Toward Standardized Assessment of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical: Effects of Visual Stimulus Intensity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Subjects
- -
- Significant MS-related disability that interfered with task comprehension and/or execution;
- -
- Uncorrected ophthalmological impairment that prevented consistent task completion;
- -
- Age greater than 55 years;
- -
- Other neurological, vestibular, or otological disorders.
- -
- Any known neurological or otological diseases;
- -
- Age greater than 55;
- -
- Significant uncorrected ophthalmological impairment.
2.2. Sample Size Justification
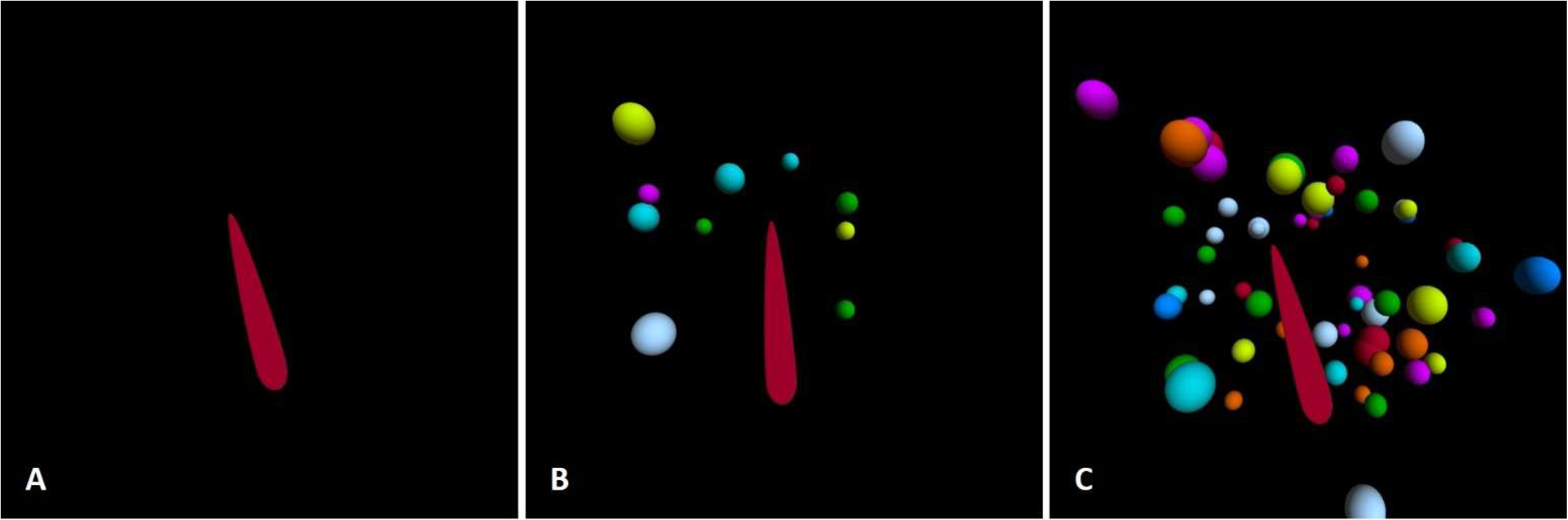
2.3. Experimental Setup
- -
- 10 spheres, 10°/s.
- -
- 10 spheres, 30°/s.
- -
- 10 spheres, 60°/s.
- -
- Increased visual field coverage (IVFC)—60 spheres, 10°/s (Figure 1C).
