Clinical Application of a Customized Gene Panel for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Variants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients Recruitment and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Next-Generation Sequencing
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACMG | American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics |
| ASD | Autism spectrum disorder |
| IGV | Integrated genomics viewer |
| MAF | Minor allele frequency |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| SFARI | Simons Foundation Autism Research Initiative |
| VUS | Variant of uncertain significance |
| WES | Whole exome sequencing |
References
- Mahjouri, S.; Lord, C.E. What the DSM-5 Portends for Research, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2012, 14, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrington, S.J.; Kent, R.G.; Maljaars, J.; Le Couteur, A.; Gould, J.; Wing, L.; Noens, I.; Van Berckelaer-Onnes, I.; Leekam, S.R. DSM-5 Autism Spectrum Disorder: In Search of Essential Behaviours for Diagnosis. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2014, 8, 701–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013; ISBN 0-89042-555-8. [Google Scholar]
- Matin, B.K.; Byford, S.; Soltani, S.; Kazemi-Karyani, A.; Atafar, Z.; Zereshki, E.; Soofi, M.; Rezaei, S.; Rakhshan, S.T.; Jahangiri, P. Contributing Factors to Healthcare Costs in Individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 22, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiurazzi, P.; Kiani, A.K.; Miertus, J.; Paolacci, S.; Barati, S.; Manara, E.; Stuppia, L.; Gurrieri, F.; Bertelli, M. Genetic Analysis of Intellectual Disability and Autism. Acta Biomed. 2020, 91, e2020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacchelli, E.; Cameli, C.; Viggiano, M.; Igliozzi, R.; Mancini, A.; Tancredi, R.; Battaglia, A.; Maestrini, E. An Integrated Analysis of Rare CNV and Exome Variation in Autism Spectrum Disorder Using the Infinium PsychArray. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanski, A.; Calle-López, Y.; Leu, C.; Pérez-Palma, E.; Pestana-Knight, E.; Lal, D. Clinical Sequencing Yield in Epilepsy, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and Intellectual Disability: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, F.; Shah, J.; Jain, D.; Shah, S.; Patel, H.; Patel, K.; Solanki, D.I.; Iyer, A.S.; Menghani, B.; Mhatre, P.; et al. Comparative Yield of Molecular Diagnostic Algorithms for Autism Spectrum Disorder Diagnosis in India: Evidence Supporting Whole Exome Sequencing as First Tier Test. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lob, K.; Sawka, D.M.; Gaitanis, J.N.; Liu, J.S.; Nie, D.A. Genetic Diagnostic Yield in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and Epilepsy Phenotypes in Children with Genetically Defined ASD. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammimies, K.; Marshall, C.R.; Walker, S.; Kaur, G.