Airway Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Review of Microbial Shifts and Therapeutic Impacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
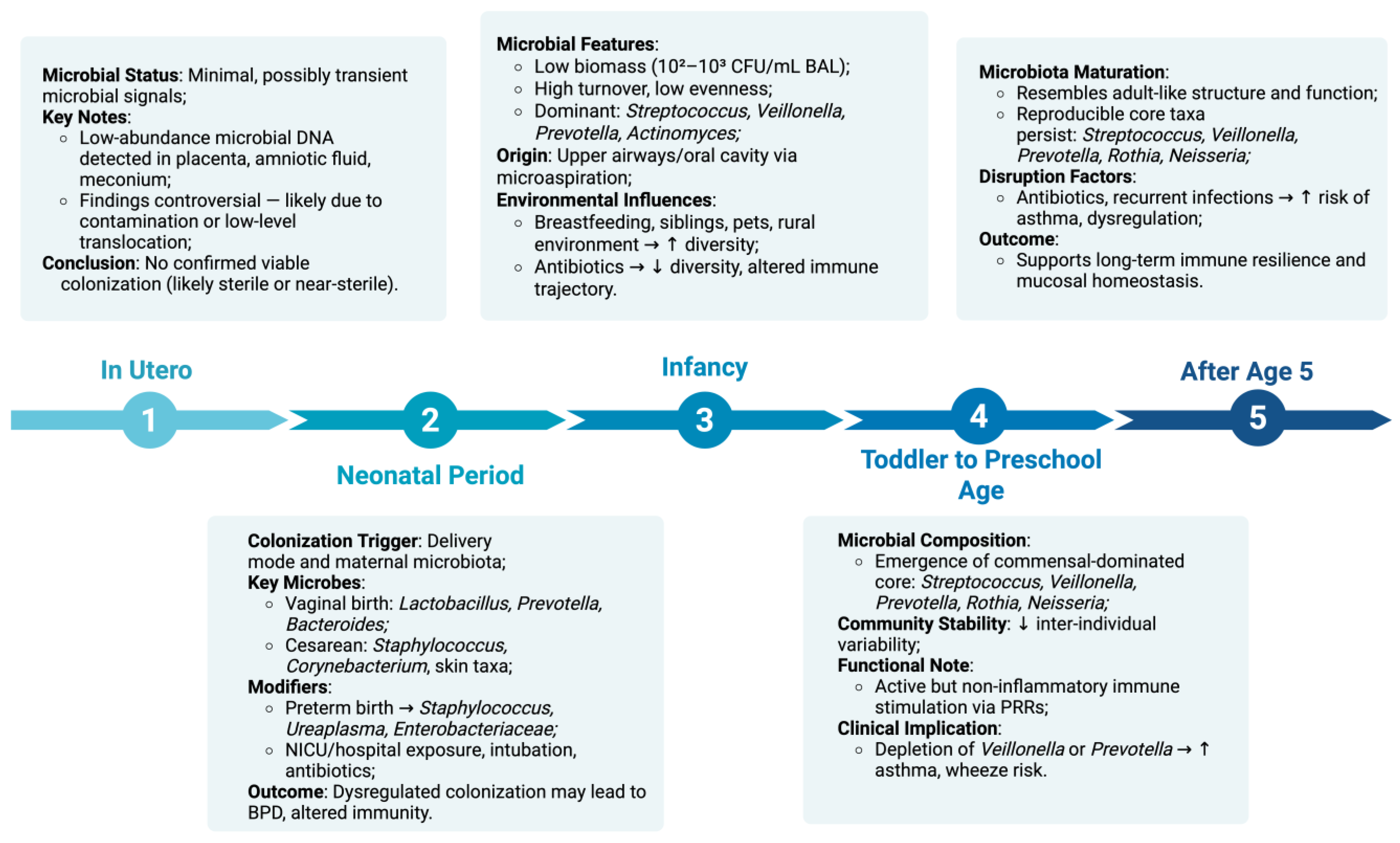
2. The Healthy Pediatric Lung Microbiome
2.1. In Utero Controversy and Initial Colonization
2.2. Neonatal Period
2.3. Infancy (0–12 Months)
2.4. Toddler to Preschool Age (1–5 Years)
2.5. After Age 5
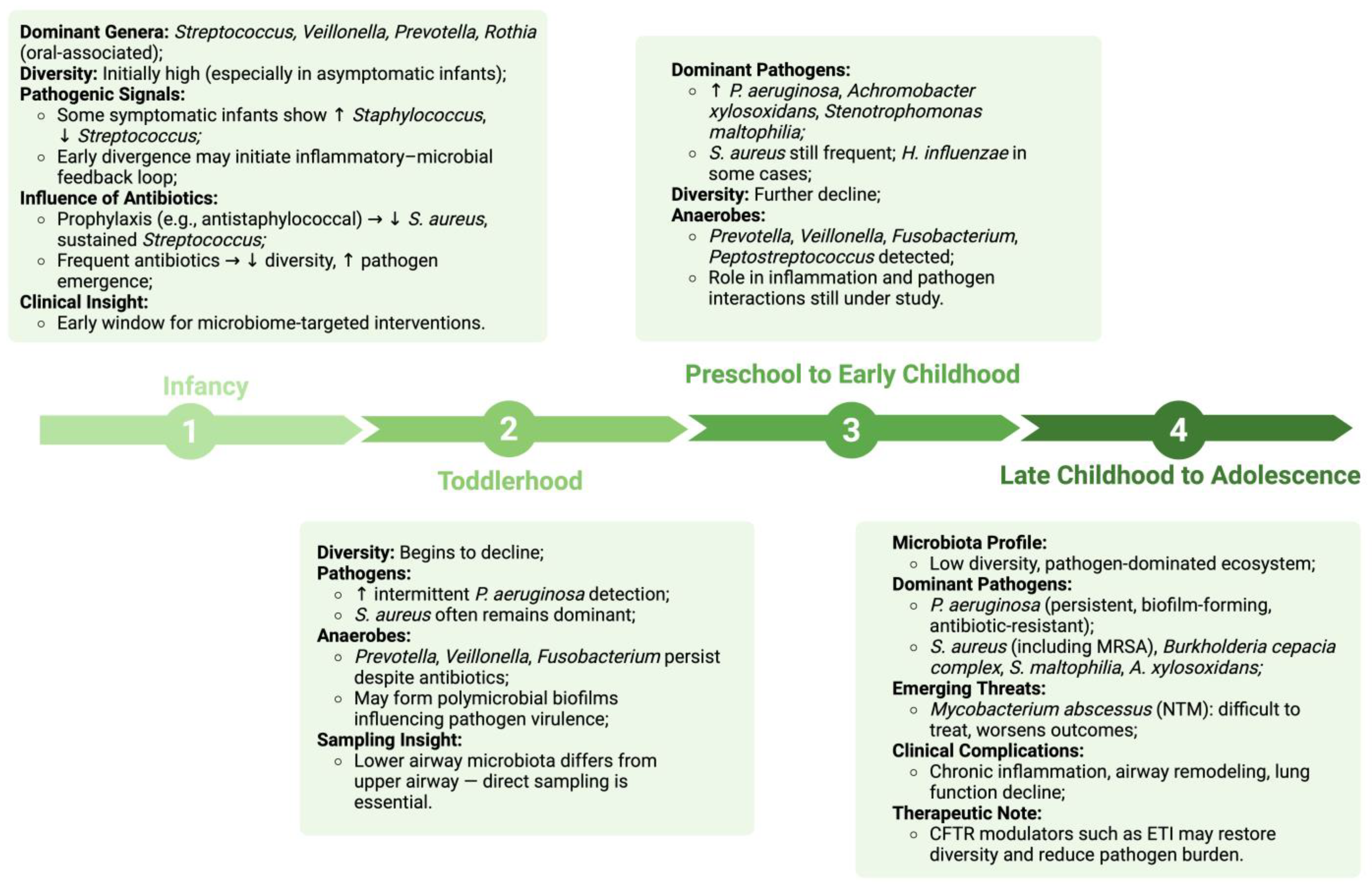
3. Microbial Composition and Successional Shifts in the Pediatric CF Lung Microbiome
3.1. Early Colonization Patterns in Cystic Fibrosis
3.2. Microbial Succession and Age-Related Shifts in Children with Cystic Fibrosis
3.2.1. Infancy (0–12 Months)
3.2.2. Toddlerhood (1–3 Years)
3.2.3. Preschool to Early Childhood (3–6 Years)
3.2.4. Late Childhood to Adolescence (7–18 Years)
3.3. Pathogenic Microbes in Pediatric CF Lungs
3.3.1. Staphylococcus aureus
3.3.2. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3.3.3. Haemophilus influenzae
3.3.4. Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
3.3.5. Burkholderia cepacia Complex
3.3.6. Achromobacter spp
3.3.7. Mycobacterium abscessus
3.4. Anaerobes
4. Influence of Therapeutic Interventions on the Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Lung Microbiome
4.1. CFTR Modulators and Their Influence on Lung Microbiome and Infection Patterns
- Potentiators—such as ivacaftor, which enhance the gating function of CFTR channels already present at the cell surface, allowing chloride ions to flow more effectively.
- Correctors—including lumacaftor, tezacaftor, and elexacaftor, which assist in proper protein folding and facilitate trafficking of CFTR to the apical membrane.
- Amplifiers–like nesolicaftor, currently in experimental stages, which aim to increase the overall production of CFTR protein by boosting gene expression [118].
- Read-through agents—exemplified by ataluren (PTC124), are developed for Class I CFTR mutations caused by premature stop codons. These agents facilitate the ribosome’s ability to bypass the stop signal, enabling synthesis of a full-length CFTR protein. Laboratory studies have demonstrated partial recovery of channel activity, yet large clinical trials have shown inconsistent clinical benefits, with modest improvements in chloride transport but no sustained gains in lung function or exacerbation reduction. Current research is exploring their use in combination with other modulator classes to enhance therapeutic outcomes [119,120,121].
- Stabilizers—experimental compounds designed to increase the persistence of CFTR protein at the apical cell surface, reducing its premature internalization and degradation. This approach is particularly suited for mutations where functional CFTR reaches the membrane but exhibits reduced stability. Although none have received regulatory approval, preclinical evidence indicates that combining stabilizers with correctors and potentiators may prolong CFTR activity and improve long-term channel function [119,120,121].
4.2. Antibiotic Interventions and Their Influence on the Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Lung Microbiome
Antibiotic Treatment and Extra-Intestinal Consequences
4.3. Probiotics and Their Potential Role in Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis Management
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CF | Cystic fibrosis |
| CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| BAL | Bronchoalveolar lavage |
| BPD | Bronchopulmonary dysplasia |
| NICU | Neonatal intensive care unit |
| PRRs | Pattern recognition receptors |
| NTM | Non-tuberculous mycobacterium |
| MRSA | Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus |
| rhDNase | Recombinant human deoxyribonuclease |
| PLV | Panton-Valentin leucocidin |
| ACME | Arginine catabolic mobile element |
| Agr | Accessory gene regulator |
| SarA | Staphylococcal accessory regulator |
| SigB | Alternative sigma factor B |
| SCVs | Small colony variants |
| CRMS | CFTR—related metabolic syndrome |
| ETI | Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor |
| BCC | Burkholderia cepacia Complex |
| Mabs | Mycobacterium abscessus |
| DCCs | Dominant circulating clones |
| MAC | Mycobacterium avium complex |
| SCFAsGPR41 | Short-chain fatty acids G-protein coupled receptor 41 |
| ER | Endoplasmatic reticulum |
| TDM | Therapeutic drug monitoring |
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
| LGG | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG |
References
- Polgreen, P.M.; Comellas, A.P. Clinical Phenotypes of Cystic Fibrosis Carriers. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Garratt, A.; Hill, A. Worldwide Rates of Diagnosis and Effective Treatment for Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotet, V.; Gutierrez, H.; Farrell, P.M. Newborn Screening for CF across the Globe—Where Is It Worthwhile? Int. J. Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Valdez, J.A.; Aguilar-Alonso, L.A.; Gándara-Quezada, V.; Ruiz-Rico, G.E.; Ávila-Soledad, J.M.; Reyes, A.A.; Pedroza-Jiménez, F.D. Cystic fibrosis: Current concepts. Boletin Medico Hosp. Infant. Mex. 2021, 78, 6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco, L.; Chávez, M.; Saldaña, Y.; Velázquez, R.; Carnevale, A.; González–del Ángel, A.; Jiménez, S. Fibrosis quística: La frontera del conocimiento molecular y sus aplicaciones clínicas. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2006, 58, 139–152. [Google Scholar]
