A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Age ≥18 years (age in our cohort ranged from 20 to 63 years old);
- Diagnosis of otosclerosis confirmed through audiometric evaluation and clinical examination (normal tympanic membranes, a history of conductive hearing loss with a bilateral type A tympanogram, bilaterally absent stapedial reflex [16]);
- A CT scan indicating the typical hypodense lesions of the bony capsule of the labyrinth;
- Subjective chronic presence of tinnitus;
- No other ongoing hearing interventions;
- Provided written informed consent to participate in the study.
- Patient refusal to participate;
- Absence of tinnitus symptoms, despite having a confirmed diagnosis of otosclerosis;
- Presence of ongoing liver disease or anemia, conditions that could interfere with calcium and fluoride metabolism;
- Cardiovascular disease (with or without chronic medication), due to its potential impact on tinnitus;
- Chronic kidney disease;
- Patients with psychiatric comorbidity.
3. Results
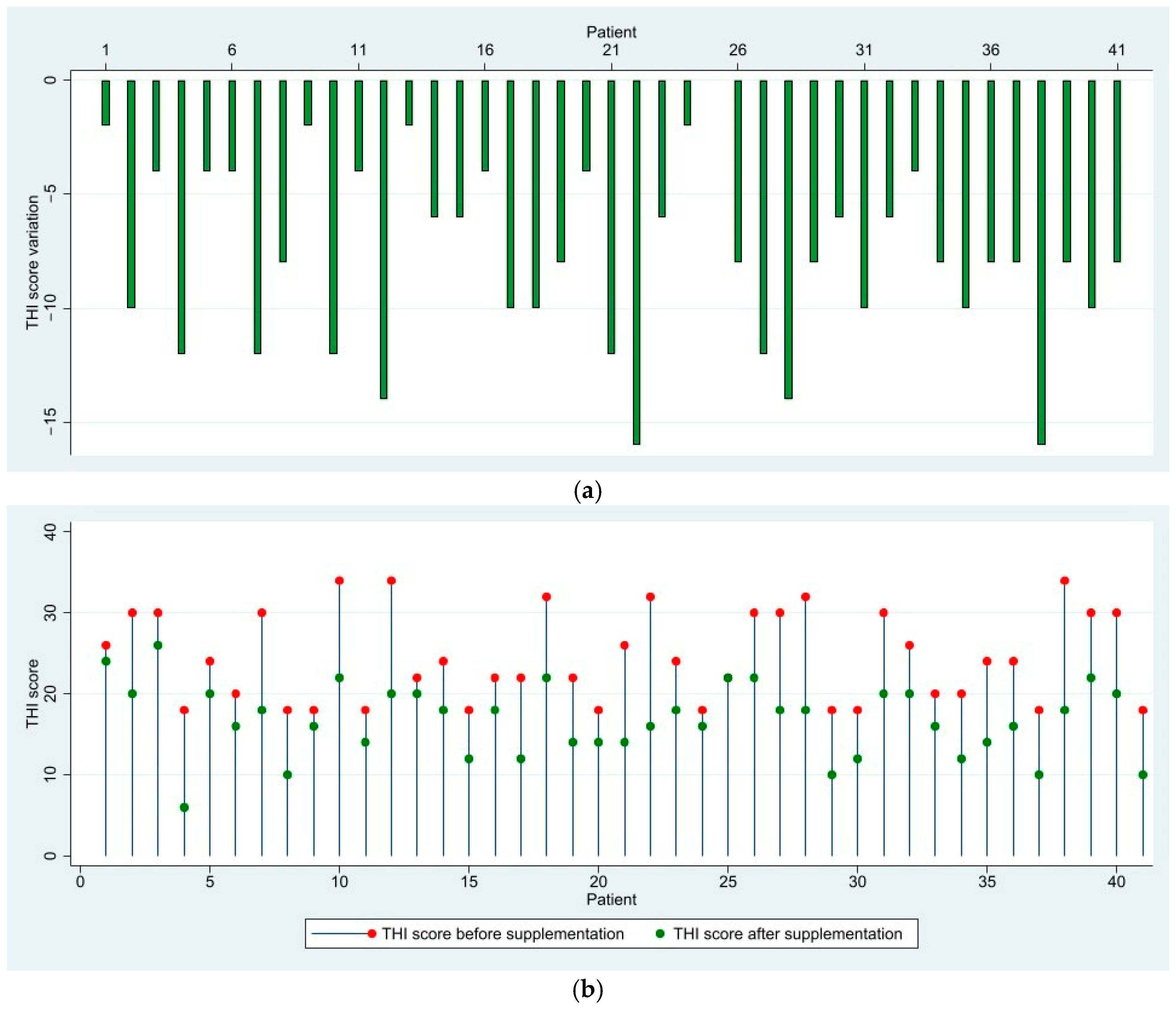
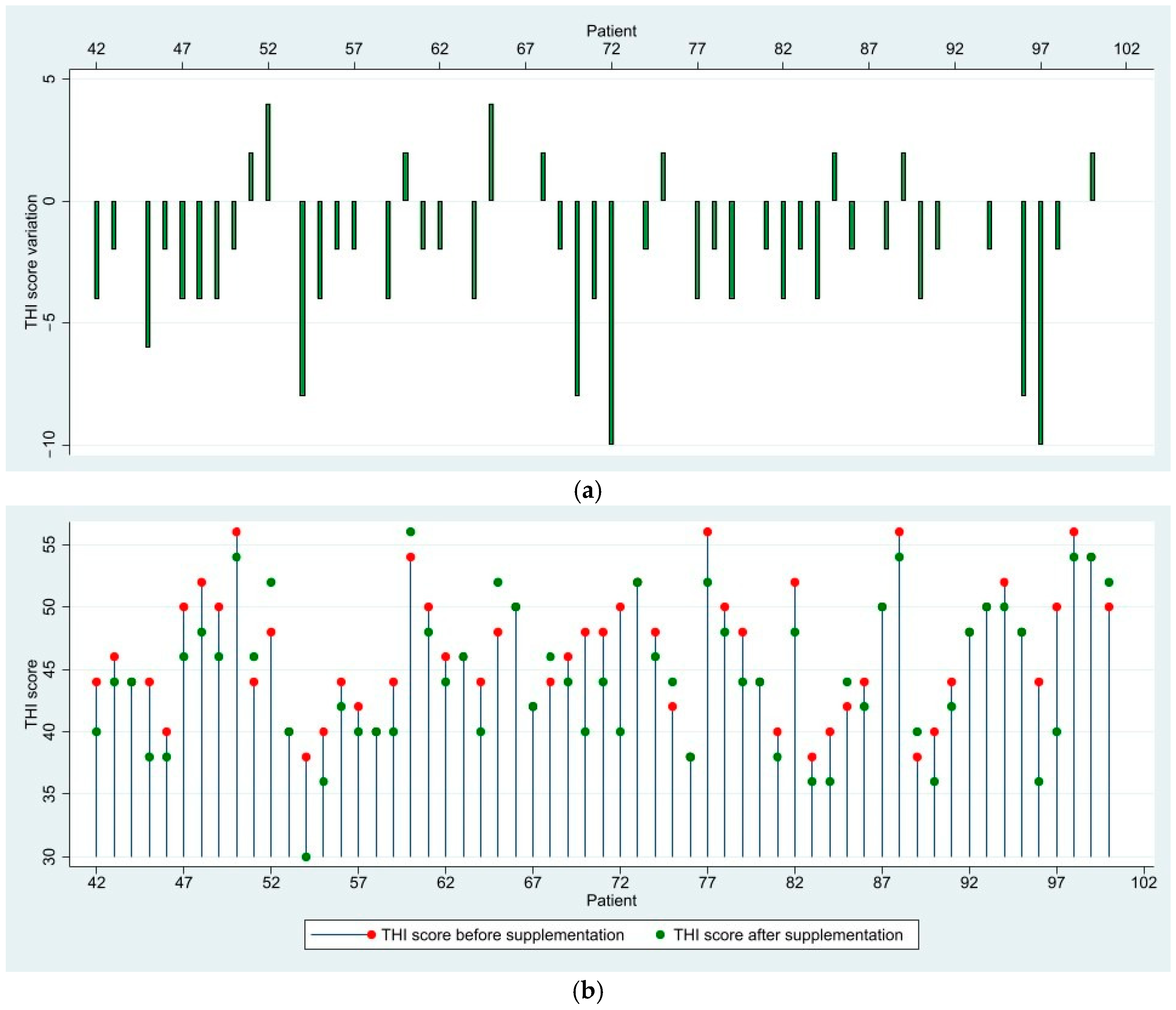
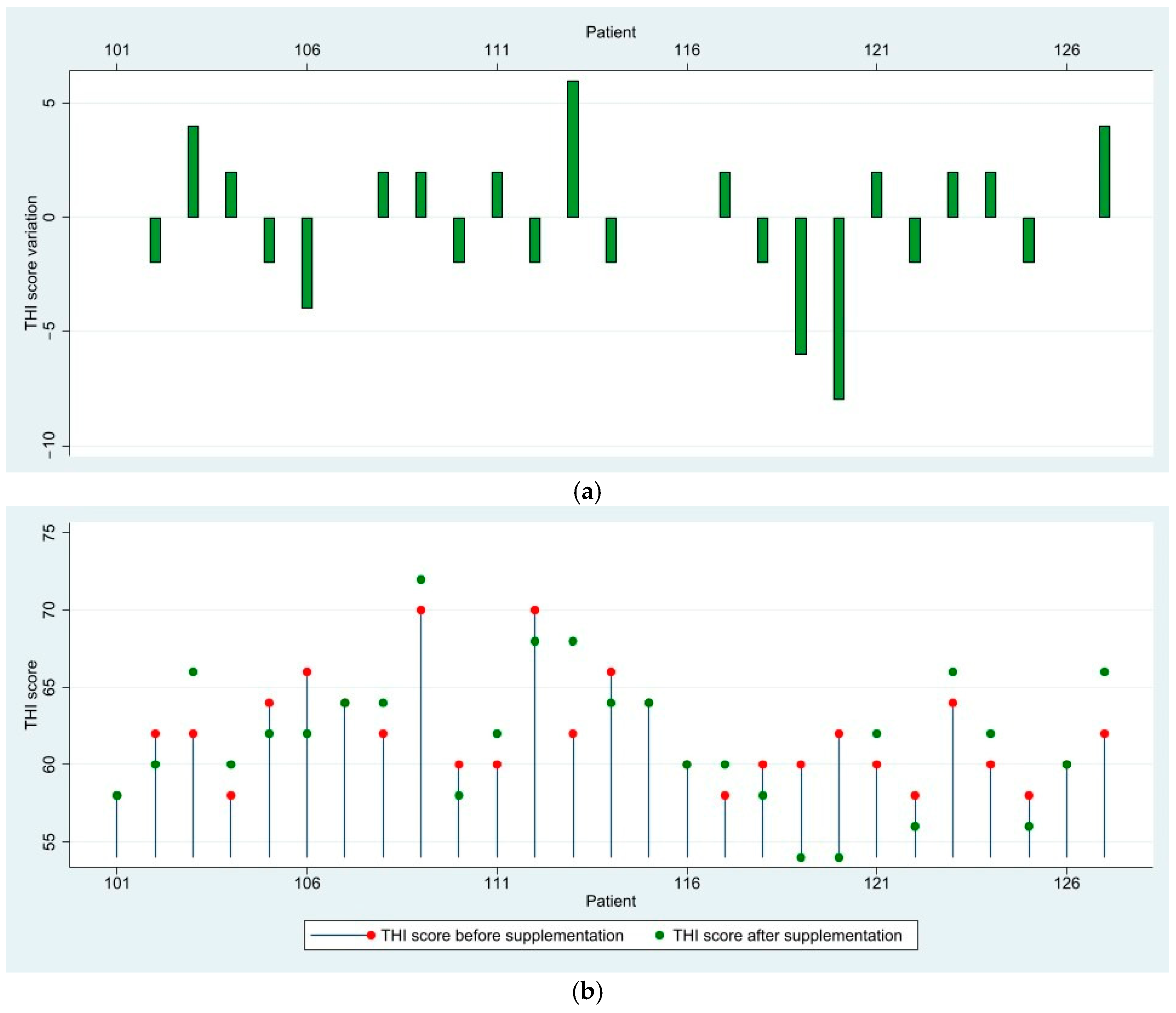
3.1. THI Score Results and Variation
3.2. Statistical Analysis of THI Scores
3.2.1. Descriptive Statistics for the THI Score Variation
3.2.2. Normality Test (Shapiro–Wilk)
3.2.3. One-Way ANOVA and Post Hoc Comparisons
- (1)
- F(2,124) = 51.52, p < 0.0001, indicating a statistically significant difference in THI reductions across severity groups.
