Ivermectin Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-β and Syndecan-1 Expression
Abstract
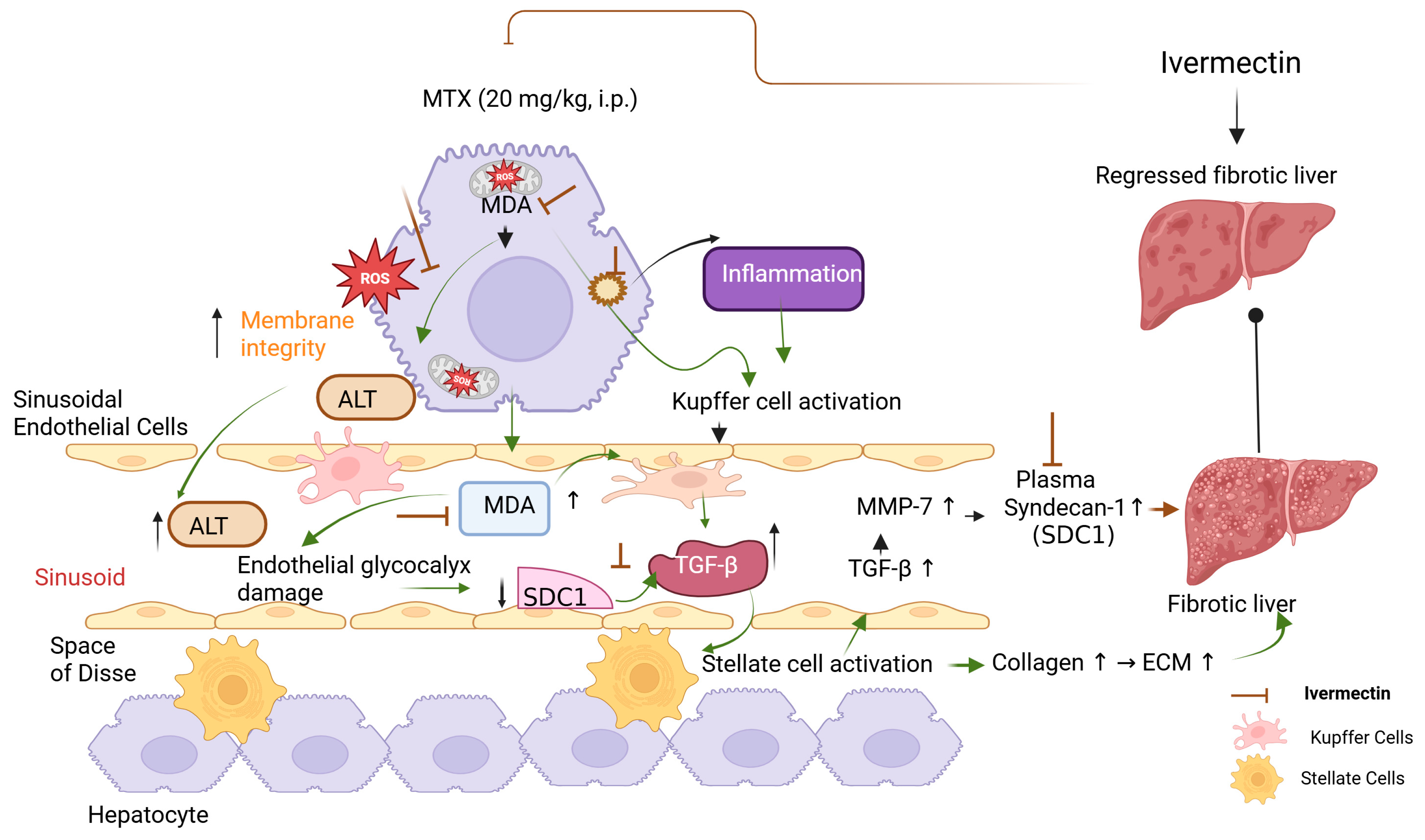