- Rafeeq, M.M.; Murad, H.A.S. Cystic Fibrosis: Current Therapeutic Targets and Future Approaches. J. Transl. Med. 2017, 15, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naehrig, S.; Chao, C.-M.; Naehrlich, L. Cystic Fibrosis. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2017, 114, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, B.; Dalpke, A.H.; Boutin, S. Changes in the Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiome in Response to CFTR Modulator Therapy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 548613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittman, J.E.; Wylie, K.M.; Akers, K.; Storch, G.A.; Hatch, J.; Quante, J.; Frayman, K.B.; Clarke, N.; Davis, M.; Stick, S.M.; et al. Association of Antibiotics, Airway Microbiome, and Inflammation in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2017, 14, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnane, B.; Walsh, A.M.; Walsh, C.J.; Crispie, F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Cotter, P.D.; McDermott, M.; Renwick, J.; McNally, P. The Lung Microbiome in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Prospective Cohort Study. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frayman, K.B.; Wylie, K.M.; Armstrong, D.S.; Carzino, R.; Davis, S.D.; Ferkol, T.W.; Grimwood, K.; Storch, G.A.; Ranganathan, S.C. Differences in the Lower Airway Microbiota of Infants with and without Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2019, 18, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltz, D.A.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Welsh, M.J. Origins of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, S.C.; Hall, G.L.; Sly, P.D.; Stick, S.M.; Douglas, T.A. Early Lung Disease in Infants and Preschool Children with Cystic Fibrosis. What Have We Learned and What Should We Do about It? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanick, E.T.; Wagner, B.D.; Robertson, C.E.; Ahrens, R.C.; Chmiel, J.F.; Clancy, J.P.; Gibson, R.L.; Harris, W.T.; Kurland, G.; Laguna, T.A.; et al. Airway Microbiota across Age and Disease Spectrum in Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Cox, M.J.; Cuthbertson, L.; James, P.; Cookson, W.O.C.; Davies, J.C.; Moffatt, M.F.; Bush, A. Longitudinal Development of the Airway Microbiota in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, S.; Gerasimidis, K.; Milling, S.; Dicker, A.; Hansen, R.; Langley, R. The Lower Airway Microbiome in Paediatric Health and Chronic Disease. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2024, 52, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, M.I.; Graeber, S.Y.; Stahl, M.; Sommerburg, O.; Mall, M.A.; Dalpke, A.H.; Boutin, S. A Volatile and Dynamic Longitudinal Microbiome Is Associated with Less Reduction in Lung Function in Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 763121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, R.P.; Erb-Downward, J.R.; Huffnagle, G.B. The Role of the Bacterial Microbiome in Lung Disease. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2013, 7, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, W.H.; De Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.A.; Bogaert, D. The Microbiota of the Respiratory Tract: Gatekeeper to Respiratory Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilty, M.; Burke, C.; Pedro, H.; Cardenas, P.; Bush, A.; Bossley, C.; Davies, J.; Ervine, A.; Poulter, L.; Pachter, L.; et al. Disordered Microbial Communities in Asthmatic Airways. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dwyer, D.N.; Dickson, R.P.; Moore, B.B. The Lung Microbiome, Immunity, and the Pathogenesis of Chronic Lung Disease. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4839–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.N.; Clemente, J.C.; Tsay, J.-C.J.; Koralov, S.B.; Keller, B.C.; Wu, B.G.; Li, Y.; Shen, N.; Ghedin, E.; Morris, A.; et al. Enrichment of the Lung Microbiome with Oral Taxa Is Associated with Lung Inflammation of a Th17 Phenotype. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budden, K.F.; Gellatly, S.L.; Wood, D.L.A.; Cooper, M.A.; Morrison, M.; Hugenholtz, P.; Hansbro, P.M. Emerging Pathogenic Links between Microbiota and the Gut–Lung Axis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanos, V.; Pintus, M.C.; Pintus, R.; Marcialis, M.A. Lung Microbiota in the Acute Respiratory Disease: From Coronavirus to Metabolomics. J. Pediatr. Neonatal Individ. Med. 2020, 9, e090139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Arrieta, M.-C.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Walter, J. A Critical Assessment of the “Sterile Womb” and “in Utero Colonization” Hypotheses: Implications for Research on the Pioneer Infant Microbiome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattaroni, C.; Watzenboeck, M.L.; Schneidegger, S.; Kieser, S.; Wong, N.C.; Bernasconi, E.; Pernot, J.; Mercier, L.; Knapp, S.; Nicod, L.P.; et al. Early-Life Formation of the Microbial and Immunological Environment of the Human Airways. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 857–865.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, C.V.; Travers, C.; Aghai, Z.H.; Eipers, P.; Jilling, T.; Halloran, B.; Carlo, W.A.; Keeley, J.; Rezonzew, G.; Kumar, R.; et al. The Airway Microbiome at Birth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirr, S.; Willers, M.; Viemann, D. The Neonate Respiratory Microbiome. Acta Physiol. 2025, 241, e14266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannaraj, P.S.; Li, F.; Cerini, C.; Bender, J.M.; Yang, S.; Rollie, A.; Adisetiyo, H.; Zabih, S.; Lincez, P.J.; Bittinger, K.; et al. Association Between Breast Milk Bacterial Communities and Establishment and Development of the Infant Gut Microbiome. JAMA Pediatr. 2017, 171, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, S.M.; Mok, D.; Pham, K.; Kusel, M.; Serralha, M.; Troy, N.; Holt, B.J.; Hales, B.J.; Walker, M.L.; Hollams, E.; et al. The Infant Nasopharyngeal Microbiome Impacts Severity of Lower Respiratory Infection and Risk of Asthma Development. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosch, A.A.T.M.; Levin, E.; Van Houten, M.A.; Hasrat, R.; Kalkman, G.; Biesbroek, G.; De Steenhuijsen Piters, W.A.A.; De Groot, P.-K.C.M.; Pernet, P.; Keijser, B.J.F.; et al. Development of Upper Respiratory Tract Microbiota in Infancy Is Affected by Mode of Delivery. EBioMedicine 2016, 9, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassour, M.; Vatanen, T.; Siljander, H.; Hämäläinen, A.-M.; Härkönen, T.; Ryhänen, S.J.; Franzosa, E.A.; Vlamakis, H.; Huttenhower, C.; Gevers, D.; et al. Natural History of the Infant Gut Microbiome and Impact of Antibiotic Treatment on Bacterial Strain Diversity and Stability. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 343ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.L.; Gold, M.J.; Hartmann, M.; Willing, B.P.; Thorson, L.; Wlodarska, M.; Gill, N.; Blanchet, M.; Mohn, W.W.; McNagny, K.M.; et al. Early Life Antibiotic-driven Changes in Microbiota Enhance Susceptibility to Allergic Asthma. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Graeber, S.Y.; Stahl, M.; Dittrich, A.S.; Mall, M.A.; Dalpke, A.H. Chronic but Not Intermittent Infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Is Associated with Global Changes of the Lung Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Opportunistic Pathogens in Cystic Fibrosis: Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Lung Infection. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, S3–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunney, M.M.; Field, T.R.; Moriarty, T.F.; Patrick, S.; Doering, G.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Wolfgang, M.C.; Boucher, R.; Gilpin, D.F.; McDowell, A.; et al. Detection of Anaerobic Bacteria in High Numbers in Sputum from Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirst, M.E.; Baker, D.; Li, E.; Abu-Hasan, M.; Wang, G.P. Upper versus Lower Airway Microbiome and Metagenome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis and Their Correlation with Lung Inflammation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Françoise, A.; Héry-Arnaud, G. The Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Disease. Genes 2020, 11, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, J.C.; Koestler, D.C.; Stanton, B.A.; Davidson, L.; Moulton, L.A.; Housman, M.L.; Moore, J.H.; Guill, M.F.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L.; et al. Serial Analysis of the Gut and Respiratory Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis in Infancy: Interaction between Intestinal and Respiratory Tracts and Impact of Nutritional Exposures. mBio 2012, 3, e00251-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Costello, E.K.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Delivery Mode Shapes the Acquisition and Structure of the Initial Microbiota across Multiple Body Habitats in Newborns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11971–11975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flight, W.G.; Smith, A.; Paisey, C.; Marchesi, J.R.; Bull, M.J.; Norville, P.J.; Mutton, K.J.; Webb, A.K.; Bright-Thomas, R.J.; Jones, A.M.; et al. Rapid Detection of Emerging Pathogens and Loss of Microbial Diversity Associated with Severe Lung Disease in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2022–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coburn, B.; Wang, P.W.; Diaz Caballero, J.; Clark, S.T.; Brahma, V.; Donaldson, S.; Zhang, Y.; Surendra, A.; Gong, Y.; Elizabeth Tullis, D.; et al. Lung Microbiota across Age and Disease Stage in Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, A.F.; Staudinger, B.J.; Dowd, S.E.; Joshi-Datar, A.; Wolcott, R.D.; Aitken, M.L.; Fligner, C.L.; Singh, P.K. Direct Sampling of Cystic Fibrosis Lungs Indicates That DNA-Based Analyses of Upper-Airway Specimens Can Misrepresent Lung Microbiota. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13769–13774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.; Burrell, A.; Ansusinha, E.; Peng, D.; Chaney, H.; Sami, I.; Perez, G.F.; Koumbourlis, A.C.; McCarter, R.; Freishtat, R.J.; et al. Airway Microbial Diversity Is Decreased in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis Compared to Healthy Controls but Improved with CFTR Modulation. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhlebach, M.S.; Zorn, B.T.; Esther, C.R.; Hatch, J.E.; Murray, C.P.; Turkovic, L.; Ranganathan, S.C.; Boucher, R.C.; Stick, S.M.; Wolfgang, M.C. Initial Acquisition and Succession of the Cystic Fibrosis Lung Microbiome Is Associated with Disease Progression in Infants and Preschool Children. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, C.; Guilloux, C.-A.; Beauruelle, C.; Gouriou, S.; Ramel, S.; Dirou, A.; Le Bihan, J.; Revert, K.; Ropars, T.; Lagrafeuille, R.; et al. An Observational Study of Anaerobic Bacteria in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Using Culture Dependant and Independent Approaches. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeplassche, E.; Sass, A.; Ostyn, L.; Burmølle, M.; Kragh, K.N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Coenye, T.; Crabbé, A. Antibiotic Susceptibility of Cystic Fibrosis Lung Microbiome Members in a Multispecies Biofilm. Biofilm 2020, 2, 100031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A. Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiome: Overturning the Old, Opening the Way for the New. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00561-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reasoner, S.A.; Bernard, R.; Waalkes, A.; Penewit, K.; Lewis, J.; Sokolow, A.G.; Brown, R.F.; Edwards, K.M.; Salipante, S.J.; Hadjifrangiskou, M.; et al. Longitudinal Profiling of the Intestinal Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis Treated with Elexacaftor-Tezacaftor-Ivacaftor 2023. medRxiv 2023, Preprint. [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard, A.C.; Waters, V.J. Microbiology of Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 40, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardy, E.E.; Petit, R.A.; Raghuram, V.; Alexander, A.M.; Read, T.D.; Goldberg, J.B. Genotypic and Phenotypic Diversity of Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Cystic Fibrosis Patient Lung Infections and Their Interactions with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. mBio 2020, 11, e00735-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aurora, P.; Duncan, J.A.; Lum, S.; Davies, G.; Wade, A.; Stocks, J.; Viviani, L.; Raywood, E.; Pao, C.; Ruiz, G.; et al. Early Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Predicts Poorer Pulmonary Function in Preschool Children with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepac-Ceraj, V.; Lemon, K.P.; Martin, T.R.; Allgaier, M.; Kembel, S.W.; Knapp, A.A.; Lory, S.; Brodie, E.L.; Lynch, S.V.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; et al. Relationship between Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Tract Bacterial Communities and Age, Genotype, Antibiotics and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.J.; LiPuma, J.J. The Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2016, 37, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, R.J.; Hiller, E.J.; Ispahani, P.; Baker, M. Haemophilus Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. Arch. Dis. Child. 1990, 65, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; McCoy, K.S. Biofilm Aggregates and the Host Airway-Microbial Interface. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 969326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmarina, G.; Pukhalskaya, D.; Shmarin, V.; Semykin, S.; Avakyan, L.; Krasovsky, S.; Goryainova, A.; Kostyuk, S.; Zinchenko, R.; Kashirskaya, N. Burkholderia Cepacia in Cystic Fibrosis Children and Adolescents: Overall Survival and Immune Alterations. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1374318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez Santana, J.C.; Coria Jiménez, V.R. Burkholderia cepacia Complex in Cystic Fibrosis: Critical Gaps in Diagnosis and Therapy. Ann. Med. 2024, 56, 2307503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccò, V.; Alicandro, G.; Consales, A.; Rosazza, C.; Sciarrabba, C.S.; Cariani, L.; Colombo, C. Cepacia Syndrome in Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review of the Literature and Possible New Perspectives in Treatment. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2023, 58, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terlizzi, V.; Tomaselli, M.; Giacomini, G.; Dalpiaz, I.; Chiappini, E. Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia in People with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review of Prevalence, Risk Factors and Management. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 42, 1285–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capaldo, C.; Beauruelle, C.; Saliou, P.; Rault, G.; Ramel, S.; Héry-Arnaud, G. Investigation of Stenotrophomonas Maltophilia Epidemiology in a French Cystic Fibrosis Center. Respir. Med. Res. 2020, 78, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, N.C.; Bartelt, L.A.; Lachiewicz, A.M.; Tompkins, K.M.; Miller, M.B.; Alby, K.; Jones, M.B.; Carr, A.L.; Alexander, J.; Gainey, A.B.; et al. Cefiderocol for the Treatment of Adult and Pediatric Patients with Cystic Fibrosis and Achromobacter xylosoxidans Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1754–e1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, A.; Veschetti, L.; Saitta, G.M.; Passarelli Mantovani, R.; Carelli, M.; Burlacchini, G.; Preato, S.; Sorio, C.; Melotti, P.; Montemari, A.L.; et al. Achromobacter spp. Adaptation in Cystic Fibrosis Infection and Candidate Biomarkers of Antimicrobial Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-On, O.; Mei-Zahav, M.; Levine, H.; Mussaffi, H.; Blau, H.; Ben Zvi, H.; Prais, D.; Stafler, P. The Association of Achromobacter xylosoxidans Airway Infection with Disease Severity in Cystic Fibrosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, T.; Bell, S. Cystic Fibrosis-Related Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Disease. Clin. Chest Med. 2023, 44, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, J.A.; Dedrick, R.M.; Gray, A.L.; Vladar, E.K.; Smith, B.E.; Freeman, K.G.; Malcolm, K.C.; Epperson, L.E.; Hasan, N.A.; Hendrix, J.; et al. Host and Pathogen Response to Bacteriophage Engineered against Mycobacterium Abscessus Lung Infection. Cell 2022, 185, 1860–1874.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kevat, A.; Martinez, E.; Teese, N.; Johnson, K.; Ranganathan, S.; Harrison, J.; Massie, J.; Daley, A. Investigating Transmission of Mycobacterium Abscessus amongst Children in an Australian Cystic Fibrosis Centre. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2020, 19, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzstein, N.; Diricks, M.; Kohl, T.A.; Wichelhaus, T.A.; Andres, S.; Paulowski, L.; Schwarz, C.; Lewin, A.; Kehrmann, J.; Kahl, B.C.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology of Mycobacterium Abscessus Isolates Recovered from German Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e01714-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorth, P.; Ehsan, Z.; Rezayat, A.; Caldwell, E.; Pope, C.; Brewington, J.J.; Goss, C.H.; Benscoter, D.; Clancy, J.P.; Singh, P.K. Direct Lung Sampling Indicates That Established Pathogens Dominate Early Infections in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 1190–1204.