2.4. Measuring the Visual Dependence
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Group Differences in Static SVV Performance
4.2. The Effects of Dynamic Stimulus Intensity
4.3. Test-Induced Dizziness
4.4. Clinical Applicability
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kheradmand, A.; Winnick, A. Perception of Upright: Multisensory Convergence and the Role of Temporo-Parietal Cortex. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatt, B.N.; Sparto, P.J.; Terhorst, L.; Winser, S.; Heyman, R.; Whitney, S.L. Relationship between Subjective Visual Vertical and Balance in Individuals with Multiple Sclerosis. Physiother. Res. Int. 2019, 24, e1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Fonseca, B.A.V.; Pereira, C.B.; Jorge, F.; Simm, R.; Apostolos-Pereira, S.; Callegaro, D. A Disturbed Processing of Graviceptive Pathways May Be Involved in the Pathophysiology of Balance Disorders in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2016, 74, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakimovski, D.; Bittner, S.; Zivadinov, R.; Morrow, S.A.; Benedict, R.H.; Zipp, F.; Weinstock-Guttman, B. Multiple Sclerosis. Lancet 2024, 403, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, M.H.; Nilsagard, Y. Balance, Gait, and Falls in Multiple Sclerosis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusin, F.S.; Tomaz, A.; Ganança, M.M.; Oliveira, E.M.; Gonçalves, A.B.F.; Caovilla, H.H. Postural Control in Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 26, e592–e604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, C.J.; Rosenberg, A. Gravity Estimation and Verticality Perception. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 159, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, G.D.; Christy, J.B.; Motl, R.W. Comprehensive Clinical Assessment of Vestibular Function in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Phys. Ther. 2021, 45, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulozienė, I.; Totilienė, M.; Balnytė, R.; Kuzminienė, A.; Kregždytė, R.; Paulauskas, A.; Blažauskas, T.; Marozas, V.; Uloza, V.; Kaski, D. Subjective Visual Vertical and Visual Dependency in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 44, 102255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T.; Dieterich, M. Vestibular Syndromes in the Roll Plane: Topographic Diagnosis from Brainstem to Cortex. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 36, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwergal, A.; Rettinger, N.; Frenzel, C.; Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T.; Strupp, M. A Bucket of Static Vestibular Function. Neurology 2009, 72, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulozienė, I.; Totilienė, M.; Paulauskas, A.; Blažauskas, T.; Marozas, V.; Kaski, D.; Ulozas, V. Subjective Visual Vertical Assessment with Mobile Virtual Reality System. Medicina 2017, 53, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaleski-King, A.; Pinto, R.; Lee, G.; Brungart, D. Use of Commercial Virtual Reality Technology to Assess Verticality Perception in Static and Dynamic Visual Backgrounds. Ear Hear. 2018, 41, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterich, M.; Brandt, T. Perception of Verticality and Vestibular Disorders of Balance and Falls. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrero-Gaitán, E.; Molina, F.; Montilla-Ibañez, M.-d.-A.; Del-Pino-Casado, R.; Rodriguez-Almagro, D.; Lomas-Vega, R. Misperception of Visual Vertical in Peripheral Vestibular Disorders. A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Laryngoscope 2021, 131, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichgans, J.; Held, R.; Young, L.R.; Brandt, T. Moving Visual Scenes Influence the Apparent Direction of Gravity. Science 1972, 178, 1217–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakin, C.J.; Peters, A.; Giunti, P.; Day, B.L. Cerebellar Degeneration Increases Visual Influence on Dynamic Estimates of Verticality. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 3589–3598.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, R.; Mallinson, A.; Ceyte, H.; Caudron, S.; Van Nechel, C.; Bisdorff, A.; Magnusson, M.; Petersen, H.; Kingma, H.; Perrin, P. Discussion about Visual Dependence in Balance Control: European Society for Clinical Evaluation of Balance Disorders. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2017, 13, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faralli, M.; Ricci, G.; Molini, E.; Longari, F.; Altissimi, G.; Frenguelli, A. Determining Subjective Visual Vertical: Dynamic versus Static Testing. Otol. Neurotol. 2007, 28, 1069–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, M.; Thiry, A.; Tardivet, L. Two Conditions to Fully Recover Dynamic Canal Function in Unilateral Peripheral Vestibular Hypofunction Patients. J. Vestib. Res. 2021, 31, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Kamo, T.; Ogihara, H.; Tani, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Igarashi, T.; Kimura, A. Effects of Subjective Visual Verticality and Visual Dependence on Balance Function in Older Adults Using a Smartphone-Based Virtual Reality System. Perception 2025, 54, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.-P.; Hong, Y.-C.; Schubert, M.C. Visual Vertigo and Motion Sickness Is Different between Persistent Postural-Perceptual Dizziness and Vestibular Migraine. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 45, 104321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzak, R.A.; Jahrami, H.; Husni, M.; Ali, M.E.; Bagust, J. Perceptual Visual Dependence for Spatial Orientation in Patients with Schizophrenia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0278718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polman, C.H.; Reingold, S.C.; Edan, G.; Filippi, M.; Hartung, H.-P.; Kappos, L.; Lublin, F.D.; Metz, L.M.; McFarland, H.F.; O’Connor, P.W.; et al. Diagnostic Criteria for Multiple Sclerosis: 2005 Revisions to the “McDonald Criteria”. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 58, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valančius, D.; Ulytė, A.; Masiliūnas, R.; Paškonienė, A.; Ulozienė, I.; Kaski, D.; Vaicekauskienė, L.; Lesinskas, E.; Jatužis, D.; Ryliškienė, K. Validation and Factor Analysis of the Lithuanian Version of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2019, 15, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating Neurologic Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis: An Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, S.; Kamo, T.; Ogihara, H.; Tani, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Igarashi, T.; Kimura, A. Test-Retest Reliability of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical and Visual Dependency in Older Adults Using Virtual Reality Methods. Percept. Mot. Ski. 2024, 131, 2069–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, I.A.H.; de Vrijer, M.; Selen, L.P.J.; van Gisbergen, J.A.M.; Medendorp, W.P. Multisensory Processing in Spatial Orientation: An Inverse Probabilistic Approach. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 5365–5377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.B.; Kanashiro, A.K.; Maia, F.M.; Barbosa, E.R. Correlation of Impaired Subjective Visual Vertical and Postural Instability in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2014, 346, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, I.V.; Guettard, E.; Leman, M.C.; Colle, F.M.; Yelnik, A.P. Subjective Visual Vertical Perception Relates to Balance in Acute Stroke. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2006, 87, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, I.V.; Hubeaux, K.; Gellez-Leman, M.C.; Guichard, J.P.; Vicaut, E.; Yelnik, A.P. Influence of Subjective Visual Vertical Misperception on Balance Recovery after Stroke. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2007, 78, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piscicelli, C.; Pérennou, D. Visual Verticality Perception after Stroke: A Systematic Review of Methodological Approaches and Suggestions for Standardization. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 60, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronstein, A.M. Multisensory Integration in Balance Control. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016, 137, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.A.; Crane, B.T. Static and Dynamic Visual Vertical Perception in Subjects with Migraine and Vestibular Migraine. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 2016, 2, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, C.; Lacour, M.; Ahmadi, A.E.; Magnan, J.; Borel, L. Changes of Visual Vertical Perception: A Long-Term Sign of Unilateral and Bilateral Vestibular Loss. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MS Group | Control Group | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Static SVV, median (min.–max.) | 1.8 (0.1–4.6) | 0.9 (0–2.4) | <0.001 |
| Dynamic SVV deviations, median (min.–max.) | |||
