The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in (Advanced) Gastric Cancer—From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Impact
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria (PICOTS Framework)
- Population (P): Patients with gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
- Intervention (I): Studies evaluating Axl expression, signaling pathways, or therapeutic targeting of Axl (e.g., small-molecule inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, antibody–drug conjugates).
- Comparator (C): Non-tumor gastric tissue, Axl-negative cohorts, standard of care, or alternative targeted therapies (when applicable).
- Outcomes (O): Biological function of Axl in tumor progression, immune modulation, and drug resistance; prognostic or predictive biomarker value; efficacy and safety outcomes of Axl-targeting strategies.
- Timing (T): No restriction on follow-up duration.
- Setting (S): Preclinical (cell line, animal models) and clinical studies (retrospective/prospective cohorts, trials).
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction and Reviewer Agreement
2.5. Limitations of the Scoping Review
3. Axl’s Role in Gastric Cancer
3.1. Axl Structure and Ligands
3.2. Axl in Cancer Pathophysiology
3.3. Correlation with Clinical Outcomes
| Axl Status/Biomarker | Main Findings/Correlations | Clinical Implications | Relevant References |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Axl expression (IHC, ~30–50% of GC cases) | Associated with advanced pathological features: deeper invasion (T3–T4), lymphovascular and perineural invasion, lymph node metastasis, higher TNM stage (III–IV), poorly differentiated/diffuse histology, EMT phenotype (↑ mesenchymal markers, ↑ microvessel density). | Marker of aggressiveness, invasiveness, and metastatic potential. | [36,37,38] |
| High Axl expression (tumor tissue—survival data) | Kaplan–Meier analysis: significantly reduced overall survival (HR ~2.2, p < 0.001). Independent negative prognostic marker by multivariate Cox regression in TCGA cohort. | Prognostic biomarker for poor outcome. | [38,39] |
| Meta-analysis (25 studies, >3000 patients, including GC) | Axl overexpression correlated with worse OS (HR ≈ 2.03) and DFS (HR ≈ 1.85), and advanced TNM stage, LN involvement, distant metastasis. | Broadly supports Axl as a pan-cancer poor prognostic factor, validated in GC. | [40] |
| Soluble Axl (sAxl, serum) | Elevated levels linked to tumor burden, vascular invasion, poor survival, and treatment response in HCC, melanoma, PDAC. Not yet validated in GC, but mechanistically plausible. | Promising non-invasive biomarker for real-time disease monitoring in GC (prospective validation needed). | [41,42,43] |
4. Therapeutic Targeting of Axl in Gastric Cancer
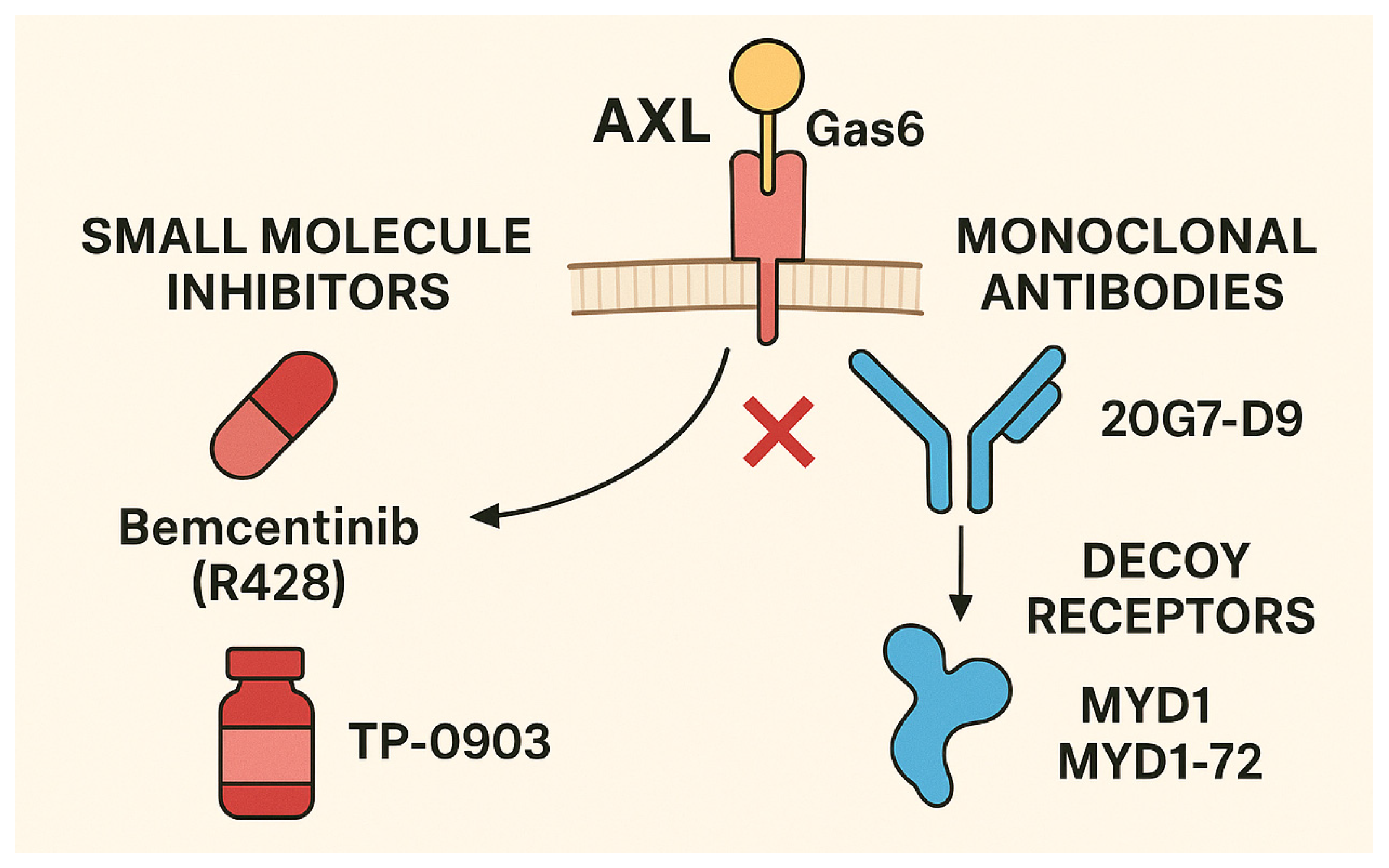
4.1. Axl Inhibitors in Development
4.2. Preclinical Evidence in Gastric Cancer
4.3. Clinical Trials
4.4. Combination Strategies
5. Axl, Tumor Microenvironment, and Therapeutic Implications
