Platelet-Rich Plasma Provides Superior Clinical Outcomes Without Radiologic Differences in Lateral Epicondylitis: Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Which injection treatment demonstrates greater success in the mid-term?
- What is the mid-term radiological changes observed before and after the injection treatments?
2. Materials and Methods
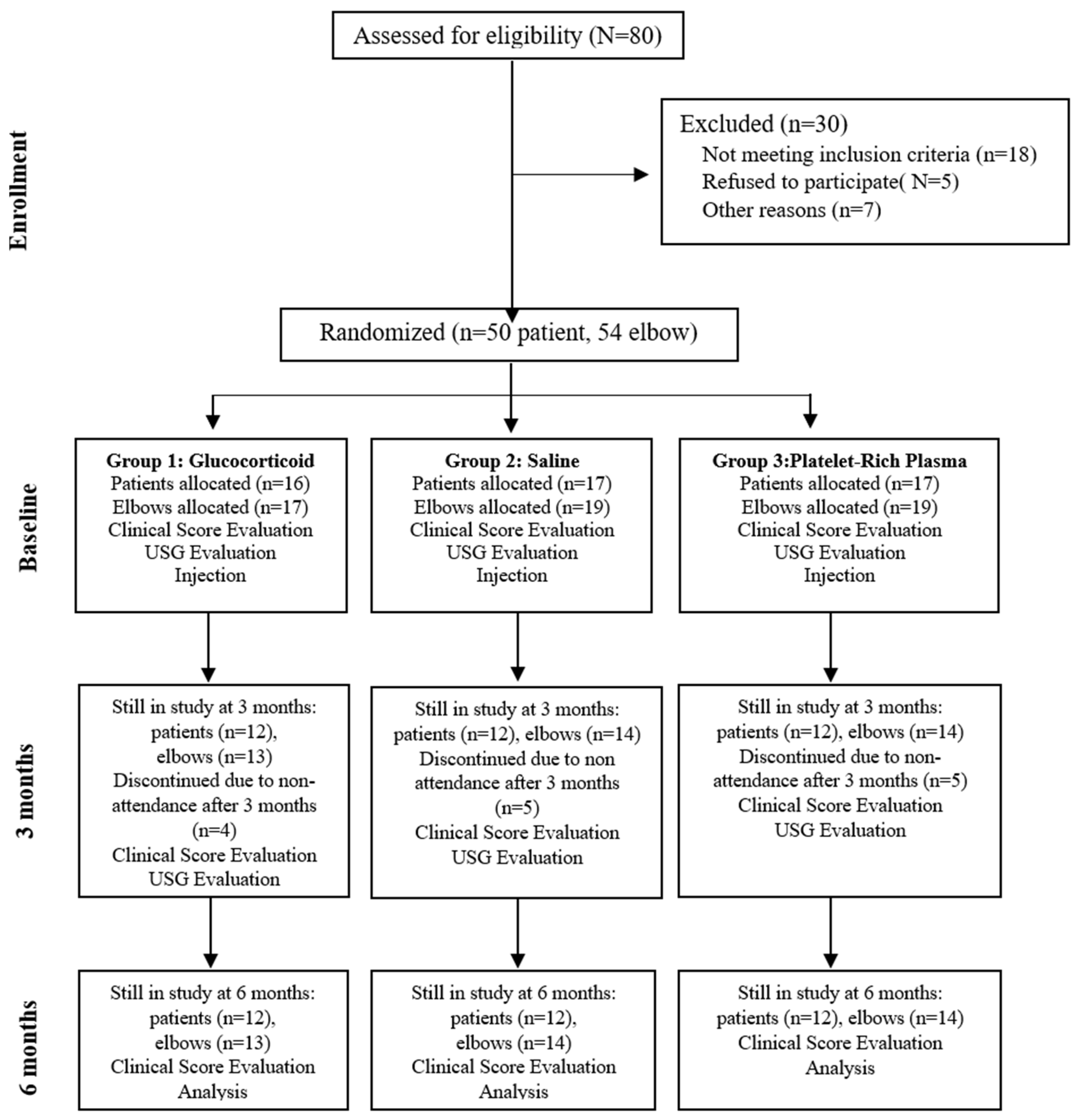
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Human Ethics and Consent to Participate
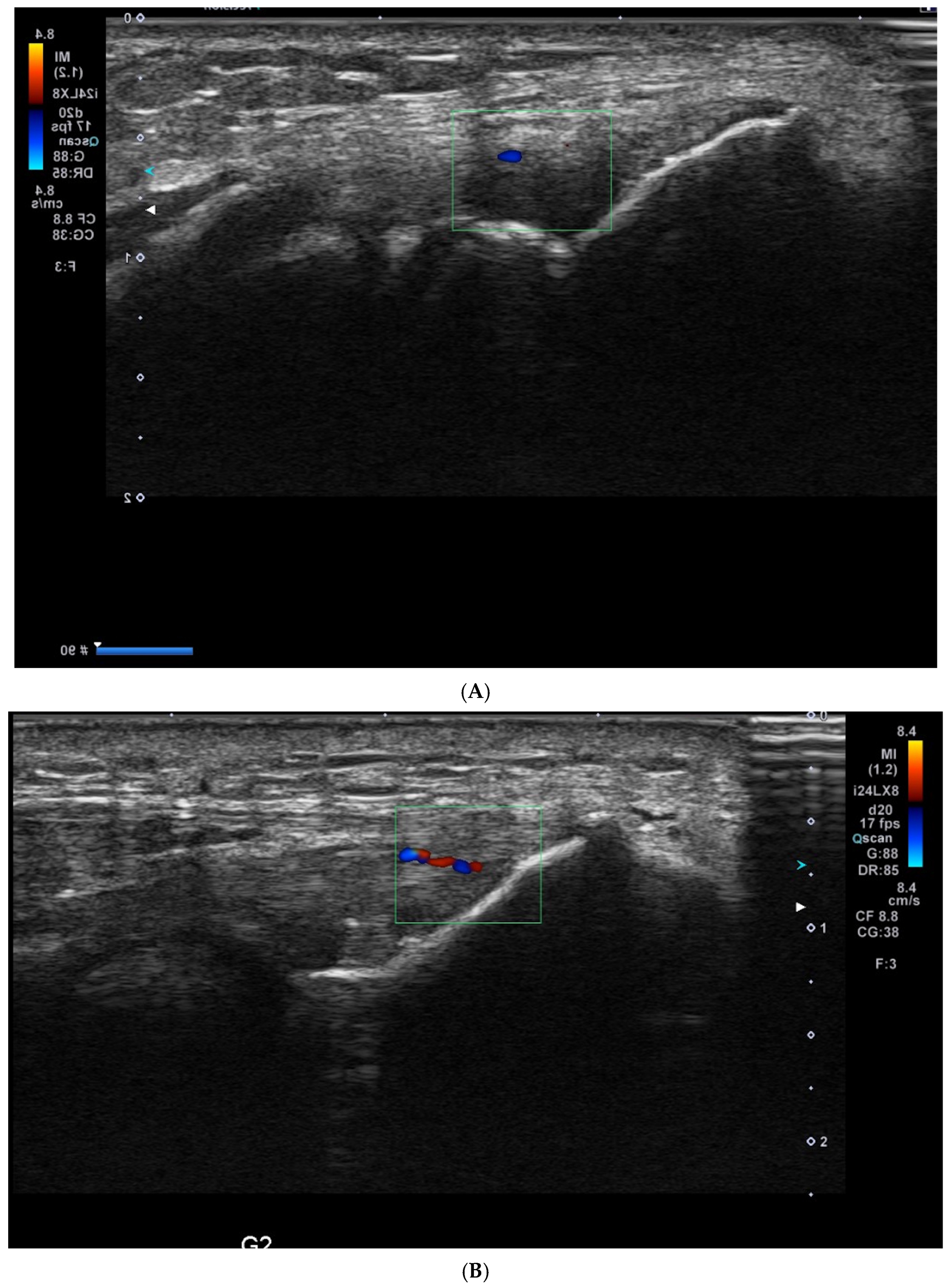
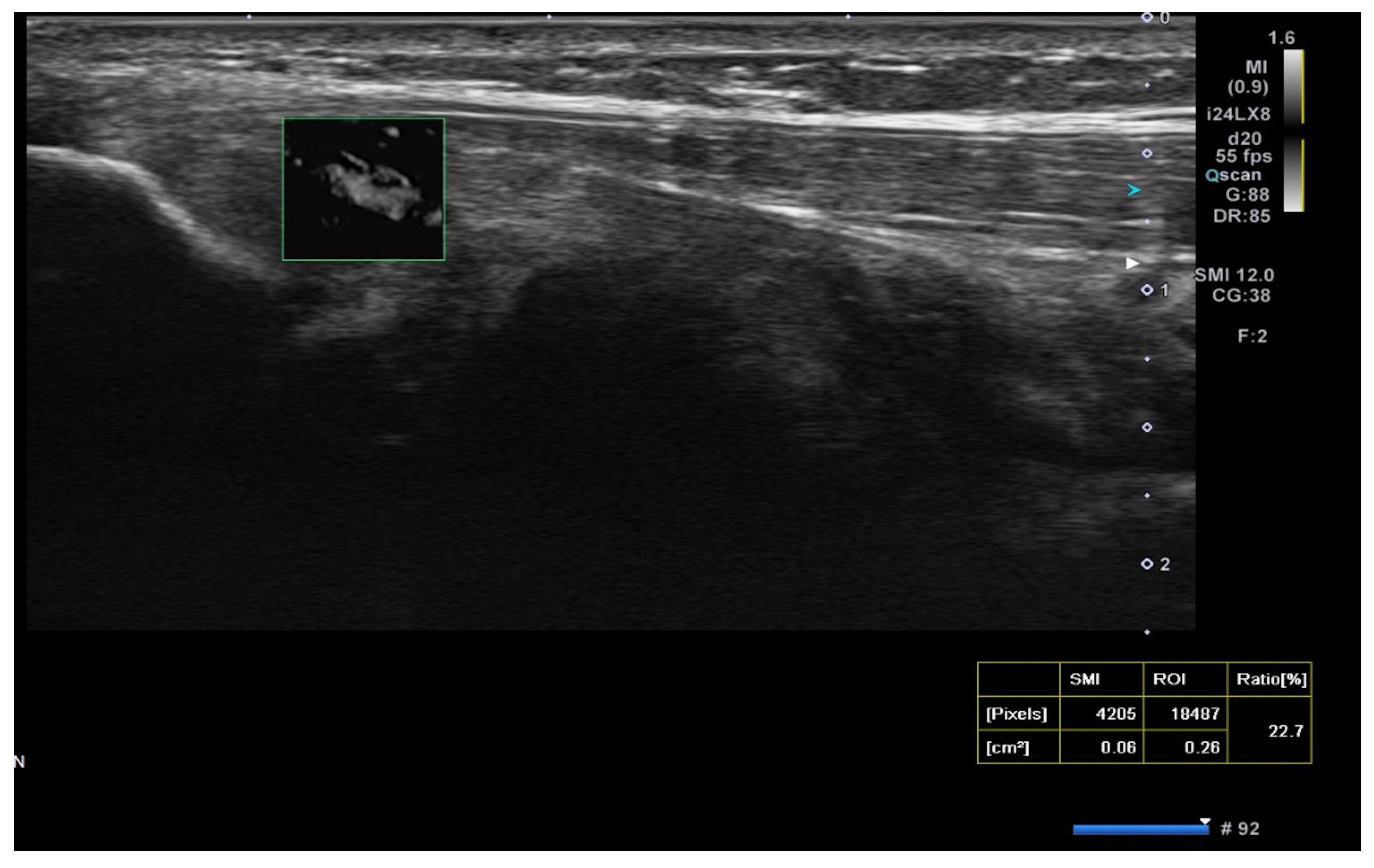
2.3. USG Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, T.T.; Shapiro, M.A.; Schultz, E.; Kalish, P.E. Comparison of sonography and MRI for diagnosing epicondylitis. J. Clin. Ultrasound 2002, 30, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, M.; Vilchez-Cavazos, F.; Álvarez-Villalobos, N.; Blázquez-Saldaña, J.; Peña-Martínez, V.; Villarreal-Villarreal, G.; Acosta-Olivo, C. Clinical efficacy of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled clinical trials. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, P.L.; Amadio, P.C.; Bombardier, C. Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: The DASH (disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand) [corrected]. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG). Am. J. Ind. Med. 1996, 29, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker-Bone, K.; Palmer, K.T.; Reading, I.; Coggon, D.; Cooper, C. Occupation and epicondylitis: A population-based study. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadehkhaiyat, O.; Fisher, A.C.P.; Kemp, G.J.M.; Frostick, S.P.M. Pain, Functional Disability, and Psychologic Status in Tennis Elbow. Clin. J. Pain 2007, 23, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boden, A.L.; Scott, M.T.; Dalwadi, P.P.; Mautner, K.; Mason, R.A.; Gottschalk, M.B. Platelet-rich plasma versus Tenex in the treatment of medial and lateral epicondylitis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2019, 28, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidt, N.; Assendelft, W.; Arola, H.; Malmivaara, A.; Green, S.; Buchbinder, R.; van der Windt, D.; Bouter, L. Effectiveness of physiotherapy for lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review. Ann. Med. 2003, 35, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasas, C.; Papadimitriou, G.; Charalambidis, C.; Paraskevopoulos, I.; Papanikolaou, A. Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous whole blood for the treatment of chronic lateral elbow epicondylitis: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 2130–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzocca, A.D.; McCarthy, M.B.R.; Intravia, J.; Beitzel, K.; Apostolakos, J.; Cote, M.P.; Bradley, J.; Arciero, R.A. An In Vitro Evaluation of the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma, Ketorolac, and Methylprednisolone. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2013, 29, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisset, L.; Beller, E.; Jull, G.; Brooks, P.; Darnell, R.; Vicenzino, B. Mobilisation with movement and exercise, corticosteroid injection, or wait and see for tennis elbow: Randomised trial. BMJ 2006, 333, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiri, R.; Viikari-Juntura, E.; Varonen, H.; Heliövaara, M. Prevalence and Determinants of Lateral and Medial Epicondylitis: A Population Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 164, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.E.; Puskas, B.L.; Mandelbaum, B.R.; Gerhardt, M.B.; Rodeo, S.A. Platelet-rich plasma: From basic science to clinical applications. Am. J. Sports Med. 2009, 37, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merolla, G.; Dellabiancia, F.; Ricci, A.; Mussoni, M.P.; Nucci, S.; Zanoli, G.; Paladini, P.; Porcellini, G. Arthroscopic Debridement Versus Platelet-Rich Plasma Injection: A Prospective, Randomized, Comparative Study of Chronic Lateral Epicondylitis With a Nearly 2-Year Follow-Up. Arthrosc. J. Arthrosc. Relat. Surg. 2017, 33, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arirachakaran, A.; Sukthuayat, A.; Sisayanarane, T.; Laoratanavoraphong, S.; Kanchanatawan, W.; Kongtharvonskul, J. Platelet-rich plasma versus autologous blood versus steroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2016, 17, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosens, T.; Peerbooms, J.C.; van Laar, W.; den Oudsten, B.L. Ongoing positive effect of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection in lateral epicondylitis: A double-blind randomized controlled trial with 2-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2011, 39, 