Arthroscopic Resection of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome: Long-Term Clinical Results at Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Diagnosis
2.2. Surgical Technique
2.3. Clinical Evaluation
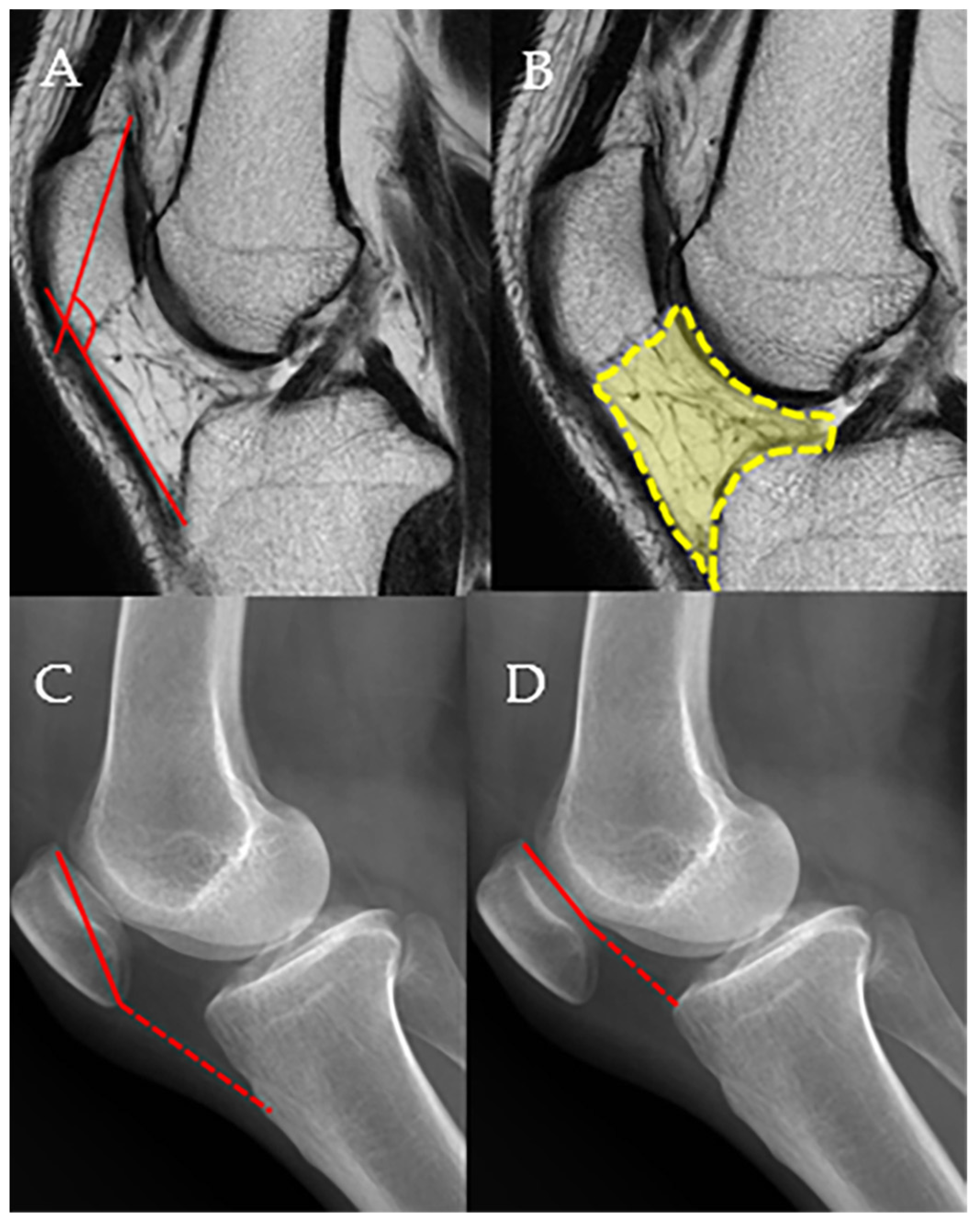
2.4. Radiologic Measurements
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKP | Anterior knee pain |
| PFJ | Patellofemoral joint |
| IPFP | Infrapatellar fat pad |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| AL | Anterolateral |
| SL | Superolateral |
| AM | Anteromedial |
| VAS | Visual analog scale |
| IKDC | International Knee Documentation Committee |
| AP | Anteroposterior |
| PPTA | Patella–patellar tendon angle |
| IPFV | Infrapatellar fat pad volume |
| ISR | Insall–Salvati ratio |
| CDI | Caton–Deschamp index |
| ICC | Intraclass correlation coefficient |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| PVNS | Pigmented villonodular synovitis |
References
- Borja, M.J.; Jose, J.; Vecchione, D.; Clifford, P.D.; Lesniak, B.P. Prefemoral fat pad impingement syndrome: Identification and diagnosis. Am. J. Orthop. 2013, 42, E9–E11. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchis-Alfonso, V.; Dye, S.F. How to deal with anterior knee pain in the active young patient. Sports Health 2017, 9, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.M.; Joo, Y.B.; Lee, W.Y.; Park, I.Y.; Park, Y.C. Patella-patellar tendon angle decreases in patients with infrapatellar fat pad syndrome and medial patellar plica syndrome. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2020, 28, 2609–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boling, M.; Padua, D.; Marshall, S.; Guskiewicz, K.; Pyne, S.; Beutler, A. Gender differences in the incidence and prevalence of patellofemoral pain syndrome. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2010, 20, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodju, L.; Viitanen, S. Patellofemoraalinen Kipuoireyhtymä 11–19-Vuotiailla Jalkapalloilijoilla. Bachelor’s Thesis, LAB University of Applied Sciences, Lahti, Finland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.-M.; Joo, Y.-B. Arthroscopic treatment of infrapatellar fat pad impingement between the patella and femoral trochlea: Comparison of the clinical outcomes of partial and subtotal resection. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2019, 31, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffa, A. The influence of the adipose tissue with regard to the pathology of the knee joint. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1904, 43, 795–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saddik, D.; McNally, E.; Richardson, M. MRI of Hoffa’s fat pad. Skelet. Radiol. 2004, 33, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Engelhardt, L.V.; Tokmakidis, E.; Lahner, M.; Dàvid, A.; Haage, P.; Bouillon, B.; Lichtinger, T.K. Hoffa’s fat pad impingement treated arthroscopically: Related findings on preoperative MRI in a case series of 62 patients. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2010, 130, 1041–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, S.F.; Vaupel, G.L.; Dye, C.C. Conscious neurosensory mapping of the internal structures of the human knee without intraarticular anesthesia. Am. J. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magi, M.; Branca, A.; Bucca, C.; Langerame, V. Hoffa disease. Ital. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 1991, 17, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Crossley, K.; Bennell, K.; Green, S.; Cowan, S.; McConnell, J. Physical therapy for patellofemoral pain: A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2002, 30, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ja, M. Hoffa disease: Chronic impingement of the infrapatellar fat pad. Am. J. Knee Surg. 1983, 1, 134–139. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, D.; Alvand, A.; Beacon, J. Impingement of infrapatellar fat pad (Hoffa’s disease): Results of high-portal arthroscopic resection. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2007, 23, 1180–1186.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogilvie-Harris, D.; Giddens, J. Hoffa’s disease: Arthroscopic resection of the infrapatellar fat pad. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 1994, 10, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grando, H.; Chang, E.Y.; Chen, K.C.; Chung, C.B. MR imaging of extrasynovial inflammation and impingement about the knee. Magn. Reson. Imaging Clin. 2014, 22, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, A.; Wahba, A.; Smith, T.O.; Donell, S.T. The surgical treatment of anterior knee pain due to infrapatellar fat pad pathology: A systematic review. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morini, G.; Chiodi, E.; Centanni, F.; Gattazzo, D. Hoffa’s disease of the adipose pad: Magnetic resonance versus surgical findings. Radiol. Medica 1998, 95, 278–285. [Google Scholar]
- Emad, Y.; Ragab, Y. Liposynovitis prepatellaris in athletic runner (Hoffa’s syndrome): Case report and review of the literature. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1201–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoo, J.L.; Johnson, C.; McConnell, J. Evaluation and treatment of disorders of the infrapatellar fat pad. Sports Med. 2012, 42, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, J.A.; Lenchik, L.; Ruhoy, M.K.; Schweitzer, M.E.; Resnick, D. MR imaging of the infrapatellar fat pad of Hoffa. Radiographics 1997, 17, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, J.; Feucht, M.J.; Bode, G.; Dovi-Akue, D.; Südkamp, N.P.; Niemeyer, P. Association between patellar cartilage defects and patellofemoral geometry: A matched-pair MRI comparison of patients with and without isolated patellar cartilage defects. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 838–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellgren, J.H.; Lawrence, J. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1957, 16, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelleyra Lastoria, D.A.; Benny, C.K.; Hing, C.B. Predisposing factors for Hoffa’s fat pad syndrome: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Relat. Res. 2023, 35, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibri, Z.; Martin, D.; Mansour, R.; Kamath, S. The association of infrapatellar fat pad oedema with patellar maltracking: A case–control study. Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 41, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Middelkoop, M.; Macri, E.M.; Eijkenboom, J.F.; van der Heijden, R.A.; Crossley, K.M.