Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: Insights from Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers
2.1. Tau Protein
2.2. Amyloid Beta
2.3. Neurofilament Light Chain
2.4. α-Synuclein
2.5. Inflammatory Biomarkers
2.6. Proteomics
2.7. Other Biomarkers
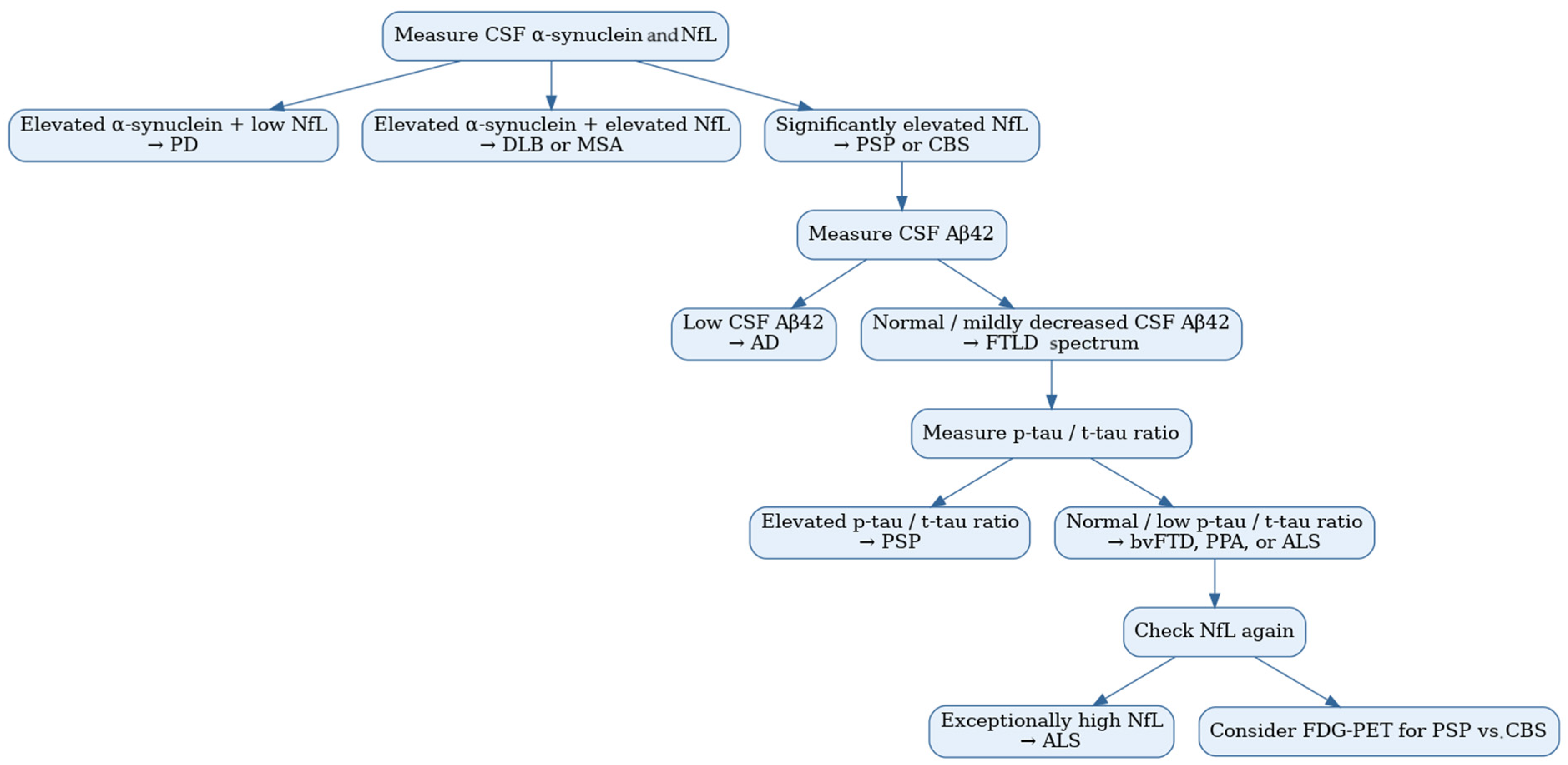
2.8. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker Combinations
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3R | three-repeat |
| 4R | four-repeat |
| Aβ | amyloid beta |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AGD | argyrophilic grain disease |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| APD | atypical parkinsonian disorder |
| APP | amyloid precursor protein |
| AUC | area under the curve |
| bvFTD | behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia |
| CBD | corticobasal degeneration |
| CBS | corticobasal syndrome |
| CHIT1 | chitotriosidase 1 |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| CTE | chronic traumatic encephalopathy |
| DaT | dopamine transporter |
| DLB | dementia with Lewy bodies |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FDG | fludeoxyglucose-18 |
| FTD | frontotemporal dementia |
| FTLD | frontotemporal lobar degeneration |
| FTLD-TDP | frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP 43 |
| FTLD-17 | frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| IL-1β | interleukin 1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| MAPT | microtubule-associated protein Tau gene |
| MCI | mild cognitive impairment |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemotactic protein-1 |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MSA | multiple system atrophy |
| MTBDs | microtubule-binding domains |
| NfL | neurofilament light chain |
| NPH | normal pressure hydrocephalus |
| PAR | protein aggregation rate |
| PCA | posterior cortical atrophy |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| PDD | Parkinson’s disease dementia |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PPA | primary progressive aphasia |
| PSP | progressive supranuclear palsy |
| PSP-P | PSP-Richardson’s syndrome |
| PSP-RS | PSP with predominant parkinsonism |
| p-tau | hyperphosphorylated tau |
| p-tau181 | tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 |
| p-tau217 | tau phosphorylated at threonine 217 |
| RT-QuIC | real-time quaking-induced conversion |
| SAA | seed amplification assay |
| sAPP | soluble amyloid precursor protein |
| SCD | subjective cognitive decline |
| SPECT | single-photon emission computed tomography |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor α |
| t-tau | total tau |
| UCH-L1 | ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 |
| VaD | vascular dementia |
| VBM | voxel-based morphometry |
| YKL-40 | chitinase-3-like-1 |
References
- Höglinger, G.U.; Respondek, G.; Stamelou, M.; Kurz, C.; Josephs, K.A.; Lang, A.E.; Mollenhauer, B.; Müller, U.; Nilsson, C.; Whitwell, J.L.; et al. Clinical Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: The Movement Disorder Society Criteria. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 853–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; Bak, T.H.; Bhatia, K.P.; Borroni, B.; Boxer, A.L.; Dickson, D.W.; Grossman, M.; Hallett, M.; et al. Criteria for the Diagnosis of Corticobasal Degeneration. Neurology 2013, 80, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, F.; Martin, P.R.; Botha, H.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Bower, J.H.; Masumoto, J.Y.; Maraganore, D.; Hassan, A.; Eggers, S.; Boeve, B.F.; et al. Sensitivity and Specificity of Diagnostic Criteria for Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, S.K.; Rittman, T.; Xuereb, J.H.; Bak, T.H.; Hodges, J.R.; Rowe, J.B. Validation of the New Consensus Criteria for the Diagnosis of Corticobasal Degeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2014, 85, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, E.; Holland, N.; Chelban, V.; Jones, P.S.; Lamb, R.; Rawlinson, C.; Guo, T.; Costantini, A.A.; Tan, M.M.X.; Heslegrave, A.J.; et al. Diagnosis Across the Spectrum of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shir, D.; Pham, N.T.T.; Botha, H.; Koga, S.; Kouri, N.; Ali, F.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Boeve, B.F.; Kremers, W.K.; et al. Clinicoradiologic and Neuropathologic Evaluation of Corticobasal Syndrome. Neurology 2023, 101, e289–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, Y.; Huyghe, L.; Quenon, L.; Ghysens, O.; Malotaux, V.; Tomé, S.O.; Thal, D.R.; Hanseeuw, B.J. Autopsy-Proven Patient with Corticobasal Degeneration Presenting with Visuo-Constructive Disorders as Initial Symptoms: How Advanced MRI Sequences Can Help Clinical Practice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikkinen, S.; Katisko, K.; Haapasalo, A.; Portaankorva, A.; Hartikainen, P.; Solje, E. Overlap in the Diagnostic Criteria of Frontotemporal Dementia Syndromes with Parkinsonism. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2025, 104, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpirou Nouh, C.; Younes, K. Diagnosis and Management of Progressive Corticobasal Syndrome. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2024, 26, 319–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez-Gonzalez, M. Implementing a Tridimensional Diagnostic Framework for Personalized Medicine in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2025, 21, e14591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKhann, G.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Chertkow, H.; Hyman, B.T.; Jack, C.R.; Kawas, C.H.; Klunk, W.E.