1200–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klifto, K.M.; Colbert, S.H.; Richard, M.J.; Anakwenze, O.A.; Ruch, D.S.; Klifto, C.S. Platelet-rich plasma vs. corticosteroid injections for the treatment of recalcitrant lateral epicondylitis: A cost-effectiveness Markov decision analysis. J. Shoulder Elb. Surg. 2022, 31, 991–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.-L.; Wang, H.-Q. Management of Lateral Epicondylitis: A Narrative Literature Review. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 6965381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, S.E.G.; Miller, K.; Elfar, J.C.; Hammert, W.C. Non-Surgical Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis: A Aystematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Hand 2014, 9, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peerbooms, J.C.; Sluimer, J.; Bruijn, D.J.; Gosens, T. Positive effect of an autologous platelet concentrate in lateral epicondylitis in a double-blind randomized controlled trial: Platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injection with a 1-year follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehr, R. Sixteen S-squared over D-squared: A relation for crude sample size estimates. Stat. Med. 1992, 11, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, S.; Karahan, A.Y.; Oncu, F.; Bakdik, S.; Durmaz, M.S.; Tolu, I. Diagnostic Performance of Superb Microvascular Imaging and Other Sonographic Modalities in the Assessment of Lateral Epicondylosis. J. Ultrasound Med. 2018, 37, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompe, J.D.; Overend, T.J.; MacDermid, J.C. Validation of the Patient-rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation Questionnaire. J. Hand Ther. 2007, 20, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnanmäki, L.; Kanto, K.; Karjalainen, T.; Leppänen, O.V.; Lehtinen, J. Platelet-rich Plasma or Autologous Blood Do Not Reduce Pain or Improve Function in Patients with Lateral Epicondylitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2020, 478, 1892–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredberg, U.; Bolvig, L.; Pfeiffer-Jensen, M.; Clemmensen, D.; Jakobsen, B.