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Machlowska, J.; Baj, J.; Sitarz, M.; Maciejewski, R.; Sitarz, R. Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Genomic Characteristics and Treatment Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-J.; Zhao, H.-P.; Yu, Y.; Wang, J.-H.; Guo, L.; Liu, J.-Y.; Pu, J.; Lv, J. Updates on global epidemiology, risk and prognostic factors of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 29, 2452–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wonglhow, J.; Tantipisit, J.; Wetwittayakhlang, P.; Sunpaweravong, P.; Sathitruangsak, C.; Kanjanapradit, K.; Thongwatchara, P.; Dechaphunkul, A. Association Between Epstein-Barr Virus Infection and PD-L1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: Prevalence, Clinicopathological Features, and Prognostic Implications. Cancers 2025, 17, 1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Ruiz-García, E.; Alsina, M.; Ruiz-Pace, F.; Schooten, T.G.-V.; Martínez-Ciarpaglini, C.; Fernández-Figueroa, E.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Díaz-Romero, C.; Lino-Silva, L.; et al. Integrated clinico-molecular analysis of gastric cancer in European and Latin American populations: LEGACY project. ESMO Open 2025, 10, 104482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, Y.-S.; Na, D.; Lee, J.-S.; Chae, J.; Kim, E.; Jang, G.; Lee, J.; Min, J.; Ock, C.-Y.; Kong, S.-H.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Adenocarcinoma of the Gastroesophageal Junction Between Esophageal and Gastric Adenocarcinomas. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 706–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Bi, X.-W.; Zhao, J.-L.; Shi, Y.-X.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, L.-H.; Zhang, A.-Q.; Huang, H.; et al. Trastuzumab Plus Endocrine Therapy or Chemotherapy as First-line Treatment for Patients with Hormone Receptor-Positive and HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer (SYSUCC-002). Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Y. Receptor tyrosine kinases: Biological functions and anticancer targeted therapy. MedComm 2023, 4, e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Nagamura, Y.; Miyazaki, M. Receptor Tyrosine Kinases Amplified in Diffuse-Type Gastric Carcinoma: Potential Targeted Therapies and Novel Downstream Effectors. Cancers 2022, 14, 3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Shen, D.; Yin, X.; Gavine, P.; Zhang, T.; Su, X.; Zhan, P.; Xu, Y.; Lv, J.; Qian, J.; et al. HER2, MET and FGFR2 oncogenic driver alterations define distinct molecular segments for targeted therapies in gastric carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wium, M.; Ajayi-Smith, A.F.; Paccez, J.D.; Zerbini, L.F. The Role of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in Carcinogenesis and Development of Therapeutic Resistance: An Overview of Molecular Mechanisms and Future Applications. Cancers 2021, 13, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelsen, A.S.T.; Lotsberg, M.L.; Khouzam, R.A.; Thiery, J.-P.; Lorens, J.B.; Chouaib, S.; Terry, S. Dissecting the Role of AXL in Cancer Immune Escape and Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Sharma, A.; Patne, K.; Tabasum, S.; Suryavanshi, J.; Rawat, L.; Machaalani, M.; Eid, M.; Singh, R.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; et al. AXL signaling in cancer: From molecular insights to targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repici, A.; Ardizzone, A.; De Luca, F.; Colarossi, L.; Prestifilippo, A.; Pizzino, G.; Paterniti, I.; Esposito, E.; Capra, A.P. Signaling Pathways of AXL Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Contribute to the Pathogenetic Mechanisms of Glioblastoma. Cells 2024, 13, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zang, H.; Wen, Q.; Fan, S. AXL in cancer: A modulator of drug resistance and therapeutic target. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, T.; Knyazev, P.G.; Clout, N.J.; Cheburkin, Y.; Göhring, W.; Ullrich, A.; Timpl, R.; Hohenester, E. Structural basis for Gas6-Axl signalling. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Pu, D.; Wang, R.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, N.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Li, L. Gas6/AXL pathway: Immunological landscape and therapeutic potential. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1121130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apostolo, D.; D’onghia, D.; Nerviani, A.; Ghirardi, G.M.; Sola, D.; Perazzi, M.; Tonello, S.; Colangelo, D.; Sainaghi, P.P.; Bellan, M. Could Gas6/TAM Axis Provide Valuable Insights into the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis? Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 7486–7504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemke, G. Phosphatidylserine Is the Signal for TAM Receptors and Their Ligands. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Bosch, N.; Cristóbal, H.; Iglesias, M.; Gironella, M.; Barranco, L.; Visa, L.; Calafato, D.; Jiménez-Parrado, S.; Earl, J.; Carrato, A.; et al. Soluble AXL is a novel blood marker for early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and differential diagnosis from chronic pancreatitis. EBioMedicine 2022, 75, 103797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, G.; Bahia, D.M.; Lee, M.L.M.; de Souza, M.P.; Kimura, E.Y.S.; Rezende, D.C.; Silva, M.C.d.A.; Chauffaille, M.d.L.L.F.; Yamamoto, M. MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways are activated in adolescent and adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Rep. 2023, 6, e1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-W.; Lee, J.M.; Park, S.W. Divergent roles of the regulatory subunits of class IA PI3K. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 14, 1152579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaltriti, M.; Elkabets, M.; Baselga, J. Molecular Pathways: AXL, a Membrane Receptor Mediator of Resistance to Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Dou, Y.; He, Y. AXL: Shapers of tumor progression and immunosuppressive microenvironments. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, Y.-S.; Shin, S.; An, H.-G.; Kwon, T.-U.; Baek, H.-S.; Kwon, Y.-J.; Chun, Y.-J. Synergistic Induction of Apoptosis by the Combination of an Axl Inhibitor and Auranofin in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Biomol Ther 2020, 28, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.-N.; Chen, M.; DeArmond, D.T.; Chiu, C.H.-L.; Limboy, C.A.; Tan, X.; Kusi, M.; Chou, C.-W.; Lin, L.-L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. AXL-initiated paracrine activation of pSTAT3 enhances mesenchymal and vasculogenic supportive features of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiedu, M.K.; Beauchamp-Perez, F.D.; Ingle, J.N.; Behrens, M.D.; Radisky, D.C.; Knutson, K.L. AXL induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and regulates the function of breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Gu, L.