| 10°/s | 4.3 (2.2–22.7) | 2.1 (0.3–7.4) | <0.001 |
| 30°/s | 6.2 (2.4–23.1) | 3.7 (0.5–12.4) | <0.001 |
| 60°/s | 5.6 (1.4–36.8) | 3.8 (1.3–10.4) | 0.005 |
| IVFC | 6.4 (3.3–20.4) | 5.2 (1.3–10.7) | 0.005 |
| Visual dependence, median (min.–max.) | |||
| 10°/s | 4.2 (0.75–22.7) | 2.02 (0.15–7.35) | <0.001 |
| 30°/s | 6.25 (1.65–23.1) | 3.65 (0.65–12.4) | <0.001 |
| 60°/s | 4.2 (0.6–36.85) | 3.82 (1.3–10.4) | 0.151 |
| IVFC | 6.4 (2.8–20.4) | 5.15 (0.8–10.65) | 0.014 |
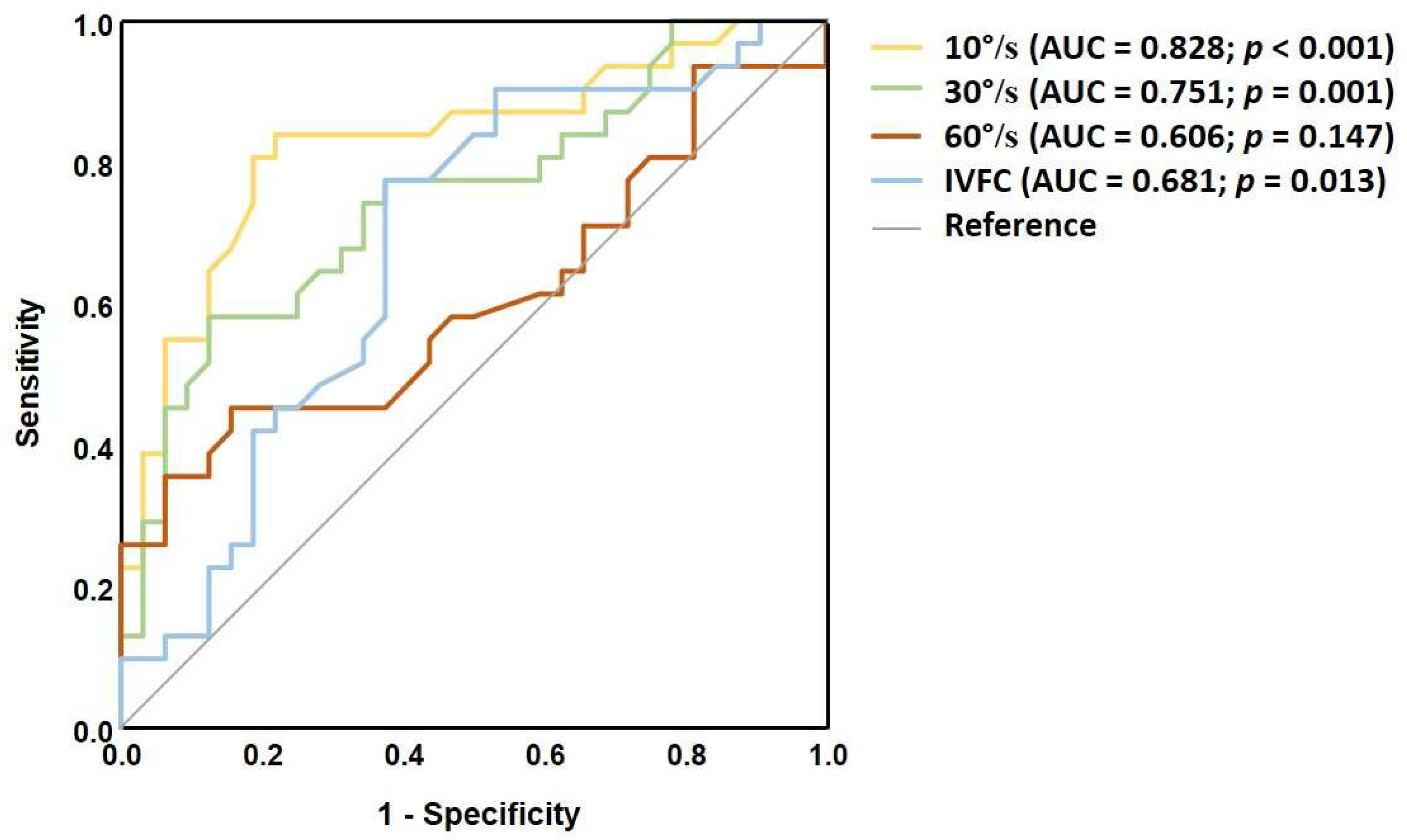
| Pair of Dynamic Stimuli | MS Group (p-Value *) | Control Group (p-Value *) |
|---|---|---|
| 10°/s vs. 30°/s | 0.006 | <0.001 |
| 10°/s vs. 60°/s | 0.036 | <0.001 |
| 10°/s vs. IVFC | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 30°/s vs. 60°/s | 0.563 | 0.024 |
| Visual Stimulus Intensity | MS Group | Control Group | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10°/s | 20 (0–61) | 10 (0–43) | 0.018 |
| 30°/s | 33 (4–80) | 25 (0–72) | 0.216 |
| 60°/s | 50 (4–91) | 42.5 (0–75) | 0.302 |
| 10°/s, IVFC | 33 (3–72) | 34 (5–75) | 0.815 |
| Stimulus | VD vs. VAS | VAS vs. DHI | DHI vs. VD/SVV |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10°/s | ρ = 0.542 (p = 0.002) | ρ = 0.523 (p = 0.003) | n/s |
| 30°/s | ρ = 0.448 (p = 0.012) | ρ = 0.468 (p = 0.008) | n/s |
| 60°/s | n/s | n/s | n/s |
| 10°/s, IVFC | n/s | ρ = 0.585 (p < 0.001) | n/s |
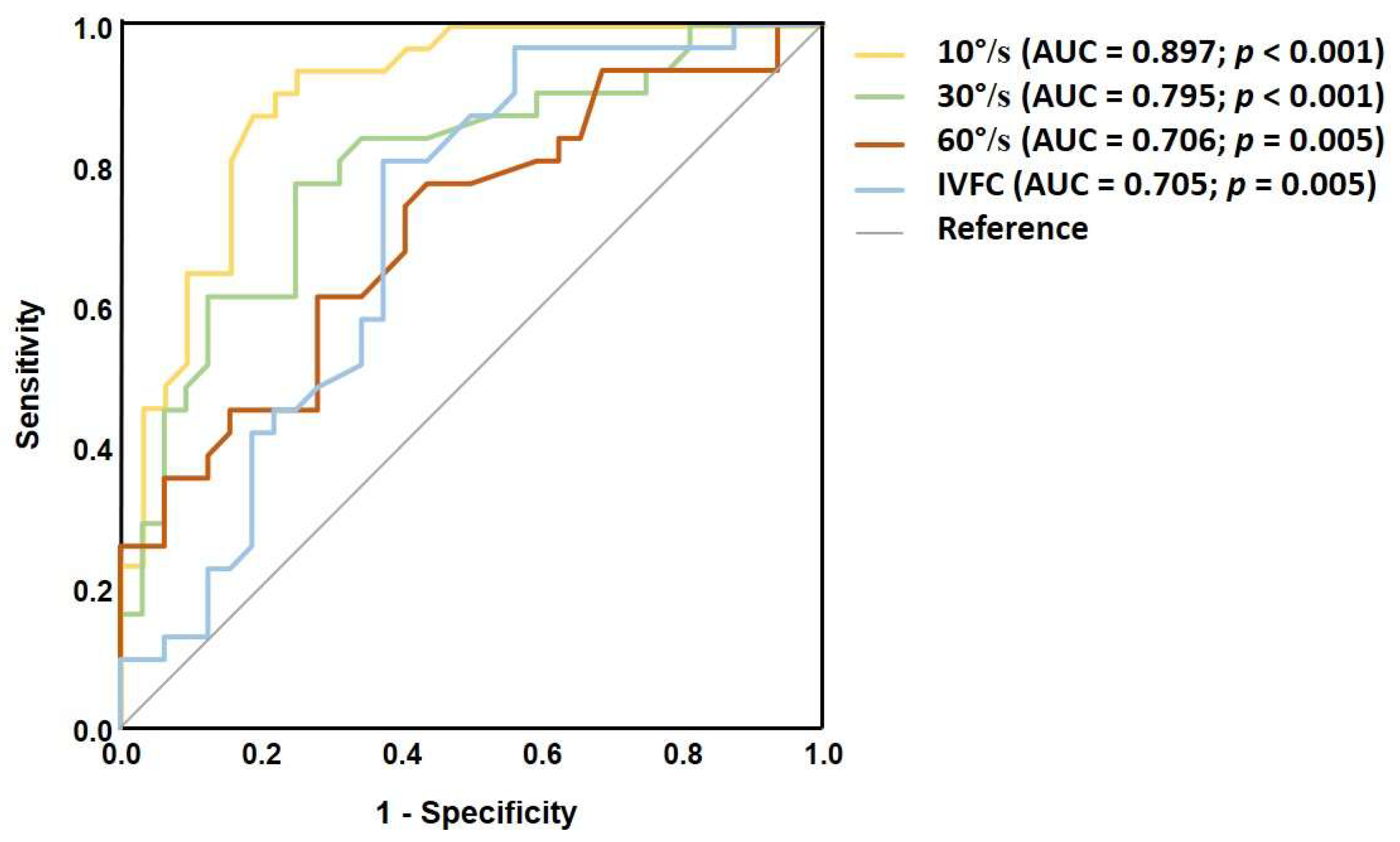
| Visual Stimulus Intensity | Cut-Off Value(deg) | Abnormal in the MS Group, n (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 10°/s | 2.9 | 29 (93%) |
| 30°/s | 3.8 | 26 (84%) |
| 60°/s | 3.9 | 23 (74%) |
| 10°/s, IVFC | 5.5 | 25 (80%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klėgėris, T.; Kaski, D.; Balnytė, R.; Uloza, V.; Kuzminienė, A.; Ulozienė, I. Toward Standardized Assessment of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical: Effects of Visual Stimulus Intensity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina 2025, 61, 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081482
Klėgėris T, Kaski D, Balnytė R, Uloza V, Kuzminienė A, Ulozienė I. Toward Standardized Assessment of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical: Effects of Visual Stimulus Intensity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081482
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlėgėris, Tautvydas, Diego Kaski, Renata Balnytė, Virgilijus Uloza, Alina Kuzminienė, and Ingrida Ulozienė. 2025. "Toward Standardized Assessment of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical: Effects of Visual Stimulus Intensity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081482
APA StyleKlėgėris, T., Kaski, D., Balnytė, R., Uloza, V., Kuzminienė, A., & Ulozienė, I. (2025). Toward Standardized Assessment of Dynamic Subjective Visual Vertical: Effects of Visual Stimulus Intensity in Health and Multiple Sclerosis. Medicina, 61(8), 1482. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081482