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K. Ultrasonography as a tool for diagnosis, guidance of local steroid injection and, together with pressure algometry, monitoring of the treatment of athletes with chronic jumper’s knee and Achilles tendinitis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 33, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düger, T.; Yakut, E.D.; Öksüz, Ç.; Yörükan, S.; Bilgutay, B.; Ayhan, Ç.; Leblebicioglu, G.; Kayihan, H.; Kirdi, N.; Yakut, Y.; et al. Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand (DASH) Questionnaire. Turk. J. Physiother. Rehabil.-Fiz. Rehabil. 2006, 17, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Karjalainen, T.V.; Silagy, M.; O’Bryan, E.; Johnston, R.V.; Cyril, S.; Buchbinder, R. Autologous blood and platelet-rich plasma injection therapy for lateral elbow pain. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 9, CD010951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Nafa, W.; Munro, W. The effect of corticosteroid versus platelet-rich plasma injection therapies for the management of lateral epicondylitis: A systematic review. SICOT-J 2018, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprak, U.; Baskan, B.; Ustuner, E.; Oten, E.; Altin, L.; Karademir, M.A.; Bodur, H. Common extensor tendon thickness measurements at the radiocapitellar region in diagnosis of lateral elbow tendinopathy. Diagn. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 18, 566–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, L.; Ercan, I.; Konur, S. Reliability and validity of Turkish version of the patient rated tennis elbow evaluation. Rheumatol. Int. 2010, 30, 1049–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Cha, J.G.; Jin, W.; Kim, B.S.; Park, J.S.; Lee, H.K.; Hong, H.S. Utility of Sonographic Measurement of the Common Tensor Tendon in Patients With Lateral Epicondylitis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2011, 196, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, D.E.; Katz, J.N.; Fossel, A.H.; Wright, J.G.; Tarasuk, V.; Bombardier, C. Measuring the whole or the parts? Validity, reliability, and responsiveness of the Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand outcome measure in different regions of the upper extremity. J. Hand Ther. 2001, 14, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, S.; Gerhardt, M.; Mandelbaum, B. Platelet rich plasma injection grafts for musculoskeletal injuries: A review. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2008, 1, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanzmann, M.C.; Audigé, L. Platelet-rich plasma for chronic lateral epicondylitis: Is one injection sufficient? Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg. 2015, 135, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colloca, L.; Miller, F.G. The Nocebo Effect and Its Relevance for Clinical Practice. Psychosom. Med. 2011, 73, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti, F.; Lanotte, M.; Lopiano, L.; Colloca, L. When words are painful: Unraveling the mechanisms of the nocebo effect. Neuroscience 2007, 147, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, S.; de La Lama, M.; Adler, R.S.; Gulotta, L.V.; Skonieczki, B.; Chang, A.; Moley, P.; Cordasco, F.; Hannafin, J.; Fealy, S. Platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of lateral epicondylitis: Sonographic assessment of tendon morphology and vascularity (pilot study). Skelet. Radiol. 2012, 42, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Verma, S.; Batra, S.; Bhatnagar, N.; Arora, S. Platelet-Rich Plasma versus Corticosteroid Injection for Recalcitrant Lateral Epicondylitis: Clinical and Ultrasonographic Evaluation. J. Orthop. Surg. 2015, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, T.P.; Fredberg, U.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Christensen, R.; Jensen, P.; Ellingsen, T. Treatment of Lateral Epicondylitis With Platelet-Rich Plasma, Glucocorticoid, or Saline. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Demographics | Glucocorticoid | Saline | PRP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | |
| Age | 42.2 | 10.9 | 40.7 | 9.4 | 43.4 | 6.2 |
| Female | Male | Female | Male | Female | Male | |
| Gender | 7 | 5 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 6 |
| Dominant Side | 6 | 7 | 9 | |||
| Glucocorticoid | Saline | PRP | Glucocorticoid vs. Saline | Glucocorticoid vs. PRP | Saline vs. PRP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | p Value | p Value | p Value |
| VAS at Baseline | 6.1 | 2.07 | 7.2 | 1.3 | 6.5 | 1.4 | |||
| PRTEE at Baseline | 46.1 | 12.4 | 48.9 | 9.2 | 48.2 | 8.2 | |||
| DASH at Baseline | 48.3 | 9.3 | 50.8 | 6.9 | 48 | 5.6 | |||
| VAS at 3 Months | 4.1 | 1.6 | 6.3 | 2.1 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 0.02 | 0.7 | 0.001 |