-N.; Shan, B.-E.; Geng, C.-Z.; Sang, M.-X. Biomarkers for EMT and MET in breast cancer: An update. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4869–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Yan, Y.; Song, B.; Zhu, S.; Mei, Q.; Wu, K. Focal adhesion kinase: From biological functions to therapeutic strategies. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Axl signaling is an important mediator of tumor angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 2887–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperb, N.; Tsesmelis, M.; Wirth, T. Crosstalk between Tumor and Stromal Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Chen, M.; Nie, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yiu, A.; Chen, H.; Xu, N.; Huang, M.; Ye, K.; et al. In vitro and in vivo antiangiogenic activity of desacetylvinblastine monohydrazide through inhibition of VEGFR2 and Axl pathways. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 843–858, Erratum in Am. J. Cancer Res. 2023, 13, 352–354. [Google Scholar]
- Rosell, R.; Karachaliou, N.; Morales-Espinosa, D.; Costa, C.; Molina, M.A.; Sansano, I.; Gasco, A.; Viteri, S.; Massuti, B.; Wei, J.; et al. Adaptive resistance to targeted therapies in cancer. Transl. Lung. Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam-Artigues, A.; Arenas, E.J.; Martínez-Sabadell, A.; Brasó-Maristany, F.; Cervera, R.; Tormo, E.; Hernando, C.; Martínez, M.T.; Carbonell-Asins, J.; Simón, S.; et al. Targeting HER2-AXL heterodimerization to overcome resistance to HER2 blockade in breast cancer. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabk2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidkovka, N.; Belkhiri, A. Altered expression of AXL receptor tyrosine kinase in gastrointestinal cancers: A promising therapeutic target. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1079041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, H.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Huang, C.-Y.; Chu, S.-E.; Liang, Y.-J.; Sun, J.-T.; Chen, Y.-L. Association Between Phosphorylated AXL Expression and Survival in Patients with Gastric Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Kong, Q.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y. Integrated analysis of myeloperoxidase in gastric health and cancer: Associations with pepsinogen levels, immune regulation, and prognosis in a large healthy population-based and TCGA cohorts. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1590257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, X.S.; Yang, J.X.; Guo, J.H.; Chao, T.F.; Tong, Y. The prognostic role of Gas6/Axl axis in solid malignancies: A meta-analysis and literature review. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichl, P.; Mikulits, W. Accuracy of serum Axl as a biomarker for early and advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Flem-Karlsen, K.; McFadden, E.; Ann Flørenes, V.; Davidson, B. Soluble AXL is a marker of disease progression and prognosis in malignant melanoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Bosch, N.; Cristóbal, H.; Iglesias, M.; Gironella, M.; Barranco, L.; Visa, L.; Calafato, D.; Jiménez-Parrado, S.; Earl, J.; Carrato, A.; et al. Soluble AXL as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic cancer: Improving the performance of CA 19–9. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 885–901. [Google Scholar]
