Impact of Glycemic Control After Reperfusion on the Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury Following Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
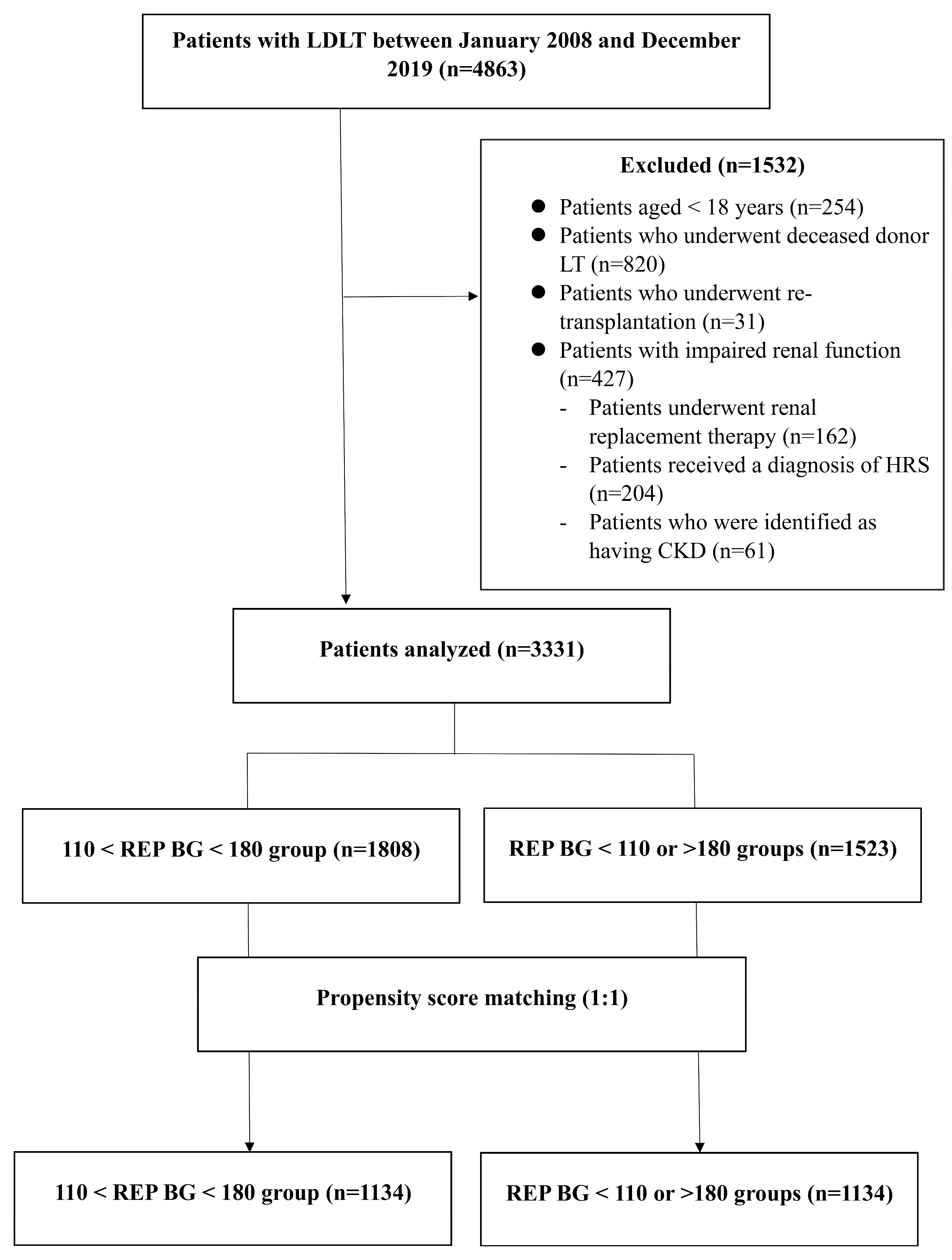
2.1. Study Design and Participation
2.2. Clinical Data Collection
2.3. Anesthetic Techniques and Surgical Procedures
2.4. Immunosuppression Protocol
2.5. Data Collection and Assessment
2.6. Primary and Secondary Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
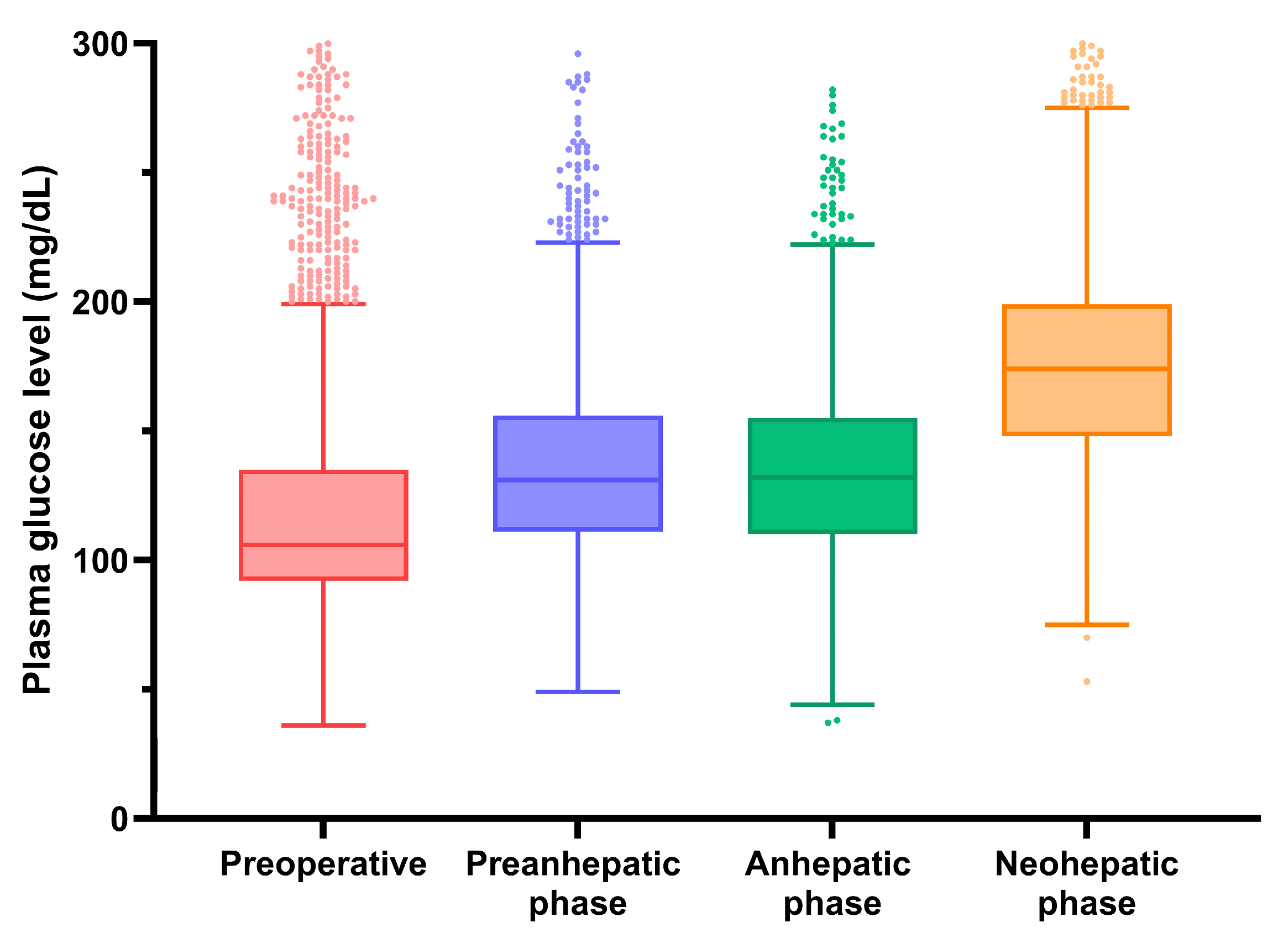
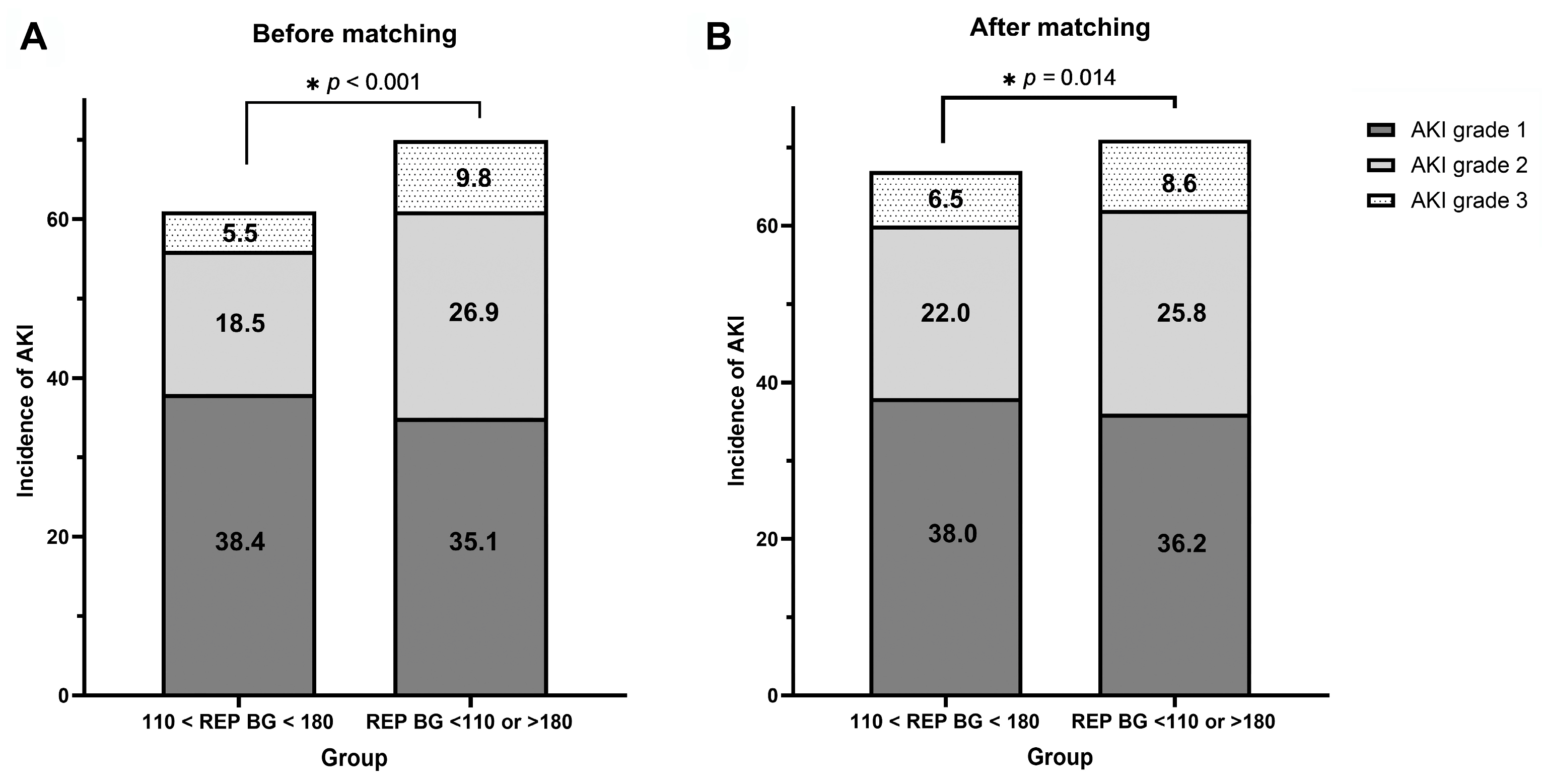
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BG | Blood glucose |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CKD-EPI | Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration |
| CNI | Calcineurin inhibitor |
| CTP | Child–Turcotte–Pugh score |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| FC | Fatty change |
| GRWR | Graft-to-recipient weight ratio |
| HBV | Hepatitis B virus |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | Hepatitis C virus |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| INR | International normalized ratio |
| KDIGO | Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes |
| LDLT | Living donor liver transplantation |
| LT | Liver transplantation |
| MMF | Mycophenolate mofetil |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| p | p-value |
| PRBC | Packed red blood cell |
| PSM | Propensity score matching |
| PT | Prothrombin time |
| REP BG | Reperfusion blood glucose |
| SCr | Serum creatinine |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
| STROCSS | Strengthening the Reporting of Cohort, Cross-sectional and Case-control Studies in Surgery |
| SVR | Systemic vascular resistance |
| cTAC | Mean tacrolimus trough level |
References
- Johnston, L.E.; Kirby, J.L.; Downs, E.A.; LaPar, D.J.; Ghanta, R.K.; Ailawadi, G.; Kozower, B.D.; Kron, I.L.; McCall, A.L.; Isbell, J.M. Virginia Interdisciplinary Cardiothoracic Outcomes Research (VICTOR) Center. Postoperative hypoglycemia is associated with worse outcomes after cardiac operations. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2017, 103, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, T.; Shojima, N.; Noma, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kadowaki, T. Glycemic control, mortality, and hypoglycemia in critically ill patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Intensive Care Med. 2017, 43, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, C.D.; Sabang, R.L.; Nogueira Cordeiro, M.F.; Hassan, I.F.; Goldberg, M.D.; Scurlock, C.S. Hyperglycemia in medically critically Ill patients: Risk factors and clinical outcomes. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, e568–e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangraw, R.E. Metabolic issues in liver transplantation. Int. Anesthesiol. Clin. 2006, 44, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadieh, H.; Azar, S.T. Liver disease and diabetes: Association, pathophysiology, and management. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 104, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfortmueller, C.A.; Wiemann, C.; Funk, G.C.; Leichtle, A.B.; Fiedler, G.M.; Exadaktylos, A.K.; Lindner, G. Hypoglycemia is associated with increased mortality in patients with acute decompensated liver cirrhosis. J. Crit. Care 2014, 29, 316.e7–316.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.; Hsu, C.; Neelakanta, G.; Nourmand, H.; Braunfeld, M.; Wray, C.; Steadman, R.H.; Hu, K.Q.; Cheng, R.T.; Xia, V.W. Severe intraoperative hyperglycemia is independently associated with surgical site infection after liver transplantation. Transplantation 2009, 87, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallia, A.; Parikh, N.D.; Molitch, M.E.; Mahler, E.; Tian, L.; Huang, J.J.; Levitsky, J. Posttransplant hyperglycemia is associated with increased risk of liver allograft rejection. Transplantation 2010, 89, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, N.; Derby, T.; Gupta, S.; Fulkerson, C.; Oakes, D.J.; Schmidt, K.; Parikh, N.D.; Norvell, J.P.; Levitsky, J.; Rademaker, A.; et al. Inpatient hypoglycemic events in a comparative effectiveness trial for glycemic control in a high-risk population. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barri, Y.M.; Sanchez, E.Q.; Jennings, L.W.; Melton, L.B.; Hays, S.; Levy, M.F.; Klintmalm, G.B. Acute kidney injury following liver transplantation: Definition and outcome. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Li, Y.; Xia, Q.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Y.; Che, M.; Dai, H.; Qian, J.; Ni, Z.; Axelsson, J.; et al. Strong impact of acute kidney injury on survival after liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2010, 42, 3634–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, E.; Alam, A.; Tchervenkov, J.; Cantarovich, M. Impact of acute kidney injury following liver transplantation on long-term outcomes. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e12863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, M.; Umeda, Y.; Sadamori, H.; Nagasaka, T.; Takaki, A.; Matsuda, H.; Shinoura, S.; Yoshida, R.; Nobuoka, D.; Satoh, D.; et al. Risk factors for acute renal injury in living donor liver transplantation: Evaluation of the RIFLE criteria. Transpl. Int. 2013, 26, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Lyu, L.; Ma, X.; Miao, G.; Chu, H. Modifiable risk factors of acute kidney injury after liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmi, I.A.; Damian, D.; Al-Khafaji, A.; Planinsic, R.; Boucek, C.; Sakai, T.; Chang, C.C.