Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variants in Children with PAX2 Mutation-Associated Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Clinical Assessment and Ancillary Examinations
2.3. Whole-Exome Genetic Testing
2.4. Pathogenicity, Stability, and Biophysical Prediction In Silico
3. Results
3.1. General Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Characteristics
3.2.1. Renal Manifestations
3.2.2. Extrarenal Manifestations
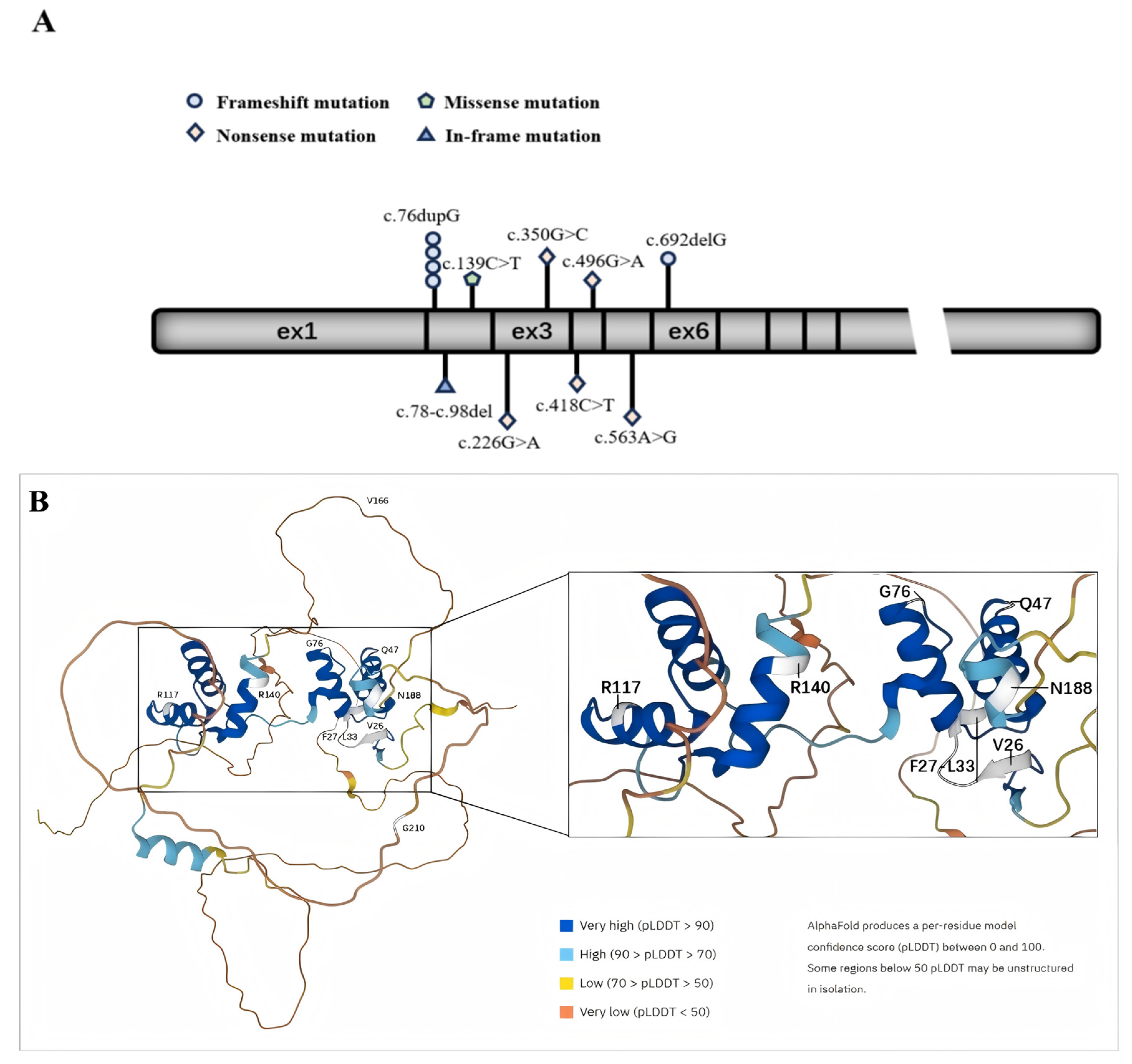
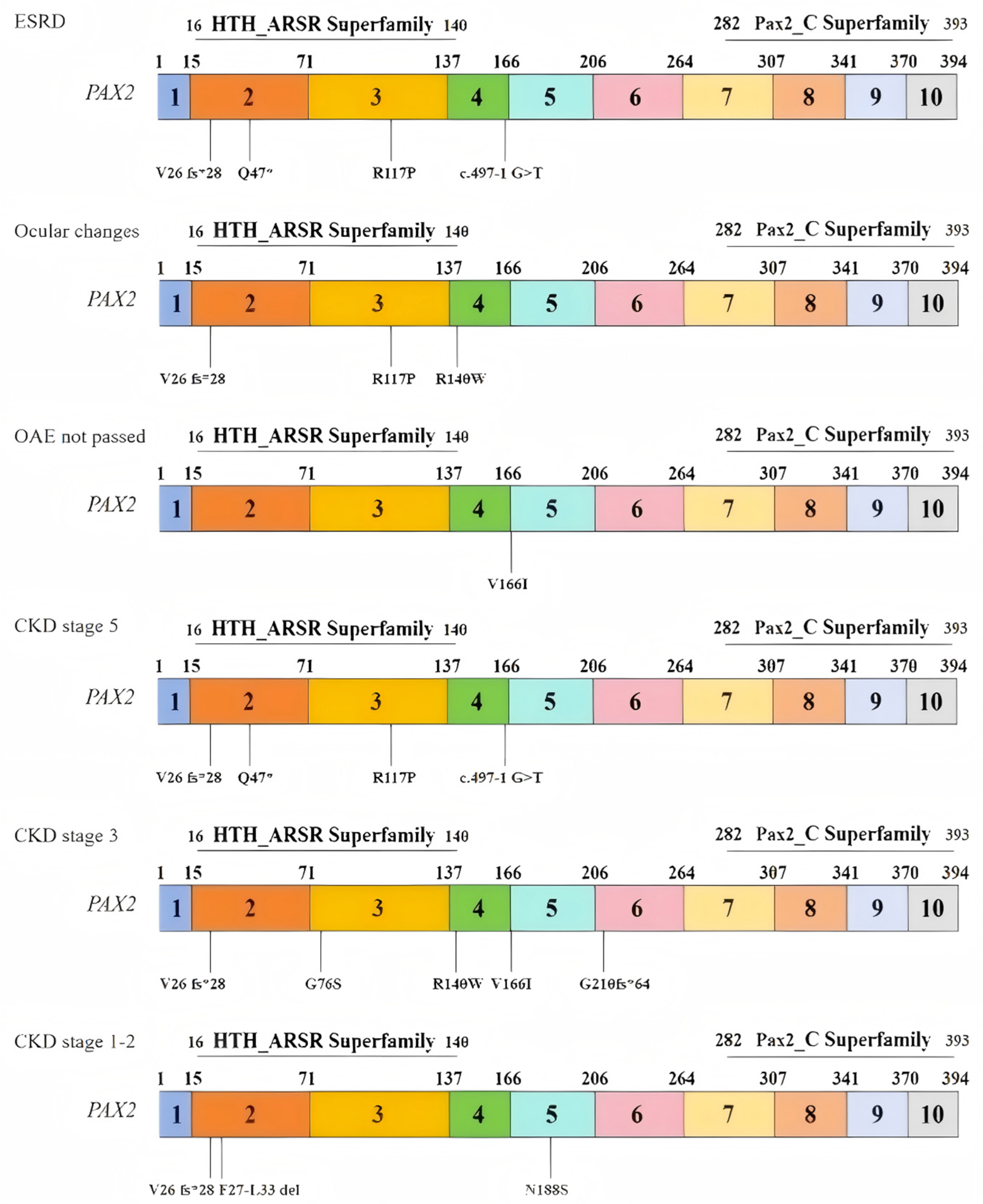
3.3. PAX2 Mutations
3.3.1. Variants Report
3.3.2. Pathogenicity and Stability Prediction Using In Silico Tools
3.3.3. Biophysical Characterization and Conservation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Terzić, J.; Muller, C.; Gajović, S.; Saraga-Babić, M. Expression of PAX2 gene during human development. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1998, 42, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres, M.; Gómez-Pardo, E.; Dressler, G.R.; Gruss, P. Pax-2 controls multiple steps of urogenital development. Development 1995, 121, 4057–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, B.; Davidson, E.A.; Liu, W.; Nebert, D.W.; Bruford, E.A.; Zhao, H.; Dermitzakis, E.T.; Thompson, D.C.; Vasiliou, V. Overview of PAX gene family: Analysis of human tissue-specific variant expression and involvement in human disease. Hum. Genet. 2021, 140, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harshman, L.A.; Brophy, P.D. PAX2 in human kidney malformations and disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 1265–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muntean, C.; Chirtes, C.; Baczoni, B.; Banescu, C. PAX2 Gene Mutation in Pediatric Renal Disorders-A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bower, M.; Salomon, R.; Allanson, J.; Antignac, C.; Benedicenti, F.; Benetti, E.; Binenbaum, G.; Jensen, U.B.; Cochat, P.; DeCramer, S.; et al. Update of PAX2 mutations in renal coloboma syndrome and establishment of a locus-specific database. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, S. Novel genetic aspects of congenital anomalies of kidney and urinary tract. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2012, 24, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.M.; Biesecker, L.G.; Rehm, H.L. Overview of Specifications to the ACMG/AMP Variant Interpretation Guidelines. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2019, 103, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bendl, J.; Stourac, J.; Salanda, O.; Pavelka, A.; Wieben, E.D.; Zendulka, J.; Brezovsky, J.; Damborsky, J. PredictSNP: Robust and accurate consensus classifier for prediction of disease-related mutations. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Lin, J.; Chu, Y.W. iStable: Off-the-shelf predictor integration for predicting protein stability changes. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14 (Suppl. S2), S2–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavtigian, S.V.; Deffenbaugh, A.M.; Yin, L.; Judkins, T.; Scholl, T.; Samollow, P.B.; de Silva, D.; Zharkikh, A.; Thomas, A. Comprehensive statistical study of 452 BRCA1 missense substitutions with classification of eight recurrent substitutions as neutral. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaser, F.; Pupko, T.; Paz, I.; Bell, R.E.; Bechor-Shental, D.; Martz, E.; Ben-Tal, N. ConSurf: Identification of functional regions in proteins by surface-mapping of phylogenetic information. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; You, N.; Wu, S.; Shen, N. MAGPIE: Accurate pathogenic prediction for multiple variant types using machine learning approach. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obrycki, Ł.; Sarnecki, J.; Lichosik, M.; Sopińska, M.; Placzyńska, M.; Stańczyk, M.; Mirecka, J.; Wasilewska, A.; Michalski, M.; Lewandowska, W.; et al. Kidney length normative values in children aged 0–19 years—A multicenter study. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2022, 37, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Fang, Y.; Shi, H.; Xiang, T.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Tang, X.; Fang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Phenotypic spectrum and genetics of PAX2-related disorder in the Chinese cohort. BMC Med. Genom. 2021, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhai, S.-B.; Zhao, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, B.-C.; Ma, Q.-S. New PAX2 heterozygous mutation in a child with chronic kidney disease: A case report and review of the literature. BMC Nephrol. 2018, 19, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Su, B.; Zhang, H.; Xu, K.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; et al. Diverse phenotypes in children with PAX2-related disorder. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iatropoulos, P.; Daina, E.; Mele, C.; Maranta, R.; Remuzzi, G.; Noris, M. Discordant phenotype in monozygotic twins with renal coloboma syndrome and a PAX2 mutation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2012, 27, 1989–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porteous, S.; Torban, E.; Cho, N.-P.; Cunliffe, H.; Chua, L.; McNoe, L.; Ward, T.; Souza, C.; Gus, P.; Giugliani, R.; et al. Primary renal hypoplasia in humans and mice with PAX2 mutations: Evidence of increased apoptosis in fetal kidneys of Pax2(1Neu) +/− mutant mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilliard, S.A.; El-Dahr, S.S. Epigenetics mechanisms in renal development. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2016, 31, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.; Lemire, M.; Hudson, T.; Qu, H.; Benjamin, A.; Roy, A.; Pascuet, E.; Goodyer, M.; Raju, C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. A common variant of the PAX2 gene is associated with reduced newborn kidney size. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.; Luo, Y.; Fu, Q.; Sun, X.; Mi, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H. Clinical spectrum, genetics and management insights of PAX2-related disorder in nine children. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negrisolo, S.; Benetti, E. PAX2 and CAKUT Phenotypes: Report on Two New Variants and a Review of Mutations from the Leiden Open Variation Database. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.Y.; Shi, Y.Q.; Zhong, C.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, H.; Wu, D.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, M. Detection of De Novo PAX2 Variants and Phenotypes in Chinese Population: A Single-Center Study. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 799562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Patients | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ESRD | un ESRD | ||||||||||||
| General characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| Gender | F | M | F | F | F | M | F | F | M | M | M | F | F | F |
| Onset age (years) | 0.2 | 9.9 | 1 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 9 | 7 | 5.9 | prenatal | 12.8 | 6.5 | prenatal | NB |
| ESRD/age | Y/11 | Y/10 | Y/1 | Y/6 | Y/8 | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Visit age | 11.7 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 12.1 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 0.5 | 12.8 | 13.5 | 0.1 | 4 |
| Growth retardation | - | - | + | - | - | - | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| sCr (umol/L) | 513 | 1089 | 350 | 1080 | 381 | 206 | 141 | 68 | 61 | 61 | 207 | 87 | 21 | 135 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 10 | 5.5 | 15 | 4 | 12 | 41.03 | 49.78 | 73.7 | 76.8 | 43.2 | 36.8 | 71 | 104 | 54.35 |
| CKD stage | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 |
| Urine testing indicators | ||||||||||||||
| PU | +/NP | +/NP | +/NP | +/NP | +/NP | + | + | - | - | + | +/NP | - | - | + |
| HU/HBC per HB | - | +/4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | +/5 | - | - | - | - | |
| 24 h UP (mg) | 1280 | 1585 | 1697 | 916 | 2427 | 2272 | 563 | 172 | 66 | NA | 4119 | 160 | NA | 682 |
| ACR (mg/gCr) | 1615 | 7337 | 1804 | 2358 | 1958 | 1615 | 466 | 118 | 32 | 2589 | 2902 | 15 | 84 | 1180 |
| α1MG/CR (mg/gCr) | 269 | 197 | 225 | 245 | 315 | 19 | 269 | 8 | 7 | 269 | 80 | 11 | 21 | 124 |
| Urinary system Image Assessment | 13/14 (92%) Ultrasound describes small kidney size (<−2 SD) | |||||||||||||
| Kidney size (US) | ||||||||||||||
| Age | 11.7 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 12 | 12.1 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 0.5 | 12.8 | 13.5 | 0.1 | 4 |
| L (cm) | 5.1 × 2.8 | 6.5 × 3.2 | 5.2 × 2.3 | 5.4 × 1.9 | −2SD | 8.3 × 4.5 | 4.6 × 2.3 | 6.7 × 2.5 | 4.8 | 4.2 × 2.0 | 8.3 × 3.8 | 9.6 × 3.1 | 4.8 × 2.1 | −2SD |
