Remimazolam-Based Anesthesia and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Perioperative Characteristics
3.2. Correlation Between Biomarkers and POD
3.3. Predictive Value of Biomarkers for POD
3.4. Propensity Score Matching Analysis
3.5. Predictive Cut-Offs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists. |
| BA | Balanced Anesthesia. |
| BMI | Body Mass Index. |
| CRP | C-reactive Protein. |
| IA | Inhalational Anesthesia. |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio. |
| PCA | Patient-Controlled Analgesia. |
| PLR | Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio. |
| POD | Postoperative Delirium. |
| PSM | Propensity Score Matching. |
| R-TIVA | Remimazolam-based Total Intravenous Anesthesia. |
| SII | Systemic Immune–Inflammation Index. |
References
- Robinson, T.N.; Eiseman, B. Postoperative delirium in the elderly: Diagnosis and management. Clin. Interv. Aging 2008, 3, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcantonio, E.R. Delirium in hospitalized older adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1456–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasqui, E.; de Donato, G.; Brancaccio, B.; Casilli, G.; Ferrante, G.; Cappelli, A.; Palasciano, G. The predictive role of inflammatory biochemical markers in post-operative delirium after vascular surgery procedures. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2022, 18, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Jiménez, E.; Muñoz-Sanjose, A.; Mediavilla, R.; Martínez-Alés, G.; Louzao, I.I.; Andreo, J.; Cebolla, S.; Bravo-Ortiz, M.-F.; Bayón, C. Prospective analysis between neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio on admission and development of delirium among older hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 764334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toft, K.; Tontsch, J.; Abdelhamid, S.; Steiner, L.; Siegemund, M.; Hollinger, A. Serum biomarkers of delirium in the elderly: A narrative review. Ann. Intensive Care 2019, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.-J.; Wang, D.-X.; Jia, H.-Q.; Sun, X.-D.; Pan, L.-H.; Ye, Q.-S.; Ouyang, W.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F.-X.; et al. Impact of inhalational versus intravenous anaesthesia on early delirium and long-term survival in elderly patients after cancer surgery: Study protocol of a multicentre, open-label, and randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e018607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Lewis, S.R.; Pritchard, M.W.; Schofield-Robinson, O.J.; Shelton, C.L.; Alderson, P.; Smith, A.F. Intravenous versus inhalational maintenance of anaesthesia for postoperative cognitive outcomes in elderly people undergoing non-cardiac surgery. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 8, CD012317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Shiramoto, H.; Morimoto, Y.; Koga, M. Comparison of total intravenous with inhalational anesthesia in terms of postoperative delirium and complications in older patients: A nationwide population-based study. J. Anesth. 2022, 36, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, B.; Dubowitz, J.; Yeung, J.; Jhanji, S.; Kheterpal, S.; Avidan, M.S. On the horns of a dilemma: Choosing total intravenous anaesthesia or volatile anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 129, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-J.; Lei, L.; Qiu, D.; Chen, S.; Xing, L.