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury following orthotopic liver transplantation: Incidence, risk factors, and effects on patient and graft outcomes. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, C.E.; Der Mesropian, P.J.; Mathew, R.O.; Slawski, B. Hyperglycemia and acute kidney injury during the perioperative period. Curr. Diab Rep. 2016, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.; Ryu, H.G. Association between perioperative hyperglycemia or glucose variability and postoperative acute kidney injury after liver transplantation: A retrospective observational study. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 124, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.S. Predictive roles of intraoperative blood glucose for post-transplant outcomes in liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6835–6841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.S.; Pelletier, S.J.; Shanks, A.; Thompson, A.; Sonnenday, C.J.; Picton, P. Intraoperative glycemic control in patients undergoing orthotopic liver transplant: A single center prospective randomized study. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simha, V.; Shah, P. Perioperative glucose control in patients with diabetes undergoing elective surgery. JAMA 2019, 321, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Siddiqui, U.; Paul, J. A survey: Perioperative diabetes medications and glucose control-time to re-examine management? Can. J. Anaesth. 2019, 66, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogt, A.P.; Bally, L. Perioperative glucose management: Current status and future directions. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2020, 34, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchison, S.R.; Rettke, S.R.; Fromme, G.A.; Janossy, T.A.; Kunkel, S.E.; Williamson, K.R.; Perkins, J.D.; Rakela, J. Plasma glucose concentrations during liver transplantation. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1989, 64, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shangraw, R.E.; Hexem, J.G. Glucose and potassium metabolic responses to insulin during liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. Surg. 1996, 2, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, G.; Agha, R.; Albrecht, J.; Goel, P.; Mukherjee, I.; Pai, P.; D’Cruz, A.K.; Nixon, I.J.; Roberto, K.; Enam, S.A.; et al. STROCSS 2021: Strengthening the reporting of cohort, cross-sectional and case-control studies in surgery. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 96, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.W.; Kim, W.J.; Jeong, H.W.; Kwon, H.M.; Moon, Y.J.; Jun, I.G.; Song, J.G.; Hwang, G.S. Impact of inhalational anesthetics on liver regeneration after living donor hepatectomy: A propensity score-matched analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G. A complete treatment of adult living donor liver transplantation: A review of surgical technique and current challenges to expand indication of patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Ahn, C.S.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, D.B.; Ha, T.Y.; Song, G.W.; Jung, D.H.; Park, G.C.; Lee, S.G. A cross-sectional analysis of long-term immunosuppressive regimens after liver transplantation at Asan Medical Center: Increased preference for mycophenolate mofetil. Ann. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 2018, 22, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, S.; Lee, S.G.; Ahn, C.S.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, D.B.; Ha, T.Y.; Song, G.W.; Jung, D.H.; Choi, N.K.; Kim, K.W.; et al. A clinical assessment of mycophenolate drug monitoring after liver transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2010, 24, E35–E42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.P.; Shaz, B.H. Update on massive transfusion. Br. J. Anaesth. 2013, 111 (Suppl. S1), i71–i82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paugam-Burtz, C.; Kavafyan, J.; Merckx, P.; Dahmani, S.; Sommacale, D.; Ramsay, M.; Belghiti, J.; Mantz, J. Postreperfusion syndrome during liver transplantation for cirrhosis: Outcome and predictors. Liver Transpl. 2009, 15, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furnary, A.P.; Wu, Y.; Bookin, S.O. Effect of hyperglycemia and continuous intravenous insulin infusions on outcomes of cardiac surgical procedures: The Portland Diabetic Project. Endocr. Pract. 2004, 10 (Suppl. S2), 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khwaja, A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2012, 120, c179–c184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levey, A.S.; Eckardt, K.U.; Tsukamoto, Y.; Levin, A.; Coresh, J.; Rossert, J.; De Zeeuw, D.; Hostetter, T.H.; Lameire, N.; Eknoyan, G. Definition and classification of chronic kidney disease: A position statement from Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2089–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paka, P.; Lieber, S.R.; Lee, R.A.; Desai, C.S.; Dupuis, R.E.; Barritt, A.S. Perioperative glucose management and outcomes in liver transplant recipients: A qualitative systematic review. World J. Transplant. 