cell subsets: Regulatory T cells, innate lymphoid cells | Eosinophil counts (peripheral and tissue) reproducibly linked with recurrence Cytokines/immune markers refine endo- typing and risk assessment | Cut-offs not standardized; moderate predictive accuracy [48,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78] |
| Histologic Markers | Tissue eosinophilia (e.g., >55/HPF or ≥27%) Charcot-Leyden crystals IL-5, IL-13 expression, dense eosinophil/mast cell infiltration Eosinophilic mucin | Robust predictor in Asian cohorts Mast cell burden linked to early recurrence | Thresholds debated; invasive sampling often required [9,59,70,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
| Radiologic Predictors | Lund-Mackay CT score (LM) Ethmoid-to-maxillary opacification ratio Radiologic endotypes (e.g., CCAD, AFRS, AERD forms) | Higher LM/ethmoid dominance: poorer prognosis CCAD: lower recurrence despite ethmoid- predominance | Severity interpretation must consider disease endotype [85,86,87,88,89,90] |
| Microbiota | Staphylococcus aureus colonization Specific nasal/rectal microbial signatures | S. aureus carriage linked to higher recurrence risk Microbial diversity as possible risk modifier | Research emerging; not yet in routine use [91,92,93] |
| Integrated and Machine Learning (ML)-Based Models | Multivariable models combining: Symptoms (VAS, SNOT-22), radiology (LM), comorbidities, eosinophils, cytokines ML using miRNAs, cytokines, medication history | Superior predictive accuracy (e.g., >80%) Asia: logistic regression, nomograms Western: multivariable and ML models | No single biomarker suffices; integration improves accuracy [7,18,94,95] |
| Feature | Western Populations | Asian Populations | Clinical Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dominant Inflammatory Endotype | Predominantly type 2 (eosinophilic) inflammation | More heterogeneous; higher non-type 2 or mixed eosinophilic-neutrophilic | Endotype-driven treatment essential; differences affect biologic response and prediction models [5,6,24,46] |
| Asthma Prevalence | High, strong association with recurrence | High, especially in combination with allergic rhinitis | Asthma co-management improves outcomes; must be factored into risk models [18,24,35,40,46,47,48,50] |
| AERD Prevalence | Higher prevalence; linked to severe disease and >50% recurrence | Less frequently reported; role still relevant | Predicts severe, treatment-resistant CRS; influences surgery and biologic choice [3,21,47,94] |
| Recurrence Rates | 12–76.6%, often >30% in high-risk groups | 13.6–65.3%, most between 25–45% | Regional data must be interpreted in context of definitions and follow-up [11,12,13,14,15,16] |
| Risk Factors | Asthma, AERD, eosinophilia, CF, female sex, smoking | Tissue/blood eosinophils, uric acid, metabolic syndrome, BMI, younger age | Tailored risk stratification and monitoring required for comorbidities [3,18,20,22,28,37,39,40,41] |
| Predictive Models | Integrated models: radiologic scores, symptoms, history, biomarkers; ML-based models emerging | Emphasis on inflammatory biomarkers (e.g., eosinophils, IL-6/IL-8); logistic regression and nomograms | Region-specific models needed; integrated data improves prediction [7,8,18,94,95] |
| Biologic Use | Widely used; early integration with surgery and topical steroids | Limited use; reserved for type 2 patients due to cost/regulation | Access disparity impacts treatment outcomes and equity [5,6,25,101,115] |
| Surgical Revision Patterns | More frequent; Guide-lines support earlier revision for T2 inflammation | More conservative; lower revision rates and delayed intervention | Careful assessment of candidacy and timing critical; cultural/systemic constraints matter [20,55,105,106,107,115] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-S.; Feng, C.-Y.; Su, S.-H.; Wang, Y.-H.; Yang, T.-H.; Lin, C.-F. Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps After Surgery: Risk Factors, Predictive Models, and Treatment Approaches with a Focus on Western and Asian Differences. Medicina 2025, 61, 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091620
Chen Y-S, Feng C-Y, Su S-H, Wang Y-H, Yang T-H, Lin C-F. Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps After Surgery: Risk Factors, Predictive Models, and Treatment Approaches with a Focus on Western and Asian Differences. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091620
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Shyue, Chi-Yu Feng, Shih-Hao Su, Yu-Han Wang, Ting-Hua Yang, and Chih-Feng Lin. 2025. "Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps After Surgery: Risk Factors, Predictive Models, and Treatment Approaches with a Focus on Western and Asian Differences" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091620
APA StyleChen, Y.-S., Feng, C.-Y., Su, S.-H., Wang, Y.-H., Yang, T.-H., & Lin, C.-F. (2025). Recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps After Surgery: Risk Factors, Predictive Models, and Treatment Approaches with a Focus on Western and Asian Differences. Medicina, 61(9), 1620. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091620