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S.M.; de Kanter, J.L.; Oei, E.H.; Collins, N.J. Are patellofemoral joint alignment and shape associated with structural magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities and symptoms among people with patellofemoral pain? Am. J. Sports Med. 2018, 46, 3217–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Jung, J.-Y. Superolateral Hoffa’s fat pad oedema: Relationship with cartilage T2* value and patellofemoral maltracking. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 118, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Xu, J.; Wang, K.; Zheng, S.; He, F.; Huan, S.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Laslett, L.; Ding, C. Association between infrapatellar fat pad volume and knee structural changes in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuckpaiwong, B.; Charles, H.C.; Kraus, V.B.; Guilak, F.; Nunley, J.A. Age-associated increases in the size of the infrapatellar fat pad in knee osteoarthritis as measured by 3T MRI. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Ba, H.; Feng, J.; Peng, C.; Liao, Y.; Li, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Shen, M.; Wu, S. Increased signal intensity, not volume variation of infrapatellar fat pad in knee osteoarthritis: A cross-sectional study based on high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. J. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, 10225536221092215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Park, J.-H.; Lee, A.-H.; Lee, D.-H. An unusual presentation of Hoffa’s disease in an elderly patient with no trauma history: A case report. Acta Orthop. Traumatol. Turc. 2011, 45, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.; Reed, D.; Matthews, J.; Pandit, H.; McNally, E.; Athanasou, N.; Gibbons, C. The management of solitary tumours of Hoffa’s fat pad. Knee 2011, 18, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Case | Age | Sex | Site | BMI | Follow-Up (Months) | Tegner Activity | Hoffa’s Test | MRI | VAS | PPTA | IFPV | ISR | CDI | PFJ Arthritis (0/1/2/3/4) | Biopsy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | F | R | 21.62 | 148.4 | 3 | positive | positive | 7 | 133.6 | 528.6 | 0.92 | 0.96 | 0 | Consistent with Hoffa’s disease |
| 2 | 29 | M | R | 26.18 | 149.0 | 5 | positive | positive | 6 | 125.3 | 783.9 | 1.12 | 1.31 | 0 | Consistent with Hoffa’s disease |
| 3 | 46 | F | R | 23.34 | 141.8 | 3 | positive | negative | 6 | 133.4 | 491.4 | 0.99 | 0.76 | 1 | Mild synovial hyperplasia |
| 4 | 21 | M | R | 22.43 | 145.2 | 4 | negative | negative | 7 | 144.8 | 829.0 | 1.22 | 1.14 | 0 | Mild synovial hyperplasia |
| 5 | 19 | M | L | 21.08 | 147.1 | 4 | positive | positive | 8 | 136.7 | 799.8 | 1.07 | 1.15 | 0 | Mild fibrosis |
| 6 | 30 | F | L | 20.05 | 135.5 | 3 | positive | negative | 7 | 133.7 | 626.2 | 1.63 | 1.13 | 0 | Synovial hyperplasia and proliferation adipocyte |
| 7 | 27 | M | R | 23.45 | 154.0 | 4 | negative | positive | 7 | 141.1 | 740.2 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0 | Mild fibrosis |
| 8 | 47 | F | L | 21.07 | 147.5 | 3 | positive | negative | 6 | 130.2 | 591.2 | 1.12 | 0.91 | 1 | Mild fibrosis |
| 9 | 45 | F | L | 19.6 | 132.1 | 3 | positive | negative | 8 | 135.8 | 627.1 | 0.81 | 1.01 | 0 | Increase in mature adipose tissue, consistent with fat pad |