- (2)
- Post hoc Bonferroni tests revealed significant differences in some groups;
- (a)
- Mild vs. moderate tinnitus: p < 0.0001 (significant difference);
- (b)
- Mild vs. severe tinnitus: p < 0.0001 (significant difference);
- (c)
- Moderate vs. severe tinnitus: p = 0.077 (not statistically significant).
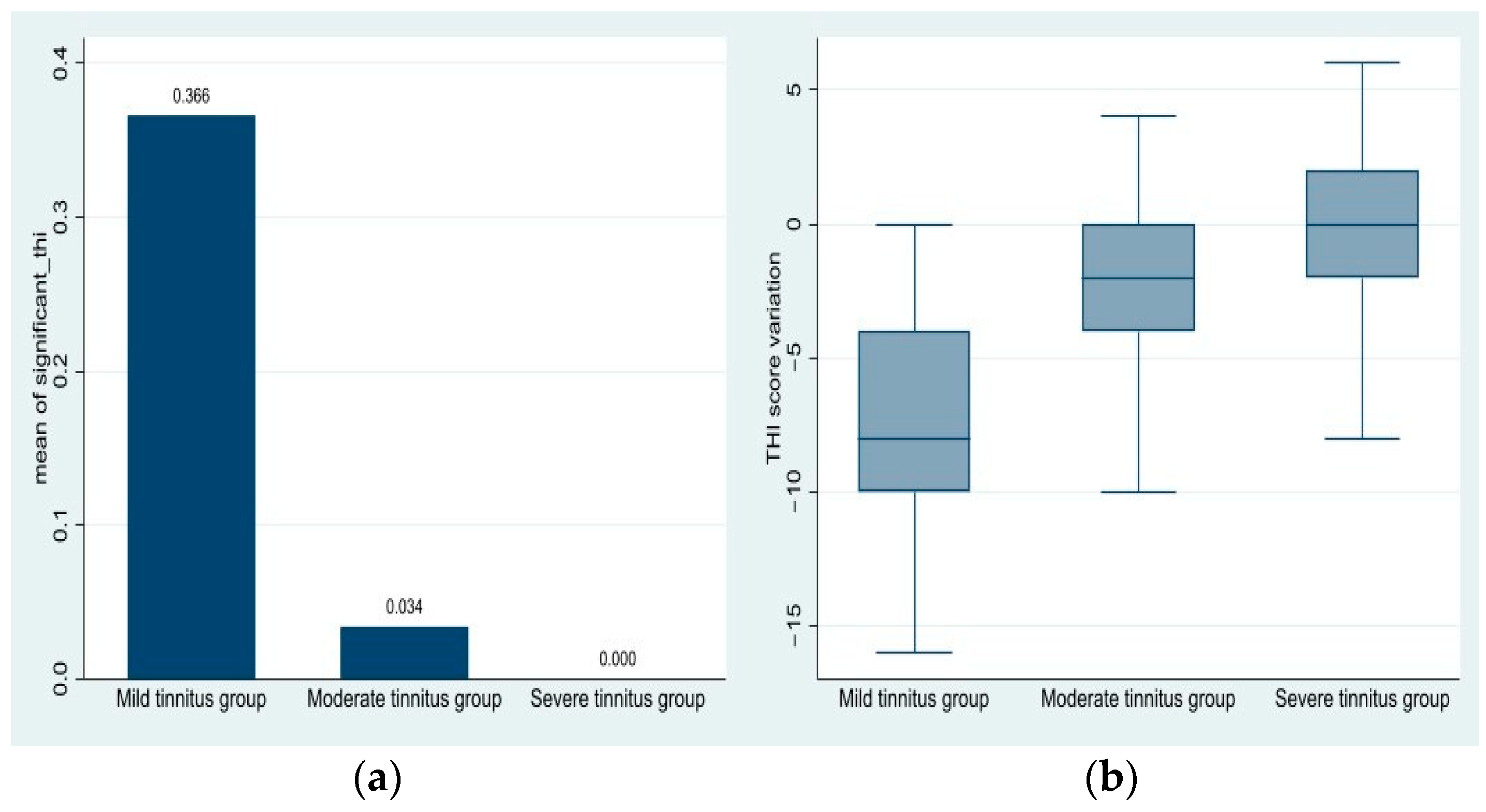
3.2.4. Proportion of Patients with Significant THI Reduction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| THI | Tinnitus Handicap Inventory |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ALKP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ACP | Acid phosphatase |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| RCCT | Randomized clinical control trial |
References
- Mudry, A. Adam Politzer (1835–1920) and the description of otosclerosis. Otol. Neurotol. 2006, 27, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedmann, I.; Arnold, W. Pathology of the Ear; Churchill Livingstone: Edinburgh, Scotland, 1994; Volume 174, p. 63. [Google Scholar]
- Uppal, S.; Bajaj, Y.; Rustom, I.; Coatesworth, A.P. Otosclerosis 1: The aetiopathogenesis of otosclerosis. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 1526–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karosi, T.; Sziklai, I. Etiopathogenesis of otosclerosis. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2010, 267, 1337–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menger, D.J.; Tange, R.A. The aetiology of otosclerosis: A review of the literature. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 2003, 28, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deggouj, N.; Castelein, S.; Gerard, J.M.; Decat, M.; Gersdorff, M. Tinnitus and otosclerosis. B-ENT 2009, 5, 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- McCormack, A.; Edmondson-Jones, M.; Somerset, S.; Hall, D. A systematic review of the reporting of tinnitus prevalence and severity. Hear Res. 2016, 337, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šaboviča, J.; Klagiša, R. Stapedoplasty-surgical treatment of hearing loss caused by otosclerosis. Soc. Welf. Interdiscip. Approach 2016, 6, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Persson, P.; Harder, H.; Magnuson, B. Hearing results in otosclerosis surgery after partial stapedectomy, total stapedectomy and stapedotomy. Acta Otolaryngol. 1997, 117, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Chandrasekhar, S.S.; Del Signore, A. Florical and Early Otosclerosis. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2011, 145 (Suppl. S2), P213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentschel, M.A.; Huizinga, P.; Van Der Velden, D.L.; Wegner, I.; Bittermann, A.J.; Van Der Heijden, G.J.; Grolman, W. Limited evidence for the effect of sodium fluoride on deterioration of hearing loss in patients with otosclerosis: A systematic review of the literature. Otol. Neurotol. 