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
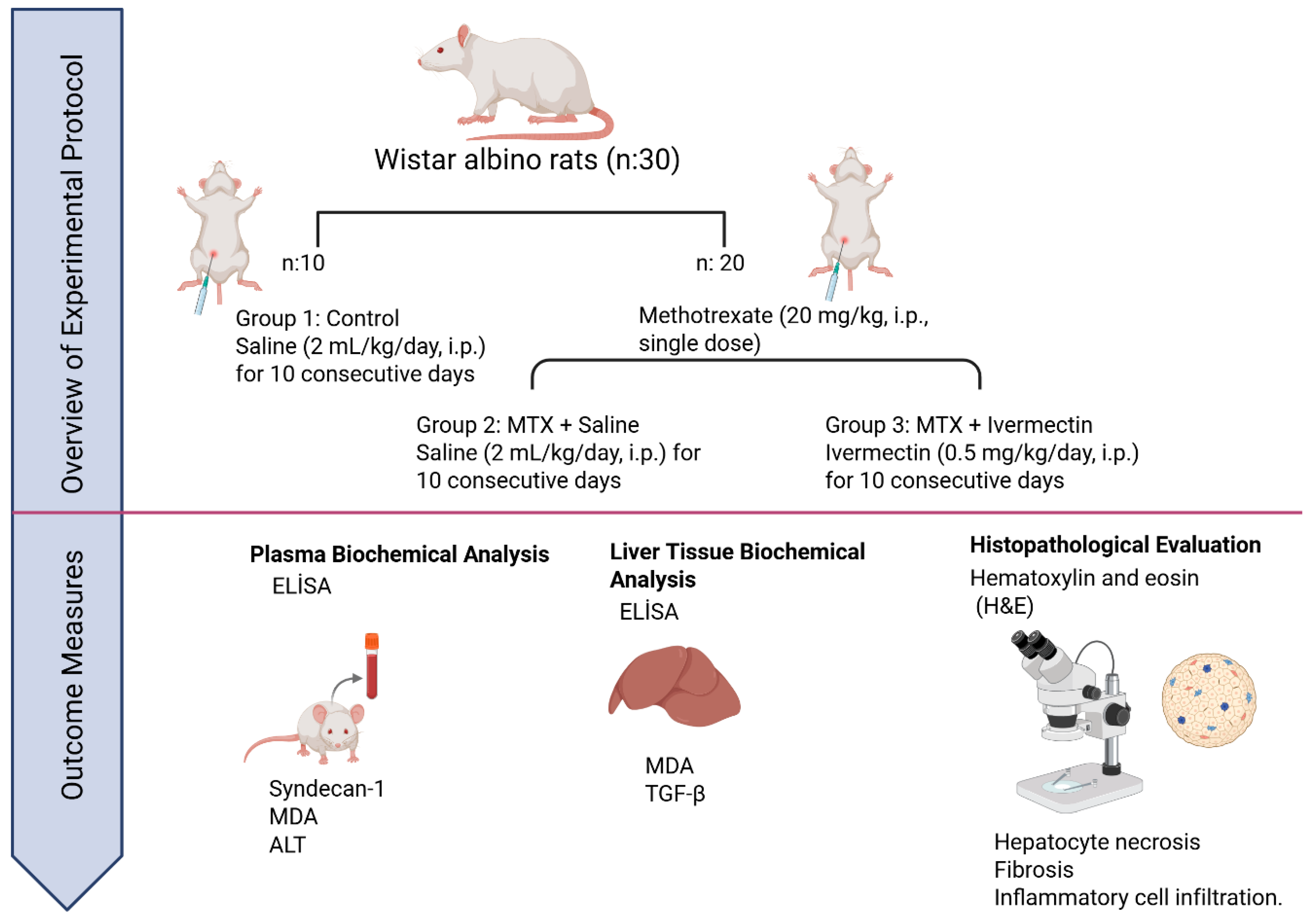
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Protocol
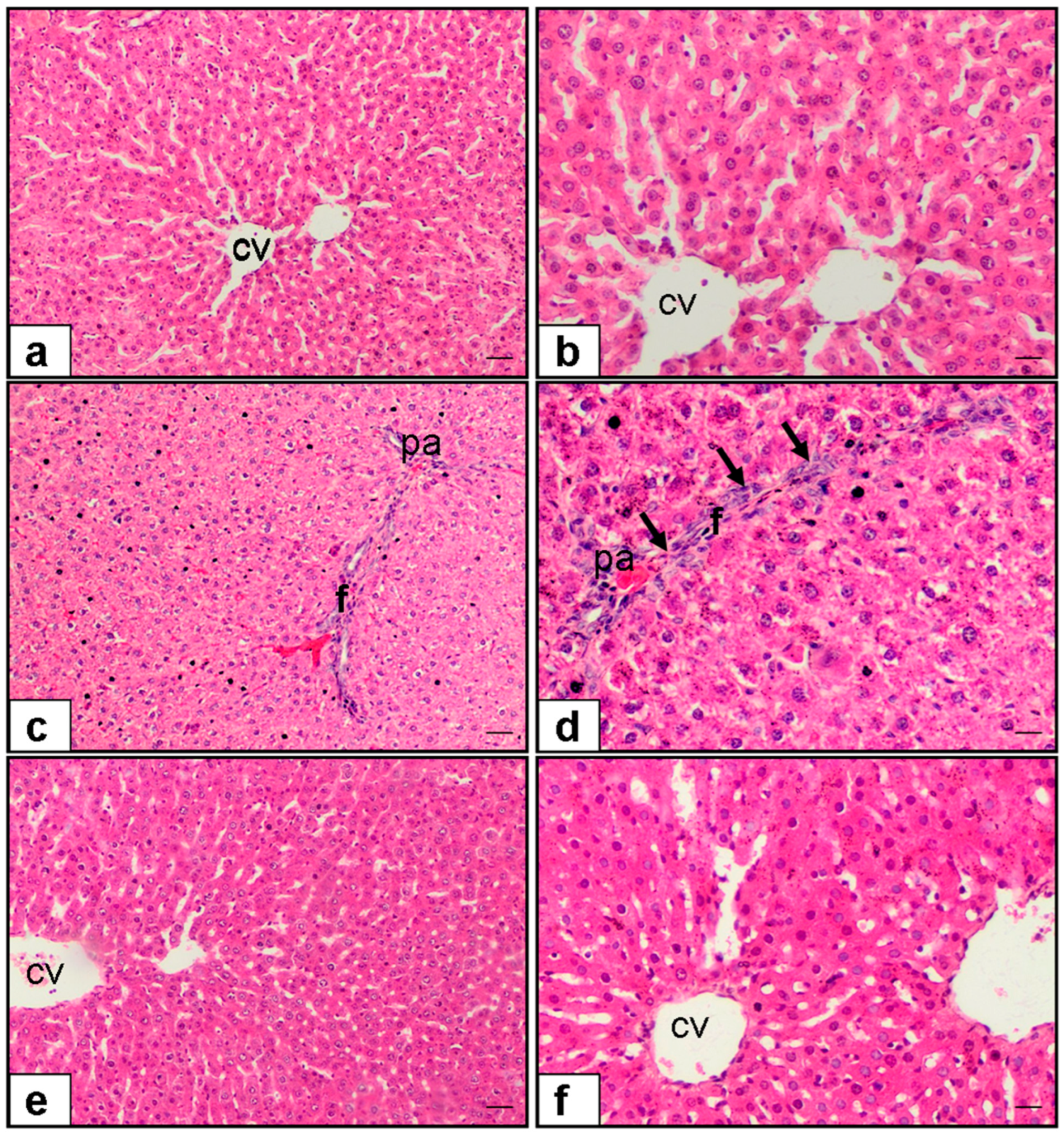
2.3. Histopathological Evaluation
- 0: Absent;
- 1: Minimal (<5% involvement);
- 2: Mild (5–25%);
- 3: Moderate (26–50%);
- 4: Marked (>50%).