| 10 | 43 | F | R | 19.86 | 137.8 | 3 | positive | negative | 6 | 142.5 | 530.2 | 0.88 | 0.99 | 0 | Mild synovial hyperplasia |
| 11 | 19 | M | L | 22.05 | 145.7 | 4 | positive | positive | 7 | 136.3 | 777.1 | 0.87 | 0.81 | 1 | Mild fibrosis |
| 12 | 33 | F | R | 28.23 | 145.3 | 2 | positive | negative | 8 | 143.0 | 585.9 | 1.03 | 1.14 | 0 | Mild fibrosis |
| 13 | 22 | M | R | 24.81 | 148.5 | 3 | positive | negative | 8 | 138.4 | 886.0 | 1.12 | 1.09 | 0 | Consistent with Hoffa’s disease |
| 14 | 48 | M | L | 29.21 | 122.5 | 4 | positive | positive | 8 | 137.0 | 586.3 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 1 | Mild synovial hyperplasia |
| 15 | 28 | F | L | 21.04 | 141.1 | 2 | positive | negative | 7 | 134.2 | 657.3 | 0.81 | 1.00 | 0 | Mild synovial hyperplasia with fatty change |
| 16 | 20 | F | L | 19.77 | 122.4 | 2 | positive | positive | 8 | 130.0 | 511.8 | 1.13 | 1.00 | 0 | Mild synovial hyperplasia |
| 17 | 30 | F | L | 21.51 | 149.8 | 2 | positive | negative | 7 | 139.7 | 637.4 | 0.96 | 1.12 | 0 | Mild synovial hyperplasia with fatty change |
| 18 | 23 | M | L | 23.63 | 149.5 | 4 | negative | negative | 8 | 136.3 | 769.4 | 1.12 | 1.18 | 0 | Synovial hyperplasia and increased capillaries |
| Variables | Preoperative | Postoperative (2 Years) | Postoperative (Final Follow-Up) | p-Value a | p-Value b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAS | 7.25 ± 0.79 | 2.43 ± 1.50 | 3.66 ± 1.50 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Kujala | 52.35 ± 5.23 | 88.61 ± 5.53 | 82.36 ± 6.53 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| IKDC 2000 | 48.50 ± 8.38 | 82.39 ± 6.25 | 77.49 ± 5.19 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Tegner activity | 3.0 ± 1.0 | 6.01 ± 0.87 | 5.83 ± 0.76 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Lysholm | 49.13 ± 7.12 | 83.17 ± 6.54 | 76.83 ± 5.72 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Variables | Preoperative | Postoperative (2 Years) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISR | 1.04 ± 0.18 | 1.04 ± 0.19 | n.s |
| CDI | 1.05 ± 0.14 | 1.07 ± 0.17 | n.s |
| PF arthritis(0/1/2/3/4) | 14/4/0/0/0/ | 14/2/2/0/0/ | n.s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.-C.; Kim, Y.-M.; Joo, Y.-B. Arthroscopic Resection of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome: Long-Term Clinical Results at Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up. Medicina 2025, 61, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060997
Park Y-C, Kim Y-M, Joo Y-B. Arthroscopic Resection of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome: Long-Term Clinical Results at Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060997
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Young-Cheol, Young-Mo Kim, and Yong-Bum Joo. 2025. "Arthroscopic Resection of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome: Long-Term Clinical Results at Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up" Medicina 61, no. 6: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060997
APA StylePark, Y.-C., Kim, Y.-M., & Joo, Y.-B. (2025). Arthroscopic Resection of Infrapatellar Fat Pad Impingement Syndrome: Long-Term Clinical Results at Minimum 10-Year Follow-Up. Medicina, 61(6), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060997






