Adherence to Compression Garments in Lymphedema Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
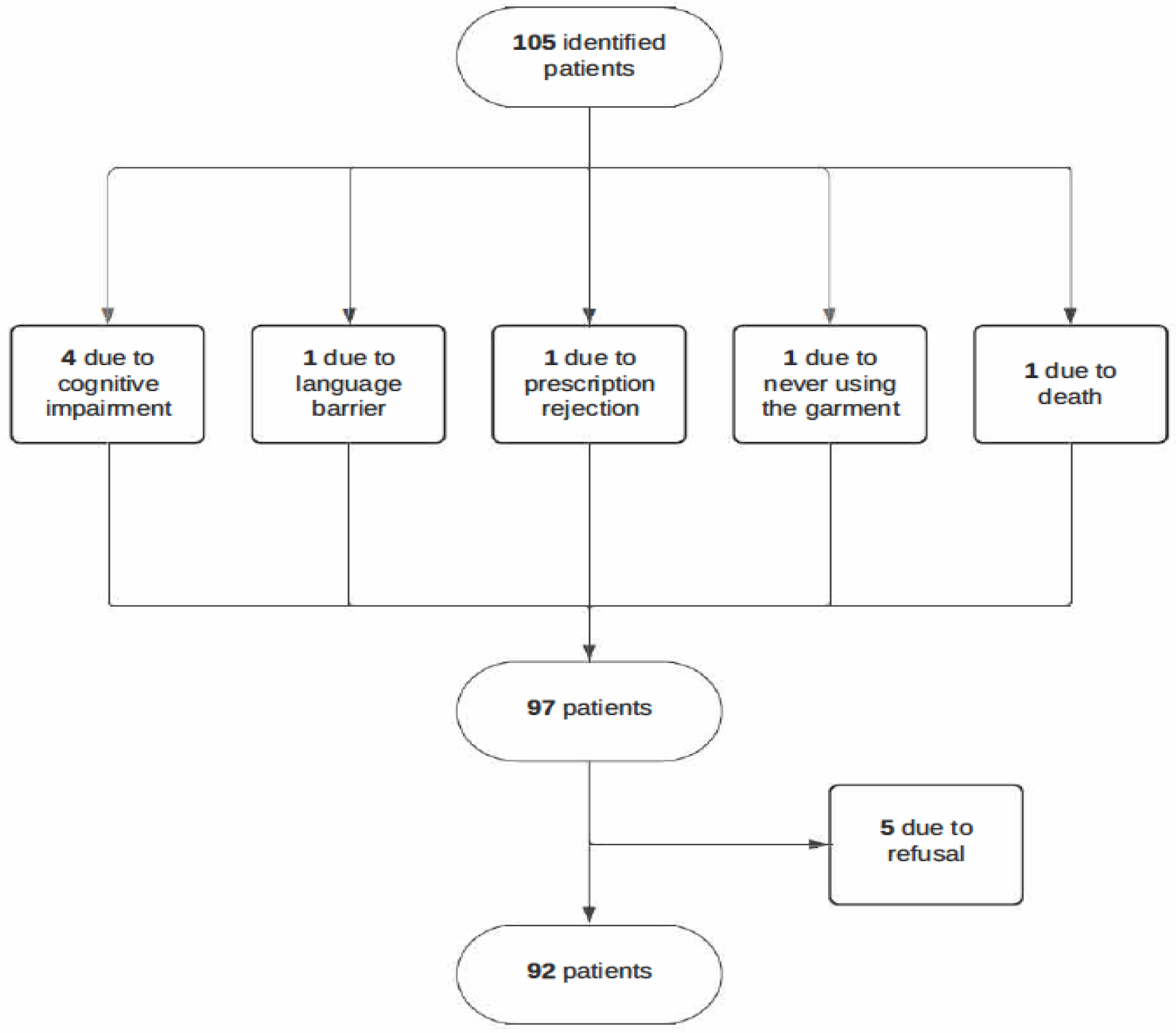
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Variables of Interest
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Status of Lymphedema Patients and Follow-Up
3.3. Types of Garments and Usage Habits
3.4. Adherence to Compression Systems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDT | Complex Decongestive Therapy |
| H.U.G.C. | University Hospital of Gran Canaria |
| CEIB | Biomedical Research Ethics Committee |
| ORs | odds ratios |
References
- Rockson, S.G.; Rivera, K.K. Estimating the Population Burden of Lymphedema. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1131, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Executive Committee of the International Society of Lymphology. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2020 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphology. Lymphology 2020, 53, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSipio, T.; Rye, S.; Newman, B.; Hayes, S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, M.; Deveaux, A.; White, H.; Rayson, D. Compression garments versus compression bandaging in decongestive lymphatic therapy for breast cancer-related lymphedema: A randomized controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, P.A.S.; Hawkins, K.; Hood, S. Role of patient adherence in maintenance of results after manipulative therapy for lymphedema. J. Soc. Integr. Oncol. 2006, 4, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzo, J.; Manheimer, E.; McNeely, M.L.; Howell, D.M.; Weiss, R.; I Johansson, K.; Bao, T.; Bily, L.; Tuppo, C.M.; Williams, A.F.; et al. Manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema following breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, 2015, CD003475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasinski, B.B. Complete Decongestive Therapy for Treatment of Lymphedema. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 29, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinig, B.; Wollina, U. Komplexe physikalische Entstauungstherapie [Complex decongestive therapy]. Hautarzt 2015, 66, 810–818. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Wu, P.; Qiang, W.; Fu, X.; Zhu, F.; Pang, L.; Wang, F.; Lu, Q. Factors associated with lymphedema self-management behaviours among breast cancer survivors: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2023, 32, 7330–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheer, R. Compression garments for managing lymphoedema. J. Lymphoedema 2017, 12, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Pigot, A.; Piller, N.; Phillips, J. The Use of Compression in the Management of Lymphoedema. Autralalasian Lymphology Association. 2021. Available online: https://instituteoflymphoedema.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/ALA-Position-Paper_use-of-compression.pdf (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Alcorso, J.; Sherman, K.A.; Koelmeyer, L.; Mackie, H.; Boyages, J. Psychosocial factors associated with adherence for self-management behaviors in women with breast cancer-related lymphedema. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdinç Gündüz, N.; Şahin, E.; Dilek, B.; Ellidokuz, H.; Akalln, E. Adherence to Compression Garment Wear and Associated Factors Among Patients with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: A Pilot Study from a Turkish Tertiary Center. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2022, 20, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.; Wigg, J. Getting the right fit: Made-to-measure garments for lymphoedema management. Br. J. Community Nurs. 2013, 18 (Suppl. 4), S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich-Schupke, S.; Stücker, M. Round-knit or flat-knit compression garments for maintenance therapy of lymphedema of the leg?—Review of the literature and technical data. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2019, 17, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, S.R.; Hugi, M.R.; Olivotto, I.A.; Levine, M. The Steering Committee for Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Care and Treatment of Breast Cancer. Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment of breast cancer: 11. Lymphedema. CMAJ 2001, 164, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Donahue, P.M.C.; MacKenzie, A.; Filipovic, A.; Koelmeyer, L. Advances in the prevention and treatment of breast cancer-related lymphedema. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 200, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostby, P.L.; Armer, J.M. Complexities of Adherence and Post-Cancer Lymphedema Management. J. Pers. Med. 2015, 5, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca-Mandic, P.; Solid, C.A.; Armer, J.M.; Skoracki, R.; Campione, E.; Rockson, S.G. Lymphedema self-care: Economic cost savings and opportunities to improve adherence. Cost. Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2023, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Li, N.; Liao, H.; Zhang, M. Factors Associated with Adherence to Complete Decongestion Therapy in Women with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Eur. J. Cancer Care 2023, 2023, 6652771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.C.; Kumar, A.; Cheville, A.; Tchou, J.; Troxel, A.; Harris, S.; Schmitz, K. Association between Lymphedema Self-Care Adherence and Lymphedema Outcomes among Women with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Assoc. Acad. Physiatr. 2015, 94, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Chen, L. Breast cancer-related lymphedema patient and healthcare professional experiences in lymphedema self-management: A qualitative study. Support. Care Cancer 2021, 29, 8027–8044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierla, R.; Lee, T.S.M.; Black, D.; Kilbreath, S.L. Lymphedema following breast cancer: Regions affected, severity of symptoms, and benefits of treatment from the patients’ perspective. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 17, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Brown, J.C.; Cheville, A.L.; Tchou, J.C.; Harris, S.R.; Schmitz, K.H. Prescription and adherence to lymphedema self-care modalities among women with breast cancer-related lymphedema. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyages, J.; Xu, Y.; Kalfa, S.; Koelmeyer, L.; Parkinson, B.; Mackie, H.; Viveros, H.; Gollan, P.; Taksa, L. Financial cost of lymphedema borne by women with breast cancer. Psychooncology 2017, 26, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhurst, E.; Dylke, E.S.; Kilbreath, S.L. Use of compression garments by women with lymphoedema secondary to breast cancer treatment. Support. Care Cancer 2018, 26, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.; Højris, I.; Erlandsen, M.; Andersen, J. Treatment of breast-cancer-related lymphedema with or without manual lymphatic drainage–A randomized study. Acta Oncol. 2000, 39, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, M.J.; DePompolo, R.W.; Garden, F.H. Focused review: Postmastectomy lymphedema. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1996, 77 (Suppl. 3), S74–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boris, M.; Weindorf, S.; Lasinkski, S. Persistence of lymphedema reduction after noninvasive complex lymphedema therapy. Oncology 1997, 11, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Partsch, H.; Stout, N.; Forner-Cordero, I.; Flour, M.; Moffatt, C.; Szuba, A.; Milic, D.; Szolnoky, G.; Brorson, H.; Abel, M.; et al. Clinical trials needed to evaluate compression therapy in breast cancer related lymphedema (BCRL). Proposals from an expert group. Int. Angiol. 2010, 29, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lymphedema Framework. International Consensus. Best Practice for the Manegement of Lymphedema. 2006. Available online: https://www.lympho.org/uploads/files/files/Best_practice.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- MacRae, B.A.; Cotter, J.D.; Laing, R.M. Compression garments and exercise: Garment considerations, physiology and performance. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 815–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignes, S.; Porcher, R.; Arrault, M.; Dupuy, A. Factors influencing breast cancer-related lymphedema volume after intensive decongestive physiotherapy. Support. Care Cancer 2011, 19, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryans, K.; Perdomo, M.; Davies, C.C.; Levenhagen, K.; Gilchrist, L. Rehabilitation interventions for the management of breast cancer-related lymphedema: Developing a patient-centered, evidence-based plan of care throughout survivorship. J. Cancer Surviv. 2023, 17, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikan Dönmez, A.; Kuru Alici, N.; Borman, P. Lived Experiences for Supportive Care Needs of Women with Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: A Phenomenological Study. Clin. Nurs. Res. 2021, 30, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridner, S.H. Pathophysiology of lymphedema. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 29, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Lu, Q.; Pang, D.; Shen, A.; Shih, Y.A.; Wei, X. Experiences of breast cancer survivors with lymphedema self-management: A systematic review of qualitative studies. J. Cancer Surviv. 2023, 17, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Adherence | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Categories | Total | Yes n = 36 | No n = 56 | p-Value a |
| Etiology | Primary | 15 (16.3%) | 10 (66.7%) | 5 (33.3%) | 0.02 |
| Secondary | 77 (83.7%) | 26 (33.8%) | 51 (66.2%) | ||
| Affected Limb | Lower limb | 33 (35.9%) | 18 (54.5%) | 15 (45.5%) | 0.03 |
| Upper limb | 59 (64.1%) | 18 (30.5%) | 41 (69.5%) | ||
| Edema Severity | Mild | 17 (18.5%) | 7 (41.2%) | 10 (58.8%) | 0.24 |
| Moderate | 57(62.0%) | 18 (31.6%) | 39 (68.4%) | ||
| Severe | 18(19.6%) | 11 (61.1%) | 7 (38.9%) | ||
| Medical Check-Ups | Yes | 79(85.9%) | 31 (39.2%) | 48 (60.8%) | 0.96 |
| No | 13(14.1%) | 5 (38.5%) | 8 (61.5%) | ||
| Check-Up Frequency | Every 3–4 months | 3 (3.3%) | 1 (33.3%) | 2 (66.7%) | 0.96 |
| Every 5–6 months | 63 (68.5%) | 22 (34.9%) | 41 (65.1%) | ||
| Every year | 26 (28.3%) | 13 (50.0%) | 13 (50.0%) | ||
| OR (IC95%) | AOR (IC95%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affected Limb | 0.146 | ||
| Upper limb | |||
| Lower limb | 2.73 (1.13, 6.6) | 2.36 (0.74, 7.52) | |
| Etiology | 0.01 | ||
| Secondary | |||
| Primary | 3.92 (1.21, 12.68) | 8.86 (1.43, 54.93) | |
| Severity Level | 0.035 | ||
| Moderate | |||
| Severe | 3.4 (1.13, 10.23) | 4.57 (1.22, 17.04) | |
| Mild | 1.52 (0.5, 4.63) | 2.74 (0.73, 10.32) | |
| Perception of Use | <0.001 | ||
| Uncomfortable | |||
| Comfortable | 4.4 (1.18, 16.41) | 13.51 (2.35, 77.59) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medina Rodríguez, M.E.; Socorro Suárez, R.; Albornoz Cabello, M.; Aranda Rodríguez, C.; Domínguez Trujillo, P.D.; Peña Curbelo, V. Adherence to Compression Garments in Lymphedema Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2025, 61, 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040685
Medina Rodríguez ME, Socorro Suárez R, Albornoz Cabello M, Aranda Rodríguez C, Domínguez Trujillo PD, Peña Curbelo V. Adherence to Compression Garments in Lymphedema Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):685. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040685
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedina Rodríguez, María Elena, Raúl Socorro Suárez, Manuel Albornoz Cabello, Carolina Aranda Rodríguez, Pino Delia Domínguez Trujillo, and Victoria Peña Curbelo. 2025. "Adherence to Compression Garments in Lymphedema Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study" Medicina 61, no. 4: 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040685
APA StyleMedina Rodríguez, M. E., Socorro Suárez, R., Albornoz Cabello, M., Aranda Rodríguez, C., Domínguez Trujillo, P. D., & Peña Curbelo, V. (2025). Adherence to Compression Garments in Lymphedema Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina, 61(4), 685. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040685