- Kimani, S.G.; Kumar, S.; Bansal, N.; Singh, K.; Kholodovych, V.; Comollo, T.; Peng, Y.; Kotenko, S.V.; Sarafianos, S.G.; Bertino, J.R.; et al. Small molecule inhibitors block Gas6-inducible TAM activation and tumorigenicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, S.J.; Pan, A.; Franci, C.; Hu, Y.; Chang, B.; Li, W.; Duan, M.; Torneros, A.; Yu, J.; Heckrodt, T.J.; et al. R428, a selective small molecule inhibitor of Axl kinase, blocks tumor spread and prolongs survival in models of metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1544–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Song, Q.; Yu, Q. Axl inhibitor R428 induces apoptosis of cancer cells by blocking lysosomal acidification and recycling independent of Axl inhibition. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1466–1482. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, T.; Yin, X.; Ma, X. Therapeutic progress and challenges for triple negative breast cancer: Targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubasch, A.S.; Peterlin, P.; Cluzeau, T.; Götze, K.S.; Sockel, K.; Teipel, R.; Jentzsch, M.; Attalah, H.; Sebert, M.; Chermat, F.; et al. Efficacy and safety of bemcentinib in patients with advanced myelodysplastic neoplasms or acute myeloid leukemia failing hypomethylating agents- the EMSCO phase II BERGAMO trial. Leukemia 2023, 37, 2309–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Arner, E.N.; Rizvi, A.; Toombs, J.E.; Huang, H.; Warner, S.L.; Foulks, J.M.; Brekken, R.A. AXL Inhibitor TP-0903 Reduces Metastasis and Therapy Resistance in Pancreatic Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakemura, R.L.; Hefazi, M.; Cox, M.J.; Siegler, E.L.; Sinha, S.; Hansen, M.J.; Stewart, C.M.; Feigin, J.M.; Roman, C.M.; Schick, K.J.; et al. AXL Inhibition Improves the Antitumor Activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 1222–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, X.; Koul, S.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.; Halmos, B. AXL kinase as a novel target for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9546–9563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconet, W.; Chentouf, M.; du Manoir, S.; Chevalier, C.; Sirvent, A.; Aït-Arsa, I.; Busson, M.; Jarlier, M.; Radosevic-Robin, N.; Theillet, C.; et al. Therapeutic Activity of Anti-AXL Antibody against Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts and Metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2806–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Xing, C.; Chen, J.; Frey, G.; Boyle, W.J.; Short, J.M. Preclinical development of mecbotamab vedotin (BA3011), a novel, AXL-specific conditional active biologic antibody-drug conjugate. Antib. Ther. 2025, 8, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshuizen, J.; Koopman, L.A.; Krijgsman, O.; Shahrabi, A.; van den Heuvel, E.G.; A Ligtenberg, M.A.; Vredevoogd, D.W.; Kemper, K.; Kuilman, T.; Song, J.