| R (cm) | 4.7 × 2.6 | Absent | 4.6 × 2.1 | 5.1 × 2 | −2SD | 7.8 × 3.3 | 5.8 × 2.7 | 7.2 × 2.3 | 6.7 | 4.3 × 1.9 | 8.1 × 4.0 | 8.8 × 3.6 | 5.0 × 1.6 | −2SD |
| Cysts/Location | - | - | +/R/S | - | +/B/M | +/B/M | +/L/S | - | - | +/B/M | - | - | - | - |
| Additional | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Hydronephrosis | - | - | - | - | Stone, Hydronephrosis | - |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ESRD | un ESRD | ||||||||||||
| Extrarenal manifestations | ||||||||||||||
| Eyes | NA | NA | Papill-edema | NA | NA | NA | NA | - | - | NA | Papill-edema | Morning glory anomaly | NA | NA |
| Ears | - | NA | - | NA | NA | - | - | NA | NA | NA | - | - | NA | OAE not passed |
| Neurological system | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Bones | - | - | - | - | - | - | Scoliosis | - | - | - | - | Scoliosis | - | - |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group | ESRD | un ESRD | ||||||||||||
| Nucleotide change | c.139 C>T | c.76 dupG | c.350 G>C | c.497-1 G>T | EXON:1-10del | c.226 G>A | c.76 dupG | c.76 dupG | c.78–c.98 del | c.629 delG | c.418 C>T | c.76 dupG: | c.563 A>G | c.496 G>A |
| Amino change | p.Q47* | p.V26 fs*28 | p.R117P | - | - | p.G76S | p.V26 fs*28 | p.V26 fs*28 | p.F27-L33 del | p.G210 fs*64 | p.R140W | p.V26 fs*28 | p.N188S | p.V166I |
| Pathoge-nicity | P | P | P | P | P | VUS | P | P | VUS | P | LP | P | LP | LP |
| EXON | 2 | 2 | 3 | - | 1-10 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 4 |
| Type | N | F | M | S | CNV | M | F | F | I | F | M | F | M | M |
| Zygosity/ segregation | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/M | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/D | Het/F | Het/F | Het/F |
| Family history | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | Father uremia | Father uremia | kidney stones | - |
| Reported | - | + | + | + | - | + | + | + | - | - | + | + | + | - |
| Serial Number | Accession Number | Amino Acid Change | Predict SNP | MAPP | PhD-SNP | PolyPhen-1 | PolyPhen-2 | SIFT | SNAP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NP_000269.3 | V166I | N | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| 2 | NP_000269.3 | G76S | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| 3 | NP_000269.3 | R117P | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| 4 | NP_000269.3 | R140W | D | D | D | D | D | D | D |
| 5 | NP_000269.3 | N188S | N | N | D | N | N | N | N |
| Serial Number | Accession Number | Amino Acid Change | Nucleotide Change | Chr | Start | End | MAGPIE Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NP_000269.3 | V166I | c.496G>A | 10 | 100779583 | 100779583 | 0.993759408 |
| 2 | NP_000269.3 | G76S | c.226G>A | 10 | 100750707 | 100750707 | 0.947722773 |
| 3 | NP_000269.3 | R117P | c.350G>C | 10 | 100750831 | 100750831 | 0.904887777 |
| 4 | NP_000269.3 | R140W | c.418C>T | 10 | 100749841 | 100749841 | 0.999467114 |
| 5 | NP_000269.3 | N188S | c.563A>G | 10 | 100781312 | 100781312 | 0.036130005 |
