The Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Nitric Oxide Production and Release in Erythrocytes
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
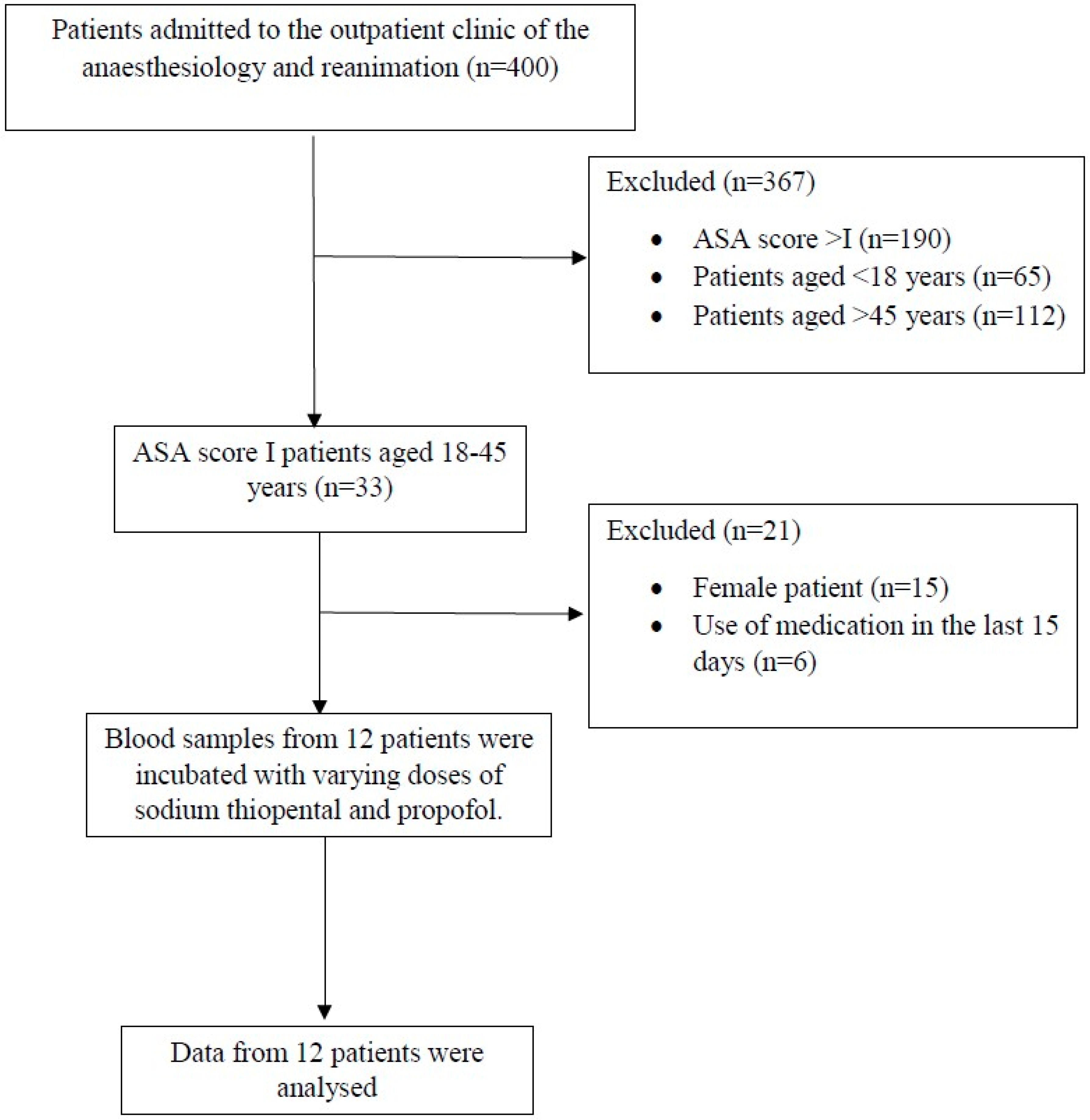
2.1. Study Design and Ethical Approval
2.2. Participants
2.3. Outcome
2.4. Blood Samples and Preparation of RBC Suspensions
2.5. Demonstration of NO Generation
2.6. Demonstration of Intracellular Calcium (Ca+2) Levels
2.7. Demonstration of Nitrite/Nitrate Levels
2.8. RBC Deformability Measurements
2.9. RBC Aggregation Measurements
2.10. Statistical Analysis
Sample Size
2.11. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. NO Generation from RBCs in Response to Thiopental and Propofol Incubation
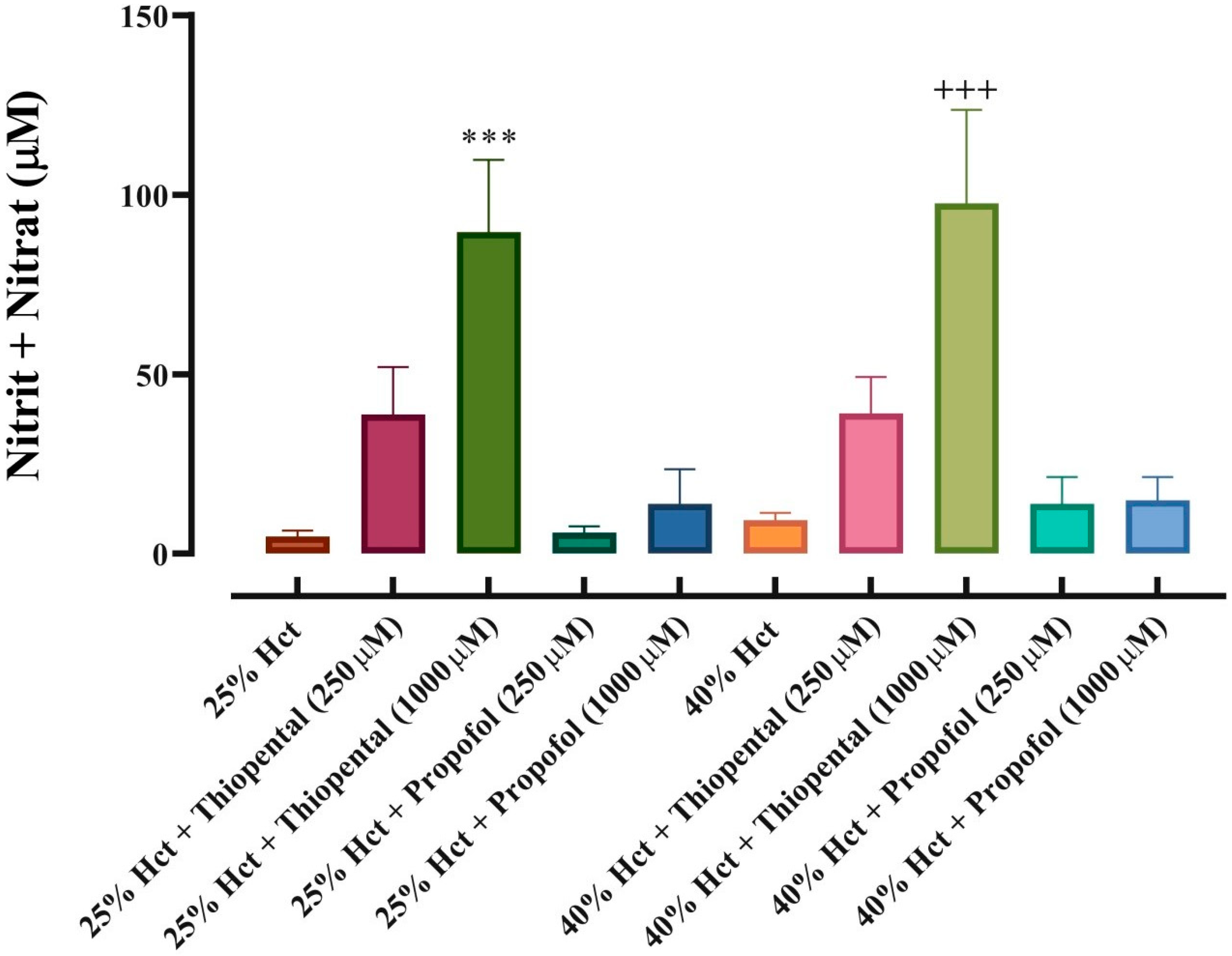
3.3. NO Output from Red Blood Cells in Response to Thiopental and Propofol Incubation
3.4. Intracellular Ca+2 Concentrations
3.5. Haemorheological Analysis
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| RBC | Erythrocyte |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| Ca+2 | Calcium |
| ST | Sodium thiopental |
| NOS | Nitric oxide synthase |
| DAF-FM-DA | 4-amino-5-methylamino-20,70-difluorofluorescein diacetate |
| EI | Elongation index |
| SS1/2 | Half-maximal erythrocyte deformation |
| AI | Aggregation index |
| L-NAME | L-N-acetyl-methyl-arginine |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- Skibiski, J.; Patel, P.; Abdijadid, S. Barbiturates; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.S.; Hayes, I.; Buggy, D.J. Pharmacology of anaesthetic agents I: Intravenous anaesthetic agents. Contin. Educ. Anaesth. Crit. Care Pain 2014, 14, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtkamp, M. Pharmacotherapy for Refractory and Super-Refractory Status Epilepticus in Adults. Drugs 2018, 78, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.A.; Jung, W.; Jung, Y.J.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kang, K.; Choi, H.; Kong, D.S.; Seol, H.J.; Lee, J.I. Early prediction of neurological outcome after barbiturate coma therapy in patients undergoing brain tumor surgery. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, D.W. Cardiac output decrease and propofol: What is the mechanism? Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 163–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, C.S.; Serrao, J.M. Propofol-induced cardiovascular depression: Science and art. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 115, 641–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peck, T.; Harris, B. Pharmacology for Anaesthesia and Intensive Care; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wu, B.; Sun, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, M.; Jiang, W. Translocation of protein kinase C isoforms is involved in propofol-induced endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation. Br. J. Anaesth. 2010, 104, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Q.; Cui, D.; Wang, L. Protein Kinase C Isoforms Distinctly Regulate Propofol-induced Endothelium-dependent and Endothelium-independent Vasodilation. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, L.; Martinez-Cuesta, M.A.; Muedra, V.; Beltran, B.; Esplugues, J. Role of the endothelium in the relaxation induced by propofol and thiopental in isolated arteries from man. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 1997, 49, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelsson, G.; Sandstrom, K.; Wallerstedt, S.M.; Hidestal, J.; Tornebrandt, K.; Bodelsson, M. Effects of propofol on substance P-induced relaxation in isolated human omental arteries and veins. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2000, 17, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forstermann, U.; Sessa, W.C. Nitric oxide synthases: Regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 829–837, 37a–37d. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Lacchini, R.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Clinical and pharmacogenetic impact of endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms on cardiovascular diseases. Nitric Oxide 2017, 63, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toda, N.; Toda, H.; Hatano, Y. Nitric oxide: Involvement in the effects of anesthetic agents. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 822–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Ferreira, G.C.; Garcia, W.N.P.; Lacchini, R.; Garcia, L.V.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors enhance the hypotensive effects of propofol by increasing nitric oxide production. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajecki, D.; Gawrys, J.; Szahidewicz-Krupska, E.; Doroszko, A. Role of Erythrocytes in Nitric Oxide Metabolism and Paracrine Regulation of Endothelial Function. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnider, T.W.; Minto, C.F.; Filipovic, M. The Drug Titration Paradox: Correlation of More Drug with Less Effect in Clinical Data. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulooze, S.C.; Krekels, E.H.J.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; van Noort, M. The Drug Titration Paradox in the Presence of Intra-Individual Variation: Can we Estimate the True Concentration-Effect Relationship? AAPS J. 2025, 27, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnider, T.W.; Minto, C.F.; Luginbuhl, M.; Egan, T.D. The drug titration paradox: More drug does not correlate with more effect in individual clinical data. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 129, 861–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egan, T.D. The drug titration paradox: Something obvious finally understood. Br. J. Anaesth. 2022, 128, 900–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, F.; Mabasa, V.H.; Ensom, M.H. A critical review: Does thiopental continuous infusion warrant therapeutic drug monitoring in the critical care population? Ther. Drug Monit. 2009, 31, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabricot, E.; Seqat, I.; Dailler, F.; Rheims, S.; Boulogne, S.; Balanca, B. How to monitor thiopental administration in the intensive care unit for refectory status epilepticus or intracranial hypertension? Crit. Care 2021, 25, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stover, J.F.; Lenzlinger, P.M.; Stocker, R.; Morganti-Kossmann, M.C.; Imhof, H.G.; Trentz, O.; Kossmann, T. Thiopental in CSF and serum correlates with prolonged loss of cortical activity. Eur. Neurol. 1998, 39, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazama, T.; Ikeda, K.; Morita, K.; Katoh, T.; Kikura, M. Propofol concentration required for endotracheal intubation with a laryngoscope or fiberscope and its interaction with fentanyl. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.K.; Lynch, C., 3rd; Johns, R.A. Effects of propofol and thiopental in isolated rat aorta and pulmonary artery. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, W. Propofol induces endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation and activation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells by inhibiting protein kinase C delta expression. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2010, 27, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeman, M.R.; Dobbe, J.G.; Ince, C. The Laser-assisted Optical Rotational Cell Analyzer (LORCA) as red blood cell aggregometer. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2001, 25, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Baskurt, O.K.; Meiselman, H.J. Analyzing shear stress-elongation index curves: Comparison of two approaches to simplify data presentation. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2004, 31, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, N.L.; Stylianou, M.P. Advances in and limitations of up-and-down methodology: A precis of clinical use, study design, and dose estimation in anesthesia research. Anesthesiology 2007, 107, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Garg, A.X.; Kurz, A.; Turan, A.; Rodseth, R.N.; Cywinski, J.; Thabane, L.; Sessler, D.I. Relationship between intraoperative mean arterial pressure and clinical outcomes after noncardiac surgery: Toward an empirical definition of hypotension. Anesthesiology 2013, 119, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saugel, B.; Sessler, D.I. Perioperative Blood Pressure Management. Anesthesiology 2021, 134, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jor, O.; Maca, J.; Koutna, J.; Gemrotova, M.; Vymazal, T.; Litschmannova, M.; Sevcik, P.; Reimer, P.; Mikulova, V.; Trlicova, M.; et al. Hypotension after induction of general anesthesia: Occurrence, risk factors, and therapy. A prospective multicentre observational study. J. Anesth. 2018, 32, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hino, H.; Matsuura, T.; Kihara, Y.; Tsujikawa, S.; Mori, T.; Nishikawa, K. Comparison between hemodynamic effects of propofol and thiopental during general anesthesia induction with remifentanil infusion: A double-blind, age-stratified, randomized study. J. Anesth. 2019, 33, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakazu, C.Z.; Lippmann, M. Playing with fire: Debate about propofol-induced hypotension. Br. J. Anaesth. 2015, 114, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragasin, F.S.; Davidge, S.T. The effects of propofol on vascular function in mesenteric arteries of the aging rat. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H466–H474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, W.S.; Ding, X.; Murray, P.A. Propofol and thiopental attenuate adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel relaxation in pulmonary veins. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 291, L636–L643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, C.; Escalante, B.; Terron, J.A.; Valencia, I.; Castillo, E.F. Effects of thiopental on endothelium-dependent responses in rat aorta. Arch. Med. Res. 1997, 28, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De La Cruz, J.P.; Paez, M.V.; Carmona, J.A.; De La Cuesta, F.S. Antiplatelet effect of the anaesthetic drug propofol: Influence of red blood cells and leucocytes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 128, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira-Paula, G.H.; Lacchini, R.; Pinheiro, L.C.; Ferreira, G.C.; Luizon, M.R.; Garcia, W.N.P.; Garcia, L.V.; Tanus-Santos, J.E. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase polymorphisms affect the changes in blood pressure and nitric oxide bioavailability induced by propofol. Nitric Oxide 2018, 75, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinbongard, P.; Schulz, R.; Rassaf, T.; Lauer, T.; Dejam, A.; Jax, T.; Kumara, I.; Gharini, P.; Kabanova, S.; Ozuyaman, B.; et al. Red blood cells express a functional endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Blood 2006, 107, 2943–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basarici, I.; Ozen, N.; Kilavuz, E.; Kisak, F.; Basrali, F.; Yaras, N.; Koksoy, S.; Celik, M.L.; Ulker, P. Concealed role of red blood cells in pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension: Decreased red blood cell nitric oxide generation and effect of Rho-Kinase inhibitor fasudil. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2020, 76, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, C.C.; Gladwin, M.T.; Kim-Shapiro, D.B. Erythrocytes and Vascular Function: Oxygen and Nitric Oxide. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, F.; Suvorava, T.; Heuser, S.K.; Li, J.; LoBue, A.; Barbarino, F.; Piragine, E.; Schneckmann, R.; Hutzler, B.; Good, M.E.; et al. Red Blood Cell and Endothelial eNOS Independently Regulate Circulating Nitric Oxide Metabolites and Blood Pressure. Circulation 2021, 144, 870–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I. Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of eNOS. Pflug. Arch. 2010, 459, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Correa, J.A.; Cruz-Andreotti, E.; Arrebola, M.M.; Lopez-Villodres, J.A.; Jodar, M.; De La Cruz, J.P. Effects of propofol on the leukocyte nitric oxide pathway: In vitro and ex vivo studies in surgical patients. Naunyn Schmiedeberg Arch. Pharmacol. 2008, 376, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Chung, H.G.; Myung, S.A.; Rha, J.H.; Yang, S.; Nam, M.H.; Shin, S.H.; Lim, C.H. In vitro effect of clinical propofol concentrations on red blood cell aggregation and deformability. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2012, 51, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor-Kucukatay, M.; Yalcin, O.; Gokalp, O.; Kipmen-Korgun, D.; Yesilkaya, A.; Baykal, A.; Ispir, M.; Senturk, U.K.; Kaputlu, I.; Baskurt, O.K. Red blood cell rheological alterations in hypertension induced by chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in rats. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2000, 22, 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Alexy, T.; Detterich, J.; Connes, P.; Toth, K.; Nader, E.; Kenyeres, P.; Arriola-Montenegro, J.; Ulker, P.; Simmonds, M.J. Physical Properties of Blood and their Relationship to Clinical Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 906768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minto, C.F.; Egan, T.D.; Schnider, T.W. Drug Titration Paradox: An Emerging Concept in Clinical Pharmacology. Anesthesiology 2024, 140, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; McEwan, A.I.; Jhaveri, R.; Wilkinson, M.; Goodman, D.; Smith, L.R.; Canada, A.T.; Glass, P.S. The interaction of fentanyl on the Cp50 of propofol for loss of consciousness and skin incision. Anesthesiology 1994, 81, 820–828; discussion 826A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yu, F.