-K.; Zhao, J.-W.; Mao, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-J. Effect of remimazolam on postoperative delirium in older adult patients undergoing orthopedic surgery: A prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Oh, C.; Jung, J.; Hong, B.; Jo, Y.; Lee, S.; Lim, C.; Baek, S.; Shin, M.; Seo, H.; et al. Retrospective comparison of the effects of remimazolam and dexmedetomidine on postoperative delirium in elderly patients undergoing orthopedic surgery of the lower extremities under spinal anesthesia. J. Anesth. 2024, 38, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukimoto, S.; Kitaura, A.; Kuroda, H.; Imaizumi, U.; Yoshino, F.; Yoshida, A.; Nakao, S.; Ohta, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Sanuki, T. Anti-inflammatory potential of remimazolam: A laboratory and clinical investigation. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2024, 12, e1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Lin, S.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Huang, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, S.; Tang, J. Remimazolam protects against LPS-induced endotoxicity improving survival of endotoxemia mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 739603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, L.; An, S.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Zeng, Z. Remimazolam reduces sepsis-associated acute liver injury by activation of peripheral benzodiazepine receptors and p38 inhibition of macrophages. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 108331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inouye, S.K.; van Dyck, C.H.; Alessi, C.A.; Balkin, S.; Siegal, A.P.; Horwitz, R.I. Clarifying confusion: The confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Y.; Lou, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Mi, W.; Cao, J. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts postoperative delirium in elderly patients after surgery: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2022, 22, 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.Z.; Liu, C.X.; Zhou, L.G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y. Postoperative delirium, neuroinflammation, and influencing factors of postoperative delirium: A review. Medicine 2023, 102, e32991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, Y.; Schneider, B.; Spies, C.; Heinrich, M.; von Haefen, C.; Kho, W.; Pohrt, A.; Müller, A. In a secondary analysis from a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial dexmedetomidine blocks cholinergic dysregulation in delirium pathogenesis in patients with major surgery. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, M.; Nieuwenhuijs-Moeke, G.J.; Absalom, A.; van Leeuwen, B.; van der Wal-Huisman, H.; Plas, M.; Bosch, D.J. Association between anaesthesia-related factors and postoperative neurocognitive disorder: A post-hoc analysis. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023, 23, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhart, C.S.; Dell-Kuster, S.; Gamberini, M.; Moeckli, A.; Grapow, M.; Filipovic, M.; Seeberger, M.D.; Monsch, A.U.; Strebel, S.P.; Steiner, L.A. Modifiable and nonmodifiable risk factors for postoperative delirium after cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2010, 24, 555–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Wang, F.; Shen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Zhang, L. Association between increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and postoperative delirium in elderly patients with total hip arthroplasty for hip fracture. BMC Psychiatry 2020, 20, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forget, P.; Khalifa, C.; Defour, J.P.; Latinne, D.; Van Pel, M.C.; De Kock, M. What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio? BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templeton, A.J.; Mcnamara, M.G.; Šeruga, B.; Vera-Badillo, F.E.; Aneja, P.; Ocaña, A.; Leibowitz-Amit, R.; Sonpavde, G.; Knox, J.J.; Tran, B.; et al. Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biau, D.J.; Kernéis, S.; Porcher, R. Statistics in brief: The importance of sample size in the planning and interpretation of medical research. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 2282–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaloun, H.E.; Lee, I.K.; Kim, M.K.; Sung, N.Y.; Al Turkistania, S.A.; Park, S.M.; Won, D.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Kye, B.-H.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Influence of the enhanced recovery after surgery protocol on postoperative inflammation and short-term postoperative surgical outcomes after colorectal cancer surgery. Ann. Coloproctol. 2020, 36, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, E.; Wu, J.; Zhou, X.; Yin, Y. The neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality among U.S. adults with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from NHANES 1999–2020. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1309835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
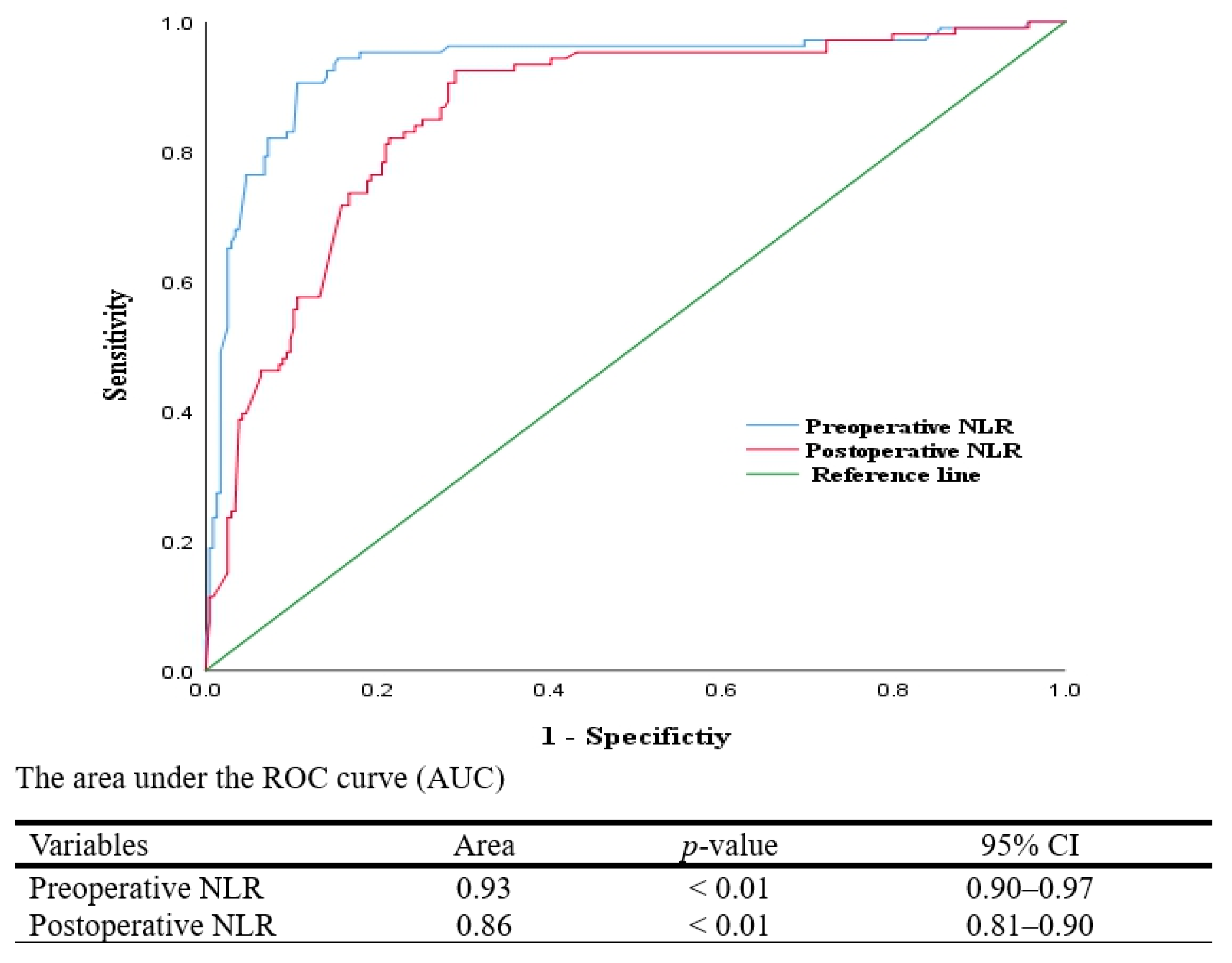
| Group | Remimazolam-Based TIVA Group (n = 111) | Inhalational Anesthesia Group (n = 117) | Balanced Anesthesia Group (n = 112) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | |||||
| Age (years) | 69.3 ± 3.0 | 70.1 ± 3.1 | 69.7 ± 3.5 | >0.05 | |
| Sex (M/F) | 58/53 | 60/57 | 59/53 | >0.05 | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.6 ± 1.9 | 23.8 ± 1.8 | 23.7 ± 1.8 | >0.05 | |
| ASA classification (I/II/III/IV) | 12/44/49/6 | 12/44/53/8 | 9/46/49/8 | >0.05 | |
| Type of surgery | >0.05 | ||||
| Urologic | 33 (29.7) | 38 (32.5) | 30 (26.8 | ||
| Gastrointestinal | 35 (31.5) | 37 (31.6) | 36 (32.1) | ||
| Colorectal | 34 (30.6) | 33 (28.2) | 33 (29.5) | ||
| Gynecologic | 9 (8.1) | 9 (7.7) | 13 (11.6) | ||
| Fluid amount administered (mL) | 1962.2 ± 197.3 | 1969.2 ± 189.6 | 1974.1 ± 184.4 | >0.05 | |
| Duration of anesthesia (min) | 203.9 ± 21.5 | 202.6 ± 19.7 | 205.7 ± 18.8 | >0.05 | |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 178.6 ± 20.8 | 177.2 ± 19.4 | 179.9 ± 18.6 | >0.05 | |
| Transfusion (packed RBC > 3) | 21 (18.9) | 23 (19.7) | 25 (22.3) | >0.05 | |
| HOT | 12 (10.8) | 29 (24.8) | 18 (16.1) | 0.02 | |
| Bradycardia | 8 (7.2) | 23 (19.7) | 15 (13.4) | 0.02 | |
| Vasoactive agents | 10 (9.0) | 26 (22.2) | 14 (12.5) | 0.01 | |
| DM | 35 (31.5) | 35 (29.9) | 37 (33.0) | >0.05 | |