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Lionel, A.C.; Yuen, R.K.C.; Uddin, M.; Roberts, W.; Weksberg, R.; et al. Molecular Diagnostic Yield of Chromosomal Microarray Analysis and Whole-Exome Sequencing in Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. JAMA 2015, 314, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, P.; Zito, A.; Cocciadiferro, D.; Novelli, A.; Pessina, C.; Mazza, T.; Ferri, M.; Piccinelli, P.; Luoni, C.; Termine, C.; et al. Unveiling Genetic Insights: Array-CGH and WES Discoveries in a Cohort of 122 Children with Essential Autism Spectrum Disorder. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo-Dougovito, A.M.; Reeve, R.E. Exploring the Interaction of Motor and Social Skills With Autism Severity Using the SFARI Dataset. Percept. Mot. Skills 2017, 124, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpi, M.N.T.; Simpson, T.I. SFARI Genes and Where to Find Them; Modelling Autism Spectrum Disorder Specific Gene Expression Dysregulation with RNA-Seq Data. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahams, B.S.; Arking, D.E.; Campbell, D.B.; Mefford, H.C.; Morrow, E.M.; Weiss, L.A.; Menashe, I.; Wadkins, T.; Banerjee-Basu, S.; Packer, A. SFARI Gene 2.0: A Community-Driven Knowledgebase for the Autism Spectrum Disorders (ASDs). Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Goode, S.; Heemsbergen, J.; Jordan, H.; Mawhood, L.; Schopler, E. Austism Diagnostic Observation Schedule: A Standardized Observation of Communicative and Social Behavior. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1989, 19, 185–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, A.; Vinci, M.; Treccarichi, S.; Greco, D.; Rizzo, B.; Gloria, A.; Federico, C.; Saccone, S.; Musumeci, S.A.; Calì, F. Potential Association of the CSMD1 Gene with Moderate Intellectual Disability, Anxiety Disorder, and Obsessive–Compulsive Personality Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopanos, C.; Tsiolkas, V.; Kouris, A.; Chapple, C.E.; Albarca Aguilera, M.; Meyer, R.; Massouras, A. VarSome: The Human Genomic Variant Search Engine. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1978–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.J.; Velmeshev, D.; Hernandez-Pineda, D.; Sethi, S.; Sorrells, S.; Banerjee, P.; Sullivan, C.; Gupta, A.R.; Kriegstein, A.R.; Corbin, J.G. Identification of Amygdala-Expressed Genes Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Autism 2020, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scattoni, M.L.; Fatta, L.M.; Micai, M.; Sali, M.E.; Bellomo, M.; Salvitti, T.; Fulceri, F.; Castellano, A.; Molteni, M.; Gambino, G.; et al. Autism Spectrum Disorder Prevalence in Italy: A Nationwide Study Promoted by the Ministry of Health. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry Ment. Health 2023, 17, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalsner, L.; Twachtman-Bassett, J.; Tokarski, K.; Stanley, C.; Dumont-Mathieu, T.; Cotney, J.; Chamberlain, S. Genetic Testing Including Targeted Gene Panel in a Diverse Clinical Population of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: Findings and Implications. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2018, 6, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M.; El-Khechen, D.; Black, M.H.; Farwell Hagman, K.D.; Tang, S.; Powis, Z. Outcomes of Diagnostic Exome Sequencing in Patients With Diagnosed or Suspected Autism Spectrum Disorders. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 70, 34–43.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Chi, C.; Tsai, C. Diagnostic Yield and Treatment Impact of Whole-genome Sequencing in Paediatric Neurological Disorders. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2021, 63, 934–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Nonrandom Occurrence of Multiple de Novo Coding Variants in a Proband Indicates the Existence of an Oligogenic Model in Autism. Genet. Med. 2020, 22, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhao, P.A.; Eichler, E.E. Rare Variants and the Oligogenic Architecture of Autism. Trends Genet. 2022, 38, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaki, H.; Iwata, K.; Manabe, T.; Mori, N. Triggers for Autism: Genetic and Environmental Factors. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 2012, 4, JCNSD.S9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Yip, B.H.K.; Windham, G.C.; Sourander, A.; Francis, R.; Yoffe, R.; Glasson, E.; Mahjani, B.; Suominen, A.; Leonard, H.; et al. Association of Genetic and Environmental Factors with Autism in a 5-Country Cohort. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Molecular Genetic Study of Autism Consortium (IMGSAC). A Genomewide Screen for Autism: Strong Evidence for Linkage to Chromosomes 2q, 7q, and 16p. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheson, H.B.; Bradford, Y.; Folstein, S.E.; Gardiner, M.B.; Santangelo, S.L.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; Haines, J.L. Defining the Autism Minimum Candidate Gene Region on Chromosome 7. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2003, 117B, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, M.; Cantor, R.M.; Liu, J.; Gilliam, T.C.; Geschwind, D.H. Evidence for a Language Quantitative Trait Locus on Chromosome 7q in Multiplex Autism Families. Am. J. Human. Genet. 2002, 70, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstein, S.E.; Mankoski, R.E. Chromosome 7q: Where Autism Meets Language Disorder? Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 67, 278–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukier, H.N.; Skaar, D.A.; Rayner-Evans, M.Y.; Konidari, I.; Whitehead, P.L.; Jaworski, J.M.; Cuccaro, M.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Gilbert, J.R. Identification of Chromosome 7 Inversion Breakpoints in an Autistic Family Narrows Candidate Region for Autism Susceptibility. Autism Res. 2009, 2, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwerse, J.G.; Ruivenkamp, C.A.; Hansson, K.; Marijnissen, G.M.; Peters, D.J.M.; Breuning, M.H.; Hilhorst-Hofstee, Y. A Complex Chromosome 7q Rearrangement Identified in a Patient with Mental Retardation, Anxiety Disorder, and Autistic Features. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawar, A.; Manoj, G.; Nair, P.P.; Deshpande, P.; Suravajhala, R.; Suravajhala, P. Variants of Uncertain Significance: At the Crux of Diagnostic Odyssey. Gene 2025, 962, 149587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, P. Integrated Analysis and Identification of Genetic Risk Alleles Related to Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Proceedings of the 2023 11th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology, ICBCB 2023, Hangzhou, China, 21–23 April 2023; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 40–48. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; You, Y.; Yue, W.; Jia, M.; Yu, H.; Lu, T.; Wu, Z.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, D. Genetic Evidence for Possible Involvement of the Calcium Channel Gene CACNA1A in Autism Pathogenesis in Chinese Han Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.-S.; Kim, M.J.; Choi, J.E.; Islam, M.A.; Lee, Y.-K.; Xiong, Y.; Shim, K.-W.; Yang, J.-E.; Lee, R.U.; Lee, J.; et al. Dysfunction of NMDA Receptors in Neuronal Models of an Autism Spectrum Disorder Patient with a DSCAM Mutation and in Dscam-Knockout Mice. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 7538–7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosco, L.A.; Ross, A.P.; Cates, S.L.; Scott, S.E.; Wu, D.; Sohn, J.; Pleasure, D.; Pleasure, S.J.; Adamopoulos, I.E.; Zarbalis, K.S. Loss of Wdfy3 in Mice Alters Cerebral Cortical Neurogenesis Reflecting Aspects of the Autism Pathology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovato, D.V.; Herai, R.R.; Pignatari, G.C.; Beltrão-Braga, P.C.B. The Relevance of Variants With Unknown Significance for Autism Spectrum Disorder Considering the Genotype–Phenotype Interrelationship. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronemus, M.; Iossifov, I.; Levy, D.; Wigler, M. The Role of de Novo Mutations in the Genetics of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The Contribution of de Novo Coding Mutations to Autism Spectrum Disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, E.; Chawla, D. Broader Autism Phenotype in Parents of Children with Autism: A Systematic Review of Percentage Estimates. J. Child. Fam. Stud. 2018, 27, 1705–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, R.S.E.; Losh, M.; Parlier, M.; Reznick, J.S.; Piven, J. The Broad Autism Phenotype Questionnaire. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2007, 37, 1679–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, J.; Bernier, R. The Broader Autism Phenotype and Its Implications on the Etiology and Treatment of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism Res. Treat. 2011, 2011, 545901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sluijs, P.J.; Jansen, S.; Vergano, S.A.; Adachi-Fukuda, M.; Alanay, Y.; AlKindy, A.; Baban, A.; Bayat, A.; Beck-Wödl, S.; Berry, K.; et al. The ARID1B Spectrum in 143 Patients: From Nonsyndromic Intellectual Disability to Coffin–Siris Syndrome. Genet. Med. 2019, 21, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, S.