-Y.; et al. Cooperative targeting of melanoma heterogeneity with an AXL antibody-drug conjugate and BRAF/MEK inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Siemann, D.W. Therapeutic Targeting of the Gas6/Axl Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariolis, M.S.; Miao, Y.R.; Diep, A.; Nash, S.E.; Olcina, M.M.; Jiang, D.; Jones, D.S., 2nd; Kapur, S.; Mathews, I.I.; Koong, A.C.; et al. Inhibition of the GAS6/AXL pathway augments the efficacy of chemotherapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuh, K.C.; Bookman, M.A.; Liu, J.F.; Coleman, R.L.; Herzog, T.J.; Thaker, P.H.; Monk, B.J.; Anderson, R.; McIntyre, G.; Rangwala, R.; et al. Phase 1b study of AVB-500 in combination with paclitaxel or pegylated liposomal doxorubicin platinum-resistant recurrent ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 163, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, C.A.; Ham, I.-H.; Oh, H.J.; Lee, D.; Woo, J.; Son, S.-Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Lorens, J.B.; Brekken, R.A.; Kim, T.-M.; et al. Inhibiting the GAS6/AXL axis suppresses tumor progression by blocking the interaction between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells in gastric carcinoma. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Shi, H.; Wu, M.; Wei, X. A dual MET/AXL small-molecule inhibitor exerts efficacy against gastric carcinoma through killing cancer cells as well as modulating tumor microenvironment. MedComm 2020, 1, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Song, J.; Kwok, T.; Nguyen, E.V.; Shen, X.; Daly, R.J. Proteome-based molecular subtyping and therapeutic target prediction in gastric cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2024, 18, 1437–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-X.; Liu, F.-R.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Z.-Q.; Liu, Q.-W.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Y.-P.; Fang, W.-F.; Xi, N.; et al. Preclinical characterization and phase I clinical trial of CT053PTSA targets MET, AXL, and VEGFR2 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1024755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.Y.; Jeong, H.K. Immune Evasion Mechanism and AXL. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 756225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, X.H.; Sundararajan, V.; Wu, Z.; Phua, Z.J.C.; Ho, Y.Y.; Peh, K.L.E.; Chiu, Y.C.; Tan, T.Z.; Kappei, D.; Ho, Y.S.; et al. The effect of inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase AXL on DNA damage response in ovarian cancer. Commun Biol. 2023, 6, 660, Erratum in Commun Biol. 2023, 6, 759. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-023-05139-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandewalle, N.; De Beule, N.; De Becker, A.; De Bruyne, E.; Menu, E.; Vanderkerken, K.; Breckpot, K.; Devoogdt, N.; De Veirman, K. AXL as immune regulator and therapeutic target in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: From current progress to novel strategies. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadahiro, H.; Kang, K.D.; Gibson, J.T.; Minata, M.; Yu, H.; Shi, J.; Chhipa, R.; Chen, Z.; Lu, S.; Simoni, Y.; et al. Activation of the Receptor Tyrosine Kinase AXL regulates the Immune Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3002–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, D.K.; Synn, C.-B.; Lee, H.K.; Park, S.; Jung, D.