Proposing an Optimal Occlusal Angle for Minimizing Masticatory and Cervical Muscle Activity in the Supine Position: A Resting EMG and Mixed-Effects Modeling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Participants
2.2. Pillow Height
2.3. Participant Posture
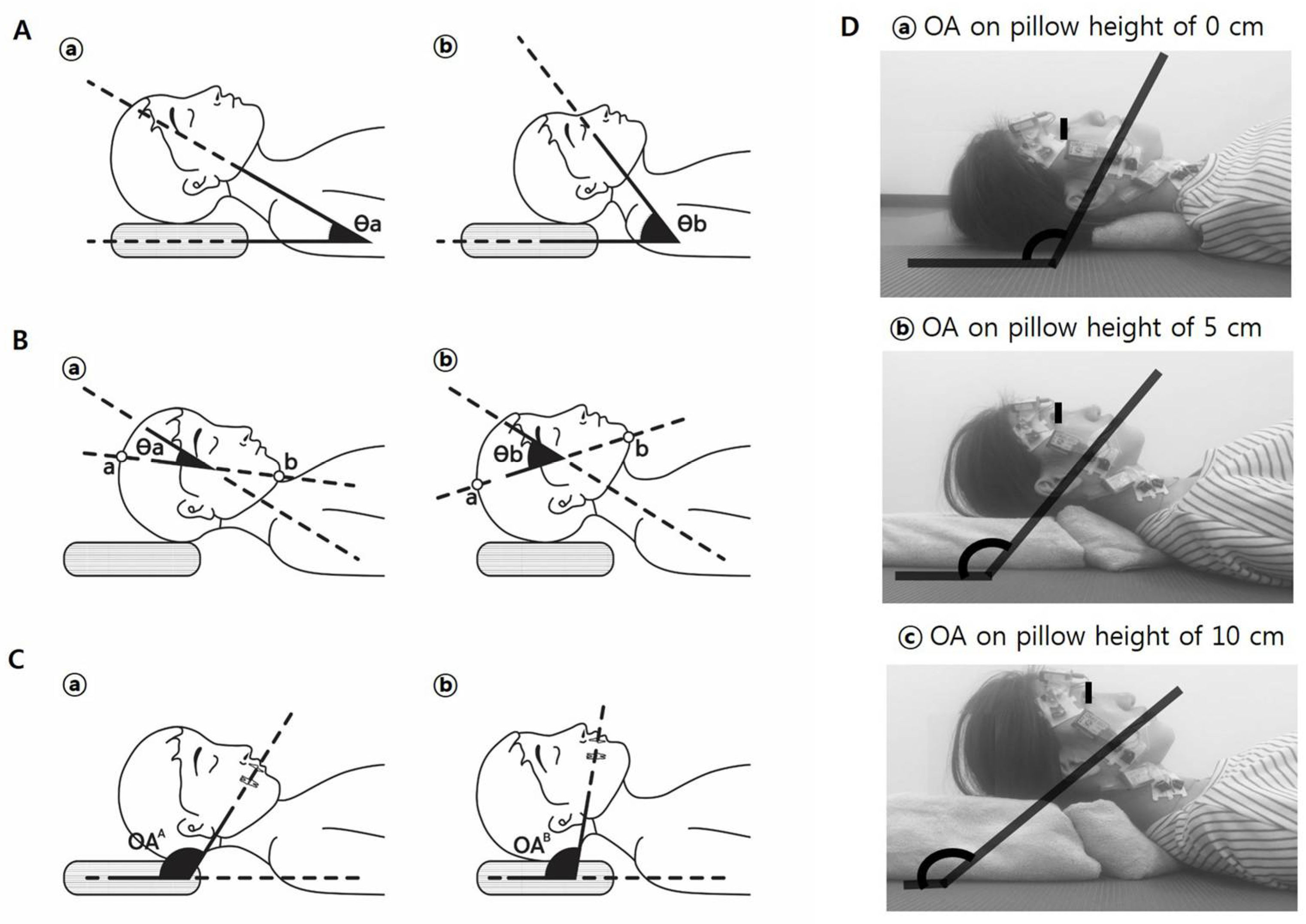
2.4. Measurement of OA
2.5. Measurement of MCM Activity Using Surface Electromyography Protocol
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Association Between OA and Baseline Characteristics (Age, Height, Weight, and BMI) of Participants
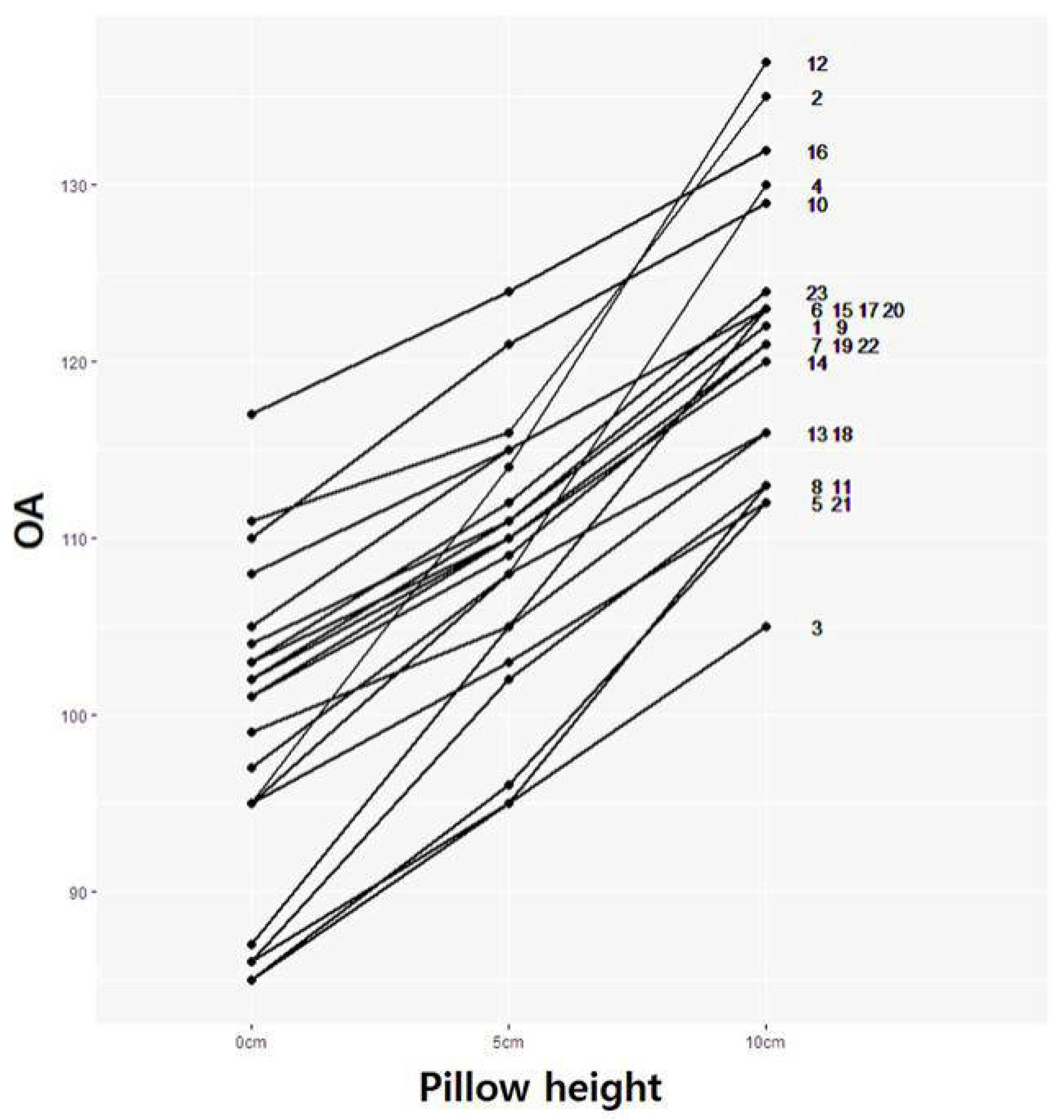
3.2. OA Change According to OA Modulated by Pillow Height
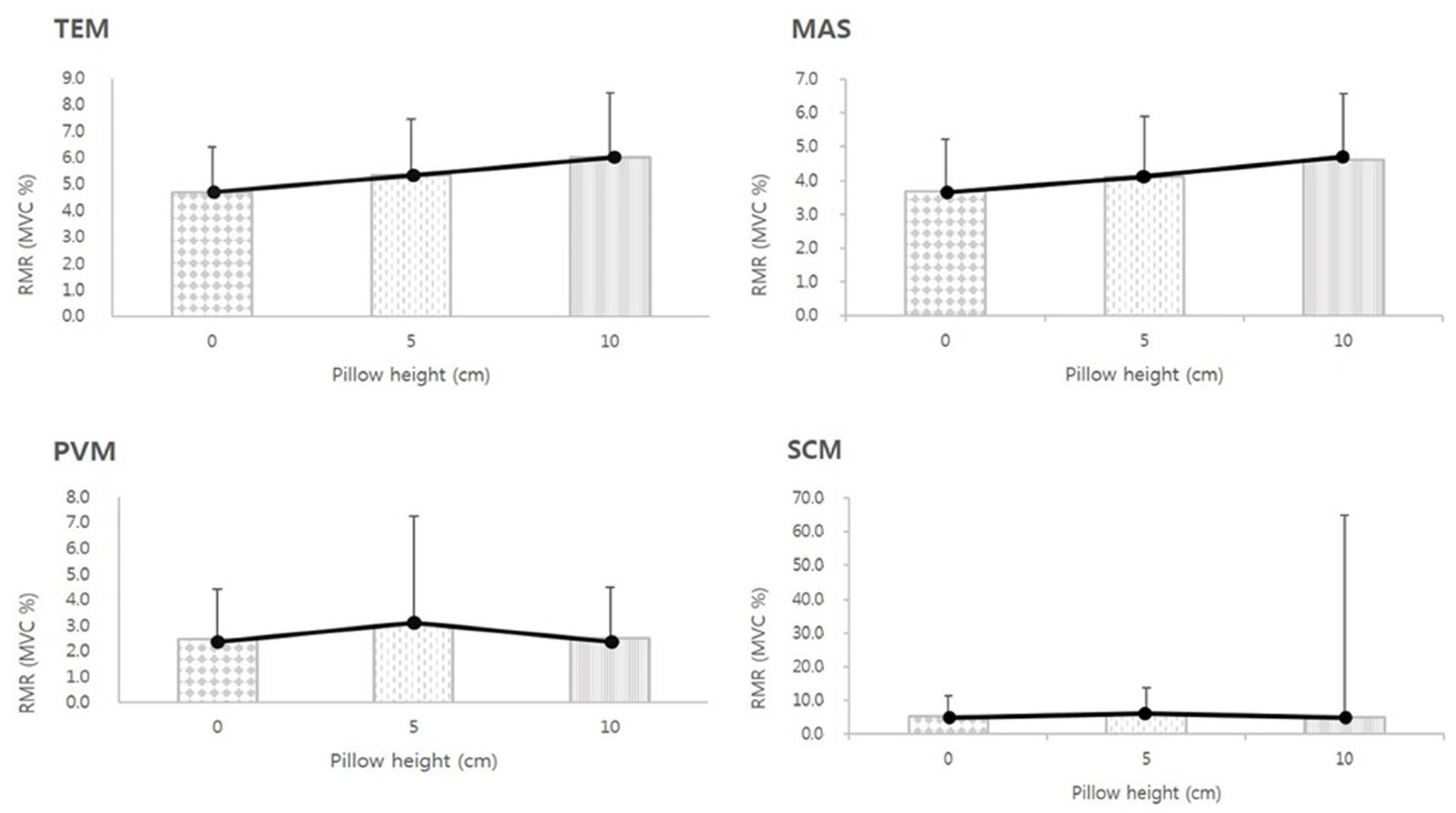
3.3. RMR of MCMs According to Pillow Height
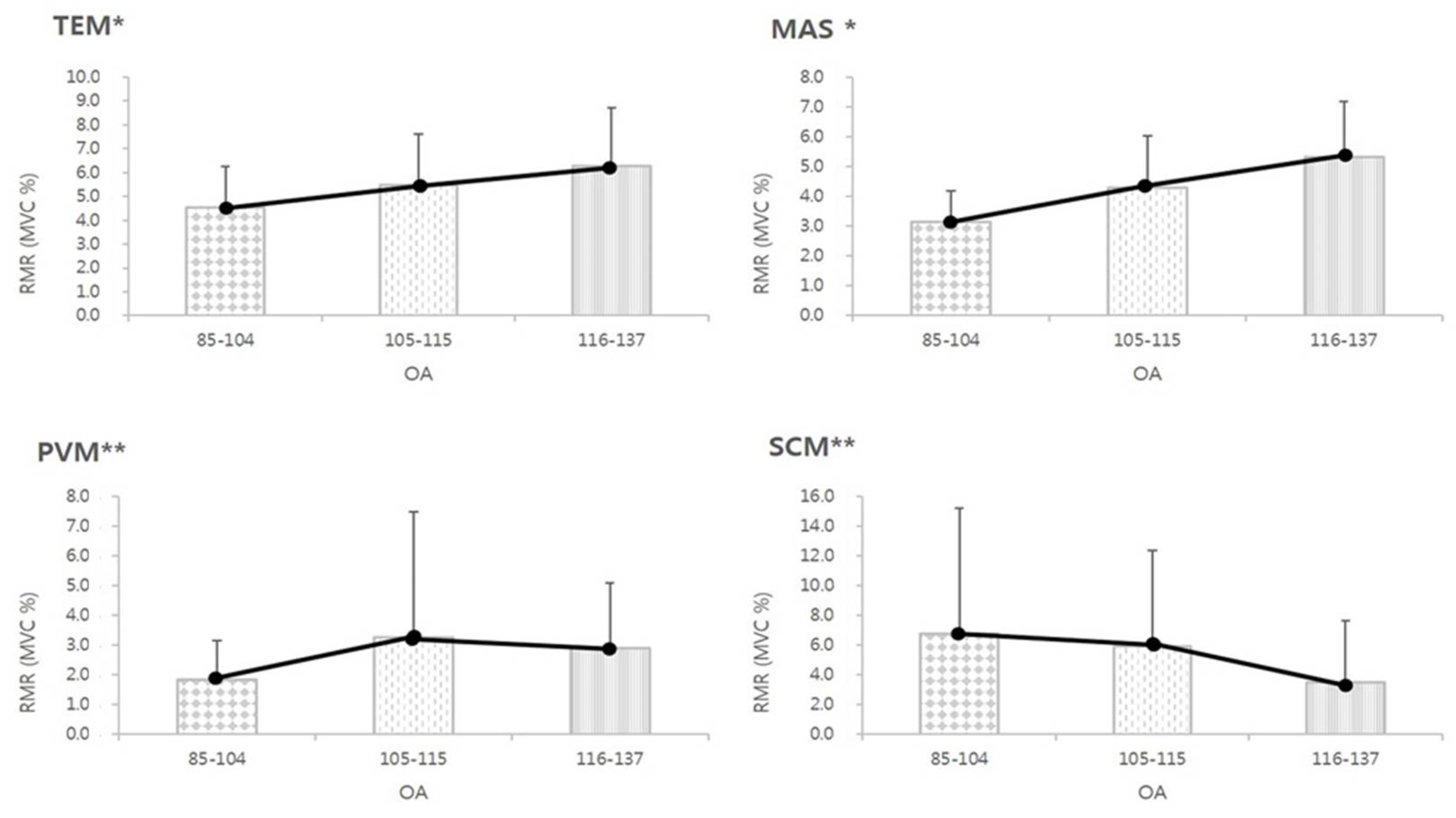
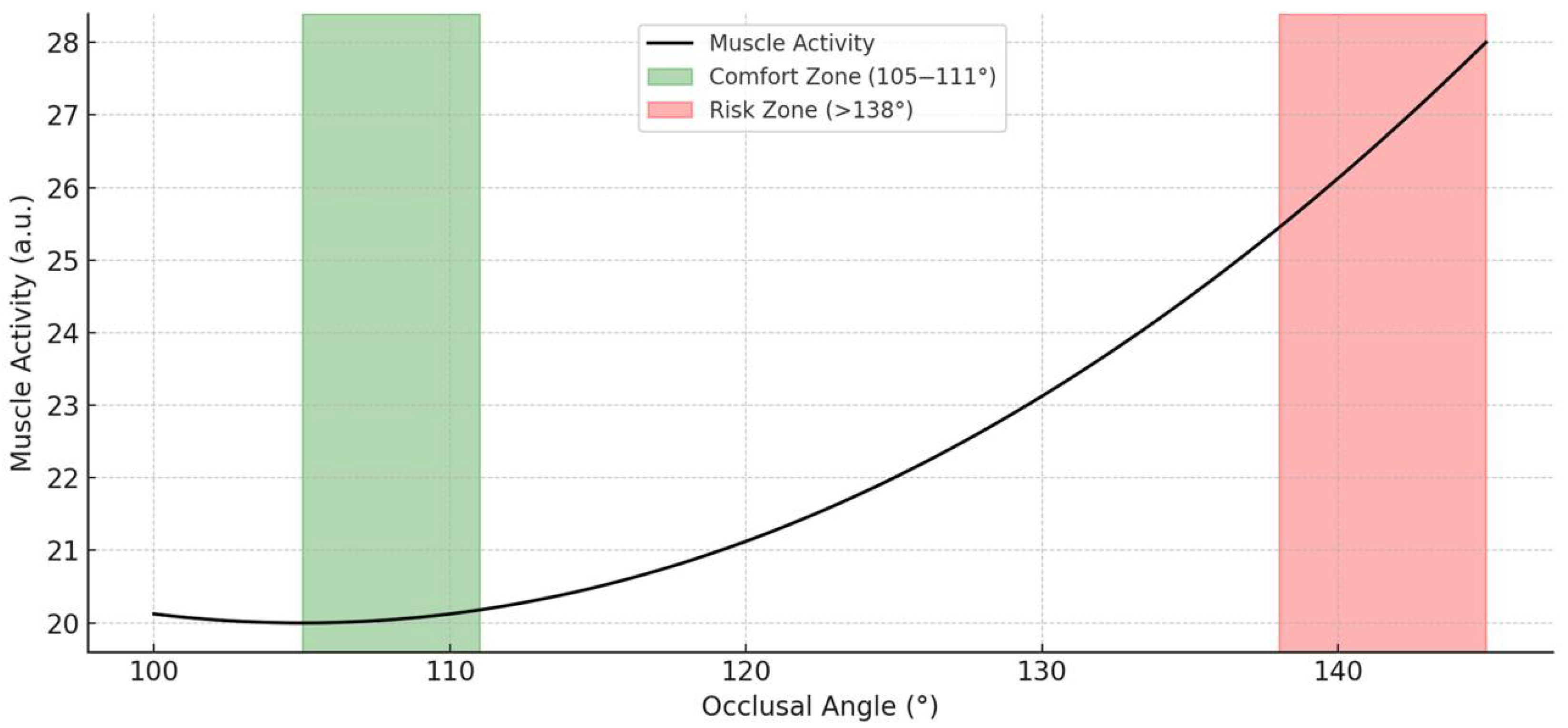
3.4. The RMR of MCM According to the OA
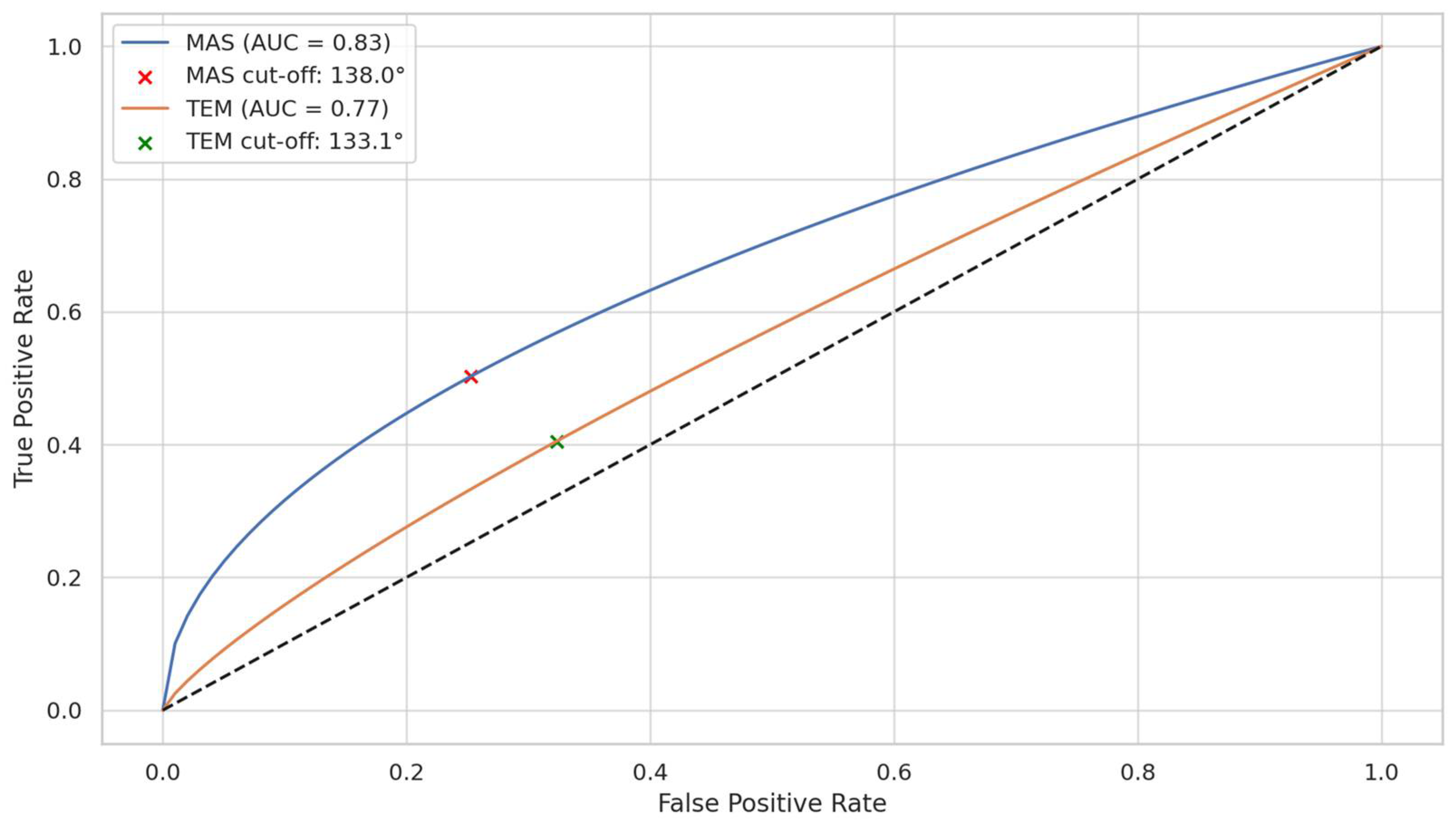
3.5. Discriminative Ability of OA to Predict Muscle Hyperactivity
3.6. Linear Regression Analysis of OA and Muscle Activity
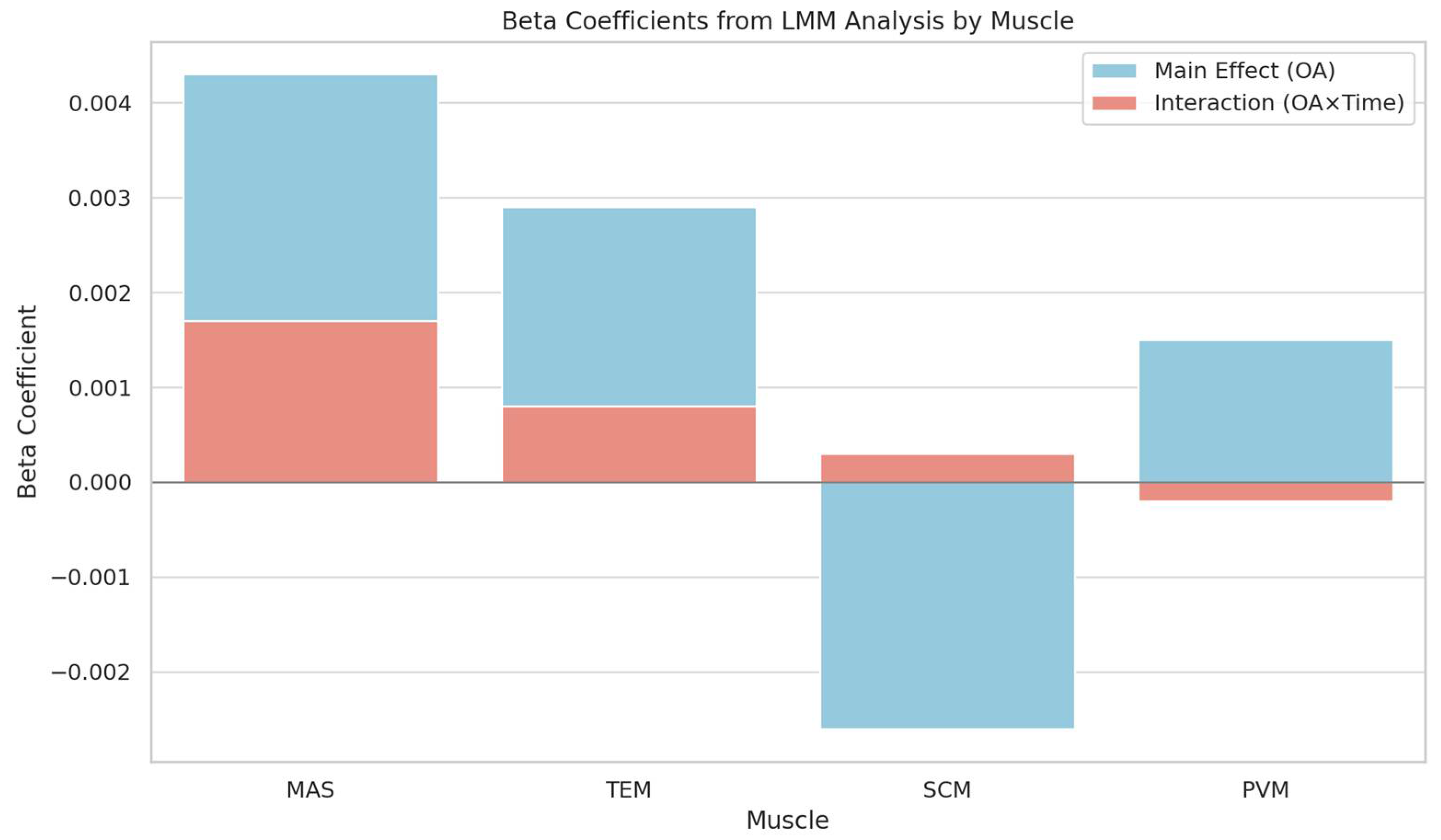
3.7. Linear Mixed-Effects Model Analysis of RMR According to OA and Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OA | Occlusal Angle |
| MAS | Masseter Muscle |
| TEM | Temporalis Muscle |
| SCM | Sternocleidomastoid Muscle |