-L.; Lim, K.-S.; Salleh, M.Z.; Teh, L.-K. A Heterozygous Pathogenic RELN Variant in Autosomal Dominant Lateral Temporal Epilepsy. Seizure Eur. J. Epilepsy 2025, 129, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, N.; Guerrini, R.; Billington, C.J.; Barkovich, A.J.; Dinkel, P.; Freri, E.; Heide, M.; Gershon, E.S.; Gertler, T.S.; Hopkin, R.J.; et al. Monoallelic and Biallelic Mutations in RELN Underlie a Graded Series of Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Brain 2022, 145, 3274–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, P.R.; Ebstein, F.; Hsieh, T.; Motta, M.; Radio, F.C.; Herkert, J.C.; Rinne, T.; Thiffault, I.; Rapp, M.; Alders, M.; et al. Loss-of-Function Variants in CUL3 Cause a Syndromic Neurodevelopmental Disorder. Ann. Neurol. 2025, 97, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasham, J.; Leslie, J.S.; Harrison, J.W.; Deline, J.; Williams, K.B.; Kuhl, A.; Scott Schwoerer, J.; Cross, H.E.; Crosby, A.H.; Baple, E.L. No Association between SCN9A and Monogenic Human Epilepsy Disorders. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Laan, L.; Silva, A.; Kleinendorst, L.; Rooney, K.; Haghshenas, S.; Lauffer, P.; Alanay, Y.; Bhai, P.; Brusco, A.; de Munnik, S.; et al. CUL3-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder: Clinical Phenotype of 20 New Individuals and Identification of a Potential Phenotype-Associated Episignature. Hum. Genet. Genom. Adv. 2025, 6, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvagiannis, K.; de Vries, B.B.; Vissers, L.E. WAC-Related Intellectual Disability. In GeneReviews®; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Rylaarsdam, L.; Guemez-Gamboa, A. Genetic Causes and Modifiers of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trost, B.; Engchuan, W.; Nguyen, C.M.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Dolzhenko, E.; Backstrom, I.; Mirceta, M.; Mojarad, B.A.; Yin, Y.; Dov, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Detection of Tandem DNA Repeats That Are Expanded in Autism. Nature 2020, 586, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, I.; Huang, B.; Mousavi, N.; Ma, N.; Lamkin, M.; Yanicky, R.; Shleizer-Burko, S.; Lohmueller, K.E.; Gymrek, M. Patterns of de Novo Tandem Repeat Mutations and Their Role in Autism. Nature 2021, 589, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
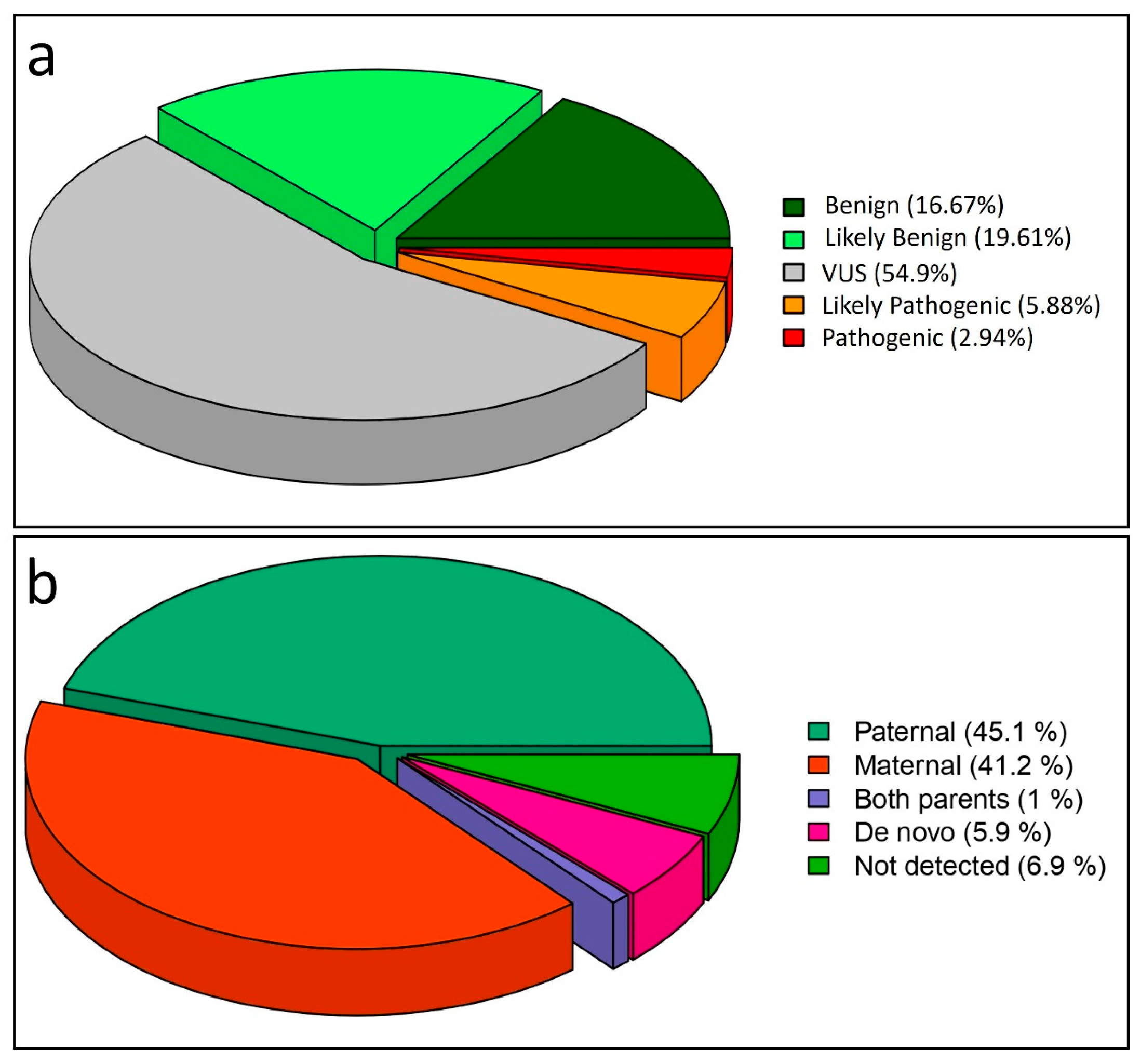
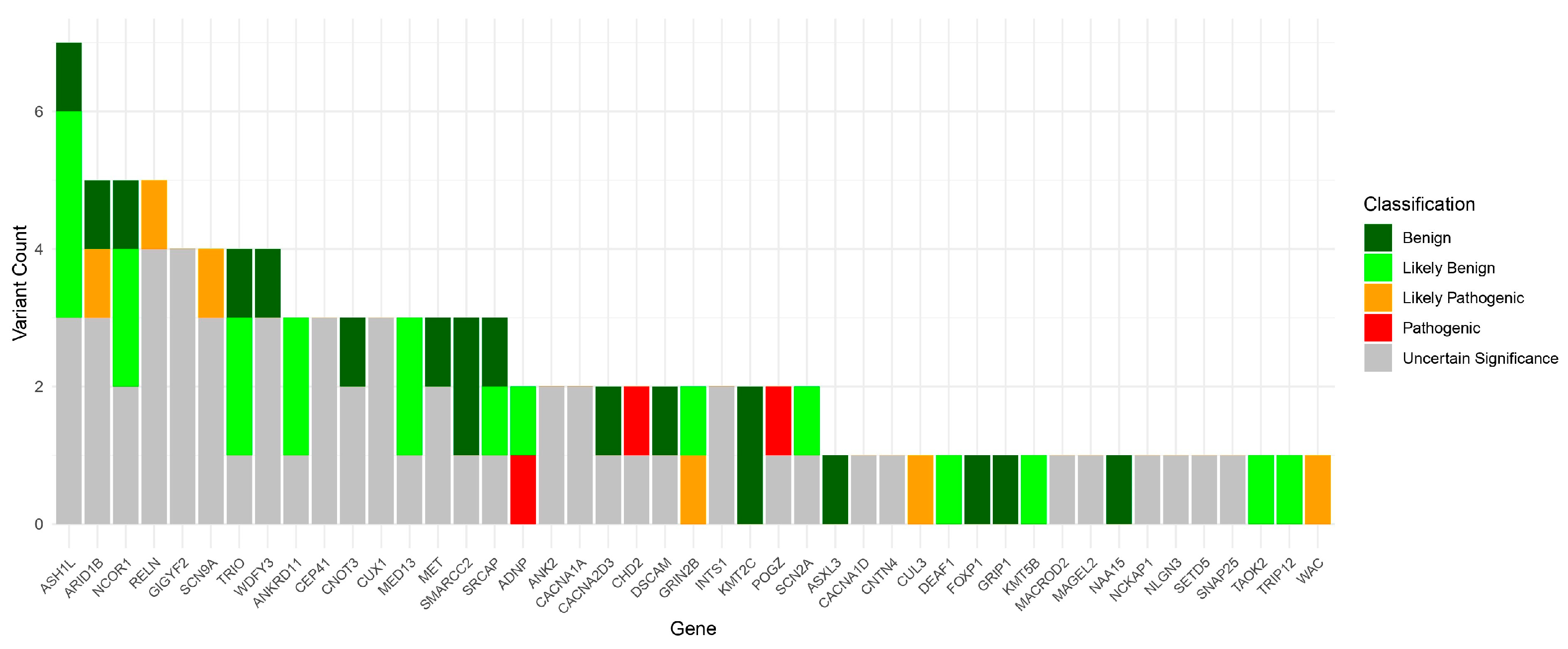

| Patient | Gene | Coding | Protein | ACMG | ClinVar |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P4 | POGZ | c.2323_2324delCT | p.Leu775ValfsTer4 | P (PVS1 1, PM2 2, PS2 3) | SCV006076861 |
| P5 | POGZ | c.1352C>T | p.Pro451Leu | VUS (BP4 4, PM2, PS2, PP4 5) | SCV006076862 |
| P11 | NCOR1 | c.3409G>A | p.Gly1137Arg | VUS (BP4, PM2, PS2) | SCV006076865 |
| P17 | CHD2 | c.3323_3324delCT | p.Ser1108Ter | P (PVS1, PM2, PS2, PP5 6) | SCV001592231 |
| P18 | ADNP | c.14delC | p.Pro5fs | P (PVS1, PP5, PS2, PM2) | SCV003803113 |
| P50 | GRIN2B | c.2141T>A | p.Val714Glu | LP (PP3, PM1 7, PM2, PS2) | SCV006076866 |