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Manly, J.J.; Mayeux, R.; et al. The Diagnosis of Dementia Due to Alzheimer’s Disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Workgroups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jack, C.R.; Bennett, D.A.; Blennow, K.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dunn, B.; Haeberlein, S.B.; Holtzman, D.M.; Jagust, W.; Jessen, F.; Karlawish, J.; et al. NIA-AA Research Framework: Toward a Biological Definition of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2018, 14, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.; Andrews, J.S.; Beach, T.G.; Buracchio, T.; Dunn, B.; Graf, A.; Hansson, O.; Ho, C.; Jagust, W.; McDade, E.; et al. Revised Criteria for Diagnosis and Staging of Alzheimer’s Disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 5143–5169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeith, I.G.; Boeve, B.F.; Dickson, D.W.; Halliday, G.; Taylor, J.-P.; Weintraub, D.; Aarsland, D.; Galvin, J.; Attems, J.; Ballard, C.G.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Neurology 2017, 89, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Postuma, R.B.; Berg, D.; Stern, M.; Poewe, W.; Olanow, C.W.; Oertel, W.; Obeso, J.; Marek, K.; Litvan, I.; Lang, A.E.; et al. MDS Clinical Diagnostic Criteria for Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisoni, G.B.; Festari, C.; Massa, F.; Cotta Ramusino, M.; Orini, S.; Aarsland, D.; Agosta, F.; Babiloni, C.; Borroni, B.; Cappa, S.F.; et al. European Intersocietal Recommendations for the Biomarker-Based Diagnosis of Neurocognitive Disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, K.A. Molecular Imaging of Extrapyramidal Movement Disorders with Dementia: The 4R Tauopathies. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2021, 51, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Neve, R.L.; Kosik, K.S. The Microtubule Binding Domain of Tau Protein. Neuron 1989, 2, 1615–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buée, L.; Bussière, T.; Buée-Scherrer, V.; Delacourte, A.; Hof, P.R. Tau Protein Isoforms, Phosphorylation and Role in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Brain Res. Rev. 2000, 33, 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiani, C.M.; Scaramuzzino, L.; Parrotta, E.I.; Cuda, G.; Quattrone, A.; Quattrone, A. Serum Tau Species in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: A Pilot Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.-M.; Yang, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T. Tauopathies: New Perspectives and Challenges. Mol. Neurodegener. 2022, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, P.; Sehar, U.; Bisht, J.; Selman, A.; Culberson, J.; Reddy, P.H. Phosphorylated Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcon, B.; Zhang, W.; Murzin, A.G.; Murshudov, G.; Garringer, H.J.; Vidal, R.; Crowther, R.A.; Ghetti, B.; Scheres, S.H.W.; Goedert, M. Structures of Filaments from Pick’s Disease Reveal a Novel Tau Protein Fold. Nature 2018, 561, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srulijes, K.; Mallien, G.; Bauer, S.; Dietzel, E.; Gröger, A.; Ebersbach, G.; Berg, D.; Maetzler, W. In Vivo Comparison of Richardson’s Syndrome and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy-Parkinsonism. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borroni, B.; Gardoni, F.; Parnetti, L.; Magno, L.; Malinverno, M.; Saggese, E.; Calabresi, P.; Spillantini, M.G.; Padovani, A.; Di Luca, M. Pattern of Tau Forms in CSF Is Altered in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Neurobiol. Aging 2009, 30, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroni, B.; Malinverno, M.; Gardoni, F.; Grassi, M.; Parnetti, L.; Agosti, C.; Alberici, A.; Premi, E.; Bonuccelli, U.; Gasparotti, R.; et al. A Combination of CSF Tau Ratio and Midsaggital Midbraintopons Atrophy for the Early Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 22, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiperij, H.B.; Verbeek, M.M. Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Can Measurement of Tau Forms Help? Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 204.e17–204.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, E.; Ghetti, B.; Zanusso, G.; Oblak, A.; Furman, J.L.; Diamond, M.I.; Kraus, A.; Caughey, B. Ultrasensitive and Selective Detection of 3-Repeat Tau Seeding Activity in Pick Disease Brain and Cerebrospinal Fluid. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 133, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saijo, E.; Metrick, M.A.; Koga, S.; Parchi, P.; Litvan, I.; Spina, S.; Boxer, A.; Rojas, J.C.; Galasko, D.; Kraus, A.; et al. 4-Repeat Tau Seeds and Templating Subtypes as Brain and CSF Biomarkers of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagshal, D.; Sankaranarayanan, S.; Guss, V.; Hall, T.; Berisha, F.; Lobach, I.; Karydas, A.; Voltarelli, L.; Scherling, C.; Heuer, H.; et al. Divergent CSF τ Alterations in Two Common Tauopathies: Alzheimer’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicognola, C.; Hansson, O.; Scheltens, P.; Kvartsberg, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Teunissen, C.E.; Blennow, K. Cerebrospinal Fluid N-224 Tau Helps Discriminate Alzheimer’s Disease from Subjective Cognitive Decline and Other Dementias. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horie, K.; Barthélemy, N.R.; Spina, S.; VandeVrede, L.; He, Y.; Paterson, R.W.; Wright, B.A.; Day, G.S.; Davis, A.A.; Karch, C.M.; et al. CSF Tau Microtubule-Binding Region Identifies Pathological Changes in Primary Tauopathies. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilcher, R.; Wall, S.; Groß, M.; Katzdobler, S.; Wagemann, O.; Palleis, C.; Weidinger, E.; Fietzek, U.; Bernhardt, A.; Kurz, C.; et al. Combining Cerebrospinal Fluid and PI-2620 Tau-PET for Biomarker-based Stratification of Alzheimer’s Disease and 4R-tauopathies. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 6896–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, C.; Mallipeddi, N.; Ghoshal, N.; Wright, B.A.; Day, G.S.; Davis, A.A.; Kim, A.H.; Zipfel, G.J.; Bateman, R.J.; Gabelle, A.; et al. MAPT R406W Increases Tau T217 Phosphorylation in Absence of Amyloid Pathology. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2021, 8, 1817–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Grinberg, L.T.; Boxer, A.; Ossenkoppele, R.; Jonsson, M.; Seeley, W.; Ehrenberg, A.; Spina, S.; Janelidze, S.; Rojas-Martinex, J.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Autopsy-Confirmed Alzheimer Disease and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Neurology 2022, 98, e1137–e1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, T.; Kasuga, K. Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, H.M.; Swerdlow, R.H. Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing and Bioenergetics. Brain Res. Bull. 2017, 133, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, B.T.; Phelps, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Bigio, E.H.; Cairns, N.J.; Carrillo, M.C.; Dickson, D.W.; Duyckaerts, C.; Frosch, M.P.; Masliah, E.; et al. National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association Guidelines for the Neuropathologic Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoonenboom, N.S.M.; Reesink, F.E.; Verwey, N.A.; Kester, M.I.; Teunissen, C.E.; van de Ven, P.M.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L.; Blankenstein, M.A.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers for Differential Dementia Diagnosis in a Large Memory Clinic Cohort. Neurology 2012, 78, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech, S.; Hjermind, L.E.; Salvesen, L.; Nielsen, J.E.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Jørgensen, H.L.; Rosengren, L.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Winge, K. Amyloid-Related Biomarkers and Axonal Damage Proteins in Parkinsonian Syndromes. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yao, J.; Yao, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Guan, S.H. CSF SAPPα and SAPPβ Levels in Alzheimer’s Disease and Multiple Other Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Network Meta-Analysis. Neuromolecular Med. 2020, 22, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nutu, M.; Bourgeois, P.; Zetterberg, H.; Portelius, E.; Andreasson, U.; Parent, S.; Lipari, F.; Hall, S.; Constantinescu, R.; Hansson, O.; et al. Aβ1-15/16 as a Potential Diagnostic Marker in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Neuromolecular Med. 2013, 15, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichmann, M.; Epelbaum, S.; Samri, D.; Levy Nogueira, M.; Michon, A.; Hampel, H.; Lamari, F.; Dubois, B. Free and Cued Selective Reminding Test—Accuracy for the Differential Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Large-Scale Biomarker-Characterized Monocenter Cohort Study (ClinAD). Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboudiyat, C.; Gefen, T.; Varelas, E.; Weintraub, S.; Rogalski, E.; Bigio, E.H.; Mesulam, M.M. Cerebrospinal Fluid Markers Detect Alzheimer’s Disease in Nonamnestic Dementia. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 598–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraskevas, G.P.; Constantinides, V.C.; Boufidou, F.; Tsantzali, I.; Pyrgelis, E.S.; Liakakis, G.; Kapaki, E. Recognizing Atypical Presentations of Alzheimer’s Disease: The Importance of CSF Biomarkers in Clinical Practice. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirinzi, T.; Sancesario, G.M.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Scalise, S.; Colona, V.L.; Imbriani, P.; Mercuri, N.B.; Bernardini, S.; Lang, A.E.; Pisani, A. Clinical Value of CSF Amyloid-Beta-42 and Tau Proteins in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. J. Neural Transm. 2018, 125, 1373–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Seo, J.D.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, H.-S.; Jeon, S.; Pak, K.; Lee, M.J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, K.; et al. Comparison of Amyloid in Cerebrospinal Fluid, Brain Imaging, and Autopsy in a Case of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2020, 34, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borroni, B.; Premi, E.; Agosti, C.; Alberici, A.; Cerini, C.; Archetti, S.; Lanari, A.; Paghera, B.; Lucchini, S.; Caimi, L.; et al. CSF Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pattern in Corticobasal Syndrome: Evidence for a Distinct Disorder. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Di Stefano, F.; Kas, A.; Habert, M.O.; Decazes, P.; Lamari, F.; Lista, S.; Hampel, H.; Teichmann, M. The Phenotypical Core of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related and Nonrelated Variants of the Corticobasal Syndrome: A Systematic Clinical, Neuropsychological, Imaging, and Biomarker Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2016, 12, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Efthymiopoulou, E.; Stefanis, L.; Kapaki, E. Clinical, Neuropsychological and Imaging Characteristics of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients Presenting as Corticobasal Syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 398, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Boufidou, F.; Bourbouli, M.; Stefanis, L.; Kapaki, E. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker Profiling in Corticobasal Degeneration: Application of the AT(N) and Other Classification Systems. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 82, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Jiao, F.; Chen, M.; Yao, R.; Liang, X.; Ju, Z.; Ge, J.; Li, G.; et al. 18 F-Florzolotau Positron Emission Tomography Imaging of Tau Pathology in the Living Brains of Patients with Corticobasal Syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Cordero, I.; Anastassiadis, C.; Khoja, A.; Morales-Rivero, A.; Thapa, S.; Vasilevskaya, A.; Davenport, C.; Sumra, V.; Couto, B.; Multani, N.; et al. Evaluating the Effect of Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Biomarker Change in Corticobasal Syndrome and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Ann. Neurol. 2024, 96, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppens, S.; Lehmann, S.; Hopley, C.; Hirtz, C. Neurofilament-Light, a Promising Biomarker: Analytical, Metrological and Clinical Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.V.; Veeranna; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3257–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, A.; Rao, M.V.; Veeranna; Nixon, R.A. Neurofilaments and Neurofilament Proteins in Health and Disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9, a018309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmberg, B.; Rosengren, L.; Karlsson, J.; Johnels, B. Increased Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Neurofilament Protein in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Multiple-system Atrophy Compared with Parkinson’s Disease. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Petzold, A.; Süßmuth, S.D.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Ludolph, A.C.; Kassubek, J.; Tumani, H. Neurofilament Heavy-chain NfHSMI35 in Cerebrospinal Fluid Supports the Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsonian Syndromes. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 2224–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painous, C.; Pascual-Diaz, S.; Muñoz-Moreno, E.; Sánchez, V.; Pariente, J.; Prats-Galino, A.; Soto, M.; Fernández, M.; Pérez-Soriano, A.; Camara, A.; et al. Midbrain and Pons MRI Shape Analysis and Its Clinical and CSF Correlates in Degenerative Parkinsonisms: A Pilot Study. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 4540–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Hauer, K.; Pawlik, D.; Leuzy, A.; Janelidze, S.; Hall, S.; Hansson, O.; Smith, R. Performance of [18F]RO948 PET, MRI and CSF Neurofilament Light in the Differential Diagnosis of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherling, C.S.; Hall, T.; Berisha, F.; Klepac, K.; Karydas, A.; Coppola, G.; Kramer, J.H.; Rabinovici, G.; Ahlijanian, M.; Miller, B.L.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Concentration Reflects Disease Severity in Frontotemporal Degeneration. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 75, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, B.; Portelius, E.; Cullen, N.C.; Sandelius, Å.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Höglund, K.; Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; et al. Association of Cerebrospinal Fluid Neurofilament Light Protein Levels with Cognition in Patients with Dementia, Motor Neuron Disease, and Movement Disorders. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Ding, J.; Liu, Y.; Lin, H.; Chang, T. Cerebrospinal Fluid NFL in the Differential Diagnosis of Parkinsonian Disorders: A Meta-Analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 685, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Q.; Hou, X.-H.; Ou, Y.-N.; Yu, J.-T.; Tan, L. Neurofilament Light Chain in Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood as a Biomarker for Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 72, 1353–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, G.; Lees, A.; Stern, M. Milestones in Parkinson’s Disease—Clinical and Pathologic Features. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.; Malek, N.; Grosset, K.; Cullen, B.; Gentleman, S.; Grosset, D.G. Neuropathology of Dementia in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Autopsy Studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Multiple System Atrophy: An Oligodendroglioneural Synucleinopathy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 1141–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Sekiya, H.; Kondru, N.; Ross, O.A.; Dickson, D.W. Neuropathology and Molecular Diagnosis of Synucleinopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabresi, P.; Di Lazzaro, G.; Marino, G.; Campanelli, F.; Ghiglieri, V. Advances in Understanding the Function of Alpha-Synuclein: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. Brain 2023, 146, 3587–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.K.; Meisl, G.; Andrzejewska, E.A.; Krainer, G.; Dear, A.J.; Castellana-Cruz, M.; Turi, S.; Edu, I.A.; Vivacqua, G.; Jacquat, R.P.B.; et al. α-Synuclein Oligomers Form by Secondary Nucleation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokuda, T.; Qureshi, M.M.; Ardah, M.T.; Varghese, S.; Shehab, S.A.S.; Kasai, T.; Ishigami, N.; Tamaoka, A.; Nakagawa, M.; El-Agnaf, O.M.A. Detection of Elevated Levels of α-Synuclein Oligomers in CSF from Patients with Parkinson Disease. Neurology 2010, 75, 1766–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondello, S.; Constantinescu, R.; Zetterberg, H.; Andreasson, U.; Holmberg, B.; Jeromin, A. CSF α-Synuclein and UCH-L1 Levels in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aerts, M.B.