| PVM | Posterior Vertebral Muscle |
| MCM | Masticatory and Cervical Muscles |
| RMR | Resting Muscle Activity Ratio |
| LMM | Linear Mixed-Effects Model |
| ICC | Intraclass Correlation Coefficient |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| WCSS | Within-Cluster Sum of Squares |
| ANOVA | Analysis of Variance |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
References
- Chun-Yiu, J.P.; Man-Ha, S.T.; Chak-Lun, A.F. The effects of pillow designs on neck pain, waking symptoms, neck disability, sleep quality and spinal alignment in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Biomech. 2021, 85, 105353. [Google Scholar]
- Erfanian, P.; Tenzif, S.; Guerriero, R.C. Assessing effects of a semi-customized experimental cervical pillow on symptomatic adults with chronic neck pain with and without headache. J. Can Chiropr. Assoc. 2004, 48, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santander, H.; Miralles, R.; Pérez, J.; Valenzuela, S.; Ravera, M.J.; Ormeño, G.; Villegas, R. Effects of head and neck inclination on bilateral sternocleidomastoid EMG activity in healthy participants and in patients with myogenic cranio-cervical-mandibular dysfunction. Cranio 2000, 18, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiatkulanusorn, S.; Suato, B.P.; Werasirirat, P. Analysis of neck and back muscle activity during the application of various pillow designs in patients with forward head posture. J. Back. Musculoskelet. Rehabil. 