| Patient | Gene | Coding | Protein | Inherithance | ACMG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P29 | ARID1B | c.4692_4696delTGGCGinsGGGC | p.Gly1566AlafsTer11 | Maternal | LP (PVS1 1, PM2 2) |
| P23 | CUL3 | c.957delC | p.Tyr320IlefsTer2 | Maternal | LP (PVS1, PM2) |
| P47 | RELN | c.754A>T | p.Ile252Phe | Maternal | LP (PM2, PP2 3, PP4 4, PP5 5) |
| P33 | SCN9A | c.2159T>A | p.Ile720Lys | Maternal | LP (BP4 6, PP4, PM2, PM5 7) |
| P46 | WAC | c.42-9_42-6delGTTT | p.? | Paternal | LP (PM2, PP3, PP4) |
| Gene | Phenotype | MIM | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|
| ADNP | Helsmoortel-van der Aa syndrome | 615873 | AD 1 |
| ARID1B | Coffin–Siris syndrome 1 | 135900 | AD |
| CHD2 | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 94 | 615369 | AD |
| CUL3 | Neurodevelopmental disorder with or without autism or seizures | 619239 | AD |
| Pseudohypoaldosteronism, type IIE | 614496 | AD | |
| GRIN2B | Developmental and epileptic encephalopathy 27 | 616139 | AD |
| Intellectual developmental disorder, autosomal dominant 6 | 613970 | AD | |
| POGZ | White–Sutton syndrome | 616364 | AD |
| RELN | {Epilepsy, familial temporal lobe, 7} | 616436 | AD |
| Lissencephaly 2 (Norman-Roberts type) | 257320 | AR 2 | |
| SCN9A | Erythermalgia, primary | 133020 | AD |
| Insensitivity to pain, congenital | 243000 | AR | |
| Neuropathy, hereditary sensory and autonomic, type IID | 243000 | AR | |
| Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder | 167400 | AD | |
| Small fiber neuropathy | 133020 | AD | |
| WAC | Desanto-Shinawi syndrome | 616708 | AD |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greco, V.; Greco, D.; Treccarichi, S.; Bottitta, M.; Failla, P.; Musumeci, A.; Papa, C.; Chiavetta, V.; Calì, F.; Vinci, M. Clinical Application of a Customized Gene Panel for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Variants. Medicina 2025, 61, 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071273
Greco V, Greco D, Treccarichi S, Bottitta M, Failla P, Musumeci A, Papa C, Chiavetta V, Calì F, Vinci M. Clinical Application of a Customized Gene Panel for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Variants. Medicina. 2025; 61(7):1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071273
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreco, Vittoria, Donatella Greco, Simone Treccarichi, Maria Bottitta, Pinella Failla, Antonino Musumeci, Carla Papa, Valeria Chiavetta, Francesco Calì, and Mirella Vinci. 2025. "Clinical Application of a Customized Gene Panel for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Variants" Medicina 61, no. 7: 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071273
APA StyleGreco, V., Greco, D., Treccarichi, S., Bottitta, M., Failla, P., Musumeci, A., Papa, C., Chiavetta, V., Calì, F., & Vinci, M. (2025). Clinical Application of a Customized Gene Panel for Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder-Associated Variants. Medicina, 61(7), 1273. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61071273