2018, 8, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. The pathobiology of diabetic complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, R.; Xu, F.; Dang, K.; Liu, T.; Behrends, M.; Brakeman, P.R.; Wiener-Kronish, J.; Niemann, C.U. Transient hyperglycemia affects the extent of ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Anesthesiology 2008, 108, 402–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razavi Nematollahi, L.; Kitabchi, A.E.; Stentz, F.B.; Wan, J.Y.; Larijani, B.A.; Tehrani, M.M.; Gozashti, M.H.; Omidfar, K.; Taheri, E. Proinflammatory cytokines in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemic stress in healthy subjects. Metabolism 2009, 58, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, S.; Xiong, X.; Zhou, L.; Shi, J.; Chen, D. Intraoperative glucose and kidney injury after on-pump cardiac surgery: A retrospective cohort study. J. Surg. Res. 2024, 300, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordillo, R.; Ahluwalia, T.; Woroniecki, R. Hyperglycemia and acute kidney injury in critically ill children. Int. J. Nephrol. Renovasc Dis. 2016, 9, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, S.; Choi, J.; Lim, S.; Choi, H.J.; Park, J.; Hong, S.H.; Park, C.S.; Choi, J.H.; Chae, M.S. Stress burden related to postreperfusion syndrome may aggravate hyperglycemia with insulin resistance during living donor liver transplantation: A propensity score-matching analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, L.S.; Amdur, R.L.; Amodeo, S.; Kimmel, P.L.; Palant, C.E. The severity of acute kidney injury predicts progression to chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2011, 79, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Fan, L.C.; Zhao, X.; Xia, W.; Luo, A.L.; Tian, Y.K.; Wang, X.R. Risk factors for acute kidney injury after orthotopic liver transplantation: A single-center data analysis. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technolog Med. Sci. 2017, 37, 861–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Peralvarez, M.; Germani, G.; Darius, T.; Lerut, J.; Tsochatzis, E.; Burroughs, A.K. Tacrolimus trough levels, rejection and renal impairment in liver transplantation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Transpl. 2012, 12, 2797–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.M.; Hwang, G.S. Cardiovascular dysfunction and liver transplantation. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2018, 71, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozhathil, D.K.; Li, Y.F.; Smith, J.K.; Tseng, J.F.; Saidi, R.F.; Bozorgzadeh, A.; Shah, S.A. Impact of center volume on outcomes of increased-risk liver transplants. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Before PSM | After PSM | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Optimal REP BG (n = 1808) | Non-Optimal REP BG (n = 1523) | p | SMD | Optimal REP BG (n= 1134) | Non-Optimal REP BG (n = 1134) | p | SMD | |