2.4. Biochemical Evaluation
2.4.1. Plasma Analysis
Plasma Syndecan-1 Measurement
Plasma ALT Determination
Plasma Lipid Peroxidation
2.4.2. Liver Tissue Biochemical Analysis
Liver TGF-β Measurement
Liver Lipid Peroxidation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Statistical Power and Sample Size Justification
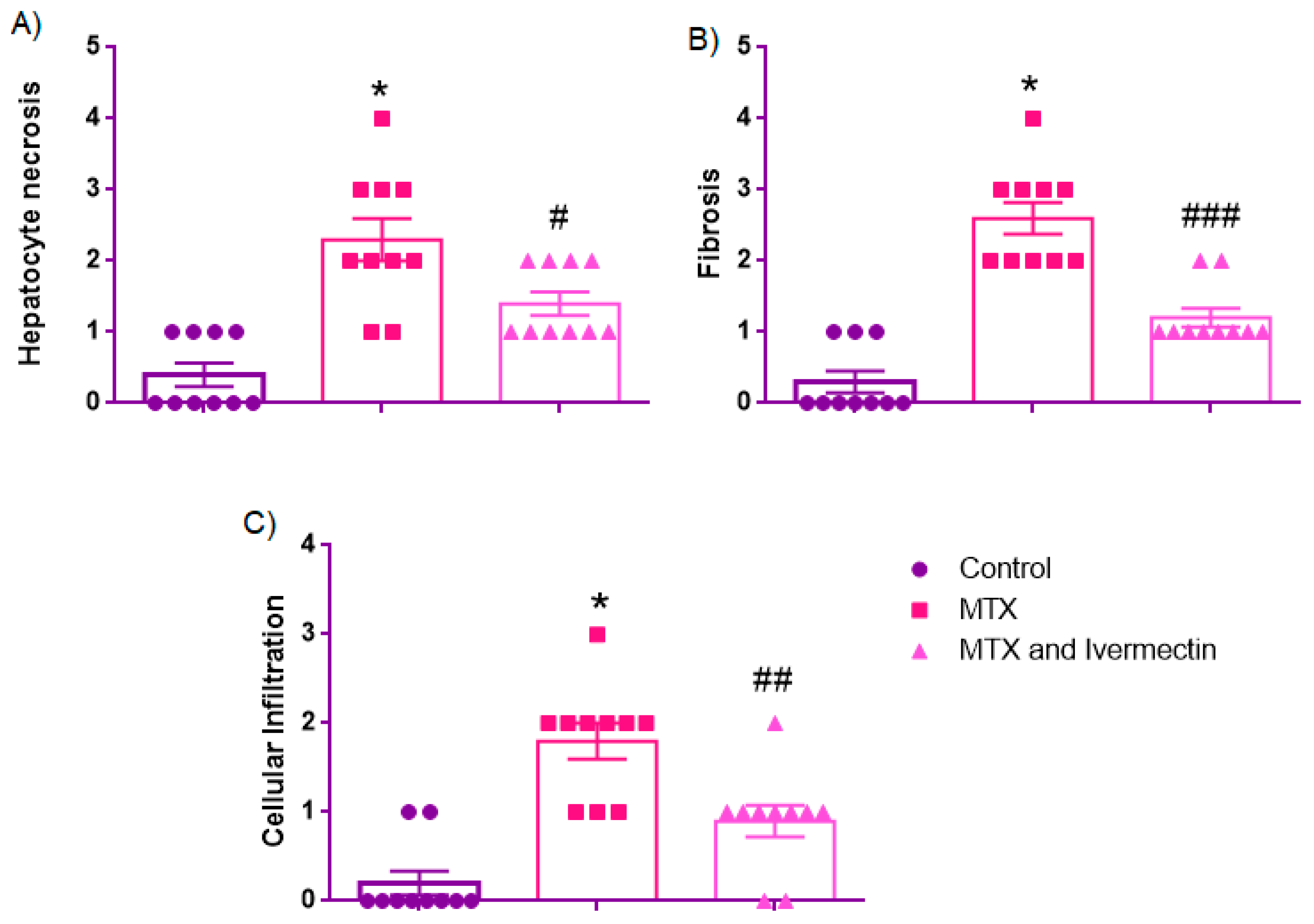
3.2. Histopathological Scores
3.2.1. Hepatocyte Necrosis
3.2.2. Fibrosis
3.2.3. Cellular Infiltration
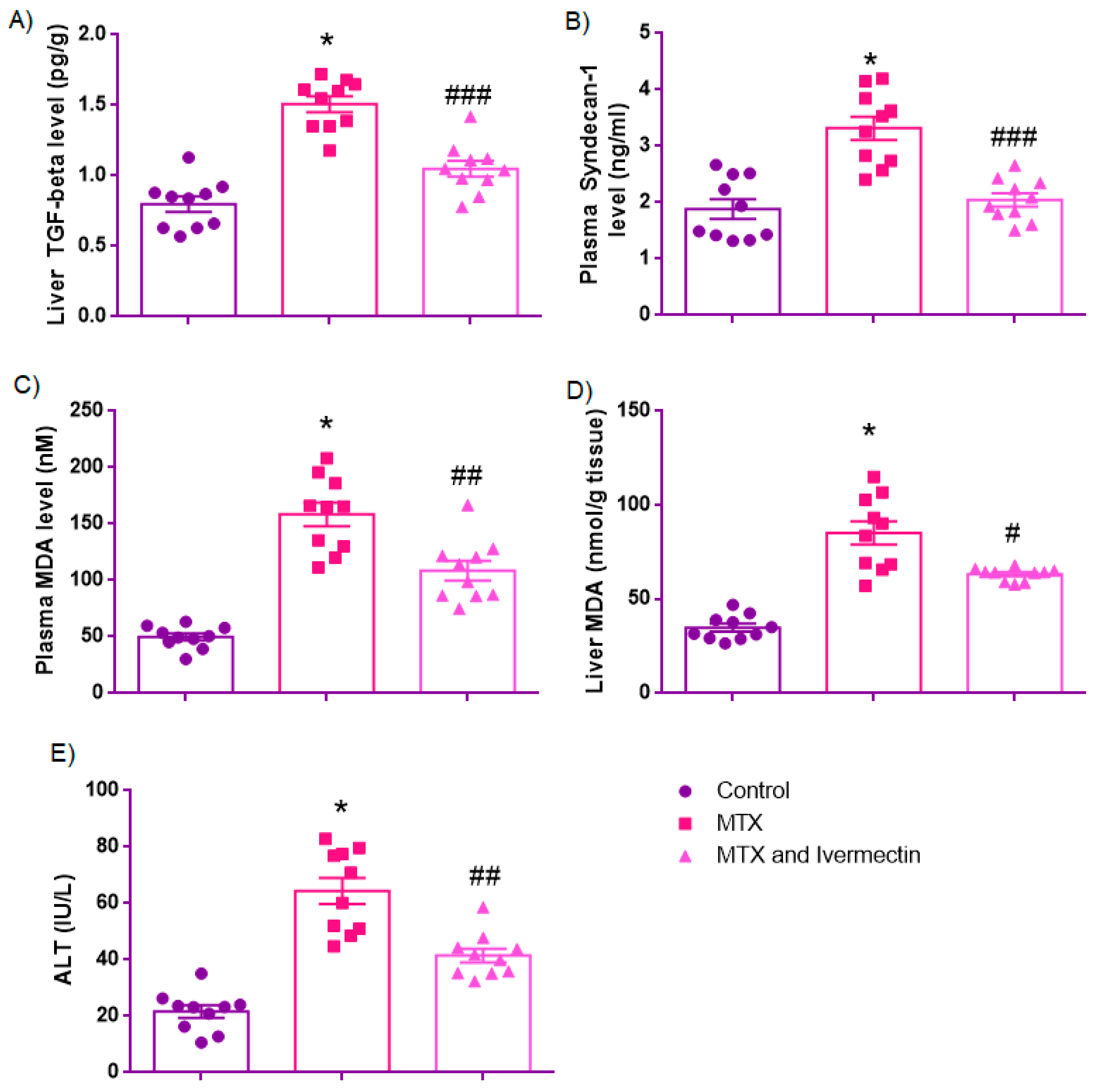
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
3.3.1. Liver TGF-β Levels (pg/g)
3.3.2. Syndecan-1 (SDC-1)
3.3.3. Plasma MDA Levels (nM)
3.3.4. Liver MDA Levels (nmol/g Tissue)
3.3.5. ALT Levels (IU/L)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weinblatt, M.E. Methotrexate in rheumatoid arthritis: A quarter century of development. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 2013, 124, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Karamallah, M.H.; Kalantar, H. Protective effects of apigenin on altered lipid peroxidation, inflammation, and antioxidant factors in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneum, M.; El-Gerbed, M.S. Human placental extract ameliorates methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via regulating antioxidative and anti-inflammatory responses. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2021, 88, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prestigiacomo, V.; Weston, A.; Messner, S.; Lampart, F.; Suter-Dick, L. Pro-fibrotic compounds induce stellate cell activation, ECM-remodelling and Nrf2 activation in a human 3D-multicellular model of liver fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Messner, C.J.; Gaiser, C.; Hämmerli, C.; Suter-Dick, L. Methotrexate-induced liver injury is associated with oxidative stress, impaired mitochondrial respiration, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorgun, O.; Erbaş, O. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells mitigate methotrexate-induced liver cirrhosis (fibrosis) model. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 11882–11889. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, P.I.; Stensballe, J.; Rasmussen, L.S.; Ostrowski, S.R. A high admission syndecan-1 level, a marker of endothelial glycocalyx degradation, is associated with inflammation, protein C depletion, fibrinolysis, and increased mortality in trauma patients. Ann. Surg. 2011, 254, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Atkinson, S.C.; Wang, C.; Lee, A.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Borg, N.A.; Jans, D.A. The broad spectrum antiviral ivermectin targets the host nuclear transport importin α/β1 heterodimer. Antivir. Res. 2020, 177, 104760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerzada, M.N.; Verma, S. Ivermectin as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent. Chem. Biol. Act. Ivermectin 2023, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, D.F.