2021, 34, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.C.; Chan, R.C.; Wu, H.L.; Lai, C.J. Effect of pillow size preference on extensor digitorum communis muscle strength and electromyographic activity during maximal contraction in healthy individuals: A pilot study. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2015, 78, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sacco, I.C.; Pereira, I.L.; Dinato, R.C.; Silva, V.C.; Friso, B.; Viterbo, S.F. The effect of pillow height on muscle activity of the neck and mid-upper back and patient perception of comfort. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2015, 38, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.X.; Yang, P.F.; Yang, A.L.; Gong, Y.F.; Shang, P.; Yuan, X.C. Ergonomic Consideration in Pillow Height Determinants and Evaluation. Healthcare 2021, 9, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.J.; Grimmer-Somers, K.; Trott, P. Pillow use: The behaviour of cervical pain, sleep quality and pillow comfort in side sleepers. Man. Ther. 2009, 14, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, C.; Miralles, R.; Miranda, C.; Valenzuela, S.; Casassus, R.; Santander, H.; Ormeño, G. Effects of two types of pillows on bilateral sternocleidomastoid EMG activity in healthy participants and in patients with myogenic cranio-cervical-mandibular dysfunction. Cranio 1999, 17, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kofide, E.A.; Al-Namankani, E. The association between posture of the head and malocclusion in Saudi participants. Cranio 2007, 25, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, C.M.; Huddleston Slater, J.J.; Lobbezoo, F.; Naeije, M. Kinematics of the human mandible for different head postures. J. Oral Rehabil. 2000, 27, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koolstra, J.H.; van Eijden, T.M. The Jaw Open-Close Movements Predicted by Biomechanical Modelling. J. Biomech. 1997, 30, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makofsky, H.W.; Sexton, J.C.; Diamond, J.; Haden, K. The Effect of Head Posture on Muscle Contact Position Using the T-Scan System of Occlusal Analysis. Cranio 1991, 9, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Chen, H.L. Ergonomic approach for pillow concept design. Appl. Ergon. 2016, 52, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, K.; Cho, M. Analysis of the pulmonary functions of normal adults according to occlusal angle (OA), as modulated by pillow height. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 3085–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.P.; Costa, D.R.; Oliveira, A.I.; Carvalho, E.A.; Conti, P.C.; Costa, Y.M.; Bonjardim, L.R. Short-term transcutaneous elec-trical nerve stimulation reduces pain and improves the masticatory muscle activity in temporomandibular disorder patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017, 25, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrout, P.E.; Fleiss, J.L. Intraclass correlations: Uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull. 1979, 86, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddu, S.C.; Dyasanoor, S.; Valappila, N.J.; Ravi, B.V. The evaluation of head and craniocervical posture among patients with and without temporomandibular joint disorders—A comparative study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, ZC55–ZC58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulin, E.F.; Guedes, C.G.; Feltrin, P.P.; Joffiley, C.M. Association between temporomandibular disorders and abnormal head postures. Braz. Oral Res. 2015, 29, S1806-83242015000100260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woda, A.; Pionchon, P.; Palla, S. Regulation of mandibular postures: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 2001, 12, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, S.; Carra, M.C.; Huynh, N.T.; Rompré, P.H.; Lavigne, G.J. Females with sleep bruxism show lower theta and alpha electro-encephalographic activity irrespective of transient morning masticatory muscle pain. J. Orofac. Pain 2013, 27, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamato, A.; Panza, F.; Di Venere, D.; Solfrizzi, V.; Frisardi, V.; Ranieri, M.; Fiore, P. Effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A treatment of neck pain related to nocturnal bruxism: A case report. J. Chiropr. Med. 2010, 9, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, L.M.N.; Rossetti, P.H.O.; Conti, P.C.R.; Araujo, C.D.R.P.D. Association between sleep bruxism and temporomandibular disorders: A polysomnographic pilot study. Cranio 2008, 26, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclean, L.F.; Brenman, H.S.; Friedman, M.G. Effects of changing body position on dental occlusion. J. Dent. Res. 1973, 52, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.E.; Christensen, L.V. Mandibular reference positions. J. Oral Rehabil. 1985, 12, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, K.G.; Janal, M.N.; Sirois, D.A.; Dubrovsky, B.; Wigren, P.E.; Klausner, J.J.; Krieger, A.C.; Lavigne, G.J. Masticatory muscle sleep background electromyographic activity is elevated in myofascial temporomandibular disorder patients. J. Oral Rehabil. 