-S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Byeon, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; et al. Incorporation of SKI-G-801, a Novel AXL Inhibitor, With Anti-PD-1 Plus Chemotherapy Improves Anti-Tumor Activity and Survival by Enhancing T Cell Immunity. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 821391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayford, A.; Gärtner, F.; Ramnefjell, M.P.; Lorens, J.B.; Micklem, D.R.; Aanerud, M.; Engelsen, A.S.T. AXL expression reflects tumor-immune cell dynamics impacting outcome in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitor monotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1444007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, F.Z.; Della Corte, C.M.; Ciaramella, V.; Erra, S.; Ronchi, A.; Fiorelli, A.; Vicidomini, G.; Santini, M.; Scognamiglio, G.; Morgillo, F.; et al. AXL and MET Tyrosine Kinase Receptors Co-Expression as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xiong, X.; Abdalla, A.; Alejo, S.; Zhu, L.; Lu, F.; Sun, H. HGF-induced formation of the MET-AXL-ELMO2-DOCK180 complex promotes RAC1 activation, receptor clustering, and cancer cell migration and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 15397–15418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.S.; Miller, M.A.; Gertler, F.B.; Lauffenburger, D.A. The receptor AXL diversifies EGFR signaling and limits the response to EGFR-targeted inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auyez, A.; Sayan, A.E.; Kriajevska, M.; Tulchinsky, E. AXL Receptor in Cancer Metastasis and Drug Resistance: When Normal Functions Go Askew. Cancers 2021, 13, 4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Hammes, S.R. AXL cooperates with EGFR to mediate neutrophil elastase-induced migration of prostate cancer cells. iScience 2021, 24, 103270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanzaki, R.; Naito, H.; Kise, K.; Takara, K.; Eino, D.; Minami, M.; Shintani, Y.; Funaki, S.; Kawamura, T.; Kimura, T.; et al. Gas6 derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes migration of Axl-expressing lung cancer cells during chemotherapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, K.; Yu, J.; Sun, E. A retrospective analysis of the correlation between AXL expression and clinical outcomes of patients with urothelial bladder carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iweala, E.E.J.; Amuji, D.N.; Oluwajembola, A.M.; Ugbogu, E.A. Targeting c-Met in breast cancer: From mechanisms of chemoresistance to novel therapeutic strategies. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2024, 7, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
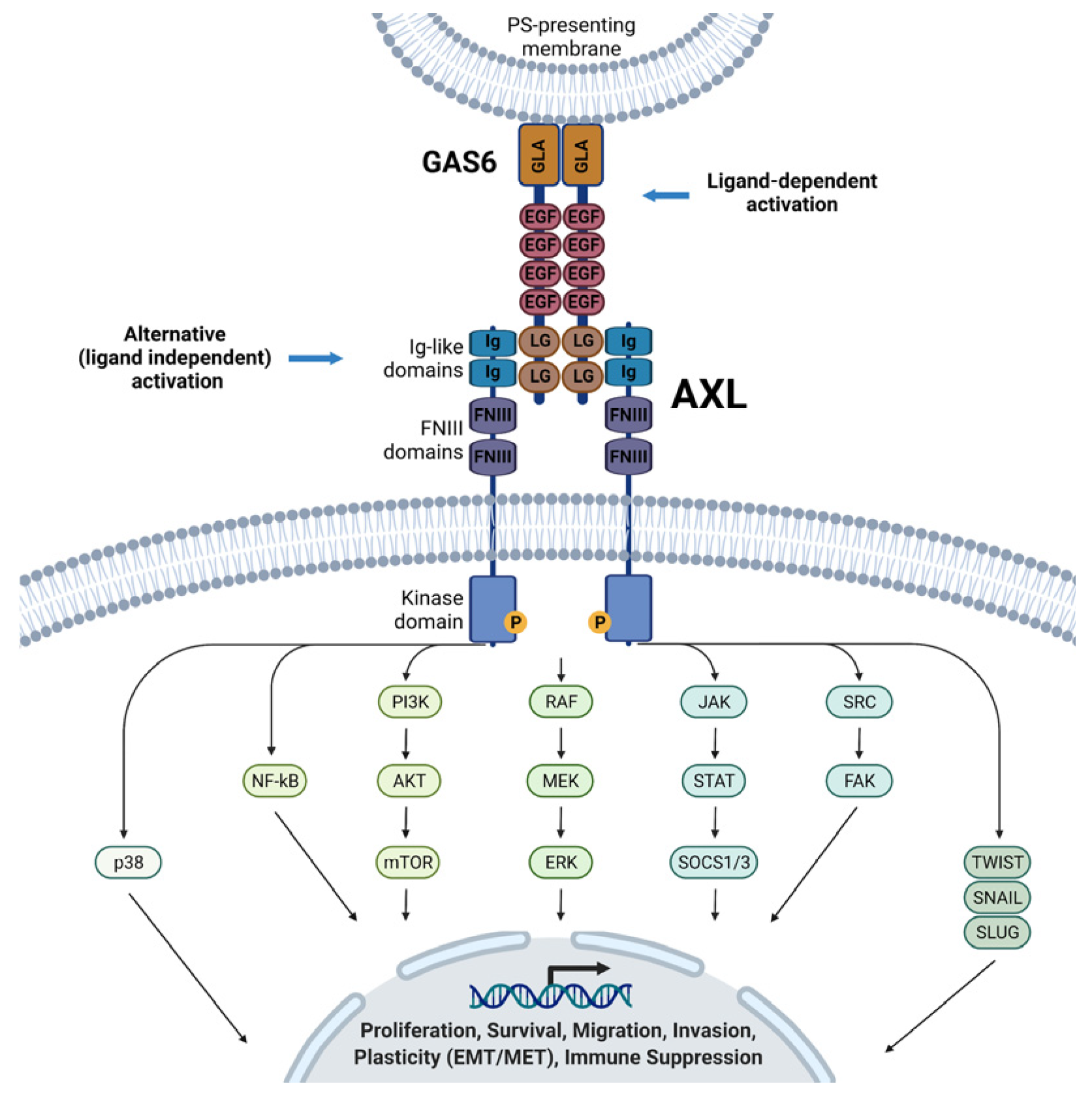
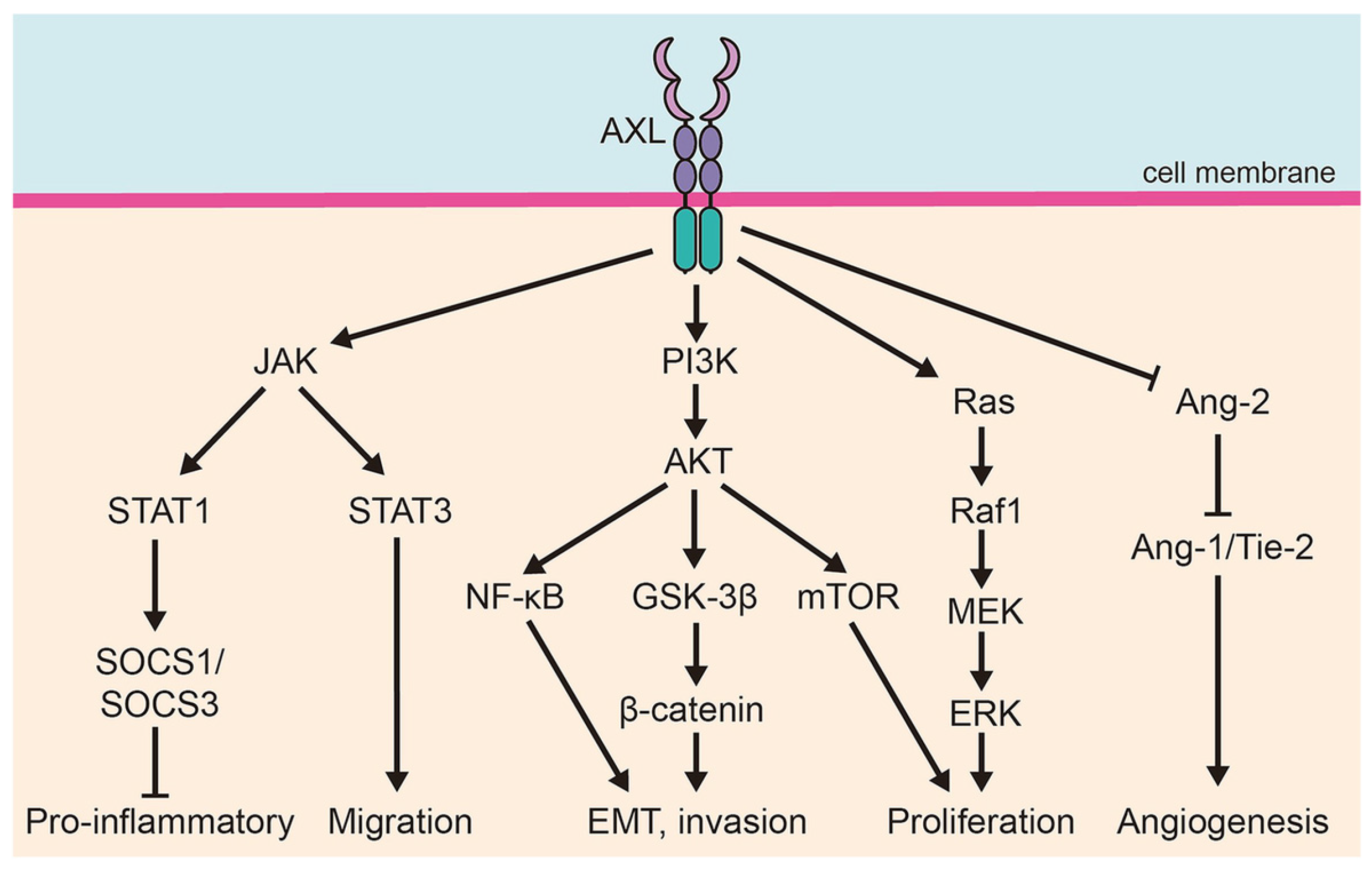
| Biological Process | Mechanism of Axl Involvement | Related Pathways | Potential Implications in GC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell proliferation and survival | Activation of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways via recruitment of p85 and Grb2 | PI3K, AKT, MAPK, ERK | Promotes cell cycle progression, inhibits apoptosis, supports tumor growth |
| Apoptosis resistance | Upregulates anti-apoptotic proteins (e.g., BCL-2, Cyclin D1), downregulates pro-apoptotic proteins (e.g., BAX) | AKT, STAT3 | Confers resistance to cisplatin and other chemotherapies |