2014, 35, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, C.W.; Jacobson, G.P.; Spitzer, J.B. Development of the Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1996, 122, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashi, A.; Bhardwaj, M. Study on blood biochemical diagnostic indices for hepatic function biomarkers in endemic skeletal fluorosis. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2011, 143, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.K.; Sousa, J.M.; dos Santos, V.R.; Nunes, P.B.; Bittencourt, L.O.; Charone, S.; Lima, R.R. Biomarkers in the Biomonitoring of Fluoride Toxicity: An Overview. In Biomarkers in Toxicology. Biomarkers in Disease: Methods, Discoveries and Applications; Patel, V.B., Preedy, V.R., Rajendram, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, B.L.; Hodgson, S.F.; Hoffman, D.L.; Kelly, P.J.; Johnson, K.A.; Taves, D. Treatment of Primary Osteoporosis With Fluoride and Calcium: Clinical Tolerance and Fracture Occurrence. JAMA 1980, 243, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, N.; Hohman, M.H.; Khan, M.A.B. Otosclerosis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560671/ (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- Lee, T.L.; Wang, M.C.; Lirng, J.F.; Liao, W.H.; Yu, E.C.; Shiao, A.S. High-resolution computed tomography in the diagnosis of otosclerosis in Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2009, 72, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dudau, C.; Salim, F.; Jiang, D.; Connor, S.E. Diagnostic efficacy and therapeutic impact of computed tomography in the evaluation of clinically suspected otosclerosis. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinjung, T.; Peter, N.; Schecklmann, M.; Langguth, B. The Current State of Tinnitus Diagnosis and Treatment: A Multidisciplinary Expert Perspective. JARO 2024, 25, 413–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCombe, A.; Baguley, D.; Coles, R.; McKenna, L.; McKinney, C.; Windle-Taylor, P.; British Association of Otolaryngologists, Head and Neck Surgeons. Guidelines for the grading of tinnitus severity: The results of a working group commissioned by the British Association of Otolaryngologists, Head and Neck Surgeons, 1999. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied. Sci. 2001, 26, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabuk, G.B.; Buyuklu, A.F.; Karamert, R.; Aksoy, S. Investigation of the applicability of internet-based approach to subjective tinnitus. Acta Otolaryngol. 2024, 144, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.U.; Bahng, J. A Study on the Rehabilitation Effects of Tinnitus Counseling for Hearing Aid Users Who Suffer from Tinnitus. Audiol. Speech Res. 2024, 20, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.biap.org/es/recommandations/recommendations/tc-02-classification/213-rec-02-1-en-audiometric-classification-of-hearing-impairments/file (accessed on 1 March 2025).