| Demographic characteristics | ||||||||
| Age, years | 53.7 ± 8.2 | 52.9 ± 8.8 | 0.007 | 0.094 | 53.4 ± 8.2 | 53.3 ± 8.7 | 0.754 | −0.013 |
| Sex, male | 1095 (71.9%) | 1369 (75.7%) | 0.012 | 0.087 | 820 (72.3%) | 821 (72.4%) | 0.963 | −0.002 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.6 ± 3.6 | 24.2 ± 3.3 | 0.007 | 0.094 | 24.4 ± 3.3 | 24.5 ± 3.5 | 0.603 | 0.022 |
| Pre-operative variables | ||||||||
| DM | 463 (30.4%) | 322 (17.8%) | <0.001 | 0.298 | 266 (23.5%) | 298 (26.3%) | 0.120 | −0.065 |
| HTN | 238 (15.6%) | 312 (17.3%) | 0.207 | 0.044 | 179 (15.8%) | 181 (16.0%) | 0.909 | −0.005 |
| MELD_Na score | 16.6 ± 7.8 | 13.2 ± 7.2 | <0.001 | 0.457 | 15.2 ± 7.2 | 15.0 ± 7.8 | 0.468 | −0.031 |
| CTP | 8.5 ± 2.2 | 7.4 ± 2.2 | <0.001 | 0.493 | 8.1 ± 2.1 | 8.0 ± 2.3 | 0.247 | −0.005 |
| HCC | 744 (48.9%) | 1044 (57.7%) | <0.001 | 0.179 | 592 (52.2%) | 579 (51.1%) | 0.585 | 0.023 |
| Original disease | ||||||||
| HBV | 917 (60.2%) | 1188 (65.7%) | 0.001 | 0.144 | 705 (62.2%) | 695 (61.3%) | 0.666 | 0.018 |
| HCV | 122 (8.0%) | 99 (5.5%) | 0.003 | 0.101 | 76 (6.7%) | 78 (6.9%) | 0.867 | −0.007 |
| Alcoholic | 320 (21.0%) | 291 (16.1%) | <0.001 | 0.127 | 225 (19.8%) | 231 (20.4%) | 0.753 | −0.013 |
| GRWR, % | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | <0.001 | 0.248 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | 1.1 ± 0.3 | 0.493 | −0.029 |
| Pre-operative lab data | ||||||||
| Hematocrit, % | 31.4 ± 5.9 | 33.5 ± 6.4 | <0.001 | 0.335 | 32.0 ± 6.0 | 32.1 ± 6.3 | 0.930 | 0.004 |
| Platelets, ×103/µL | 67.6 ± 45.2 | 82.4 ± 55.3 | <0.001 | 0.294 | 78.3 ± 71.4 | 77.0 ± 53.7 | 0.628 | 0.020 |
| Prothrombin time, INR | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 1.4 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | 0.261 | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 1.5 ± 0.7 | 0.264 | 0.047 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.153 | 0.050 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.091 | 0.071 |
| Albumin, g/dL | 3.0 ± 0.6 | 3.2 ± 0.6 | <0.001 | 0.389 | 3.1 ± 0.5 | 3.1 ± 0.6 | 0.276 | 0.046 |
| Sodium, mmol/L | 137.2 ± 5.4 | 139.0 ± 4.3 | <0.001 | 0.360 | 137.9 ± 4.9 | 138.3 ± 4.7 | 0.069 | 0.076 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 5.8 ± 8.8 | 3.8 ± 6.9 | <0.001 | 0.261 | 5.0 ± 8.0 | 4.9 ± 8.1 | 0.834 | 0.006 |
| AST, IU/L | 69.3 ± 175.7 | 57.6 ± 114.4 | 0.025 | 0.079 | 65.9 ± 132.9 | 65.4 ± 137.4 | 0.926 | 0.004 |
| ALT, IU/L | 53.2 ± 215.7 | 50.5 ± 171.1 | 0.699 | 0.014 | 50.7 ± 175.9 | 57.4 ± 201.5 | 0.402 | 0.035 |
| HbA1c, % | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 5.8 ± 1.4 | <0.001 | 0.143 | 5.7 ± 1.3 | 5.8 ± 1.4 | 0.429 | 0.037 |