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Liu, K.K.; Paress, P.S.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Arena, J.P. Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1994, 371, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kositz, C.; Bradley, J.; Hutchins, H.; Last, A.; D’Alessandro, U.; Marks, M. Broadening the range of use cases for ivermectin–a review of the evidence. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 116, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolstenholme, A.J.; Rogers, A.T. Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin anthelmintics. Parasitology 2006, 131 (Suppl. 1), S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laing, R.; Gillan, V.; Devaney, E. Ivermectin–old drug, new tricks? Trends Parasitol. 2017, 33, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priel, A.; Silberberg, S.D. Mechanism of ivermectin facilitation of human P2X4 receptor channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 2004, 123, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, B.; Blavo, C.; Parmar, M.S. Ivermectin: A multifaceted drug with a potential beyond anti-parasitic therapy. Cureus 2024, 16, e56025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Feng, X.; Rong, H.; Pan, Z.; Inaba, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; et al. The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, E.T.; Alimba, C.G.; Olowu, E.A.; Otubanjo, A.O. Artemether-Lumefantrine treatment combined with albendazole and ivermectin induced genotoxicity and hepatotoxicity through oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2015, 2, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobenhofer, E.K.; Boorman, G.A.; Phillips, K.L.; Heinloth, A.N.; Malarkey, D.E.; Blackshear, P.E.; Houle, C.; Hurban, P. Application of visualization tools to the analysis of histopathological data enhances biological insight and interpretation. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 34, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taskin, B.; Erdoğan, M.A.; Yiğittürk, G.; Günenç, D.; Erbaş, O. Antifibrotic Effect of Lactulose on a Methotrexate-Induced Liver Injury Model. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 7942531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, N.; Parlakpinar, H.; Cetin, A.; Erdogan, A.; Cetin Ozturk, I. Protective effect of β-carotene on methotrexate–induced oxidative liver damage. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 38, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, R.; Carey, J.J. Risk of liver disease in methotrexate treated patients. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyata, M.; Ishiwata, S.; Kuroda, M.; Tasaki, K.; Migita, K.; Ohira, H. Hepatic failure in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate: A case report. Medicine 2023, 102, e32711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutter, R.V.; Shipkey, F.H.; Tan, C.T.; Murphy, M.L.; Chowdhury, M. Hepatic fibrosis in children with acute leukemia. A complication of therapy. Cancer 1960, 13, 288–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerassi, I.; Farber, S.; Abir, E.; Neikirk, W. Continuous infusion of methotrexate in children with acute leukemia. Cancer 1967, 20, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, S.; Ranjan, R.; Ramachandran, S.; Beriwal, A. High-dose methotrexate-induced reversible grade 4 hyperbilirubinaemia and transaminitis in an adolescent with Burkitt Leukaemia. BMJ Case Rep. CP 2021, 14, e237512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Sepand, M.R.; Seyednejad, S.A.; Omidi, A.; Akbariani, M.; Gholami, M.; Sabzevari, O. Ellagic acid reduces methotrexate-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction via up-regulating Nrf2 expression and inhibiting the IĸBα/NFĸB in rats. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 27, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Sharma, H.; Kumar, U.; Mayachari, A.; Sangli, G.; Singh, S. Protective effects of Glycyrrhiza glabra supplementation against methotrexate-induced hepato-renal damage in rats: An experimental approach. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 263, 113209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, A.U.; Erisgin, Z.; Turedi, S.; Tekelioglu, Y. Methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rats and the therapeutic properties of vitamin E: A histopathologic and flowcytometric research. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2023, 9, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassiman, D.; Denef, C.; Desmet, V.J.; Roskams, T. Human and rat hepatic stellate cells express neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors. Hepatology 2001, 33, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Minicis, S.; Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. NADPH oxidase in the liver: Defensive, offensive, or fibrogenic? Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunali-Akbay, T.U.Ğ.B.A.; Sehirli, O.; Ercan, F.; Şener, G. Resveratrol protects against methotrexate-induced hepatic injury in rats. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 13, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morsy, M.A.