- Dziendziel, B.; Skarżyński, P.H.; Rajchel, J.J.; Gos, E.; Skarżyński, H. Prevalence and severity of tinnitus in Polish otosclerosis patients qualified for stapes surgery. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 276, 1585–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarzynski, P.H.; Dziendziel, B.; Gos, E.; Wlodarczyk, E.; Miaskiewicz, B.; Rajchel, J.J.; Skarzynski, H. Prevalence and Severity of Tinnitus in Otosclerosis: Preliminary Findings from Validated Questionnaires. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2019, 15, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos Macías, A.; Falcón González, J.C.; Manrique, M.; Morera, C.; García-Ibáñez, L.; Cenjor, C.; Coudert-Koall, C.; Killian, M. Cochlear implants as a treatment option for unilateral hearing loss, severe tinnitus and hyperacusis. Audiol. Neurootol. 2015, 20 (Suppl. S1), 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goderie, T.; van Wier, M.F.; Lissenberg-Witte, B.I.; Merkus, P.; Smits, C.; Leemans, C.R.; Kramer, S.E. Factors Associated With the Development of Tinnitus and With the Degree of Annoyance Caused by Newly Developed Tinnitus. Ear Hear. 2022, 43, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A.F.; Moreira, F.C.; Costa, I.E.; Azevedo, C.; Mar, F.; Dias, L. Tinnitus and Otosclerosis: An Exploratory Study about the Prevalence, Features and Impact in Daily Life. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 26, e390–e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wakabayashi, S.; Oishi, N.; Shinden, S.; Ogawa, K. Factor analysis and evaluation of each item of the tinnitus handicap inventory. Head Face Med. 2020, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ding, Y. The causal relationship between anxiety and tinnitus severity: A Mendelian randomization study. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2024, 25, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Wang, J.; Chuan, D.; Fan, J.; Chen, Z. Impact of anxiety associated with COVID-19 on tinnitus. MedRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elhmid, I.H.; Abish, Y.G.; Zaghloul, B.A.; Hussein, H.A.; Ghanem, S.S. Correlation between audiological and radiological findings in otosclerosis: Randomized clinical study. Egypt. J. Otolaryngol. 2024, 40, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albera, A.; Parandero, F.; Andriani, R.; Albera, R.; Riva, G.; Canale, A. Prognostic factors influencing postoperative air-bone gap in stapes surgery. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.I.; Hossain, M.D.; Asaduzzaman, A.K.M. Audioogical Outcome of Stapedotomy for Primary Otosclerosis. J. Bangladesh Coll. Physicians Surg. 2022, 40, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajati, M.; Poursadegh, M.; Bakhshaee, M.; Abbasi, A.; Shahabi, A. Outcome of stapes surgery for tinnitus recovery in otosclerosis. Int. Tinnitus J. 2012, 17, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terzić, N.; Jakovljević, V.L.; Milanović, N.; Jaćimović, V.; Zivić, L. Condition of hearing sense and tinnitus before and after the treatment of otosclerosis. Med. Pregl. 2010, 63, 648–651. (In Serbian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.K.; Dubey, D. Current pharmacological treatment of tinnitus. Matrix Sci. Pharma 2022, 6, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, J.