| PRTEE at 3 Months | 34.2 | 9.5 | 47.4 | 8.5 | 19 | 11.5 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| DASH at 3 Months | 34.6 | 13.1 | 49.1 | 8.1 | 19.2 | 11.3 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.001 |
| VAS at 6 Months | 4.4 | 1.9 | 5.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| PRTEE at 6 Months | 34.2 | 9.5 | 47.4 | 8.5 | 19 | 11.5 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| DASH at 6 Months | 32.6 | 13.7 | 47.4 | 8.5 | 13.7 | 10.5 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Glucocorticoid | Saline | PRP | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | Mean | SE | p Value |
| US Vascularity at Baseline | 2.2 | 1.43 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 2.9 | 1.1 | 0.09 |
| SMI at Baseline | 9.8 | 9.3 | 9.3 | 7.5 | 12.4 | 6.9 | 0.6 |
| US Vascularity After Treatment | 2.1 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 0.3 |
| SMI After Treatment | 9.8 | 7.8 | 10.2 | 8.4 | 7.06 | 6.6 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kizilkurt, T.; Aydin, A.S.; Yagci, T.F.; Ersen, A.; Ercan, C.C.; Salmaslioglu, A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Provides Superior Clinical Outcomes Without Radiologic Differences in Lateral Epicondylitis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina 2025, 61, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050894
Kizilkurt T, Aydin AS, Yagci TF, Ersen A, Ercan CC, Salmaslioglu A. Platelet-Rich Plasma Provides Superior Clinical Outcomes Without Radiologic Differences in Lateral Epicondylitis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina. 2025; 61(5):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050894
Chicago/Turabian StyleKizilkurt, Taha, Ahmet Serhat Aydin, Taha Furkan Yagci, Ali Ersen, Celal Caner Ercan, and Artür Salmaslioglu. 2025. "Platelet-Rich Plasma Provides Superior Clinical Outcomes Without Radiologic Differences in Lateral Epicondylitis: Randomized Controlled Trial" Medicina 61, no. 5: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050894
APA StyleKizilkurt, T., Aydin, A. S., Yagci, T. F., Ersen, A., Ercan, C. C., & Salmaslioglu, A. (2025). Platelet-Rich Plasma Provides Superior Clinical Outcomes Without Radiologic Differences in Lateral Epicondylitis: Randomized Controlled Trial. Medicina, 61(5), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050894