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akil, N.; Muhlebach, M.S. Biology and Management of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, S64–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, S.; Hain, T.; Chao, C.-M.; Rudloff, S. Respiratory and Intestinal Microbiota in Pediatric Lung Diseases—Current Evidence of the Gut–Lung Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlüter, D.K.; Ostrenga, J.S.; Carr, S.B.; Fink, A.K.; Faro, A.; Szczesniak, R.D.; Keogh, R.H.; Charman, S.C.; Marshall, B.C.; Goss, C.H.; et al. Lung Function in Children with Cystic Fibrosis in the USA and UK: A Comparative Longitudinal Analysis of National Registry Data. Thorax 2022, 77, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahl, B.C.; Belling, G.; Reichelt, R.; Herrmann, M.; Proctor, R.A.; Peters, G. Thymidine-Dependent Small-Colony Variants of Staphylococcus aureus Exhibit Gross Morphological and Ultrastructural Changes Consistent with Impaired Cell Separation. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 410–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean-Pierre, V.; Boudet, A.; Sorlin, P.; Menetrey, Q.; Chiron, R.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Marchandin, H. Biofilm Formation by Staphylococcus Aureus in the Specific Context of Cystic Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolter, D.J.; Ramsey, B.W. Not Quite the Bully in the Schoolyard: Staphylococcus aureus Can Survive and Coexist with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Cystic Fibrosis Lung. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Déziel, E.; D’Argenio, D.A.; Lépine, F.; Emerson, J.; McNamara, S.; Gibson, R.L.; Ramsey, B.W.; Miller, S.I. Selection for Staphylococcus aureus Small-Colony Variants Due to Growth in the Presence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19890–19895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnett, M.A.; Baker, E.; Mims, C.; Self, S.T.; Gutierrez, H.H.; Guimbellot, J.S. Outcomes of Children with Cystic Fibrosis Screen Positive, Inconclusive Diagnosis/CFTR Related Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1127659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, D.K.; Muhlebach, M.S.; Smyth, A.R. Interventions for the Eradication of Meticillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) in People with Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 2023, CD009650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drevinek, P.; Canton, R.; Johansen, H.K.; Hoffman, L.; Coenye, T.; Burgel, P.-R.; Davies, J.C. New Concepts in Antimicrobial Resistance in Cystic Fibrosis Respiratory Infections. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heirali, A.; Thornton, C.; Acosta, N.; Somayaji, R.; Laforest Lapointe, I.; Storey, D.; Rabin, H.; Waddell, B.; Rossi, L.; Arrieta, M.C.; et al. Sputum Microbiota in Adults with CF Associates with Response to Inhaled Tobramycin. Thorax 2020, 75, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.E.; Mehta, S.; Murray, K.; Higgins, L.; Do, K.; Johnson, J.E.; Wagner, R.; Wendt, C.H.; O’Connor, J.B.; Harris, J.K.; et al. An Integrated Metaproteomics Workflow for Studying Host-Microbe Dynamics in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Samples Applied to Cystic Fibrosis Disease. mSystems 2024, 9, e00929-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanamurthy, V.; Sweetnam, J.M.; Denner, D.R.; Chen, L.W.; Naureckas, E.T.; Laxman, B.; White, S.R. The Metabolic Footprint of the Airway Bacterial Community in Cystic Fibrosis. Microbiome 2017, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.M.; Niccum, D.; Dunitz, J.M.; Hunter, R.C. Evidence and Role for Bacterial Mucin Degradation in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Disease. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.J.; Allgaier, M.; Taylor, B.; Baek, M.S.; Huang, Y.J.; Daly, R.A.; Karaoz, U.; Andersen, G.L.; Brown, R.; Fujimura, K.E.; et al. Airway Microbiota and Pathogen Abundance in Age-Stratified Cystic Fibrosis Patients. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döring, G.; Gulbins, E. Cystic Fibrosis and Innate Immunity: How Chloride Channel Mutations Provoke Lung Disease. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledger, E.L.; Smith, D.J.; Teh, J.J.; Wood, M.E.; Whibley, P.E.; Morrison, M.; Goldberg, J.B.; Reid, D.W.; Wells, T.J. Impact of CFTR Modulation on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infection in People with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2024, 230, e536–e547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardines, R.; Giufrè, M.; Pompilio, A.; Fiscarelli, E.; Ricciotti, G.; Bonaventura, G.D.; Cerquetti, M. Haemophilus Influenzae in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: Antimicrobial Susceptibility, Molecular Epidemiology, Distribution of Adhesins and Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 302, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Principi, N.; Esposito, S. Biofilm Production and Its Implications in Pediatrics. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.C.; Soge, O.O.; No, D.B. Characterization of Macrolide Resistance Genes in Haemophilus Influenzae Isolated from Children with Cystic Fibrosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, S.C.; Judd, L.M.; Carzino, R.; Ranganathan, S.; Holt, K.E. Genomic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Haemophilus Colonizing the Airways of Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis. mSystems 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do Carmo Silva, P.; Hill, D.; Harrison, F. Optimizing Synthetic Cystic Fibrosis Sputum Media for Growth of Non-Typeable Haemophilus Influenzae. Access Microbiol. 