| Intra-operative variables | ||||||||
| Duration of anesthesia, min | 866.7 ± 150.2 | 830.8 ± 142.7 | <0.001 | 0.245 | 851.2 ± 145.5 | 850.0 ± 149.3 | 0.847 | −0.008 |
| Crystalloid infusion, mL | 7902.1 ± 4015.8 | 7343.4 ± 4126.3 | <0.001 | 0.137 | 7515.8 ± 3545.8 | 7636.8 ± 4762.4 | 0.493 | 0.029 |
| Colloid infusion, mL | 4285.3 ± 3083.0 | 3541.2 ± 3303.5 | <0.001 | 0.233 | 4036.4 ± 3988.3 | 4001.5 ± 3921.1 | 0.812 | 0.010 |
| Massive transfusion | 734 (48.2%) | 437 (24.2%) | <0.001 | 0.516 | 432 (38.1%) | 419 (37.0%) | 0.573 | −0.024 |
| Urine output, mL | 1892.4 ± 984.2 | 2065.1 ± 1134.9 | <0.001 | 0.163 | 2006.8 ± 1316.5 | 2014.5 ± 1089.0 | 0.879 | 0.006 |
| Total ischemic time, min | 127.4 ± 32.0 | 127.0 ± 37.8 | 0.767 | 0.010 | 126.2 ± 31.0 | 127.5 ± 34.0 | 0.336 | 0.040 |
| Post-reperfusion syndrome | 934 (61.3%) | 986 (54.5%) | <0.001 | 0.138 | 676 (59.6%) | 680 (60.0%) | 0.864 | 0.007 |
| Use of vasopressor, % | 992 (65.1) | 1209 (66.9) | 0.299 | 0.037 | 743 (65.5) | 770 (67.9) | 0.247 | 0.051 |
| Postoperative variable | ||||||||
| Mean cTAC, ng/mL | 9.9 ± 2.7 | 9.3 ± 2.8 | <0.001 | 0.212 | 6.5 ± 3.2 | 6.7 ± 3.3 | 0.159 | 0.069 |
| Donor characteristics | ||||||||
| Age, years | 28.7 ± 8.4 | 28.3 ± 8.3 | 0.170 | 0.048 | 28.5 ± 8.6 | 28.5 ± 8.6 | 0.660 | −0.019 |
| Sex, male | 1043 (68.5%) | 1238 (68.5%) | 0.995 | <0.001 | 773 (68.2%) | 773 (68.2%) | 0.964 | −0.002 |
| Pre-operative FC | 6.6 ± 8.3 | 6.8 ± 8.2 | 0.515 | 0.023 | 6.6 ± 8.2 | 6.8 ± 823 | 0.559 | 0.025 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | p | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| Pre-operative variables | ||||||
| Age, years | 1.00 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.744 | |||
| Sex, male | 0.91 | 0.77–1.07 | 0.262 | |||
| DM | 1.18 | 1.00–1.41 | 0.055 | |||
| HTN | 1.06 | 0.87–1.29 | 0.556 | |||
| MELD_Na score | 1.04 | 1.03–1.05 | <0.001 | |||
| CTP | 1.18 | 1.14–1.22 | <0.001 | 1.14 | 1.09–1.19 | <0.001 |
| HBV | 0.91 | 0.78–1.05 | 0.200 | |||
| HCV | 1.59 | 1.16–2.19 | 0.004 | 1.59 | 1.15–2.23 | 0.006 |
| Alcoholic | 1.06 | 0.88–1.28 | 0.553 | |||
| HCC | 0.72 | 0.62–0.83 | <0.001 | |||
| GRWR (%) | 0.50 | 0.37–0.67 | <0.001 | 0.51 | 0.37–0.71 | <0.001 |
| Intra-operative variables | ||||||
| Non-optimal REP BG * | 1.54 | 1.33–1.79 | <0.001 | 1.25 | 1.06–1.47 | 0.007 |
| Duration of anesthesia, hours | 1.24 | 1.20–1.29 | <0.001 | 1.17 | 1.13–1.22 | <0.001 |
| Cold ischemic time, hours | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.657 | |||
| Warm ischemic time, hours | 1.01 | 1.01–1.02 | <0.001 | |||
| Massive transfusion | 2.03 | 1.73–2.39 | <0.001 | |||
| Post-reperfusion syndrome | 0.87 | 0.75–1.01 | 0.059 | |||