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Lian, J. The median effective concentration (EC50) of propofol with different doses of fentanyl during colonoscopy in elderly patients. BMC Anesth. 2016, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawidowicz, A.L.; Kalitynski, R.; Kobielski, M.; Pieniadz, J. Influence of propofol concentration in human plasma on free fraction of the drug. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2006, 159, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.E., Jr. Plasma levels of thiopental necessary for anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1978, 49, 192–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, O.R.; Varvel, J.R.; Shafer, S.L.; Stanski, D.R. Thiopental pharmacodynamics. II. Quantitation of clinical and electroencephalographic depth of anesthesia. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, H.; Simon, N.; Duboin, M.P.; Urien, S. Population pharmacokinetics of high-dose thiopental in patients with cerebral injuries. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 62, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Doses | Sodium Thiopental Molecular Weight: 264.32 5 mg/50 µL (378 mM) | Propofol Molecular Weight: 178.271 10 mg/mL (56 mM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1000 µM | 264.3 µg/mL | 178.3 µg/mL |
| 500 µM | 132.2 µg/mL | 89.1 µg/mL |
| 250 µM | 66 µg/mL | 44.6 µg/mL |
| 100 µM | 26.4 µg/mL | 17.8 µg/mL |
| Parameters | n = 12 |
|---|---|
| Age, year | 27.5 (25–30 (22–33)) |
| Sex (male) | 12 (100) |
| Height, cm | 179 (177–181.5 (172–186)) |
| Weight, kg | 80 (79–84.5 (77–90)) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.2 (24.5–26.5 (24.3–27.4)) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Arslan, U.; Ulker, P.; Yildirim, A.; Cengiz, M.; Yilmaz, M.; Arici, A.G.; Gunduz, E.; Kavakli, A.S.; Hizay, A.; Arslan, O.; et al. The Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Nitric Oxide Production and Release in Erythrocytes. Medicina 2025, 61, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050841
Arslan U, Ulker P, Yildirim A, Cengiz M, Yilmaz M, Arici AG, Gunduz E, Kavakli AS, Hizay A, Arslan O, et al. The Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Nitric Oxide Production and Release in Erythrocytes. Medicina. 2025; 61(5):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050841
Chicago/Turabian StyleArslan, Ulku, Pinar Ulker, Ahmet Yildirim, Melike Cengiz, Murat Yilmaz, Ayse Gulbin Arici, Emel Gunduz, Ali Sait Kavakli, Arzu Hizay, Oguzhan Arslan, and et al. 2025. "The Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Nitric Oxide Production and Release in Erythrocytes" Medicina 61, no. 5: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050841
APA StyleArslan, U., Ulker, P., Yildirim, A., Cengiz, M., Yilmaz, M., Arici, A. G., Gunduz, E., Kavakli, A. S., Hizay, A., Arslan, O., Tavsanoglu, Z. Y., & Ozturk, N. (2025). The Effects of Propofol and Thiopental on Nitric Oxide Production and Release in Erythrocytes. Medicina, 61(5), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61050841