| HTN | 45 (40.5) | 46 (39.3) | 44 (39.3 | >0.05 | |
| CAD | 5 (4.5) | 5 (4.3) | 4 (3.6) | >0.05 | |
| COPD | 6 (5.4) | 6 (5.1) | 3 (2.7) | >0.05 | |
| PAOD | 18 (16.2) | 24 (20.5) | 22 (19.6) | >0.05 | |
| Psychiatric disease | 16 (14.4) | 15 (12.8) | 14 (12.5) | >0.05 | |
| CVA | 22 (19.8) | 29 (24.8) | 24 (21.4) | >0.05 | |
| Polypharmacy | 23 (20.7) | 19 (16.2) | 24 (21.4) | >0.05 | |
| Emergency surgery | 12 (10.8) | 16 (13.7) | 12 (10.7) | >0.05 | |
| Hospitalization (days) | 8.7 ± 1.7 | 9.0 ± 1.5 | 8.7 ± 1.4 | >0.05 | |
| Postoperative delirium | 34 (30.6) | 39 (33.3) | 33 (29.5) | >0.05 | |
| Cumulative PCA volume (mL) | 343.3 ± 34.7 | 330.5 ± 27.2 | 329.7 ± 39.1 | >0.05 | |
| Preoperative SII (×109/L) | 388.8 ± 147.5 | 389.4 ± 174.0 | 392.4 ± 179.4 | >0.05 | |
| Postoperative SII (×109/L) | 562.9 ± 151.0 | 625.6 ± 133.4 * | 603.0 ± 165.5 | <0.01 | |
| Preoperative NLR | 4.5 ± 4.1 | 4.9 ± 4.1 | 4.2 ± 3.2 | >0.05 | |
| Postoperative NLR | 6.0 ± 4.1 | 8.3 ± 6.2 * | 6.9 ± 4.5 | <0.01 | |
| Preoperative PLR | 166.6 ± 74.1 | 172.0 ± 81.7 | 170.1 ± 89.2 | >0.05 | |
| Postoperative PLR | 204.5 ± 108.2 | 240.9 ± 125.5 * | 217.9 ± 97.9 | 0.04 | |
| Preoperative CRP (mg/L) | 3.9 ± 2.1 | 3.8 ± 2.4 | 3.9 ± 2.6 | >0.05 | |
| Postoperative CRP (mg/L) | 6.5 ± 3.1 | 7.7 ± 3.7 * | 6.8 ± 3.5 | 0.03 | |
| Pre Operative SII | Post Operative SII | Pre Operative NLR | Post Operative NLR | Pre Operative PLR | Post Operative PLR | Pre Operative CRP | Post Operative CRP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POD | rpb = 0.39 | rpb = 0.36 | rpb = 0.72 | rpb = 0.58 | rpb = 0.44 | rpb = 0.37 | rpb = 0.42 | rpb = 0.34 |
| p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 | p < 0.01 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers | OR | p-Value | 95% CI | OR | p-Value | 95% CI |
| Preoperative SII | 1.01 | <0.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 1.00 | 0.03 | 1.00–1.01 |
| Postoperative SII | 1.01 | <0.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 1.00 | 0.01 | 1.00–1.01 |
| Preoperative NLR | 2.03 | <0.01 | 1.75–2.37 | 1.71 | <0.01 | 1.46–2.00 |
| Postoperative NLR | 1.35 | <0.01 | 1.24–1.47 | 1.32 | <0.01 | 1.13–1.55 |
| Preoperative PLR | 1.01 | <0.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 1.01 | 0.05 | 1.00–1.01 |
| Postoperative PLR | 1.01 | <0.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0.99–1.00 |
| Preoperative CRP | 1.05 | <0.01 | 0.97–1.13 | 0.92 | 0.43 | 0.74–1.13 |
| Postoperative CRP | 1.33 | <0.01 | 1.25–1.42 | 1.13 | 0.01 | 1.03–1.24 |
| Before Matching | After Matching | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No POD (n = 234) | POD (n = 106) | p-Value | No POD (n = 106) | POD (n = 106) | p- Value | |
| Age (years) | 69.1 ± 2.7 | 71.0 ± 3.8 | <0.01 | 69.3 ± 2.9 | 71.0 ± 3.8 | <0.01 |
| Sex (M/F) | 113/121 | 64/62 | >0.05 | 56/50 | 64/42 | 0.04 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.6 ± 1.8 | 23.9 ± 1.7 | 0.12 | 23.2 ± 1.8 | 23.9 ± 1.7 | <0.01 |
| ASA classification (I/II/III/IV) | 28/117/81/8 | 5/17/70/14 | <0.01 | 10/41/51/4 | 5/17/70/14 | <0.01 |
| Type of surgery | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||||
| Urologic | 66 (28.2) | 35 (33.3) | 34 (32.1) | 35 (33.0) | ||
| Gastrointestinal | 81 (34.6) | 27 (25.5) | 36 (34.0) | 27 (25.5) | ||