| Use of vasopressor | 0.62 | 0.53–0.73 | <0.001 | 0.74 | 0.62–0.88 | <0.001 |
| Donor-related variables | ||||||
| Donor age, years | 1.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.191 | |||
| Donor sex, male | 1.04 | 0.89–1.21 | 0.650 | |||
| Pre-operative FC | 0.99 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.227 | |||
| Postoperative variables | ||||||
| Mean cTAC | 1.10 | 1.07–1.13 | <0.001 | 1.10 | 1.07–1.14 | <0.001 |
| Crude | Propensity Score-Matching | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Event/N (%) | OR | 95% CI | p | Event/N (%) | OR | 95% CI | p | |
| AKI | ||||||||
| Optimal REP BG | 1129/1808 (62.4) | 1 (reference) | 754/1134 (66.5) | 1 (reference) | ||||
| Non-optimal REP BG | 1094/1523 (71.8) | 1.53 | 1.32–1.78 | <0.001 | 801/1134 (70.6) | 1.21 | 1.02–1.45 | 0.037 |
| Severe AKI | ||||||||
| Optimal REP BG | 435/1808 (24.1) | 1 (reference) | 323/1134 (28.5) | 1 (reference) | ||||
| Non-optimal REP BG | 559/1523 (36.7) | 1.83 | 1.58–2.13 | < 0.001 | 391/1134 (34.5) | 1.32 | 1.11–1.58 | 0.002 |
| CKD | ||||||||
| Optimal REP BG | 814/1780 (45.7) | 1 (reference) | 512/1132 (45.2) | 1 (reference) | ||||
| Non-optimal REP BG | 772/1490 (51.8) | 1.28 | 1.11–1.46 | 0.001 | 561/1131 (49.6) | 1.19 | 1.01–1.41 | 0.039 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, H.-M.; Jin, Y.Z.; Kim, S.-H.; Jun, I.-G.; Song, J.-G.; Hwang, G.-S. Impact of Glycemic Control After Reperfusion on the Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury Following Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Medicina 2025, 61, 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081325
Kim YJ, Kwon H-M, Jin YZ, Kim S-H, Jun I-G, Song J-G, Hwang G-S. Impact of Glycemic Control After Reperfusion on the Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury Following Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Medicina. 2025; 61(8):1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081325
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yeon Ju, Hye-Mee Kwon, Yan Zhen Jin, Sung-Hoon Kim, In-Gu Jun, Jun-Gol Song, and Gyu-Sam Hwang. 2025. "Impact of Glycemic Control After Reperfusion on the Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury Following Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis" Medicina 61, no. 8: 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081325
APA StyleKim, Y. J., Kwon, H.-M., Jin, Y. Z., Kim, S.-H., Jun, I.-G., Song, J.-G., & Hwang, G.-S. (2025). Impact of Glycemic Control After Reperfusion on the Incidence of Acute Kidney Injury Following Living Donor Liver Transplantation: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Medicina, 61(8), 1325. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61081325