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Amin, E.F.; Kamel, M.Y.; Rifaai, R.A.; Hassan, M.K. Curcumin ameliorates methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 2013, 387071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, T.; Gedikli, S.; Ozturk, N.; Aydemir Celep, N. The protective effect of N-acetylcysteine against methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity in rat. Eurasian J. Med. Invest. 2019, 3, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Choudhury, S.; Adhikary, A.; Manna, K.; Dey, S.; Sa, G.; Das, T.; Chattopadhyay, S. Pomegranate reverses methotrexate-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in hepatocytes by modulating Nrf2-NF-κB pathways. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2040–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Hozayen, W.G.; Ramadan, S.M. Berberine ameliorates methotrexate-induced liver injury by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway and PPARγ, and suppressing oxidative stress and apoptosis in rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 94, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, T.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q.; Huo, X.; Sun, H.; Sun, P.; Zheng, S.; Ma, X.; Liu, Z.; Liu, K. Hepatoprotective effect of rhein against methotrexate-induced liver toxicity. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 834, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, F. Ivermectin attenuates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in mice by suppressing hepatic stellate cell activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Song, Y.; Ci, X.; An, N.; Ju, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Han, C.; Cui, J.; Deng, X. Ivermectin inhibits LPS-induced production of inflammatory cytokines and improves LPS-induced survival in mice. Inflamm. Res. 2008, 57, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, T.; Dehpour, A.R.; Alavi, S.D.; Hosseini, S.Z.; Korani, S.; Sureda, A.; Esmaeili, J.; Shirooie, S. Synthesis and evaluation of the effects of solid lipid nanoparticles of ivermectin and ivermectin on cuprizone-induced demyelination via targeting the TRPA1/NF-kB/GFAP signaling pathway. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2023, 26, 1272. [Google Scholar]
- Kayali, A.; Bora, E.S.; Acar, H.; Yilmaz, G.; Erbaş, O. Fisetin ameliorates methotrexate induced liver fibrosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 28, 3112–3119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Yao, X.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, T.; Wu, J.; Liu, X. Sphingosine-1-phosphate induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via an MMP-7/syndecan-1/TGF-β autocrine loop. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regős, E.; Abdelfattah, H.H.; Reszegi, A.; Szilák, L.; Werling, K.; Szabó, G.; Kiss, A.; Schaff, Z.; Kovalszky, I.; Baghy, K. Syndecan-1 inhibits early stages of liver fibrogenesis by interfering with TGFβ1 action and upregulating MMP14. Matrix Biol. 2018, 68, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Zharani, M.; Alghamdi, H.A.; Aldahmash, B.A.; Elnagar, D.M.; Alhoshani, N.M.; AL-Johani, N.S.; Alkeraishan, N.; Alhenaky, A.; Aljarba, N.H.; Alkahtani, S. Ivermectin ameliorate the toxic effect of dimethylhydrazine in male Wistar rats. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 102349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi Razi, F.; Mohammad Jafari, R.; Manavi, M.A.; Sheibani, M.; Rashidian, A.; Tavangar, S.M.; Beighmohammadi, M.T.; Dehpour, A.R. Ivermectin ameliorates bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in male rats by inhibiting the inflammation and oxidative stress. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2024, 46, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Control | MTX | MTX and Ivermectin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatocyte necrosis | 0.0 [IQR: 0.0–1.0] | 2.0 [1.75–3.0] * | 1.0 [1.0–2.0] # |
| Fibrosis | 0.0 [0.0–1.0]) | 2.5 [2.0–3.0] * | 1.0 [1.0–1.25] ### |
| Cellular infiltration | 0.0 [0.0–0.25] | 2.0 [1.0–2.0] * | 1.0 [0.75–1.0] ## |
| Parameters | Control | MTX | MTX and Ivermectin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Liver TGF beta level (pg/g) | 0.79 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.05 * | 1.05 ± 0.05 ### |
| Plasma syndecan-1 level (ng/mL) | 1.71 [1.39–2.50] | 3.39 [2.69–3.92] * | 2.01 [1.75–2.37] ### |
| Plasma MDA level (nM) | 49.66 ± 3.12 | 158.4± 10.45 * | 108.5 ± 8.68 ## |
| Liver MDA level (nmol/g tissue) | 34.80 ± 2.08 | 85.21 ± 6.21 * | 63.18 ± 1.07 # |
| ALT (IU/L) | 21.61 ± 2.22 | 64.44 ± 4.63 * | 41.51 ± 2.45 ## |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dibekoğlu, C.; Kemertaş, K.; Aygun, H.; Erbaş, O. Ivermectin Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-β and Syndecan-1 Expression. Medicina 2025, 61, 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061036
Dibekoğlu C, Kemertaş K, Aygun H, Erbaş O. Ivermectin Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-β and Syndecan-1 Expression. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061036
Chicago/Turabian StyleDibekoğlu, Cengiz, Kubilay Kemertaş, Hatice Aygun, and Oytun Erbaş. 2025. "Ivermectin Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-β and Syndecan-1 Expression" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061036
APA StyleDibekoğlu, C., Kemertaş, K., Aygun, H., & Erbaş, O. (2025). Ivermectin Attenuates Methotrexate-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Reducing TGF-β and Syndecan-1 Expression. Medicina, 61(6), 1036. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061036