| 6 | NP_000269.3 | p.Q47* | c.139C>T | 10 | 100779505 | 100779505 | 0.94064358 |
| 7 | NP_000269.3 | p.V26 fs*28 | c.76dupG | 10 | 100749778 | 100749778 | 0.968490245 |
| 8 | NP_000269.3 | p.F27-L33 del | c.78-c.98del | 10 | 100749783 | 100749803 | 0.067596214 |
| 9 | NP_000269.3 | p.G210 fs*64 | c.629delG | 10 | 100806442 | 100806442 | 0.97295275 |
| 10 | NP_000269.3 | - | c.497-1G>T | 10 | 100781245 | 100781245 | −1 (invalid for splicing) |
| Serial Number | Accession Number | Amino Acid Change | i-Mutant2.0 SEQ | DDG | MUpro | Conf. Score | iStable | Conf. Score | GV | GD | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NP_000269.3 | V166I | D | −0.52 | D | −1 | D | 0.708591 | 0 | 29.61 | Class C25 |
| 2 | NP_000269.3 | G76S | D | −1.33 | I | 0.084420636 | I | 0.506123 | 0 | 55.27 | Class C55 |
| 3 | NP_000269.3 | R117P | D | −0.86 | D | −0.46061846 | D | 0.751511 | 0 | 102.71 | Class C65 |
| 4 | NP_000269.3 | R140W | D | −0.35 | D | −0.7478608 | D | 0.828271 | 0 | 101.29 | Class C65 |
| 5 | NP_000269.3 | N188S | D | −0.65 | I | 0.17276469 | I | 0.654345 | 0 | 46.24 | Class C45 |
| Serial Number | Mutation | TANGO | WALTZ | LIMBO | FoldX |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | R117P | does not affect the aggregation tendency of your protein | does not affect the amyloid propensity of your protein | increases the chaperone binding tendency of your protein | reduces the protein stability |
| 5 | R140W | does not affect the aggregation tendency of your protein | does not affect the amyloid propensity of your protein | does not affect the chaperone binding tendency of your protein | has no effect on the protein stability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, Y.; Li, N.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, K.; Wang, J.; Sheng, A.; Fu, H.; Hu, L.; Mao, J. Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variants in Children with PAX2 Mutation-Associated Disorders. Medicina 2025, 61, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060959
Jin Y, Li N, Chen Z, Zeng K, Wang J, Sheng A, Fu H, Hu L, Mao J. Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variants in Children with PAX2 Mutation-Associated Disorders. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060959
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Yanyan, Na Li, Zipei Chen, Ke Zeng, Jingjing Wang, Aiqin Sheng, Haidong Fu, Lidan Hu, and Jianhua Mao. 2025. "Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variants in Children with PAX2 Mutation-Associated Disorders" Medicina 61, no. 6: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060959
APA StyleJin, Y., Li, N., Chen, Z., Zeng, K., Wang, J., Sheng, A., Fu, H., Hu, L., & Mao, J. (2025). Clinical Characteristics and Genetic Variants in Children with PAX2 Mutation-Associated Disorders. Medicina, 61(6), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61060959