2025, 7, 000979.v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, C.V.; Pettis, M.L.; Goldberg, J.B. Antibacterial Potential of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia Complex Cystic Fibrosis Isolates. mSphere 2024, 9, e0033524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fainardi, V.; Neglia, C.; Muscarà, M.; Spaggiari, C.; Tornesello, M.; Grandinetti, R.; Argentiero, A.; Calderaro, A.; Esposito, S.; Pisi, G. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria in Children and Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis. Children 2022, 9, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Hunt, S.; Simonds, S.; Boyton, C.; Middleton, A.; Elias, M.; Towns, S.; Pandit, C.; Robinson, P.; Fitzgerald, D.A.; et al. The Changing Epidemiology of Pulmonary Infection in Children and Adolescents with Cystic Fibrosis: An 18-Year Experience. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlosnik, J.E.A.; Henry, D.A.; Hird, T.J.; Hickman, R.; Campbell, M.; Cabrera, A.; Laino Chiavegatti, G.; Chilvers, M.A.; Sadarangani, M. Epidemiology of Burkholderia Infections in People with Cystic Fibrosis in Canada between 2000 and 2017. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1549–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somayaji, R.; Yau, Y.C.W.; Tullis, E.; LiPuma, J.J.; Ratjen, F.; Waters, V. Clinical Outcomes Associated with Burkholderia Cepacia Complex Infection in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2020, 17, 1542–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canning, J.S.; Laucirica, D.R.; Ling, K.-M.; Nicol, M.P.; Stick, S.M.; Kicic, A. Phage Therapy to Treat Cystic Fibrosis Burkholderia Cepacia Complex Lung Infections: Perspectives and Challenges. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1476041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, H.; Reuwsaat, J.C.V.; Lopes, F.C.; Viezzer, G.; Volpato, F.C.Z.; Barth, A.L.; De Tarso Roth Dalcin, P.; Staats, C.C.; Vainstein, M.H.; Kmetzsch, L. Comparative Microbiome Analysis in Cystic Fibrosis and Non-Cystic Fibrosis Bronchiectasis. Respir. Res. 2024, 25, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fireizen, Y.; Ahmed, M.; Vigers, T.; Akong, K.; Ryu, J.; Hahn, A.; Fanous, H.; Koumbourlis, A.; Tirakitsoontorn, P.; Arrieta, A.; et al. Changing Epidemiology of Pediatric Pulmonary Exacerbations in Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2025, 60, e71019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsac, C.; Berdah, L.; Thouvenin, G.; Sermet-Gaudelus, I.; Corvol, H. AChromobacter xylosoxidans Airway Infection Is Associated with Lung Disease Severity in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. ERJ Open Res. 2021, 7, 00076-2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunman, B.; Emiralioglu, N.; Hazirolan, G.; Ademhan Tural, D.; Ozsezen, B.; Nayir Buyuksahin, H.; Guzelkas, I.; Yalcin, E.; Dogru, D.; Özçelik, U.; et al. Impact of Achromobacter spp. Isolation on Clinical Outcomes in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffanowski, C.; Papalia, M.; Iriarte, A.; Langleib, M.; Galanternik, L.; Gutkind, G.; Cooper, V.; Ramírez, M.S.; Radice, M. Full Characterization of Plasmids from Achromobacter Ruhlandii Isolates Recovered from a Single Patient with Cystic Fibrosis (CF). Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2022, 54, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiniano, S.L.; Nick, J.A.; Daley, C.L. Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Infections in Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2022, 43, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milczewska, J.; Syunyaeva, Z.; Żabińska-Jaroń, A.; Sands, D.; Thee, S. Changing Profile of Bacterial Infection and Microbiome in Cystic Fibrosis: When to Use Antibiotics in the Era of CFTR-Modulator Therapy. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2024, 33, 240068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherrard, L.J.; Bell, S.C.; Tunney, M.M. The Role of Anaerobic Bacteria in the Cystic Fibrosis Airway. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2016, 22, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keravec, M.; Mounier, J.; Guilloux, C.-A.; Fangous, M.-S.; Mondot, S.; Vallet, S.; Gouriou, S.; Le Berre, R.; Rault, G.; Férec, C.; et al. Porphyromonas, a Potential Predictive Biomarker of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection in Cystic Fibrosis. BMJ Open Resp. Res. 2019, 6, e000374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirković, B.; Murray, M.A.; Lavelle, G.M.; Molloy, K.; Azim, A.A.; Gunaratnam, C.; Healy, F.; Slattery, D.; McNally, P.; Hatch, J.; et al. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids, Produced by Anaerobic Bacteria, in the Cystic Fibrosis Airway. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 1314–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castner, L.M.; Zimbric, M.; Cahalan, S.; Powell, C.; Caverly, L.J. Outcomes of Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbations Treated with Antibiotics with Activity against Anaerobic Bacteria. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmody, L.A.; Zhao, J.; Schloss, P.D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Murray, S.; Young, V.B.; Li, J.Z.; LiPuma, J.J. Changes in Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiota at Pulmonary Exacerbation. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2013, 10, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, G.; Walsh, A.; Crispie, F.; Frost, S.; Greally, P.; Cotter, P.D.; O’Sullivan, O.; Renwick, J. Insights into the Adolescent Cystic Fibrosis Airway Microbiome Using Shotgun Metagenomics. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 25, 3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, M.A.; Brugha, R.; Gartner, S.; Legg, J.; Moeller, A.; Mondejar-Lopez, P.; Prais, D.; Pressler, T.; Ratjen, F.; Reix, P.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Elexacaftor/Tezacaftor/Ivacaftor in Children 6 Through 11 Years of Age with Cystic Fibrosis Heterozygous for F508del and a Minimal Function Mutation: A Phase 3b, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 206, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, K.J.; Santee, C.; McCauley, K.; Panzer, A.R.; Lynch, S.V. Gut Bifidobacteria Enrichment Following Oral Lactobacillus-Supplementation Is Associated with Clinical Improvements in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2022, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutharsan, S.; McKone, E.F.; Downey, D.G.; Duckers, J.; MacGregor, G.; Tullis, E.; Van Braeckel, E.; Wainwright, C.E.; Watson, D.; Ahluwalia, N.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Elexacaftor plus Tezacaftor plus Ivacaftor versus Tezacaftor plus Ivacaftor in People with Cystic Fibrosis Homozygous for F508del-CFTR: A 24-Week, Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Active-Controlled, Phase 3b Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, M.; Zuckerman-Levin, N.; Masarweh, K.; Hanna, M.; Laghi, L.; Marazzato, M.; Levanon, S.; Hakim, F.; Bar–Yoseph, R.; Wilschanski, M.; et al. The Effect of Probiotic Administration on Metabolomics and Glucose Metabolism in CF Patients. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio-Grau, A.; Calvo-Lerma, J.; Ferriz-Jordán, M.; García-Hernández, J.; Heredia, A.; Andrés, A. Effect of Lactobacillaceae Probiotics on Colonic Microbiota and Metabolite Production in Cystic Fibrosis: A Comparative In Vitro Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boeck, K. Cystic Fibrosis in the Year 2020: A Disease with a New Face. Acta Paediatr. 2020, 109, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; Robinson, P.D.; Shteinberg, M.; Downey, D.G. CFTR Modulator Therapy: Transforming the Landscape of Clinical Care in Cystic Fibrosis. Lancet 2023, 402, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regard, L.; Martin, C.; Da Silva, J.; Burgel, P.-R. CFTR Modulators: Current Status and Evolving Knowledge. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 44, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Pacheco, M. CFTR Modulators: The Changing Face of Cystic Fibrosis in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 10, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, D. Unraveling the Mechanism of Action, Binding Sites, and Therapeutic Advances of CFTR Modulators: A Narrative Review. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2025, 47, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laselva, O.; Guerra, L.; Castellani, S.; Favia, M.; Di Gioia, S.; Conese, M. Small-Molecule Drugs for Cystic Fibrosis: Where Are We Now? Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 72, 102098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massie, J. Should All Children with Cystic Fibrosis Who Have Responsive CFTR Mutations Be Prescribed CFTR Modulators? J. Cyst. Fibros. 2024, 23, 612–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsson, G.G.; Ronan, N.J.; Mooney, D.; McGettigan, C.; Mullane, D.; NiChroinin, M.; Shanahan, F.; Murphy, D.M.; McCarthy, M.; McCarthy, Y.; et al. Extended-Culture and Culture-Independent Molecular Analysis of the Airway Microbiota in Cystic Fibrosis Following CFTR Modulation with Ivacaftor. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2021, 20, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, P.J.; Mall, M.A.; Álvarez, A.; Colombo, C.; De Winter-de Groot, K.M.; Fajac, I.; McBennett, K.A.; McKone, E.F.; Ramsey, B.W.; Sutharsan, S.; et al. Triple Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Phe508del–Gating and –Residual Function Genotypes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Cárdenes, C.M.; Merino Sánchez-Cañete, A.; Vicente Santamaría, S.; Gascón Galindo, C.; Merino Sanz, N.; Tabares González, A.; Blitz Castro, E.; Morales Tirado, A.; Garriga García, M.; López Rozas, M.; et al. Effects on Growth, Weight and Body Composition after CFTR Modulators in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2024, 59, 3632–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, J.E.; Kasi, A.S.; Pittman, J.E.; Jensen, R.; Thia, L.P.; Robinson, P.; Tirakitsoontorn, P.; Ramsey, B.; Mall, M.A.; Taylor-Cousar, J.L.; et al. Vanzacaftor–Tezacaftor–Deutivacaftor for Children Aged 6–11 Years with Cystic Fibrosis (RIDGELINE Trial VX21-121-105): An Analysis from a Single-Arm, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2025, 13, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogen, J.D.; Onchiri, F.M.; Hamblett, N.M.; Gibson, R.L.; Morgan, W.J.; Rosenfeld, M. Association of Intensity of Antipseudomonal Antibiotic Therapy with Risk of Treatment-Emergent Organisms in Children with Cystic Fibrosis and Newly Acquired Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naehrig, S.; Schulte-Hubbert, B.; Hafkemeyer, S.; Hammermann, J.; Dumke, M.; Sieber, S.; Naehrlich, L. Chronic Inhaled Antibiotic Therapy in People with Cystic Fibrosis with Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Infection in Germany. Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 80, 102214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Patient Registry 2023 Annual Data Report; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.cff.org/sites/default/files/2024-09/2023-Patient-Registry-Annual-Data-Report.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2025).