2013, 40, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lee, Y.; Liang, J. Shape design o an optimal comfortable pillow based on the analytic hierarchy process method. J. Chiropr. Med. 2011, 10, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, P. Current concepts in muscle stretching for exercise and rehabilitation. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 2012, 7, 109–119. [Google Scholar]

| Male | Female | Total | r | |
| Age (year) | 36 ± 13.53 | 32.59 ± 11.50 | 42.44 ± 15.36 | −0.28 * |
| Height (cm) | 165.42 ± 9.2 | 160.82 ± 6.93 | 174.11 ± 6.21 | −0.35 ** |
| Weight (kg) | 62.1 ± 17.56 | 52.97 ± 6.79 | 79.33 ± 18.98 | −0.25 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 22.32 ± 3.91 | 20.41 ± 1.40 | 25.93 ± 4.62 | −0.18 |
| OA (5 cm) 1 | 104.67 ± 9.98 | 110.44 ± 5.43 | 108.86 ± 7.43 |
| OA | |||
| F-Stat | η2 | Effect Size | |
| TEM | 9.591 ** | 0.108 | Medium |
| MAS | 25.437 ** | 0.242 | Large |
| PVM | 3.609 * | 0.043 | Small |
| SCM | 3.460 * | 0.042 | Small |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, K.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Huh, S.; Song, B.-S.; Ju, H.-M.; Jeong, S.-H.; Ahn, Y.-W.; Ok, S.-M. Proposing an Optimal Occlusal Angle for Minimizing Masticatory and Cervical Muscle Activity in the Supine Position: A Resting EMG and Mixed-Effects Modeling Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071274
Kim K-H, Lee C-H, Huh S, Song B-S, Ju H-M, Jeong S-H, Ahn Y-W, Ok S-M. Proposing an Optimal Occlusal Angle for Minimizing Masticatory and Cervical Muscle Activity in the Supine Position: A Resting EMG and Mixed-Effects Modeling Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071274
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Kyung-Hee, Chang-Hyung Lee, Sungchul Huh, Byong-Sop Song, Hye-Min Ju, Sung-Hee Jeong, Yong-Woo Ahn, and Soo-Min Ok. 2025. "Proposing an Optimal Occlusal Angle for Minimizing Masticatory and Cervical Muscle Activity in the Supine Position: A Resting EMG and Mixed-Effects Modeling Study" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071274
APA StyleKim, K.-H., Lee, C.-H., Huh, S., Song, B.-S., Ju, H.-M., Jeong, S.-H., Ahn, Y.-W., & Ok, S.-M. (2025). Proposing an Optimal Occlusal Angle for Minimizing Masticatory and Cervical Muscle Activity in the Supine Position: A Resting EMG and Mixed-Effects Modeling Study. Medicina, 61(7), 1274. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071274