| Migration and invasion (EMT) | Induction of EMT transcription factors (Snail, Twist); modulation of cell adhesion and cytoskeletal dynamics | Vimentin, N-cadherin, E-cadherin, Rac1, RhoA, FAK | Enhances metastatic potential and invasiveness |
| Angiogenesis | Induces pro-angiogenic cytokines (e.g., VEGF, IL-8); enhances crosstalk with endothelial cells | VEGF, IL-8, pericyte interactions | Supports tumor vascularization and growth |
| Therapeutic resistance | Upregulation after treatment; heterodimerization with HER2, MET, FGFR2 sustains survival signaling despite therapy | PI3K/AKT, MAPK, HER2, MET, FGFR2 | Resistance to trastuzumab, TKIs, and chemotherapy; associated with poor outcomes |
| Study | Design/Approach | Most Relevant Conclusions | Potential Therapeutic/Translational Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bae et al., 2020 [57] | GC cell lines + CAF co-culture; Axl inhibition (genetic, BGB324); patient tissue analysis | CAF-derived GAS6 activates Axl → ↑ migration, survival, EMT; Axl inhibition reverses effects; P-Axl correlates with poor prognosis | Supports Axl inhibition (e.g., BGB324) as a strategy to target CAF-driven aggressiveness in GC |
| Zhu et al., LY2801653 study [58] | Dual Axl/MET inhibitor in GC cell lines and xenografts | Inhibits proliferation, migration, EMT; induces apoptosis; decreased tumor growth in high MET/AXL models; decreased angiogenesis and M2 TAMs | Dual MET/AXL inhibition may benefit Axl+/MET+ GC; reduces tumor microenvironment support |
| R428 + chemotherapy (cross-cancer data) [45] | Breast/lung cancer models; extrapolated to GC | Axl inhibition prevents AKT/STAT3 activation by chemotherapy; enhances cisplatin efficacy and delays metastasis | Supports combining Axl inhibitors with standard chemotherapy in GC to overcome drug resistance |
| Hu et al., 2024 (Phosphoproteomics) [59] | MS-based analysis of GC cell lines and subtypes | Identifies EMT and metabolism subtypes; Axl activity enriched in EMT subtype; subtype-specific kinase vulnerabilities | Axl inhibitors may be especially effective in mesenchymal/EMT-enriched GC subtypes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schreiner, O.D.; Schreiner, T.G.; Miron, L.; Ciobanu, R.C. The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in (Advanced) Gastric Cancer—From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Impact. Medicina 2025, 61, 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091619
Schreiner OD, Schreiner TG, Miron L, Ciobanu RC. The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in (Advanced) Gastric Cancer—From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Impact. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091619
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchreiner, Oliver Daniel, Thomas Gabriel Schreiner, Lucian Miron, and Romeo Cristian Ciobanu. 2025. "The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in (Advanced) Gastric Cancer—From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Impact" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091619
APA StyleSchreiner, O. D., Schreiner, T. G., Miron, L., & Ciobanu, R. C. (2025). The Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Axl in (Advanced) Gastric Cancer—From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Impact. Medicina, 61(9), 1619. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091619