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Abdo, W.F.; Bloem, B.R.; Verbeek, M.M. CSF α-Synuclein Does Not Differentiate between Parkinsonian Disorders. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 430.e1–430.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wen, M.; Yu, W.-F.; Zhang, C.-L.; Jiao, L. The Diagnostic and Differential Diagnosis Utility of Cerebrospinal Fluid α -Synuclein Levels in Parkinson’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Park. Dis. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painous, C.; Fernández, M.; Pérez, J.; de Mena, L.; Cámara, A.; Compta, Y. Fluid and Tissue Biomarkers in Parkinson’s Disease: Immunodetection or Seed Amplification? Central or Peripheral? Park. Relat. Disord. 2024, 121, 105968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manne, S.; Kondru, N.; Hepker, M.; Jin, H.; Anantharam, V.; Lewis, M.; Huang, X.; Kanthasamy, A.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Ultrasensitive Detection of Aggregated α-Synuclein in Glial Cells, Human Cerebrospinal Fluid, and Brain Tissue Using the RT-QuIC Assay: New High-Throughput Neuroimmune Biomarker Assay for Parkinsonian Disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2019, 14, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, D.P.; Fumi, R.; Theilmann Jensen, M.; Hodgson, M.; Georgiades, T.; Wu, L.; Lux, D.; Obrocki, R.; Lamoureux, J.; Ansorge, O.; et al. Evaluation of Cerebrospinal Fluid α-Synuclein Seed Amplification Assay in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 2285–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, C.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Feng, T. Comparison of Biospecimens for A-synuclein Seed Amplification Assays in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 3949–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Surova, Y.; Widner, H.; Zetterberg, H.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal Fluid Concentrations of Inflammatory Markers in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starhof, C.; Winge, K.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Skogstrand, K.; Friis, S.; Hejl, A. Cerebrospinal Fluid Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Differentiate Parkinsonian Syndromes. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayton, S.; Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Kalinowski, P.; Palmqvist, S.; Belaidi, A.A.; Roberts, B.; Roberts, A.; Stomrud, E.; Bush, A.I.; et al. The Neuroinflammatory Acute Phase Response in Parkinsonian-Related Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2022, 37, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Iwaoka, K.; Takahashi, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Yamahara, K.; Maeda, T. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Oxidative Stress Measured Using Diacron-Reactive Oxygen Metabolites and Biological Antioxidant Potential in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease and Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 757, 135975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, M.; Jiménez, J.; Narváez, A.; Antequera, D.; Llamas-Velasco, S.; Martín, A.H.S.; Arjona, J.A.M.; de Munain, A.L.; Bisa, A.L.; Marco, M.P.; et al. Kynurenic Acid Levels Are Increased in the CSF of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbari, E.; Woodside, J.; Guo, T.; Magdalinou, N.K.; Chelban, V.; Athauda, D.; Lees, A.J.; Foltynie, T.; Houlden, H.; Church, A.; et al. Proximity Extension Assay Testing Reveals Novel Diagnostic Biomarkers of Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, K.; Matsubara, K.; Fujikawa, Y.; Nagahiro, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Umegae, N.; Hayase, N.; Shiono, H.; Kobayashi, S. Nitration of Manganese Superoxide Dismutase in Cerebrospinal Fluids Is a Marker for Peroxynitrite-Mediated Oxidative Stress in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 47, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Steinacker, P.; Polischi, B.; Mammana, A.; Bartoletti-Stella, A.; Oeckl, P.; Baiardi, S.; Zenesini, C.; Huss, A.; Cortelli, P.; et al. CSF Biomarkers of Neuroinflammation in Distinct Forms and Subtypes of Neurodegenerative Dementia. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2019, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig-Schapiro, R.; Perrin, R.J.; Roe, C.M.; Xiong, C.; Carter, D.; Cairns, N.J.; Mintun, M.A.; Peskind, E.R.; Li, G.; Galasko, D.R.; et al. YKL-40: A Novel Prognostic Fluid Biomarker for Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 68, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, M.; Nakajima, M.; Motoi, Y.; Moriya, M.; Sugano, H.; Ogino, I.; Nakamura, E.; Tada, N.; Kunichika, M.; Arai, H. Leucine-Rich A2-Glycoprotein Is a Novel Biomarker of Neurodegenerative Disease in Human Cerebrospinal Fluid and Causes Neurodegeneration in Mouse Cerebral Cortex. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.C.; Li, M.; Schaak, D.; Robson, D.N.; Li, J.M. Internal State Dynamics Shape Brainwide Activity and Foraging Behaviour. Nature 2020, 577, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, R.; Andreasson, U.; Li, S.; Podust, V.N.; Mattsson, N.; Anckarsäter, R.; Anckarsäter, H.; Rosengren, L.; Holmberg, B.; Blennow, K.; et al. Proteomic Profiling of Cerebrospinal Fluid in Parkinsonian Disorders. Park. Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravinacová, S.; Bergström, S.; Olofsson, J.; de San José, N.G.; Anderl-Straub, S.; Diehl-Schmid, J.; Fassbender, K.; Fliessbach, K.; Jahn, H.; Kornhuber, J.; et al. Addressing Inter Individual Variability in CSF Levels of Brain Derived Proteins across Neurodegenerative Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paslawski, W.; Khosousi, S.; Hertz, E.; Markaki, I.; Boxer, A.; Svenningsson, P. Large-Scale Proximity Extension Assay Reveals CSF Midkine and DOPA Decarboxylase as Supportive Diagnostic Biomarkers for Parkinson’s Disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2023, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdalinou, N.K.; Noyce, A.J.; Pinto, R.; Lindstrom, E.; Holmén-Larsson, J.; Holtta, M.; Blennow, K.; Morris, H.R.; Skillbäck, T.; Warner, T.T.; et al. Identification of Candidate Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Parkinsonism Using Quantitative Proteomics. Park. Relat. Disord. 2017, 37, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.; Oh, S.; Hall, A.J.; Zhang, Z.; Tropea, T.F.; Chen-Plotkin, A.; Rosenthal, L.S.; Dawson, T.M.; Na, C.H.; Pantelyat, A.Y. Biomarker Discovery in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy from Human Cerebrospinal Fluid. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.; Li, J.; Yamakawa, M.; Loureiro, J.; Peterson, B.; Worringer, K.; Sivasankaran, R.; Palma, J.-A.; Mitic, L.; Heuer, H.W.; et al. CSF Proteomics in Patients With Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Neurology 2024, 103, e209585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasebø, E.; Opsahl, J.A.; Bjørlykke, Y.; Myhr, K.M.; Kroksveen, A.C.; Berven, F.S. Effects of Blood Contamination and the Rostro-Caudal Gradient on the Human Cerebrospinal Fluid Proteome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, W.; Takata, T.; Iwama, H.; Komatsubara, S.; Kobara, H.; Kamada, M.; Deguchi, K.; Touge, T.; Miyamoto, O.; Nakamura, T.; et al. A Cerebrospinal Fluid MicroRNA Analysis: Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 25, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerroni, R.; Liguori, C.; Stefani, A.; Conti, M.; Garasto, E.; Pierantozzi, M.; Mercuri, N.B.; Bernardini, S.; Fucci, G.; Massoud, R. Increased Noradrenaline as an Additional Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker in PSP-Like Parkinsonism. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2020, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Constantinescu, J.; Nellgård, B.; Jakobsson, P.; Brum, W.S.; Gobom, J.; Forsgren, L.; Dalla, K.; Constantinescu, R.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Synaptic Dysfunction Are Altered in Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiserova, M.; Chudackova, M.; Prikrylova Vranova, H.; Mensikova, K.; Kastelikova, A.; Stejskal, D.; Kanovsky, P. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid in Parkinson’s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes. Neurodegener. Dis. 2021, 21, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellington, H.; Paterson, R.W.; Portelius, E.; Törnqvist, U.; Magdalinou, N.; Fox, N.C.; Blennow, K.; Schott, J.M.; Zetterberg, H. Increased CSF Neurogranin Concentration Is Specific to Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2016, 86, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.; Janelidze, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Brix, B.; Mattsson, N.; Surova, Y.; Blennow, K.; Hansson, O. Cerebrospinal Fluid Levels of Neurogranin in Parkinsonian Disorders. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kanbayashi, T.; Nomura, T.; Kusumi, M.; Nakashima, K. CSF Orexin Levels of Parkinson’s Disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies, Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Degeneration. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 250, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, N.; Kanazawa, M.; Kasuga, K.; Hatakeyama, M.; Ikeuchi, T.; Onodera, O. Utility of Cerebrospinal Fluid Transferrin Receptor per Ferritin Ratio in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2024; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, S.; Sauer, M.; Brinkmalm, G.; Constantinescu, J.; Constantinescu, R.; Gomes, B.F.; Becker, B.; Nellgård, B.; Dalla, K.; Galasko, D.; et al. SCRN1: A Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarker Correlating with Tau in Alzheimer’s Disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 4609–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morenas-Rodríguez, E.; Cervera-Carles, L.; Vilaplana, E.; Alcolea, D.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Dols-Icardo, O.; Ribosa-Nogué, R.; Muñoz-Llahuna, L.; Sala, I.; Belén Sánchez-Saudinós, M.; et al. Progranulin Protein Levels in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Primary Neurodegenerative Dementias. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2016, 50, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boman, A.; Svensson, S.; Boxer, A.; Rojas, J.C.; Seeley, W.W.; Karydas, A.; Miller, B.; Kagedal, K.; Svenningsson, P. Distinct Lysosomal Network Protein Profiles in Parkinsonian Syndrome Cerebrospinal Fluid. J. Park. Dis. 2016, 6, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locascio, J.J.; Schulz-Schaeff, W.; Mollenhauer, B.; Schlossmacher, M.G.; Locascio, J.J.; Schulz-Schaeff, W.; Sixel-Döring, F.; Trenkwalder, C. α-Synuclein and Tau Concentrations in Cerebrospinal Fl Uid of Patients Presenting with Parkinsonism: A Cohort Study. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compta, Y.; Painous, C.; Soto, M.; Pulido-Salgado, M.; Fernández, M.; Camara, A.; Sánchez, V.; Bargalló, N.; Caballol, N.; Pont-Sunyer, C.; et al. Combined CSF α-SYN RT-QuIC, CSF NFL and Midbrain-Pons Planimetry in Degenerative Parkinsonisms: From Bedside to Bench, and Back Again. Park. Relat. Disord. 