- Downes, K.J.; Patil, N.R.; Rao, M.B.; Koralkar, R.; Harris, W.T.; Clancy, J.P.; Goldstein, S.L.; Askenazi, D.J. Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury during Aminoglycoside Therapy in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2015, 30, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Rasic, M.; Ascoli, C.; Hatch, J.E.; Nemsick, N.K.; Deschamp, A.R.; Davis, S.D.; Sanders, D.B.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. An Observational Study of the Lung Microbiome and Lung Function in Young Children with Cystic Fibrosis across Two Countries with Differing Antibiotic Practices. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 205, 107628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felton, E.; Burrell, A.; Chaney, H.; Sami, I.; Koumbourlis, A.C.; Freishtat, R.J.; Crandall, K.A.; Hahn, A. Inflammation in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: Contribution of Bacterial Production of Long-Chain Fatty Acids. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 90, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Schloss, P.D.; Kalikin, L.M.; Carmody, L.A.; Foster, B.K.; Petrosino, J.F.; Cavalcoli, J.D.; VanDevanter, D.R.; Murray, S.; Li, J.Z.; et al. Decade-Long Bacterial Community Dynamics in Cystic Fibrosis Airways. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 5809–5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.T.; Downes, K.J.; FakhriRavari, A.; Abdul-Mutakabbir, J.C.; Kuti, J.L.; Jorgensen, S.; Young, D.C.; Alshaer, M.H.; Bassetti, M.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. International Consensus Recommendations for the Use of Prolonged-infusion Beta-lactam Antibiotics: Endorsed by the American College of Clinical Pharmacy, British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Infectious Diseases Society of America, Society of Critical Care Medicine, and Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Pharmacotherapy 2023, 43, 740–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faino, A.V.; Hoffman, L.R.; Gibson, R.L.; Kronman, M.P.; Nichols, D.P.; Rosenfeld, M.; Cogen, J.D. Polymicrobial Infections and Antibiotic Treatment Patterns for Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2023, 22, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikic, A.; Ratjen, F.; Shaw, M.; Tullis, E.; Waters, V. The Effect of Antibiotic Changes during Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbations. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkerman-Nijland, A.M.; Akkerman, O.W.; Grasmeijer, F.; Hagedoorn, P.; Frijlink, H.W.; Rottier, B.L.; Koppelman, G.H.; Touw, D.J. The Pharmacokinetics of Antibiotics in Cystic Fibrosis. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, M.N.; Smith, S.; Flume, P.; Jahnke, N.; Prayle, A.P. Intravenous Antibiotics for Pulmonary Exacerbations in People with Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2025, 2025, CD009730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, G.; Morrison, L.; Brown, C. Nebuliser Systems for Drug Delivery in Cystic Fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 2023, CD007639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, D.L.; Bridson, C.; Dittrich, S.; Graeber, S.Y.; Stahl, M.; Wege, S.; Herth, F.; Sommerburg, O.; Schultz, C.; Dalpke, A.; et al. Changes in Microbiome Dominance Are Associated with Declining Lung Function and Fluctuating Inflammation in People with Cystic Fibrosis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 885822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, C.H.; Heltshe, S.L.; West, N.E.; Skalland, M.; Sanders, D.B.; Jain, R.; Barto, T.L.; Fogarty, B.; Marshall, B.C.; VanDevanter, D.R.; et al. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Antimicrobial Duration for Cystic Fibrosis Pulmonary Exacerbation Treatment. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 1295–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Needham, B.; Leach, S.T.; Day, A.S.; Jaffe, A.; Thomas, T.; Ooi, C.Y. Disrupted Progression of the Intestinal Microbiota with Age in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.R.; Pope, C.E.; Hayden, H.S.; Heltshe, S.; Levy, R.; McNamara, S.; Jacobs, M.A.; Rohmer, L.; Radey, M.; Ramsey, B.W.; et al. Escherichia Coli Dysbiosis Correlates with Gastrointestinal Dysfunction in Children with Cystic Fibrosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 58, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinberg, R.; Mostacci, N.; Kieninger, E.; Frauchiger, B.; Casaulta, C.; Usemann, J.; Moeller, A.; Trachsel, D.; Rochat, I.; Blanchon, S.; et al. Early Nasal Microbiota and Subsequent Respiratory Tract Infections in Infants with Cystic Fibrosis. Commun. Med. 2024, 4, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reasoner, S.A.; Enriquez, K.T.; Abelson, B.; Scaglione, S.; Schneier, B.; O’Connor, M.G.; Van Horn, G.; Hadjifrangiskou, M. Urinary Tract Infections in Cystic Fibrosis Patients. J. Cyst. Fibros. 2022, 21, e1–e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzese, E.; Raia, V.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Volpicelli, M.; De Marco, G.; Maiuri, L.; Guarino, A. Effect of Lactobacillus GG Supplementation on Pulmonary Exacerbations in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis: A Pilot Study. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Mosquera, F.E.; Perlaza, C.L.; Naranjo Rojas, A.; Murillo Rios, S.; Carrero Gallego, A.; Fischersworring, S.I.; Rodríguez, J.S.; Liscano, Y. Effectiveness of Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Symbiotic Supplementation in Cystic Fibrosis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Medicina 2025, 61, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papizadeh, M.; Nahrevanian, H.; Rohani, M.; Hosseini, S.N.; Shojaosadati, S.A. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Gorbach-Goldin (GG): A Top Well-Researched Probiotic Strain. J. Med. Bacteriol. 2016, 5, 46–59. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmani, P.; Rohani, P.; Kariman, A.; Motamed, F.; Modaresi, M.R.; Eftekhari, K.; Ayati, M.; Sohouli, M.H. The Impact of Probiotics on Pulmonary, Gastrointestinal, and Growth Outcomes in Pediatric Cystic Fibrosis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. BMC Pediatr. 2025, 25, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Pathogen Name | Typical Age of Emergence/Prevalence | Key Virulence Factors/Characteristics | Clinical Significance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus aureus | Early Childhood | Biofilm formation, exotoxins, antibiotic resistance (MRSA) | Early inflammation, exacerbations, common co-infection | [50,51] |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | School-Age, Adolescence | Biofilm (mucoid phenotype), alginate, quorum sensing, efflux pumps | Chronic infection, progressive lung damage, exacerbations | [52,53,54] |
| Haemophilus influenzae | Early Childhood | Biofilm, IgA protease | Early colonization, acute exacerbations | [55,56] |
| Burkholderia cepacia Complex | Later Childhood, Adolescence | High intrinsic resistance, biofilm, “cepacia syndrome” | Severe lung decline, poor prognosis, highly transmissible | [57,58,59] |
| Stenotrophomonas maltophilia | Later Childhood, Adolescence (increasing in younger patients) | Intrinsic multidrug resistance, biofilm formation, efflux pumps | Associated with FEV1 decline, increased hospitalizations, coinfections, and poor outcomes | [35,60,61] |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | Variable, increasing | High intrinsic resistance, biofilm | Associated with lung decline, exacerbations | [62,63,64] |
| Mycobacterium abscessus | Rare in young children. increasingly prevalent during adolescence | Most virulent NTM, biofilm formation, ability to enter non-replicating “persister” state | Accelerated lung decline, high morbidity/mortality, possible cross-infection in pediatric CF centers | [65,66,67,68] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buruiană, G.; Sima, C.M.; Anton-Păduraru, D.-T.; Bădescu, A.C.; Luncă, C.; Duhaniuc, A.; Dorneanu, O.S. Airway Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Review of Microbial Shifts and Therapeutic Impacts. Medicina 2025, 61, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091605
Buruiană G, Sima CM, Anton-Păduraru D-T, Bădescu AC, Luncă C, Duhaniuc A, Dorneanu OS. Airway Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Review of Microbial Shifts and Therapeutic Impacts. Medicina. 2025; 61(9):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091605
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuruiană, Georgiana, Cristina Mihaela Sima, Dana-Teodora Anton-Păduraru, Aida Corina Bădescu, Cătălina Luncă, Alexandru Duhaniuc, and Olivia Simona Dorneanu. 2025. "Airway Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Review of Microbial Shifts and Therapeutic Impacts" Medicina 61, no. 9: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091605
APA StyleBuruiană, G., Sima, C. M., Anton-Păduraru, D.-T., Bădescu, A. C., Luncă, C., Duhaniuc, A., & Dorneanu, O. S. (2025). Airway Microbiome in Children with Cystic Fibrosis: A Review of Microbial Shifts and Therapeutic Impacts. Medicina, 61(9), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61091605