| Colorectal | 67 (28.6) | 33 (31.1) | 29 (27.3) | 33 (31.1) | ||
| Gynecologic | 20 (8.5) | 11 (10.4) | 7 (6.6) | 11 (10.4) | ||
| Fluid amount administered (mL) | 1971.8 ± 188.0 | 1961.3 ± 195.0 | >0.05 | 1971.2 ± 188.3 | 1961.3 ± 195.0 | >0.05 |
| Duration of anesthesia (min) | 195.1 ± 12.1 | 223.8 ± 19.8 | <0.01 | 192.5 ± 11.6 | 223.8 ± 19.8 | <0.01 |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 169.7 ± 11.9 | 198.1 ± 19.0 | <0.01 | 167.4 ± 11.8 | 198.1 ± 19.0 | <0.01 |
| Transfusion (packed RBC > 3) | 27 (11.5) | 42 (39.6) | <0.01 | 10 (9.4) | 42 (39.6) | <0.01 |
| HOT | 19 (7.8) | 29 (26.1) | <0.01 | 15 (14.2) | 29 (26.1) | 0.02 |
| Bradycardia | 8 (3.3) | 17 (15.3) | <0.01 | 6 (5.7) | 17 (15.3) | 0.01 |
| Vasoactive agents | 18 (7.3) | 25 (22.5) | <0.01 | 12 (11.3) | 25 (22.5) | 0.02 |
| DM | 76 (32.5) | 31 (29.2) | >0.05 | 39 (36.8) | 31 (29.2) | >0.05 |
| HTN | 91 (38.9) | 44 (41.5) | >0.05 | 45 (42.5) | 44 (41.5) | >0.05 |
| CAD | 5 (2.1) | 9 (8.5) | <0.01 | 4 (3.8) | 9 (8.5) | >0.05 |
| COPD | 13 (5.6) | 2 (1.9) | >0.05 | 9 (8.5) | 2 (1.9) | >0.05 |
| PAOD | 43 (18.4) | 21 (19.8) | >0.05 | 20 (18.9) | 21 (19.8) | >0.05 |
| Psychiatric disease | 17 (7.3) | 28 (26.4) | <0.01 | 8 (7.5) | 28 (26.4) | <0.01 |
| CVA | 33 (14.1) | 42 (39.6) | <0.01 | 15 (14.2) | 42 (39.6) | <0.01 |
| Polypharmacy | 15 (6.4) | 43 (40.6) | <0.01 | 7 (6.6) | 43 (40.6) | <0.01 |
| Emergency surgery | 9 (3.4) | 27 (25.5) | <0.01 | 4 (3.8) | 27 (25.5) | <0.01 |
| Hospitalization (days) | 8.0 ± 0.6 | 11.0 ± 1.4 | <0.01 | 7.9 ± 0.7 | 10.6 ± 1.4 | <0.01 |
| Cumulative PCA volume (ml) | 334.4 ± 30.8 | 334.5 ± 31.5 | >0.05 | 341.9 ± 34.0 | 334.5 ± 31.5 | >0.05 |
| Preoperative SII (×109/L) | 346.6 ± 132.5 | 486.6 ± 194.1 | <0.01 | 384.3 ± 138.8 | 486.6 ± 194.1 | <0.01 |
| Postoperative SII (×109/L) | 561.4 ± 150.0 | 677.7 ± 124.0 | <0.01 | 539.0 ± 147.9 | 677.7 ± 124.0 | <0.01 |
| Preoperative NLR | 2.6 ± 1.9 | 8.6 ± 3.9 | <0.01 | 2.7 ± 2.0 | 8.6 ± 3.9 | <0.01 |
| Postoperative NLR | 5.1 ± 3.8 | 11.5 ± 5.0 | <0.01 | 4.9 ± 3.3 | 11.5 ± 5.0 | <0.01 |
| Preoperative PLR | 149.6 ± 70.6 | 213.8 ± 87.3 | <0.01 | 150.9 ± 71.8 | 213.8 ± 87.3 | <0.01 |
| Postoperative PLR | 203.1 ± 113.7 | 262.0 ± 97.3 | <0.01 | 192.2 ± 126.4 | 262.0 ± 97.3 | <0.01 |
| Preoperative CRP (mg/L) | 3.6 ± 4.8 | 4.4 ± 2.4 | 0.12 | 3.4 ± 1.9 | 4.4 ± 2.4 | <0.01 |
| Postoperative CRP (mg/L) | 6.0 ± 3.1 | 9.2 ± 3.4 | <0.01 | 5.9 ± 3.0 | 9.2 ± 3.4 | <0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, C. Remimazolam-Based Anesthesia and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061023
Lee H, Kim K, Lee C. Remimazolam-Based Anesthesia and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(6):1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061023
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hayoung, Keunyoung Kim, and Cheol Lee. 2025. "Remimazolam-Based Anesthesia and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Medicina 61, no. 6: 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061023
APA StyleLee, H., Kim, K., & Lee, C. (2025). Remimazolam-Based Anesthesia and Systemic Inflammatory Biomarkers in Relation to Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicina, 61(6), 1023. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61061023