2022, 99, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koníčková, D.; Menšíková, K.; Klíčová, K.; Chudáčková, M.; Kaiserová, M.; Přikrylová, H.; Otruba, P.; Nevrlý, M.; Hluštík, P.; Hényková, E.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid and Blood Serum Biomarkers in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: A Prospective, Open, Cross-Correlation Study. J. Neurochem. 2023, 167, 168–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinides, V.C.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Petropoulou, O.; Bougea, A.; Vekrellis, K.; Evdokimidis, I.; Stamboulis, E.; Kapaki, E. CSF Biomarkers β-Amyloid, Tau Proteins and a-Synuclein in the Differential Diagnosis of Parkinson-plus Syndromes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 382, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcolea, D.; Vilaplana, E.; Suárez-Calvet, M.; Illán-Gala, I.; Blesa, R.; Clarimón, J.; Lladó, A.; Sánchez-Valle, R.; Molinuevo, J.L.; García-Ribas, G.; et al. CSF SAPPβ, YKL-40, and Neurofilament Light in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration. Neurology 2017, 89, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rumeileh, S.; Mometto, N.; Bartoletti-Stella, A.; Polischi, B.; Oppi, F.; Poda, R.; Stanzani-Maserati, M.; Cortelli, P.; Liguori, R.; Capellari, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Patients with Frontotemporal Dementia Spectrum: A Single-Center Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 66, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meeter, L.H.H.; Vijverberg, E.G.; Del Campo, M.; Rozemuller, A.J.M.; Donker Kaat, L.; de Jong, F.J.; van der Flier, W.M.; Teunissen, C.E.; van Swieten, J.C.; Pijnenburg, Y.A.L. Clinical Value of Neurofilament and Phospho-Tau/Tau Ratio in the Frontotemporal Dementia Spectrum. Neurology 2018, 90, e1231–e1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppsson, A.; Wikkelsö, C.; Blennow, K.; Zetterberg, H.; Constantinescu, R.; Remes, A.M.; Herukka, S.K.; Rauramaa, T.; Nagga, K.; Leinonen, V.; et al. CSF Biomarkers Distinguish Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus from Its Mimics. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, S.; Öhrfelt, A.; Constantinescu, R.; Andreasson, U.; Surova, Y.; Bostrom, F.; Nilsson, C.; Widner, H.; Decraemer, H.; Nägga, K.; et al. Accuracy of a Panel of 5 Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in the Differential Diagnosis of Patients with Dementia and/or Parkinsonian Disorders. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckström, D.C.; Domellöf, M.E.; Linder, J.; Olsson, B.; Öhrfelt, A.; Trupp, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Forsgren, L. Cerebrospinal Fluid Patterns and the Risk of Future Dementia in Early, Incident Parkinson Disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalinou, N.K.; Paterson, R.W.; Schott, J.M.; Fox, N.C.; Mummery, C.; Blennow, K.; Bhatia, K.; Morris, H.R.; Giunti, P.; Warner, T.T.; et al. A Panel of Nine Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers May Identify Patients with Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2015, 86, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiadis, C.; Martinez-Valbuena, I.; Vasilevskaya, A.; Thapa, S.; Hadian, M.; Morales-Rivero, A.; Mora-Fisher, D.; Salvo, C.; Taghdiri, F.; Sato, C.; et al. CSF α-Synuclein Seed Amplification Assay in Patients with Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders. Neurology 2024, 103, e209818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.; Cong, S.; Tan, X.; Ma, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cong, S. A Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Utility of Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid in Parkinson’s Disease. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remoli, G.; Schilke, E.D.; Magi, A.; Ancidoni, A.; Negro, G.; Da Re, F.; Frigo, M.; Giordano, M.; Vanacore, N.; Canevelli, M.; et al. Neuropathological Hints from CSF and Serum Biomarkers in Corticobasal Syndrome (CBS): A Systematic Review. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2024, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, M.J. Lewy Body Dementias. Continuum Lifelong Learn. Neurol. 2019, 25, 128–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Neuropathological Spectrum of Synucleinopathies. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, J.-Y. Overlaps and Divergences between Tauopathies and Synucleinopathies: A Duet of Neurodegeneration. Transl. Neurodegener. 2024, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulthard, E.J.; Love, S. A Broader View of Dementia: Multiple Co-Pathologies Are the Norm. Brain 2018, 141, 1894–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, W.W.; Luis, C.A.; Kashuba, A.; Luis, M.; Harwood, D.G.; Loewenstein, D.; Waters, C.; Jimison, P.; Shepherd, E.; Sevush, S.; et al. Relative Frequencies of Alzheimer Disease, Lewy Body, Vascular and Frontotemporal Dementia, and Hippocampal Sclerosis in the State of Florida Brain Bank. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2002, 16, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.L.; Lee, E.B.; Xie, S.X.; Rennert, L.; Suh, E.; Bredenberg, C.; Caswell, C.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Yan, N.; Yousef, A.; et al. Neurodegenerative Disease Concomitant Proteinopathies Are Prevalent, Age-Related and APOE4-Associated. Brain 2018, 141, 2181–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannakis, A.; Konitsiotis, S. A New Paradigm for Neurodegenerative Diseases Classification: A Clinical Perspective. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2025, 134, 111099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, R.R.; Krishnan, S.; Divya, K.P.; Jisha, V.T.; Kishore, A. Subtypes of PSP and Prognosis: A Retrospective Analysis. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2021, 24, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respondek, G.; Kurz, C.; Arzberger, T.; Compta, Y.; Englund, E.; Ferguson, L.W.; Gelpi, E.; Giese, A.; Irwin, D.J.; Meissner, W.G.; et al. Which Ante Mortem Clinical Features Predict Progressive Supranuclear Palsy Pathology? Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, D.W.; Rademakers, R.; Hutton, M.L. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: Pathology and Genetics. Brain Pathol. 2007, 17, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study | 4R 1 Tauopathy | Comparison Groups | CSF Biomarker | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Srulijes and co-authors, 2011 [24] | PSP 2 (PSP-RS 3, PSP-P 4) | - | t-tau 5, p-tau 6 |
|
| Borroni and co-authors, 2009 [25] | PSP | CBD 7, PD 8, DLB 9, AD 10, FTD 11, NCs 12 | 33kDa/55kDa tau ratio |
|
| Borroni and co-authors, 2010 [26] | PSP | CBD, PD, DLB, AD, FTD, HC | 33kDa/55kDa tau ratio and midbrain-to-pons atrophy |
|
| Kuiperij and co-authors, 2012 [27] | PSP | - | 33kDa/55kDa tau ratio |
|
| Heikkinen and co-authors, 2025 [8] | PSP, CBS 13 | bvFTD 14 | t-tau, p-tau |
|
| Saijo and co-authors, 2017 [28] | PSP, CBD | Pick’s disease, AD, DLB, bvFTD, ALS 15, FTLD-TDP 16, FTLD-17 17, CTE 18, CIDP 19, cerebrovascular disease | 3R 20 tau fragment |
|
| Saijo and co-authors, 2020 [29] | PSP, CBD | Pick’s disease, DLB, MSA, ALS, FTLD-TDP, FTLD-17, CTE, PART 21 | 4R tau fragment |
|
| Wagshal and co-authors, 2015 [30] | PSP | AD, NCs | t-tau, p-tau181 |
|
| Cicognola and co-authors, 2021 [31] | PSP | PD, AD, MSA, MCI 22, SCD 23 | N-224 tau fragment |
|
| Horie and co-authors, 2022 [32] | PSP, CBD | AD, Pick’s disease, AGD 24 | Two 4R tau species with MTBDs 25 |
|
| Dilcher and co-authors, 2024 [33] | PSP, CBS | AD | p-tau181 |
|
| Sato and co-authors, 2021 [34] | PSP, CBS | AD, bvFTD | p-tau217/t-tau217 ratio, Aβ42/Aβ40 26 ratio |
|
| Study | 4R 1 Tauopathy | Comparison Groups | CSF Biomarker | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Holmberg and co-authors, 1998 [57] | PSP 2 | PD 3, MSA 4 | NfL 5 |
|
| Brettschneider and co-authors, 2006 [58] | PSP, CBD 6 | PD, MSA | NfH 7 |
|
| Painous and co-authors, 2023 [59] | PSP, CBD | PD, MSA, NCs 8 | NfL |
|
| Oliveira Hauer and co-authors, 2023 [60] | PSP | PD, DLB 9, NCs | NfL |
|
| Scherling and co-authors, 2014 [61] | PSP, CBS 10 | AD 11, PD, bvFTD 12, PPA 13, NCs | NfL |
|
| Olsson and co-authors, 2019 [62] | PSP, CBS | PD, PD with MCI 14, PDD 15, DLB, FTD, ALS 16, AD, MCI, NCs | NfL |
|
| Ge and co-authors, 2018 [63] | PSP, CBD | PD, MSA | NfL |
|
| Wang and co-authors, 2019 [64] | PSP, CBD | PD, MSA, ALS, CJD 17, HD 18 | NfL |
|
| Study | 4R 1 Tauopathy | Comparison Groups | CSF Biomarker | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Locascio and co-authors, 2011 [108] | PSP 2 | PD 3, AD 4, DLB 5, MSA 6, NPH 7 | t-tau 8, α-syn 9 |
|
| Compta and co-authors, 2022 [109] | PSP, CBD 10 | PD, MSA, NCs 11 | α-syn, NfL 12 |
|
| Konickova and co-authors, 2022 [110] | PSP, CBS 13 | PD, DLB, MSA, NCs | t-tau, p-tau 14, Aβ42 15, NfH 16, clusterin, cystatin, chromogranin A |
|
| Constantinides and co-authors, 2017 [111] | PSP, CBD | PD, MSA, NCs | t-tau, p-tau181, Aβ42, α-syn |
|
| Alcolea and co-authors, 2017 [112] | PSP, CBS | AD, bvFTD 17, PPA 18, NCs | NfL, sAPPβ 19, YKL-40 |
|
| Abu-Rumeileh and co-authors 2018 [113] | PSP, CBS | AD, bvFTD, PPA, ALS 20, NCs | t-tau, p-tau, NfL, Aβ42 |
|
| Meeter and co-authors, 2018 [114] | PSP, CBS | bvFTD, PPA, ALS, NCs | t-tau, p-tau, NfL |
|
| Jeppsson and co-authors, 2019 [115] | PSP, CBD | PSP, CBD, PD, MSA, AD, FTD, NPH, VaD 22 | Aβ42, Aβ40, Aβ38, MCP-1 23, p-tau, t-tau, sAPPα, sAPPβ, NfL |
|
| Hall and co-authors, 2012 [116] | PSP | PDD 24, DLB, MSA, AD, and healthy controls | α-syn, Aβ42, t-tau, p-tau |
|
| Backstrom and co-authors, 2015 [117] | PSP | PD, MSA, NCs | α-syn, Aβ42, t-tau, p-tau |
|
| Magdalinou and co-authors, 2015 [118] | PSP, CBS | PD, MSA, FTD, AD, NCs | α-syn, tau, Aβ, NfL, sAPPα, sAPPβ, YKL-40 |
|
| Anastassiadis and co-authors, 2024 [119] | PSP, CBS | - | α-syn, Aβ42, p-tau, t-tau, NfL |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Giannakis, A.; Konitsiotis, S.; Sioka, C. Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: Insights from Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers—A Narrative Review. Medicina 2025, 61, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040701
Giannakis A, Konitsiotis S, Sioka C. Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: Insights from Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers—A Narrative Review. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040701
Chicago/Turabian StyleGiannakis, Alexandros, Spiridon Konitsiotis, and Chrissa Sioka. 2025. "Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: Insights from Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers—A Narrative Review" Medicina 61, no. 4: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040701
APA StyleGiannakis, A., Konitsiotis, S., & Sioka, C. (2025). Differentiating Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Corticobasal Syndrome: Insights from Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers—A Narrative Review. Medicina, 61(4), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040701