-M.; Lee, S.K.; Kang, H.J.; Yeo, S.G. Review of Pharmacotherapy for Tinnitus. Healthcare 2021, 9, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gogoulos, P.P.; Sideris, G.; Nikolopoulos, T.; Sevastatou, E.K.; Korres, G.; Delides, A. Conservative Otosclerosis Treatment With Sodium Fluoride and Other Modern Formulations: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, A.; Mandour, M.; Tomoum, M.O.; Lasheen, R.M. Effectiveness of bisphosphonate for alleviating tinnitus associated with otosclerosis: A prospective case-control study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2025, 282, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, L.; Vogt, F.; Marks, E. Current Validated Medical Treatments for Tinnitus: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 53, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Xiang, M.Y.; Zhou, R.Q.; Li, W.; Wang, L.Q.; Guan, P.F.; Li, G.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, J. Effect of Sodium Salicylate on Calcium Currents and Exocytosis in Cochlear Inner Hair Cells: Implications for Tinnitus Generation. Neurosci. Bull. 2022, 38, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bener, A.; Erdoğan, A.; Üstündağ, Ü.V. The Impact of Serums Calcium 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D, Ferritin, Uric Acid, and Sleeping Disorders on Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Patients. Audiol. Res. 2024, 14, 640–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucher, K.; Johns, D.; Wagner, F.; Abd-Elaziz, K.; Derne, C.; Sverdlov, O.; Pfister, C.; Langguth, B. Efficacy and safety of single- and repeated-selurampanel dosing for 2 weeks in patients with chronic subjective tinnitus: Results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, proof-of-concept phase IIa study. Prog. Brain Res. 2021, 260, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Kumar, D.R.; Balasubramani, J.; Selvapriya, E. Efficacy of Intratympanic Dexamethasone Injection in Subjective Idiopathic Tinnitus- An Interventional Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2022, 16, MC05–MC08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Mild Tinnitus n = 41 | Moderate Tinnitus n = 59 | Severe Tinnitus n = 27 | Total n = 127 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THI score Mean ± SD (min-max) | Baseline | 3 months | Baseline | 3 months | Baseline | 3 months | Baseline | 3 months | ||
| 24.49 ± 5.58 (18–34) | 16.73 ± 4.44 (6–26) | 46.37 ± 5.04 (38–56) | 44.44 ± 5.80 (30–56) | 61.85 ± 2.32 (58–70) | 61.70 ± 4.39 (54–72) | 42.60 ± 14.72 (18–70) | 39.16 ± 17.64 (6–72) | |||
| THI score difference Mean (min-max) | −7.76 (−16–0) | −1.93 (−10–4) | −0.15 (−8–6) | −3.43 (−16–6) | ||||||
| p-value | <0.001 | <0.01 | 0.805 | <0.01 | ||||||
| Group | Total Patients | % Significant Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Mild tinnitus | 41 | 36.59% |
| Moderate tinnitus | 59 | 3.39% |
| Severe tinnitus | 27 | 0.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the Lithuanian University of Health Sciences. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Osman, A.; Ghenea, A.E.; Zlatian, O.M.; Boldeanu, L.; Enache, I.; Georgescu, M.G.; Mogoanta, C.A. A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania. Medicina 2025, 61, 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040569
Osman A, Ghenea AE, Zlatian OM, Boldeanu L, Enache I, Georgescu MG, Mogoanta CA. A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania. Medicina. 2025; 61(4):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040569
Chicago/Turabian StyleOsman, Andrei, Alice Elena Ghenea, Ovidiu Mircea Zlatian, Lidia Boldeanu, Irina Enache, Madalina Gabriela Georgescu, and Carmen Aurelia Mogoanta. 2025. "A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania" Medicina 61, no. 4: 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040569
APA StyleOsman, A., Ghenea, A. E., Zlatian, O. M., Boldeanu, L., Enache, I., Georgescu, M. G., & Mogoanta, C. A. (2025). A Clinical Evaluation of Calcium and Fluoride Supplementation for Tinnitus in Non-Surgical Otosclerosis: Insights from a Tertiary Care Center in Romania. Medicina, 61(4), 569. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina61040569






